Rational Design of Effective Binders for LiFePO4 Cathodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Functions and Effects of Binders and Their Rational Design
2.1. PVDF and Related Composites
2.2. Waterborne Binders
2.3. Conductive Binders
3. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Amine, K. 30 Years of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, X.W.; Zhong, W.H. Biomaterials for High-Energy Lithium-Based Batteries: Strategies, Challenges, and Perspectives. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.X.; Maier, J.; Yu, Y. Guidelines and trends for next-generation rechargeable lithium and lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1569–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, E.S.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.P.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.X.; Yao, Y.; Chen, R.J.; Wu, F. Sustainable Recycling Technology for Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond: Challenges and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7020–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. Review on use of phase change materials in battery thermal management for electric and hybrid electric vehicles. Int. J. Energ. Res. 2016, 40, 1011–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.Q.; Li, M.; Abd El-Hady, D.; Alshitari, W.; Al-Bogami, A.S.; Lu, J.; Amine, K. Commercialization of Lithium Battery Technologies for Electric Vehicles. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, C.; Nikolowski, K.; Reuber, S.; Schneider, M.; Wolter, M.; Michaelis, A. Recent Insights into Rate Performance Limitations of Li-ion Batteries. Batter. Supercaps 2021, 4, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselin, L.S.; Juang, R.S.; Hsieh, C.T.; Sagadevan, S.; Umar, A.; Selvin, R.; Hegazy, H.H. Recent Advances and Perspectives of Carbon-Based Nanostructures as Anode Materials for Li-ion Batteries. Materials 2019, 12, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piatek, J.; Afyon, S.; Budnyak, T.M.; Budnyk, S.; Sipponen, M.H.; Slabon, A. Sustainable Li-Ion Batteries: Chemistry and Recycling. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 11, 2003456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjalal, M.; Shams, T.; Islam, M.E.; Alam, W.; Modak, M.; Bin Hossain, S.; Ramadesigan, V.; Ahmed, M.R.; Ahmed, H.; Iqbal, A. A review of thermal management for Li-ion batteries: Prospects, challenges, and issues. J. Energy Storage 2021, 39, 102518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chombo, P.V.; Laoonual, Y. A review of safety strategies of a Li-ion battery. J. Power Source 2020, 478, 228649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, N.; Wu, F.X.; Lee, J.T.; Yushin, G. Li-ion battery materials: Present and future. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, C.M.; Mauger, A. NCA, NCM811, and the Route to Ni-Richer Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energies 2020, 13, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonia, F.J.; Aslam, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Understanding the processing-structure-performance relationship of graphene and its variants as anode material for Li-ion batteries: A critical review. Carbon 2020, 156, 130–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.B.; Liu, J.L.; Chao, D.L.; Mai, L.Q. Vanadate-Based Materials for Li-Ion Batteries: The Search for Anodes for Practical Applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirocak, D.E.; Srinivasan, S.S.; Stefanakos, E.K. A Review on Nanocomposite Materials for Rechargeable Li-ion Batteries. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shetti, N.P.; Dias, S.; Reddy, K.R. Nanostructured organic and inorganic materials for Li-ion batteries: A review. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2019, 104, 104684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.D.; Lee, J.Y. High capacity conversion anodes in Li-ion batteries: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 2019, 44, 10852–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striebel, K.; Shim, J.; Sierra, A.; Yang, H.; Song, X.Y.; Kostecki, R.; McCarthy, K. The development of low cost LiFePO4-based high power lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Source 2005, 146, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruce, P.G.; Scrosati, B.; Tarascon, J.M. Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2930–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.M.; Jiang, G.Q.; Gu, C.Y.; Ni, J.F. Revisiting polyanionic LiFePO4 battery material for electric vehicles. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2021, 14, 2130006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.M.; Xu, H.Y.; Ruan, J.H.; Li, D.C.; Wang, A.G.; Sun, D.S. A Review on Application of LiFePO4 based composites as electrode materials for Lithium Ion Batteries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; He, P.; Zhou, H.S. Olivine LiFePO4: Development and future. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Li, H.Q.; He, P.; Hosono, E.; Zhou, H.S. Nano active materials for lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.T.; Huang, W.Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Pan, F. Structure and performance of the LiFePO4 cathode material: From the bulk to the surface. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 15036–15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.L.; Pan, Y.D.; Wang, J.Z.; Liu, H.K.; Dou, S.X. Small things make a big difference: Binder effects on the performance of Li and Na batteries. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20347–20359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.C.; Song, Y.; Wang, G.K.; Liu, Y.X.; Wu, Z.G.; Zhong, B.H.; Zhong, Y.J.; Guo, X.D. A review of rational design and investigation of binders applied in silicon-based anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Source 2021, 485, 229331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Dahbi, M.; Komaba, S. Polymer binder: A key component in negative electrodes for high-energy Na-ion batteries. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 13, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preman, A.N.; Lee, H.; Yoo, J.; Kim, I.T.; Saito, T.; Ahn, S.-k. Progress of 3D network binders in silicon anodes for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 25548–25570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommier, C.; Ji, X.L. Electrolytes, SEI Formation, and Binders: A Review of Nonelectrode Factors for Sodium-Ion Battery Anodes. Small 2018, 14, 1703576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.M.; Lizundia, E.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Polymers for advanced lithium-ion batteries: State of the art and future needs on polymers for the different battery components. Prog. Energ. Combust. 2020, 79, 100846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.L.; Hartley, J.M.; Lambert, S.M.; Shiref, M.; Harper, G.D.J.; Kendrick, E.; Anderson, P.; Ryder, K.S.; Gaines, L.; Abbott, A.P. The importance of design in lithium ion battery recycling-a critical review. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 7585–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ren, J.G.; Liu, R.; Yue, M.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yuan, G.H. The progress of novel binder as a non-ignorable part to improve the performance of Si-based anodes for Li-ion batteries. Int. J. Energ. Res. 2018, 42, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, K.; Jeong, J.; Cho, K.Y.; Ryou, M.H.; Lee, Y.M. Highly Adhesive and Soluble Copolyimide Binder: Improving the Long-Term Cycle Life of Silicon Anodes in Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 14851–14858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.Q.; Weng, Q.; Tang, Z.Y. Chitosan oligosaccharides: A novel and efficient water soluble binder for lithium zinc titanate anode in lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 151, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versaci, D.; Nasi, R.; Zubair, U.; Amici, J.; Sgroi, M.; Dumitrescu, M.A.; Francia, C.; Bodoardo, S.; Penazzi, N. New eco-friendly low-cost binders for Li-ion anodes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 3429–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.J.; Joo, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Hwang, C.; Jung, G.Y.; Bae, S.; Son, Y.; Cho, J.; Song, H.K.; Kwak, S.K.; et al. Significance of ferroelectric polarization in poly (vinylidene difluoride) binder for high-rate Li-ion diffusion. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magasinski, A.; Zdyrko, B.; Kovalenko, I.; Hertzberg, B.; Burtovyy, R.; Huebner, C.F.; Fuller, T.F.; Luzinov, I.; Yushin, G. Toward Efficient Binders for Li-Ion Battery Si-Based Anodes: Polyacrylic Acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3004–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.J.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.C.; Wang, H.Q.; Yuan, X.M.; Li, Q.Y. Effect of different binders on electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/C cathode material in lithium ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.; Costa, C.M.; Silva, M.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Influence of fluoropolymer binders on the electrochemical performance of C-LiFePO4 based cathodes. Solid State Ion. 2016, 295, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sha, Z.F.; Cui, X.; Qiu, S.Q.; He, C.G.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, X.G.; Yang, Y.K. Incorporation of redox-active polyimide binder into LiFePO4 cathode for high-rate electrochemical energy storage. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.Y.; Su, Y.F.; Bao, L.Y.; Li, N.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, F. High-performance LiFePO4/C electrode with polytetrafluoroethylene as an aqueous-based binder. J. Power Source 2015, 298, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, W.; Lestriez, B.; Jouanneau, S.; Guyomard, D. Optimizing the surfactant for the aqueous processing of LiFePO4 composite electrodes. J. Power Source 2010, 195, 2835–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, W.; Lestriez, B.; Jouanneau, S.; Guyomard, D. Design of Aqueous Processed Thick LiFePO4 Composite Electrodes for High-Energy Lithium Battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, A133–A144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, W.; Moreau, P.; Lestriez, B.; Jouanneau, S.; Guyomard, D. Is LiFePO4 stable in water? Toward greener li-ion batteries. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2008, 11, A4–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, W.; Moreau, P.; Lestriez, B.; Jouanneau, S.; Le Cras, F.; Guyomard, D. Stability of LiFePO4 in water and consequence on the Li battery behaviour. Ionics 2008, 14, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerfi, A.; Kaneko, M.; Petitclerc, M.; Mori, M.; Zaghib, K. LiFePO4 water-soluble binder electrode for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Source 2007, 163, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Zang, D.S.; Paik, U. Dispersion properties of aqueous-based LiFePO4 pastes and their electrochemical performance for lithium batteries. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 108, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.P.; Liang, Y.; Li, W.S.; Xing, L.D.; Liao, Y.H. Preparation and performances of LiFePO4 cathode in aqueous solvent with polyacrylic acid as a binder. J. Power Source 2009, 189, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, S.F.; Schappacher, F.; Balducci, A.; Passerini, S.; Winter, M. Low Cost, Environmentally Benign Binders for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A320–A325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.H.; Zhong, H.X.; Jiao, S.R.; Shao, H.Q.; Zhang, L.Z. Investigation on Carboxymethyl Chitosan as New Water Soluble Binder for LiFePO4 Cathode in Li-Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 127, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.R.; Wang, J.L.; Zhong, H.X.; Ding, J.N.; Zhang, L.Z. Cyanoethylated Carboxymethyl Chitosan as Water Soluble Binder with Enhanced Adhesion Capability and electrochemical performances for LiFePO4 Cathode. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 182, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, L. N-cyanoethyl polyethylenimine as a water-soluble binder for LiFePO4 cathode in lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 9690–9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chockla, A.M.; Bogart, T.D.; Hessel, C.M.; Klavetter, K.C.; Mullins, C.B.; Korgel, B.A. Influences of Gold, Binder and Electrolyte on Silicon Nanowire Performance in Li-Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 18079–18086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, I.; Zdyrko, B.; Magasinski, A.; Hertzberg, B.; Milicev, Z.; Burtovyy, R.; Luzinov, I.; Yushin, G. A Major Constituent of Brown Algae for Use in High-Capacity Li-Ion Batteries. Science 2011, 334, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufficy, M.K.; Khan, S.A.; Fedkiw, P.S. Galactomannan binding agents for silicon anodes in Li-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12023–12030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.T.; Huang, L.; Sun, S.G. A Robust Ion-Conductive Biopolymer as a Binder for Si Anodes of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3599–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruba, R.; Datta, M.K.; Damodaran, K.; Jampani, P.H.; Gattu, B.; Patel, P.P.; Shanthi, P.M.; Damle, S.; Kumta, P.N. Guar gum: Structural and electrochemical characterization of natural polymer based binder for silicon-carbon composite rechargeable Li-ion battery anodes. J. Power Source 2015, 298, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, L.; Zhang, L.Z.; Zhong, H.X. Carboxymethyl chitosan: A new water soluble binder for Si anode of Li-ion batteries. J. Power Source 2014, 247, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y. Cross-Linked Chitosan as an Efficient Binder for Si Anode of Li-ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2658–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryou, M.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, I.; Kim, S.; Jeong, Y.K.; Hong, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, T.S.; Park, J.K.; Lee, H.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive Binders for High-Performance Silicon Nanoparticle Anodes in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Chai, L.L.; Xue, P.; Hao, W.W.; Zheng, H.H. A coordinatively cross-linked polymeric network as a functional binder for high-performance silicon submicro-particle anodes in lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 19036–19045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Li, J.T.; Huang, L.; Sun, S.G. A high-performance alginate hydrogel binder for the Si/C anode of a Li-ion battery. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 6386–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, M.; Xu, Y.N.; Zhao, H.; Gu, X.X.; Qiu, J.X.; Li, S.; Wu, M.Y.; Song, X.Y.; Yan, C.; Liu, G.; et al. Dual-functional gum arabic binder for silicon anodes in lithium ion batteries. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Q.R.; Xue, L.X.; Wei, Z.B.; Liu, F.; Du, X.D.; DesMarteau, D.D. Improvement in LiFePO4-Li battery performance via poly(perfluoroalkylsulfonyl)imide (PFSI) based ionene composite binder. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 15016–15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Shao, Z.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, F.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, D.X.; Wang, Y.L. Enhanced Cyclability of C/Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathodes with a Novel water-soluble lithium-ion binder. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 145, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Shao, Z.Q.; Wang, D.X.; Wang, F.J.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, J.Q. Novel polymer Li-ion binder carboxymethyl cellulose derivative enhanced electrochemical performance for Li-ion batteries. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Shao, Z.Q.; Wang, D.X.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, F.J.; Wang, J.Q. Enhanced electrochemical properties of LiFePO4 (LFP) cathode using the carboxymethyl cellulose lithium (CMC-Li) as novel binder in lithium-ion battery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Shao, Z.Q.; Wang, D.X.; Wang, F.J.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, J.Q. Carboxymethyl cellulose lithium (CMC-Li) as a novel binder and its electrochemical performance in lithium-ion batteries. Cellulose 2014, 21, 2789–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.R.; Zhong, H.X.; Zhang, L.Z. Water-soluble binder PAALi with terpene resin emulsion as tackifier for LiFePO4 cathode. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ren, J.G.; Liu, R.; Bai, Y.; Li, X.L.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yue, M.; He, X.Q.; Yuan, G.H. Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of LiFePO4 Cathode Using Waterborne Lithiated Ionomer Binder in Li-Ion Batteries with Low Amount. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12650–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseeva, S.N.; Levin, O.V.; Tolstopyatova, E.G.; Alekseeva, E.V.; Kondratiev, V.V. Effect of addition of a conducting polymer on the properties of the LiFePO4-based cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2015, 88, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseeva, S.N.; Levin, O.V.; Tolstopjatova, E.G.; Alekseeva, E.V.; Apraksin, R.V.; Kondratiev, V.V. New functional conducting poly-3,4-ethylenedioxythiopene: Polystyrene sulfonate/carboxymethylcellulose binder for improvement of capacity of LiFePO4-based cathode materials. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.R.; Komsiyska, L.; Osters, O.; Wittstock, G. PEDOT: PSS as a Functional Binder for Cathodes in Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A674–A678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.R.; Komsiyska, L.; Osters, O.; Wittstock, G. Effect of solid loading on the processing and behavior of PEDOT:PSS binder based composite cathodes for lithium ion batteries. Synth. Met. 2016, 215, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.X.; He, A.Q.; Lu, J.D.; Sun, M.H.; He, J.R.; Zhang, L.Z. Carboxymethyl chitosan/conducting polymer as water-soluble composite binder for LiFePO4 cathode in lithium ion batteries. J. Power Source 2016, 336, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubarkov, A.V.; Drozhzhin, O.A.; Karpushkin, E.A.; Stevenson, K.J.; Antipov, E.V.; Sergeyev, V.G. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonic acid)-polymer composites as functional cathode binders for high power LiFePO4 batteries. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2019, 297, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.; Qiu, J.X.; Li, S.; Yan, C.; Kiefel, M.J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, S.Q. Multifunctional SA-PProDOT Binder for Lithium Ion Batteries. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 4440–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Zou, S.; Tang, A.; Chen, L.; Deng, Z.; Pollet, B.G.; Ji, S. Three-dimensional hierarchical walnut kernel shape conducting polymer as water soluble binder for lithium-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 269, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Duh, J.G. Ionic network for aqueous-polymer binders to enhance the electrochemical performance of Li-Ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 294, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshetu, G.G.; Mecerreyes, D.; Forsyth, M.; Zhang, H.; Armand, M. Polymeric ionic liquids for lithium-based rechargeable batteries. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2019, 4, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Shi, L.Y.; Jungsuttiwong, S.; Yuan, S. Ionic liquids for high performance lithium metal batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 59, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Saruhan, B. Application of Ionic Liquids for Batteries and Supercapacitors. Materials 2021, 14, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Zamory, J.; Bedu, M.; Fantini, S.; Passerini, S.; Paillard, E. Polymeric ionic liquid nanoparticles as binder for composite Li-ion electrodes. J. Power Source 2013, 240, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Zhang, M.; Kong, X.Y.; Huang, W.W.; Zhang, Q.C. Recent Advance in Ionic-Liquid-Based Electrolytes for Rechargeable Metal-Ion Batteries. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.S.P.; Lopez-Ruiz, B. Electrochemical biosensor based on ionic liquid polymeric microparticles. An analytical platform for catechol. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, Q.; Ren, Y.Y.; Qi, H.J.; Guo, J.N.; Sun, Z.; Yan, F. Poly(ionic liquid)-Based Conductive Interlayer as an Efficient Polysulfide Adsorbent for a Highly Stable Lithium-Sulfur Battery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11396–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Singh, P.; Appadoo, D.; Martin, D.E. Synthesis and characterization of olivine LiNiPO4 for aqueous rechargeable battery. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 4356–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandhasamy, S.; Singh, P.; Thurgate, S.; Ionescu, M.; Appadoo, D.; Minakshi, M. Olivine-type cathode for rechargeable batteries: Role of chelating agents. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 82, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minakshi, M.; Kandhasamy, S. Influence of sol-gel derived lithium cobalt phosphate in alkaline rechargeable battery. J. Sol.-Gel Sci Technol. 2012, 64, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, A.; Minakshi, M.; Tripathy, B.C. Probing the electrochemical properties of biopolymer modified EMD nanoflakes through electrodeposition for high performance alkaline batteries. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 5557–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.M.; Geiculescu, O.; DesMarteau, D.; Creager, S. Ionomer Binders Can Improve Discharge Rate Capability in Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, A207–A213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.S.; Bockenfeld, N.; Balducci, A.; Winter, M.; Passerini, S. Natural cellulose as binder for lithium battery electrodes. J. Power Source 2012, 199, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.A.; Zeng, T.; Qu, C.M.; Lu, H.; Jia, M.; Lai, Y.Q.; Li, J. Cycle performance improvement of LiFePO4 cathode with polyacrylic acid as binder. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 80, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunliu, Z.; Can, T.; Junjie, B.; Yiping, H.; Gewen, X. Waterborne Polyurethane Used as Binders for Lithium-Ion Battery with Improved Electrochemical Properties. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1090, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Aldalur, I.; Heng, Z.; Piszcz, M.; Oteo, U.; Rodriguez-Martinez, L.M.; Shanmukaraj, D.; Rojo, T.; Armand, M. Jeffaminereg based polymers as highly conductive polymer electrolytes and cathode binder materials for battery application. J. Power Source 2017, 347, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.R.; Zhong, H.X.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, L.Z. Investigation on xanthan gum as novel water soluble binder for LiFePO4 cathode in lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Min, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Park, S.H.; Choi, J.W. Low Molecular Weight Spandex as a Promising Polymeric Binder for LiFePO4 Electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, R.; Oliveira, J.; Silva, M.P.; Costa, P.; Hilliou, L.; Silva, M.M.; Costa, C.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Poly(styrene-butene/ethylene-styrene): A New Polymer Binder for High-Performance Printable Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2018, 1, 3331–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, S.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Yin, Y.; Ma, Z. Lithium sulfonate-grafted poly(vinylidenefluoride-hexafluoro propylene) ionomer as binder for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 20025–20031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, C.; Yan, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. Improving the processability and cycling stability of nano-LiFePO4 cathode by using PVDF/TX binary binder. Compos. Interfaces 2019, 26, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, J.C.; Barray, F.; Gagnon, C.; Clement, D.; Hovington, P.; Demers, H.; Guerfi, A.; Zaghib, K. Amphiphilic latex as a water-based binder for LiFePO4 cathode. J. Power Source 2019, 415, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranque, P.; George, C.; Dubey, R.K.; van der Jagt, R.; Flahaut, D.; Dedryvere, R.; Fehse, M.; Kassanos, P.; Jager, W.F.; Sudholter, E.J.R.; et al. Scalable Route to Electroactive and Light Active Perylene Diimide Dye Polymer Binder for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2020, 3, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, L.; Hu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Yan, Y. Fluorinated polyimide with sulfonyl group as a novel binder for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 2021, 27, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
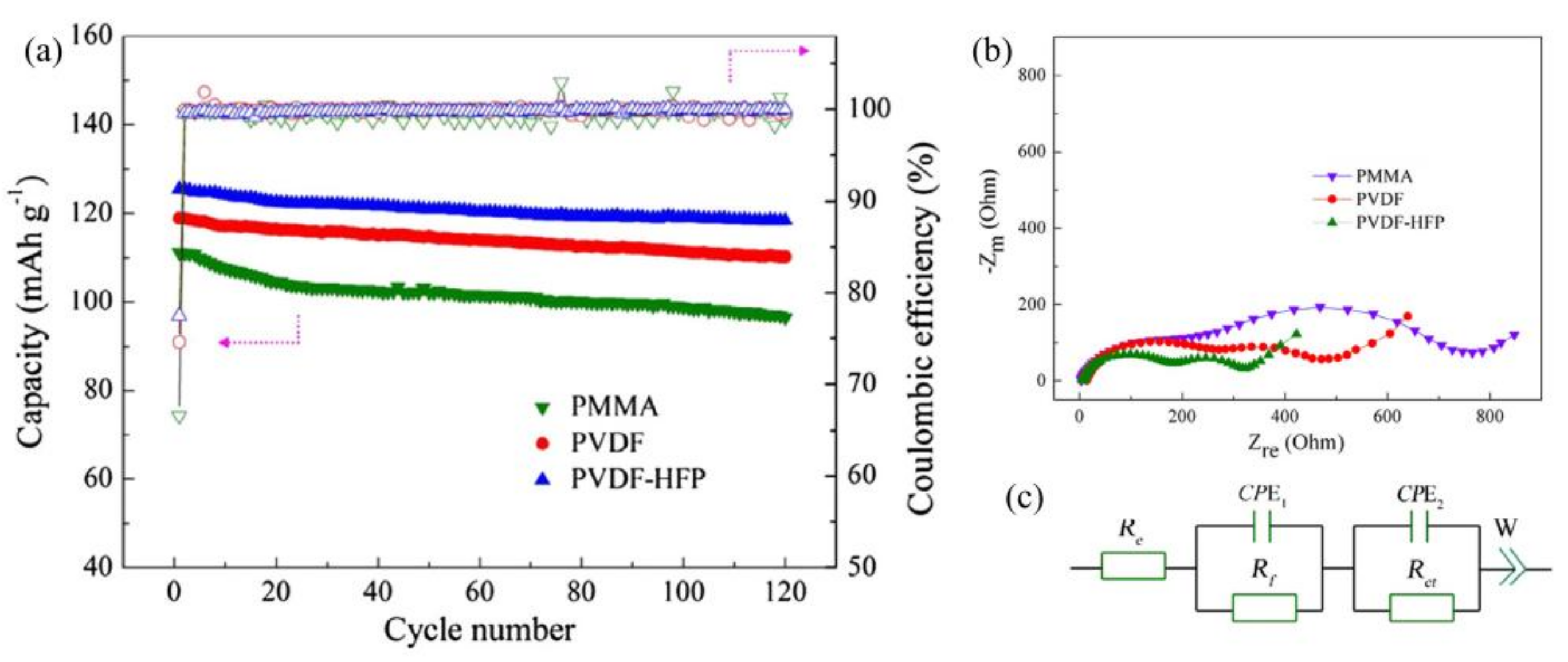



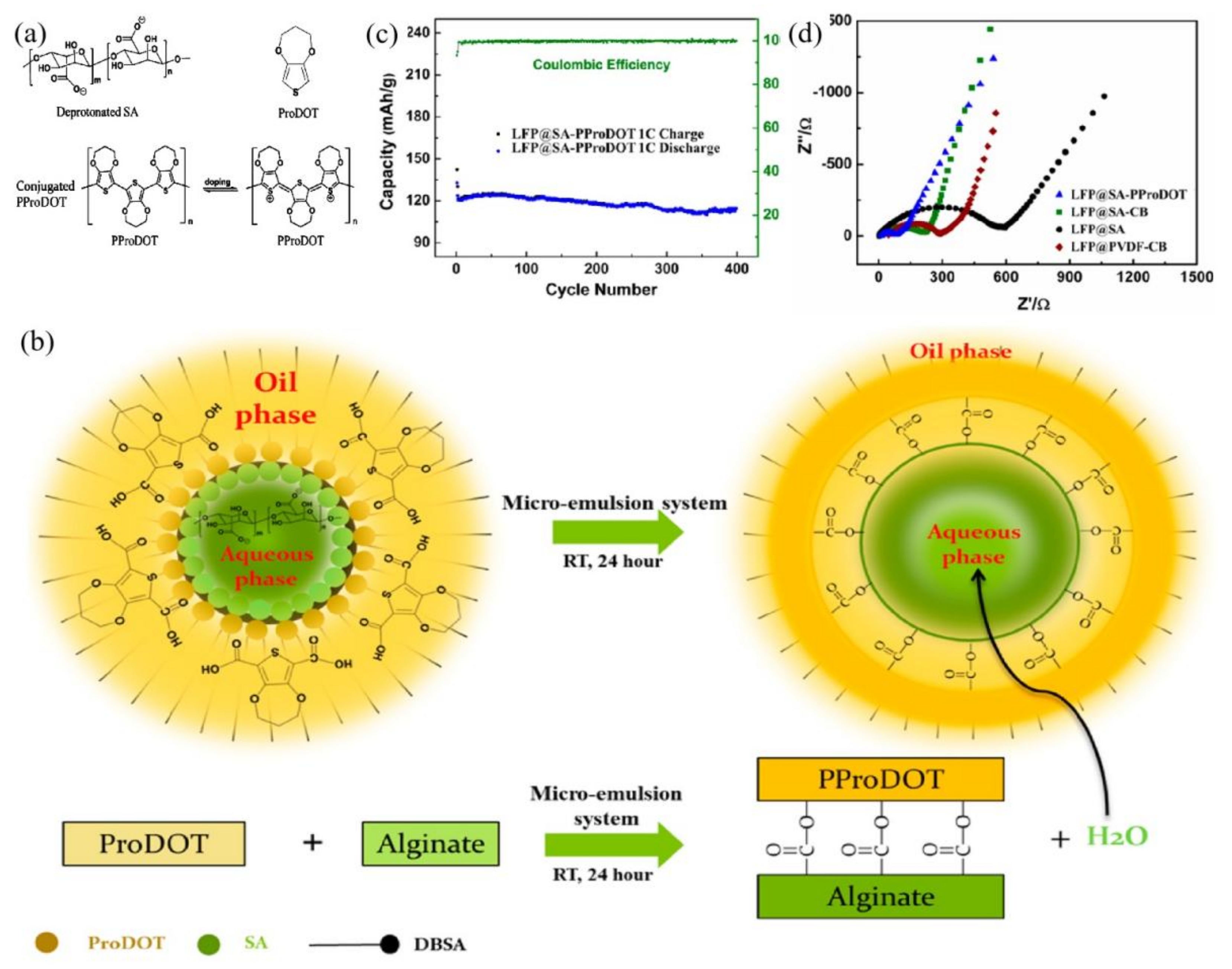

| Binder | Content of Binder (%)/Conductive Additive (%)/Solvent | Rate/Retention | Voltage Range (V)/Temperature (°C) | Ref./Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WSB+CMC | 4/6/water | 1C/100% @200 cycles | 2.5–4.0/60 | [47]/2007 |
| PAA | 10/0/water | 0.2 mA g−1/98.8% @50 cycles | 2.5–4.2/25 | [49]/2009 |
| CMC | 5/7/water | 1C/75% @1000 cycles | 2.8–4.2/25 | [50]/2010 |
| Lithiated perfluorosulfonate ionomer | 20/20/NMP | -/- | 2.5--/25 | [92]/2011 |
| Cellulose | 4/10.7/water | 1C/92% @50 cycles | 2.8–4.2/25 | [93]/2012 |
| CMC-Li | 10/10/water | -/96.2% @200 cycles | 2.0–4.2/25 | [69]/2014 |
| PAA | 7/10.3/NMP | 175 mA g−1/99.3% @200 cycles | 2.5–4.2/25 | [94]/2012 |
| PolyVIMTFSI-c | 10/10/NMP | -/- | 2.8–4.2/25 | [84]/2013 |
| PFSILi+PVDF | 10/10/NMP | -/- | 2.7–4.2/25 | [65]/2013 |
| PVDF-HFP | 10/10/NMP | 1C/- @120 cycles | 2.5–4.2/25 | [39]/2014 |
| CMC-Li | 10/10/water | -/- | 2.0–4.2/25 | [66,67]/2014 |
| SA-PProDOT | 20/0/water | 1C/86.6% @400 cycles | 2.0–4.2/25 | [78]/2015 |
| CN-CCTS | 5/5/water | 0.2C/99.2% @100 cycles | 2.5–4.0/25 | [52]/2015 |
| PEDOT:PSS | 4/4/water | 1C/99% @150 cycles | 2.0–4.0/25 | [72]/2015 |
| PTFE | 5/5/water | 0.2C/97.5% @100 cycles | 2.0–3.8/25 | [42]/2015 |
| PEDOT:PSS+CMC | 4/0/water | 1C/99% @100 cycles | 2.0–4.0/20 ± 2 | [73]/2015 |
| PEDOT:PSS | 8/0/water | 1C/100% @100 cycles | 2.8–4.2/25 | [74]/2015 |
| polyurethane | 10/10/water | -/- | 2.8–4.2/25 | [95]/2015 |
| PVDF-TrFE | 10/10/organic | 1C/89% @50 cycles | 2.5–4.2/25 | [40]/2016 |
| PEDOT:PSS | 8/0/water | -/- | - | [75]/2016 |
| CCTS+PEDOT:PSS | 4/6/water | 0.2C/100% @100 cycles | 2.5–4.0/25 | [76]/2016 |
| Jeffamine® compounds | 30/7 | 0.1C/92% @ 100 cycles | 2.4–3.9/70 | [96]/2017 |
| Xanthan gum (XG) | 5/5 | 0.2C/96.9% @100 cycles | 2.5–4.0/25 | [97]/2017 |
| L-spandex | 10/10 | 0.5C/100.7% @100cycles | 2.0–4.0/25 | [98]/2017 |
| PSBA-Li | 1.5/3/water | 0.5C/108.5% @200 cycles | 2.5–3.7/25 | [71]/2018 |
| PAALi-TS | 5/5/water | 0.2C/97.47% @100 cycles | 2.5–4.0/25 | [70]/2018 |
| SEBS | 10/10/organic | 2C/87% @50 cycles | 2.5–4.2/25 | [99]/2018 |
| CPB | 5/5/water | 0.2C/94.5% @100 cycles | 2.8–4.2/25 | [79]/2018 |
| CN-PEI | 7/13/water | 0.5C/99.6% @100 cycles | 2.5–4.0/25 | [53]/2018 |
| Lithium sulfonate-grafted P(VDF-HFP) | 10/10/NMP | 1C/92%@50 cycles | 2.4–4.3/25 | [100]/2018 |
| PEDOT:PSS-SPPO | 5/0/water | C/3 /99.6% @ 30 cycles | 2.0–4.0/25 | [77]/2019 |
| LPPS | 10/10/water | 1C/170 mAhg−1@ 200 cycles | 2.5–4.2/25 | [80]/2019 |
| PVDF/TX | 5/5/NMP | 0.2C/ 97.4%@100 cycles | 2.5–4.0/25 | [101]/2019 |
| PEGMA | 10/5 | 0.25C/127 mAhg−1@ 200th cycle | 2.0–4.0/25 | [102]/2019 |
| PVDF/Polyimide | 10/10 (3:7) | 1C/141 mAhg−1@ 300 cycles | 2.5–3.7/25 | [41]/2020 |
| PPDI | 8/2/organic | 1C/nearly 100%@ 50 cycles | - | [103]/2020 |
| SFPI | 10/10/organic | 0.5C/94.1% @100 cycles | 2.5–3.8/25 | [104]/2021 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; He, X.; Zhuo, H.; Chen, S. Rational Design of Effective Binders for LiFePO4 Cathodes. Polymers 2021, 13, 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183146
Huang S, Huang X, Huang Y, He X, Zhuo H, Chen S. Rational Design of Effective Binders for LiFePO4 Cathodes. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183146
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shu, Xiaoting Huang, Youyuan Huang, Xueqin He, Haitao Zhuo, and Shaojun Chen. 2021. "Rational Design of Effective Binders for LiFePO4 Cathodes" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183146
APA StyleHuang, S., Huang, X., Huang, Y., He, X., Zhuo, H., & Chen, S. (2021). Rational Design of Effective Binders for LiFePO4 Cathodes. Polymers, 13(18), 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183146







