Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Biosynthesized Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite from Chlorella vulgaris
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alga
2.2. Extraction of Cellulose from Alga
2.3. Synthesis of Nanocellulose
2.4. Synthesis of AuNPs
2.5. Au/cellulose Nanocomposite Preparation
2.6. Characterization of AuNPs, Nanocellulose, and Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite
2.6.1. UV-Visible Spectroscopy Analysis
2.6.2. TEM Analysis
2.6.3. Zeta Potential Measurement
2.6.4. FTIR Measurement
2.7. Cell Lines
2.8. Cell Viability and Cytotoxic Effects
2.9. Total RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis
2.11. Flowcytometry Analysis (FCM)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoparticle’s Characterization
3.1.1. Visual Inspection and UV Absorbance Spectroscopic Studies
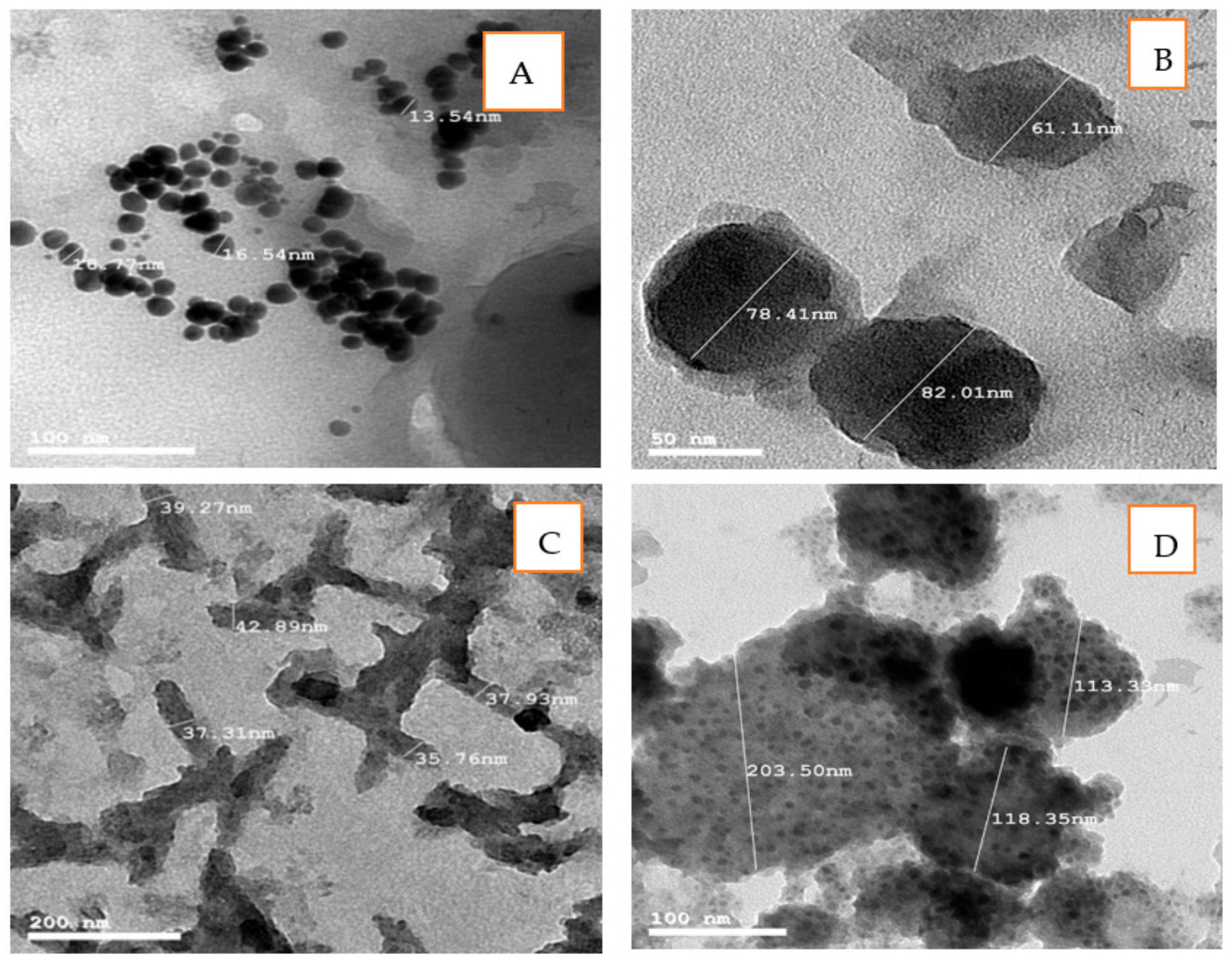
3.1.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.1.3. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
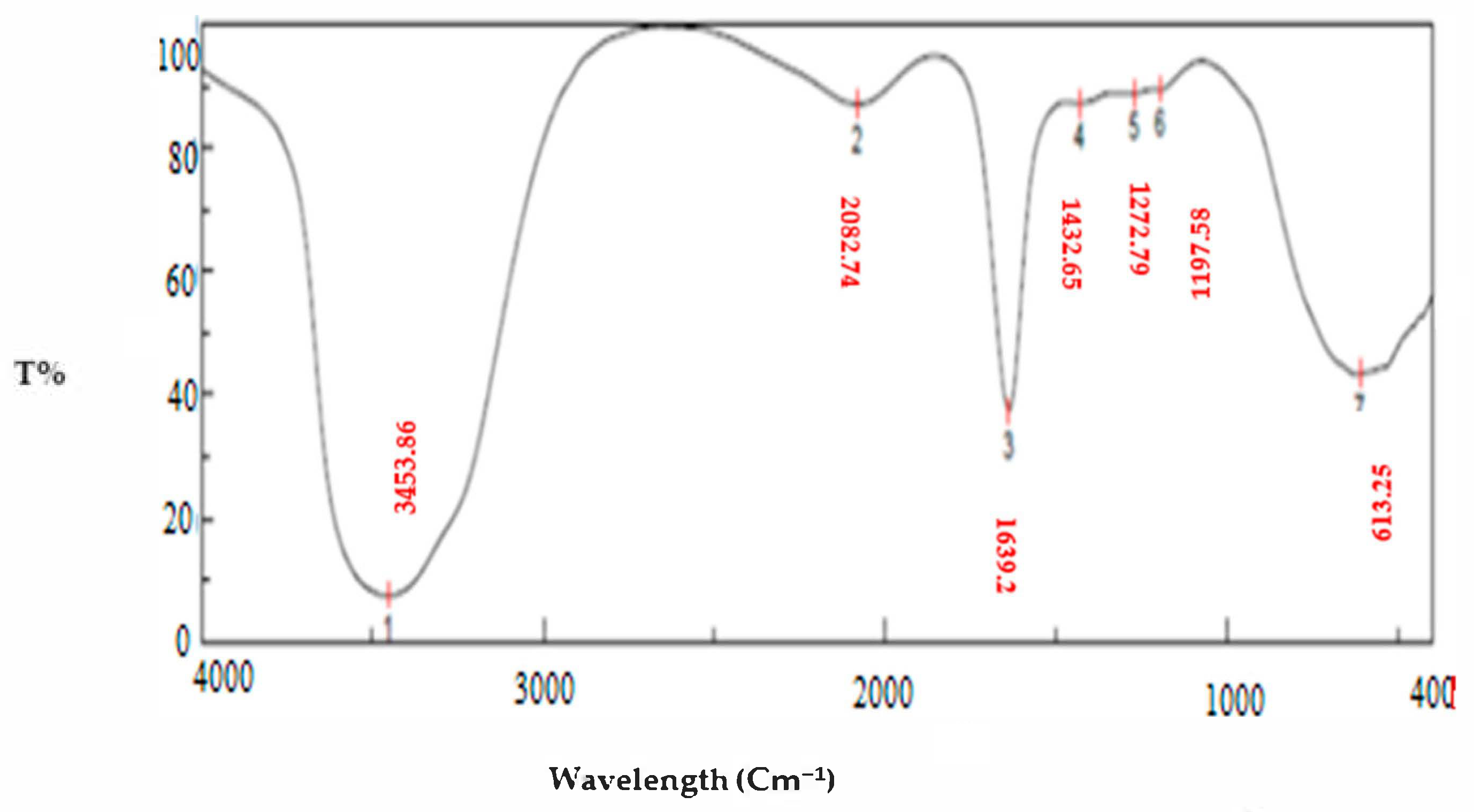
3.1.4. FTIR Studies
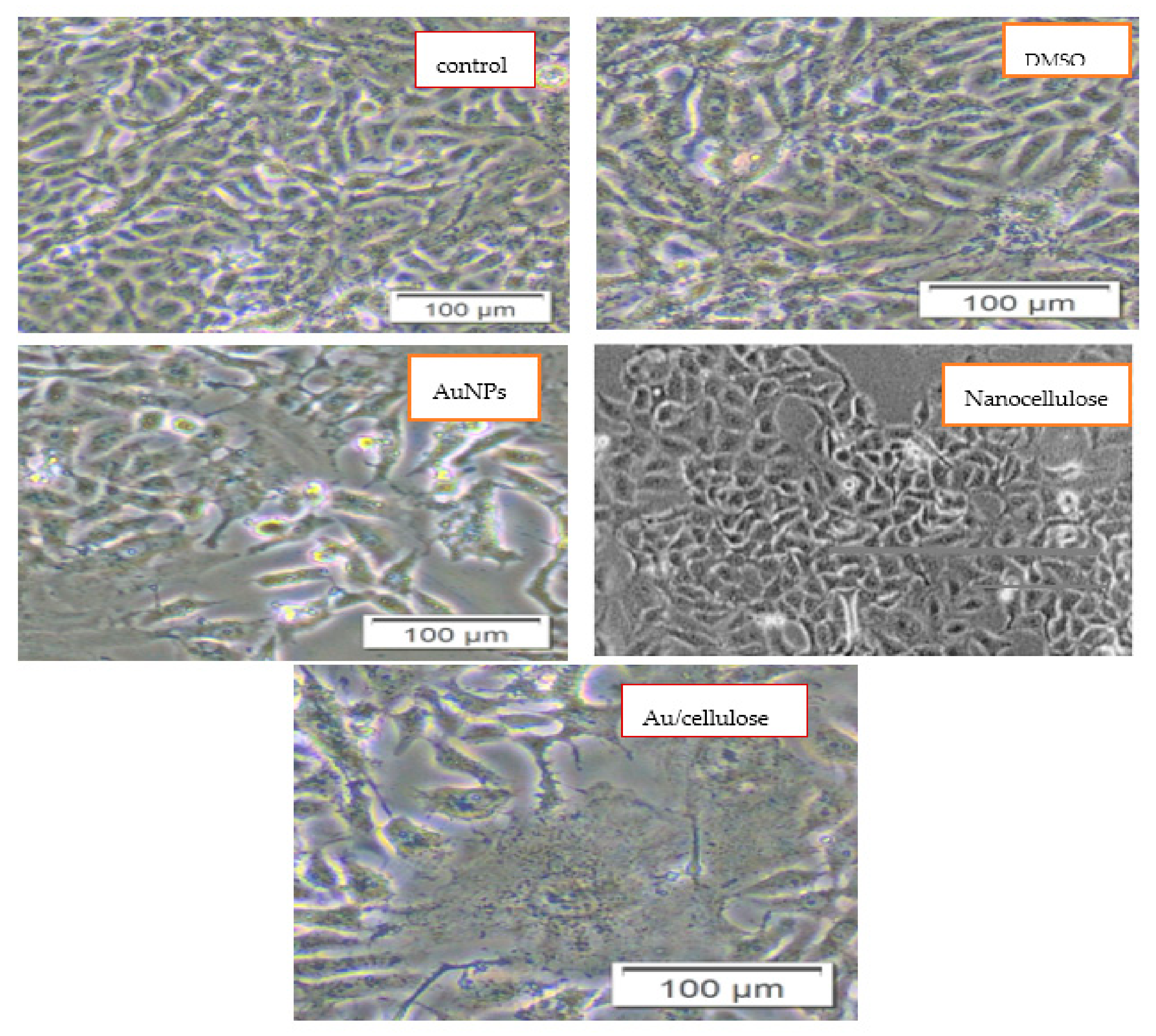
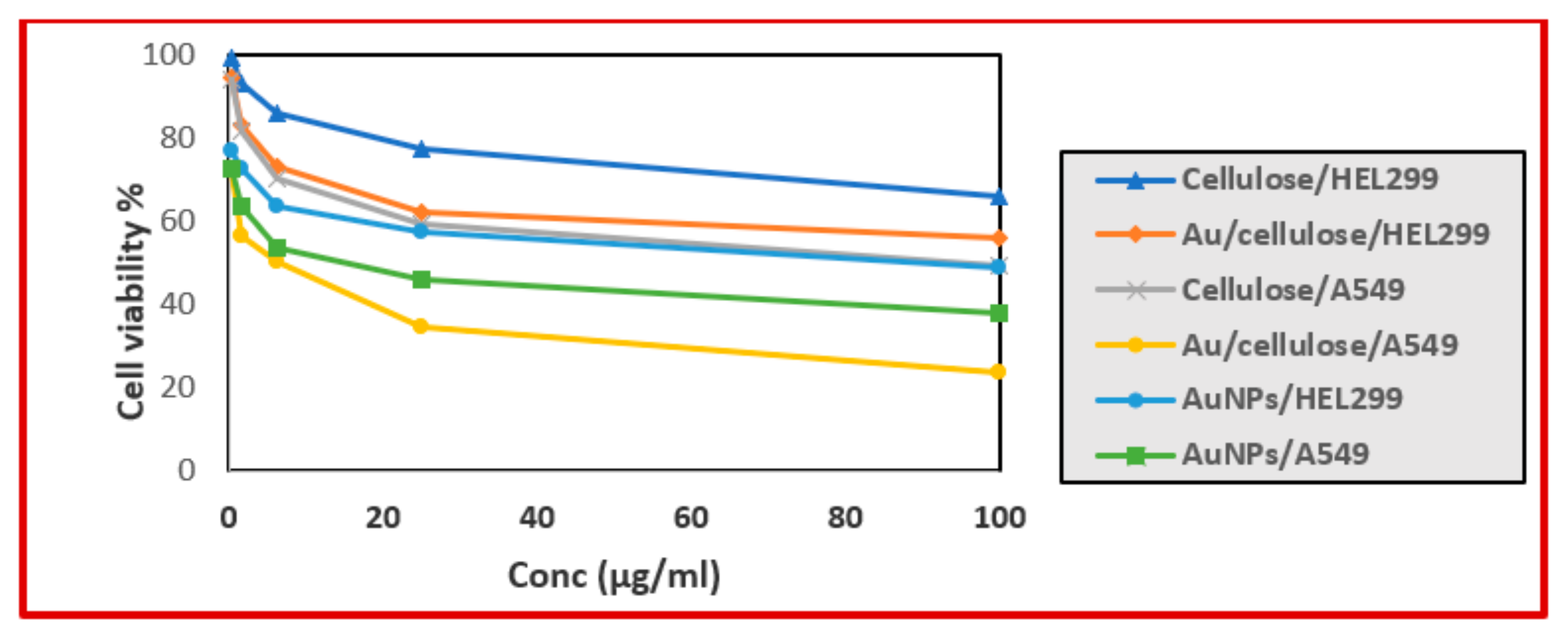
3.2. Cytotoxic Effect of Nanocellulose and Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite on A594 Cells
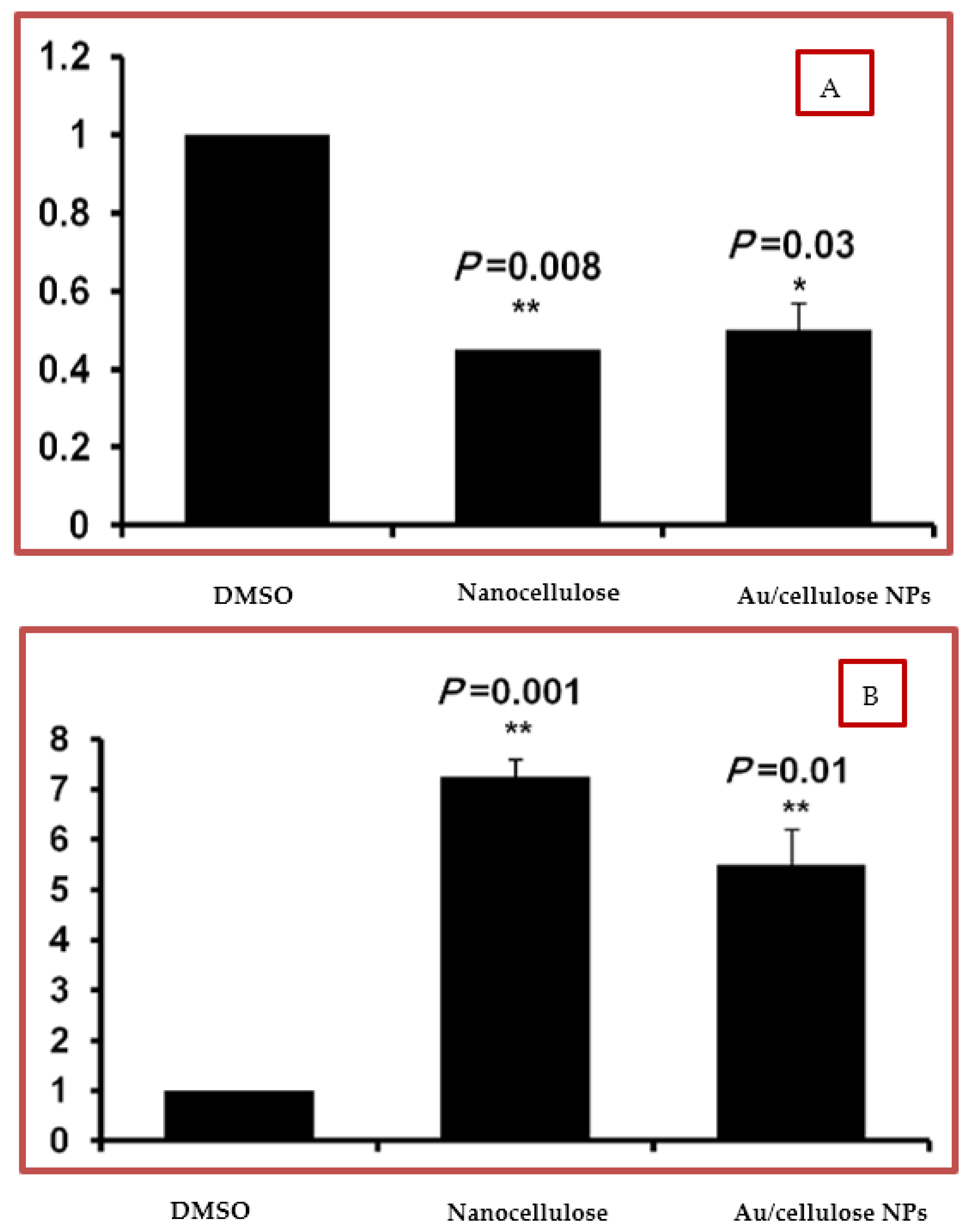
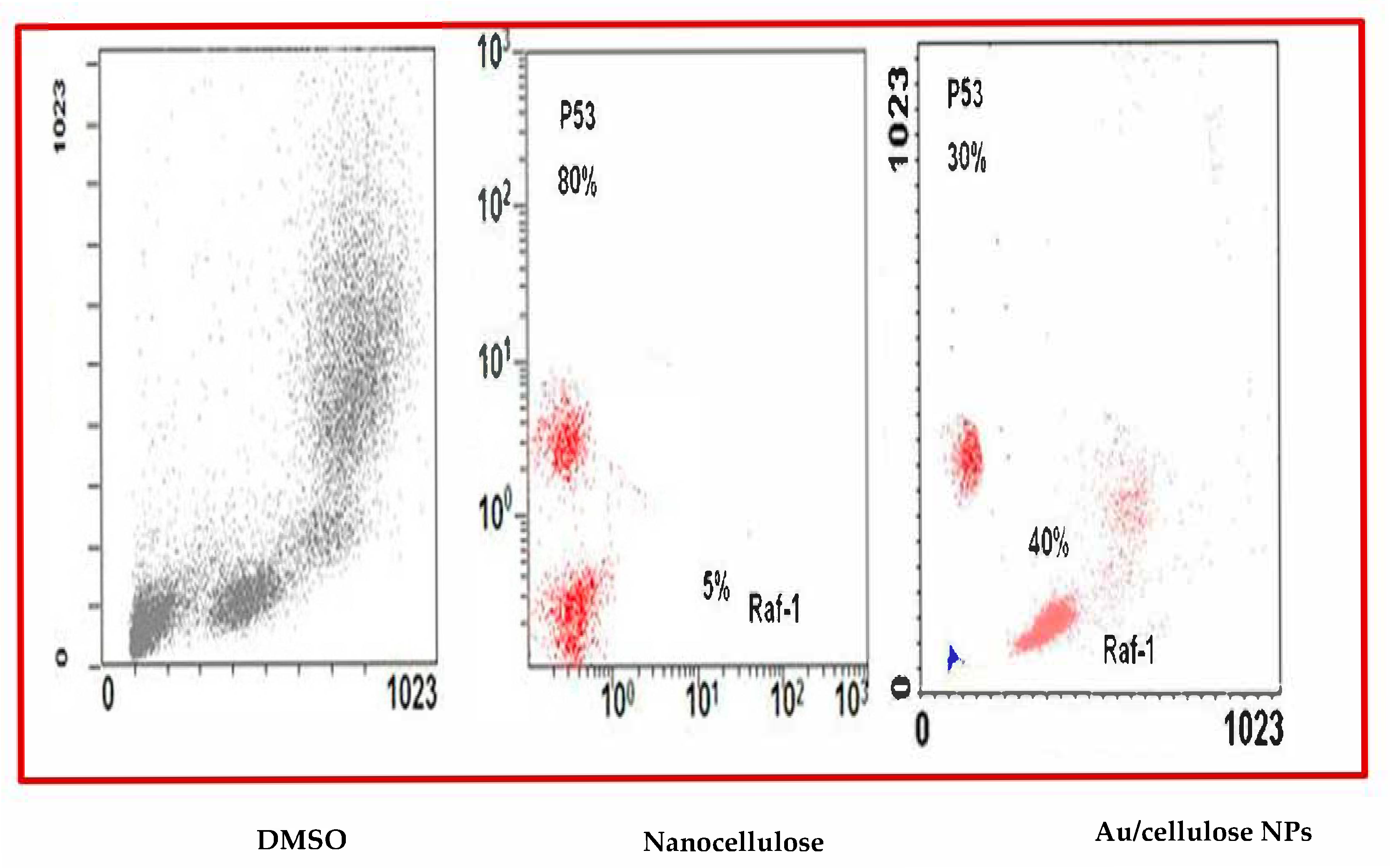
3.3. Effect of Nanocellulose and Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite on Raf-1 Gene and p53 Gene Expression
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, L.; Zheng, G.; Yao, J.; Liu, N.; Weil, B.; Eskilsson, M.; Karabulut, E.; Ruan, Z.; Fan, S.; Bloking, J.T.; et al. Transparent and conductive paper from nanocellulose fibers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck-Candanedo, S.; Roman, M.; Gray, D.G. Effect of Reaction Conditions on the Properties and Behavior of Wood Cellulose Nanocrystal Suspensions. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Pal, T. Interparticle coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: From theory to applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4797–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondeau, D.; Roy, L.; Dumont, S.; Godin, G.; Martineau, I. Physicians’ and pharmacists’ attitudes toward the use of sedation at the end of life: Influence of prognosis and type of suffering. J. Palliat. Care 2005, 21, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Wei, Q.; Yang, J.; Yan, L.; Feng, R.; Chen, G.; Du, B.; Li, H. Highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions by amine-functionalized mesoporous Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohani, M.; Habibi, Y.; Belgacem, N.M.; Ebrahim, G.; Karimi, A.N.; Dufresne, A. Cellulose whiskers reinforced polyvinyl alcohol copolymers nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 2489–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Song, Z.; Qian, X.; Ni, Y. Review on Use of Fillers in Cellulosic Paper for Functional Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokarya, R.; Abu el-nagab, M.N.; Bekhit, M.; Atta, S. A potential antibiofilm, antimicrobial and anticancer activities of chitosan capped gold nanoparticles prepared by γ–irradiation. Mater. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanpuria, P.; Rana, N.K. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles: Technological concepts and future applications. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 10, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelana, C.; Abdul Rahumana, A.; Kirthi, A.V.; Marimuthua, S.; Santhoshkumara, T.; Bagavana, A.; KGaurav, K.; Karthik, L.; Bhaskara, K.V. Raob Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 90, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.; Karthika, V. Antibacterial activity of ruthenium nanoparticles synthesized using Gloriosa superba L. leaf extract. J. Nanostruct Chem. 2014, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Gupta, R.K. Nanotechnology and potential of microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Al-Enazi, N.M.; Ibraheem, I.B. Green biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Galaxaura elongata and characterization of their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 3029–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parial, D.; Patra, H.K.; Dasgupta AK, R.; Pal, R. Screening of different algae for green synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Eur. J. Phycol. 2012, 47, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Sun, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Liu, J. Nanocellulose from various biomass wastes: Its preparation and potential usages towards the high value-added products. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2021, 5, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youlden, D.R.; Cramb, S.M.; Baade, P.D. The international epidemiology of lung cancer: Geographical distribution and secular trends. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanns, M.I.; Unger, R.E.; Kehe, K.; Peters, K.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Lung epithelial cell lines in coculture with human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells: Development of an alveolo-capillary barrier in vitro. Lab. Investig. 2004, 84, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cainap, C.; Nagy, V.; Seicean, A.; Gherman, A.; Laszlo, I.; Lisencu, C.; Nadim, A.; Constantin, A.M.; Cainap, S. Results of third-generation epirubicin/cisplatin/xeloda adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with radically resected gastric cancer. J. BU ON 2016, 21, 349–359. [Google Scholar]
- Abd, E.I.; Maksoud, A.I.; Taher, R.F.; Gaara, A.H.; Abdelrazik, E.; Keshk, O.S.; Elawdan, K.A.; Morsy, S.E.; Salah, A.; Khalil, H. Selective Regulation of B-Raf Dependent K-Ras/Mitogen-Activated Protein by Natural Occurring Multi-kinase Inhibitors in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Braicu, C.; Buse, M.; Busuioc, C.; Drula, R.; Gulei, D.; Raduly, L.; Rusu, A.; Irimie, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Slaby, O.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on MAPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosarin, F.S.; Arulmozhi, V.; Nagarajan, S.; Mirunalini, S. Antiproliferative effect of silver nanoparticles synthesized using amla on Hep2 cell line. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, C.; Wang, K.; Oppong-Gyebi, A.; Hu, J. Application of Nanotechnology in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy—A Mini-Review. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 2964–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Nasiri, N.; Ikram, M.; Nafees, M.; Qureshi, M.Z.; Ali, S.; Tricoli, A. Eco-friendly biosynthesis, anticancer drug loading and cytotoxic effect of capped ag-nanoparticles against breast cancer. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devi, J.S. Anticancer Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by the Seaweed Ulva lactuca Invitro. J. Nanomed. Biother. Discov. 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraju, N.; Venkatalakshmi, R.P.; Chinnasamy, A.; Kannaiyan, P. Synthesis of silver nanopar-ticles and the antibacterial and anticancer activities of the crude extract of sargassum polycystum C. Agardh. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2012, 4, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, V.; Revathidevi, S.; Shanmuganayagam, T.; Muthulakshmic, L.; Rajaram, R. Biogenic gold nanoparticles induce cell cycle arrest through oxidative stress and sensitize mitochondrial membranes in A549 lung cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 20598–20608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, P.; Lu, X. Effects of Internalized Gold Nanoparticles with Respect to Cytotoxicity and Invasion Activity in Lung Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Saravanakumar, K.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Wang, M. Preparation, characterization and anti-cancer activity of graphene oxide–silver nanocomposite. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 210, 111984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wen, C.; Song, L.; Zhao, N.; Xu, F.J. Multifunctional hetero-nanostructures of hydroxyl-rich polycation wrapped cellulose-gold hybrids for combined cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2017, 255, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlstrom, N.; Edlund, U.; Pavia, H.; Toth, G.; Jaworski, A.; Pell AJFerdinand, X.; Choong, F.X.; Shirani, H.; Peter, K.; Nilsson, R.; et al. Cellulose from the green macroalgae Ulva lactuca: Isolation, characterization, optotracing, and production of cellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 2020, 27, 3707–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zain, N.F.M.; Yusop, S.M.; Ahmad, I. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose and Nanocellulose from Pomelo (Citrus grandis) Albedo. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 5, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna, M.; Babu, D.R.; Gengan, R.M.; Chandra, S.; Rao, G.N. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine algae and evaluation of their catalytic activity. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalil, H.; El Malah, T.; Abd El Maksoud, A.I.; El Halfawy, I.; El Rashedy, A.A.; El Hefnawy, M. Identification of novel and efficacious chemical compounds that disturb influenza A virus entry in vitro. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L. A high-throughput method to monitor the expression of microRNA precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morales-Kastresana, A.; Telford, B.; Musich, T.A.; McKinnon, K.; Clayborne, C.; Braig, Z.; Rosne, A.; Demberg, T.; Watson, D.C.; Karpova TSFreeman, G.J.; et al. Labeling extracellular vesicles for nanoscale flow cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, H.; Tazi, M.; Kyle Caution, K.; Ahmed, A.; Kanneganti AAssanid, K.; Koppd, B.; Marsh, C.; Dakhlallah, D.; Amer, A.O. Aging is associated with hypermethylation of autophagy genes in macrophages. Epigenetics 2016, 11, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Focsan, M.; Gabudean, A.M.; Canpean, V.; Maniu, D.; Astilean, S. Formation of size and shape tunable gold nanoparticles in solution by bio-assisted synthesis with bovine serum albumin in native and denatured state. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 939–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications, and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parial, D.; Patra, H.K.; Roychoudhury, P.; Dasgupta, A.K.; Pal, R. Gold nanorod production by cyanobacteria—A green chemistry approach. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S. Anticancer activity of eco-friendly gold nanoparticles against lung and liver cancer cells. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smitha, S.L.; Philip, D.; Gopchandran, K.G. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Cinnamomum zeylanicum leaf broth. Spectrochim. Acta Part. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 74, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oza, G.; Pandey, S.; Mewada, A.; Kalita, G.; I Sharon, M. Facile Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Exploiting Optimum pH and Temperature of Fresh Water Algae Chlorella pyrenoidusa. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Bakir, E.M.; Younis NSMohamed, M.E.; El Semary, N.A. Cyanobacteria as Nanogold Factories: Chemical and Anti-Myocardial Infarction Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Lyngbya majuscula. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lani, N.S.; Ngadi, N.; Johari, A.; Jusoh, M. Isolation, characterization, and application of nanocellulose from oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber as nanocomposites. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 702538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othman, S.H.; Abdul Rashid, S.; Mohd Ghazi, T.I.; Abdullah, N. Dispersion and stabilization of photocatalytic TiO2 nanoparticles in aqueous suspension for coatings applications. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 718214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honary, S.; Zahir, F. Effect of zeta potential on the properties of nano-drug delivery systems—A review (Part 1). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, R.; Eldridge, D.; Palombo, E.; Harding, I. Optimisation and stability assessment of solid lipid nanoparticles using particle size and zeta potential. J. Phys. Sci. 2014, 25, 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, M.T.; Ahmadpour, E.; Rahimi Esboei, B.; Spotin, A.; Kohansal Koshki, M.H.; Alizadeh, A.; Honary, S.; Barabadi, H.; Ali Mohammadi, M. Scolicidal Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles against Echinococcus Granulosus Protoscolices. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 19, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gericke, M.; Pinches, A. Microbial production of gold nanoparticles. Gold Bull. 2006, 39, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutic 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singaravelu, G.; Arockiamary, J.S.; Kumar, V.G.; Govindaraju, K. A novel extracellular synthesis of monodisperse gold nanoparticles using marine alga, Sargassum wightii Greville. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 57, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Mahadevan, A.; Sathishkumar, M.; Pavagadhi, S.; Balasubramanian, R. Biosynthesis of Au(0) from Au(III) via biosorption and bioreduction using brown marine alga Turbinaria conoides. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto AB, D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to read and interpret FTIR spectroscope of organic material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, J.; Nallamuthu, T. Characterization of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Chlorella vulgaris and their anti-pathogenic properties. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santhoshkumar, J.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Venkat Kumar, S. Phyto-assisted synthesis, characterization and applications of gold nanoparticles—A review. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 11, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalingam, M.; Kalpana, V.N.; Rajeswari, V.D.; Panneerselvam, A. Biosynthesis, characterization, and evaluation of bioactivities of leaf extract-mediated biocompatible gold nanoparticles from Alternanthera bettzickiana. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 19, e00268. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; El-Kassas, H.Y. Algal production of nano-silver and gold: Their antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities: A review. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoudmann, N.; Schmutz, M.; Hirsch, C.; Nowack, B.; Som, C. Human hazard potential of nanocellulose: Quantitative insights from the literature. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Venkatachalam, K.; Hu, X.; Wang, M. pH-sensitive release of fungal metabolites from chitosan nanoparticles for effective cytotoxicity in prostate cancer (PC3) cells. Process. Biochem. 2021, 102, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Matsubara, H. Recent advances in p53 research and cancer treatment. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 978312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the p53 network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, T.; Sontag, E.; Chen, P.; Levine, A. Transcriptional control of human p53-regulated genes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. The cell-cycle arrest and apoptotic and progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 6, a026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masliah-planchon, J.; Garinet, S.; Pasmant, E. RAS-MAPK pathway epigenetic activation in cancer: miRNAs in action RAS-MAPK the RAS-MAPK pathway in human. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 38892–38897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peyssonnaux, C.; Eychène, A. The Raf/MEK/ERK pathway: New concepts of activation. Biol. Cell. 2001, 93, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Matsubara, Y. Ras/MAPK syndromes and childhood hemato-oncological diseases. Int. J. Hematol. 2013, 97, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makita, Y.; Narumi, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Niihori, T.; Kure, S.; Fujieda, K.; Matsubara, Y.; Aoki, Y. Leukemia in Cardio-facio-cutaneous (CFC) syndrome: A patient with a germline mutation in BRAF proto-oncogene. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2007, 29, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, M.R.M.; Baig, M.; Mohamoud, H.S.; Ulhaq, Z.; Hoessli, D.C.; Khogeer, G.S.; Al-Sayed, R.R.; Al-Aama, J.Y. BRAF gene: From human cancers to developmental syndromes. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Camarillo, C.; Ocampo, E.A.; Casamichana, M.L.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Álvarez-Sánchez, E.; Marchat, L.A. Protein kinases and transcription factors activation in response to UV-radiation of skin: Implications for carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 142–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Their Role in Radiation Response. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; XU, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signaling pathway and tumorigenesis (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Chuang, M.J.; Tang, S.H.; Wu, S.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Sun, G.H.; Hsiao, P.W.; Huang, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Yu, C.P.; et al. Novel cancer therapeutics with allosteric modulation of the mitochondrial C-Raf-DAPK complex by Raf inhibitor combination therapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3568–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammadinejad, R.; Moosavi, M.A.; Tavakol, S.; Vardar, D.O.; Hosseini, A.; Rahmati, M.; Dini, L.; Hussain, S.; Mandegary, A.; Klionsky, D.J. Necrotic, apoptotic, and autophagic cell fates triggered by nanoparticles. Autophagy 2019, 15, 4–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brazil, D.P.; Yang, Z.Z.; Hemmings, B.A. Advances in protein kinase B signaling: AKTion on multiple fronts. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Grahama, P.H.; Nia, J.; Hao, J.; Buccia, J.; Cozzib, P.J.; Lia, Y. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in the treatment of prostate cancer radioresistance. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 96, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniele, S.; Costa, B.; Zappelli, E.; Da Pozzo, E.; Sestito, S.; Nesi, G.; Campiglia, P.; Marinelli, L.; Novellino, E.; Rapposelli, S.; et al. Combined inhibition of AKT/mTOR and MDM2 enhances Glioblastoma Multiforme cell apoptosis and differentiation of cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, M.E.; de Souza, J.A.; Geyer, S.; Wirth, L.J.; Menefee, M.E.; Liu, S.V.; Shah, K.; Wright, J.; Shah, M.H. Cabozantinib as salvage therapy for patients with tyrosine kinase inhibitor-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: Results of a multicenter phase II international thyroid oncology group trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, H.; Meng, N.; Lu, W.; Li, G.; Han, Y.; Dai, X.; Xia, Y.; Song, X.; Yang, S.; et al. A novel, orally available multikinase inhibitor, potently inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in preclinical models. Br. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1766–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Date, A.; Chawda, H.; Patel, I. Polysaccharides as potential anticancer agents—A review of their progress. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 210, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.A.H.; Alsharidah, M.; Al Rugaie, O.; Tawfeek, H.M.; Tolba, N.S. Silver Nanoparticle-Coated Ethyl Cellulose Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor-α of Breast Cancer Cells. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | IC50 µg/mL | |
|---|---|---|
| HEL299 | A549 | |
| AuNPs | 95.668 ± 3.59 | 13.43 ± 0.76 |
| Nanocellulose | 2055.9 ± 51.19 | 86.61 ± 3.21 |
| Au/cellulose nanocomposite | 182.75 ± 6.45 | 4.67 ± 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamouda, R.A.; Abd El Maksoud, A.I.; Wageed, M.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Elebeedy, D.; Khalil, H.; Hassan, A.; Abdella, A. Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Biosynthesized Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite from Chlorella vulgaris. Polymers 2021, 13, 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193340
Hamouda RA, Abd El Maksoud AI, Wageed M, Alotaibi AS, Elebeedy D, Khalil H, Hassan A, Abdella A. Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Biosynthesized Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite from Chlorella vulgaris. Polymers. 2021; 13(19):3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193340
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamouda, Ragaa A., Ahmed I. Abd El Maksoud, Madonna Wageed, Amenah S. Alotaibi, Dalia Elebeedy, Hany Khalil, Amr Hassan, and Asmaa Abdella. 2021. "Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Biosynthesized Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite from Chlorella vulgaris" Polymers 13, no. 19: 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193340
APA StyleHamouda, R. A., Abd El Maksoud, A. I., Wageed, M., Alotaibi, A. S., Elebeedy, D., Khalil, H., Hassan, A., & Abdella, A. (2021). Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Biosynthesized Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite from Chlorella vulgaris. Polymers, 13(19), 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193340






