Hydrophilic Surface-Modified PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Oil–Water Emulsion Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
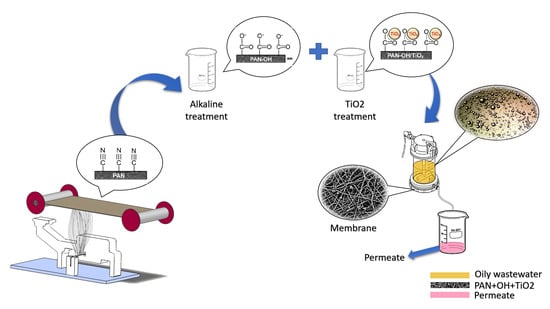
2.1. Membrane Preparation
2.2. Surface Modification
2.3. Characterisation
2.4. Emulsion Preparation
2.5. Filtration Test
3. Results
3.1. Membrane Characterisation
3.2. Separation Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goh, P.S.; Ong, C.S.; Ng, B.C.; Ismail, A.F. 5—Applications of Emerging Nanomaterials for Oily Wastewater Treatment. In Nanotechnology in Water and Wastewater Treatment; Ahsan, A., Ismail, A.F., Eds.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 101–113. ISBN 978-0-12-813902-8. [Google Scholar]
- Scharnagl, N.; Buschatz, H. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Membranes for Ultra- and Microfiltration. Desalination 2001, 139, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Economy, J. Solvent Resistant Hydrolyzed Polyacrylonitrile Membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2827–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryjak, M.; Hodge, H.; Dach, B. Modification of Porous Polyacrylonitrile Membrane. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1998, 260, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Mirasol, J.R.; Cordero, T.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Investigation of Needleless Electrospun PAN Nanofiber Mats. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1952, 020085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Großerhode, C.; Wehlage, D.; Grothe, T.; Grimmelsmann, N.; Fuchs, S.; Hartmann, J.; Mazur, P.; Reschke, V.; Siemens, H.; Rattenholl, A.; et al. Investigation of Microalgae Growth on Electrospun Nanofiber Mats. AIMS Bioeng. 2017, 4, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, S.; Wehlage, D.; Juhász Junger, I.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning a Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. Catalysts 2019, 9, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grothe, T.; Wehlage, D.; Boehm, T.; Remche, A.; Ehrmann, A. Needleless Electrospinning of PAN Nanofibre Mats. Tekstilec 2017, 60, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Most Recent Developments in Electrospun Magnetic Nanofibers: A Review. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2020, 15, 1558925019900843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Conductive Electrospun Nanofiber Mats. Materials 2019, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Siekierka, A.; Bryjak, M. Surface Modification of Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes for Oily Wastewater Separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56704–56712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Li, Y.-J.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.-L. Super-Wetting, Photoactive TiO2 Coating on Amino-Silane Modified PAN Nanofiber Membranes for High Efficient Oil-Water Emulsion Separation Application. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 580, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Böttjer, R.; Wehlage, D.; Grothe, T.; Klöcker, M.; García-Mateos, F.J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Ehrmann, A. Morphological Study of Stabilization and Carbonization of Polyacrylonitrile/TiO2 Nanofiber Mats. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14, 1558925019862242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pan, X.; Xue, Q.; He, D.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Q. Antifouling Hydrolyzed Polyacrylonitrile/Graphene Oxide Membrane with Spindle-Knotted Structure for Highly Effective Separation of Oil-Water Emulsion. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 532, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, M.; Nabavi, S.R.; Emadi, H.; Faraji, M. Development of a Superhydrophilic Nanofiber Membrane for Oil/Water Emulsion Separation via Modification of Polyacrylonitrile/Polyaniline Composite. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Moreno, I.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L. Characterization and Optimization of the Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyacrylonitrile Membranes. Polymers 2019, 11, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y. Surface Modification of Polyacrylonitrile-Based Carbon Fiber and Its Interaction with Imide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyraz, E.; Yalcinkaya, F.; Hruza, J.; Maryska, J. Surface-Modified Nanofibrous PVDF Membranes for Liquid Separation Technology. Materials 2019, 12, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kujawski, W.; Adamczak, P.; Narebska, A. A Fully Automated System for the Determination of Pore Size Distribution in Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration Membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1989, 24, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Hruza, J. Effect of Laminating Pressure on Polymeric Multilayer Nanofibrous Membranes for Liquid Filtration. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, S. Membrane Fouling and Wetting in Membrane Distillation and Their Mitigation by Novel Membranes with Special Wettability. Water Res. 2017, 112, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-G.; Wan, L.-S.; Xu, Z.-K. Surface Engineerings of Polyacrylonitrile-Based Asymmetric Membranes towards Biomedical Applications: An Overview. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, F.; Calandra, P.; Salvato, G. Octanoic Acid as a Novel Solvent for Low Electric Field Electrorheological Fluids. ScienceJet 2013, 2, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Shriver, D.F.; Atkins, P.W. Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-7167-2873-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhaowen, C.; Xu, W. Properties of Partially Hydrolyzed PAN Fibers. Front. Chem. Chin. 2009, 4, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Abuzade, R.A.; Zadhoush, A.; Gharehaghaji, A.A. Air Permeability of Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanoweb. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C. Self-Cleaning Applications of TiO2 by Photo-Induced Hydrophilicity and Photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176–177, 396–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Siekierka, A.; Bryjak, M. Preparation of Fouling-Resistant Nanofibrous Composite Membranes for Separation of Oily Wastewater. Polymers 2017, 9, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Yalcinkaya, B.; Hruza, J.; Hrabak, P. Effect of Nanofibrous Membrane Structures on the Treatment of Wastewater Microfiltration. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.J.D.; Kim, K.J. The Effect of Surfactant Pretreatment on the Ultrafiltration of Proteins. Desalination 1985, 53, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, R.B.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Schomp, W.G.; Bewley, J.L. Membrane Ultrafiltration of a Nonionic Surfactant. AIChE J. 1973, 19, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Jumawan, A.B.; Grieves, R.B.; Witherup, S.O. Ultrafiltration of Complex Wastewaters: Recycling for Nonpotable Use. J. (Water Pollut. Control Fed.) 1978, 50, 846–861. [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson, A.-S.; Jönsson, B. The Influence of Nonionic and Ionic Surfactants on Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Ultrafiltration Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 56, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourirajan, S.; Sirianni, A.F. Membrane Separation Studies with Some Polyoxyethylated Alkylphenols in Aqueous Solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1966, 5, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Meng, H.; Ji, S. Hydrolysis Differences of Polyacrylonitrile Support Membrane and Its Influences on Polyacrylonitrile-Based Membrane Performance. Desalination 2009, 242, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Q.; Yang, X.; Luo, Y.; Tang, H.; Luo, X.; Tan, Y.; Ma, M. A Superhydrophobic Poly(Dimethylsiloxane)-TiO2 Coated Polyurethane Sponge for Selective Absorption of Oil from Water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 162, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. Facile Construction of Robust Fluorine-Free Superhydrophobic TiO2@fabrics with Excellent Anti-Fouling, Water-Oil Separation and UV-Protective Properties. Mater. Des. 2017, 128, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A.; Chikuni, M.; Kojima, E.; Kitamura, A.; Shimohigoshi, M.; Watanabe, T. Photogeneration of Highly Amphiphilic TiO2 Surfaces. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A.; Chikuni, M.; Kojima, E.; Kitamura, A.; Shimohigoshi, M.; Watanabe, T. Light-Induced Amphiphilic Surfaces. Nature 1997, 388, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Su, Y.; Wu, H.; You, X.; Shen, J.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Z. Assembly of Self-Cleaning Perfluoroalkyl Coating on Separation Membrane Surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 496, 143674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, W.; Peng, J.; Jiang, Z. Grafting Perfluoroalkyl Groups onto Polyacrylonitrile Membrane Surface for Improved Fouling Release Property. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.-Y.; Shao, Z.-D.; Wang, L.; Cheng, X.; Zheng, Y.-M. Sol–Gel SiO2 on Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber for Efficient Oil-in-Water Emulsion Separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 16129–16142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, L.; Yan, K.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.J. Polydopamine Nanocluster Decorated Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane for Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 547, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; McCutcheon, J.R.; Rahaman, M.S. A High Flux Polyvinyl Acetate-Coated Electrospun Nylon 6/SiO2 Composite Microfiltration Membrane for the Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsion with Improved Antifouling Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Polymer | Abbreviation | Density (g/m2) | Modification | Fibre Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAN | S1 | 1 | - | 143.76 ± 30.83 |
| S2 | 3 | - | 168.43 ± 26.52 | |
| S3 | 3 | NaOH | 165.38 ± 36.36 | |
| S4 | 3 | NaOH + TiO2 | 207.03 ± 56.44 | |
| S5 | 3 | KOH | 170.43 ± 42.67 | |
| S6 | 3 | KOH + TiO2 | 179.12 ± 34.56 |
| Abbreviation | Mean Pore Size (µm) |
|---|---|
| S1 | 1.74 |
| S2 | 0.90 |
| S3 | 0.45 |
| S4 | 0.45 |
| S5 | 0.44 |
| S6 | 0.38 |
| Sample Code | Bursting Strength [kPa] | Air Permeability [l/m2/s] |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 189.33 ± 34.32 | 6.06 ± 0.85 |
| S2 | 241 ± 20.05 | 4.07 ± 0.57 |
| S3 | 149 ±17.00 | 3.45 ± 0.42 |
| S4 | 148 ± 14.50 | 3.64 ± 0.09 |
| S5 | 125 ± 46.5 | 2.51 ± 0.01 |
| S6 | 90 ± 18.00 | 2.62 ± 0.96 |
| Sample | CA Before Separation (°) | CA After Separation (°) | Image (Before Separation) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 73.93 ± 2.61 | 39.90 ± 3.47 |  |
| S2 | 78.86 ± 3.92 | 69.80 ± 1.50 |  |
| S3 | 0 | 0 | - |
| S4 | 19 ± 6.65 | 0 | - |
| S5 | 0 | 0 | - |
| S6 | 0 | 43.85 ± 4.30 | - |
| Sample | Permeate | O/W Ratio in Permeate (v/v) % |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | water | 0/100 |
| S2 | water | 0/100 |
| S3 | water | 0/100 |
| S4 | oil + water | 10/90 |
| S5 | water | 0/100 |
| S6 | oil + water | 10/90 |
| Membrane | Feed | Pressure Applied (Bar) | Flux-Permeability | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAN–OH, TiO2 grafted PAN-OH | 50/50 v/v oil/water emulsion | 0.02 | 600–2600 L/(m2 hbar) for emulsion | This work |
| TiO2 coated amino-silane modified PAN nanofibre | 1/1000 wt/wt oil/water emulsion | 0.01 | Up to 2000 L/(m2 h) for emulsion | Wang et al. [13] |
| Polyacrylonitrile/polyaniline composite | 1000 ppm emulsion | 0.5–2.3 | ~2000 L/(m2 h) for emulsion at 0.5 bar | Shakiba et al. [15] |
| HPAN-PEI-PFOS | 1 g/L oil/water emulsion | 0.5–1 | ~220 L/(m2 h) for emulsion at 0.5 bar | Yu et al. [40] |
| Perfluoroalkyl coated polyacrylonitrile | 1000 ppm emulsion | 1 | ~150 L/(m2 h) for emulsion at 1 bar | Zhao et al. [41] |
| PAN@SiO2 nanofibre membrane | 1/100 v/v oil/water emulsion | 0.01 | 1000–4000 L/(m2 h) | Ying et al. [42] |
| PAN/HPEI/PDA nanofibre membrane | 1/100 v/v oil/water emulsion | 0.1–0.2 | ~1200 L/(m2 h) | Wang et al. [43] |
| Polyvinyl acetate-coated electrospun nylon 6/SiO2 | 1000 mg/L oil in water | 0.28 | ~2500 L/(m2 hbar) | Islam et al. [44] |
| Commercial PSf | 1000 mg/L oil in water | 0.28 | ~800 L/(m2 hbar) | Islam et al. [44] |
| Commercial PVDF | 1000 mg/L oil in water | 0.28 | ~200 L/(m2 hbar) | Islam et al. [44] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boyraz, E.; Yalcinkaya, F. Hydrophilic Surface-Modified PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Oil–Water Emulsion Separation. Polymers 2021, 13, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020197
Boyraz E, Yalcinkaya F. Hydrophilic Surface-Modified PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Oil–Water Emulsion Separation. Polymers. 2021; 13(2):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020197
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoyraz, Evren, and Fatma Yalcinkaya. 2021. "Hydrophilic Surface-Modified PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Oil–Water Emulsion Separation" Polymers 13, no. 2: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020197
APA StyleBoyraz, E., & Yalcinkaya, F. (2021). Hydrophilic Surface-Modified PAN Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Oil–Water Emulsion Separation. Polymers, 13(2), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020197