Nanosilica-Toughened Epoxy Resins
Abstract
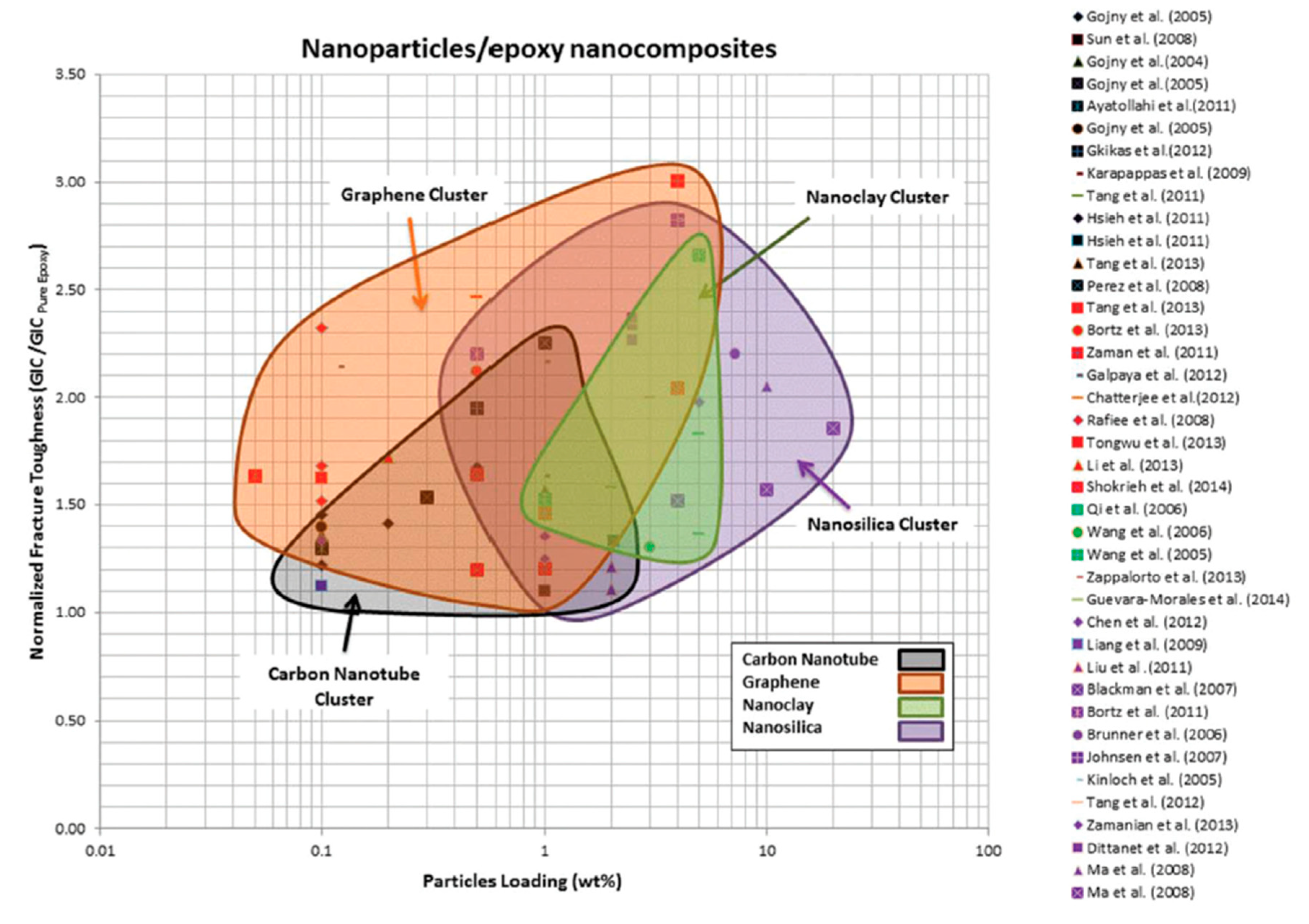
1. Introduction
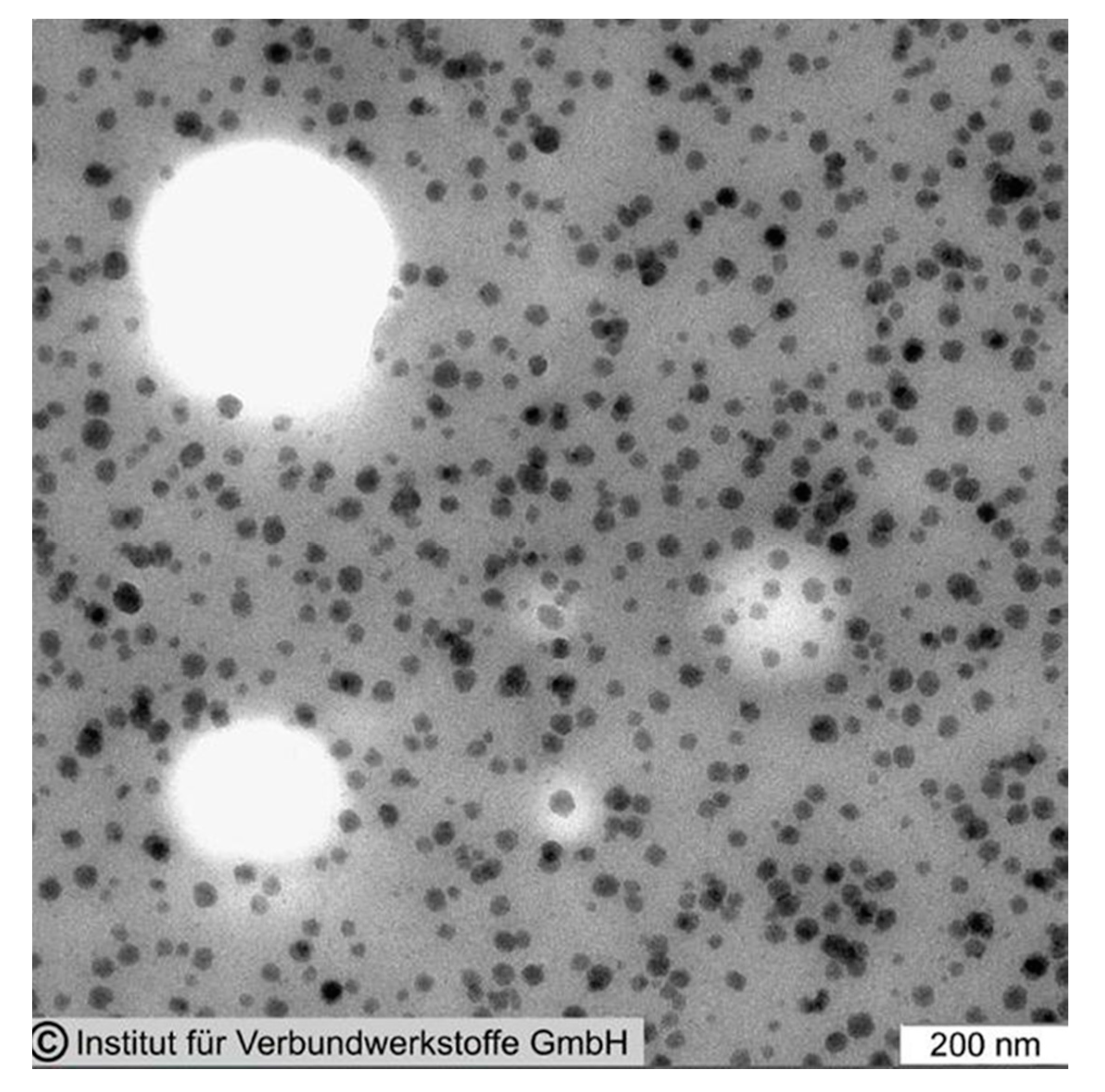
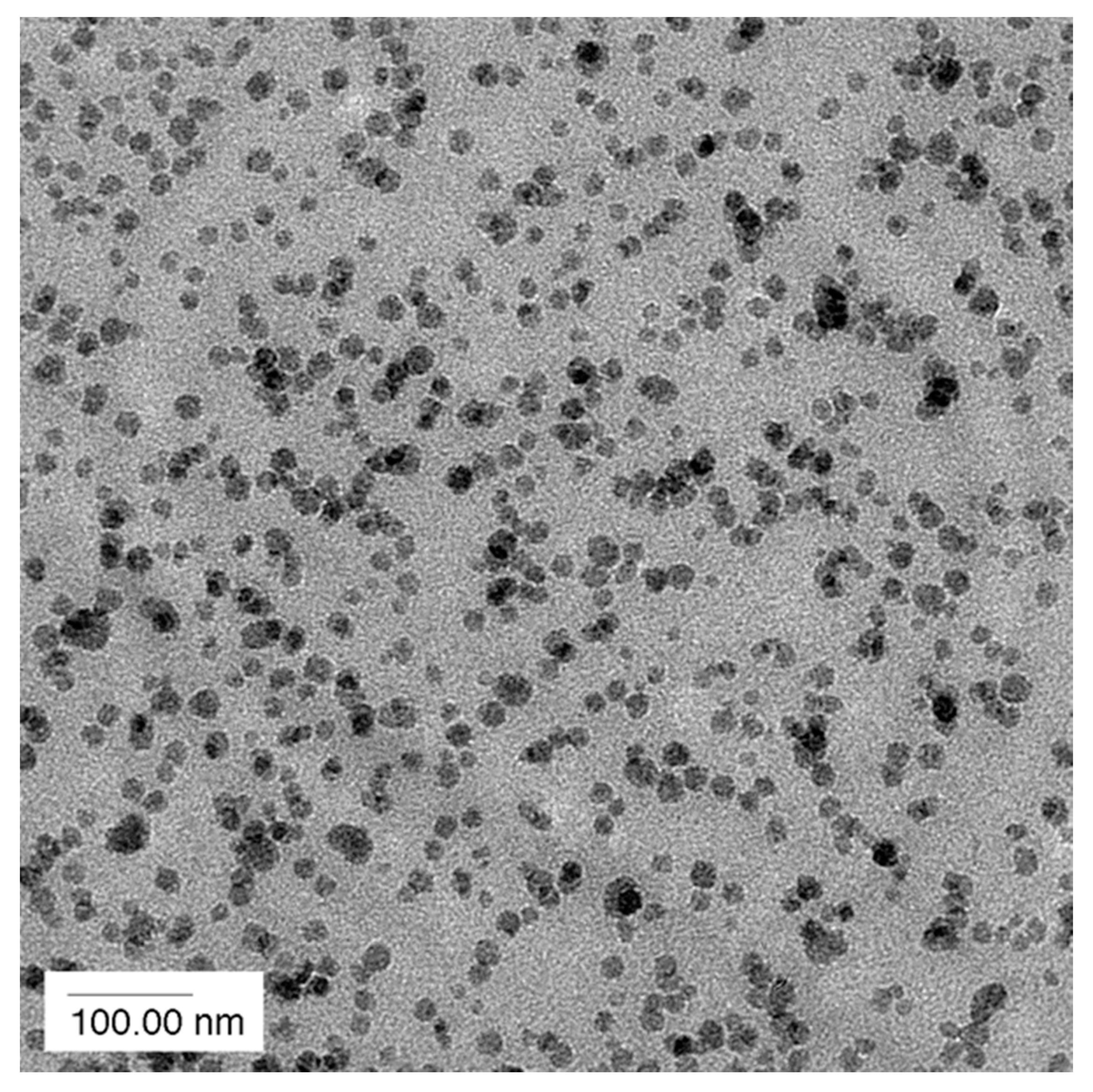
2. Epoxy Resins Modified with Silica Nanoparticles
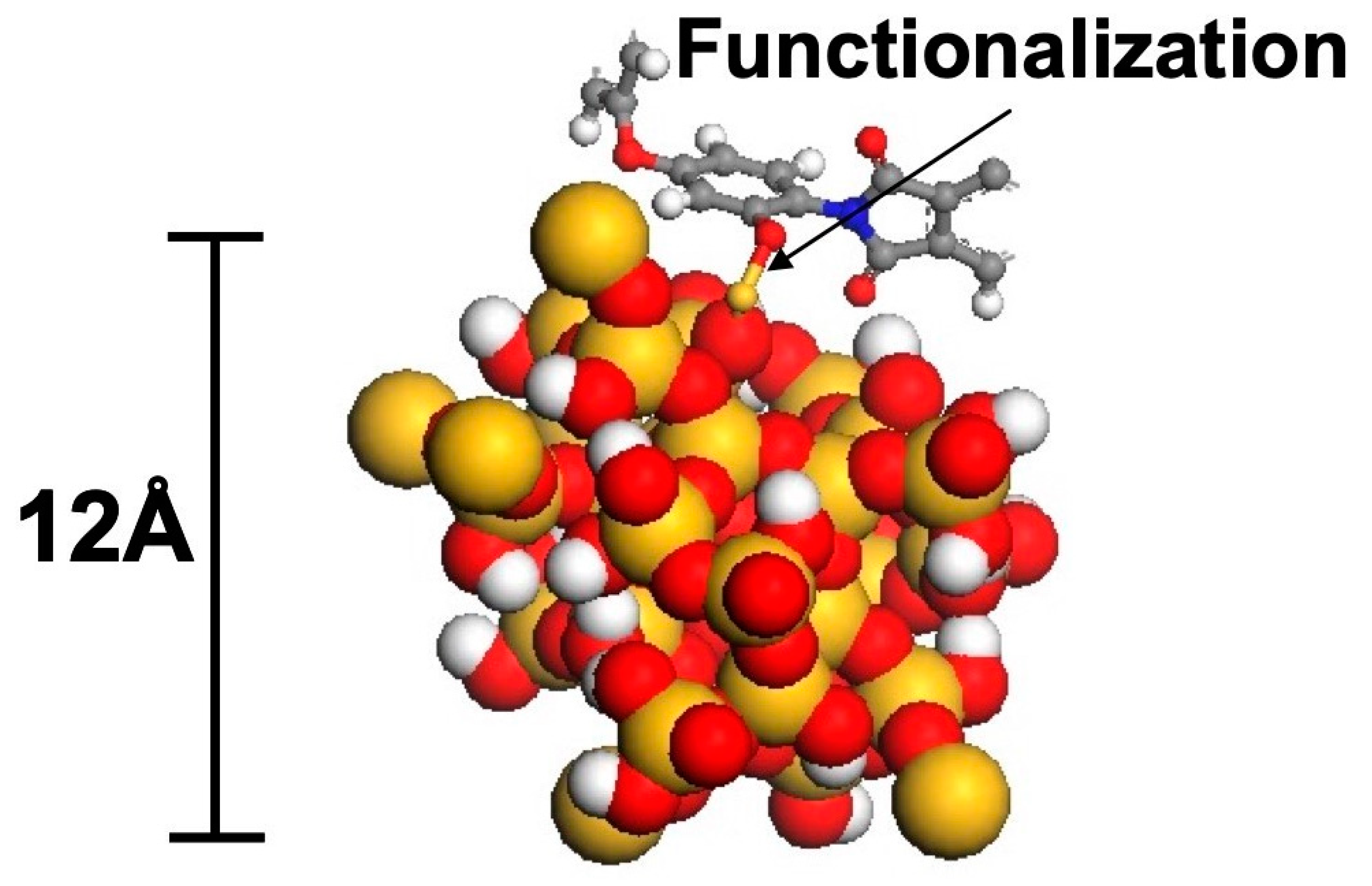
2.1. Toxicological Aspects of Silica Nanoparticles in Epoxy Resins
2.2. Property Improvements of Epoxy Resins by Silica Nanoparticle Modification
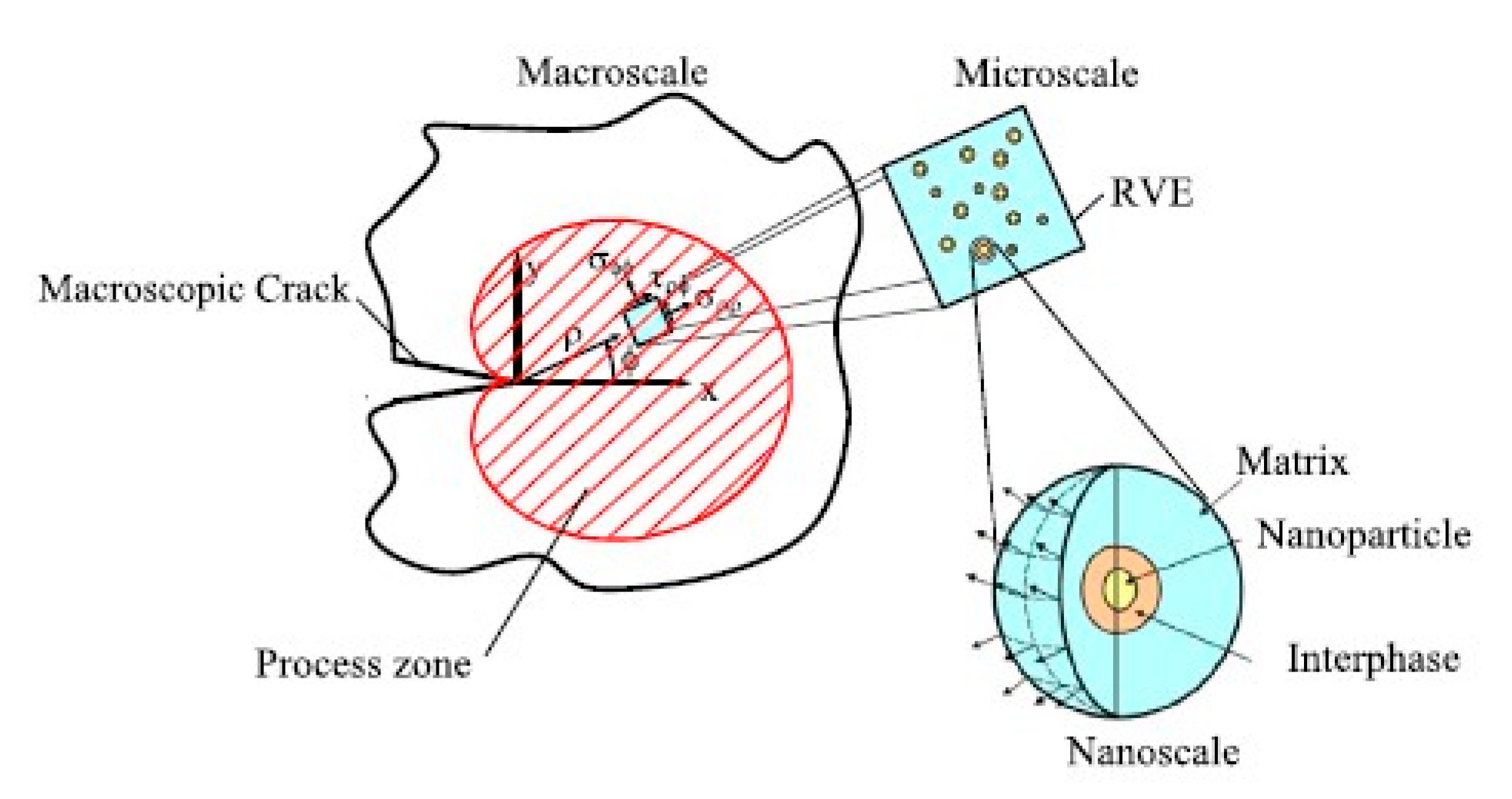
2.3. Toughness Increase of Epoxy Resins by Nanosilica Modification and Mechanisms
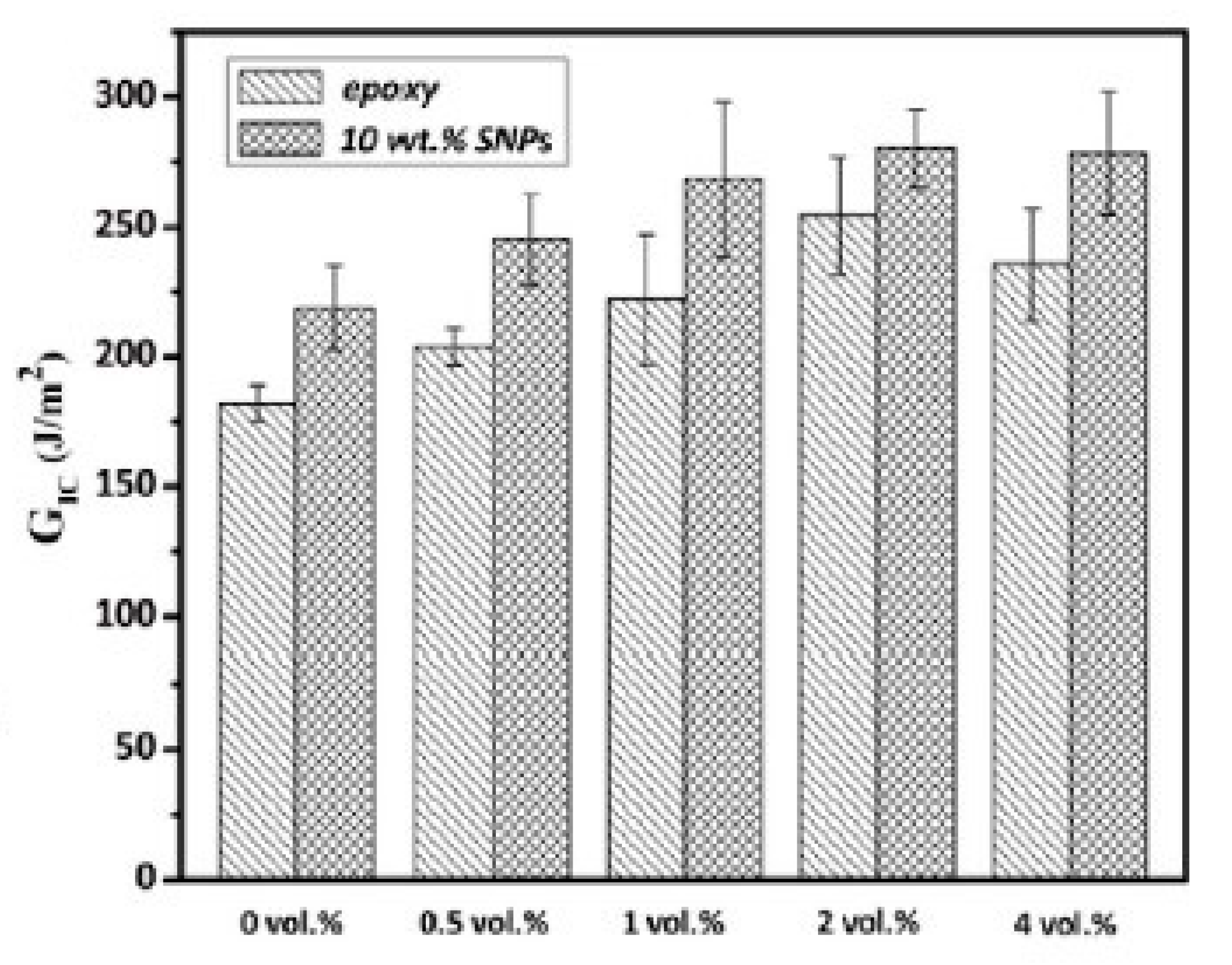
2.4. Synergy Between Elastomeric Tougheners and Silica Nanoparticles: Further Property Improvements
3. Improving Epoxy Resin Applications with Silica Nanoparticles
3.1. Adhesives
3.2. Stereolithography (SLA)
3.3. Coatings
3.4. Electronic Applications
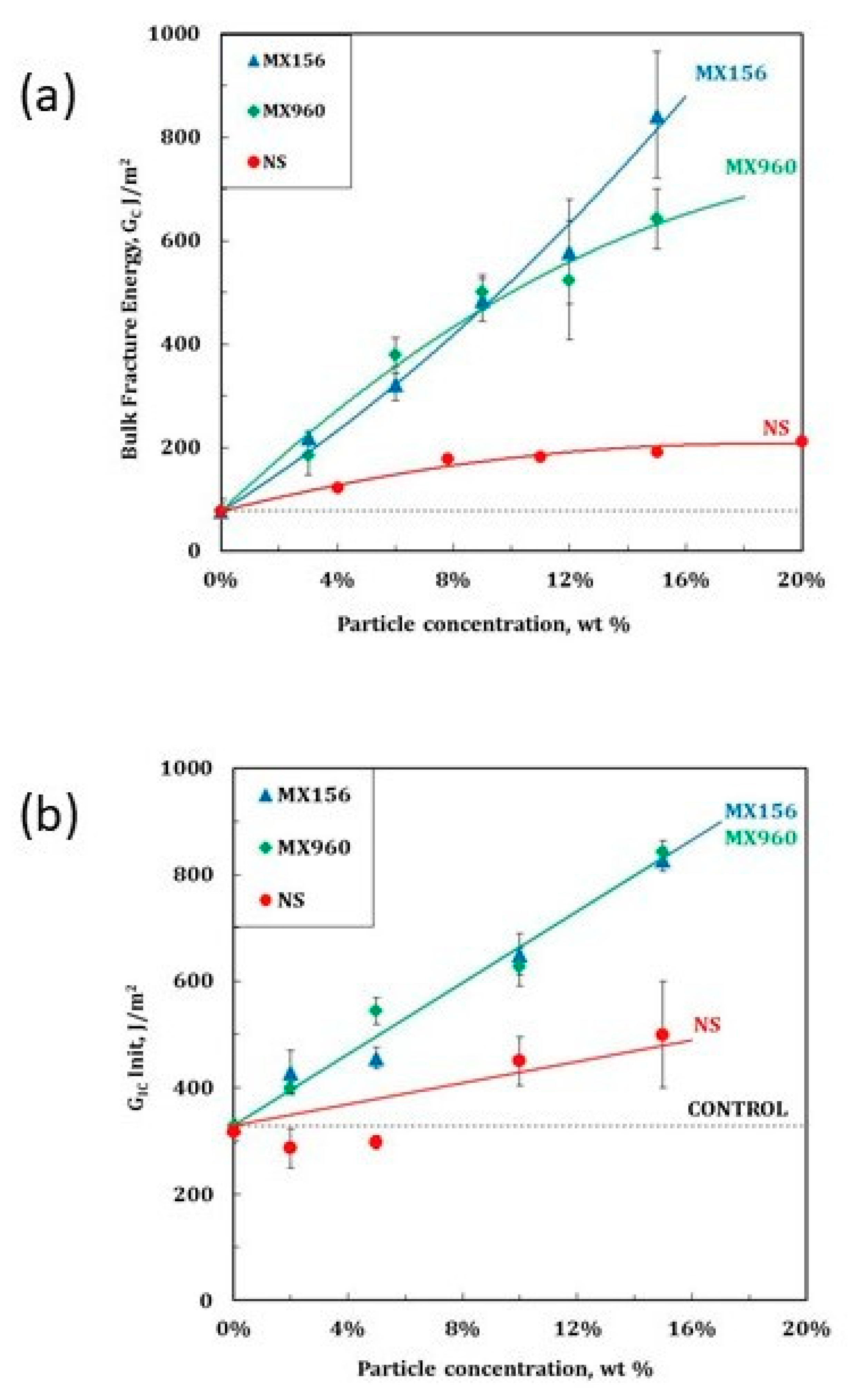
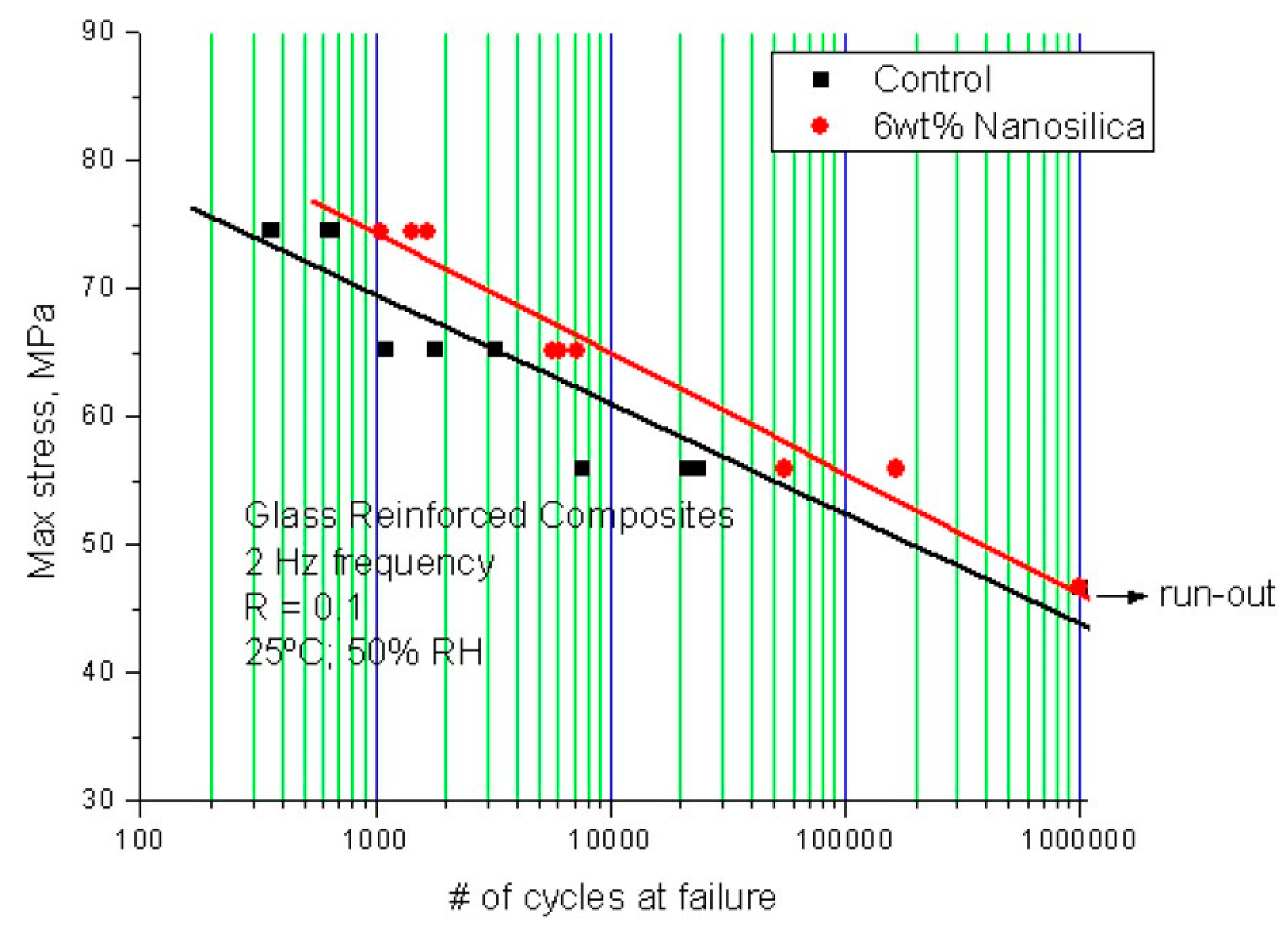
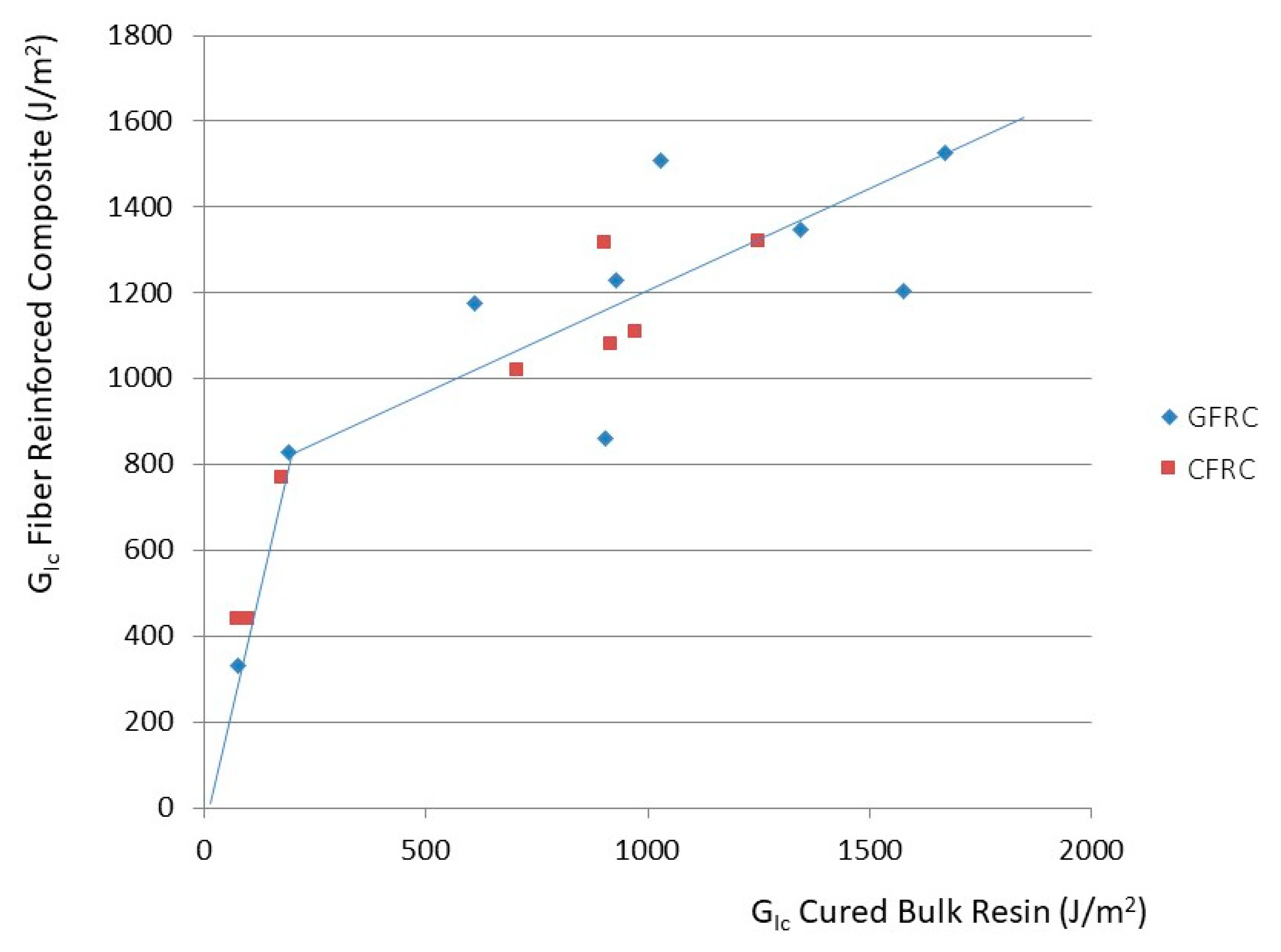
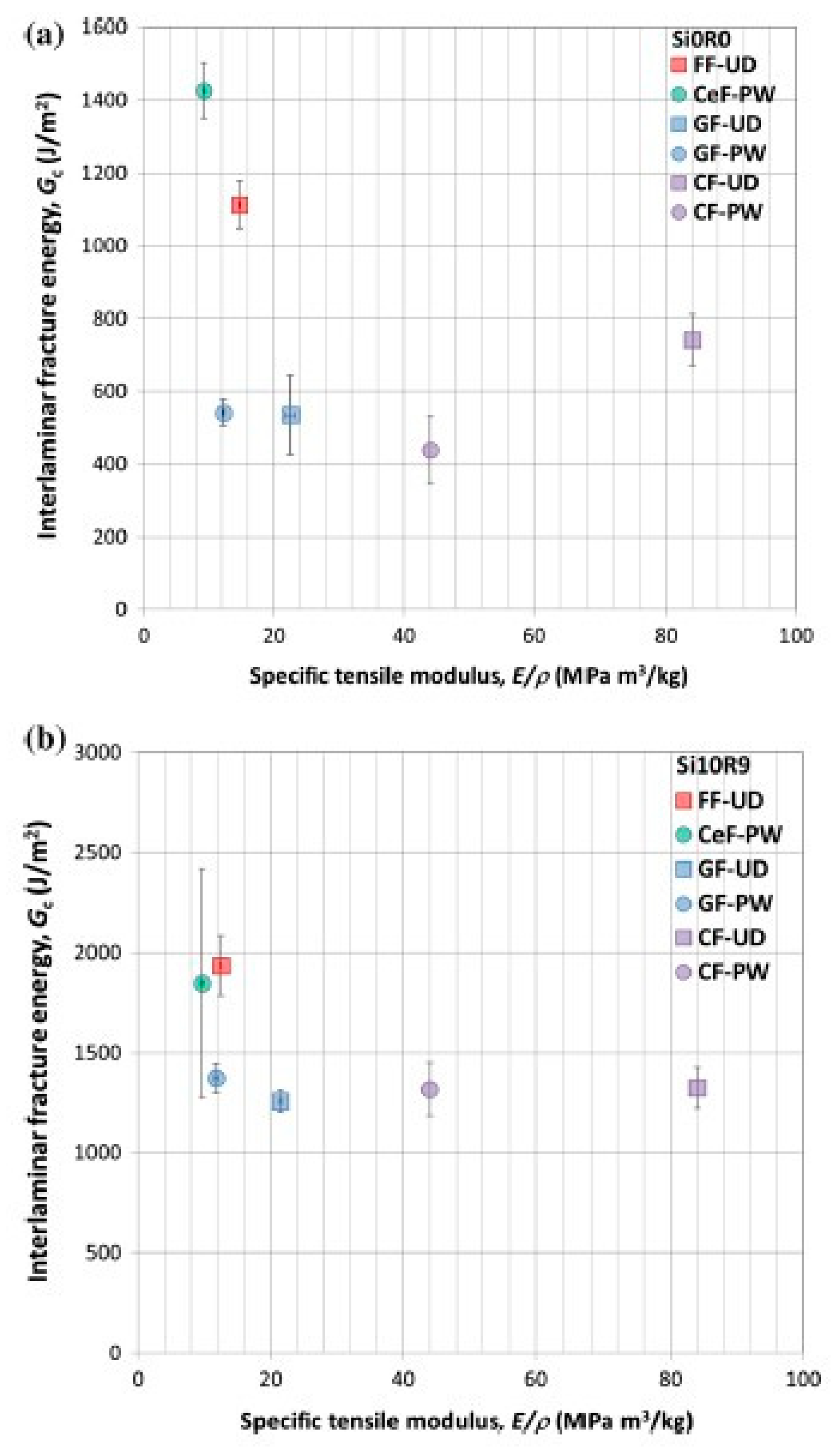
3.5. Fiber-Reinforced Composites
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N. Some basic aspects of polymer nanocomposites: A critical review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domun, N.; Hadavinia, H.; Zhang, T.; Sainsbury, T.; Liaghat, G.H.; Vahid, S. Improving the fracture toughness and the strength of epoxy using nanomaterials—A review of the current status. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10294–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegard, G.M.; Clancy, T.; Gates, T.S. Modeling of the Mechanical Properties of Nanoparticle/Polymer Composites*Originally published as Odegard, G. M., T. C. Clancy, and T. S. Gates, Modeling of the mechanical properties of nanoparticle/polymer composites. Polymer 2005, 46, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product Information Nanopox, Hanse Chemie; GmbH: Geesthacht, Germany, 2005.
- Adhesive & Sealant. Available online: http://www.nanopox.com (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Ziemann, C.; Rittinghausen, S.; Ernst, H.; Kolling, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; Creutzenberg, O. Mode of Action of Fine and Ultrafine Dusts in Lungs. In Project F 2135; BAUA Dortmund: Berlin/Dresden, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, C.A.; Elsaesser, A.; Arkusz, J.; Smok, A.; Palus, J.; Lesniak, A.; Salvati, A.; Hanrahan, J.P.; de Jong, W.H.; Dziubaltowska, E.; et al. Reproducible comet assay of amorphous silica nanoparticles detects no genotoxicity. Nanoletters 2008, 8, 3069–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruijtier-Poelloth, C. The toxicological mode of action and the safety of synthetic amorphous silica—A nanostructured material. Toxicology 2012, 294, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L.C.; Lison, D.; Martens, J.A.; Hoet, P.H. The nanosilica hazard: Another variable entity. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duschl, A.; Windgasse, G.J. A survey on the state of nanosafety research in the European Union and the United States. Nanoparticle Res. 2018, 20, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roenner, N.; Hutheesing, K.; Fergusson, A.; Rein, G. Simultaneous improvements in flammability and mechanical toughening of epoxy resins through nano-silica addition. Fire Saf. J. 2017, 91, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeublein, M.; Peter, K.; Bakis, G.; Maekimieni, R.; Altstaedt, V.; Moeller, M. Investigation on the Flame Retardant Properties and Fracture Toughness of DOPO and Nano-SiO2 Modified Epoxy Novolac Resin and Evaluation of Its Combinational Effects. Materials 2019, 12, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenger, S. Epoxy resin composites with surface-modified silicon dioxide nanoparticles: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapiai, N.; Jumahat, A.; Manap, N.; Usoff, M. Effect of nanofillers dispersion on mechanical properties of clay/epoxy and silica/epoxy nanocomposites. J. Teknol. 2015, 76, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, T.; Bie, B.-X.; Luo, S.-N.; Zhang, Z. High strain rate compression of epoxy based nanocomposites. Compos. Part A 2016, 90, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, A.I.; Haeusler, I.; Oesterle, W.; Wetzel, B.; Zhang, G. Modeling of the stress–strain behavior of an epoxy-based nanocomposite filled with silica nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorvaldsen, T.; Johnsen, B.B.; Olsen, T.; Hansen, F.K. Investigation of theoretical models for the elastic stiffness of nanoparticle-modified polymer composites. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, A.; Zhang, H.; Owais, M.; Zhao, J.; Chu, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z. Wear and friction of epoxy based nanocomposites with silica nanoparticles and wax-containing microcapsules. Compos. Part A 2018, 107, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Chen, S.; Campbell, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y. Fracture toughness and wear properties of nanosilica/epoxy composites under marine environment. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 177, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.T.; Liu, H.Y.; Saintier, N.; Mai, Y.W. Cyclic fatigue of polymer nanocomposites. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2009, 16, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, B.R.K.; Kinloch, A.J.; Sohn Lee, J.; Taylor, A.C.; Agarwal, R.; Schueneman, G.; Sprenger, S. The fracture and fatigue behaviour of nano-modified epoxy polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 7049–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Taylor, A.C.; Dransfeld, C.; Sprenger, S.; Ritter, K.; Masania, K. Cure Kinetics of Fast-Cure Epoxy With Silica Nanoparticles. JEC Compos. Mag. 2016, 107, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, A.; Masania, K.; Taylor, A.C.; Dransfeld, C. Fast-curing epoxy polymers with silica nanoparticles: Properties and rheo-kinetic modelling. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, S. Epoxy resins modified with elastomers and surface-modified silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2013, 54, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.D.; Xu, F.; Du, X.D.; Lee, Z.H.; Wang, X.J. Temperature effects on rigid nano-silica and soft nano-rubber toughening in epoxy under impact loading. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45319–45327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, W.L. The use of tapered double cantilever beam (TDCB) in investigating fracture properties of particles modified epoxy. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Maxwell, D.L.; Young, R.J. The fracture of hybrid-particulate composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1985, 20, 4169–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.H.; Kinloch, A.J.; Masania, K.; Taylor, A.C.; Sprenger, S. The mechanisms and mechanics of the toughening of epoxy polymers modified with silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2010, 51, 6284–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittanet, P.; Pearson, R.A. Effect of silica nanoparticle size on toughening mechanisms of filled epoxy. Polymer 2012, 53, 1890–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guild, F.J.; Kinloch, A.J.; Masania, K.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, A.C. The fracture of thermosetting epoxy polymers containing silica nanoparticles. Strength Fract. Complex. 2018, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappalorto, M.; Salviato, M.; Quaresimin, M. A multiscale model to describe nanocomposite fracture toughness enhancement by the plastic yielding of nanovoids. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappalorto, M.; Pontefisso, A.; Fabrizi, A.; Quaresimin, M. Mechanical behaviour of epoxy/silica nanocomposites: Experiments and modelling. Compos. Part A 2015, 72, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresimin, M.; Schulte, K.; Zappalorto, M.; Chandrasekaran, S. Toughening mechanisms in polymer nanocomposites: From experiments to modelling. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 123, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, C.; Chemie Ag, H.; Sprenger, S. Polymeric Epoxy Resin Composition. WO 2004081076, 23 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Poonpipat, Y.; Leelachai, K.; Pearson, R.A.; Dittanet, P. Fracture behavior of silica nanoparticles reinforced rubber/epoxy composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2017, 36, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y.; Ye, L. Role of rigid nanoparticles and CTBN rubber in the toughening of epoxies with different cross-linking densities. Compos. Part A 2016, 80, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolan, D.; Ivankovic, A.; Kinloch, A.J.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, A.C. Toughening of epoxy-based hybrid nanocomposites. Polymer 2016, 97, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, W.L.; Taylor, A.C. Fracture and toughening mechanisms of silica- and core–shell rubber-toughened epoxy at ambient and low temperature. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 13938–13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utaloff, K.; Kothmann, M.H.; Ciesielski, M.; Doering, M.; Neumeyer, T.; Altstaedt, V.; Gorman, I.; Henningsen, M. Improvement of fracture toughness and glass transition temperature of DGEBA -based epoxy systems using toughening and crosslinking modifiers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelachai, K.; Kongkachuichay, P.; Dittanet, P. Toughening of epoxy hybrid nanocomposites modified with silica nanoparticles and epoxidized natural rubber. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, S.; Eger, C.; Kinloch, A.J.; Lee, J.H.; Taylor, A.C.; Egan, D. Nanoadhesives: Toughness and high Strength. Adhaes. Kleb. Dicht. 2003, 03, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, C.H.; Saber, N.; Kuan, H.C.; Dai, J.; Friedrich, K.; Ma, J. Nanosilica-toughened polymer adhesives. Mater. Des. 2014, 61, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Mai, Y.W. On adhesive properties of nano-silica/epoxy bonded single-lap joints. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Huang, M.; Yu, B.; Sprenger, S.; Yang, J. Effects of nano-silica contents on the properties of epoxy nanocomposites and Ti-epoxy assembles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 129, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojibabu, P.; Zhang, Y.X.; Prusty, B.G. A review of research advances in epoxy-based nanocomposites as adhesive materials. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 96, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, M.; Suriano, R.; Muscatello, A.; Turri, S.; Levi, M. Near-visible stereolithography of a low shrinkage cationic/free-radical photopolymer blend and its nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevajothi, K.; Subasri, R.; Soma Raju, K.R.C. Transparent, non-fluorinated, hydrophobic silica coatings with improved mechanical properties. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 2111–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergely, R.C.R.; Sottos, N.R.; White, S.R. Regenerative Polymeric Coatings Enabled by Pressure Responsive Surface Valves. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, H. Next-Generation Composite Coating System: Nanocoating. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Uchida, K.; Tanaka, T. Voltage Endurance Characteristics of Epoxy/Silica Nanocomposites. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2011, 94, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Lee, J.J.; Bae, B.S.; Park, S.J.; Yoo, S.; Jung, K.H. Silica nanoparticle-embedded sol–gel organic/inorganic hybrid nanocomposite for transparent OLED encapsulation. Org. Electron. 2012, 13, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Xue, Y.; Xue, Z.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Mai, Y.W. Structure, rheological, thermal conductive and electrical insulating properties of high-performance hybrid epoxy/nanosilica/AgNWs nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 128, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.G.; Han, Y.C.; Im, H.G.; Bae, B.S.; Choi, K.C. Highly reliable hybrid nano-stratified moisture barrier for encapsulating flexible OLEDs. Org. Electron. 2016, 33, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.G.; Kwon, S.; Han, J.H.; Im, H.G.; Bae, B.S.; Choi, K.C. A mechanically enhanced hybrid nano-stratified barrier with a defect suppression mechanism for highly reliable flexible OLEDs. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6370–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Jeong, E.G.; Choi, K.C. Reliable high temperature, high humidity flexible thin film encapsulation using Al2O3/MgO nanolaminates for flexible OLEDs. Nanores 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veena, M.G.; Renukappa, N.M.; Shivakumar, K.N.; Seetharamu, S. Dielectric properties of nanosilica filled epoxy nanocomposites. Sãdhanã 2016, 41, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.M.; Tveten, E.G.; Glaum, J.; Glomm Ese, M.H.; Hvidsten, S.; Glomm, W.; Einarsrud, M.A. Epoxy-Based Nanocomposites for High-Voltage Insulation: A Review. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.; Carlotti, S. The Effect of Hybridized Carbon Nanotubes, Silica Nanoparticles, and Core-Shell Rubber on Tensile, Fracture Mechanics and Electrical Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.; Martin, R.; Faria, H.; Ibarboure, E.; Carlotti, S. Epoxy based hybrid nanocomposites: Fracture mechanisms, tensile properties and electrical properties. Mater. Today Proc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, S. Improving mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced composites based on epoxy resins containing industrial surface-modified silica nanoparticles: Review and outlook. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, B.M.; Maldonado, J.; Klunker, F.; Ermanni, P. Particle distribution from in-plane resin flow in a resin transfer molding process. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Influence of nanoparticles on the interfacial properties of fiber-reinforced-epoxy composites. Compos. Part A 2017, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, S.A.; Taylor, A.C. Toughening performance of glass fibre composites with core-shell rubber and silica nanoparticle modified matrices. Compos. Part A 2017, 80, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, S.A.; Taylor, A.C. Fracture behaviour of rubber- and silica nanoparticle-toughened glass fibre composites under static and fatigue loading. Compos. Part A 2018, 109, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.S.; Trevino, E.; Gaikwad, S.; Sprenger, S.; Rosas, I.; Andrews, M.J. Low velocity impact studies on glass reinforced composites using rubber microparticles and silica nanoparticles modified epoxy resin. Nanosci. Nanoeng. Appl. 2013, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger, S.; Kothmann, M.H.; Altstaedt, V. Carbon fiber-reinforced composites using an epoxy resin matrix modified with reactive liquid rubber and silica nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 105, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.S.; Akinola, A.T.; Espinoza, S.; Gaikwad, S.; Vasudevan, D.K.K.; Kumar, K.; Sprenger, S. Tension–tension fatigue performance and stiffness degradation of nanosilica-modified glass fiber-reinforced composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landowski, M.; Imielinska, K. Impact behaviour of glass fibre/epoxy composites with nano-enhanced resin after water exposure. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2015, 15, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, W.; Tang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, P. A general strength model for fiber bundle composites under transverse tension or interlaminar shear. Compos. Part A 2019, 121, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhang, H.P.; Xu, X.; Tang, Y. Hybrid enhancements by polydopamine and nanosilica on carbon fibre reinforced polymer laminates under marine environment. Compos. Part A 2018, 112, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, J.; Mahrholz, T.; Sinapius, M. Identification and quantitation of processing parameters controlling the surface quality of carbon fibre-reinforced composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 638–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abliz, D.; Finke, B.; Berg, D.C.; Schilde, C.; Ziegmann, G. Flow of quasi-spherical nanoparticles in liquid composite molding processes. Part I: Influence of particle size and fiber distance distribution. Compos. Part A 2019, 125, 105563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abliz, D. Functionalization of Fiber Composites with Nanoparticle-Modified Resin Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Clausthal University of Technology, Clausthal, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Landowski, M.; Strugala, G.; Budzik, M.; Imielinska, K. Impact damage in SiO2 nanoparticle enhanced epoxy—Carbon fibre composites. Compos. Part B 2017, 113, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolan, D.; Kinloch, A.J.; Ivankovic, A.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, A.C. Mechanical and fracture performance of carbon fibre reinforced composites with nanoparticle modified matrices. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2016, 2, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolan, D.; Ivankovic, A.; Kinloch, A.J.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, A.C. Toughened carbon fibre-reinforced polymer composites with nanoparticle-modified epoxy matrices. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 1767–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.N.; Carolan, D.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, A.C. Fracture and fatigue behaviour of carbon fibre composites with nanoparticle-sized fibres. Compos. Struct. 2019, 217, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnati, S.R.; Agbo, P.; Zhang, L. Applications of Silica Nanoparticles in Glass/Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Nanocomposite. Compos. Commun. 2020, 17, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, S. Fiber-reinforced composites based on epoxy resins modified with elastomers and surface-modified silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Taylor, A.C.; Techapaitoon, M.; Teo, W.S.; Sprenger, S. Tough, natural-fibre composites based upon epoxy matrices. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 6947–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Taylor, A.C.; Techapaitoon, M.; Teo, W.S.; Sprenger, S. From matrix nano- and micro-phase tougheners to composite macro-properties. Philos. Trans. A 2016, 374, 20150275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sprenger, S. Nanosilica-Toughened Epoxy Resins. Polymers 2020, 12, 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081777
Sprenger S. Nanosilica-Toughened Epoxy Resins. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081777
Chicago/Turabian StyleSprenger, Stephan. 2020. "Nanosilica-Toughened Epoxy Resins" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081777
APA StyleSprenger, S. (2020). Nanosilica-Toughened Epoxy Resins. Polymers, 12(8), 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081777




