Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.3. Characterization of the Solution Properties
2.3.1. Viscosity Measurement
2.3.2. Surface Tension Measurement
2.3.3. Conductivity Measurement
2.4. Electrospinning
2.5. Characterization of the Blended Gelatin/Pullulan Nanofibrous Membrane
2.5.1. Morphological Characterization of Nanofiber Membrane
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.5.3. Tensile Strength Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Solution Properties
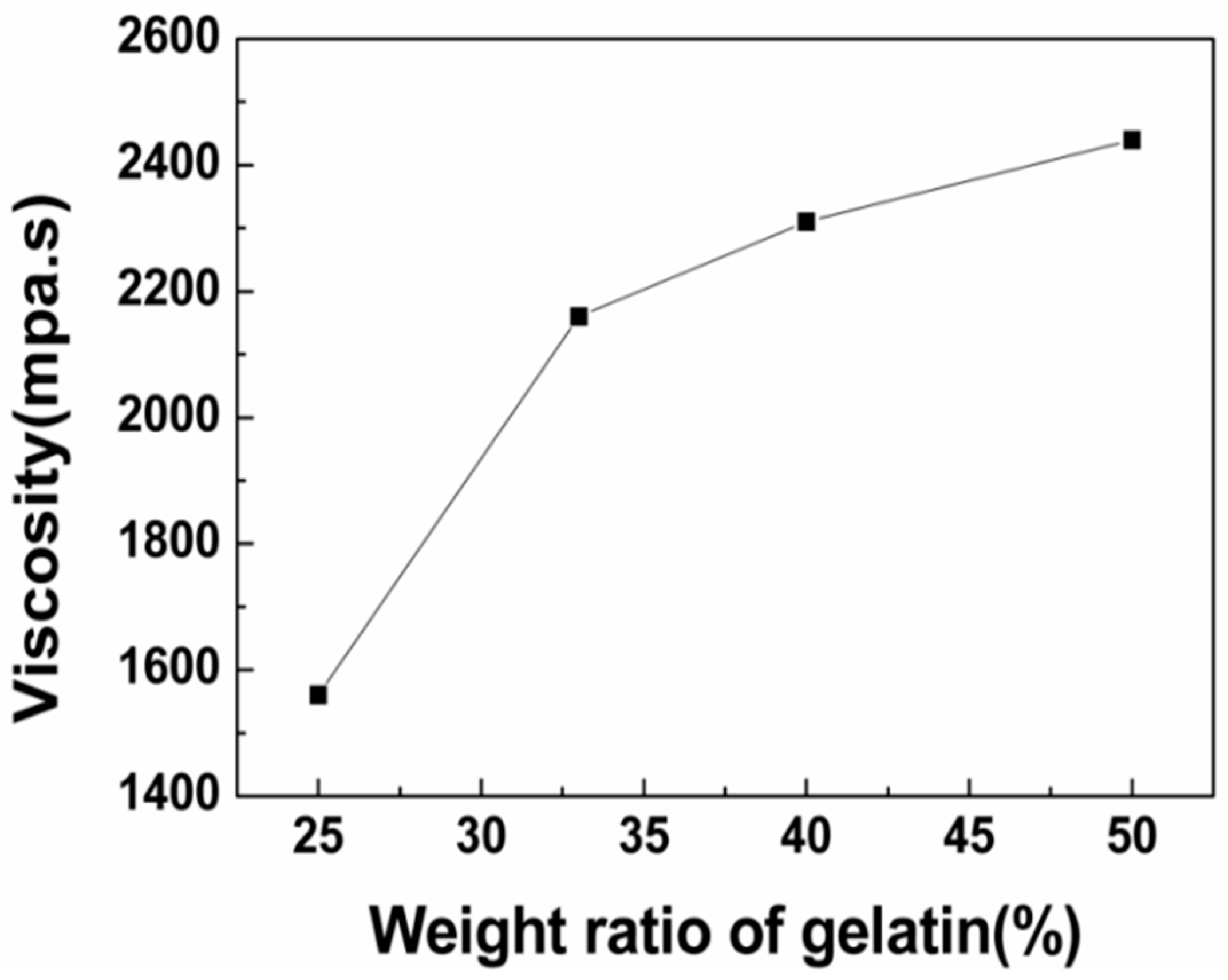
3.1.1. Viscosity of the Solution
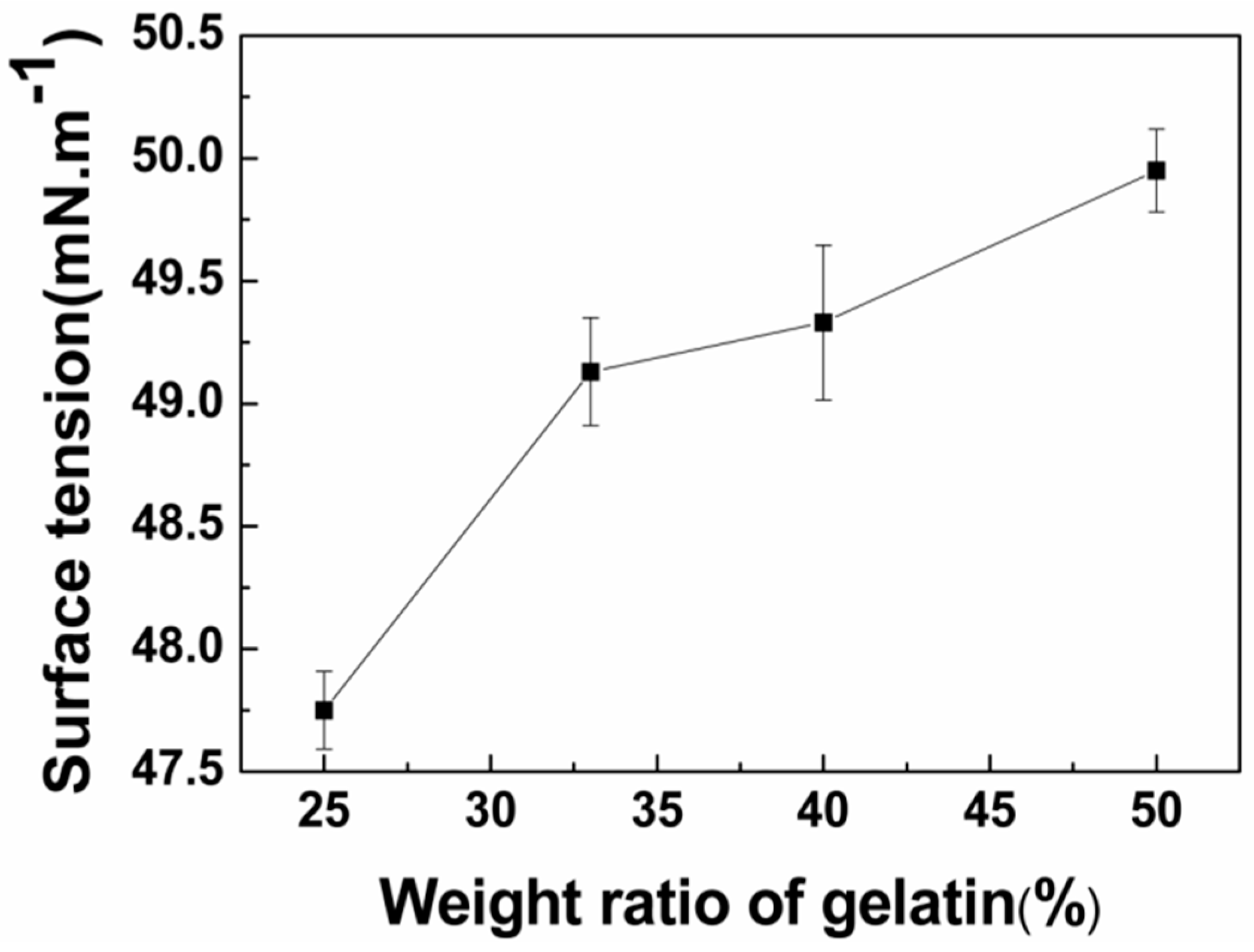
3.1.2. Surface Tension Analysis of Blended Gelatin/Pullulan Solutions
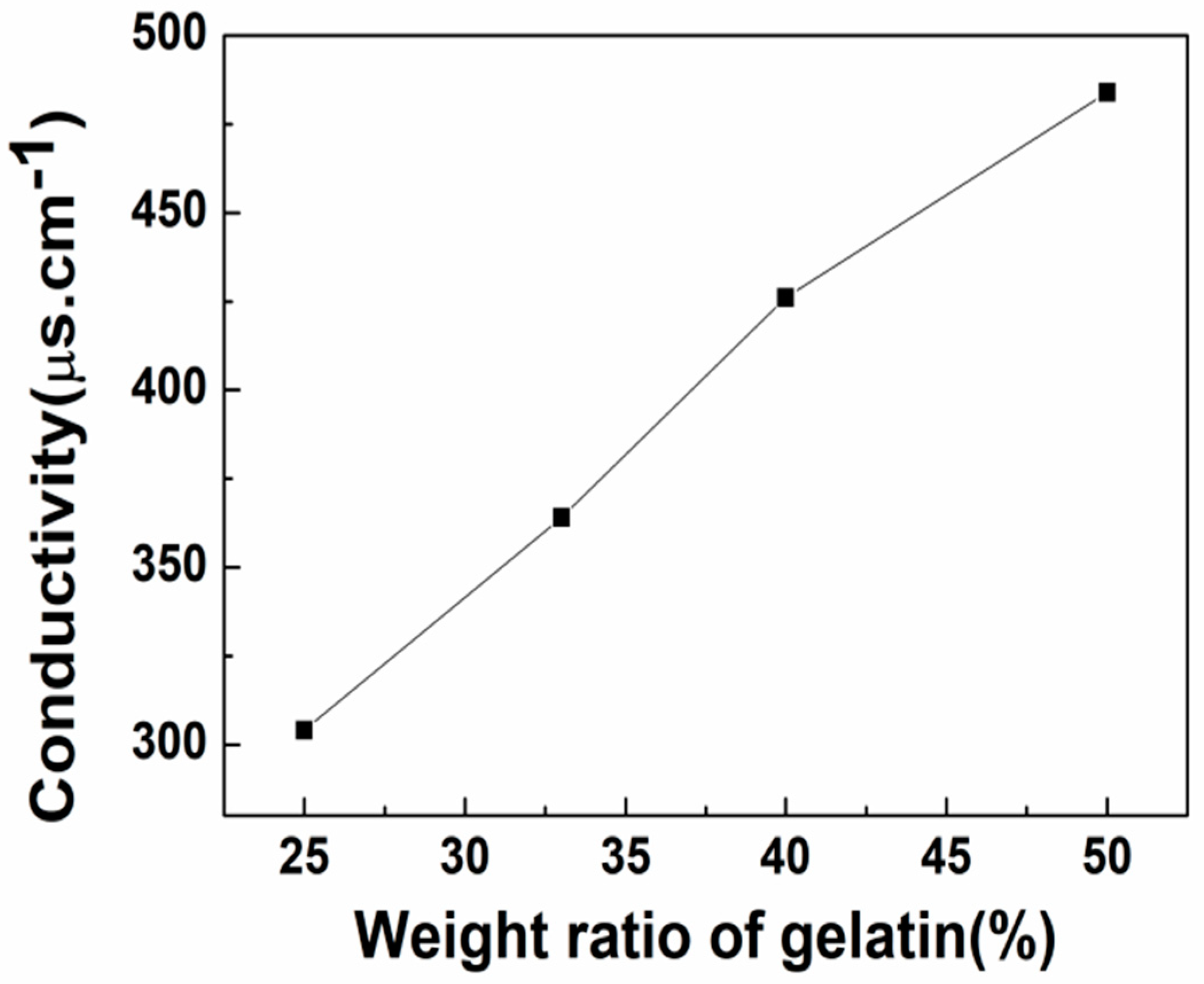
3.1.3. Conductivity Analysis of Blended Gelatin/Pullulan Solutions
3.2. Characterization of Blended Gelatin/Pullulan Nanofiber Membranes
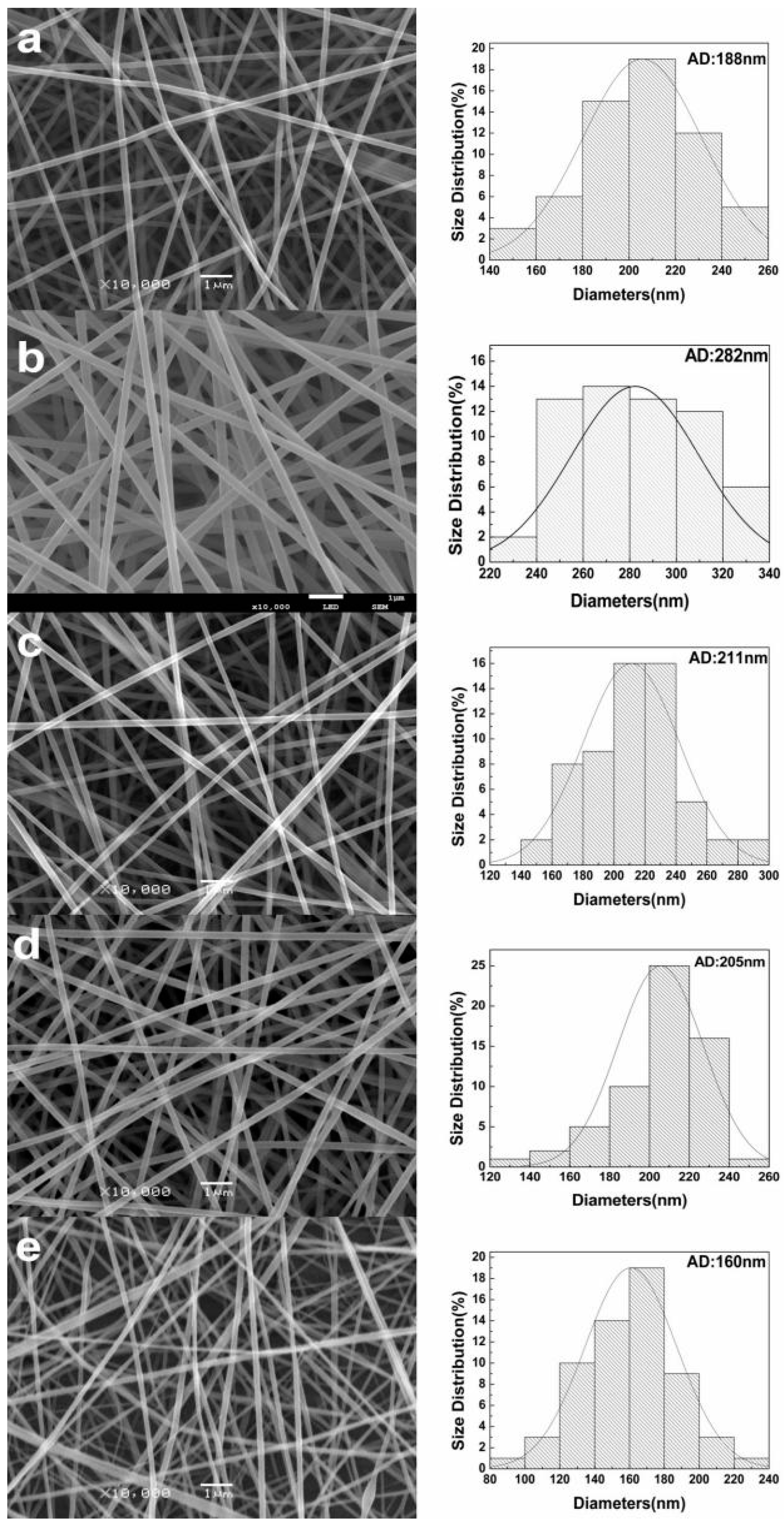
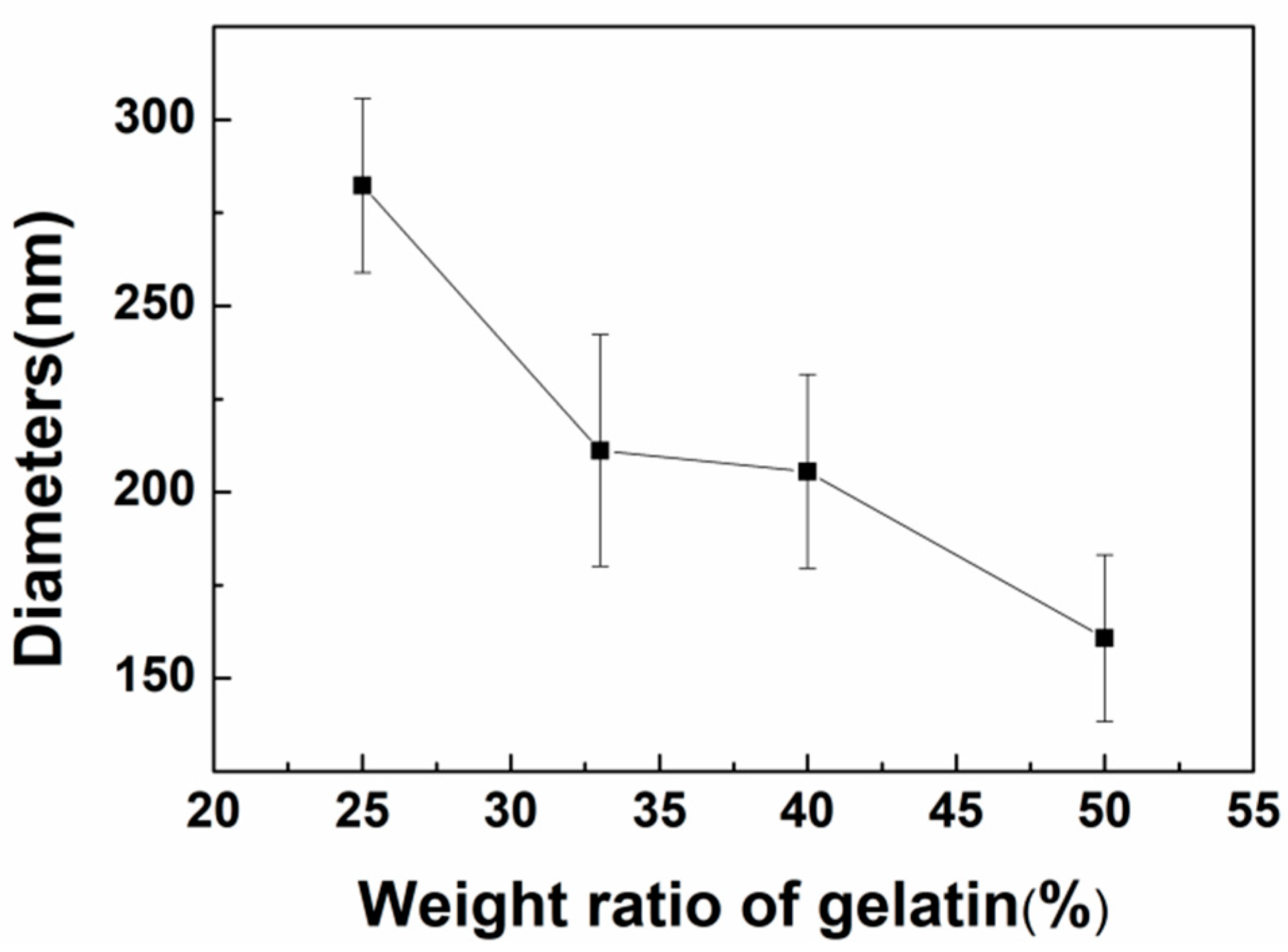
3.2.1. Morphological Characterization of Nanofibers
3.2.2. FTIR Analysis of Gelatin/Pullulan Nanofibers
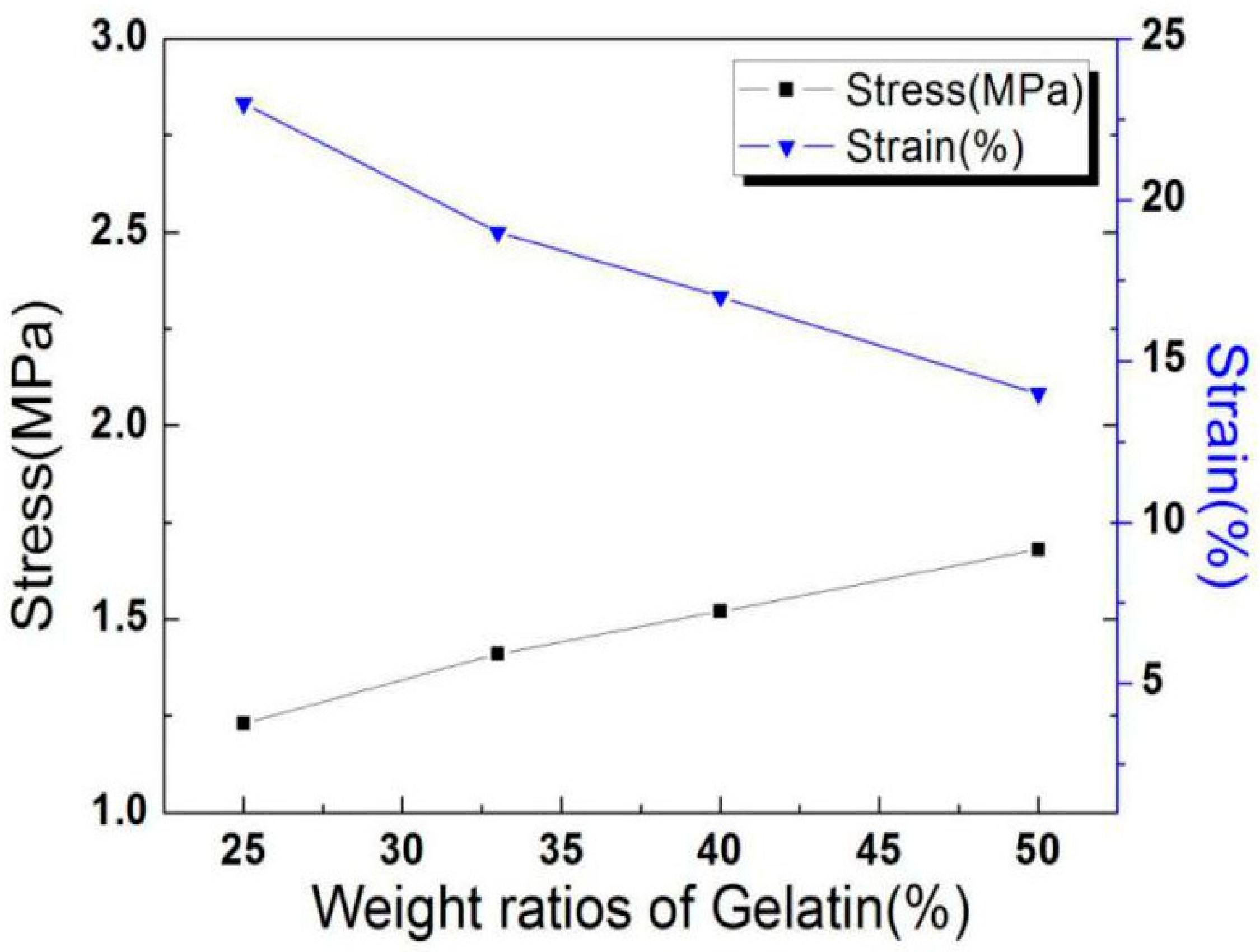
3.2.3. Analysis of Tensile Strength of Nanofibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomasula, P.M.; Sousa, A.M.M.; Liu, S.C.; Li, R.; Bonnaillie, L.M.; Liu, L.S. Electrospinning ofcasein/pullulan blends for food-grade applications. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Clark, R.L. Electrohydrodynamic atomization: A versatile process for preparing materials for biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 573–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Içoğlu, H.İ.; Oğulata, R.T. Effect of ambient parameters on morphology of electrospun poly(trimethylene terephthalate) (ptt) fibers. Tekst Konfeksiyon 2017, 27, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Ouyang, H.W.; Lim, C.T. Electrospinning of gelatin fibers and gelatin/PCL composite fibrous scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2005, 72B, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.G.; Courts, A. The Science and Technology of Gelatin; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Tungkavet, T.; Pattavarakorn, D.; Sirivat, A. Bio-compatible gelatins (Ala-Gly-Pro-Arg-Gly-Glu-4Hyp-Gly-Pro-) and electromechanical properties: Effects of temperature and electric field. J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, A.; Zheng, J.; Han, C.C. Gelatinand gelatin−hyaluronic acid nanofibrous membranes produced by electrospinning of their aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2243–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigani, B.; Black, L.; Ferrari, F. Electrospun gelatin–chondroitin sulfate scaffolds loaded with platelet lysate promote immature cardiomyocyte proliferation. Polymers 2018, 10, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; He, A.; Han, C.C. Electrospinning of hyaluronic acid (HA) and HA/gelatin blends. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp-Erbay, E.; Yeşilsu, A.F.; Türe, M. Fish gelatin antimicrobial electrospun nanofibers for active food-packaging applications. J. Nano Res. 2019, 56, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.B.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Bao, W.W. Study on the properties of the electrospun silk fibroin/gelatin blend nanofibers for scaffolds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Daelemans, L.; Steyaert, I.; Schoolaert, E.; Goudenhooft, C.; Rahier, H.; De Clerck, K. Nanostructured hydrogels by blend electrospinning of polycaprolactone/gelatin nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raut, P.W.; Shitole, A.A.; Khandwekar, A. Engineering biomimetic polyurethane using polyethylene glycol and gelatin for blood-contacting applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 10457–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaee, S.; Labbaf, S.; Enayati, M.H.; Baharlou Houreh, A.; Esfahani, M.H.N. Creation of a unique architectural structure of bioactive glass sub-micron particles incorporated in a polycaprolactone/gelatin fibrous mat; characterization, bioactivity and cellular evaluations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2019, 107, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Tomasula, P.; DeSousa, A.M.M.; Liu, S.C.; Tunick, M.; Liu, K.; Liu, L. Electrospinning pullulan fibers from salt solutions. Polymers 2017, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, S.; Introzzi, L.; Fuentes-Alventosa, J.M.; Santo, N.; Rocca, R.; Piergiovanni, L. Self-assembled pullulan–silica oxygen barrier hybrid coatings for food packaging applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hallora, D.P.; Zolotarsky, Y. Pullulan and Polyvinyl Alcohol Based Film Forming Compositions. U.S. Patent No. 2003086954, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shahriar, S.M.S.; Mondal, J.; Hasan, M.N.; Revuri, V.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, Y.K. Electrospinning nanofibers for therapeutics delivery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinar, O.; Filiz, Y. Pullulan: Production and usage in food industry. Afr. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Yeum, J.H.; Das, A.K. Effect of pullulan/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend system on the montmorillonite structure with property characterization of electrospun pullulan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/montmorillonite nanofibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, R.; Ji, B.C.; Cho, J.W.; Son, T.W.; Oh, W.; Yeu, J.H. Preparation and characterization of electrospun pullulan/montmorillonite nanofiber mats in aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Vázquez, G.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.D.; Mendoza, S. Electrospun fibers from blends of pea (pisum sativum) protein and pullulan. Food Hydrocolloids 2018, 83, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofiber fabrication as synthetic extracellular matrix and its potential for vascular tissue engineering. Tiss. Eng. Part A 2004, 10, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Electrospinning and mechanical characterization of gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 5361–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Rabbani, M.M.; Yang, S.B. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/pullulan blend nanofibres prepared from aqueous solutions using electrospinning method. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2014, 22, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Yun, Y.; Shao, L. Studies on influencing factors in viscosity of gelatin. Sci. Technol. Gel. 2014, 34, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.H.; Peard, G.T. The surface tension of gelatin solutions. Biochem. J. 1925, 19, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilija, Z.; Budimir, M. Parameters dependence of fibers diameter and pores area in electrospinning. Adv. Eng. Forum. 2018, 26, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.M.; Shivkumar, S. N,N-Dimethylformamide additions to the solution for the electrospinning of poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2004, 289, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.S.; Ji, H.Y.; Taek, S.L.; Woo, H.P. The effects of solution properties and polyelectrolyte on electrospinning of ultrafine poly(ethylene oxide) fibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | Hydrogen Bond Type | Abbreviations | Wave Number (cm−1) | Relative Strength (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | Intramolecular hydrogen bond | (II) OH. . .OH | 3413 | 26.98 | 42.12 |
| (IV) Annular polymer | 3185 | 15.14 | |||
| Intermolecular hydrogen bond | (III) OH. . .ether O | 3292 | 48.10 | 57.88 | |
| (I) OH. . .π | 3510 | 5.04 | |||
| (V) OH. . .N | 3073 | 4.74 | |||
| Pullulan | Intramolecular hydrogen bond | (II) OH. . .OH | 3444 | 18.32 | 46.88 |
| (IV) Annular polymer | 3194 | 28.56 | |||
| Intermolecular hydrogen bond | (III) OH. . .ether O | 3325 | 46.01 | 53.12 | |
| (I) OH. . .π | 3522 | 4.36 | |||
| (V) OH. . .N | 3094 | 2.75 | |||
| Gelatin/ pullulan | Intramoleculr hydrogen bond | (II) OH. . .OH | 3435 | 20.84 | 41.34 |
| (IV) Annular polymer | 3193 | 20.50 | |||
| Intermolecular hydrogen bond | (III) OH. . .ether O | 3312 | 49.23 | 58.66 | |
| (I) OH. . .π | 3504 | 0.78 | |||
| (V) OH. . .N | 3084 | 8.65 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lyu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F. Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091424
Wang Y, Guo Z, Qian Y, Zhang Z, Lyu L, Wang Y, Ye F. Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers. Polymers. 2019; 11(9):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091424
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuanduo, Ziyang Guo, Yongfang Qian, Zhen Zhang, Lihua Lyu, Ying Wang, and Fang Ye. 2019. "Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers" Polymers 11, no. 9: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091424
APA StyleWang, Y., Guo, Z., Qian, Y., Zhang, Z., Lyu, L., Wang, Y., & Ye, F. (2019). Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers. Polymers, 11(9), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091424





