Amphiphilic Molecular Brushes with Regular Polydimethylsiloxane Backbone and Poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline Side Chains. 2. Self-Organization in Aqueous Solutions on Heating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Investigated Samples of PDMS-g-PiPrOx
2.2. Investigation of Self-Organization in Aqueous Solutions
3. Results
3.1. Behavior of Molecular Brush Solutions at Low Temperatures
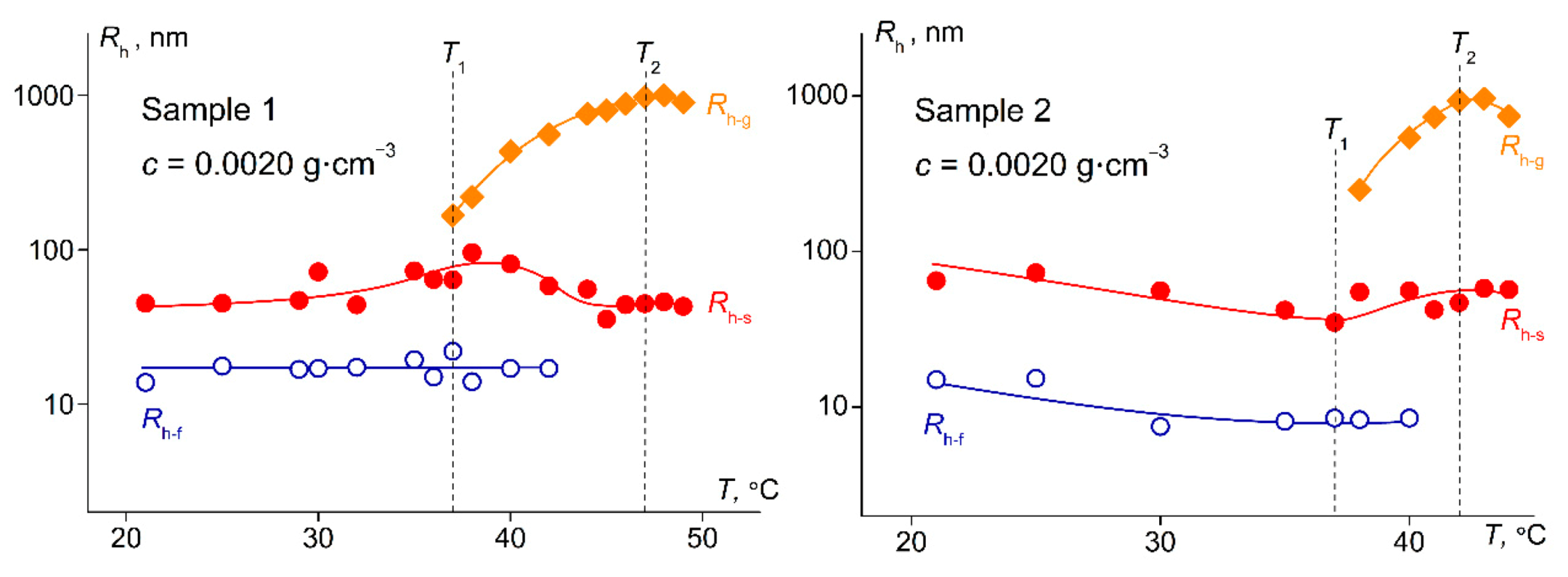
3.2. Dependence of the Characteristics of PDMS-g-PiPrOx Aqueous Solutions on Temperature
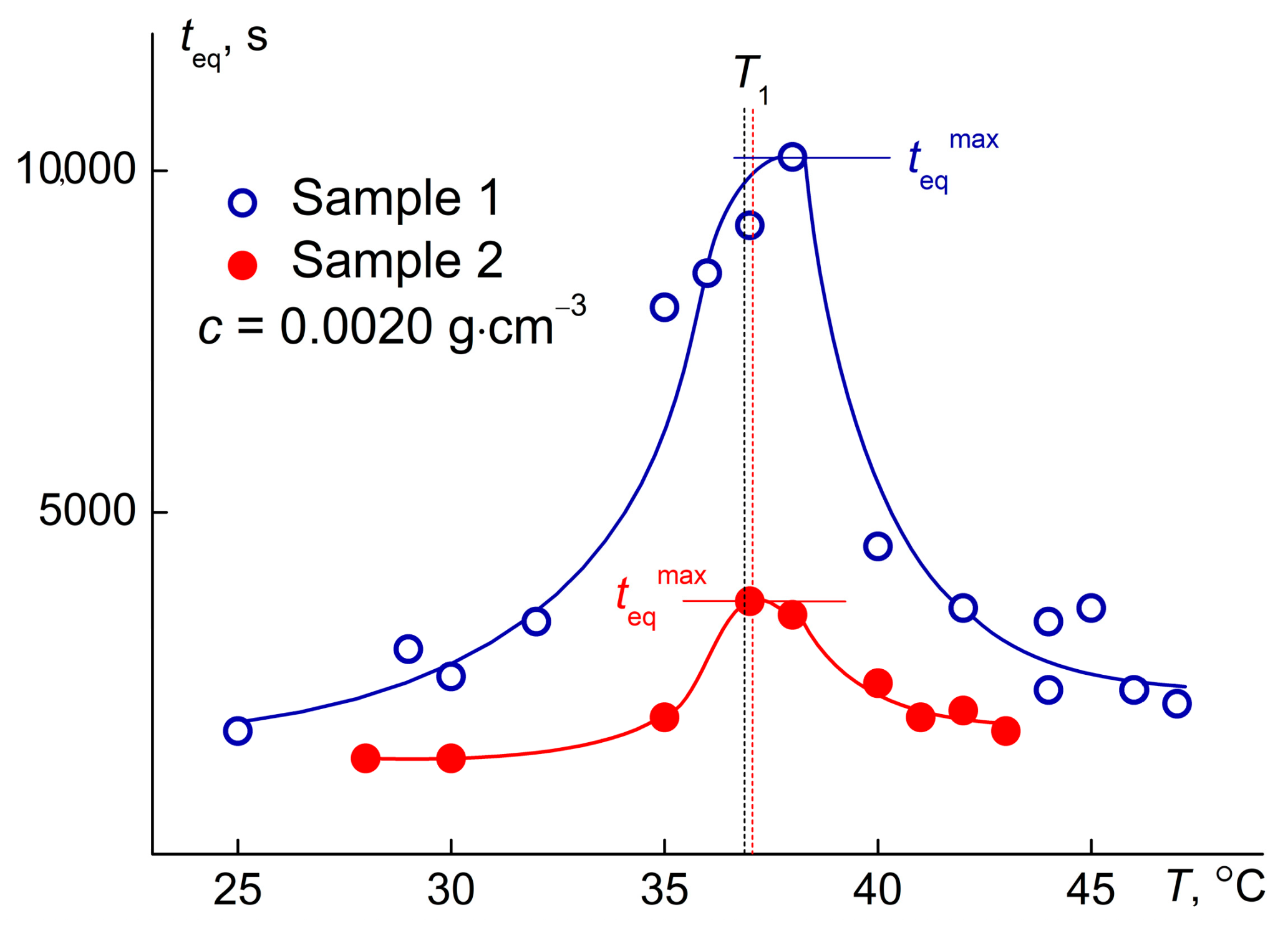
3.3. Phase Separation Temperatures of PDMS-g-PiPrOx Aqueous Solutions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, M.A.; Georgiou, T.K. Thermoresponsive polymers for biomedical applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1215–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, B.; Theato, P. Chemical strategies for the synthesis of protein-polymer Conjugates. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2013, 253, 37–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bagán, H.; Kamra, T.; Jiang, L.; Ye, L. Thermoresponsive Polymer Brushes on Organic Microspheres for Biomolecular Separation and Immobilization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 218, 1600432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.M.; Spencer, D.S.; Peppas, N.A. Advanced architectures in the design of responsive polymers for cancer nanomedicine. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordat, A.; Boissenot, T.; Nicolas, J.; Tsapis, N. Thermoresponsive polymer nanocarriers for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, O.; Monnery, B.D.; Filippov, S.K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Hruby, M. Poly(2-oxazoline)s-are they more advantageous for biomedical applications than other polymers? Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1648–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossegger, E.; Schenk, V.; Wiesbrock, F. Design strategies for functionalized poly(2-oxazoline)s and derived materials. Polymers 2013, 5, 956–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudryavtseva, A.A.; Kurlykin, M.P.; Tarabukina, E.B.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Behavior of thermosensitive graft copolymer with aromatic polyester backbone and poly-2-ethyl-2-oxazoline side chains in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2017, 22, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.; Tarabukina, E.; Kudriavtseva, A.; Fatullaev, E.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A. Molecular brushes with poly-2-ethyl-2-oxazoline side chains and aromatic polyester backbone manifesting double stimuli responsiveness. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, N.V.; Simonova, M.A.; Zelinskii, S.N.; Annenkov, V.V.; Filippov, A.P. Synthesis, molecular characteristics, and stimulus-sensitivity of graft copolymer of chitosan and poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide). J. Molec. Liq. 2019, 292, 111355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabukina, E.; Fatullaev, E.; Krasova, A.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Sheiko, S.S.; Filippov, A. Synthesis, structure, hydrodynamics and thermoresponsiveness of graft copolymer with aromatic polyester backbone at poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline side chains. Polymers 2020, 12, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V. pH-responsive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H.; Winnik, F.M. Non-ionic thermoresponsive polymers in water. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2011, 242, 29–89. [Google Scholar]
- Jochum, F.D.; Theato, P. Temperature-and light-responsive smart polymer materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7468–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastakoti, B.P.; Guragain, S.; Nakashima, K.; Yamauchi, Y. Stimuli-induced core–corona inversion of micelle of poly(acrylic acid)-block-poly(n-isopropylacrylamide) and its application in drug delivery. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruta, Y.; Shimamura, M.; Matsuura, M.; Maekawa, Y.; Funatsu, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Ayano, E.; Okano, T.; Kanazawa, H. Temperature-responsive fluorescence polymer probes with accurate thermally controlled cellular uptakes. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, D.M.; Wright, R.A.E.; Woodcock, J.W.; Hu, B.; Zhao, B. Tertiary-amine-containing thermo- and pH-sensitive hydrophilic aba triblock copolymers: Effect of different tertiary amines on thermally induced sol–gel transitions. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Jarrett, K.; Saunders, M.; Roth, P.J.; Buckley, C.E.; Lowe, A.B. Triply responsive soft matter nanoparticles based on poly[oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate-block-3-phenylpropyl methacrylate] copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 2740–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, T.; Demco, D.E.; Fechete, R.; Möller, M.; Singh, S. Poly(vinylamine-co-N-isopropylacrylamide) linear polymer and hydrogels with tuned thermoresponsivity. Soft Matter. 2020, 16, 6549–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerman, M.A.; Van der Laan, H.L.; Bender, J.C.M.E.; Hoogenboom, R.; Jansen, J.A.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.; Van Hestet, J.C.M. Synthesis of pH- and thermoresponsive poly(2-n-propyl-2-oxazoline) based copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, R.; Schlaad, H. Thermoresponsive poly(2-oxazoline)s, polypeptoids, and polypeptides. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amirova, A.; Rodchenko, S.; Makhmudova, Z.; Cherkaev, G.; Milenin, S.; Tatarinova, E.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Synthesis, characterization, and investigation of thermosensitive star-shaped poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazolines) based on carbosilane dendrimers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 218, 1600387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbraeken, B.; Monnery, B.D.; Lava, K.; Hoogenboom, R. The chemistry of poly(2-oxazoline)s. Europ. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Hoogenboom, R.; Schubert, U.S. Temperature responsive bio-compatible polymers based on poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(2-oxazoline)s. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 686–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Antonietti, M.; Schlaad, H. Unexpected thermal characteristics of aqueous solutions of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline). Soft Matter. 2007, 3, 430–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Sato, T.; Terao, K.; Qiu, X.P.; Winnik, F.M. Self-association of a thermosensitive poly(alkyl-2-oxazoline) block copolymer in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 6111–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambermont-Thijs, H.M.L.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fustin, C.A.; Bomal-D’Haese, C.; Gohy, J.F.; Schubert, U.S. Solubility behavior of amphiphilic block and random copolymers based on 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline and 2-nonyl-2-oxazoline in binary water-ethanol mixtures. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassner, M.; Lava, K.; de la Rosa, V.R.; Hoogenboom, R. Tuning the LCST of poly(2-cyclopropyl-2-oxazoline) via gradient copolymerization with 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2014, 52, 3118–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Luxenhofer, R.; Jordan, R. Thermoresponsive poly (2-oxazoline) molecular brushes by living ionic polymerization: Modulation of the cloud point by random and block copolymer pendant chains. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Kataoka, K. Comprehensive and accurate control of thermosensitivity of poly(2- alkyl-2-oxazoline)s via well-defined gradient or random copolymerization. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 3599–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kataoka, K. Precise control of lower critical solution temperature of thermosensitive poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) via gradient copolymerization with 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline as a hydrophilic comonomer. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6622–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Jaksch, S.; Schubel, R.; Wegener, E.; Di, Z.; Han, Y.; Meister, A.; Kressler, J.; Kabanov, A.V.; Luxenhofer, R.; et al. Drug-induced morphology switch in drug delivery systems based on poly(2-oxazoline)s. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2686–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassi, E.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Pispas, S. Amphiphilic poly(2-oxazoline) copolymers as self-assembled carriers for drug delivery applications. Europ. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grube, M.; Leiske, M.N.; Schubert, U.S.; Nischang, I. POx as an alternative to PEG? A hydrodynamic and light scattering study. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, V.P.; Cattoz, B.; Strong, A.; Schwarz, A.; Becer, C.R. Brush copolymers from 2–oxazoline and acrylic monomers via an inimer approach. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, R. Poly(2-oxazoline)s: A polymer class with numerous potential applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7978–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaad, H.; Diehl, C.; Gress, A.; Meyer, M.; Demirel, A.L.; Nur, Y.; Bertin, A. Poly(2-oxazoline)s as smart bioinspired polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, R.; Schlaad, H. Bioinspired poly(2-oxazoline)s. Polymers 2011, 3, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oleszko-Torbus, N.; Mendrek, B.; Kowalczuk, A.; Utrata-Wesołek, A.; Dworak, A.; Wałach, W. Selective partial hydrolysis of 2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline copolymers towards decreasing the ability to crystallize. Materials 2020, 13, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezonenko, T.; Qiu, X.P.; Winnik, F.M.; Sato, T. Dehydration, micellization, and phase separation of thermosensitive polyoxazoline star block copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, A.; Kronek, J.; Bosowska, K.; Trzebicka, B.; Dworak, A. Star poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s–synthesis and thermosensitivity. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezov, A.A.; Gubarev, A.S.; Podsevalnikova, A.N.; Tsvetkov, N.V. Temperature-responsive star-shaped poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) with central thiacalix[4] arene fragments: Structure and properties in solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodov, V.V.; Tikhonov, P.A.; Buzin, M.I.; Vasil’ev, V.G.; Milenin, S.A.; Shragin, D.I.; Papkov, V.S.; Muzafarov, A.M. Synthesis and thermal and rheological properties of polydimethylsiloxanes modified with benzoic acid fragments. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2018, 60, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodov, V.V.; Milenin, S.A.; Demchenko, N.V.; Muzafarov, A.M. Carboxyl-containing polydimethylsiloxanes: Synthesis and properties. INEOS Open. 2020, 3, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, V. Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 209–248. [Google Scholar]
- Higashihara, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Yoo, H.S.; Hayashi, M.; Hirao, A. Combining living anionic polymerization with branching reactions in an iterative fashion to design branched polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 1031–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Pietrasik, J.; Sheiko, S.S.; Matyjaszewski, K. Stimuli-responsive molecular brushes. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbey, R.; Lavanant, L.; Paripovic, D.; Schüwer, N.; Sugnaux, C.; Tugulu, S.; Klok, H.A. Polymer brushes via surface-initiated controlled radical polymerization: Synthesis, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5437–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodchenko, S.; Amirova, A.; Milenin, S.; Ryzhkov, A.; Talalaeva, E.; Kalinina, A.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Amphiphilic molecular brushes with regular polydimethylsiloxane backbone and poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline side chains. 1. Synthesis, characterization and conformation in solution. Europ. Polym. J. 2020, 140, 110035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, O.V. Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 47–80. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.L.; Cordero, R.; Tran, H.; Ober, C.K. 50th anniversary perspective: Polymer brushes: Novel surfaces for future materials. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 4089–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Yokozawa, T. Chain-growth condensation polymerization for controlled synthesis of polymers. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2013, 262, 191–238. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Bhushan, B. Smart polymer brushes and their emerging applications. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8557–8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.V.; Meleshko, T.K.; Kashina, A.V.; Yakimansky, A.V. Amphiphilic multicomponent molecular brushes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2019, 88, 1248–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, E.; Pfukwa, R.; Maiz, J.; Müller, A.J.; Klumperman, B. Synthesis, structure, and crystallization behavior of amphiphilic heteroarm molecular brushes with crystallizable poly(ethylene oxide) and n-alkyl side chains. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadasha, W.; Mothunya, M.; Akeroyd, N.; Klumperman, B. Synthesis and self-assembly of amphiphilic hetero-arm molecular brushes. Aust. J. Chem. 2011, 64, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Wagner, M.; Baykal, D.; Hoeppener, S.; Paulus, R.M.; Festag, G.; Altuntas, E.; Schacher, F.H.; Schubert, U.S. Easy access to amphiphilic heterografted poly(2-oxazoline) comb copolymers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5107–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, J.; Muth, S.; Fischer, K.; Schmidt, M. Collapse of cylindrical brushes with 2-isopropyloxazoline side chains close to the phase boundary. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-doxorubicin conjugate-based dual endosomal pH-sensitive micelles with enhanced antitumor efficacy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagli, E.; Yildirim, E.; Yang, S.; Erel-Goktepe, I. An experimental and computational approach to pH-dependent self-aggregation of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2019, 57, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, A.; Rodchenko, S.; Filippov, A. Time dependence of the aggregation of star-shaped poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazolines) in aqueous solutions. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; ShamsiJazeyi, H.; Pesek, S.L.; Agrawal, A.; Hammouda, B.; Verduzco, R. Thermoresponsive PNIPAAM bottlebrush polymers with tailored side-chain length and end-group structure. Soft Matter. 2014, 10, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippov, A.P.; Belyaeva, E.V.; Zakharova, N.V.; Sasina, A.S.; Ilgach, D.M.; Meleshko, T.K.; Yakimansky, A.V. Double stimuli-responsive behavior of graft-copolymer with polyimide backbone and poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) side chains. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ge, Z.; Fang, J.; Liu, S. Synthesis and self-assembly of coil-rod double hydrophilic diblock copolymer with dually responsive asymmetric centipede-shaped polymer brush as the rod Segment. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2916–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Wu, D.; Song, X.; Zhao, H. Synthesis and self-assembly of amphiphilic asymmetric macromolecular brushes. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7434–7445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratohvil, J.P.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Concentration dependence of the translational diffusion and the sedimentation velocity of sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles in water and in 0.1 m sodium chloride solutions at 25 °C. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 1254–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcasu, A.Z. Temperature and concentration dependence of diffusion coefficient in dilute solutions. Polymer 1981, 22, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, C.C.; Akcasu, A.Z. Concentration dependence of diffusion coefficient at various molecular weights and temperatures. Polymer 1981, 22, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siebel, D.; Scharfer, P.; Schabel, W. Determination of concentration-dependent diffusion coefficients in polymer−solvent systems: Analysis of concentration profiles measured by Raman spectroscopy during single drying experiments excluding boundary conditions and phase equilibrium. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 8608–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumoto, Y.; Tsuchiizu, A.; Qiu, X.; Winnik, F.M. Dissecting the mechanism of the heat-induced phase separation and crystallization of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) in water through vibrational spectroscopy and molecular orbital calculations. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3531–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, P. Classical Light Scattering from Polymer Solution, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 1–346. [Google Scholar]
- Schärtl, W. Light Scattering from Polymer Solutions and Nanoparticle Dispersions, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–187. [Google Scholar]
- Øgendal, L.H. Light Scattering Demystified: Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; University of Copenhagen Education: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017; pp. 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics, 6th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1932; pp. 1–738. [Google Scholar]
- Tsvetkov, V.N. Rigid-Chain Polymers Hydrodynamic and Optical Properties in Solution, 1st ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 1–512. [Google Scholar]
- Kirila, T.; Smirnova, A.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Self-organization in aqueous solutions of thermosensitive star-shaped and linear gradient copolymers of 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline and 2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2020, 298, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirila, T.Y.; Kurlykin, M.P.; Ten’kovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Behavior of a thermosensitive star-shaped polymer with polyethyloxazoline-block-polyisopropyloxazoline copolymer arms. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2018, 60, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodchenko, S.; Amirova, A.; Milenin, S.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Self-organization of thermosensitive star-shaped poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazolines) influenced by arm number and generation of carbosilane dendrimer core in aqueous solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2020, 298, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.P.; Amirova, A.I.; Ten′kovtsev, A.V. Establishment of equilibrium in solutions of thermoresponsive polyoxazoline after discrete temperature changes. Fibre Chem. 2015, 47, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Xu, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S.; Wu, C. Comparative study of temperature-induced association of cyclicand linear poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) chains in dilute solutions by laser light scattering and stopped-flow temperature jump. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 4416–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, H.; Yin, Q.; Liu, H.L.; Hu, Y. Effect of composition of PDMAEMA-b-PAA block copolymers on their pH- and temperature-responsive behaviors. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirova, A.I.; Dudkina, M.M.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Self-assembly of star-shaped poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) in aqueous solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, A.I.; Golub, O.V.; Kirila, T.U.; Razina, A.B.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Influence of arm length on aqueous solution behavior of thermosensitive poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline). Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten’kovtsev, A.V.; Trofimov, A.E.; Shcherbinskaya, L.I. Thermoresponsive star-shaped poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazolines) based on octa-tert-butylcalix[8]arene. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2012, 54, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.T.T.; Zhu, K.; Kjøniksen, A.L.; Nyström, B. Temperature-responsive self-assembly of charged and uncharged hydroxyethylcellulose-graft-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymer in aqueous solution. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Luxenhofer, R.; Jordan, R. Thermoresponsive poly(2-oxazoline) molecular brushes by living ionic polymerization: Kinetic investigations of pendant chain grafting and cloud point modulation by backbone and side chain length variation. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeser, J.; Moingeon, F.; Heinrich, B.; Masson, P.; Arnaud-Neu, F.; Rawiso, M.; Méry, S. Dendronized polymers with peripheral oligo(ethylene oxide) chains: Thermoresponsive behavior and shape anisotropy in solution. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 8925–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Rogers, S.; Vollrath, A.; Hoeppener, S.; Rudolph, T.; Fritz, N.; Hoogenboom, R.; Schubert, U.S. Aqueous solution behavior of comb-shaped poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline). J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 2013, 51, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Huglin, M.B.; Jones, T.G.J. Parameters affecting the lower critical solution temperature of linear and crosslinked poly(n-ethylacrylamide) in aqueous media. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2003, 204, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, D.G.; Ousalem, M.; Zhu, X.X. Effect of the molecular weight on the lower critical solution temperature of poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide) in aqueous solutions. Can. J. Chem. 2001, 79, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, F.; Fujisawa, K.; Nakajima, A. Lower critical solution temperature in linear polyethylene–n-alkane systems. Polym. J. 1973, 4, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amirova, A.; Rodchenko, S.; Milenin, S.; Tatarinova, E.; Kurlykin, M.; Ten’kovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Influence of a hydrophobic core on thermoresponsive behavior of dendrimer-based star-shaped poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) in aqueous solutions. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodchenko, S.; Amirova, A.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Milenin, S.; Filippov, A. Amphiphilic Molecular Brushes with Regular Polydimethylsiloxane Backbone and Poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline Side Chains. 2. Self-Organization in Aqueous Solutions on Heating. Polymers 2021, 13, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010031
Rodchenko S, Amirova A, Kurlykin M, Tenkovtsev A, Milenin S, Filippov A. Amphiphilic Molecular Brushes with Regular Polydimethylsiloxane Backbone and Poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline Side Chains. 2. Self-Organization in Aqueous Solutions on Heating. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodchenko, Serafim, Alina Amirova, Mikhail Kurlykin, Andrey Tenkovtsev, Sergey Milenin, and Alexander Filippov. 2021. "Amphiphilic Molecular Brushes with Regular Polydimethylsiloxane Backbone and Poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline Side Chains. 2. Self-Organization in Aqueous Solutions on Heating" Polymers 13, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010031
APA StyleRodchenko, S., Amirova, A., Kurlykin, M., Tenkovtsev, A., Milenin, S., & Filippov, A. (2021). Amphiphilic Molecular Brushes with Regular Polydimethylsiloxane Backbone and Poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline Side Chains. 2. Self-Organization in Aqueous Solutions on Heating. Polymers, 13(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010031





