Electrically-Tunable Blue Phase Liquid Crystal Microlens Array Based on a Photoconductive Film
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
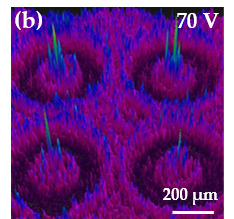
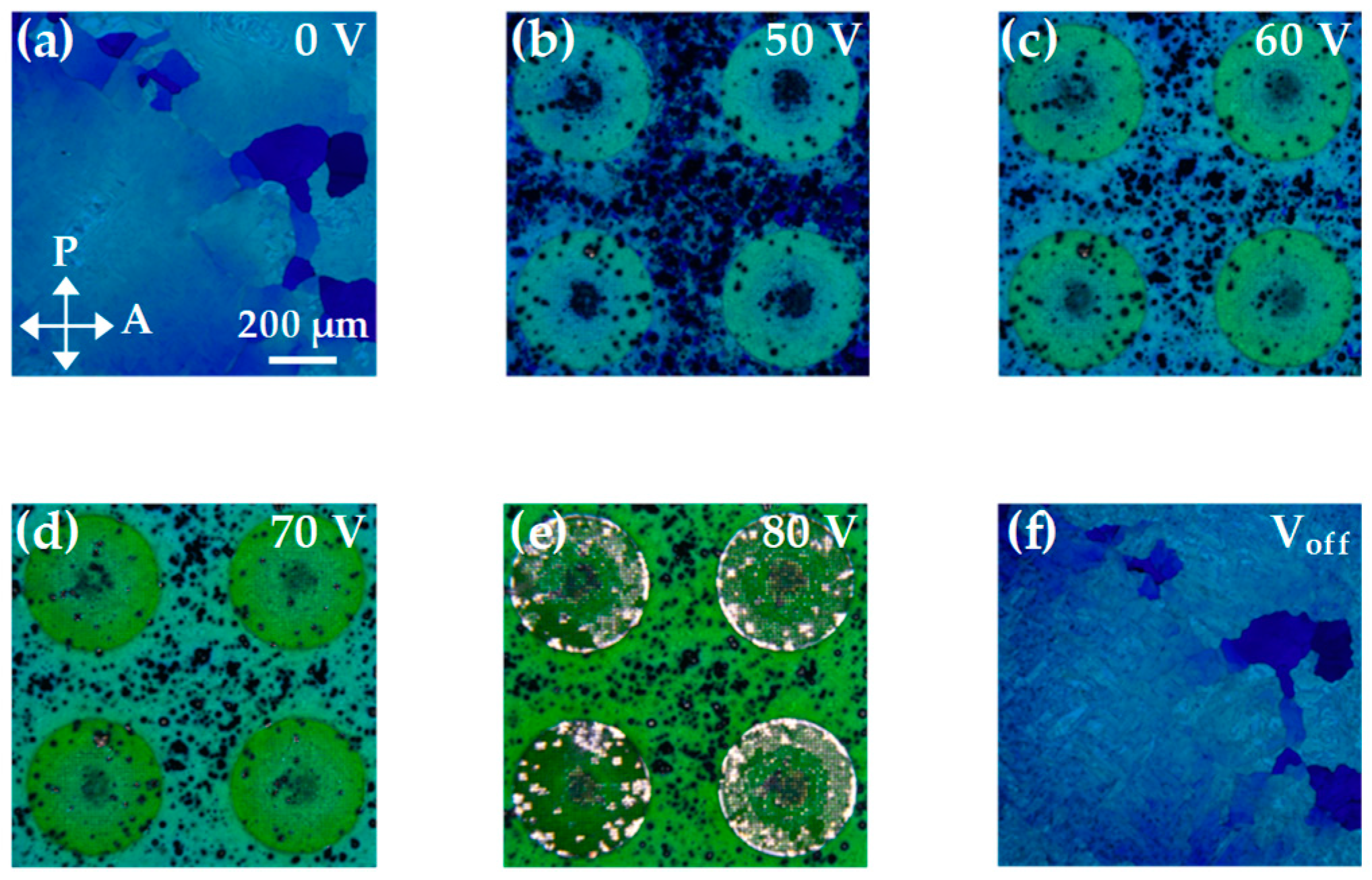
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferstl, M.; Frisch, A.M. Static and dynamic Fresnel zone lenses for optical interconnections. J. Mod. Opt. 1996, 43, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Bush, R.C.; Harvey, J.C.; Foley, M.F. P-95: Fresnel lenses in rear projection displays. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2001, 32, 934–937. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.G.; Sun, X.F.; Song, Y.; Shieh, H.P.D. 2-D/3-D switchable display by Fresnel-type LC lens. J. Displ. Technol. 2011, 7, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastani, K.; Marrakchi, A.; Habiby, S.F.; Hubbard, W.M.; Gilchrist, H.; Nahory, R.E. Binary phase Fresnel lenses for generation of two-dimensional beam arrays. Appl. Opt. 1991, 30, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McManamon, P.F.; Dorschner, T.A.; Corkum, D.L.; Friedman, L.J.; Hobbs, D.S.; Holz, M.; Liberman, S.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Resler, D.P.; Sharp, R.C.; et al. Optical phased array technology. Proc. IEEE 1996, 84, 268–298. [Google Scholar]
- Naumov, A.F.; Loktev, M.Y.; Guralnik, I.R.; Vdovin, G.V. Liquid-crystal adaptive lenses with modal control. Opt. Lett. 1998, 23, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowel, S.T.; Cleverly, D.S.; Kornriech, P.G. Focusing by electrical modulation of refraction in a liquid crystal cell. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 278–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Sato, S. Optical properties of liquid crystal lens of any size. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, L571–L573. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.K.; Jung, S.M.; Lee, B.J.; Shin, H.H. Electric-field-driven LC lens for 3-D/2-D autostereoscopic display. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2009, 17, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, H.S.; Lin, H.C.; Tsou, Y.S.; Hsu, H.K.; Li, W.Y. Polarizer-free and fast response microlens arrays using polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S.T. Polarization independent adaptive microlens with a blue-phase liquid crystal. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 8045–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, F.; Dou, H.; Li, G.P.; Song, Y.L.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.H. A polarisation-independent blue-phase liquid crystal lens array using gradient electrodes. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.P.; Fan, H.X.; Wang, Q.H. A polarisation-independent blue-phase liquid crystal microlens using an optically hidden dielectric structure. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.T. High-efficiency and fast-response tunable phase grating using a blue phase liquid crystal. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 1404–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, K. Polarization independent blue phase liquid crystal gratings based on periodic polymer slices structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 153104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Pan, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Niu, G.; Huang, W.; Yuan, X.; Guo, J.; Cao, H.; Yang, H. Wide blue phase range in a hydrogen-bonded self-assembled complex of chiral fluoro-substituted benzoic acid and pyridine derivative. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2050–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, W.; Xiao, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, L.; Xiao, J.; Yang, H.; Lu, Y. Hysteresis-free blue phase liquid-crystal-stabilized by ZnS nanoparticles. Small 2012, 8, 2189–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, W.; Xiao, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Yang, P. Low voltage and hysteresis-free blue phase liquid crystal dispersed by ferroelectric nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19629–19633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zou, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Xiao, J.; Li, F.; Song, P.; Yang, H. Asymmetric tunable photonic bandgaps in self organized 3d nanostructure of polymer stabilized blue phase I modulated by voltage polarity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Peng, F.; Wu, S.T. Polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystals. Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, S.T. Polarization independent blue-phase liquid crystal cylindrical lens with a resistive film. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2568–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.H.; Huang, L.S.; Lin, C.H.; Kuo, C.T. Polarization-independent and fast tunable microlens array based on blue phase liquid crystals. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, S.J.; Zhou, P.C.; Liu, S.X.; Lu, J.G.; Li, X.; Su, Y.K. Polymer-Stabilized Blue Phase Liquid Crystals for Photonic Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1600102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.M.; Gauza, S.; Xianyu, H.; Wu, S.T. Submillisecond gray-level response time of a polymer-stabilized blue-phase liquid crystal. J. Displ. Technol. 2010, 6, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Fuh, A.Y.G.; Cheng, K.T. Particular thermally induced phase separation of liquid crystal and poly(N-vinyl carbazole) films and its application. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 16777–16784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.C.; Wang, J.D.; Lee, C.R.; Mo, T.S. Electrically controllable and polarization-independent Fresnel zone plate in a circularly symmetric hybrid-aligned liquid crystal film with a photoconductive polymer layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 181104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimirov, F.L.; Chaika, A.N.; Morichev, I.E.; Pletneva, N.I.; Naumov, A.F.; Loktev, M.Y. Modulation characteristics of optically controllable transparencies based on a photoconductor–liquid-crystal structure. J. Opt. Technol. 2000, 67, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Li, C.C.; Jau, H.C.; Yu, L.C.; Hong, C.L.; Guo, D.Y.; Wang, C.T.; Lin, T.H. Electric field–driven shifting and expansion of photonic band gaps in 3D liquid photonic crystals. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyadyusha, A.; Kaczmarek, M.; Slussarenko, S. Dynamics and uniformity of reorientation in liquid crystal cells with PVK alignment layers. J. Electron. Liq. Cryst. Commun. 2003, 1–10. [Google Scholar]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, B.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chuang, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-T. Electrically-Tunable Blue Phase Liquid Crystal Microlens Array Based on a Photoconductive Film. Polymers 2020, 12, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010065
Huang B-Y, Huang S-Y, Chuang C-H, Kuo C-T. Electrically-Tunable Blue Phase Liquid Crystal Microlens Array Based on a Photoconductive Film. Polymers. 2020; 12(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Bing-Yau, Shuan-Yu Huang, Chia-Hsien Chuang, and Chie-Tong Kuo. 2020. "Electrically-Tunable Blue Phase Liquid Crystal Microlens Array Based on a Photoconductive Film" Polymers 12, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010065
APA StyleHuang, B. -Y., Huang, S. -Y., Chuang, C. -H., & Kuo, C. -T. (2020). Electrically-Tunable Blue Phase Liquid Crystal Microlens Array Based on a Photoconductive Film. Polymers, 12(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010065