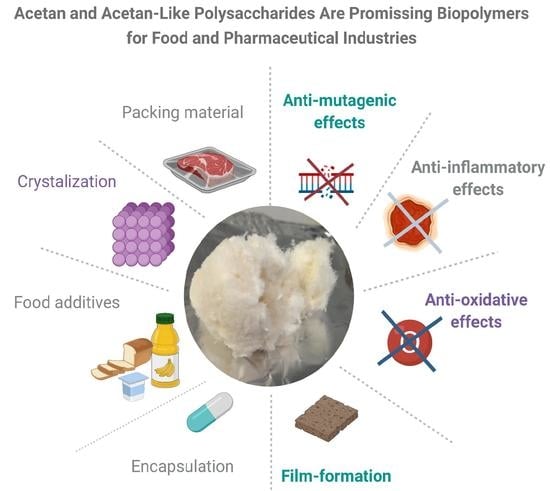
Acetan and Acetan-Like Polysaccharides: Genetics, Biosynthesis, Structure, and Viscoelasticity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemical Composition and Synthesis of Acetan and Acetan-Like Polysaccharides
3. Genetic Basis of Acetan Production in Komagataeibacter spp. and Acetobacter spp.
4. Viscoelasticity of Acetan Solutions
Viscoelasticity of Acetan Binary Mixtures
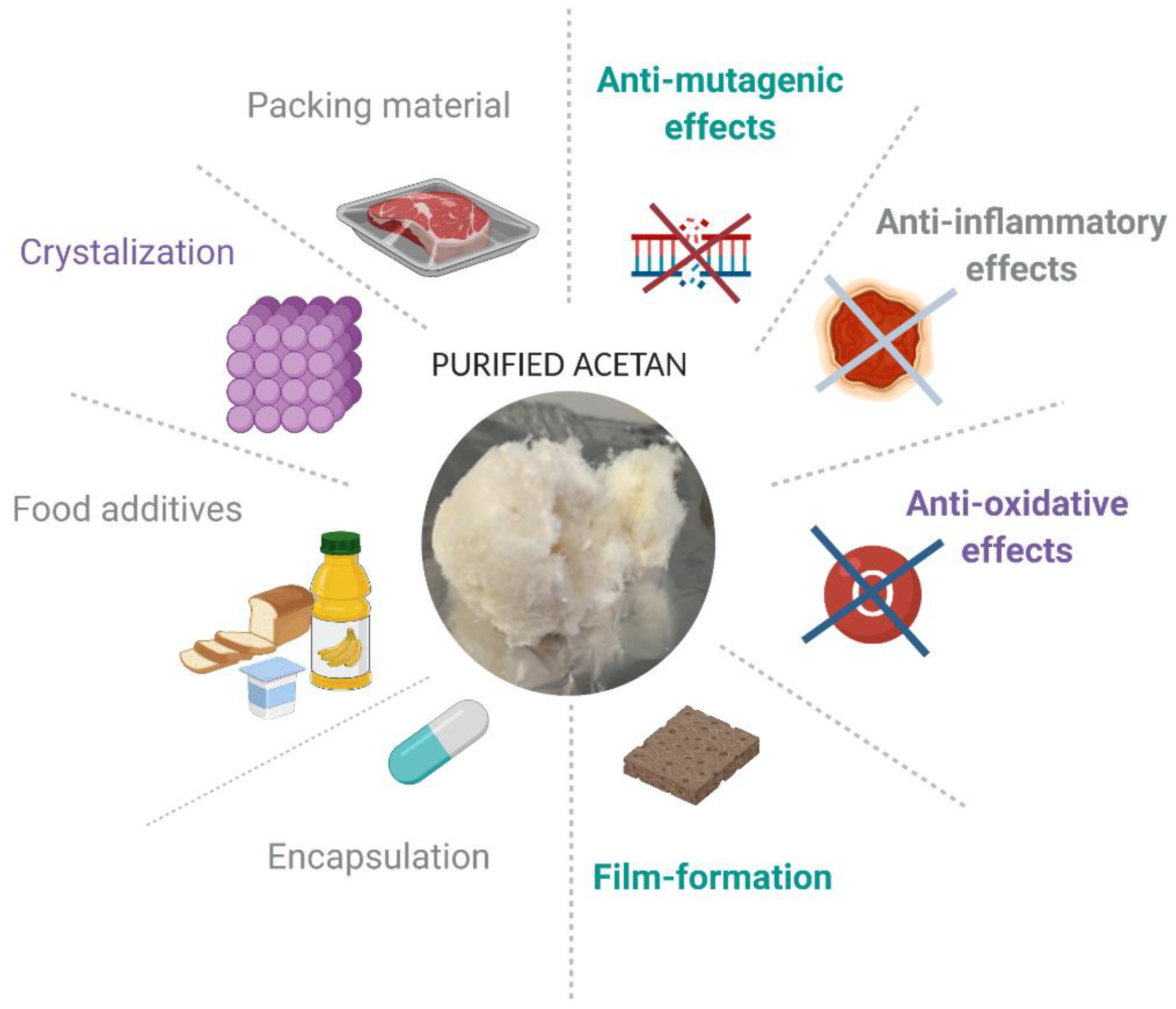
5. Potential Applications of Acetan in Industry
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Couso, R.O.; Ielpi, L.; Dankert, M.A. A Xanthan-gum-like Polysaccharide from Acetobacter xylinum. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1987, 133, 2123–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marič, L.; Cleenwerck, I.; Accetto, T.; Vandamme, P.; Trček, J. Description of Komagataeibacter melaceti sp. nov. and Komagataeibacter melomenusus sp. nov. Isolated from Apple Cider Vinegar. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Catchmark, J.M. Characterization of water-soluble exopolysaccharides from Gluconacetobacter xylinus and their impacts on bacterial cellulose crystallization and ribbon assembly. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3965–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Catchmark, J.M. Characterization of cellulose and other exopolysaccharides produced from Gluconacetobacter strains. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Mitarai, M.; Sugano, Y.; Shoda, M. Role of water-soluble polysaccharides in bacterial cellulose production. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 83, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangok, B.; Sugano, Y.; Shoda, M. Comparison of Bacterial Cellulose Production in a Jar Fermentor Between Acetobacter xylinus BPR2001 and its Mutant, Acetan-Nonproducing Strain EP1. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 15, 247–253. [Google Scholar]
- Molina-Ramírez, C.; Castro, M.; Osorio, M.; Torres-Taborda, M.; Gómez, B.; Zuluaga, R.; Gómez, C.; Gañán, P.; Rojas, O.J.; Castro, C. Effect of different carbon sources on bacterial nanocellulose production and structure using the low pH resistant strain Komagataeibacter medellinensis. Materials 2017, 10, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, C.; Cleenwerck, I.; Trček, J.; Zuluaga, R.; de Vos, P.; Caro, G.; Aguirre, R.; Putaux, J.L.; Gañán, P. Gluconacetobacter medellinensis sp. nov., cellulose- and non-cellulose-producing acetic acid bacteria isolated from vinegar. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, C.H.S.G.; Rouws, L.F.M.; Simões-Araújo, J.L.; Vidal, M.S.; Baldani, J.I. Exopolysaccharide production is required for biofilm formation and plant colonization by the nitrogen-fixing endophyte Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrato, R.V.; Meneses, C.H.S.G.; Vidal, M.S.; Santana-Filho, A.P.; Iacomini, M.; Sassaki, G.L.; Baldani, J.I. Structural studies of an exopolysaccharide produced by Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Pal5. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, P.E.; Lindberg, J.; Wimalasiri, K.M.S.; Dankert, M.A. Structural studies of acetan, an exopolysaccharide elaborated by Acetobacter xylinum. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 245, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibberg, D.; Alkhateeb, R.S.; Winkler, A.; Albersmeier, A.; Schatschneider, S.; Albaum, S.; Niehaus, K.; Hublik, G.; Pühler, A.; Vorhölter, F.J. Draft genome of the xanthan producer Xanthomonas campestris NRRL B-1459 (ATCC 13951). J. Biotechnol. 2015, 204, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valla, S.; Kjosbakken, J. Isolation and characterization of a new extracellular polysaccharide from a cellulose-negative strain of Acetobacter xylinum. Can. J. Microbiol. 1981, 27, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couso, R.O.; Ielpi, L.; Garcia, R.C.; Dankert, M.A. Biosynthesis of Polysaccharides in Acetobacter xylinum. Eur. J. Biochem. 1982, 123, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.M.; Poelwijk, E.S.; Morris, V.J.; Gasson, M.J. Cloning of the aceF gene encoding the phosphomannose isomerase and GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase activities involved in acetan biosynthesis in Acetobacter xylinum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 154, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ojinnaka, C.; Jay, A.J.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Brownsey, G.J.; Morris, E.R.; Morris, V.J. Structure and conformation of acetan polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1996, 19, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Qu, J.; Tian, X.; Zhao, X.; Shen, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, P.; Li, G.; Ma, T. Tailor-made polysaccharides containing uniformly distributed repeating units based on the xanthan gum skeleton. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradali, M.F.; Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial biopolymers: From pathogenesis to advanced materials. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial polymers: Biosynthesis, modifications and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Iannino, N.I.; Couso, R.O.; Dankert, M.A. Lipod-linked Intermediates and Synthesis of Acetan in Acetobacter xylinum. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1988, 134, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Semino, C.E.; Dankert, M.A. In vitro biosynthesis of acetan using electroporated Acetobacter xylinum cells as enzyme preparations. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1993, 139, 2745–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Sugano, Y.; Shoda, M. Novel glycosyltransferase genes involved in the acetan biosynthesis of Acetobacter xylinum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 295, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorhölter, F.J.; Schneiker, S.; Goesmann, A.; Krause, L.; Bekel, T.; Kaiser, O.; Linke, B.; Patschkowski, T.; Rückert, C.; Schmid, J.; et al. The genome of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris B100 and its use for the reconstruction of metabolic pathways involved in xanthan biosynthesis. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 134, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.M.; Morris, V.J.; Gasson, M.J. Identification, cloning and sequencing the aceA gene involved in acetan biosynthesis in Acetobacter xylinum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 137, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brandt, J.U.; Jakob, F.; Behr, J.; Geissler, A.J.; Vogel, R.F. Dissection of exopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Kozakia baliensis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Petroni, E.A.; Ielpi, L. Isolation and Nucleotide Sequence of the GDP-Mannose: Cellobiosyl- Gene from Acetobacter xylinum. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4814–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, K.J.; Jay, A.J.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Morris, V.J.; Gasson, M.J.; Griffin, A.M. Generation of novel polysaccharides by inactivation of the aceP gene from the acetan biosynthetic pathway in Acetobacter xylinum. Microbiology 1999, 145, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryngajłło, M.; Kubiak, K.; Jędrzejczak-Krzepkowska, M.; Jacek, P.; Bielecki, S. Comparative genomics of the Komagataeibacter strains—Efficient bionanocellulose producers. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, J.U.; Jakob, F.; Wefers, D.; Bunzel, M.; Vogel, R.F. Characterization of an acetan-like heteropolysaccharide produced by Kozakia baliensis NBRC 16680. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemura, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Koizumi, K.; Utamura, T. Occurrence of extracellular (1→2)-β-D-glucans and (1→2)-β-D-gluco-oligosaccharides in Acetobacter. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1985, 131, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tayama, K.; Minakami, H.; Fujiyama, S.; Masai, H.; Misaki, A. Structure of an Acidic Polysaccharide Elaborated by Acetobacter sp. NBI 1005. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, H.; Duboc, P.; Marison, I.; Von Stockar, U. Influence of Nutritional Factors on the Nature, Yield, and Composition of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Gluconacetobacter xylinus I-2281. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valepyn, E.; Berezina, N.; Paquot, M. Optimization of Production and Preliminary Characterization of New Exopolysaccharides from Gluconacetobacter hansenii LMG1524. Adv. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakami, H.; Entani, E.; Tayama, K.; Fujiyama, S.; Masai, H. Isolation and Characterization of a New Polysaccharide-producing Acetobacter sp. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1984, 48, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar]
- Zeidan, A.A.; Poulsen, V.K.; Janzen, T.; Buldo, P.; Derkx, P.M.F.; Øregaard, G.; Neves, A.R. Polysaccharide production by lactic acid bacteria: From genes to industrial applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, S168–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquhoun, I.J.; Defernez, M.; Morris, V.J. NMR studies of acetan and the related bacterial polysaccharide, CR1/4, produced by a mutant strain of Acetobacter xylinum. Carbohydr. Res. 1995, 269, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.M.; Morris, V.J.; Gasson, M.J. Genetic analysis of the acetan biosynthetic pathway in Acetobacter xylinum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1994, 16, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.M.; Morris, V.J.; Gasson, M.J. Genetic analysis of the acetan biosynthetic pathway in Acetobacter xylinum: Nucleotide sequence analysis of the aceB, aceC, aceD and aceE genes. DNA Seq. 1996, 6, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Katzen, F.; Pühler, A.; Ielpi, L. Xanthan gum biosynthesis and application: A biochemical/genetic perspective. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzen, F.; Ferreiro, D.U.; Oddo, C.G.; Ielmini, M.V.; Becker, A.; Pühler, A.; Ielpi, L. Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris gum mutants: Effects on xanthan biosynthesis and plant virulence. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda Ramulu, H.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D490–D495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Bryant, D. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.M.; Harrison, A.O.; Mcallister, S.M.; Polson, S.W.; Wommack, K.E. Iroki: Automatic customization and visualization of phylogenetic trees. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, V.J.; Brownsey, G.J.; Cairns, P.; Chilvers, G.R.; Miles, M.J. Molecular origins of acetan solution properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1989, 11, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, S.E.; Bert, G.; Hartmann, J.; Jumel, K.; Colfen, H. Physicochemical Studies on Xylinan (Acetan). III. Hydrodynamic Characterization by Analytical Ultracentrifugation and Dynamic Light Scattering. Biopolymers 1996, 39, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berth, G.; Dautzenberg, H.; Christensen, B.E.; Rother, G. Physicochemical Studies on Xylinan (Acetan). I. Characterization by Gel Permeation Chromatography on Sepharose CI-2B Coupled with Static Light Scattering and Viscometry. Biopolymers 1996, 39, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berth, G.; Dautzenberg, H.; Christensen, B.E.; Smidsrod, O. Physicochemical Studies on Xylinan (Acetan). II. Characterization by Static Light Scattering. Biopolymers 1996, 728, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.J. Acetan—A new bacterial polysaccharide. In Biotechnology and Bioactive Polymers; Gebelein, C.G., Carraher, C.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ridout, M.J.; Brownsey, G.J.; Morris, V.J.; Cairns, P. Physicochemical characterization of an acetan variant secreted by Acetobacter xylinum strain CR1/4. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1994, 16, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.E.; Smidsrød, O.; Stokke, B.T. The role of side-chains in the Cr3+-induced gelation of xanthan and xylinan (acetan) variants. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridout, M.J.; Cairns, P.; Brownsey, G.J.; Morris, V.J. Evidence for intermolecular binding between deacetylated acetan and the glucomannan konjac mannan. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 309, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridout, M.J.; Brownsey, G.J.; Morris, V.J. Synergistic interactions of acetan with carob or konjac mannan. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 2539–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojinnaka, C.; Brownsey, G.J.; Morris, E.R.; Morris, V.J. Effect of deacetylation on the synergistic interaction of acetan with locust bean gum or konjac mannan. Carbohydr. Res. 1997, 305, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, D.; Seal, R. Natural Food Additives, Ingredients and Flavourings; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012; 480p. [Google Scholar]
- Sabaa, M.W.; Hanna, D.H.; Abu Elella, M.H.; Mohamed, R.R. Encapsulation of bovine serum albumin within novel xanthan gum based hydrogel for protein delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djekic, L.; Martinović, M.; Dobričić, V.; Čalija, B.; Medarević, Đ.; Primorac, M. Comparison of the Effect of Bioadhesive Polymers on Stability and Drug Release Kinetics of Biocompatible Hydrogels for Topical Application of Ibuprofen. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcial-Coba, M.S.; Knøchel, S.; Nielsen, D.S. Low-moisture food matrices as probiotic carriers. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, C. The anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides in vitro: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 253, 117308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Yajima, T.; Nishimura, H.; Aiba, K.; Ishimitsu, R.; Matsuguchi, T.; Fushimi, T.; Ohshima, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Yoshikai, Y. Soluble branched β-(1,4)glucans from Acetobacter species show strong activities to induce interleukin-12 in vitro and inhibit T-helper 2 cellular response with immunoglobulin E production in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38571–38578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yajima, T.; Saito, K.; Nishimura, H.; Fushimi, T.; Ohshima, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Yoshikai, Y. Immunostimulating properties of intragastrically administered Acetobacter-derived soluble branched (1,4)-β-D-glucans decrease murine susceptibility to Listeria monocytogenes. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 7005–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiryo, Y.; Yajima, T.; Saito, K.; Nishimura, H.; Fushimi, T.; Ohshima, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Naito, S.; Yoshikai, Y. Soluble branched (1,4)-β-D-glucans from Acetobacter species enhance antitumor activities against MHC class I-negative and -positive malignant melanoma through augmented NK activity and cytotoxic T-cell response. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 115, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Bacterial Strain Designation according to the Present Taxonomy | Carbon Source in Growth Medium | Source of Extracellular Polysaccharide | Molecular Weight of Polysaccharide (Da or g/mol) | Monosaccharide Composition of Water-Soluble Polysaccharide | Analytical Method for Monosaccharides Identification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Komagataeibacter xylinus ATCC 10245, cellulose neg. mutant | Glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | >106 | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid | Gas-liquid chromatography, colorimetric analysis | [13] |
| Komagataeibacter medellinensis IFO 3288 | Glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | >1.5 × 105 | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, uronic acid | Gas-liquid chromatography, colorimetric analysis | [30] |
| Komagataeibacter xylinus IFO 13693 | Glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | >1.5 × 105 | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, uronic acid | Gas-liquid chromatography, colorimetric analysis | [30] |
| Komagataeibacter xylinus NBI 1005 | Sucrose | Precipitation from liquid medium | 106 | Glucose, mannose, galactose, glucuronic acid | Paper chromatography, 13C-NMR spectroscopy | [31] |
| Komagataeibacter xylinus NRRL B42 | Glucose | Extraction from cellulose-biofilm and precipitation from liquid medium | 2 × 106 | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid | Gas-liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry | [1] |
| Komagataeibacter xylinus I-2281 | Sucrose or glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid | Anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detector | [32] |
| Komagataeibacter hansenii LMG 1524 | Sucrose | Precipitation from liquid medium | 1.8 × 103, 2.5 × 103 | Glucose, galactose, mannose, xylose, arabinose, rhamnose | Gas-chromatography | [33] |
| Komagataeibacter hansenii ATCC 53582 | Glucose | Extraction from cellulose-biofilm | Approximately 1.5 × 105, 3 × 104, <5 × 103 | Glucose, mannose | Capillary ion chromatography | [3] |
| Komagataeibacter hansenii ATCC 53582 | Glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Approximately 1.5 × 105, 4 × 104, 104 | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid | Capillary ion chromatography | [3] |
| Komagataeibacter xylinus ATCC 53524 | Glucose | Extraction from cellulose-biofilm | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter xylinus ATCC 53524 | Galactose | Extraction from cellulose-biofilm | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter xylinus ATCC 53524 | Glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, galactose, glucuronic acid | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter xylinus ATCC 53524 | Galactose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter hansenii ATCC 53582 | Glucose | Extraction from cellulose-biofilm | Not known | Glucose, mannose | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter hansenii ATCC 53582 | Galactose | Extraction from cellulose-biofilm | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter hansenii ATCC 53582 | Glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter hansenii ATCC 53582 | Galactose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, galactose, glucuronic acid | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter sucrofermentans ATCC 700178 | Glucose | Extraction from cellulose-biofilm | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter sucrofermentans ATCC 700178 | Galactose | Extraction from cellulose-biofilm | Not known | Glucose, mannose | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter sucrofermentans ATCC 700178 | Glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, galactose, glucuronic acid | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Komagataeibacter sucrofermentans ATCC 700178 | Galactose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Not known | Glucose, mannose, rhamnose, galactose, glucuronic acid | Capillary ion chromatography | [4] |
| Acetobacter estunensis IFO 13751T | Sucrose | Precipitation from liquid medium | 106 | Glucose, mannose, galactose, glucuronic acid | Gas-liquid chromatography | [34] |
| Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus PAI5 | Mannitol | Precipitation from liquid medium | 8.72 × 105 | Glucose, mannose, galactose | Gas chromatography with mass spectroscopy | [10] |
| Kozakia baliensis NBRC 16680 | Glucose or fructose and glucose | Precipitation from liquid medium | Not known | Glucose, mannose, glucuronic or uronic acid, galactose or glucose | Gas chromatography with mass spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy | [29] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trček, J.; Dogsa, I.; Accetto, T.; Stopar, D. Acetan and Acetan-Like Polysaccharides: Genetics, Biosynthesis, Structure, and Viscoelasticity. Polymers 2021, 13, 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050815
Trček J, Dogsa I, Accetto T, Stopar D. Acetan and Acetan-Like Polysaccharides: Genetics, Biosynthesis, Structure, and Viscoelasticity. Polymers. 2021; 13(5):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050815
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrček, Janja, Iztok Dogsa, Tomaž Accetto, and David Stopar. 2021. "Acetan and Acetan-Like Polysaccharides: Genetics, Biosynthesis, Structure, and Viscoelasticity" Polymers 13, no. 5: 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050815
APA StyleTrček, J., Dogsa, I., Accetto, T., & Stopar, D. (2021). Acetan and Acetan-Like Polysaccharides: Genetics, Biosynthesis, Structure, and Viscoelasticity. Polymers, 13(5), 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050815