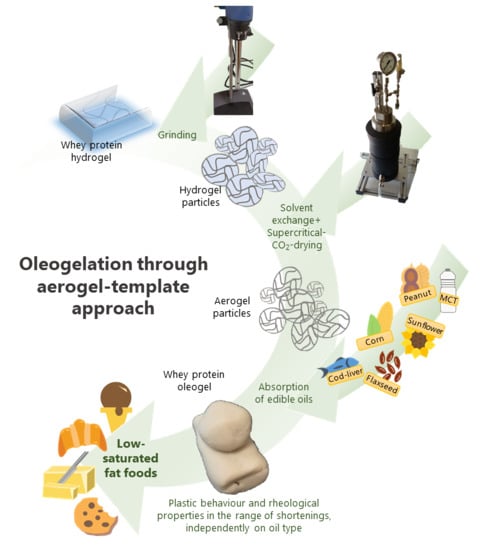
Conversion of Whey Protein Aerogel Particles into Oleogels: Effect of Oil Type on Structural Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Oleogels
2.3. Oil Viscosity
2.4. Image Acquisition
2.5. Optical Microscopy
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7. Confocal Microscopy
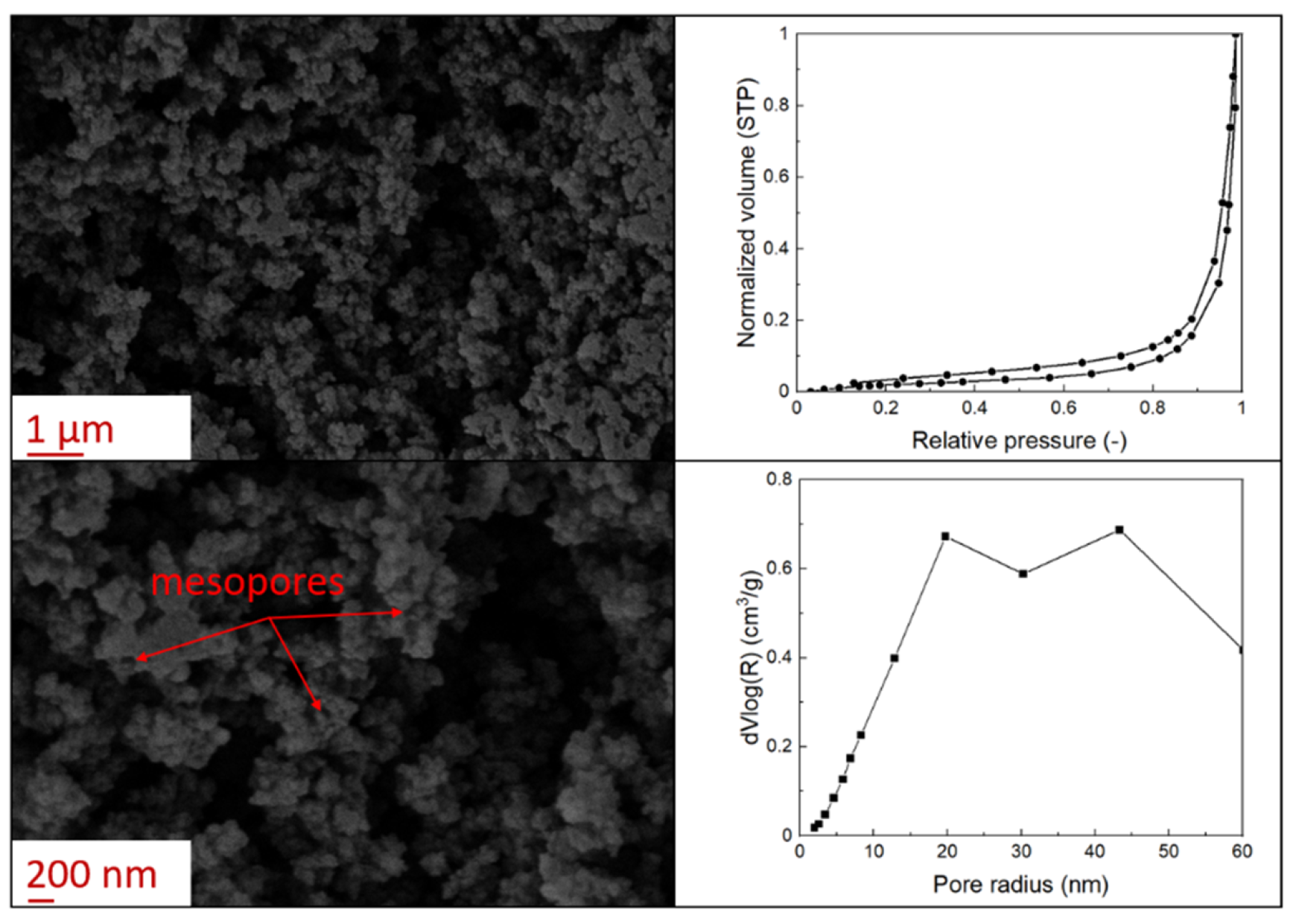
2.8. Specific Surface Area and Pore Size
2.9. Specific Density
2.10. Oil Content
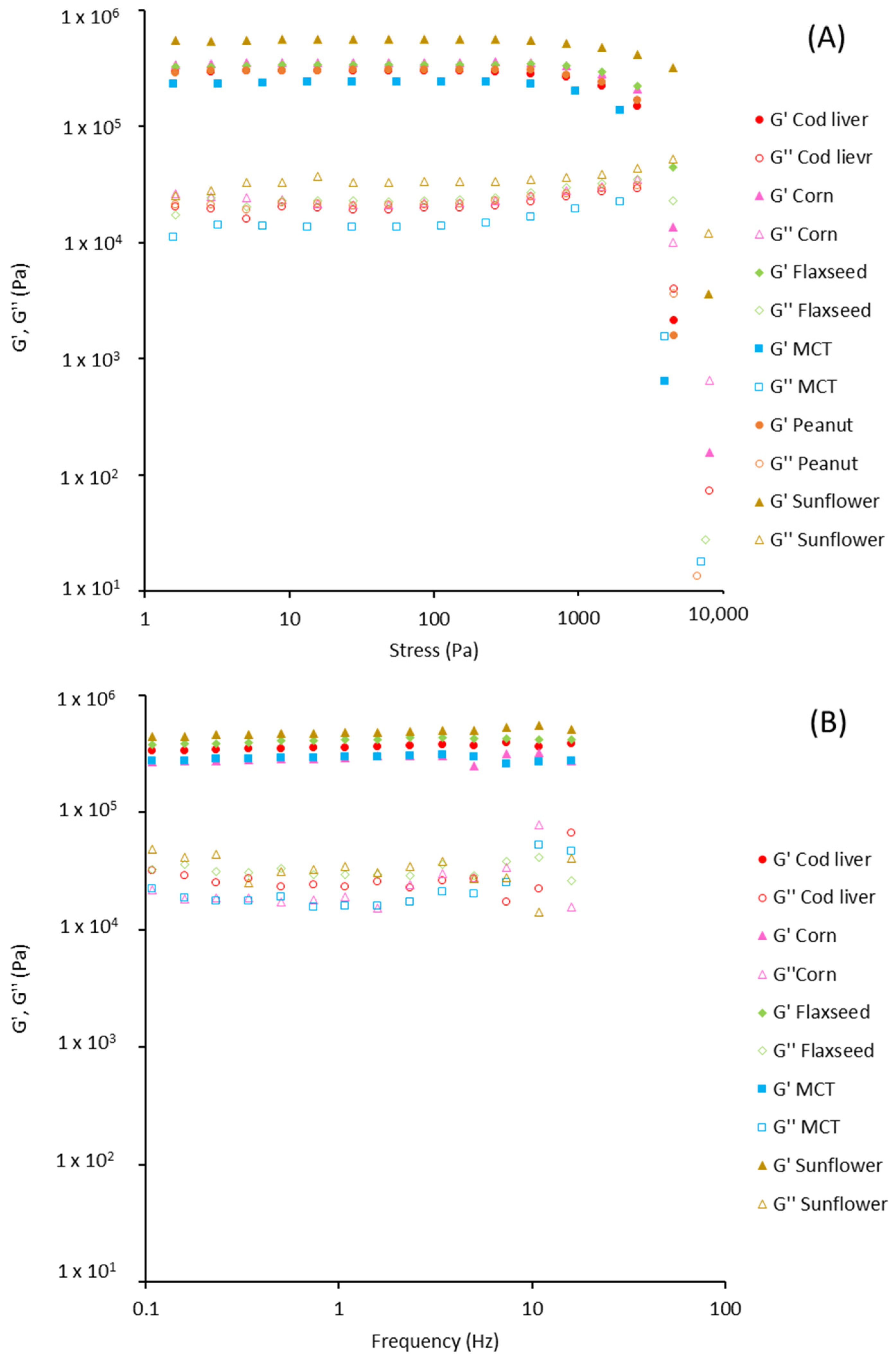
2.11. Rheological Analysis
2.12. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Aerogel Particle Properties
3.2. Oil Properties
3.3. Oleogel Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, A.R. Alternative Routes to Oil Structuring; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, H.S. A critical review on structures, health effects, oxidative stability, and sensory properties of oleogels. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 26, 101657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Maleky, F. A critical review of the last 10 years of oleogels in food. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, E.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Organogels: An alternative edible oil-structuring method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 749–780. [Google Scholar]
- Calligaris, S.; Alongi, M.A.; Lucci, P.; Anese, M. Effect of different oleogelators on lipolysis and curcuminoid bioaccessibility upon in vitro digestion of sunflower oil oleogels. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Lv, M.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Rogers, M.; Cao, Y.; Lan, Y. In vitro gastrointestinal digestibility of phytosterol oleogels: Influence of self-assembled microstructures on emulsification efficiency and lipase activity. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9503–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, T.C.; Martins, A.J.; Pastrana, L.; Pereira, M.C.; Cerqueira, M.A. Oleogel-based systems for the delivery of bioactive compounds in foods. Gels 2021, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.R.; Dewettinck, K. Edible oil structuring: An overview and recent updates. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.R.; Cludts, N.; Sintang, M.D.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Edible oleogels based on water soluble food polymers: Preparation, characterization and potential application. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gravelle, A.J.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Ethylcellulose oleogels: Manufacturing considerations and effects of oil oxidation. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, E. Edible oleogels: How suitable are proteins as a structurant? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 27, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R. Structuring edible oils with hydrocolloids: Where do we stand? Food Biophys. 2018, 13, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzocco, L.; Valoppi, F.; Calligaris, S.; Andreatta, F.; Spilimbergo, S.; Nicoli, M.C. Exploitation of κ-carrageenan aerogels as template for edible oleogel preparation. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 71, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazzotta, S.; Calligaris, S.; Manzocco, L. Structure of oleogels from κ-carrageenan templates as affected by supercritical-CO2-drying, freeze-drying and lettuce-filler addition. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, A.; Hendriks, J.; van der Linden, E.; Scholten, E. Protein oleogels from protein hydrogels via a stepwise solvent exchange route. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13850–13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, A.; Wesseling, A.; van der Linden, E.; Scholten, E. Protein oleogels from heat-set whey protein aggregates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 486, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, K.; Budtova, T.; Ratke, L.; Gurikov, P.; Baudron, V.; Preibisch, I.; Niemeyer, P.; Smirnova, I.; Milow, B. Review on the production of polysaccharide aerogel particles. Materials 2018, 11, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selmer, I.; Karnetzke, J.; Kleemann, C.; Lehtonen, M.; Mikkonen, K.S.; Kulozik, U.; Smirnova, I. Encapsulation of fish oil in protein aerogel micro-particles. J. Food Eng. 2019, 260, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzocco, L.; Mikkonen, K.S.; García-González, C.A. Aerogels as porous structures for food applications: Smart ingredients and novel packaging materials. Food Struct. 2021, 28, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, M.; García-González, C.A.; Subrahmanyam, R.P.; Smirnova, I.; Kulozik, U. Preparation of novel whey protein-based aerogels as drug carriers for life science applications. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 72, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Dorado, R.; López-Iglesias, C.; García-González, C.A.; Auriemma, G.; Aquino, R.P.; Del Gaudio, P. Design of aerogels, cryogels and xerogels of alginate: Effect of molecular weight, gelation conditions and drying method on particles’ micromeritics. Molecules 2019, 24, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baudron, V.; Gurikov, P.; Smirnova, I.; Whitehouse, S. Porous starch materials via supercritical-and freeze-drying. Gels 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzocco, L.; Plazzotta, S.; Powell, J.; de Vries, A.; Rousseau, D.; Calligaris, S. Structural characterisation and sorption capability of whey protein aerogels obtained by freeze-drying or supercritical drying. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, C.; Schuster, R.; Rosenecker, E.; Selmer, I.; Smirnova, I.; Kulozik, U. In-vitro-digestion and swelling kinetics of whey protein, egg white protein and sodium caseinate aerogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, C.A.; Budtova, T.; Durães, L.; Erkey, C.; Del Gaudio, P.; Gurikov, P.; Koebel, M.; Liebner, F.; Neagu, M.; Smirnova, I. An opinion paper on zerogels for biomedical and environmental applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plazzotta, S.; Calligaris, S.; Manzocco, L. Structural characterization of oleogels from whey protein aerogel particles. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Andlinger, D.J.; Bornkeßel, A.C.; Jung, I.; Schroeter, B.; Smirnova, I.; Kulozik, U. Microstructures of potato protein hydrogels and aerogels produced by thermal crosslinking and supercritical drying. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmer, I.; Kleemann, C.; Kulozik, U.; Heinrich, S.; Smirnova, I. Development of egg white protein aerogels as new matrix material for microencapsulation in food. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 106, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, A.C.; Okuro, P.K.; Badan, A.P.; Cunha, R.L. Role of the oil on glyceryl monostearate based oleogels. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Zárate, M.; De la Peña-Gil, A.; Álvarez-Mitre, F.M.; Charó-Alonso, M.A.; Toro-Vazquez, J.F. Vegetable and mineral oil organogels based on monoglyceride and lecithin mixtures. Food Biophys. 2019, 14, 326–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valoppi, F.; Calligaris, S.; Barba, L.; Šegatin, N.; Poklar Ulrih, N.; Nicoli, M.C. Influence of oil type on formation, structure, thermal, and physical properties of monoglyceride-based organogel. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 119, 1500549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.J.; Nan, Y.; Liu, G.Q. The effects of oil type and crystallization temperature on the physical properties of vitamin C-loaded oleogels prepared by an emulsion-templated approach. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8028–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, A.; Gomez, Y.L.; Van der Linden, E.; Scholten, E. The effect of oil type on network formation by protein aggregates into oleogels. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 11803–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lizhi, H.; Toyoda, K.; Ihara, I. Dielectric properties of edible oils and fatty acids as a function of frequency, temperature, moisture and composition. J. Food Eng. 2008, 88, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.I.; Marangoni, A.G. Factors affecting the rheological properties of a structured cellular solid used as a fat mimetic. Food Res. Int. 2015, 74, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calligaris, S.; Mirolo, G.; Da Pieve, S.; Arrighetti, G.; Nicoli, M.C. Effect of oil type on formation, structure and thermal properties of γ-oryzanol and β-sitosterol-based organogels. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, C.; Selmer, I.; Smirnova, I.; Kulozik, U. Tailor made protein based aerogel particles from egg white protein, whey protein isolate and sodium caseinate: Influence of the preceding hydrogel characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, T. Formation and functionality of self-assembled whey protein microgels. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 137, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Cheftel, J.C. Texture characteristics, protein solubility, and sulfhydryl group/disulfide bond contents of heat-induced gels of whey protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, N.; Purcell, J.M.; Ptashkin, S.M. Thermal denaturation of whey proteins in skim milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 2167–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.F.; Ting, W. An automated approach for analysis of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectra of edible oils. Talanta 2012, 88, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurdeniz, G.; Tokatli, F.; Ozen, B. Differentiation of mixtures of monovarietal olive oils by mid-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohman, A.; Che Man, Y.B. Quantification and classification of corn and sunflower oils as adulterants in olive oil using chemometrics and FTIR spectra. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 250795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Niu, S.; Lu, C. Pyrolysis characteristics of castor oil through thermogravimetric coupled with fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 3705–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Oil | Castor | Cod Liver | Corn | Flax Seed | MCT | Peanut | Sunflower |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity (Pa s) | 1.010 ± 0.002 a | 0.063 ± 0.003 b,c | 0.064 ± 0.003 b,c | 0.053 ± 0.003 c | 0.030 ± 0.002 d | 0.080 ± 0.001 b | 0.077 ± 0.014 b |
| ε′ * | 4.55 | 3.20 | 3.15 | 3.27 | 3.75 | 3.10 | 3.18 |
| Oil | Appearance | Optical Micrograph | Confocal Micrograph | Oil Content (%, w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Castor |  |  | 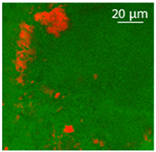 | n.d. |
| Cod liver |  | 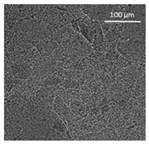 | 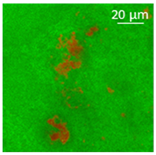 | 78.6 ± 0.7 a |
| Corn |  | 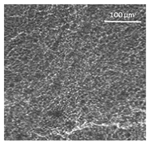 | 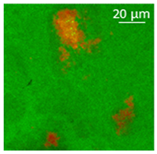 | 80.9 ± 0.4 a |
| Flaxseed |  | 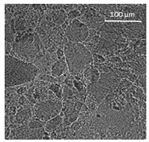 | 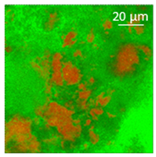 | 81.4 ± 1.6 a |
| MCT |  | 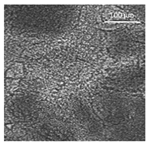 | 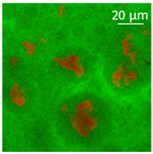 | 82.6 ± 0.6 a |
| Peanut |  | 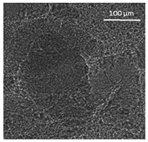 |  | 79.2 ± 1.8 a |
| Sunflower |  | 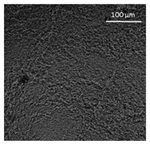 | 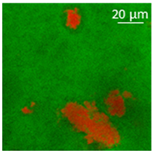 | 82.2 ± 3.7 a |
| Oil | G′ (Pa) × 105 | G″ (Pa) × 105 | Critical Stress (Pa) | Tan δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cod liver | 3.3 ± 0.4 a | 0.22 ± 0.02 a | 793.3 ± 59 a | 0.065 ± 0.002 a,b |
| Corn | 3.0 ± 0.4 a | 0.21 ± 0.04 a | 848.9 ± 30 a | 0.073 ± 0.006 a |
| Flaxseed | 4.3 ± 0.1 a | 0.29 ± 0.02 a | 873.7 ± 48 a | 0.069 ± 0.002 a |
| MCT | 3.5 ± 0.4 a | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 884.5 ± 3.8 a | 0.054 ± 0.003 b |
| Peanut | 3.9 ± 0.1 a | 0.25 ± 0.08 a | 849.2 ± 4.9 a | 0.074 ± 0.007 a |
| Sunflower | 4.4 ± 0.5 a | 0.26 ± 0.09 a | 818.7 ± 13 a | 0.067 ± 0.005 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plazzotta, S.; Jung, I.; Schroeter, B.; Subrahmanyam, R.P.; Smirnova, I.; Calligaris, S.; Gurikov, P.; Manzocco, L. Conversion of Whey Protein Aerogel Particles into Oleogels: Effect of Oil Type on Structural Features. Polymers 2021, 13, 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234063
Plazzotta S, Jung I, Schroeter B, Subrahmanyam RP, Smirnova I, Calligaris S, Gurikov P, Manzocco L. Conversion of Whey Protein Aerogel Particles into Oleogels: Effect of Oil Type on Structural Features. Polymers. 2021; 13(23):4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234063
Chicago/Turabian StylePlazzotta, Stella, Isabella Jung, Baldur Schroeter, Raman P. Subrahmanyam, Irina Smirnova, Sonia Calligaris, Pavel Gurikov, and Lara Manzocco. 2021. "Conversion of Whey Protein Aerogel Particles into Oleogels: Effect of Oil Type on Structural Features" Polymers 13, no. 23: 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234063
APA StylePlazzotta, S., Jung, I., Schroeter, B., Subrahmanyam, R. P., Smirnova, I., Calligaris, S., Gurikov, P., & Manzocco, L. (2021). Conversion of Whey Protein Aerogel Particles into Oleogels: Effect of Oil Type on Structural Features. Polymers, 13(23), 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234063