Effect of Printing Parameters on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed PLA and PETG, Using Fused Deposition Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. 3D Printing Machine and Printing Materials
3.2. Printing Procedure and Parameters
3.3. The Tensile, Compression, and Bending Test
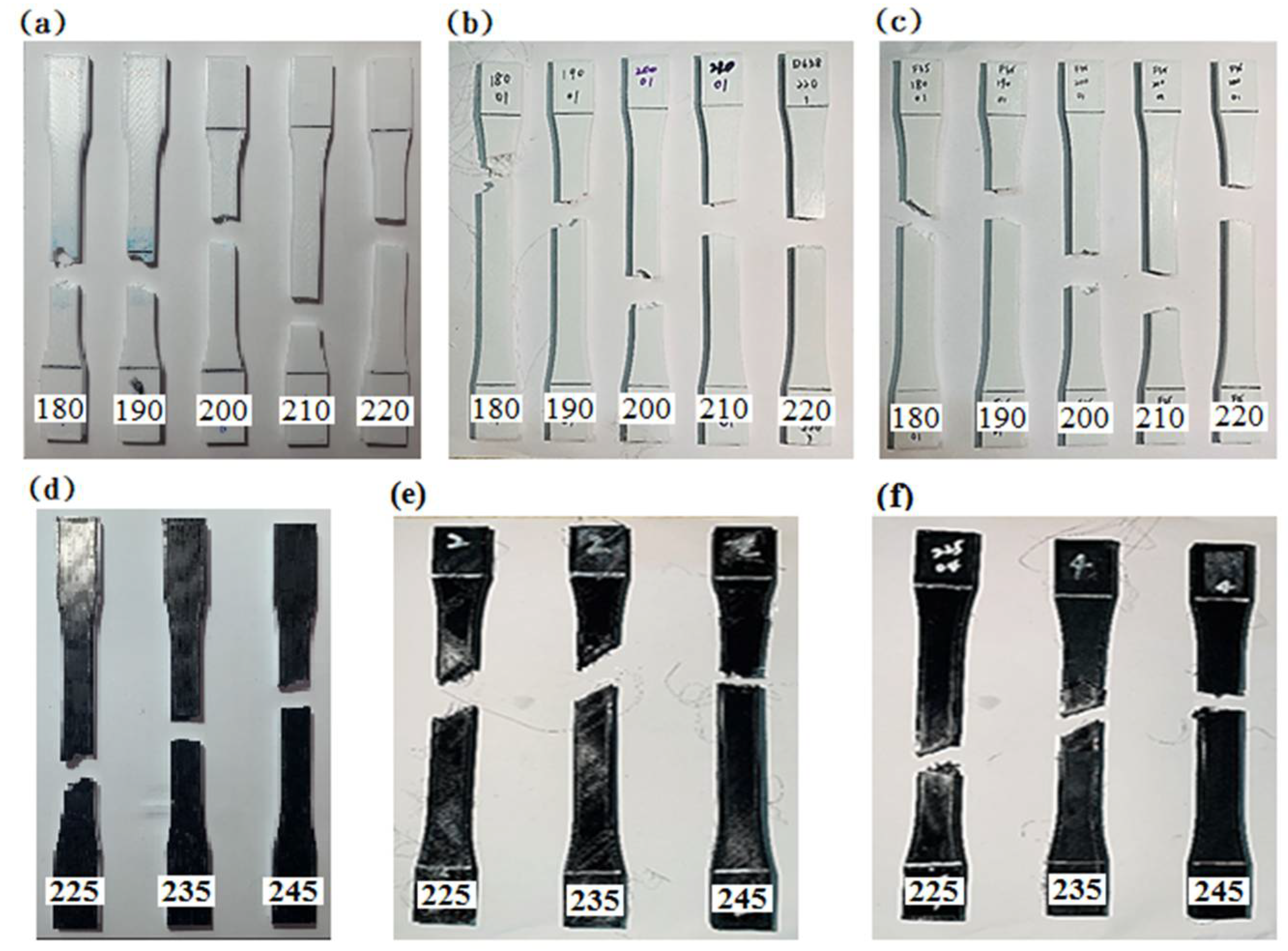
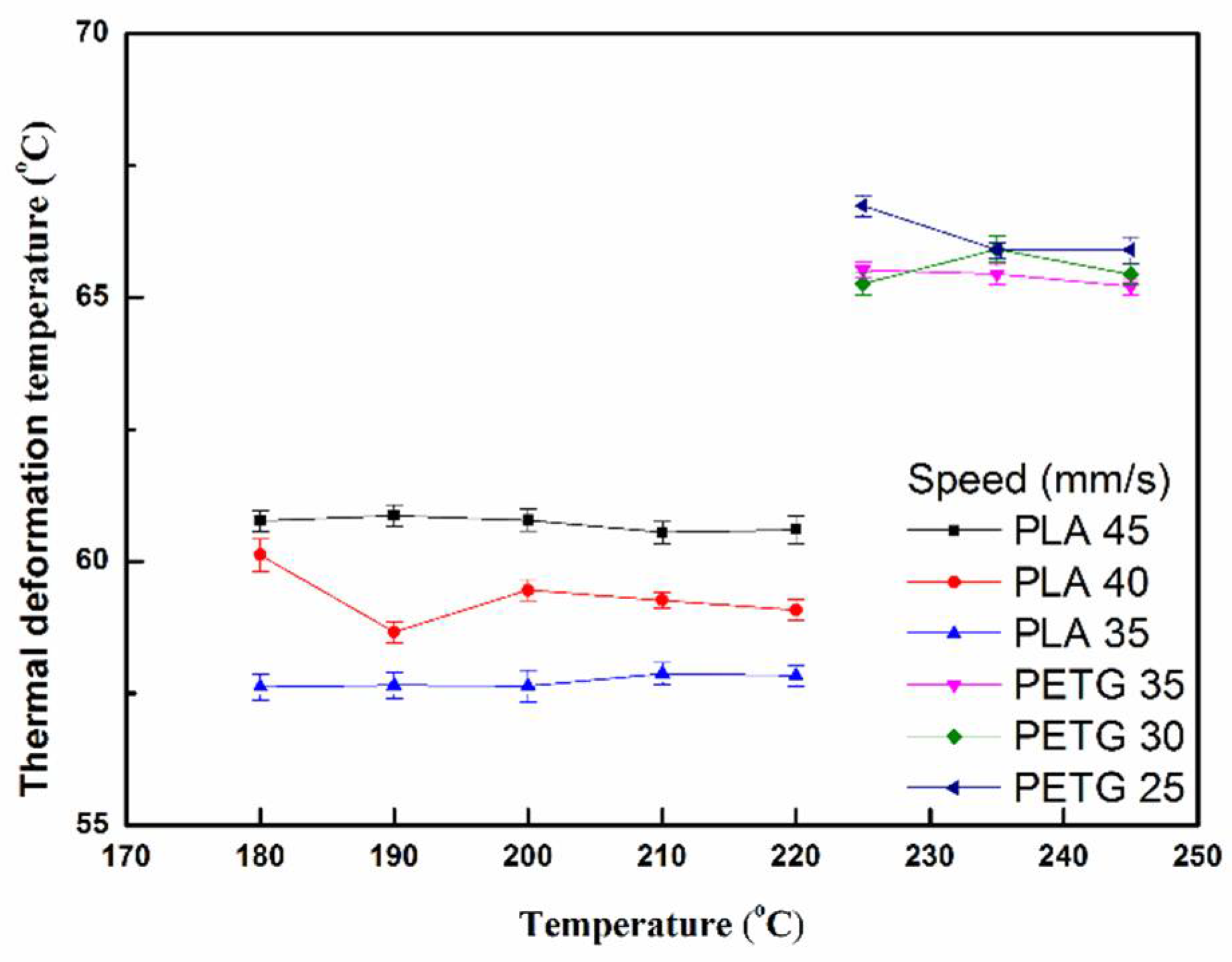
3.4. The Thermal Deformation Test
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- PLA and PETG materials exhibit obvious tensile and compression asymmetry, and the compressive stress exceeds the tensile stress.
- As the printing temperature increases, the mechanical properties of the PLA and PETG materials increase.
- As the printing speed increases, the mechanical properties of the PLA material increase, but the mechanical properties of the PETG material decrease.
- The mechanical properties of PLA are greater than those of PETG, regardless of the Young’s modulus and strength, but the opposite is the case for the thermal deformation.
- In this article, despite the PLA and PETG being below the 20% infill density conditions, the compressive strength is higher than the tensile strength, but lower than the bending strength, with a bending Young’s modulus that is higher than the tensile Young’s modulus but lower than the compressive Young’s modulus.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luis, E.; Pan, H.M.; Bastola, A.K.; Bajpai, R.; Sing, S.L.; Song, J.; Yeong, W.Y. 3D printed silicone meniscus implants: Influence of the 3D printing process on properties of silicone implants. Polymers 2020, 12, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, E.; Pan, H.M.; Sing, S.L.; Bajpai, R.; Song, J.; Yeong, W.Y. 3D direct printing of silicone meniscus implant using a novel heat-cured extrusion-based printer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, G.; Marconi, S.; Costato, L.; Auricchio, F. Influence of meso-structure and chemical composition on FDM 3D-printed parts. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 113, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, S.H. Intelligent rapid prototyping with fused deposition modelling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 1996, 2, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cai, J. Effects of fused deposition modeling process parameters on tensile, dynamic mechanical properties of 3D printed polylactic acid materials. Polym. Test. 2020, 86, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Selective laser sintering: A qualitative and objective approach. JOM 2003, 55, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yuan, S.; Chow, W.; Chua, C.K.; Zhou, K.; Wei, J. Effect of surface orientation on the tribological properties of laser sintered polyamide 12. Polym. Test. 2015, 48, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Gilbert, M.; Hague, R. A study of the impact of short-term ageing on the mechanical properties of a stereolithography resin. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 447, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Qian, B.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J. A cross-linking strategy with moderated pre-polymerization of resin for stereolithography. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29583–29588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, L.J.; Krishnadas Nair, C.G. Current trends of additive manufacturing in the aerospace industry. In Advances in 3D Printing&Additive Manufacturing Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadpoor, A.A.; Malda, J. Additive manufacturing of biomaterials, tissues, and organs. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfs, R.J.M.; Bos, F.P.; Salet, T.A.M. Early age mechanical behaviour of 3D printed concrete: Numerical modelling and experimental testing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 106, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Lim, J.H.; Tan, M.J. Mechanical properties and deformation behaviour of early age concrete in the context of digital construction. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 165, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Smith, D. Anisotropic mechanical properties of oriented carbon fiber filled polymer composites produced with fused filament fabrication. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 18, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.; Tsongas, K.; Tzetzis, D.; Antoniadis, A. Mechanical and Dynamic Behavior of Fused Filament Fabrication 3D Printed Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol Reinforced with Carbon Fibers. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2018, 57, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, L.; Alves, J.; Sabino Netto, A.; Merlini, C. Estudo comparativo entre PETG e PLA para Impressão 3D através de caracterização térmica, química e mecânica. Matéria (Rio de Janeiro) 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurohit, S.; Dave, H. Effect of process parameters on tensile strength of FDM printed PLA part. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerga, A.; Batista, M.; Salguero, J.; Girot, F. Influence of PLA Filament Conditions on Characteristics of FDM Parts. Materials 2018, 11, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinyas, M.; Athul, S.J.; Harursampath, D.; Nguyen Thoi, T. Experimental evaluation of the mechanical and thermal properties of 3D printed PLA and its composites. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 115301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, R.; Farina, I.; Colangelo, F.; Feo, L.; Fraternali, F. Multi-material additive manufacturing of sustainable innovative materials and structures. Polymers 2019, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, T.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, S. A method to predict the ultimate tensile strength of 3D printing polylactic acid (PLA) materials with different printing orientations. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 163, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, J.; Romero, P. Improvement of surface roughness and hydrophobicity in PETG parts manufactured via fused deposition modeling (FDM): An application in 3D printed self–cleaning parts. Materials 2019, 12, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guessasma, S.; Belhabib, S.; Nouri, H. Printability and tensile performance of 3D printed polyethylene terephthalate glycol using fused deposition modelling. Polymers 2019, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakradze, G.; Arājs, E.; Gaidukovs, S.; Thakur, V.K. On the heuristic procedure to determine processing parameters in additive manufacturing based on materials extrusion. Polymers 2020, 12, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengier, F.; Mehndiratta, A.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Zechmann, C.M.; Unterhinninghofen, R.; Kauczor, H.U.; Giesel, F.L. 3D printing based on imaging data: Review of medical applications. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2010, 5, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.C.; Chen, T.C.T. Quality control issues in 3D-printing manufacturing: A review. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersmann, S.; Spoerk, M.; Steene, W.V.D.; Üçal, M.; Wiener, J.; Pinter, G.; Arbeiter, F. Mechanical properties of polymeric implant materials produced by extrusion-based additive manufacturing. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 104, 103611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, G.; Sun, Z. Anisotropy of poly(lactic acid)/carbon fiber composites prepared by fused deposition modeling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadnasab, M.; Yousefi, A.A.; Ebrahimibagha, D.; Nasiri, F. Effects of processing conditions on mechanical properties of PLA printed parts. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2020, 26, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Vicente, M.; Calle, W.; Ferrandiz, S.; Conejero, A. Effect of infill parameters on tensile mechanical behavior in desktop 3D printing. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 3, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Ye, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Y.; Ouyang, H. Tensile failure strength and separation angle of FDM 3D printing PLA material: Experimental and theoretical analyses. Compos. Part B 2020, 188, 107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, W.; Yee, K.; Lee, K.Y.; Tagarielli, V.L. Measurements of the mechanical response of unidirectional 3D-printed PLA. Mater. Des. 2017, 123, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patibandla, S.; Mian, A. Layer-to-layer physical characteristics and compression behavior of 3D printed polymer metastructures fabricated using different process parameters. J. Elastomers Plast. 2020, 009524432093999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Artigues, M.M.; Roure-Fernández, F.; Ayneto-Gubert, X.; Bonada-Bo, J.; Pérez-Guindal, E.; Buj-Corral, I. Elastic asymmetry of PLA material in FDM-printed parts: Considerations concerning experimental characterisation for use in numerical simulations. Materials 2019, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santana, L.; Alves, J.L.; Sabino-Netto, A.C.; Merlini, C. A comparative study between PETG and PLA for 3D Printing through thermal, chemical and mechanical characterization. Matéria (Rio J.) 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Model | X1E |
|---|---|
| Physical dimensions | (w) 40 cm × (d) 22 cm × (h) 46 cm |
| Maximum printing area | (w) 21 cm × (d) 21 cm × (h) 24 cm |
| Print layer height | 0.04~0.32 mm |
| Wire diameter | Φ1.75 mm |
| Nozzle diameter | 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 mm |
| Platform temperature | ~110 °C |
| Nozzle printing temperature | ~300 °C |
| Cooling method | 4.5 cm turbo fan |
| Motor drive | 1/32 micro-stepping motor (8825 driver chip) |
| Name | Specification | |
|---|---|---|
| Material | PLA | PETG |
| Color | Snow white | Matt black |
| Wire diameter | 1.75 ± 0.05 mm | 1.75 ± 0.05 mm |
| Weight | 800 g | 800 g |
| Recommended printing temp | 180~210 °C | 215~235 °C |
| Recommended printing speed | 30~50 mm/s | 30~50 mm/s |
| Content | Name | Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project | ||||
| Controlling factor | Material | PLA | PETG | |
| Printing speed | 35~45 mm/s | 25~35 mm/s | ||
| Printing temperature | 180~220 °C | 225~245 °C | ||
| Fixed factor | Infill density | 20% | ||
| Raster angle | 45°/−45° | |||
| Printing pattern | rectilinear | |||
| Layer thickness | 0.2 mm | |||
| Nozzle diameter | 0.4 mm | |||
| Platform temperature | 25 °C | |||
| Model | H51A2 |
|---|---|
| Capacity | 100 kN |
| Stroke | 1100 mm (without fixture) |
| Space | Ø550 mm |
| Load resolution | 1/10,000 (maximize 1/200,000) |
| Displacement resolution | 0.001 mm |
| Motor | Servo motor |
| Speed | 0.003~375 mm/min |
| Height | 2200 mm |
| Weight | 800 kgf |
| Sampling rate | 500 Hz (Max.) |
| Current | 15 A |
| Model | QC-654 |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Room temperature ~300 °C |
| Temperature control | Temperature rise speed 2 °C/min |
| Weight sets | Basic weight support load is 3 N. Each test fixture will enclose the below quantities: 0.1 N × 1, 0.2 N × 2, 0.5 N × 1, 1 N × 1, 2 N × 2, 5 N × 1, 10 N × 1 |
| Deformation | 0.01~10 mm |
| Span | 100 mm (max.) adjustable 50 mm |
| Radius of support | Camber R angle 3.0 mm |
| Test quantity | Mechanical gauge 0.01~10 mm Electronic gauge 0.001~10 mm PLC control 0.001~10 mm Set: 1, 2, 3, 6 set |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsueh, M.-H.; Lai, C.-J.; Wang, S.-H.; Zeng, Y.-S.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Pan, C.-Y.; Huang, W.-C. Effect of Printing Parameters on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed PLA and PETG, Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers 2021, 13, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111758
Hsueh M-H, Lai C-J, Wang S-H, Zeng Y-S, Hsieh C-H, Pan C-Y, Huang W-C. Effect of Printing Parameters on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed PLA and PETG, Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers. 2021; 13(11):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111758
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsueh, Ming-Hsien, Chao-Jung Lai, Shi-Hao Wang, Yu-Shan Zeng, Chia-Hsin Hsieh, Chieh-Yu Pan, and Wen-Chen Huang. 2021. "Effect of Printing Parameters on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed PLA and PETG, Using Fused Deposition Modeling" Polymers 13, no. 11: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111758
APA StyleHsueh, M.-H., Lai, C.-J., Wang, S.-H., Zeng, Y.-S., Hsieh, C.-H., Pan, C.-Y., & Huang, W.-C. (2021). Effect of Printing Parameters on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed PLA and PETG, Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers, 13(11), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111758








