Iron-Loaded Carbon Aerogels Derived from Bamboo Cellulose Fibers as Efficient Adsorbents for Cr(VI) Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Fe/CA
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.4.1. The Effect of pH on Cr(VI) Removal Efficiency
2.4.2. The Effect of Initial Cr(VI) Concentration on Cr(Ⅵ) Removal Efficiency
2.4.3. The Effect of Contact Time on Cr(VI) Removal Efficiency
3. Results and Discussion
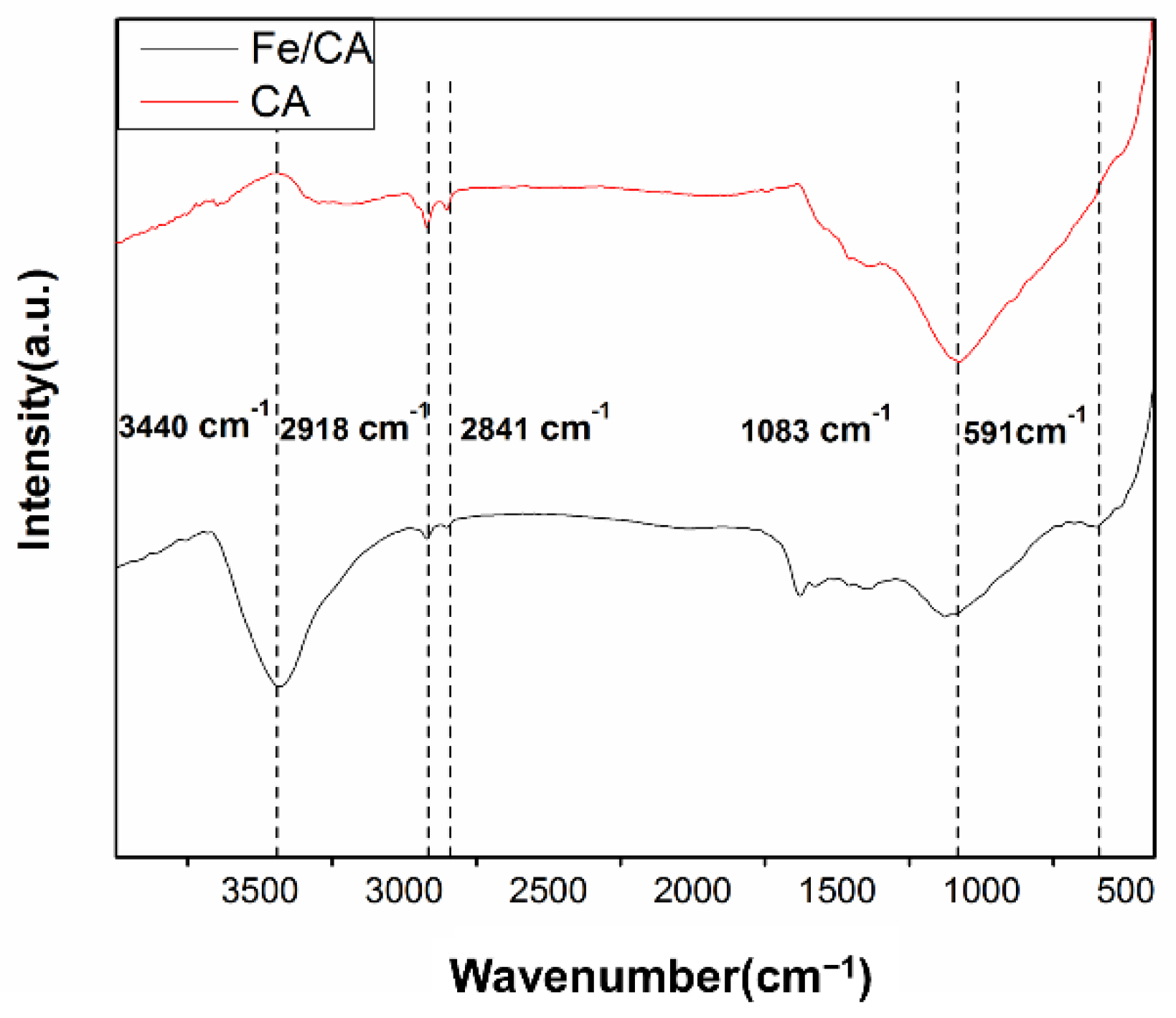
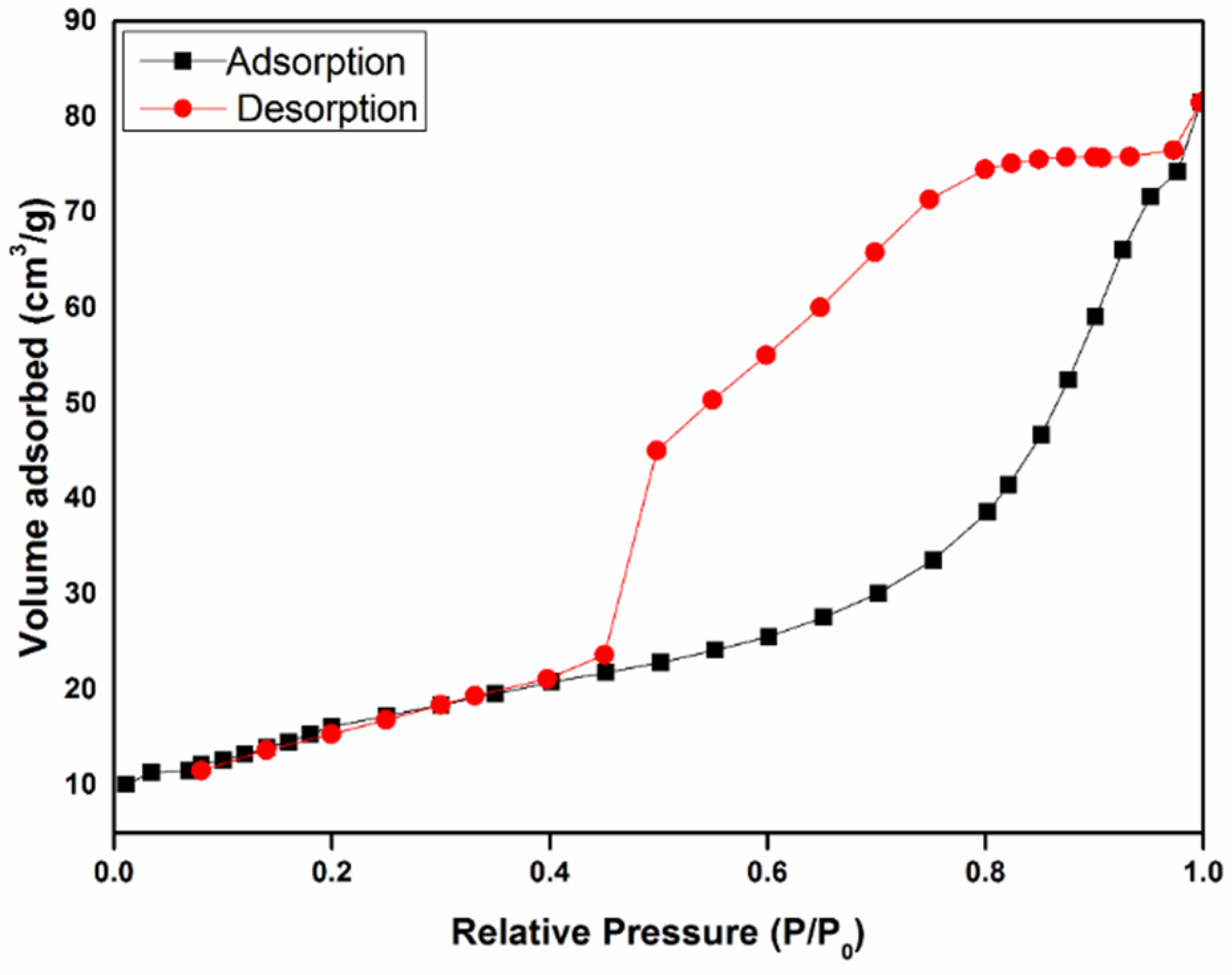
3.1. The Morphological and Structural Characterizations of CA and Fe/CA
3.2. Cr(VI) Removal Performance
3.2.1. The Effect of pH on the Adsorption Capacity
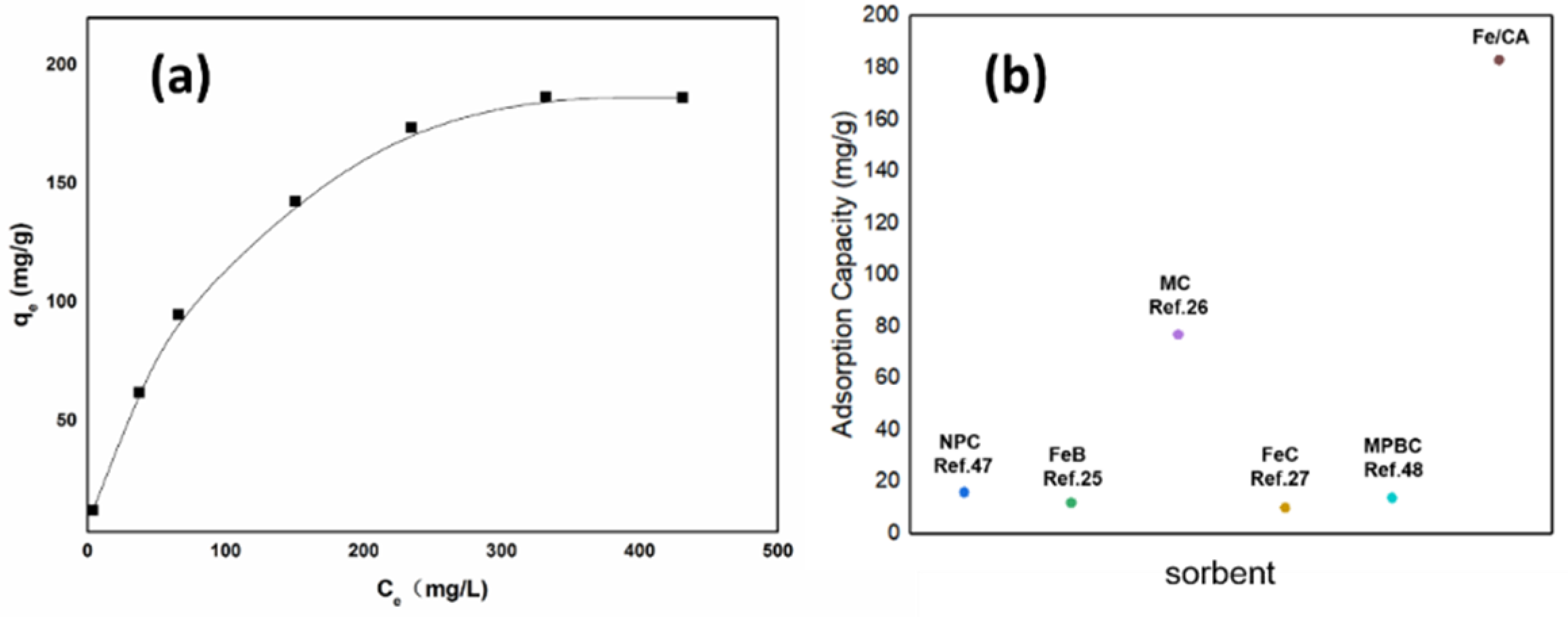
3.2.2. Adsorption Isotherms
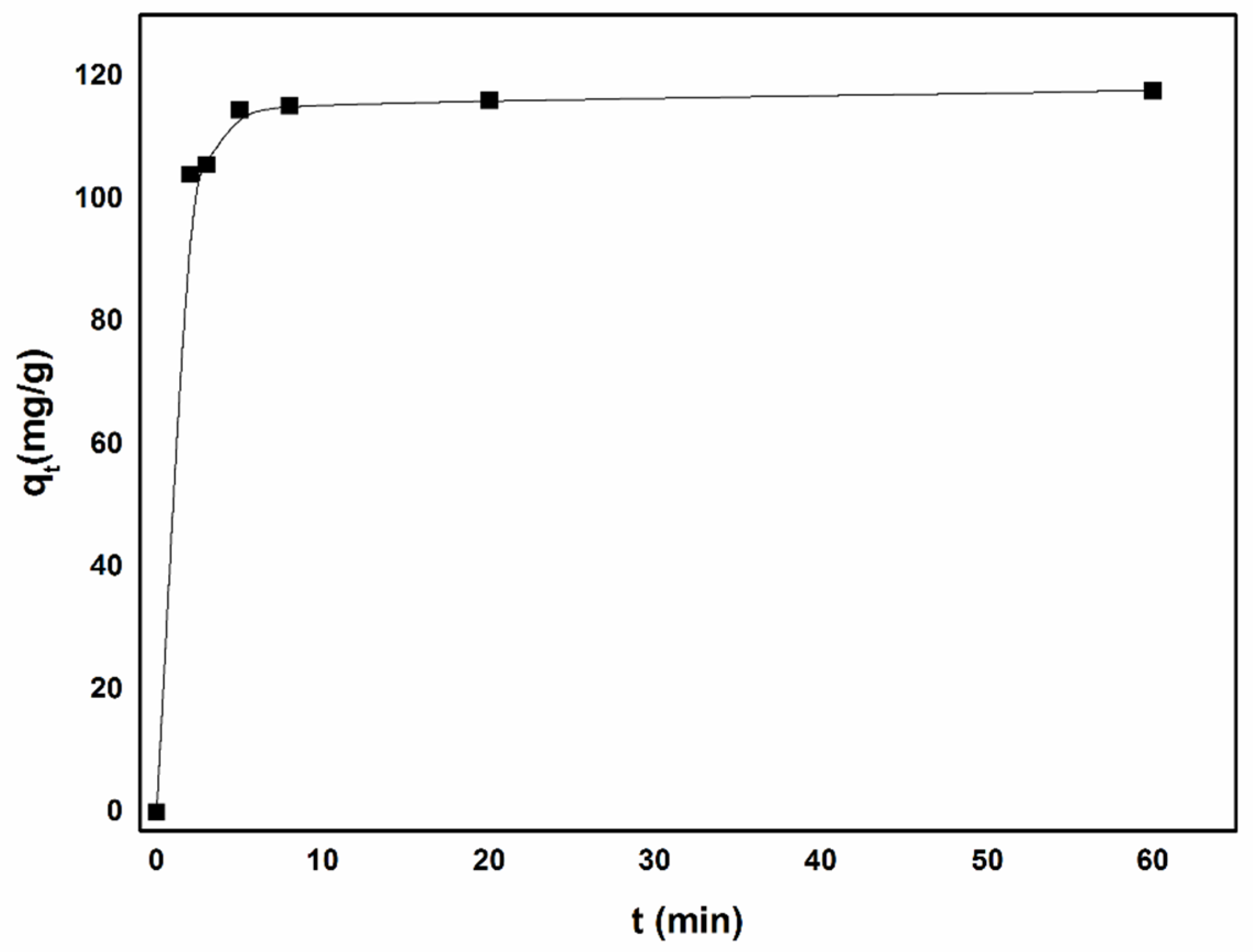
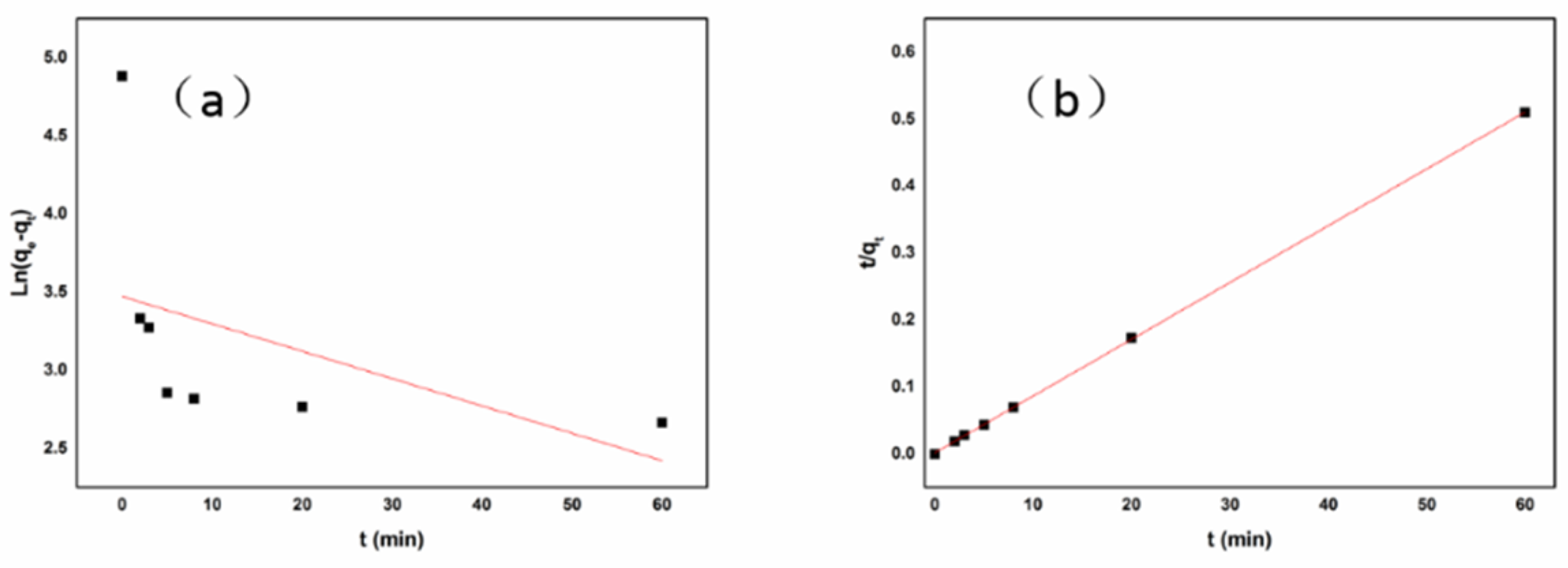
3.2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
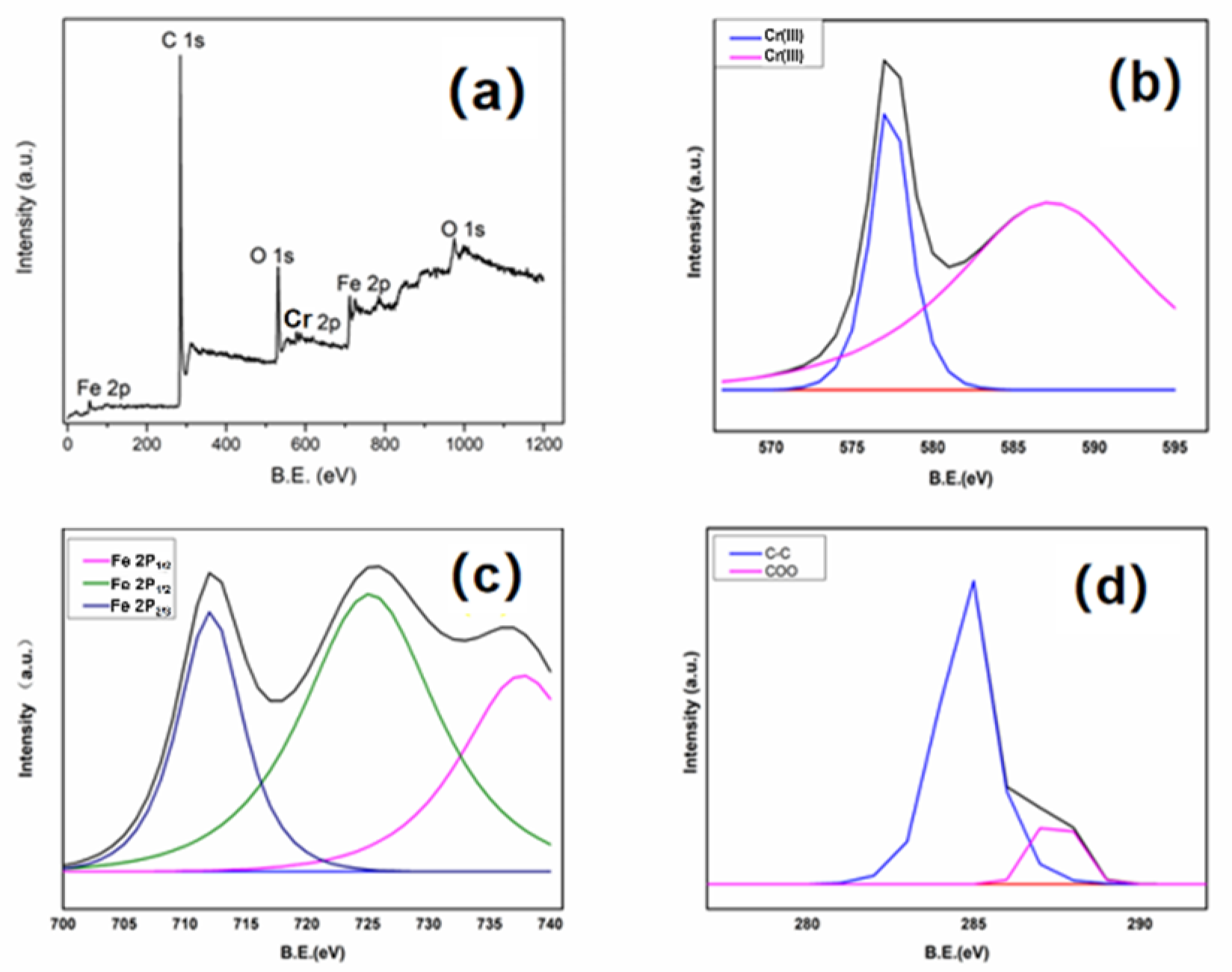
3.3. Cr(VI) Removal Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Das, S.; Ghorai, U.; Bose, M.; Ghosh, S.; Mondal, M.; Das, A.K.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.C. Microwave assisted green synthesis of Zwitterionic photolumenescent N-doped carbon dots: An efficient ‘on-off’ chemosensor for tracer Cr(+6) considering the inner filter effect and nano drug-delivery vector. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 579, 123604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Margel, S. Review: Remotely controlled magneto-regulation of therapeutics from magnetoelastic gel matrices. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 44, 107611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, B.; Fullana, A. Heavy metal release due to aging effect during zero valent iron nanoparticles remediation. Water Res. 2015, 83, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, J.; Dou, M.; Wang, F. Removal of Cr6+ from wastewater via adsorption with high-specific-surface-area nitro-gen-doped hierarchical porous carbon derived from silkworm cocoon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 405, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Grafting of polyethylenimine onto cellulose nanofibers for interfacial enhancement in their epoxy nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 157, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, F.M.; El-Ghoul, Y.; Jabli, M. Extraction of Cellulose Polymeric Material from Populus tremula Fibers: Characterization and Application to the Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Crystal Violet. Polymers 2021, 13, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaku, J.F.; Nnaji, J.C.; Ogundare, S.A.; Akpomie, K.G.; Ngwu, C.M.; Chukwuemeka-Okorie, H.O.; Zubairu, S.M.; Ugwu, B.I.; Odoemelam, S.A.; Conradie, J. Chrysophyllum albidum stem bark extract coated tillite adsorbent for the uptake of Cr(VI): Thermodynamic, kinetic, isotherm, and reusability. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; Ma, M. Functionalized electrospun nanofiber membranes for water treatment: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 739, 139944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, C.; Yu, L.; Jia, D.; Chen, W.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X. Layered silicate RUB-15 for efficient removal of UO22+ and heavy metal ions by ion-exchange. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.; Thakur, S.; Mamba, G.; Prateek; Gupta, R.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Thakur, V.K. Titania modified gum tragacanth based hydrogel nanocomposite for water remediation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 9, 104608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezarjaribi, M.; Bakeri, G.; Sillanpaa, M.; Chaichi, M.J.; Akbari, S.; Rahimpour, A. Novel adsorptive PVC nanofibrous/thiol-functionalized TNT composite UF membranes for effective dynamic removal of heavy metal ions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using carbon-based adsorbents: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 37, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owalude, S.O.; Tella, A.C. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by adsorption on modified groundnut hull. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizzi, A. Chromium Interactions in CCA/CCB Wood Preservatives. Part, I. Interactions with Wood Carbohydrates. Holzforsch.—Int. J. Biol. Chem. Phys. Technol. Wood 1990, 44, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singare, P.U. Fluidized aerobic bio-reactor technology in treatment of textile effluent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ying, L.; Liu, X.; Deng, B.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bin, B.; Ren, Z. Equilibrium adsorption study of the adsorptive removal of Cd 2+ and Cr 6+ using activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sarojini, G.; Samikkannu, V.B.; Rajamohan, N.; Kumar, P.S.; Rajasimman, M. Surface modified polymer-magnetic-algae nanocomposite for the removal of chromium- equilibrium and mechanism studies. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Lu, L. Removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by magnetic biochar derived from bagasse. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Robeldo-Cabera, A.; Lopez-Valdivieso, A. Highly surface activated carbon to remove Cr(VI) from aqueous solution with adsorbent recycling. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Yin, Y.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Jiang, L.; Ding, Y.; et al. Investigation of the adsorption-reduction mechanisms of hexavalent chromium by ramie biochars of different pyrolytic temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Chen, M.; Gu, H.; Rapole, S.B.; Pallavkar, S.; Ho, T.C.; Hopper, J.; Guo, Z. Magnetic nanocomposites for environmental remediation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z. Removal of chromium (VI) from water by porous carbon derived from corn straw: Influencing factors, regeneration and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Rui, T.; Lu, C.; He, X.; Zhang, W. Mechanically robust, flame-retardant and anti-bacterial nanocomposite films comprised of cellulose nanofibrils and magnesium hydroxide nanoplatelets in a regenerated cellulose matrix. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1859–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.K.; Frollini, E.; Thakur, V.K. Cellulose nanocrystals: Pretreatments, preparation strategies, and surface functionalization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1554–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Deng, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, K.; Zeng, G. Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cao, X.; Ouyang, X.; Sohi, S.P.; Chen, J. Adsorption kinetics of magnetic biochar derived from peanut hull on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: Effects of production conditions and particle size. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Ma, B.; Chen, S. Carbothermal preparation of porous carbon-encapsulated iron composite for the removal of trace hexavalent chromium. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Ao, C.; Xia, T.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Ultra-lightweight and highly porous carbon aerogels from bamboo pulp fibers as an effective sorbent for water treatment. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 2919–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Nayak, A. Cadmium removal and recovery from aqueous solutions by novel adsorbents prepared from orange peel and Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 180, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhenga, H.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Herbert, S.; Xing, B. Characterization and influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emission from agricultural soil. J. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174C, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Wooten, J.B.; Baliga, V.L.; Lin, X.; Chan, W.G.; Hajaligol, M.R. Characterization of chars from pyrolysis of lignin. Fuel 2004, 83, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wu, C.; Cheng, Y.; He, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, H. Carbon nanotubes promote Cr(VI) reduction by alginate-immobilized Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 77, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Cheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X. Novel fungus-Fe3O4 bio-nanocomposites as high performance adsorbents for the removal of radionuclides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Pi, J.; Zong, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Liao, Q. Chromium removal using magnetic biochar derived from herb-residue. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 68, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Magnetic Porous Carbonaceous Material Produced from Tea Waste for Efficient Removal of As(V), Cr(VI), Humic Acid, and Dyes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4371–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Ci, S.; Zhang, F.; Feng, X.; Cui, S.; Mao, S.; Luo, S.; He, Z.; Chen, J. Nitrogen-Enriched Core-Shell Structured Fe/Fe3 C–C Nanorods as Advanced Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boi, F.S.; Hu, Y.; Wen, J. New insights on the dynamics of the γ-Fe/α-Fe phase-transition inside iron-filled carbon nanotubes. Rsc Adv. 2017, 7, 25025–25030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Qian, F.; Liu, Y.; Matera, D.; Wu, G.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Controllable synthesis of magnetic carbon composites with high porosity and strong acid resistance from hydrochar for efficient removal of organic pollutants: An overlooked influence. Carbon 2016, 99, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Peng, F. Nitrogen doped carbon nanotubes with encapsulated ferric carbide as excellent electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in acid and alkaline media. J. Power Sources 2015, 286, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Bajpai, A.K. Dynamic Column Adsorption Studies of Toxic Cr(VI) Ions onto Iron Oxide Loaded Gelatin Nanopar-ticles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2011, 32, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Li, X.Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, H.P. Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface 2006, 120, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.C.; Liang, J.B.; Peng, W.Q.; Wang, Z.M.; Negishi, N.; Koike, K.; Chu, Y.H.; Yin, H.Q. Photocatalytic properties of fresh and pyrolyzed transparent nanocomposite films lay-er-by-layer fabricated from alternative layers of graphene and titanate nanotube. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 40, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, D.; Gu, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Weeks, B.L.; Guo, Z.; et al. Polyethylenimine Facilitated Ethyl Cellulose for Hexavalent Chromium Removal with a Wide pH Range. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19816–19824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Weeks, B.L.; O’Connor, R.; Huang, X.; Wei, S.; Guo, Z. Cr(VI) removal by magnetic carbon nanocomposites derived from cellulose at different carboni-zation temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9817–9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Gu, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, M.; Wei, H.; Luo, Z.; Colorado, H.A.; Yerra, N.; Ding, D.; Ho, T.C.; et al. Mesoporous magnetic carbon nanocomposite fabrics for highly efficient Cr(VI) removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, W.E.; Franca, A.S.; Oliveira, L.S.; Rocha, S.D. Untreated coffee husks as biosorbents for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhu, C.; Lu, T.; Zhang, D.; Ma, J. N-doped porous carbon with magnetic particles formed in situ for enhanced Cr(VI) removal. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4188–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguyal, F.; Sarmah, A.K.; Gao, W. Synthesis of magnetic biochar from pine sawdust via oxidative hydrolysis of FeCl2 for the removal sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Gu, H.; Yan, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Q.; Khan, M.; Zhang, X.; Weeks, B.L.; et al. Cellulose derived magnetic mesoporous carbon nanocomposites with enhanced hexavalent chromium removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17454–17462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wen, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Efficient removal of a typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 63110–63117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, X.; Yuan, W.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ao, C.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Iron-Loaded Carbon Aerogels Derived from Bamboo Cellulose Fibers as Efficient Adsorbents for Cr(VI) Removal. Polymers 2021, 13, 4338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244338
Xue X, Yuan W, Zheng Z, Zhang J, Ao C, Zhao J, Wang Q, Zhang W, Lu C. Iron-Loaded Carbon Aerogels Derived from Bamboo Cellulose Fibers as Efficient Adsorbents for Cr(VI) Removal. Polymers. 2021; 13(24):4338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244338
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Xiaolin, Wei Yuan, Zhuo Zheng, Jian Zhang, Chenghong Ao, Jiangqi Zhao, Qunhao Wang, Wei Zhang, and Canhui Lu. 2021. "Iron-Loaded Carbon Aerogels Derived from Bamboo Cellulose Fibers as Efficient Adsorbents for Cr(VI) Removal" Polymers 13, no. 24: 4338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244338
APA StyleXue, X., Yuan, W., Zheng, Z., Zhang, J., Ao, C., Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Zhang, W., & Lu, C. (2021). Iron-Loaded Carbon Aerogels Derived from Bamboo Cellulose Fibers as Efficient Adsorbents for Cr(VI) Removal. Polymers, 13(24), 4338. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244338







