Stereocomplex Poly(Lactic Acid) Amphiphilic Conetwork Gel with Temperature and pH Dual Sensitivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis
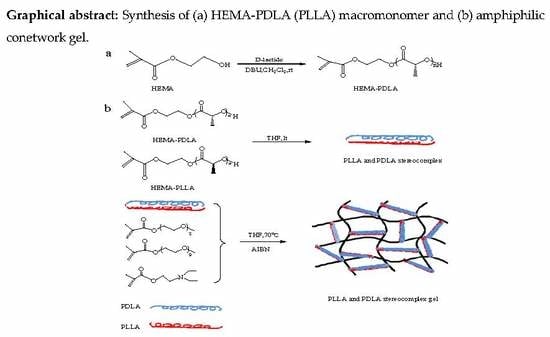
2.2.1. Synthesis of HEMA-PDLA Macromonomer
2.2.2. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Conetwork Gel
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H NMR)
2.3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4. Swelling−Deswelling Behavior of the Hydrogel
2.5. WAXD Analysis of the Hydrogel
2.6. SEM Analysis of the Hydrogel
2.7. Thermal Analysis of the Hydrogel
2.8. Mechanical Properties Analysis of the Hydrogel
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Temperature/pH Dual Sensitive Amphiphilic Conetwork Gel
3.2. Temperature Responsive Hydrogel
3.3. pH Responsive Hydrogel
3.4. WAXD Analysis of Hydrogel
3.5. Thermal Analysis of Hydrogel
3.6. SEM Analysis of Hydrogel
3.7. Mechanical Properties Analysis of Hydrogel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, A.K.; Ling, J.; Yin, L.H.; Chen, Y.; Fu, G.D. Well-defined biodegradable amphiphilic conetworks. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 6309–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.P.; Gitsov, I. Synthesis and physical properties of reactive amphiphilic hydrogels based on poly(p-chloromethylstyrene) and poly(ethylene glycol): Effects of composition and molecular architecture. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 3256–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, A.K.S.; Kumar, C.U.; Jewrajka, S.K. Effect of polyethylene glycol on properties and drug encapsulation−release performance of biodegradable/cytocompatible agarose−polyethylene glycol−polycaprolactone amphiphilic co-network gels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3182–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kali, G.; Georgiou, T.; Iva´n, B.; Patrickios, C.; Loizou, E.; Thomann, Y.; Tiller, J. Synthesis and characterization of anionic amphiphilic model conetworks based on methacrylic acid and methyl methacrylate: Effects of composition and architecture. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 2192–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pafiti, K.; Loizou, E.; Patrickios, C.; Porcar, L. End-linked semifluorinated amphiphilic polymer conetworks: Synthesis by sequential reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization and characterization. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 5195–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, C.; Kali, G.; Iván, B. Poly(N-vinylimidazole)-l-poly(tetrahydrofuran) amphiphilic conetworks and gels: Synthesis, characterization, thermal and swelling behavior. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4496–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Zangabad, P.S.; Ghasemi, A.; Amiri, M.; Bahrami, M.; Malekzad, H.; Asl, H.G. Temperature-responsive smart nanocarriers for delivery of therapeutic agents: Applications and recent advances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21107–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, N.; Scherble, J.; Hartmann, L.; Thomann, R.; Iván, B.; Mü1haupt, R.; Tiller, G.C. Nanophase separated amphiphilic conetwork coatings and membranes. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iván, B.; Almdal, K.; Mortensen, K.; Johannsen, I.; Kops, J. Synthesis, characterization, and structural investigations of Poly(ethyl acrylate)-l-polyisobutylene bicomponent conetwork. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraszti, M.; Tóth, E.; Iván, B. Poly(methacrylic acid)-l-polyisobutylene: A novel polyelectrolyte amphiphilic conetwork. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4952–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, G.; Vavra, S.; László, K.; Iván, B. Thermally responsive amphiphilic conetworks and gels based on poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and polyisobutylene. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafouris, D.; Gradzielski, M.; Patrickios, C.S. Semisegmented amphiphilic polymer conetworks: Synthesis and characterization. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, C.; Zhou, W.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Wouters, M.; Feijen, J. Rapidly in situ forming biodegradable robust hydrogels by combining stereocomplexation and photopolymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9918–9926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahama, K.; Mori, Y.; Ohya, Y.; Ouchi, T. Biodegradable nanogel formation of polylactide-grafted dextran copolymer in dilute aqueous solution and enhancement of its stability by stereocomplexation. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slager, J.; Domb, A.J. Biopolymer stereocomplexes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 549–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.; Rivilla, A.; Agirre, M.; Basterretxea, A.; Etxeberria, A.; Veloso, A.; Sardon, H. Enantioselective ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide dictated by densely substituted amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4805–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidian, M.; Tehrany, E.A.; Imran, M.; Jacquot, M.; Desobry, S. Poly-lactic acid: Production, applications, nanocomposites, and release studies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 552–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; He, C.B. Synthesis and stereocomplex crystallization of poly(lactide)-graphene oxide nanocomposites. ACS Macro. Lett. 2012, 1, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Sato, H.; Tsuji, H.; Noda, I.; Ozaki, Y. Infrared spectroscopic study of CH3…O=C interaction during poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) stereocomplex formation. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.S.; Wang, M.; Yuan, D.; He, C.B. Amphiphilic conetworks and gels physically cross-linked via stereocomplexation of polylactide. Langmuir 2013, 29, 14307–14313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.L.; Pan, P.G.; Shan, G.R.; Bao, Y.Z.; Fujita, M.; Maeda, M. Core-shell structure, biodegradation, and drug release behavior of poly(lactic acid)/poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymer micelles tuned by macromolecular stereostructure. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Sun, J.R.; Bian, X.C.; Cui, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, X.S. Investigation of poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: 3-Armed poly(L-lactide) blended with linear and 3-armed enantiomers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 9983–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.G.; Yang, J.J.; Shan, J.R.; Bao, Y.Z.; Weng, Z.X.; Cao, A.; Yazawa, K. Temperature-variable FTIR and solid-state 13C NMR investigations on crystalline structure and molecular dynamics polymorphic poly(L-lactide) and poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-lactide) stereocomplex. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Xiang, S.; Bian, X.C.; Sun, J.R.; Li, G.; Chen, X.S. Remarkable melting behavior of PLA stereocomplex in linear PLLA/PDLA blends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.G.; Han, L.L.; Bao, J.N.; Xie, Q.; Shan, G.R.; Bao, Y.Z. Competitive stereocomplexation, homocrystallization, and polymorphic crystalline transition in poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(D-lactic acid) racemic blends: Molecular weight effects. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 6462–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, H.T.; Abe, S. Stereocomplex poly(lactic acid) alloys with superb heat resistance and toughness. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3245–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobis, J.; Thomann, Y.; Tiller, J.C. Synthesis and characterization of chiral and thermo responsive amphiphilic conetworks. Polymer 2010, 51, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zednik, J.; Riva, R.; Lussis, P.; Jérôme, C.; Jérôme, R.; Lecomte, P. pH-Responsive biodegradable amphiphilic networks. Polymer 2008, 49, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.F.; Weichenhan, K.; Hoth, A. About the phase transitions in aqueous solutions of thermoresponsive copolymers and hydrogels based on 2-(2-methoxyethoxy) ethyl methacrylate and oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 2503–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.T.; Wu, P.Y. On the thermally reversible dynamic hydration behavior of oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate-based polymers in water. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikkou-Kalourkoti, M.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Patrickios, C.S. Synthesis, characterization and thermolysis of hyperbranched homo- and amphiphilic co-polymers prepared using an inimer bearing a thermolyzable acylal group. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, N.M.B.; Bakaic, E.; Patenaude, M.; Hoare, T. Injectable and tunable poly(ethylene glycol) analogue hydrogels based on poly(oligoethylene glycol methacrylate). Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3306–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, J.F. Thermo-switchable materials prepared using the OEGMA-platform. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.X.; Li, X.; Guang, N.; Tian, L.; Mao, H.G.; Ning, W.Y. Novel amphiphilic temperature responsive graft copolymers PCL-g-P(MEO2MA-co-OEGMA) via a combination of ROP and ATRP: Synthesis, characterization, and sol-gel transition. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, C.; Yang, X.D.; Shen, B.W.; Sun, Y.Q. pH- and Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogel Nanoparticles with Dual Photoluminescence for Bioprobes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5856–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, J.F.; Hoth, A. Point by point comparison of two thermosensitive polymers exhibiting a similar LCST: Is the age of poly(NIPAM) over? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13046–13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.S.; Tian, Y.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Ding, Y.P.; Ji, T.J.; Wu, M.Y.; Wu, Y. “Triple-punch” strategy for triple negative breast cancer therapy with minimized drug dosage and improved antitumor efficacy. ACS NANO 2015, 9, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Qiu, Q.; An, Z.S. Development of thermosensitive copolymers of poly(2-methoxyethyl acrylateco-poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether acrylate) and their nanogels synthesized by RAFT dispersion polymerization in water. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Yuan, D.; Fan, X.S.; Tan, B.H.; He, C.B. Poly(ethylene glycol) conjugated poly(lactide)-based polyelectrolytes: Synthesis and formation of stable self-assemblies induced by stereocomplexation. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Lin, W.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, L.J. PDEAEMA-based pH-sensitive amphiphilic pentablock copolymers for controlled anticancer drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68018–68027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatridi, Z.; Mattheolabakis, G.; Avgoustakis, K.; Tsitsilianis, C. Self-assembly and drug delivery studies of pH/thermo-sensitive polyampholytic (A-co-B)-b-C-b-(A-co-B) segmented terpolymers. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 11160–11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.L.; Pan, P.J.; Shan, G.R.; Bao, Y.Z. In situ formation and gelation mechanism of thermoresponsive stereocomplexed hydrogels upon mixing diblock and triblock poly(lactic acid)/poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 6471–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.X.; Shan, G.R.; Bao, Y.Z.; Pan, P.J. Enhancement of crystallizability and control of mechanical and shape-memory properties for amorphous enantiopure supramolecular copolymers via stereocomplexation. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7872–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakal, E.; Çavus, S. Novel poly(N-vinylcaprolactam-co-2-(diethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) gels: Characterization and detailed investigation on their stimuli-sensitive behaviors and network structure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11741–11751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.J.; Liu, T.; Liu, S.X.; Wang, Q.Q.; Li, X.; Guang, N.E. Temperature and pH responsive hydrogels based on polyethylene glycol analogues and poly(methacrylic acid) via click chemistry. Polym. Int. 2015, 64, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | [HEMA]/[PDLA] (n:n) | [HEMA]/[PLLA] (n:n) | [DEAEMA]/[MO] a (n:n) | Swelling Degree (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH = 7 | pH = 5 | THF | ||||
| gel1 | 1:9 | 1:9 | 3:7 | 45.16 | 137.74 | 10.11 |
| gel2 | 1:13 | 1:13 | 3:7 | 32.58 | 111.64 | 12.74 |
| gel3 | 1:16 | 1:16 | 3:7 | 16.48 | 109.23 | 14.84 |
| gel4 | 1:20 | 1:20 | 3:7 | 10.74 | 107.08 | 15.68 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, F.; Gao, W.; Liu, S. Stereocomplex Poly(Lactic Acid) Amphiphilic Conetwork Gel with Temperature and pH Dual Sensitivity. Polymers 2019, 11, 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121940
Wu J, Shi X, Wang Z, Song F, Gao W, Liu S. Stereocomplex Poly(Lactic Acid) Amphiphilic Conetwork Gel with Temperature and pH Dual Sensitivity. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121940
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jie, Xiaoyu Shi, Zhidan Wang, Fei Song, Wenli Gao, and Shouxin Liu. 2019. "Stereocomplex Poly(Lactic Acid) Amphiphilic Conetwork Gel with Temperature and pH Dual Sensitivity" Polymers 11, no. 12: 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121940
APA StyleWu, J., Shi, X., Wang, Z., Song, F., Gao, W., & Liu, S. (2019). Stereocomplex Poly(Lactic Acid) Amphiphilic Conetwork Gel with Temperature and pH Dual Sensitivity. Polymers, 11(12), 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121940