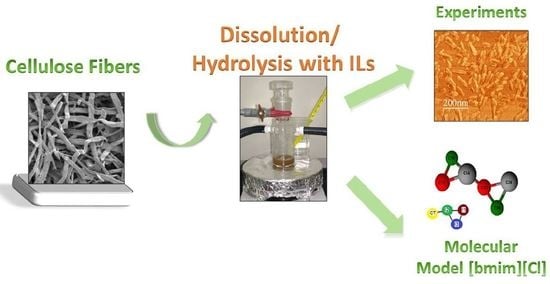
Dissolution and Hydrolysis of Bleached Kraft Pulp Using Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental and Molecular Methods
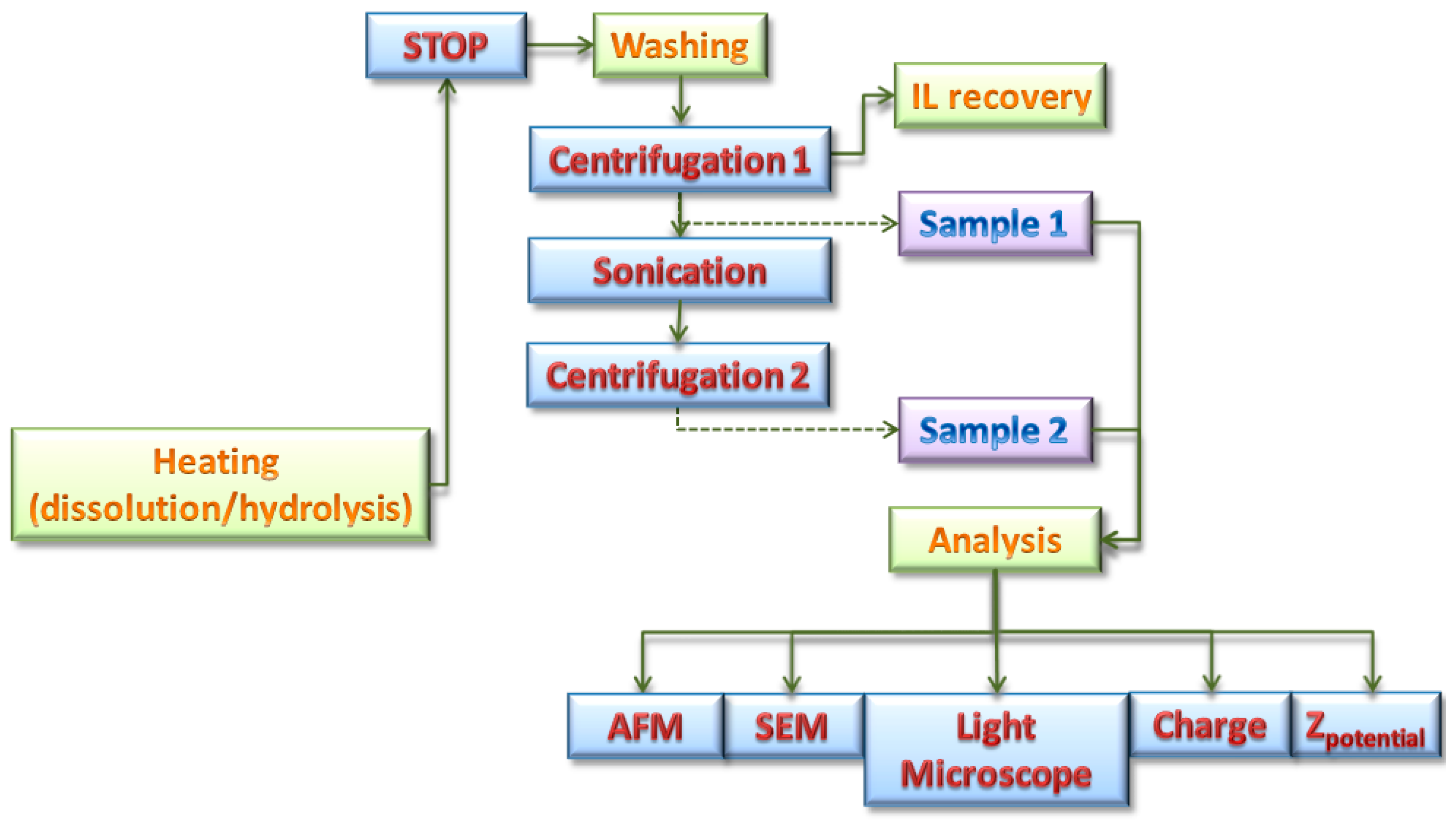
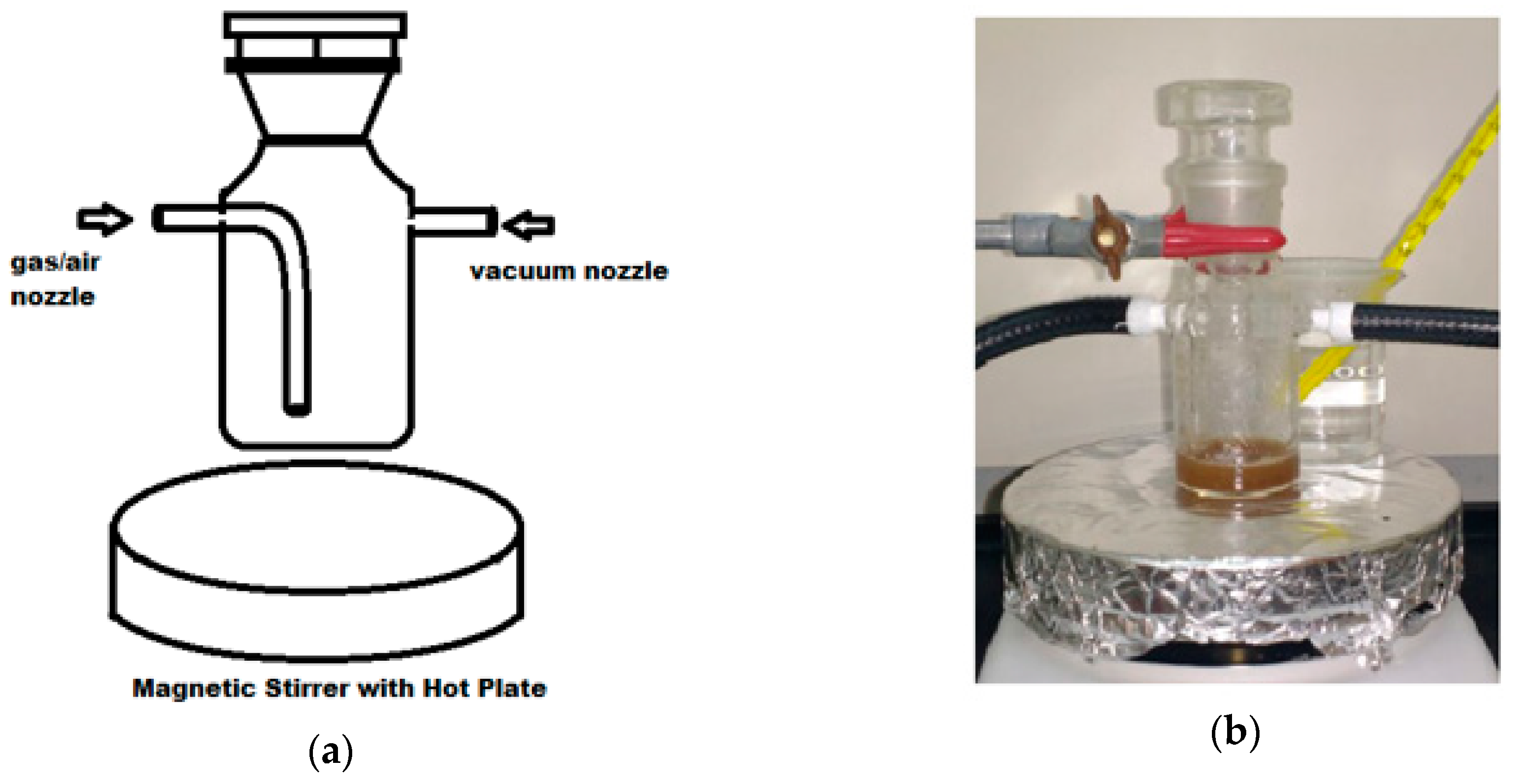
2.2.1. Dissolution and Hydrolysis
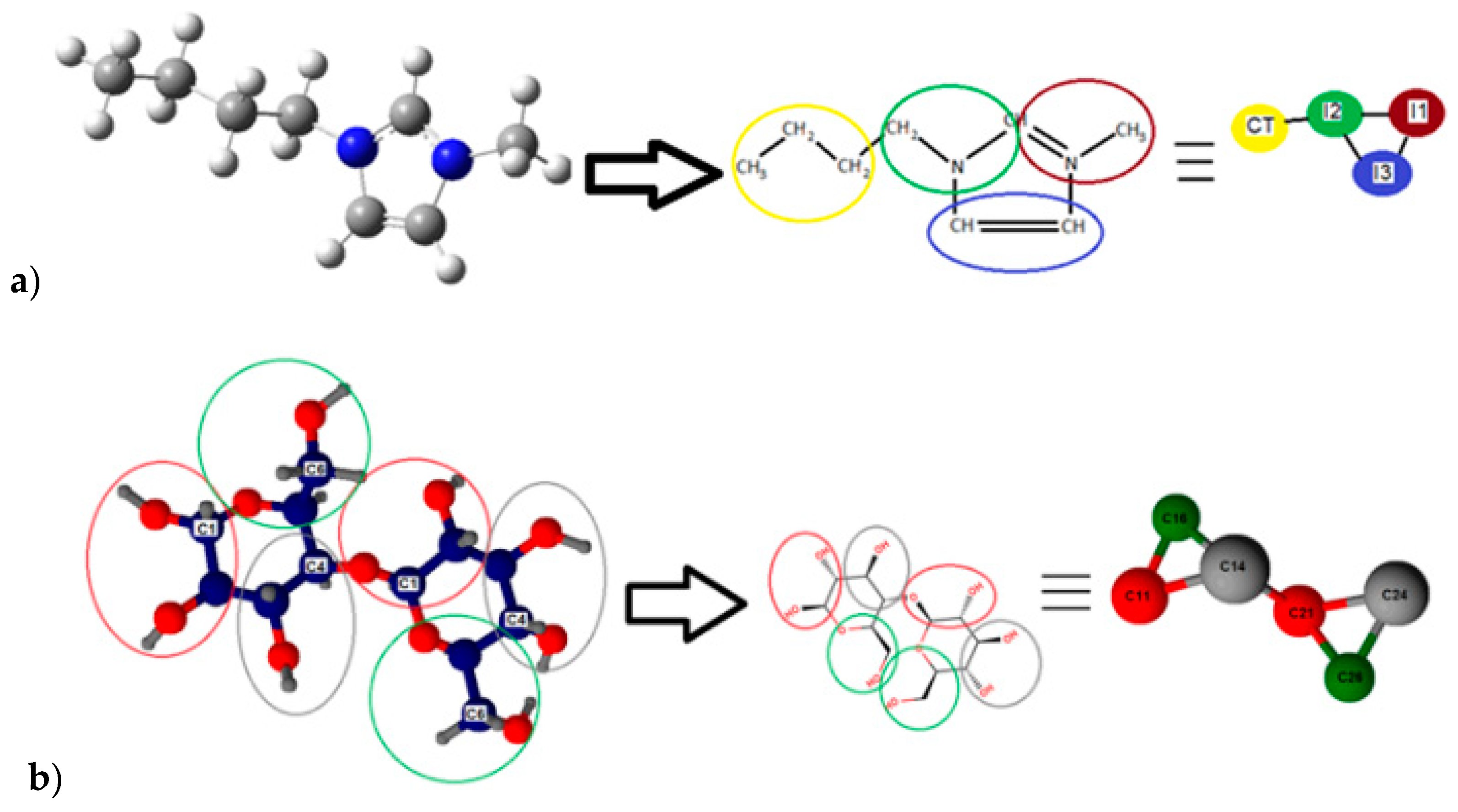
2.2.2. Molecular Simulation of [bmim][Cl] + Cellulose + Water
2.3. Instrumental Methods
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.3.3. Zeta Potential and Charge
3. Results and Discussion
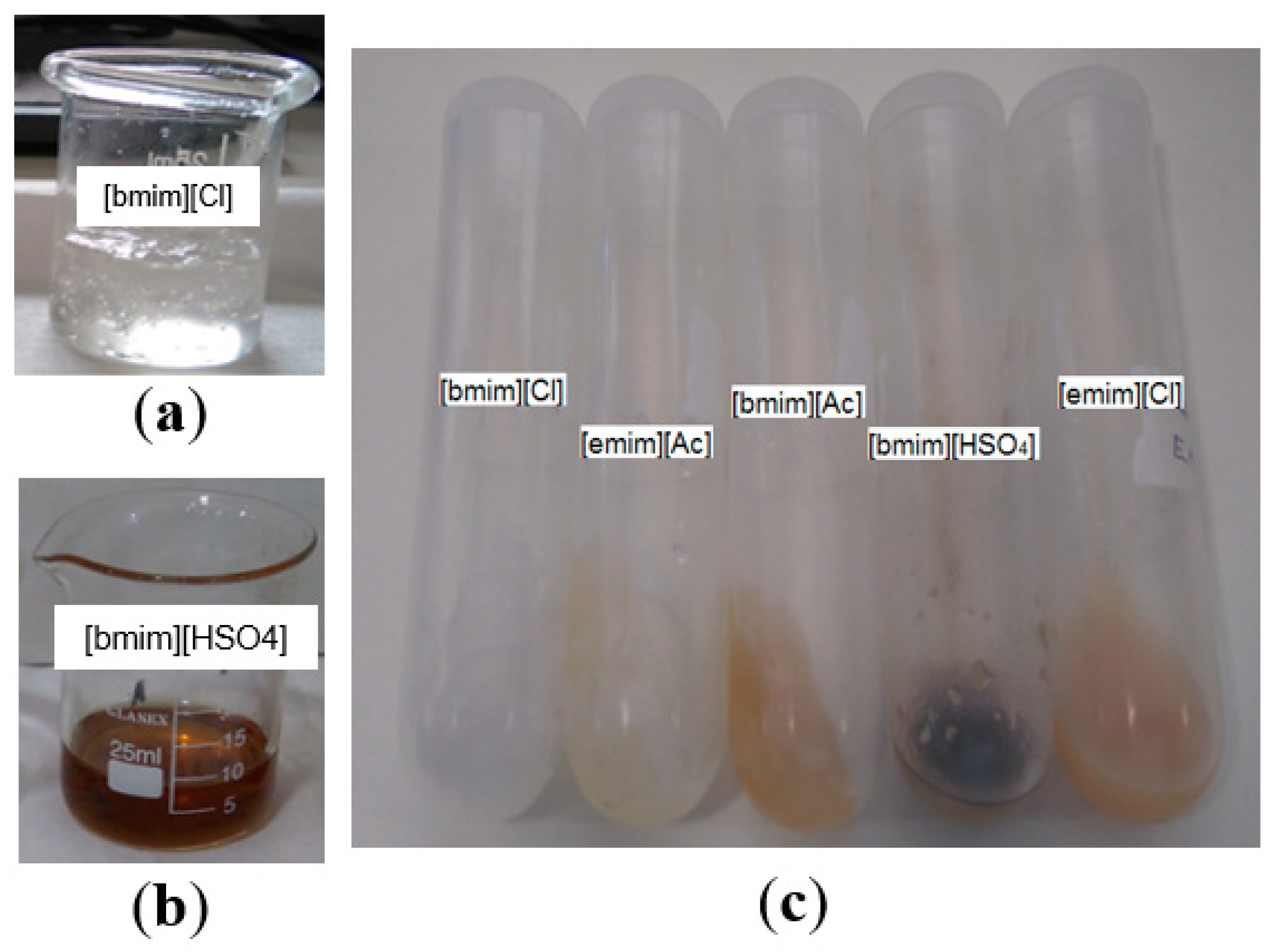
3.1. Dissolution Process
3.1.1. Experimental Results
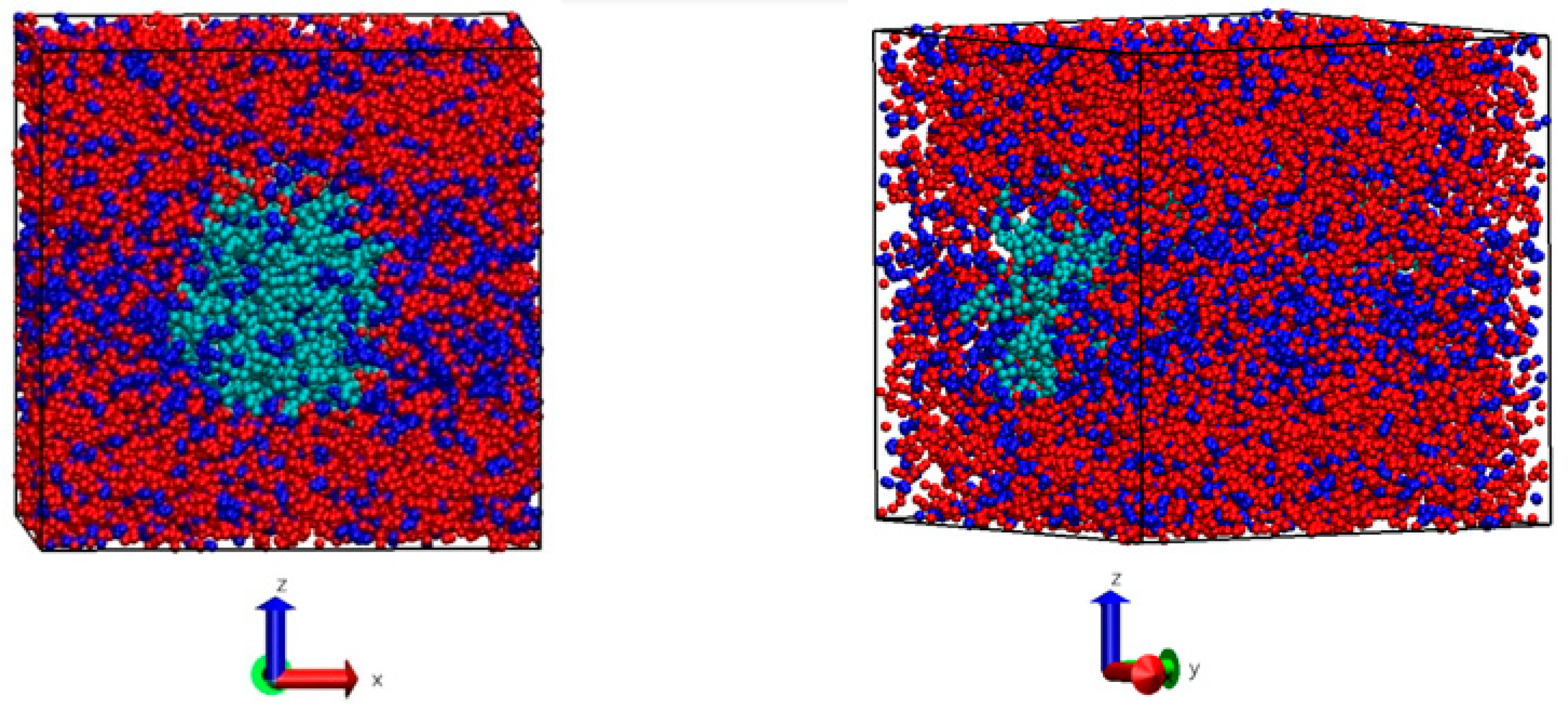
3.1.2. Molecular Dynamics Results
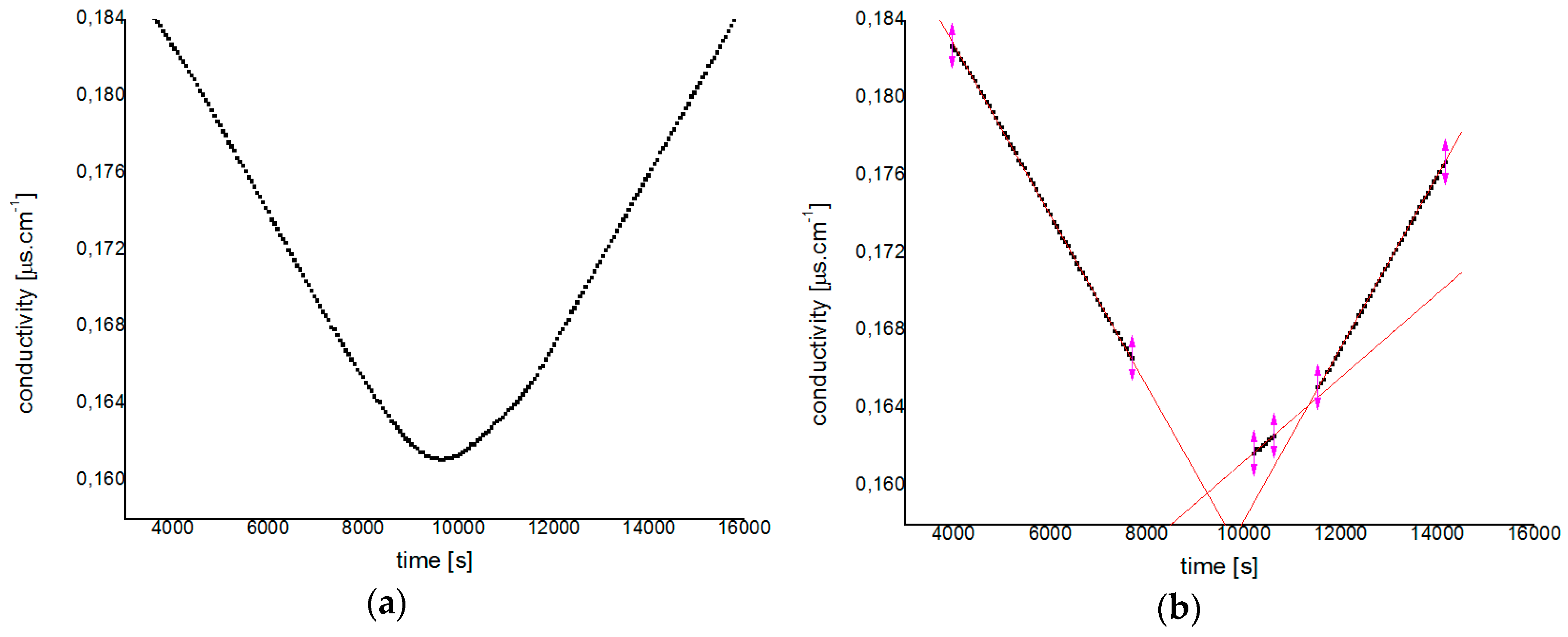
3.2. Hydrolysis Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salas, C.; Donoso, P.J.; Vargas, R.; Arriagada, C.A.; Pedraza, R.; Soto, D.P. The Forest Sector in Chile: An Overview and Current Challenges. J. For. 2016, 114, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.; Panwar, R.; Vlosky, R. The Global Forest Sector: Changes, Practices, and Prospects, 1st ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781439879276. [Google Scholar]
- Oatis, J. Chile’s Arauco to Move Ahead with $185 Million Plant. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-empresas-copec-cellulose/chiles-arauco-to-move-ahead-with-185-million-plant-idUSKCN1BO2A4 (accessed on 3 January 2019).
- Gibril, M.E.; Yue, Z.; Xin da, L.; Huan, L.; Xuan, Z.; Feng, L.H.; Muhuo, Y. Current status of applications of ionic liquids for cellulose dissolution and modifications: Review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2012, 4, 3556–3571. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquid processing of cellulose. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sixta, H. (Ed.) Handbook of Pulp, 1st ed.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH &Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; Volume 1, ISBN 3-527-30999-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ek, M.; Gellerstedt, G.; Henriksson, G. Pulp and Paper Chemistry and Technology; Ek, M., Gellerstedt, G., Henriksson, G., Eds.; Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG: Stockholm, Sweden, 2006; Volume 2, ISBN 9783110213416. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, F.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, H.; Zhou, J. Improved Synthesis of Cellulose Carbamates with Minimum Urea Based on an Easy Scale-up Method. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, P.; Cheng, G.; Xiong, B. Dissolution of cellulose in aqueous NaOH/urea solution: Role of urea. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Zha, C.; Gu, L. Direct dissolution of cellulose in NaOH/thiourea/urea aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of cellose with ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gericke, M.; Fardim, P.; Heinze, T. Ionic liquids—Promising but challenging solvents for homogeneous derivatization of cellulose. Molecules 2012, 17, 7458–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cull, S.G.; Holbrey, J.D.; Vargas-Mora, V.; Seddon, K.R.; Lye, G.J. Room-temperature ionic liquids as replacements for organic solvents in multiphase bioprocess operations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 69, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, L.C.; Rosa, J.N.; Moura Ramos, J.J.; Afonso, C.A.M. Preparation and characterization of new room temperature ionic liquids. Chem. A Eur. J. Weinh. Der Bergstr. Ger. 2002, 8, 3671–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Gilea, M.A.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Magee, J.W.; Seddon, K.R.; Widegren, J.A. The distillation and volatility of ionic liquids. Nature 2006, 439, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Rodríguez, H.; Rahman, M.; Rogers, R.D. Where are ionic liquid strategies most suited in the pursuit of chemicals and energy from lignocellulosic biomass? Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Radošević, K.; Redovniković, I.R.; Slivac, I.; Srček, V.G. Toxicity mechanisms of ionic liquids. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2017, 68, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruokonen, S.K.; Sanwald, C.; Sundvik, M.; Polnick, S.; Vyavaharkar, K.; Duša, F.; Holding, A.J.; King, A.W.T.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Lämmerhofer, M.; et al. Effect of Ionic Liquids on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Viability, Behavior, and Histology; Correlation between Toxicity and Ionic Liquid Aggregation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7116–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruokonen, S.K.; Sanwald, C.; Robciuc, A.; Hietala, S.; Rantamäki, A.H.; Witos, J.; King, A.W.T.; Lämmerhofer, M.; Wiedmer, S.K. Correlation between Ionic Liquid Cytotoxicity and Liposome–Ionic Liquid Interactions. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 2669–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkola, S.K.; Robciuc, A.; Lokajová, J.; Holding, A.J.; Lämmerhofer, M.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Holopainen, J.M.; King, A.W.T.; Wiedmer, S.K. Impact of amphiphilic biomass-dissolving ionic liquids on biological cells and liposomes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostonen, A.; Bervas, J.; Uusi-Kyyny, P.; Alopaeus, V.; Zaitsau, D.H.; Emel’Yanenko, V.N.; Schick, C.; King, A.W.T.; Helminen, J.; Kilpeläinen, I.; et al. Experimental and Theoretical Thermodynamic Study of Distillable Ionic Liquid 1,5-Diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-enium Acetate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 10445–10454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.W.T.; Asikkala, J.; Mutikainen, I.; Järvi, P.; Kilpeläinen, I. Distillable acid-base conjugate ionic liquids for cellulose dissolution and processing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6301–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, G.; King, A.W.T.; Borghei, M.; Rojas, O.J.; Lahti, J. Solvent Welding and Imprinting Cellulose Nanofiber Films Using Ionic Liquids. Biomacromolecules 2018, 20, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abushammala, H.; Krossing, I.; Laborie, M.P. Ionic liquid-mediated technology to produce cellulose nanocrystals directly from wood. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskak, N.A.M.; Julkapli, N.M.; Hamid, S.B.A. Understanding the effect of synthesis parameters on the catalytic ionic liquid hydrolysis process of cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 2017, 24, 2469–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Z.; Muhammad, N.; Sarwono, A.; Bustam, M.A.; Kumar, M.V.; Rafiq, S. Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals Using an Ionic Liquid. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabideau, B.D.; Agarwal, A.; Ismail, A.E. The role of the cation in the solvation of cellulose by imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofian, B.; Smith, J.C.; Cheng, X. Simulation of a cellulose fiber in ionic liquid suggests a synergistic approach to dissolution. Cellulose 2014, 21, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W. Cosolvent or antisolvent? A molecular view of the interface between ionic liquids and cellulose upon addition of another molecular solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 11780–11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray-Weale, A. Correlations in the Structure and Dynamics of Ionic Liquids. Aust. J. Chem. 2009, 62, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynninen, A.-P.; Panagiotopoulos, A.Z. Simulations of phase transitions and free energies for ionic systems. Mol. Phys. 2008, 106, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maginn, E.J. Molecular simulation of ionic liquids: Current status and future opportunities. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 373101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, G.; Cartes, M.; Rey-Castro, C.; Segura, H.; Mejía, A. Surface tension of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethyl sulfate or 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate with argon and carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, D.A.; Bermejo, M.D.; Cocero, M.J. Governing Chemistry of Cellulose Hydrolysis in Supercritical Water. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.; Overend, R.P.; Chornet, E.; Van Calsteren, M.-R. Mechanism of Dilute Acid Hydrolysis of Cellulose Accounting for its Degradation in the Solid State. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 1992, 12, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chng, C.-P.; Yang, L.-W. Coarse-grained models reveal functional dynamics—II. Molecular dynamics simulation at the coarse-grained level—Theories and biological applications. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2008, 2, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, C.A.; Bellesia, G.; Redondo, A.; Langan, P.; Chundawat, S.P.S.; Dale, B.E.; Marrink, S.J.; Gnanakaran, S. MARTINI coarse-grained model for crystalline cellulose microfibers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanne, M.; Rotenberg, B. New Coarse-Grained Models of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids for Bulk and Interfacial Molecular Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 7687–7693. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, B.L.; Devane, R.; Klein, M.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Nanoscale organization in room temperature ionic liquids: A coarse grained molecular dynamics simulation study. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, G.; Segura, H.; Mejía, A. Coarse-grained molecular dynamic simulations of selected thermophysical properties for 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 186, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Beckham, G.T.; Crowley, M.F.; Chang, C.H.; Matthews, J.F.; Bomble, Y.J.; Adney, W.S.; Himmel, M.E.; Nimlos, M.R. The energy landscape for the interaction of the family 1 carbohydrate-binding module and the cellulose surface is altered by hydrolyzed glycosidic bonds. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 10994–11002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Grigera, J.R.; Straatsma, T.P. The Missing Term in Effective Pair Potentials. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 6269–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, M.; Catana, D.A.; Vaca-Garcia, C.; Cecutti, C. Influence of water on the dissolution of cellulose in selected ionic liquids. Cellulose 2009, 16, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauru, L.K.J.; Hummel, M.; King, A.W.T.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Sixta, H. Role of solvent parameters in the regeneration of cellulose from ionic liquid solutions. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 2896–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathi, R.; Balamurugan, K.; Shi, J.; Subramanian, V.; Simmons, B.A.; Singh, S. Theoretical Insights into the Role of Water in the Dissolution of Cellulose Using IL/Water Mixed Solvent Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 14339–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, D.; Smit, B. Understanding Molecular Simulation, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-12-267351-4. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.; Yong, C.W.; Rodger, P.M. DL_POLY: Application to molecular simulation. Mol. Simul. 2002, 28, 385–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCAN-CM 65:02. Total acidic group content, SCAN-test Methods; Paper and Board Testing Committee: Stockholm, Sweden, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Y.; Kwak, S.-Y.; Song, Y.; Kim, H. Physical state of cellulose in BmimCl: Dependence of molar mass on viscoelasticity and sol-gel transition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, A.; Kadokawa, J.I. Fabrication and characterization of polysaccharide ion gels with ionic liquids and their further conversion into value-added sustainable materials. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszyńska, J.; Rachocki, A.; Bielejewski, M.; Tritt-Goc, J. Influence of cellulose gel matrix on BMIMCl ionic liquid dynamics and conductivity. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1641–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Dai, G. Preparations, properties, and formation mechanism of novel cellulose hydrogel membrane based on ionic liquid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.Y.; Abd Hamid, S.B.; Lai, C.W. Preparation of high crystallinity cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) by ionic liquid solvolysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 81, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Liu, C.F.; Sun, R.C. Fractionation of bagasse into cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin with ionic liquid treatment followed by alkaline extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8691–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Lopes, A.M.; João, K.G.; Morais, A.R.C.; Bogel-Łukasik, E.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Ionic liquids as a tool for lignocellulosic biomass fractionation. Sustain. Chem. Process. 2013, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, Z.; Kuehner, D.; Niu, L. Preparation of colorless ionic liquids “on water” for spectroscopy. Talanta 2009, 78, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Du, Z.; Zhang, X. Environmentally friendly and effective removal of Br− and Cl− impurities in hydrophilic ionic liquids by electrolysis and reaction. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, E.; Guo, B.; Zhang, D.; Shi, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y. Absorption of NO and NO2 in Caprolactam Tetrabutyl Ammonium Halide Ionic Liquids. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Shi, M.; Wang, F.; Chen, C.; Xu, J. Depolymerization of cellulose to glucose by oxidation–hydrolysis. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Hwang, I.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, H.S. Characteristics of the thermal degradation of glucose and maltose solutions. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 20, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S. Towards a molecular understanding of cellulose dissolution in ionic liquids: Anion/cation effect, synergistic mechanism and physicochemical aspects. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4027–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, N.; Draman, S.F.S.; Salleh, M.S.N.; Yusof, N.B. Dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquid: A review. Aip Conf. Proc. 2017, 1809, 020035. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Sale, K.L.; Holmes, B.M.; Simmons, B.A.; Singh, S. Understanding the interactions of cellulose with ILs: MD study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 4293–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.H.; Long, B.W.; Lu, Y.Z.; Meng, H.; Li, C.X. Solubility of hydrogen chloride in three 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquids in the pressure range (0 to 100) kPa and temperature range (298.15 to 363.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 2936–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunilall, V.; Bush, T.; Larsson, P.T. Supra-Molecular Structure and Chemical Reactivity of Cellulose I Studied Using CP / MAS 13 C-NMR. Cellulose-Fundamental Aspects; Intech Publishing: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ebner, G.; Schiehser, S.; Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T. Side reaction of cellulose with common 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 7322–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, T.; Heinze, T. Interaction of ionic liquids wlth polysaccharides 5. Solvents and reaction media for the modification of cellulose. BioResources 2008, 3, 576–601. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, S.; Méthot, M.; Bouchard, J. General procedure for determining cellulose nanocrystal sulfate half-ester content by conductometric titration. Cellulose 2015, 22, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- En, D.; Qu, C. Hidrólisis Ácida de Celulosa y Biomasa Lignocelulósica Asistida con Líquidos Iónicos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autonoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aguayo, M.G.; Fernández Pérez, A.; Reyes, G.; Oviedo, C.; Gacitúa, W.; Gonzalez, R.; Uyarte, O. Isolation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Rejected Fibers Originated in the Kraft Pulping Process. Polymers 2018, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.; Sattler, S.; Reza, M.; Bismarck, A.; Kontturi, E. Cellulose nanocrystals by acid vapour: Towards more effortless isolation of cellulose nanocrystals. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 202, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component (%) | Value |
|---|---|
| Glucan | 79.3 ± 0.8 |
| Xylan | 14.7 ± 0.6 |
| Total Lignin | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| Ash | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Site | ε0 (kcal/mol) | N | m | ro (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 – I1 | 0.375 | 9 | 6 | 4.693 |
| I2 – I2 | 0.345 | 9 | 6 | 4.693 |
| I3 – I3 | 0.199 | 9 | 6 | 4.120 |
| CT – CT | 0.469 | 9 | 6 | 5.249 |
| CI – CI | 0.148 | 12 | 6 | 4.232 |
| Temperature | 1 MD(g.cm−3) | 2 EXP(g.cm-3) | 3 MABD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298.15 | 1.169 | 1.082 | 7.49 |
| 323.15 | 1.157 | 1.067 | 7.77 |
| 348.15 | 1.138 | 1.053 | 7.47 |
| 363.15 | 1.130 | 1.045 | 7.51 |
| IL sample | D(nm) | Φz (mV) | ζ(µmolCOOH/gpulp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [bmim][HSO4] | 123 (48) | −24 (2.5) | 0.085 (0.02) |
| [emim][Cl] | 77 (25) | −12 (6) | 0 (0) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyes, G.; Aguayo, M.G.; Fernández Pérez, A.; Pääkkönen, T.; Gacitúa, W.; Rojas, O.J. Dissolution and Hydrolysis of Bleached Kraft Pulp Using Ionic Liquids. Polymers 2019, 11, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040673
Reyes G, Aguayo MG, Fernández Pérez A, Pääkkönen T, Gacitúa W, Rojas OJ. Dissolution and Hydrolysis of Bleached Kraft Pulp Using Ionic Liquids. Polymers. 2019; 11(4):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040673
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyes, Guillermo, María Graciela Aguayo, Arturo Fernández Pérez, Timo Pääkkönen, William Gacitúa, and Orlando J. Rojas. 2019. "Dissolution and Hydrolysis of Bleached Kraft Pulp Using Ionic Liquids" Polymers 11, no. 4: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040673
APA StyleReyes, G., Aguayo, M. G., Fernández Pérez, A., Pääkkönen, T., Gacitúa, W., & Rojas, O. J. (2019). Dissolution and Hydrolysis of Bleached Kraft Pulp Using Ionic Liquids. Polymers, 11(4), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040673