Polymers 2020, 12(7), 1489; https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071489 - 3 Jul 2020
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 6841
Abstract
Lithium phenyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphinate (LAP) is a free radical photo-initiator used to initiate free radical chain polymerization upon light exposure, and is combined with gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) to produce a photopolymer used in bioprinting. The free radicals produced under bioprinting conditions are potentially
[...] Read more.
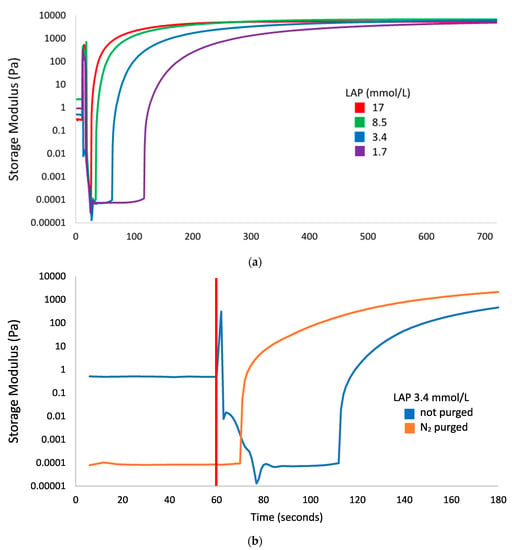
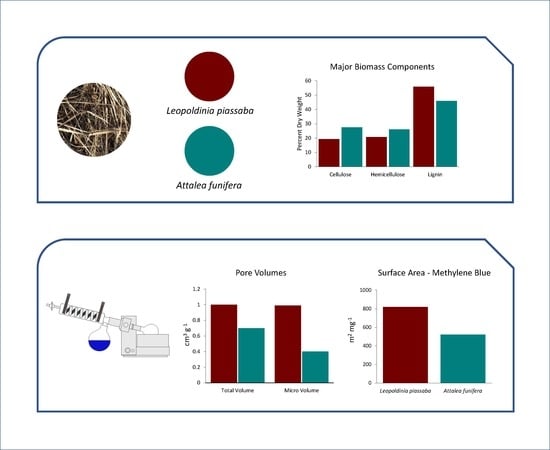
Lithium phenyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphinate (LAP) is a free radical photo-initiator used to initiate free radical chain polymerization upon light exposure, and is combined with gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) to produce a photopolymer used in bioprinting. The free radicals produced under bioprinting conditions are potentially cytotoxic and mutagenic. Since these photo-generated free radicals are highly-reactive but short-lived, toxicity assessments should be conducted with light exposure. In this study, photorheology determined that 10 min exposure to 9.6 mW/cm2 405 nm light from an LED light source fully crosslinked 10 wt % GelMA with >3.4 mmol/L LAP, conditions that were used for subsequent cytotoxicity and mutagenicity assessments. These conditions were cytotoxic to M-1 mouse kidney collecting duct cells, a cell type susceptible to lithium toxicity. Exposure to ≤17 mmol/L (0.5 wt %) LAP without light was not cytotoxic; however, concurrent exposure to ≥3.4 mmol/L LAP and light was cytotoxic. No condition of LAP and/or light exposure evaluated was mutagenic in bacterial reverse mutation assays using S. typhimurium strains TA98, TA100 and E. coli WP2 uvrA. These data indicate that the combination of LAP and free radicals generated from photo-excited LAP is cytotoxic, but mutagenicity was not observed in bacteria under typical bioprinting conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue 3D/4D Printing with Polymers, Polymer Hydrogels and Adaptive Soft Materials)
►
Show Figures