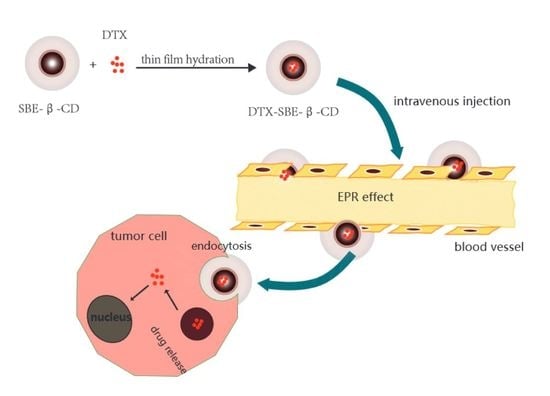
Inclusion Complex of Docetaxel with Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin: Preparation, In Vitro Cytotoxicity and In Vivo Safety
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Cell lines and Cell Culture
2.2.2. Chromatographic Conditions
2.2.3. Preparation of DTX-SBE-β-CD Inclusion Complex
2.2.4. Optimized Formulation of DTX-SBE-β-CD by Central Composite Design
2.2.5. Preparation of DTX-SBE-β-CD Inclusion Freeze-Dried Preparation
Determination of Freeze-Drying Conditions
Appearance Evaluation
Redispersibility Evaluation
2.2.6. Phase-Solubility Studies
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Infrared Fourier Transformation (FT-IR)
2.3.2. H NMR
2.3.3. Different Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.4. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
2.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.6. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.7. Biodistribution Study
2.8. Safety Study
2.8.1. Hemolytic Test
2.8.2. Vascular Stimulation Test
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Study of Mole Ratio
3.2. Optimized Formulation of DTX-SBE-β-CD by Central Composite Design
3.3. Preparation of DTX-SBE-β-CD inclusion Freeze-Dried Preparation
3.3.1. Preparation Methods
3.3.2. Appearance Character
3.3.3. Redispersibility Evaluation
3.4. Phase-Solubility Studies
3.5. Characterization
3.5.1. Infrared Fourier Transformation (FT-IR)
3.5.2. H NMR
3.5.3. Different Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.5.4. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
3.5.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
3.7. Pharmacokinetic Study
3.8. Biodistribution Study
3.9. Safety Study
3.9.1. Hemolysis Test
3.9.2. Vascular Stimulation Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jesus, A.R.; Soromenho, M.R.; Raposo, L.R.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R.; Reis, P. Enhancement of water solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs by new biocompatible N-acetyl amino acid N-alkyl cholinium-based ionic liquids. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 137, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.M.; Hu, C.S.; Shao, J.M.; Li, H.J.; Li, P.Y.; Li, X.C.; He, W.D. Fabricating ternary hydrogels of P(AM-co-DMAEMA)/PVA/ β -CD based on multiple physical crosslinkage. Polymer 2017, 119, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.K.; Chun, H.J.; Park, K. Preparation of redox-sensitive β-CD-based nanoparticles with controlled release of curcumin for improved therapeutic effect on liver cancer in vitro. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 45, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriya, P.; Partha, S.G.; Sukalyan, D. β-CD assisted aqueous dissolution of cetylpicolinium dichromates (CPDC)-Evolution of a class of green water compatible lipopathic Cr(VI) oxidants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Liu, N.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, A. Preparation of Nanocrystals for Insoluble Drugs by Top-Down Nanotechnology with Improved Solubility and Bioavailability. Molecules 2020, 25, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, L.B.; Martins, A.O.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Cesário, F.R.; Castro, F.F.; de Albuquerque, T.R.; Fernandes, M.N.; da Silva, B.A.; Júnior, L.J.; de Sousa Araújo, A.A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of the essential oil obtained from Ocimum basilicum, complexed with β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 103, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Lei, M.; Yan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C. Inclusion complexes of HP-β-cyclodextrin with agomelatine:Preparation, characterization, mechanism study and in vivo evaluation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino, R.C. Cyclodextrin Inclusion of Medicinal Compounds for Enhancement of their Physicochemical and Biopharmaceutical Properties. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2357–2370. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, Z.; Fliszár-Nyúl, E.; Dellafiora, L.; Galaverna, G.; Dall’Asta, C.; Lemli, B.; Kunsági-Máté, S.; Szente, L.; Poór, M. Cyclodextrins Can Entrap Zearalenone-14-Glucoside: Interaction of the Masked Mycotoxin with Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin Bead Polymer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukla, A.; Singh, A.P.; Ray, B.; Aswal, V.; Kar, A.G.; Maiti, P. Efficacy of polyurethane graft on cyclodextrin to control drug release for tumor treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 534, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajian, J.; Nathan, A.R.; Horst, A.R. Molecular Imprinting of Cyclodextrin Supramolecular Hydrogels Improves Drug Loading and Delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1800246. [Google Scholar]
- Saokham, P.; Muankaew, C.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. Molecules 2018, 23, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzmán-Hernández, D.S.; Ramírez-Silva, M.; Rojas-Hernández, A.; Corona-Avendaño, S.; Romero-Romo, M.A.; Palomar-Pardavé, M.E. Spectrophotometric and electrochemical quantification of the host–guest interaction of tenoxicam and β-CD in aqueous solution at different pH values. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 738, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraj, P.B.; Partha, S.G.; Sukalyan, D. β-CD assisted dissolution of quaternary ammonium permanganates in aqueous medium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 806–812. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.-T.; Yang, Y.; Cai, P.; Sun, D.-Y.; Sánchez-Murcia, P.A.; Zhang, X.; Jia, W.-Q.; Lei, L.; Guo, M.; Gago, F.; et al. A Series of Enthalpically Optimized Docetaxel Analogues Exhibiting Enhanced Antitumor Activity and Water Solubility. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, M.K.; Sami, N. Novel sulforaphane-enabled self-microemulsifying delivery systems (SFN-SMEDDS) of taxanes: Formulation development and in vitro cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Sohail, M.F.; Rehman, M.; Sarwar, H.S.; Naveed, S.; Qureshi, O.S.; Bukhari, N.I.; Hussain, I.; Webster, T.J.; Shahnaz, G. in the oral delivery of Docetaxel: Challenges, current state-of-the-art and future trends. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3145–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, M.K.; Kuncha, M.; Nayak, V.L.; Sarma, A.V.; Kumar, M.J.M.; Chauhan, A.S.; Sistla, R. An innovative in situ method of creating hybrid dendrimer nano-assembly: An efficient next generation dendritic platform for drug delivery, Nanomedicine. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 21, 102043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, S.; Tao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Liang, Y. Targeted delivery of docetaxel via Pi-Pi stacking stabilized dendritic polymeric micelles for enhanced therapy of liver cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.A.; Madni, A.; Rehman, M.; Rahim, M.A.; Jabar, A. Ionically Cross-Linked Chitosan Nanoparticles for Sustained Delivery of Docetaxel: Fabrication, Post-Formulation and Acute Oral Toxicity Evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 10035–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Zhang, X.-X.; Huang, H.-Y.; Chen, L.-Q.; Cui, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Jin, H.; Lee, B.-J.; Cao, Q.-R. Effective deactivation of A549 tumor cells in vitro and in vivo by RGD-decorated chitosan-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube loading docetaxel. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 543, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, M.M.; Alomrani, A.H.; Harisa, G.I.; Ashour, A.E.; Kumar, A.; Yassin, A.E. Novel docetaxel chitosan-coated PLGA/PCL nanoparticles with magnified cytotoxicity and bioavailability. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thotakura, N.; Sharma, G.; Singh, B.; Kumar, V.; Raza, K. Aspartic acid derivatized hydroxylated fullerenes as drug delivery vehicles for docetaxel: An explorative study. Artif. Cellsnanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, M.; Goruk, S.; Mazurak, V.; Postovit, L.; Field, C.J. Role of docosahexaenoic acid in enhancement of docetaxel action in patient-derived breast cancer xenografts. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 24, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loiseau, A.; Boudon, J.; Oudot, A.; Moreau, M.; Boidot, R.; Chassagnon, R.; Saïd, N.M.; Roux, S.; Mirjolet, C.; Millot, N. Titanate Nanotubes Engineered with Gold Nanoparticles and Docetaxel to Enhance Radiotherapy on Xenografted Prostate Tumors. Cancer 2019, 11, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gotov, O.; Battogtokh, G.; Ko, Y.T. Docetaxel-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid-Cathepsin B-Cleavable-Peptide-Gold Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4668–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, H.C.; Rijbroek, A.D.B.-V.; Van Der Wurff-Jacobs, K.M.G.; Bos, C.; Moonen, C.T.; Deckers, R. Tumor Drug Distribution after Local Drug Delivery by Hyperthermia, In Vivo. Cancers 2019, 11, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lin, G. Nanotechnology-mediated immunochemotherapy combined with docetaxel and PD-L1 antibody increase therapeutic effects and decrease systemic toxicity. J. Control Release 2018, 286, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtar, N.; Taylor, K.M.; Sheikh, K.; Somavarapu, S. Design and Development of Dry Powder Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin Complex for Pulmonary Delivery of Fisetin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 113, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.Y.; Ko, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, Y.-H. Surfactant-free solubilization and systemic delivery of anti-cancer drug using low molecular weight methylcellulose. J. Control Release 2018, 276, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Yousaf, A.M.; Li, D.X.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Cho, K.H.; Choi, H.G. Development of RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of docetaxel and curcumin in rat plasma: Validation and stability. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K.A. Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–212. [Google Scholar]
- Loftsson, T.; Hreinsdóttir, D.; Masson, M. Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 302, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| B | 2.4 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| C | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | — | — |
| Experimental Factors | Levels | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| A (h) | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| B (°C) | 25 | 35 | 45 | |||
| C (rpm) | 500 | 700 | 900 | |||
| Run | A | B | C | Drug-loading rate (%) | ||
| F1 | 2 | 25 | 700 | 4.72 | ||
| F2 | 2 | 35 | 700 | 5.02 | ||
| F3 | 1 | 25 | 900 | 2.1 | ||
| F4 | 2 | 35 | 500 | 4.85 | ||
| F5 | 3 | 45 | 500 | 2.48 | ||
| F6 | 2 | 35 | 900 | 4.85 | ||
| F7 | 2 | 35 | 700 | 5.02 | ||
| F8 | 2 | 35 | 700 | 5.02 | ||
| F9 | 2 | 45 | 700 | 3.85 | ||
| F10 | 3 | 45 | 900 | 2.45 | ||
| F11 | 3 | 25 | 500 | 2.07 | ||
| F12 | 3 | 35 | 700 | 5.1 | ||
| F13 | 2 | 35 | 700 | 5.12 | ||
| F14 | 2 | 35 | 700 | 5.0 | ||
| F15 | 3 | 25 | 900 | 1.9 | ||
| F16 | 1 | 45 | 500 | 2.36 | ||
| F17 | 1 | 35 | 700 | 4.85 | ||
| F18 | 1 | 25 | 500 | 2.14 | ||
| F19 | 1 | 45 | 900 | 2.4 | ||
| F20 | 2 | 35 | 700 | 5.26 | ||
| Docetaxel API | DTX-SBE-β-CD | |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1096.9 ± 98.0 | 2049.2 ± 147.4 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.083 | 0.083 |
| AUC(0-t) (ng/mL ∗ h) | 881.4 ± 30.4 | 1629.0 ± 34.3 |
| AUC(0-∞) (ng/mL ∗ h) | 925.8 ± 35.2 | 1700.6 ± 41.9 |
| Relative bioavailability (%) | 100 | 183.8 |
| Time | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| 0.5 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| 0.75 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| 1 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| 2 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| 3 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| 4 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, L.; Yang, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, G. Inclusion Complex of Docetaxel with Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin: Preparation, In Vitro Cytotoxicity and In Vivo Safety. Polymers 2020, 12, 2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102336
Ren L, Yang X, Guo W, Wang J, Chen G. Inclusion Complex of Docetaxel with Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin: Preparation, In Vitro Cytotoxicity and In Vivo Safety. Polymers. 2020; 12(10):2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102336
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Lili, Xiaolong Yang, Weilu Guo, Jin Wang, and Guoguang Chen. 2020. "Inclusion Complex of Docetaxel with Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin: Preparation, In Vitro Cytotoxicity and In Vivo Safety" Polymers 12, no. 10: 2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102336
APA StyleRen, L., Yang, X., Guo, W., Wang, J., & Chen, G. (2020). Inclusion Complex of Docetaxel with Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin: Preparation, In Vitro Cytotoxicity and In Vivo Safety. Polymers, 12(10), 2336. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102336