Linear Relationships between Partition Coefficients of Different Organic Compounds and Proteins in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems of Various Polymer and Ionic Compositions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Polymers
2.1.2. Organic Compounds
2.1.3. Drug Compounds
2.1.4. Proteins
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Small Organic Compounds in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems
3.2. Proteins in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems
3.3. Drugs in Octanol-Buffer Systems
3.4. Drugs Distribution between Blood and Other Tissues In Vivo
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, L.A.; Loureiro, J.A.; Gomes, J.; Uversky, V.N.; Madeira, P.P.; Zaslaysky, B.Y. Why physicochemical properties of aqueous solutions of various compounds are linearly interrelated. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, P.A. Partition of Cell Particles and Macromolecules, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Methods and Protocols; Hatti-Kaul, R. (Ed.) Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Partitioning in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems: Theory, Methods, Use, and Applications to Biotechnology; Walter, H.; Brooks, D.E.; Fisher, D. (Eds.) Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Aqueous Two-Phase Systems; Walter, H.; Johansson, G. (Eds.) Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 228. [Google Scholar]
- Zaslavsky, B.Y. Aqueous Two-Phase Partitioning: Physical Chemistry and Bioanalytical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zaslavsky, B.Y.; Uversky, V.N.; Chait, A. Analytical applications of partitioning in aqueous two-phase systems: Exploring protein structural changes and protein-partner interactions in vitro and in vivo by solvent interaction analysis method. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 622–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, E.A.; Chait, A.; Hafron, J.M.; Kernen, K.M.; Manickam, K.; Stephenson, A.J.; Wagner, M.; Zhu, H.; Kestranek, A.; Zaslavsky, B.; et al. The Single-parameter, Structure-based IsoPSA Assay Demonstrates Improved Diagnostic Accuracy for Detection of Any Prostate Cancer and High-grade Prostate Cancer Compared to a Concentration-based Assay of Total Prostate-specific Antigen: A Preliminary Report. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, P.P.; Reis, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Mikheeva, L.M.; Chait, A.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Solvent properties governing protein partitioning in polymer/polymer aqueous two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, P.P.; Reis, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Mikheeva, L.M.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Solvent properties governing solute partitioning in polymer/polymer aqueous two-phase systems: Nonionic compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, N.R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Madeira, P.P.; Teixeira, J.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Analysis of partitioning of organic compounds and proteins in aqueous polyethylene glycol-sodium sulfate aqueous two-phase systems in terms of solute-solvent interactions. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1415, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madeira, P.P.; Bessa, A.; Alvares-Ribeiro, L.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Reis, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Salt effects on solvent features of coexisting phases in aqueous polymer/polymer two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1229, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, N.R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Madeira, P.P.; Teixeira, J.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Effect of sodium chloride on solute-solvent interactions in aqueous polyethylene glycol-sodium sulfate two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1425, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- da Silva, N.R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Effects of sodium chloride and sodium perchlorate on properties and partition behavior of solutes in aqueous dextran-polyethylene glycol and polyethylene glycol-sodium sulfate two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1583, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madeira, P.P.; Bessa, A.; Loureiro, J.A.; Alvares-Ribeiro, L.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Cooperativity between various types of polar solute-solvent interactions in aqueous media. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1408, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mikheeva, L.M.; Chait, A.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Effect of salt additives on partition of nonionic solutes in aqueous PEG-sodium sulfate two-phase system. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5031–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- da Silva, N.R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Mikheeva, L.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Origin of salt additive effect on solute partitioning in aqueous polyethylene glycol-8000-sodium sulfate two-phase system. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1337, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Madeira, P.P.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Analyzing the effects of protecting osmolytes on solute-water interactions by solvatochromic comparison method: I. Small organic compounds. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 59812–59822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, P.P.; Bessa, A.; de Barros, D.P.; Teixeira, M.A.; Alvares-Ribeiro, L.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Chait, A.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Solvatochromic relationship: Prediction of distribution of ionic solutes in aqueous two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1271, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.; Madeira, P.P.; Mikheeva, L.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B. Effect of salt additives on protein partition in polyethylene glycol-sodium sulfate aqueous two-phase systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2859–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Chervenak, A.; Placko, S.; Kestranek, A.; Madeira, P.P.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Effect of ionic composition on partitioning of organic compounds in octanol-buffer systems. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 20574–20582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, P.; Aniceto, N.; Gouveia, L.F.; Morais, J.A. Tissue-to-blood distribution coefficients in the rat: Utility for estimation of the volume of distribution in man. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 526–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| logK (X). | logK (Y) | logK (Z) | k1 | k2 | k3 | N | r2 | SD | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | Phenol | Glucoside a | −0.0390.009 | 0.650.05 | 0.310.02 | 63 | 0.9802 | 0.034 | 1488 |
| Vanillin | Phenol | Benzyl alcohol | 0 | 0.430.06 | 0.310.07 | 70 | 0.9841 | 0.030 | 2069 |
| Vanillin | Coumarin | Benzyl alcohol | 0.0210.006 | 0.400.04 | 0.330.05 | 70 | 0.9883 | 0.025 | 2818 |
| Vanillin | Coumarin | Methyl anthranilate | 0.0230.008 | 0.440.06 | 0.750.07 | 70 | 0.9902 | 0.037 | 3395 |
| Vanillin | Glucoside a | Coumarin | 0 | 0.440.07 | 0.80.1 | 70 | 0.9726 | 0.052 | 1187 |
| Vanillin | Glucoside a | 2-Phenylethanol | 0 | 0.550.06 | 0.50.1 | 70 | 0.9713 | 0.046 | 1133 |
| Phenol | Methyl anthranilate | Benzyl alcohol | 0 | 0.340.07 | 0.360.06 | 70 | 0.9823 | 0.031 | 1859 |
| Benzyl alcohol | Caffeine | Coumarin | 0 | 0.80.1 | 0.80.2 | 31 | 0.9845 | 0.045 | 888 |
| Glucoside a | Coumarin | Caffeine | −0.030.01 | 0.30.1 | 0.310.06 | 31 | 0.9772 | 0.027 | 600 |
| Adenine | ADP | AMP | 0.110.01 | −0.020.002 | 0.870.03 | 18 | 0.9888 | 0.019 | 661 |
| Glucoside a | Adenine | Caffeine | −0.0300.008 | 0.790.03 | 0.080.02 | 23 | 0.9890 | 0.014 | 901 |
| AMP b | ATP b | ADP b | −0.060.02 | 0.620.06 | 0.390.05 | 18 | 0.9904 | 0.019 | 771 |
| Vanillin | Caffeine | Glucoside a | 0 | 0.270.06 | 0.60.1 | 31 | 0.9775 | 0.032 | 607 |
| 2-Phenylethanol | Coumarin | Benzyl alcohol | 0.0280.006 | 0.510.07 | 0.310.06 | 70 | 0.9849 | 0.029 | 2189 |
| Phenol | AMP b | Glucoside a | −0.130.02 | 0.660.02 | 0.120.02 | 18 | 0.9834 | 0.010 | 443 |
| Adenosine | Phenol | Glucoside a | 0 | 0.250.03 | 0.360.02 | 29 c | 0.9889 | 0.015 | 1163 |
| Methyl anthranilate | Caffeine | Glucoside a | 0 | 0.300.07 | 0.50.2 | 31 | 0.9734 | 0.035 | 512 |
| logK-X | logK-Y | logK-Z | k1 | k2 | k3 | N | r2 | SD | F | Conditions a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHY | RNase B | RNase A | −0.230.02 | 0.940.04 | −0.250.07 | 30 | 0.9840 | 0.056 | 831 | 23–28,39,42,60,63 |
| RNase B | CHTG | CHY | −0.110.03 | 0.850.05 | 0.580.03 | 22 | 0.9882 | 0.050 | 792 | 23–27,29–32,36,39–41,63,64,71,75 |
| RNase A | BHb | CHY | 0.280.01 | 0.660.04 | 0.240.03 | 23 | 0.9925 | 0.058 | 1325 | 63 |
| BHb | CHTG | CHY | 0 | 0.490.04 | 0.300.04 | 19 | 0.9873 | 0.062 | 623 | 27,36,63 |
| CHY | bLGA | ConA | −0.500.02 | 0.110.03 | 0.270.02 | 27 | 0.9232 | 0.059 | 144 | 29,30,32–35,38–41,47,60 |
| HHb | TRY | BHb | −0.310.02 | 0.790.03 | 0.140.04 | 24 | 0.9891 | 0.068 | 950 | 21,27,33 |
| bLGB | HEL | bLGA | 0 | 1.100.04 | −0.180.01 | 20 | 0.9876 | 0.045 | 679 | 23–27,35,38,60–67,70,72-75 |
| Lipase | CHTG | CHY | 0 | 2.70.7 | 0.770.08 | 13 | 0.9910 | 0.067 | 551 | 4,8,9,11,12,16,57,58 |
| CHY | bLGA | RNase A | −0.250.02 | 0.850.02 | −0.090.02 | 30 | 0.9870 | 0.050 | 1025 | 23–28,38–40,60,63 |
| HSA | bLGA | RNase A | −0.180.04 | 0.710.04 | −0.810.09 | 10 | 0.9781 | 0.057 | 156 | 28,31,34,35,37 |
| Sub A | RNase A | RNase B | 0 | −0.80.2 | 0.580.02 | 19 | 0.9803 | 0.054 | 398 | 25,26,28,33,37,38,60,62 |
| RNase A | HEL | RNase B | −0.090.02 | 0.580.02 | −0.130.02 | 27 | 0.9676 | 0.065 | 359 | 25,38–47,49,52,64,68,70–75 |
| HHb | CHTG | RNase A | −0.280.02 | −0.200.04 | 1.420.06 | 21 | 0.9888 | 0.070 | 797 | 24,25,30,60,62,63,66 |
| bLGB | HHb | ConA | −0.310.04 | 0.540.05 | 0.140.02 | 22 | 0.9622 | 0.051 | 242 | 60,62,72–75 |
| CHY | SubA | ConA | −0.910.03 | 0.400.02 | 0.60.1 | 19 | 0.9709 | 0.050 | 267 | 23,30,32,37,38,62 |
| CHTG | ConA | Lipase | −0.130.01 | 0.080.01 | 0.100.02 | 21 | 0.8672 | 0.029 | 58.8 | - |
| TRY | RNase B | RNase A | 0 | 0.510.04 | 0.610.09 | 32 | 0.9787 | 0.081 | 667 | 23,24,28,36,60,71,73 |
| HEL | TRY | CHTG | 0.390.02 | 0.150.02 | 0.580.03 | 25 | 0.9678 | 0.073 | 316 | 26,32–37,50–52,62,66,73,74 |
| bLGA | RNasa A | bLGB | −0.250.02 | 0.500.02 | 0.080.02 | 25 | 0.9884 | 0.046 | 934 | 23,39–41,45–47,60,62,65–67,72–75 |
| Benzyl alcohol | CHTG | Vanillin | 0.050.02 | 1.250.04 | −0.110.02 | 31 | 0.9920 | 0.036 | 1745 | - |
| Benzyl alcohol | HEL | Vanillin | −0.030.02 | 1.460.03 | −0.160.008 | 30 | 0.9898 | 0.041 | 1313 | 15 |
| Caffeine | CHY | Glucoside b | 0040.01 | 0.970.08 | −0.060.02 | 31 | 0.9664 | 0.040 | 403 | - |
| Caffeine | Phenol | Lipase | −0.060.01 | −0.240.07 | −0.120.04 | 25 | 0.9501 | 0.019 | 209 | 14 |
| logK-X | logK-Y | logK-Z | k1 | k2 | k3 | N | r2 | SD | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terbutaline | Piroxicam | Clonidine HCl | 0.80.1 | 0.270.09 | −0.90.06 | 7 a | 0.9888 | 0.038 | 176 |
| Atenolol | Metoprolol (1/2 tartrate) | Propranolol | 0.970.04 | −0.240.05 | 1.020.08 | 7 b | 0.9896 | 0.028 | 191 |
| Acebutolol HCl | Desipramine HCl | Metoprolol (1/2 tartrate) | −0.600.07 | 0.700.09 | 0.450.06 | 8 | 0.9941 | 0.028 | 419 |
| Atenolol | Desipramine HCl | Propranolol | 0 | −0.130.05 | 0.990.09 | 8 | 0.9850 | 0.057 | 165 |
| Minaprine 2HCl | Mefexamide HCl | Verapamil | 1.40.1 | 0.310.09 | 0.90.3 | 8 | 0.9782 | 0.11 | 112 |
| Furosemide | Doxepin HCl | Diclofenac Na | 2.90.2 | 1.80.1 | 0.20.03 | 8 | 0.9852 | 0.047 | 167 |
| Doxepin HCl | Metoprolol (1/2 tartrate) | Verapamil | 0.390.08 | 0.980.04 | 0.220.08 | 8 | 0.9988 | 0.026 | 2128 |
| Atenolol | Acebutolol HCl | Propranolol | 0.40.2 | 1.90.4 | −1.10.2 | 8 | 0.9656 | 0.23 | 70 |
| Verapamil | Acebutolol HCl | 3-Hydroxytryptophan | −2.340.05 | 0.140.02 | −0.390.05 | 7 b | 0.9553 | 0.015 | 32 |
| Chlorpromazine | Propranolol | Verapamil | 0 | 0.670.06 | 0.50.1 | 6 b,c | 0.9996 | 0.016 | 3647 |
| Carbamazepine | Doxepin HCl | Acebutolol HCl | 2.50.3 | −2.40.2 | 0.470.02 | 6 a,d | 0.9938 | 0.027 | 241 |
| logK-X | logK-Y | logK-Z | k1 | k2 | k3 | N | r2 | SD | F | Tissues a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiopental | Tenoxicam | Salicylic acid | −0.330.08 | 0.700.07 | 0.280.07 | 7 | 0.9947 | 0.088 | 372 | Liver, skin |
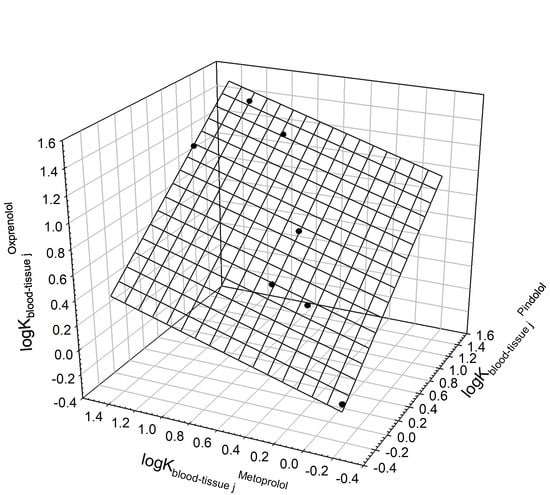
| Pindolol | Metoprolol | Oxprenolol | 0 | 0.680.09 | 0.360.09 | 7 | 0.9886 | 0.062 | 130 | Brain, heart, kidney |
| Imipramine | Diazepam | Fingolimod | 0.480.03 | 0.610.04 | 0.320.05 | 5 | 0.9998 | 0.025 | 4573 | Brain, heart |
| Acebutolol | Ftorafur | Bisoprolol | 0.30.1 | 0.580.07 | 0.80.2 | 5 | 0.9885 | 0.088 | 86.2 | Brain, liver, lungs, skin |
| Ftorafur | Fentanyl | Barbital | 0 | 0.370.09 | −0.100.03 | 8 | 0.9469 | 0.030 | 53.5 | Kidney, liver, lungs |
| Ceftazidime | Bisoprolol | Fentanyl | 0.320.05 | 0.130.04 | 0.600.04 | 5 | 0.9944 | 0.038 | 178 | Adipose, heart, liver |
| Fentanyl | Barbital | Acebutolol | 050.1 | 0.50.1 | 1.80.2 | 6 | 0.9693 | 0.096 | 47.3 | Adipose, brain, intestine |
| Acebutolol | Propranolol | Metoprolol | 0 | 0.180.07 | 0.600.06 | 5 | 0.9877 | 0.077 | 120 | Adipose, intestine, kidney, liver |
| Phenytoin | Phencyclidine | Pentazocine | 0.540.06 | 0.320.08 | 0.500.07 | 5 | 0.9985 | 0.075 | 660 | Adipose, brain, liver |
| Thiopental | Tenxicam | Timolol | 1.150.03 | −0.580.04 | 0.610.02 | 5 | 0.9970 | 0.037 | 331 | Intestine, kidney, lungs, skin |
| Tolbutamide | Triazolam | Valproic acid | 0 | 1.970.12 | 1.70.1 | 4 | 0.9969 | 0.027 | 161 | Kidney, liver |
| Quinidine | Salicylic acid | Thiopental | 0.450.01 | 0.040.01 | 0.830.01 | 4 | 0.9998 | 0.004 | 2313 | Brain, liver, muscle |
| Lomefloxacin | Nalidixic acid | Ofloxacin | 0.330.05 | 0.880.04 | 0.520.08 | 9 | 0.9969 | 0.031 | 959 | Liver |
| Barbital | Alprazolam | PEB acid b | 0.440.09 | 1.60.3 | −0.80.2 | 7 | 0.9509 | 0.055 | 38.7 | - |
| Betaxolol | Ceftazidime | Bisoprolol | 0 | 0.820.05 | 0.180.06 | 7 | 0.9905 | 0.071 | 209 | Intestine |
| Cotinine | Ceftazidime | Cefazolin | 0.180.01 | 0.940.07 | 0.950.01 | 5 | 0.9999 | 0.009 | 10617 | Liver |
| Midazolam | Metoprolol | Lomefloxacin | 0 | −0.460.08 | 0.640.05 | 6 | 0.9842 | 0.055 | 93.2 | Brain, kidney, lungs |
| Nalidixic acid | Nicotine | Oxrenolol | 0.90.1 | 0.80.1 | 0.530.08 | 5 | 0.9936 | 0.061 | 155 | Brain, intestine, lungs, skin |
| Pindolol | Oxprenolol | Phenytoin | 0 | −1.030.08 | 1.150.08 | 6 | 0.9859 | 0.030 | 105 | Kidney, lungs, muscle |
| Matrine | Midazolam | Metuprolol | 0 | 0.710.07 | 0.680.08 | 4 | 0.9961 | 0.039 | 129 | Adipose, brain, heart, muscle |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, N.R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Madeira, P.P.; Teixeira, J.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Linear Relationships between Partition Coefficients of Different Organic Compounds and Proteins in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems of Various Polymer and Ionic Compositions. Polymers 2020, 12, 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071452
da Silva NR, Ferreira LA, Madeira PP, Teixeira JA, Uversky VN, Zaslavsky BY. Linear Relationships between Partition Coefficients of Different Organic Compounds and Proteins in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems of Various Polymer and Ionic Compositions. Polymers. 2020; 12(7):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071452
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Nuno R., Luisa A. Ferreira, Pedro P. Madeira, José A. Teixeira, Vladimir N. Uversky, and Boris Y. Zaslavsky. 2020. "Linear Relationships between Partition Coefficients of Different Organic Compounds and Proteins in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems of Various Polymer and Ionic Compositions" Polymers 12, no. 7: 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071452
APA Styleda Silva, N. R., Ferreira, L. A., Madeira, P. P., Teixeira, J. A., Uversky, V. N., & Zaslavsky, B. Y. (2020). Linear Relationships between Partition Coefficients of Different Organic Compounds and Proteins in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems of Various Polymer and Ionic Compositions. Polymers, 12(7), 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071452