Controlling the Crack Propagation Path of the Veil Interleaved Composite by Fusion-Bonded Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Composite Laminates
2.3. Tests of Interlaminar Fracture Toughness
2.4. Other Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
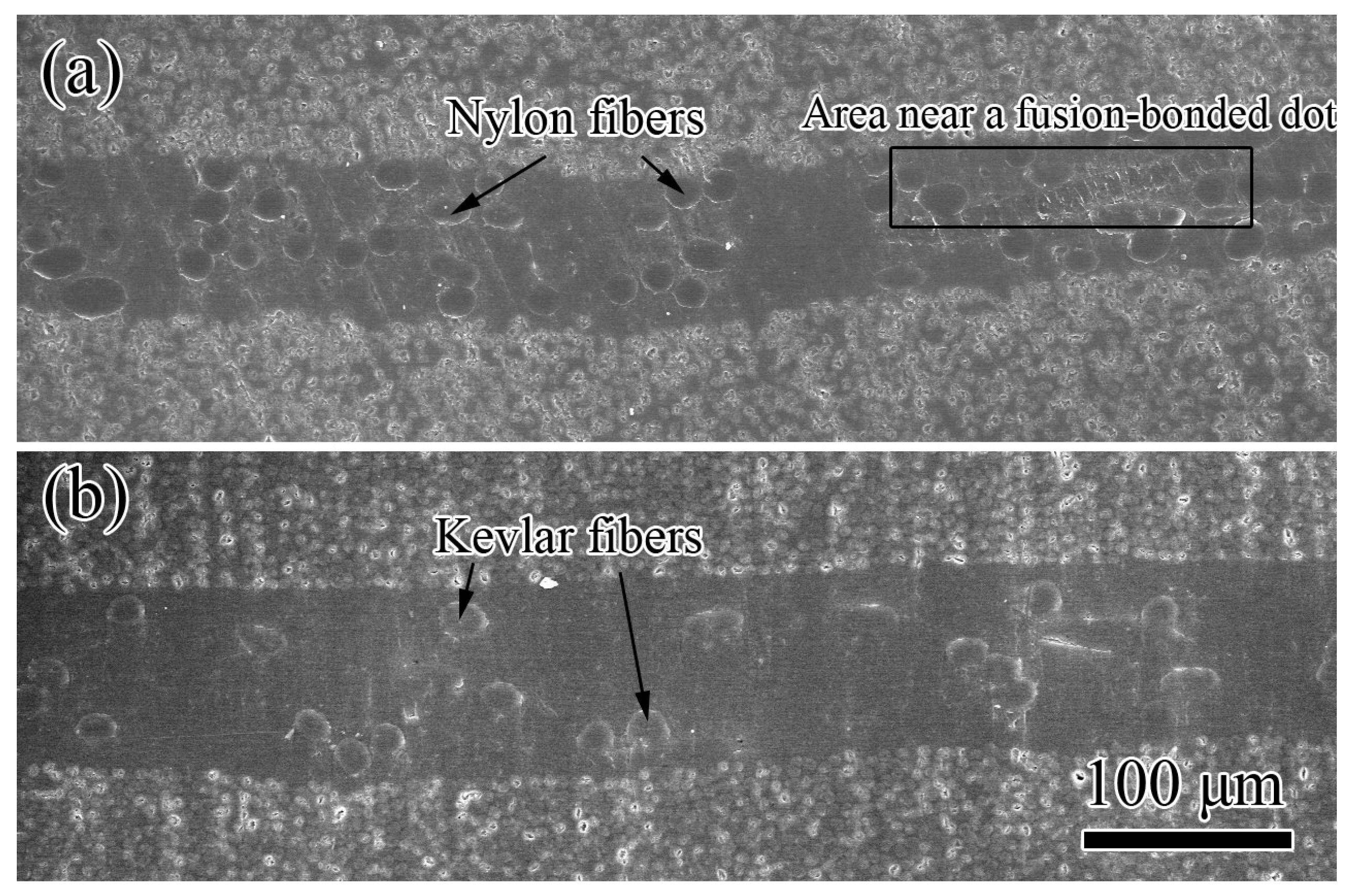
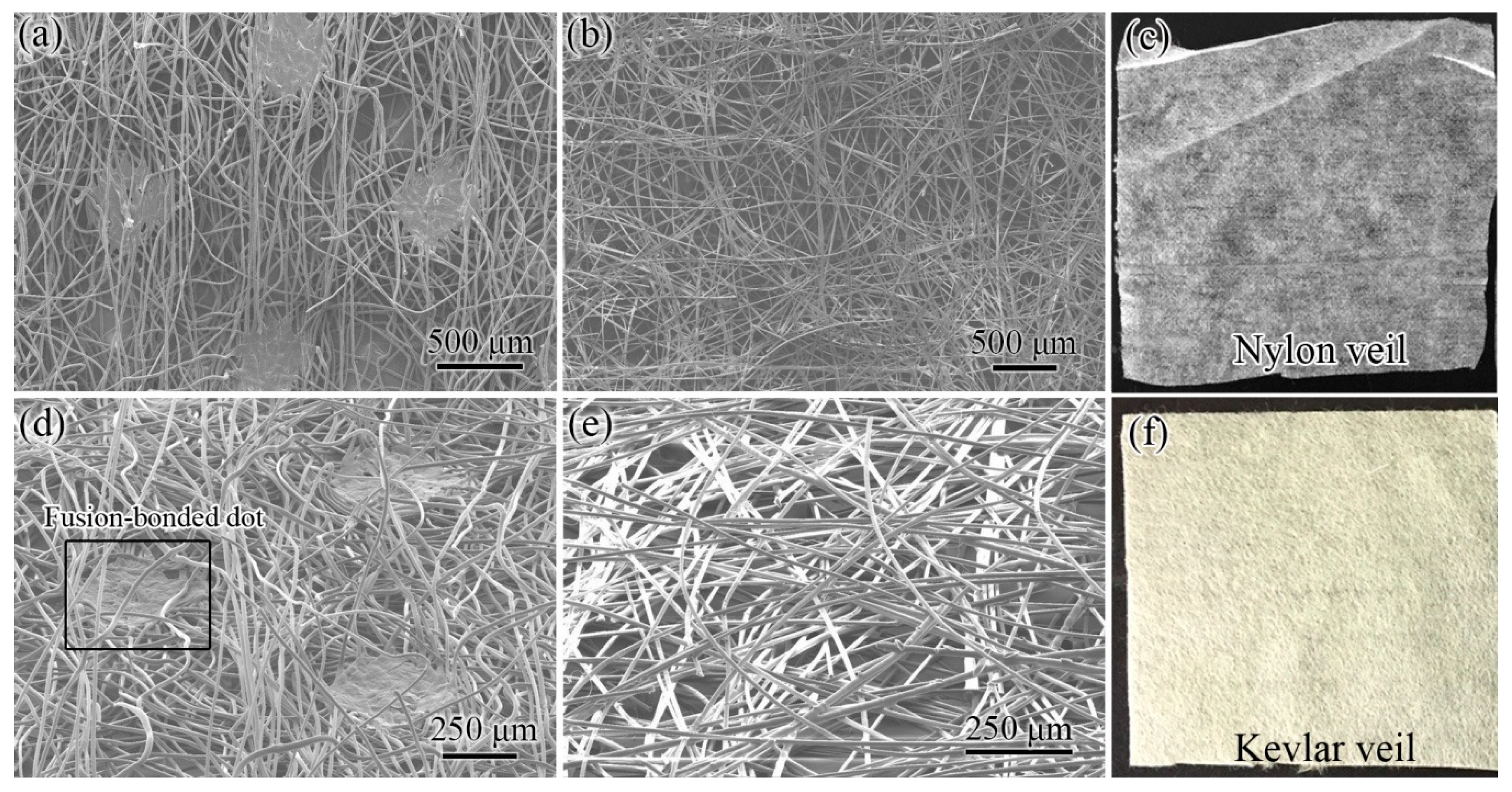
3.1. Structure of Veils
3.2. Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Composites
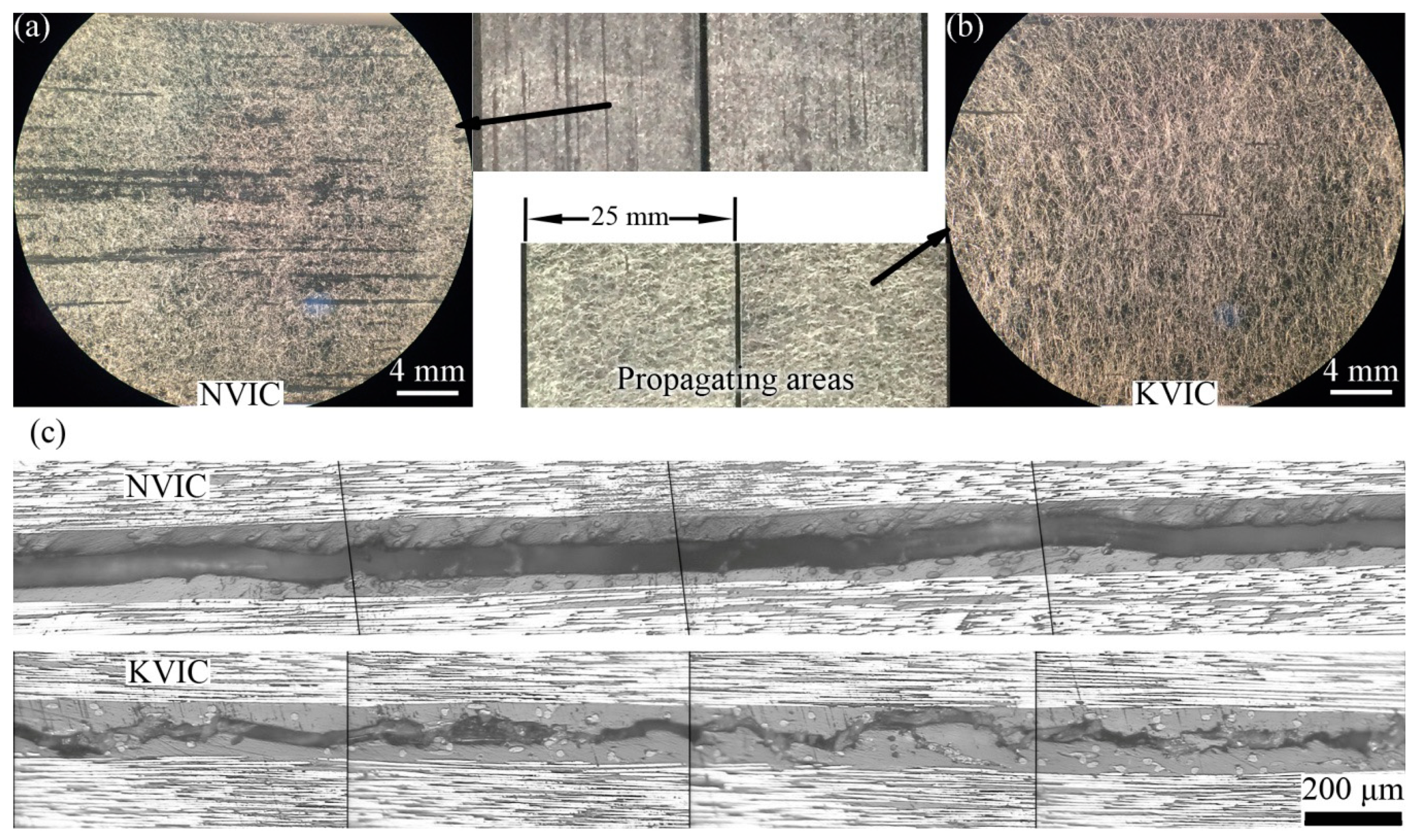
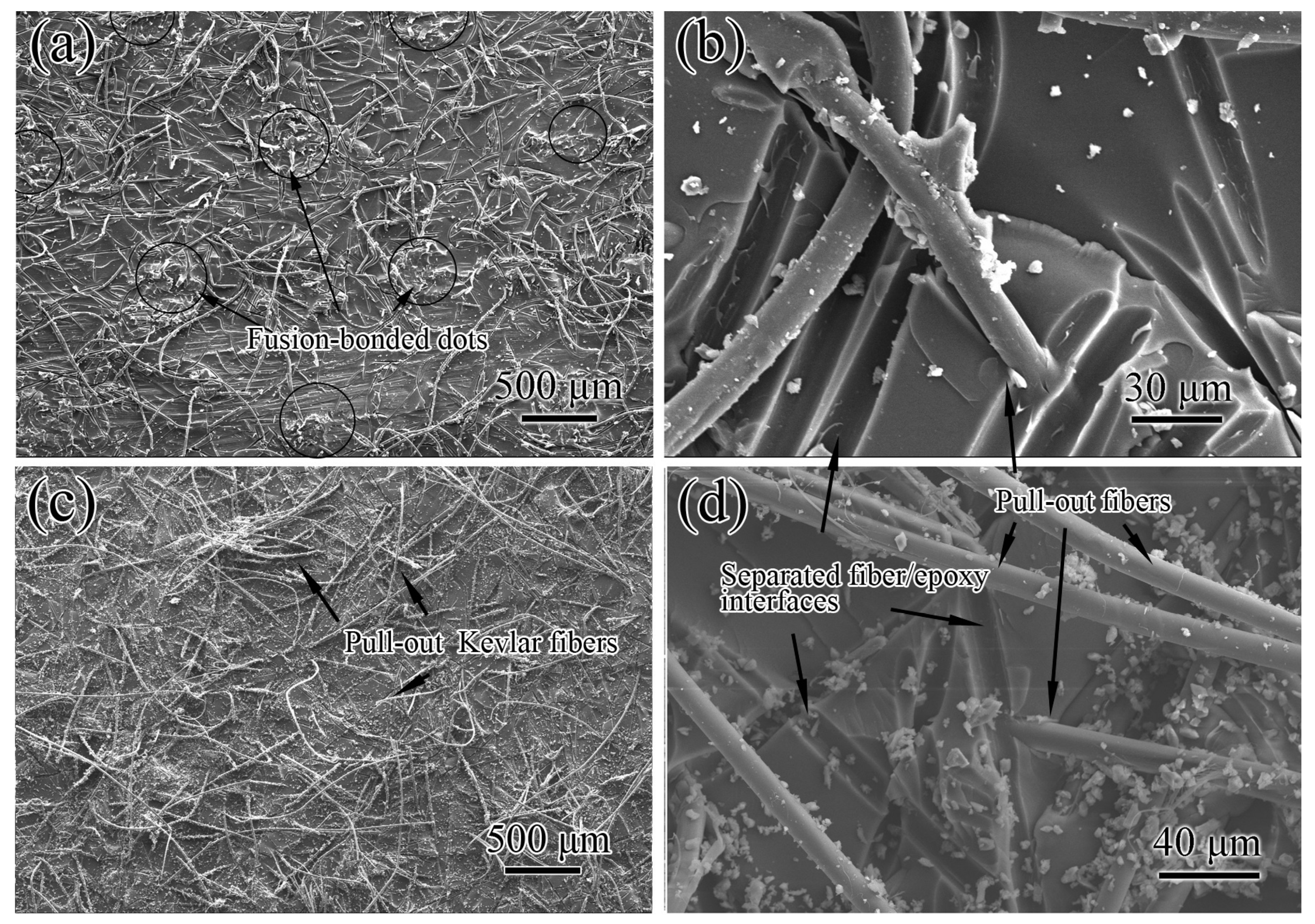
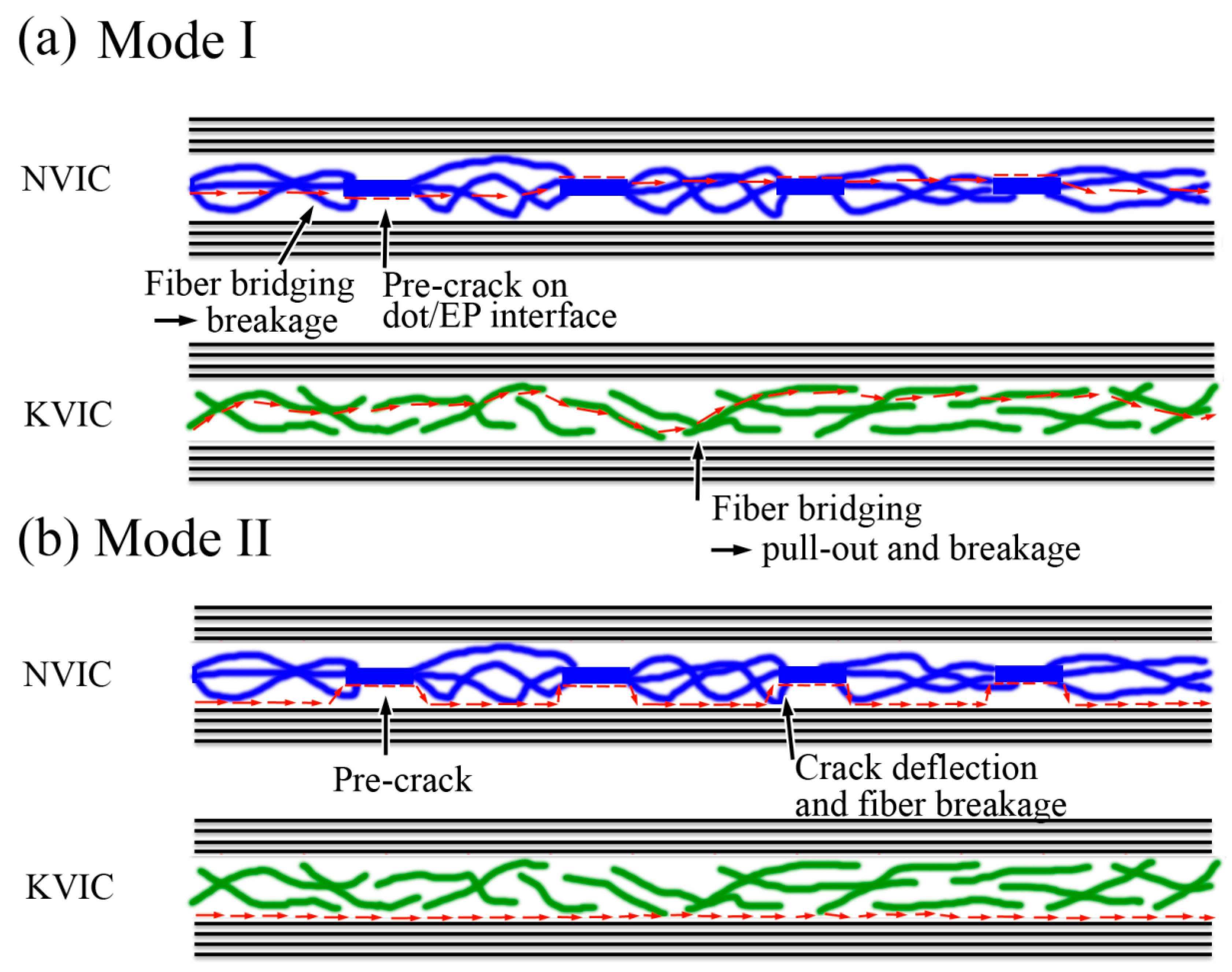
3.3. Mode I Interlaminar Fracture
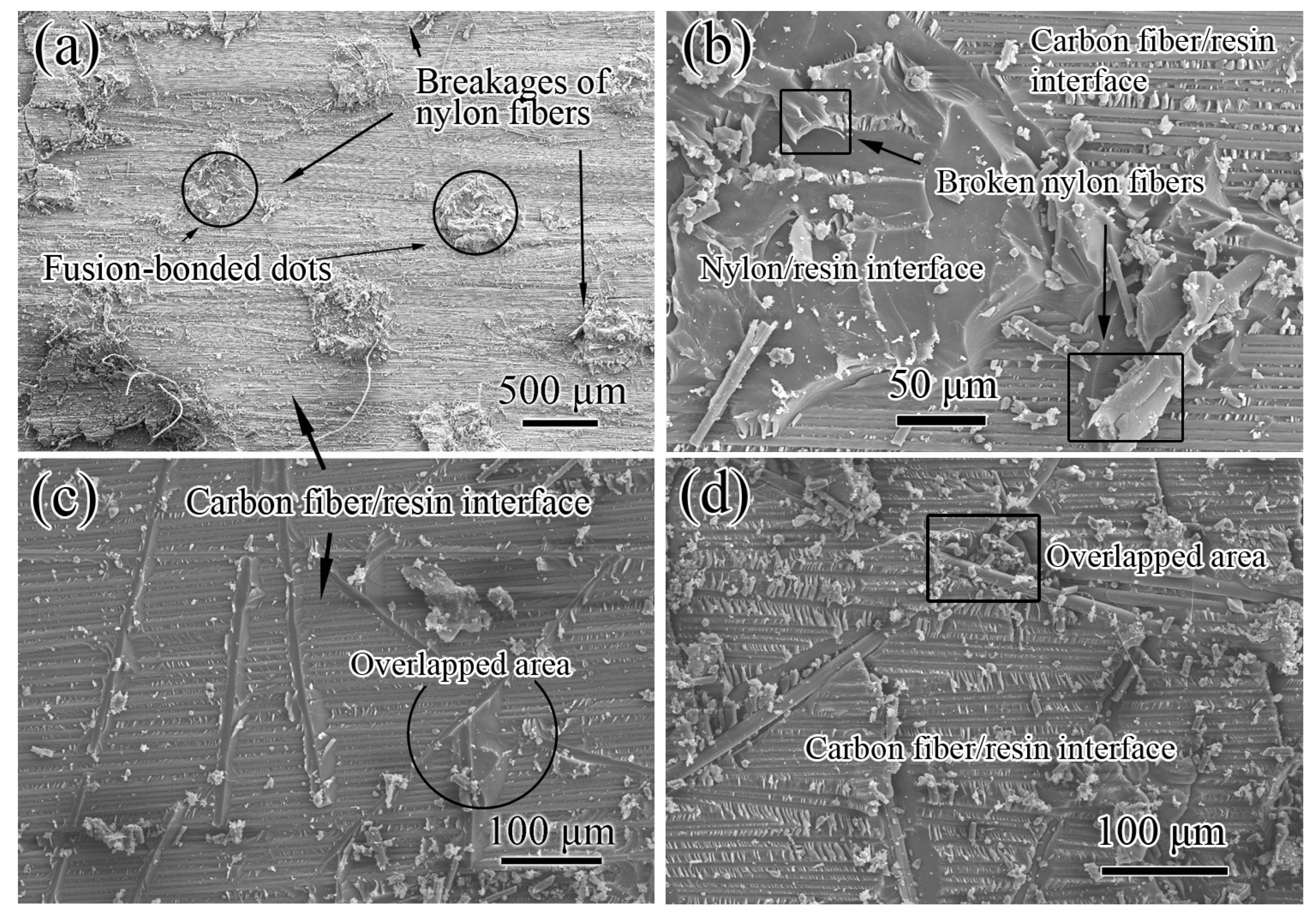
3.4. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yi, X. The Development of Advanced Composite; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Yi, X.; An, X.; Zhang, C.; Yan, L.; Deng, H. Development of interleaved fibre-reinforced thermoset polymer matrix composites. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2014, 31, 273–285. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Yi, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, L.P. Simultaneously increasing the electrical conductivity and fracture toughness of carbon-fiber composites by using silver nanowires-loaded interleaves. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 97, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.N.; Kumar, V.; VERMA, S.K. Fracture toughness behaviour of carbon fibre epoxy composite with Kevlar reinforced interleave. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2006, 132, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Yi, X. The production of tough, electrically conductive carbon fiber composite laminates for use in airframes. Carbon 2013, 58, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ye, L.; Deng, S.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y. CF/EP composite laminates with carbon black and copper chloride for improved electrical conductivity and interlaminar fracture toughness. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, B.; Guan, J.; Mirjalili, V.; Zhang, Y.; Chun, L.; Hubert, P.; Simard, B.; Kingston, C.T.; Bourne, O.; Johnston, A. Enhancement of mechanical performance of epoxy/carbon fiber laminate composites using single-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Kim, J.-K. Improved interlaminar shear properties of multiscale carbon fiber composites with bucky paper interleaves made from carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2012, 50, 5265–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Gao, J.; Mai, Y.-W. Improvement of interlaminar fracture toughness in carbon fiber/epoxy composites with carbon nanotubes/polysulfone interleaves. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 140, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskizeybek, V.; Yar, A.; Avci, A. CNT-PAN hybrid nanofibrous mat interleaved carbon/epoxy laminates with improved Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 157, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckermann, G.W.; Pickering, K.L. Mode I and Mode II interlaminar fracture toughness of composite laminates interleaved with electrospun nanofibre veils. Compos. Part A 2015, 72, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, J.E. Correlation of impact and delamination resistance in interleafedlaminates. Proc. ICCM-VI & ECCM-2 1987, 3, 96–107. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, J.E. Improved impact and delamination resistance through interleafing. Key Eng. Mater. 1989, 37, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, S.; Leibovich, H.; Green, A.; Intrater, R.; Avrahami, R.; Zussman, E.; Siegmann, A.; Sherman, D. Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of nylon 66 nanofibrilmat interleaved carbon/epoxy laminates. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzetti, R.; Yan, X.; Zucchelli, A. Influence of geometrical features of electrospun nylon6, 6 interleave on the CFRP laminates mechanical properties. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, V.A.; Hogg, P.J.; Sampson, W.W. The influence of the nonwoven veil architectures on interlaminar fracture toughness of the interleaved composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 110, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, S.; Daelemans, L.; Meireman, T.; De Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Clerck, K. Interlaminar toughening of resin transfer molded laminates by electrospun polycaprolactone structures: Effect of the interleave morphology. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 136, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwata, M.; Hogg, P.J. Interlaminar toughness of interleaved CFRP using non-woven veils: Part 1.Mode-I testing. Compos. Part A 2011, 42, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saz-Orozco, B.D.; Ray, D.; Stanley, W.F. Effect of thermoplastic veils on interlaminar fracture toughness of a glass fiber/vinyl ester composite. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, C.; Kratz, J.; Partridge, I.K. Cure path dependency of mode I fracture toughness in thermoplastic particle interleaf toughened prepreg laminates. Compos. Part A 2016, 87, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Qi, D. Effect of cooling rate and crack propagation direction on the mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of biaxial noncrimp warp-knitted fabric composites made of glass/PP commingled yarn. Polym. Compos. 2008, 29, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, G.; Liu, G.; Yi, X.; Jia, Y. Experimental and numerical analysis on Mode-I delamination of CFRP laminates toughened by polyamide non-woven fabric layer. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, K.; Ray, D.; McCarthy, M.A. Toughening effects of interleaved nylon veils on glass fabric/low-styrene-emission unsaturated polyester resin composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, J.J.; Bogdanovich, A.E.; Bradford, P.D. Carbon nanotube shear-pressed sheet interleaves for Mode I interllaminar fracture toughness enhancement. Compos. Part A 2016, 80, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5528-01. Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D790-00. Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cesano, F.; Rattalino, I.; Demarchi, D.; Bardelli, F.; Sanginario, A.; Gianturco, A.; Veca, A.; Viazzi, C.; Castelli, P.; Scarano, D.; et al. Structure and properties of metal-free conductive tracks on polyethylene/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites as obtained by laser stimulated percolation. Carbon 2013, 61, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.; Young, R. Fracture Behaviour of Polymers; Applied Science Publishers Ltd.: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]



| Interleaf | Abbreviation | Composite | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon veil | NV | Nylon veil interleaved composite | NVIC |
| Kevlar veil | KV | Kevlar veil interleaved composite | KVIC |
| Interleaf | Areal Density/(g·m-2) | Average Thickness/(μm) | Material | Diameter of Fibers/(μm) | Connection Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NV | 16.3 | ~53 | Nylon | ~13 | Fusion-bonded dots |
| KV | 15.9 | ~55 | Kevlar | ~11 | Physically stacking |
| Sample | Control [3] | NVIC | KVIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| GIC/(J/m2) | 306 | 666 | 526 |
| Std. Dev./(J/m2) | 37.2 | 22.6 | |
| GIIC/(J/m2) | 718 | 2410 | 1946 |
| Std. Dev./(J/m2) | 95 | 57 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, P.; Guo, M. Controlling the Crack Propagation Path of the Veil Interleaved Composite by Fusion-Bonded Dots. Polymers 2019, 11, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081260
Chen G, Zhang J, Liu G, Chen P, Guo M. Controlling the Crack Propagation Path of the Veil Interleaved Composite by Fusion-Bonded Dots. Polymers. 2019; 11(8):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081260
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guangchang, Jindong Zhang, Gang Liu, Puhui Chen, and Miaocai Guo. 2019. "Controlling the Crack Propagation Path of the Veil Interleaved Composite by Fusion-Bonded Dots" Polymers 11, no. 8: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081260
APA StyleChen, G., Zhang, J., Liu, G., Chen, P., & Guo, M. (2019). Controlling the Crack Propagation Path of the Veil Interleaved Composite by Fusion-Bonded Dots. Polymers, 11(8), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11081260





