Description of the Droplet Size Evolution in Flowing Immiscible Polymer Blends
Abstract
1. Introduction
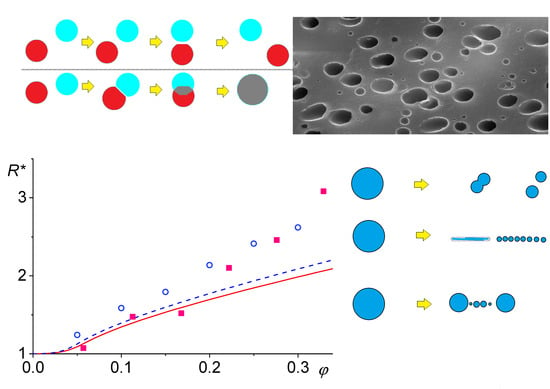
2. Droplet Breakup
2.1. Critical Capillary Number
2.2. Breakup Mechanisms
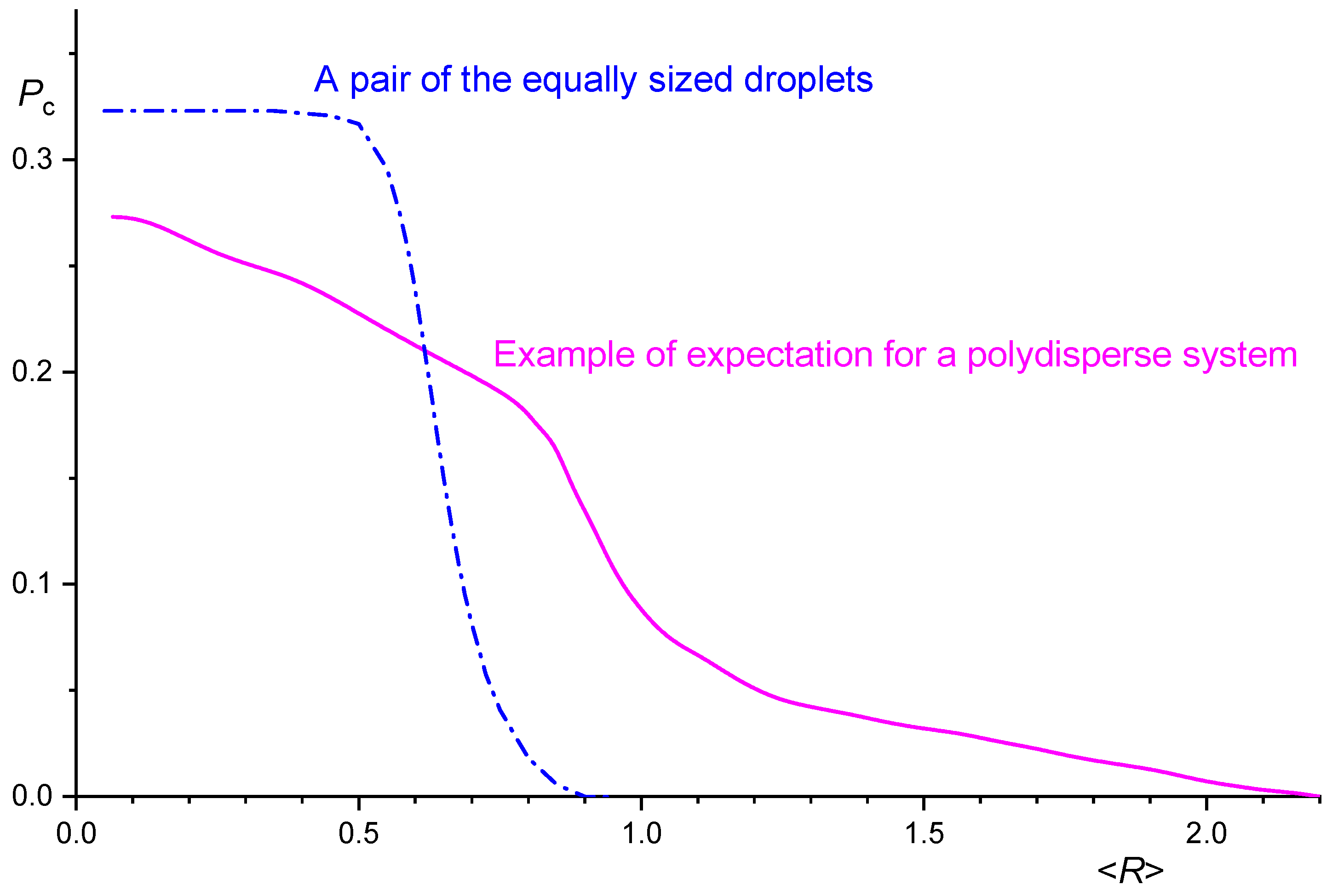
3. Coalescence
- approach of the droplets;
- drainage of the continuous phase trapped between the droplets, possibly deformed by the axial force;
- rupture of remainder of the continuous phase, usually by the formation of a “hole” on the thinnest spot; and
- evolution of a “neck” between droplets and formation of a coalesced droplet.
4. Competition between the Droplet Breakup and Coalescence
5. Discussion of Problems with Prediction of the Droplet Size Formed by Steady Mixing
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Symbols and Abbreviations
| Ac | Upstream interception area |
| A(s) | Function of far-field approaching |
| B | Width of deformed droplets |
| a, b | Adjustable dimensionless parameters of Equation (34) |
| ac, am | Parameters of Equation (64) |
| C(i, j): | Coagulation kernel—Equation (1) |
| C | Ratio of circulation length and droplet distance—Equation (33) |
| Ca | Capillary number Equation (2) |
| Cac | critical c.n. |
| CH | Parameter of coalescence in a blend—Equation (62) |
| D | Droplet deformation—Equation (7) |
| D* | Dimensionless function in Equation (37) |
| E | Rate of strain tensor |
| EDK | Volume energy—Equation (58) |
| F(i) | Overall breakup frequency—Equation (1) |
| F | Drag force |
| Fc | Driving force of the coalescence—Equation (29); FS in shear flow; Fe in uniaxial extension |
| f | General functions—Figure 3; not the same in Equation (23); another fF in Equation (61) |
| h | Distance between droplets surfaces |
| hc | critical distance |
| G’ | Storage modulus |
| G’m | s.m. of matrix |
| G’d | s.m. of the dispersed phase |
| g(m) | Function defined by Equation (31) |
| g(p) | function defined by Equation (66) |
| I | Unit second-order tensor |
| J | Rate of coalescence |
| J0 | r.c. without interdroplet interactions |
| K(p, Λ) | Function in Equations (36) and (37) |
| ki | Parameters in Equations (15b) and (64) |
| L | Length of deformed droplets |
| m | Parameter defined by Equation (32) |
| m | Orientation vectors |
| n | Number of droplets |
| ni, nj | of radius Ri, Rj |
| nk | of volume V1—Equation (1) |
| n | Number of spherical droplets in a volume unit—Equation (57) |
| nf | Number of fragments/daughter droplets |
| nf(i) | formed at breakup of a droplet of volume iV1 |
| n | Outward unit normal to the spherical contact surface |
| N1,d, N1,m | The first-normal stress differences of the droplets and matrix |
| Pc | Collision efficiency |
| p | Ratio of disperged phase and matrix viscosity ηd/ηm |
| q | The growth rate |
| R | Droplet radius |
| Rc | critical d.r. for breakup |
| R* = R/Rc | reduced d.r. |
| R0 | r. of parent droplet |
| Rf | r. of formed droplets |
| Rd | r. of daughter droplets |
| Req | equivalent d.r. def. by Equation (35) |
| RL | r. of steep decrease in Pc |
| RF | parameter of Equation (51) |
| r | The vector from the center of droplet 1 to the center of droplet 2 |
| r0 | Initial thread radius |
| rf | Radius of flattened part of a droplet—Equation (29) |
| S | Surface |
| s | Dimensionless center-to-center distance s = r/R |
| t | Time |
| tB | Breakup t. |
| ts | Local minimum of Equation (20) |
| tg | t. needed for the growth of α to its critical value |
| tc | t. of coalescence |
| ti | interaction t. |
| tB* | Dimensionless breakup time |
| u | Velocity of a particle |
| v | Velocity |
| v12(r) | relative velocity of colliding droplets |
| V1 | Elementary volume |
| x, y, z | Spatial Cartesian coordinates |
| x | 2πR/λ —Equation (20) |
| xm | Dominant wave number Equation (23) |
| α(t) | Distortion amplitude at time t |
| α0 | initial d.a. |
| β | Parameter in Equations (44)–(46) |
| Shear rate | |
| eff | effective s.r. |
| Stretching rate | |
| ζ | Friction resistance |
| η | Viscosity |
| ηm | matrix v. |
| ηd | droplets/dispersed phase v. |
| ηap | apparent v. of the blend |
| θ | Polar angle |
| Λ | Ratio of radii of smaller to larger droplet |
| λ | Wavelength of droplet breakup |
| λm | dominant w.; λ0 at t = 0 |
| λr | Ratio of the magnitude of the strain rate tensor to the sum of magnitudes of the strain rate and vorticity tensors |
| μ | Parameter of Equation (66) |
| σ | Interfacial tension |
| σef | effective if.t. |
| τm | Relaxation time |
| , | Functions in Equation (20) defined in [7] |
| φ | Azimuth |
| ϕ | Volume fraction of the dispersed phase |
| Ψ (λ, p) | Function in Equation (17) |
| Ω | Angular velocity tensor |
| ω(i, j) | Probability that a fragment formed by the breakup of a droplet of volume jV1 will have volume iV1 |
| EPR | Ethylene-propylene rubber |
| PCL | Poly(caprolactone) |
| PLA | Poly(lactic acid) |
| PP | Polypropylene |
References
- Favis, B.D. Factor influencing the morphology in immiscible polymer blends in melt processing. In Polymer Blends; Paul, D.R., Bucknall, C.B., Eds.; J. Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 501–537, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-546802-2.X5001-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fortelný, I. Theoretical aspects of phase morphology development. In Micro-and Nanostructured Multiphase Polymer Blends Systems; Harrats, C., Thomas, S., Groeninckx, G., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 43–90, doi:10.1201/9781420026542. [Google Scholar]
- Sundararaj, U. Phase morphology development in polymer blends. In Micro-and Nanostructured Multiphase Polymer Blends Systems; Harrats, C., Thomas, S., Groeninckx, G., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 133–164, doi:10.1201/9781420026542. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.-X. Macro, Micro and Nanostructured Morphologies of Multiphase Polymer Systems. In Handbook of Multiphase Polymer Systems; Boudenne, A., Ibos, L., Candau, Y., Thomas, S., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 161–249, doi:10.1002/9781119972020.ch6. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.A. Dynamics of drop deformation and breakup in viscous fluids. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1994, 26, 65–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A.; Shi, Z.H. Development of polymer blend morphology during compounding in a twin-screw extruder. Part I: Droplet dispersion and coalescence—A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1992, 32, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.M.H. Emulsions: The dynamic of liquid-liquid mixing. In Materials Science and Technology; Meijer, H.E.H., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1997; Volume 18, pp. 115–188. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.D. Multiphase Flow in Polymer Processing; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, C.L.; Moldenaers, P. Microstructural evolution in polymer blends. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2002, 34, 177–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. The formation of emulsions in definable fields of flow. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1934, 146, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffey, C.E.; Brenner, H.A. A second-order theory for shear deformation of drops. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1967, 24, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.G. The deformation of a drop in a general time-dependent fluid flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1969, 37, 601–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthes-Biesel, D.; Acrivos, A. Deformation and burst of a liquid droplet freely suspended in a linear shear field. J. Fluid Mech. 1973, 61, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, H.P. Dispersion phenomena in high viscosity immiscible fluid systems and application of static mixers as dispersion devices in such systems. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1982, 14, 225–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartok, W.; Mason, S.G. Particle motions in sheared suspensions: VII. Internal circulation in fluid droplets (theoretical). J. Colloid Sci. 1958, 13, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartok, W.; Mason, S.G. The dependence of the viscosity on the concentration of sodium carboxymethylcellulose in aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Sci. 1959, 14, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumscheidt, F.D.; Mason, S.G. Particle motions in sheared suspensions XII. Deformation and burst of fluid drops in shear and hyperbolic flow. J. Colloid Sci. 1961, 16, 238–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torza, S.; Cox, R.C.; Mason, S.G. Particle motions in sheared suspensions XXVII. Transient and steady deformation and burst of liquid drops. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1972, 38, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruijn, R.A. Deformation and Break-Up of Drops in Simple Shear Flows. Ph.D. Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, G.W.M.; Hansen, S.; Meijer, H.E.H. Constitutive modeling of dispersive mixtures. J. Rheol. 2001, 45, 659–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, E.K.; White, J.L. Manufacturing of polymer blends using polymeric and low molecular weight reactive compatibilizers. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Blends; Isayev, A.I., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 263–314. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oene, H.J. Modes of dispersion of viscoelastic fluids in flow. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1972, 40, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararaj, U.; Dori, Y.; Macosko, W. Sheet formation in immiscible polymer blends: Model experiments on initial blend morphology. Polymer 1995, 36, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodgaonkar, P.G.; Sundararaj, U. Prediction of dispersed phase drop diameter in polymer blends: The effect of elasticity. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmendorp, J.J.; Maalcke, R.J. A study on polymer blending microrheology: Part 1. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1985, 25, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, F.; Goldsmith, H.L.; Mason, S.G. Particle motions in non-Newtonian media II. Poiseuille flow. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1971, 15, 297–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, P.P.; Ryan, M.E.; Stroeve, P. Experimental study on the breakup of model viscoelastic drops in uniform shear flow. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1994, 33, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mighri, F.; Carreau, P.J.; Ajji, A. Influence of elastic properties on drop deformation in elongational flow. J. Rheol. 1997, 41, 1183–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mighri, F.; Carreau, P.J.; Ajji, A. Influence of elastic properties on drop deformation in shear flow. J. Rheol. 1998, 42, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerdwijitjarud, W.; Larson, R.G.; Sirivat, A.; Solomon, M.J. Influence of weak elasticity of dispersed phase on droplet behavior in sheared polybutadiene/poly(dimethyl siloxane) blends. J. Rheol. 2003, 47, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechbal, N.; Bousmina, M. In situ observation of unusual drop deformation and wobbling in simple shear flow. Rheol. Acta 2009, 48, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, L.; Macosko, C.W.; Pearson, S.D. Influence of normal stress difference on polymer drop deformation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretheway, D.C.; Leal, L.G. Deformation and relaxation of Newtonian drops in planar extensional flows of a Boger fluid. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2001, 99, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Sarkar, K. Deformation and breakup of a viscoelastic drop in a Newtonian matrix under steady shear. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 584, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliken, W.J.; Leal, L.G. Deformation and breakup of viscoelastic drops in planar extensional flows. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1991, 40, 355–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibillo, V.; Simeone, M.; Guido, S. Break-up of a Newtonian drop in a viscoelastic matrix under simple shear flow. Rheol. Acta 2004, 43, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flumerfelt, R.W. Drop breakup in simple shear fields of viscoelastic fluids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1972, 11, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, S.; Simeone, M.; Greco, F. Deformation of a Newtonian drop in a viscoelastic matrix under steady shear flow: Experimental validation of slow flow theory. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2003, 114, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhulst, K.; Moldenaers, P.; Minale, M. Drop shape dynamics of a Newtonian drop in a non-Newtonian matrix during transient and steady shear flow. J. Rheol. 2007, 51, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migler, K.B.; Hobbie, E.K.; Qiao, F. In line study of droplet deformation in polymer blends in channel flow. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 2282–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Schowalter, W.R. Rheological properties of nondilute suspensions of deformable particles. Phys. Fluids 1975, 18, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, K.M.B.; Agterof, W.G.M.; Mellema, J. Droplet breakup in concentrated emulsions. J. Rheol. 2001, 45, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.M.H.; Meijer, H.E.H. Dynamic of liquid-liquid mixing: A 2-zone model. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1995, 35, 1766–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Leal, L.G. Drop deformation and break-up in concentrated suspensions. J. Rheol. 2010, 54, 981–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A. On the viscosity–concentration dependence of immiscible polymer blends. J. Rheol. 1991, 35, 1615–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmendorp, J.J.; Van der Vegt, A.K. Fundamentals of morphology formation in polymer blending. In Two-Phase Polymer Systems; Utracki, L.A., Ed.; Hansen: Munich, Germany, 1991; pp. 165–184. [Google Scholar]
- Cristini, V.; Guido, S.; Alfani, A.; Bławzdziewicz, J.; Loewenberg, M. Drop breakup and fragment size distribution in shear flow. J. Rheol. 2003, 47, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Jůza, J. Prediction of average droplet size in flowing immiscible polymer blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Puyvelde, P.; Yang, H.; Mewis, J.; Moldenaers, P. Breakup of filaments in blends during simple shear flow. J. Rheol. 2000, 44, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tomotika, S. On the instability of a cylindrical thread of a viscous liquid surrounded by another viscous fluid. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1935, 150, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palierne, J.F.; Lequeux, F. Sausage instability of a thread in a matrix; linear theory for viscoelastic fluids and interface. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1991, 40, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, W. Spontane Aufteilung von Flüssigkeitszylindern in kleine Kugeln. Kolloid Z. 1953, 134, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, T.; Cox, R.G.; Mason, R.G. Breakup of extending liquid threads. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1975, 2, 113–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakhar, D.; Ottino, J.M. Breakup of liquid threads in linear flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1987, 13, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.M.H.; Meijer, H.E.H. Droplet breakup mechanisms: Stepwise equilibrium versus transient dispersion. J. Rheol. 1993, 37, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.A.; Leal, L.G. Relaxation and breakup of an initially extended drop in an otherwise quiescent fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 1989, 198, 399–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesters, A.K. The modeling of coalescence processes in fluid–liquid dispersions: A review of current understanding. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. A 1991, 69, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zeichner, G.R.; Schowalter, W.R. Use of trajectory analysis to study stability of colloidal dispersions in flow fields. AIChE J. 1977, 23, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zinchenko, A.K.; Davis, R.H. The collision rate of small drops in linear flow fields. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 265, 161–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, M.A.; Davis, R.H. The effect of slight deformation on droplet coalescence in linear flow. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoluchowski, M. Versuch einer mathematischen theorie der koagulationskinetik kollider losungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1917, 92, 129–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.J.A.; Anderson, P.D. Modeling film drainage and coalescence of drops in a viscous. Fluid Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davis, R.H. The collision of small drops due to Brownian and gravitational motion. J. Fluid Mech. 1991, 230, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.M.H. Dynamics of Liquid–Liquid Mixing. Ph.D. Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Jeelani, S.A.K.; Hartland, S. Effect of interfacial mobility on thin film drainage. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 164, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Jůza, J. Modeling of interface mobility in the description of flow-induced coalescence in immiscible polymer blends. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchenko, A.Z.; Davis, R.H. Hydrodynamical interaction of deformable drops. In Emulsions: Structure Stability and Interactions, Interface Science and Technology; Petsev, D.N., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 4, pp. 391–447, doi:10.1016/S1573-4285(04)80012-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, P.T.; Janssen, J.J.M.; Groeneweg, F.; Agterof, W.G.M. Coalescence in emulsions containing inviscid drops with high interfacial mobility. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1994, 85, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, A.; Acrivos, A. On creeping motion of two arbitrary-sized touching spheres in a linear shear fields. J. Fluid Mech. 1973, 59, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmendorp, J.J.; Van der Vegt, A.K. A study of polymer blending microrheology. Part IV. The influence of coalescence on blend morphology origination. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1986, 26, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Jůza, J. Modeling of the influence of matrix elasticity on coalescence probability of colliding droplets in shear flow. J. Rheol. 2012, 56, 1393–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Jůza, J. Consequences of the effect of matrix elasticity on the rotation of droplet pairs for collision efficiency. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jůza, J.; Fortelný, I. Flow induced coalescence in polymer blends. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2013, 7, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Jůza, J. Flow-induced coalescence in polydisperse systems. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhou, C. Coalescence of droplets in viscoelastic matrix with diffuse interface under simple shear flow. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2007, 45, 1856–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.S.; Vinogradov, G.V. Theory of dilute polymer solutions in viscoelastic fluid with a single relaxation time. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1984, 15, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, W.; Cohen, C. Concentration fluctuations of Brownian particles in a viscoelastic solvent. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 6510–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.C.; Baldessari, F.; Leal, L.G. Study of molecular weight effects on coalescence: Interface slip layer. J. Rheol. 2003, 47, 911–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemer, M.B.; Chen, X.; Papadopoulos, D.H.; Bławzdziewicz, J.; Loewenberg, M. Hindered and enhanced coalescence of drops in Stokes flows. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 114501:1–114501:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldessari, F.; Leal, L.G. Effect of overall drop deformation on flow-induced coalescence at low capillary numbers. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 013602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Baldessari, F.; Ceniceros, H.D.; Leal, L.G. Coalescence of two equal-sized deformable drops in an axisymmetric flow. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, P.; Loewenberg, M. Coalescence of Drops with Tangentially Mobile Interfaces: Effects of Ambient Flow. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1161, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannozzi, C. Relaxation and coalescence of two equal-sized viscous drops in a quiescent matrix. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 694, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdravkov, A.N.; Peters, G.W.M.; Meijer, H.E.H. Film drainage and interfacial instabilities in polymeric systems with diffuse interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rother, M.A.; Davis, R.H. Simplified model for droplet growth in shear flow. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.-P.; Bates, F.S.; Macosko, C.W. Coalescence in polymer blends during shearing. AIChE J. 2000, 46, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caserta, S.; Simeone, M.; Guido, S. A parametr investigation of shear-induced coalescence in semidilute PIB–PDMS polymer blends: Effects of shear rate, shear stress, volume fraction, and viscosity. Rheol. Acta 2006, 45, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, B.E.; Gopalkrishnan, P.; Hudson, S.D.; Jamieson, A.M.; Rother, M.A.; Davis, R.H. Droplet growth by coalescence in binary fluid mixtures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 983041–983044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, V.E.; Wolf, B.A. Bimodal drop size distribution during the early stages of shear induced coalescence. Polymer 2005, 46, 9265–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Börschig, C.; Fries, B.; Gronski, W.; Weis, C.; Friedrich, C. Shear-induced coalescence in polymer blends—Simulations and rheo small angle light scattering. Polymer 2000, 41, 3029–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, M.; Pasquino, R.; Grizzuti, N. Effect of viscosity-controlled interfacial mobility on the coalescence of immiscible polymer blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Huang, Y.; Sheng, J. Morphology development in polypropylene/polystyrene blends during coalescence under shear. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramic, A.J.; Hudson, S.D.; Jamieson, A.M.; Manas–Zloczower, I. Temporary droplet-size hysteresis in immiscible polymer blends. Polymer 2000, 41, 6263–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minale, M.; Moldenaers, P.; Mewis, J. Effect of shear history on the morphology of immiscible polymer blends. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 5470–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minale, M.; Mewis, J.; Moldenaers, P. Study of the morphological hysteresis in immiscible polymer blends. AIChE J. 1998, 44, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Netti, P.A.; Acierno, D. Microstructural evolutions of LDPE/PA6 blends by rheological and rheo–optical analyses: Influence of flow and compatibilizer on break-up and coalescence processes. Polymer 2007, 48, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, D.; Peuvrel-Disdier, E. In situ characterization by small angle light scattering of the shear-induced coalescence mechanisms in immiscible polymer blends. J. Rheol. 1999, 43, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jůza, J.; Fortelný, I. Flow-induced coalescence: Evaluation of some approximation. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 373, 1600097:1–1600097:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlazhan, S.A.; Lindt, J.T. Kinetics of structure development in liquid-liquid dispersion under simple shear flow. Theory J. Rheol. 1996, 40, 1095–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, N. Analysis of morphology formation in elastomer blends. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1977, 50, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Kovář, J. Droplet size of the minor component in the mixing of melts of immiscible polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 1989, 25, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngaae-Jørgensen, J.; Valenza, A. Structuring of polymer blends in simple shear flow. Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Symp. 1990, 38, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huneault, M.A.; Shi, Z.H.; Utracki, L.A. Development of polymer blend morphology during compounding in a twin–screw extruder. Part IV: A new computational model with coalescence. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1995, 35, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A. The mechanical stability of synthetic polymer latexes. J. Colloid Sci. 1973, 42, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Živný, A. Theory of competition between breakup and coalescence in in flowing polymer blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1995, 35, 1872–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamare, L.; Vergnes, B. Computation of morphological changes of a polymer blend along a twin–screw extruder. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, T.; Xi, H. How copolymers promote mixing of immiscible homopolymers. J. Rheol. 1996, 40, 663–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.P.; Bates, F.S.; Macosko, C.W. Modeling of coalescence in polymer blends. AIChE J. 2002, 48, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potente, H.; Bastian, M. Calculating morphology development of polymer blends on the basis of results of boundary and finite element simulation using the sigma simulation software. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2000, 40, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I. Analysis of the effect of breakup frequency on the steady droplet size in flowing polymer blends. Rheol. Acta 2001, 40, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Park, O.O. Rheology and dynamics of immiscible polymer blends. J. Rheol. 1994, 38, 1405–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Dimzoski, B.; Michálková, D.; Mikešová, J.; Kaprálková, L. Dependence of the average size of particles formed during steady mixing on their concentration in immiscible polymer blends. J. Macromol. Sci. 2013, 52, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Ostafińska, A.; Michálková, D.; Jůza, J.; Mikešová, J.; Šlouf, M. Phase structure evolution during mixing and processing of poly(lactic acid)/polycaprolactone (PLA/PCL) blends. Polym. Bull. 2015, 72, 2931–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousmina, M.; Ait-Kadi, A.; Faisant, J.B. Determination of shear rate and viscosity from batch mixer data. J. Rheol. 1999, 43, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fortelný, I.; Jůza, J. Description of the Droplet Size Evolution in Flowing Immiscible Polymer Blends. Polymers 2019, 11, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050761
Fortelný I, Jůza J. Description of the Droplet Size Evolution in Flowing Immiscible Polymer Blends. Polymers. 2019; 11(5):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050761
Chicago/Turabian StyleFortelný, Ivan, and Josef Jůza. 2019. "Description of the Droplet Size Evolution in Flowing Immiscible Polymer Blends" Polymers 11, no. 5: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050761
APA StyleFortelný, I., & Jůza, J. (2019). Description of the Droplet Size Evolution in Flowing Immiscible Polymer Blends. Polymers, 11(5), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050761