Biobased Terpene Derivatives: Stiff and Biocompatible Compounds to Tune Biodegradability and Properties of Poly(butylene succinate)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Degradation Studies
2.4. Cell Adhesion and Proliferation Assays
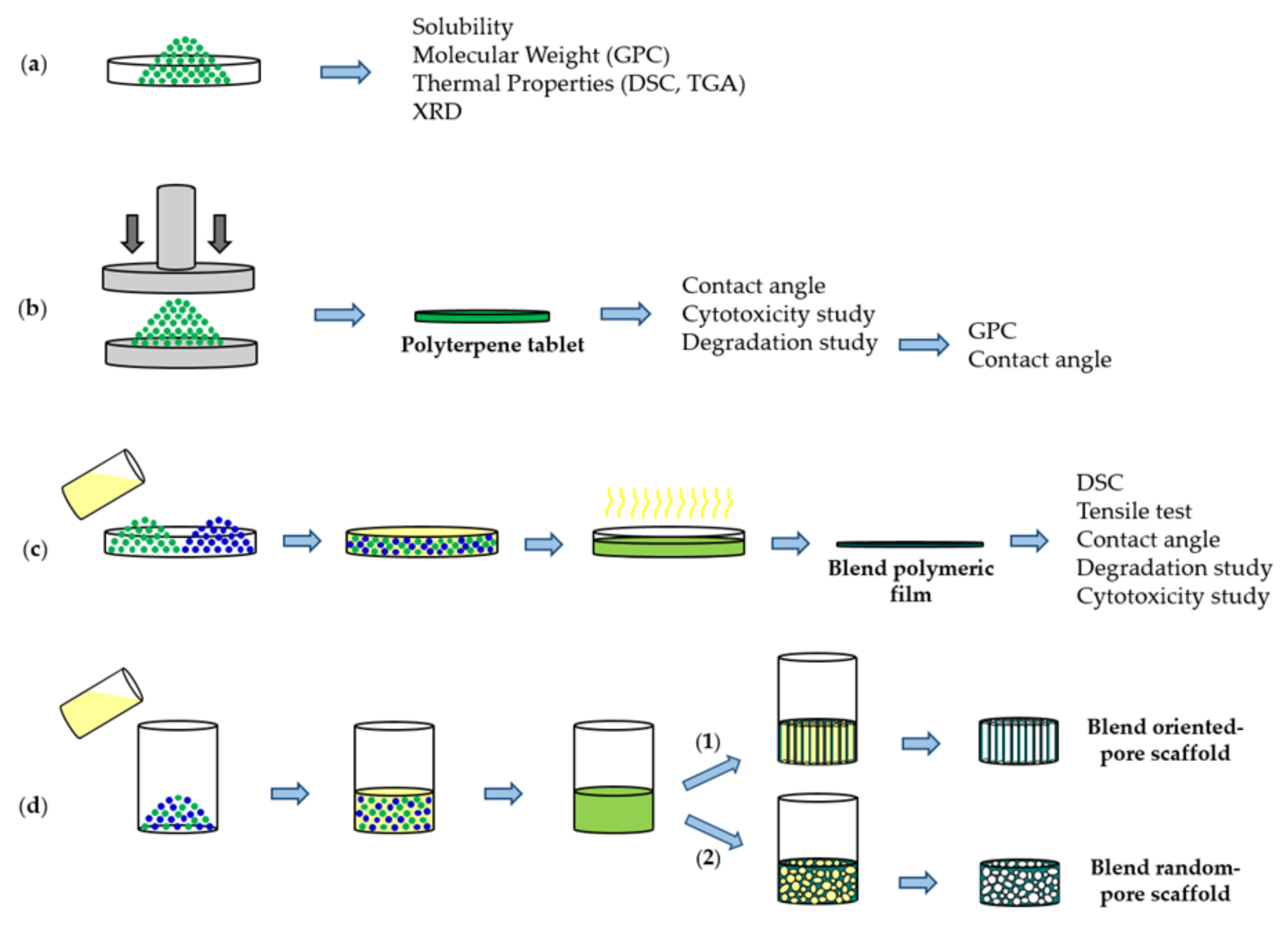
2.5. Scaffold Preparation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solubility, Molecular Weight and Hydrophobicity of the Biobased Terpene Derivatives
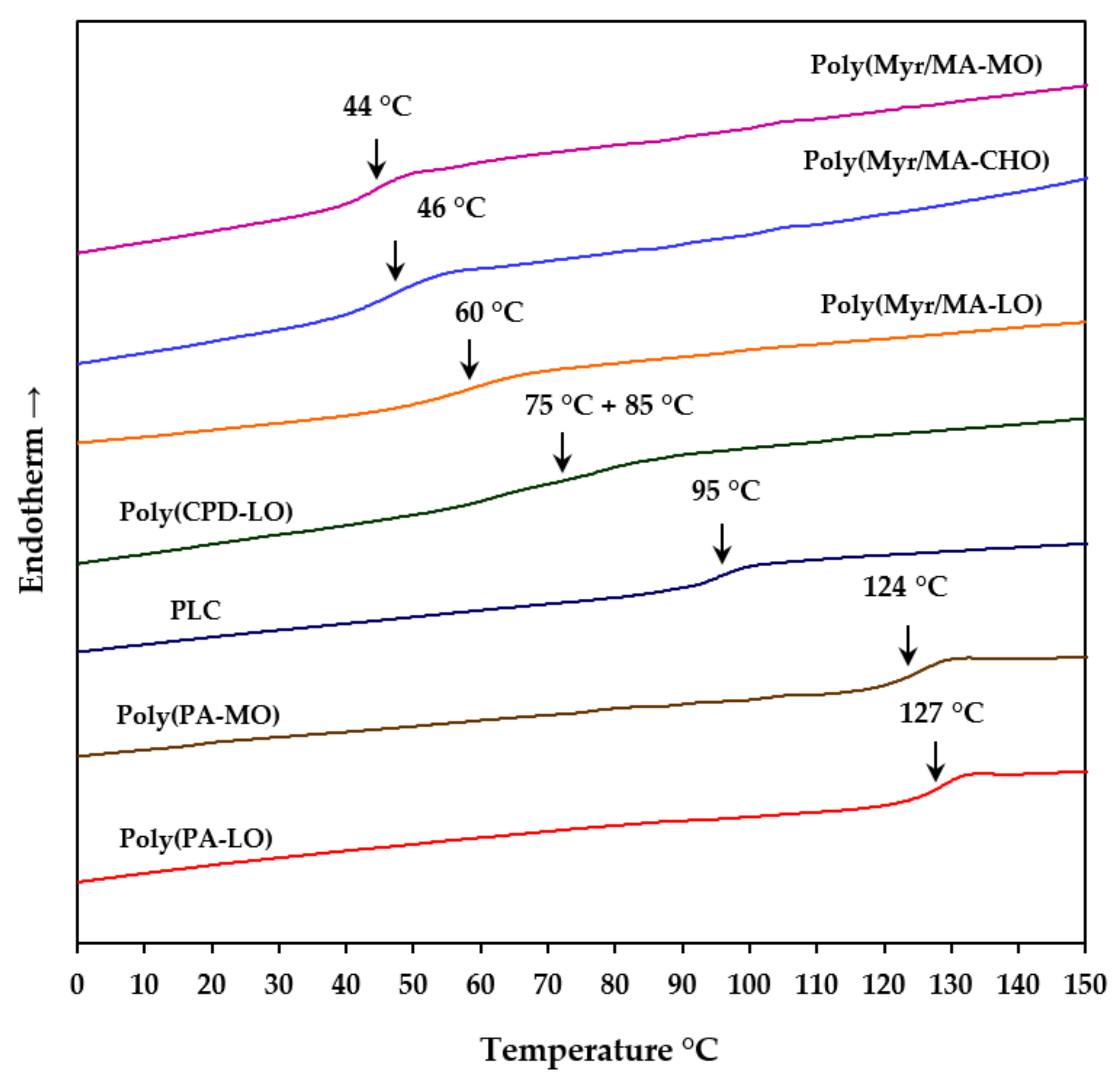
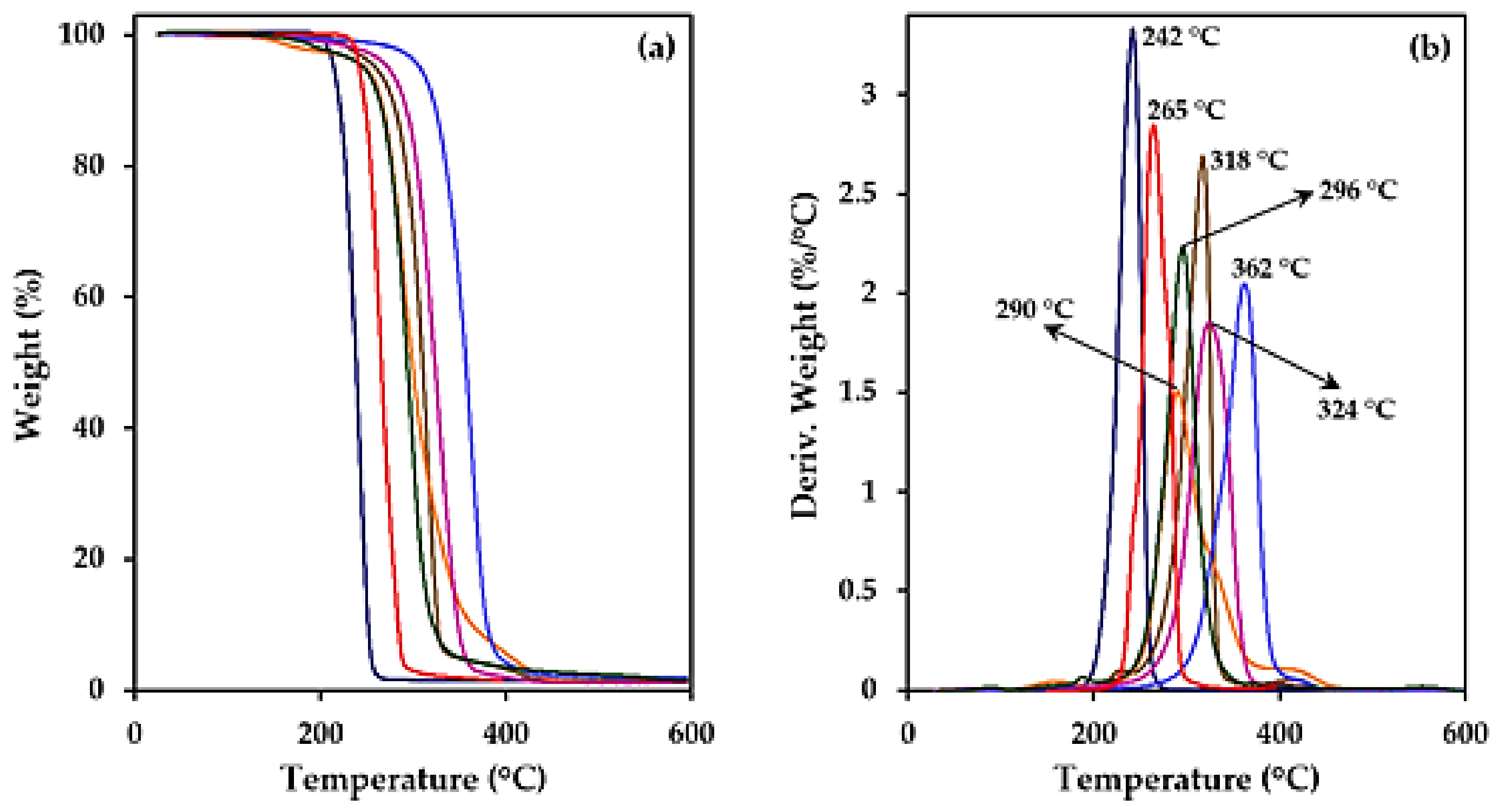
3.2. Thermal Properties of Studied Biobased Polymers
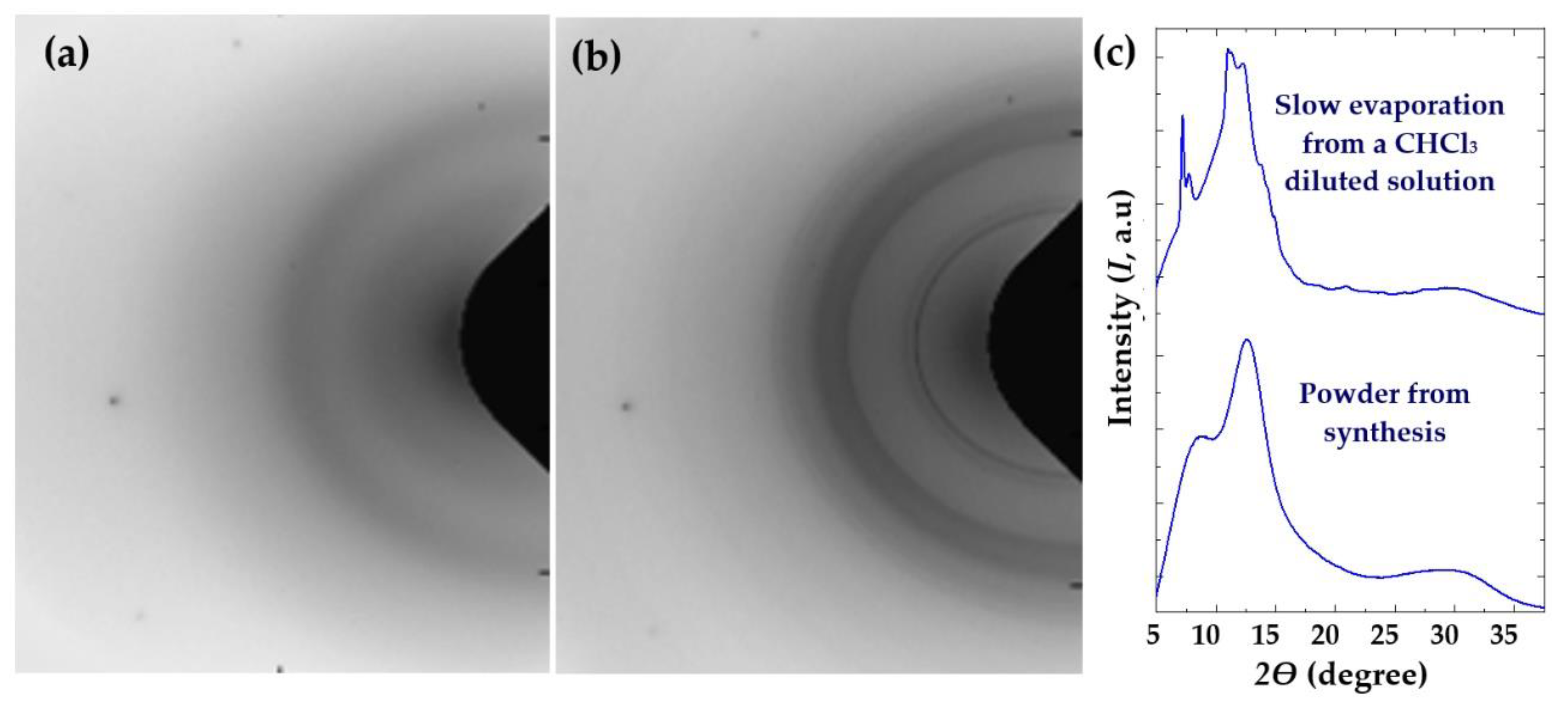
3.3. Remarks on the Crystallization of Polylimonene Carbonate
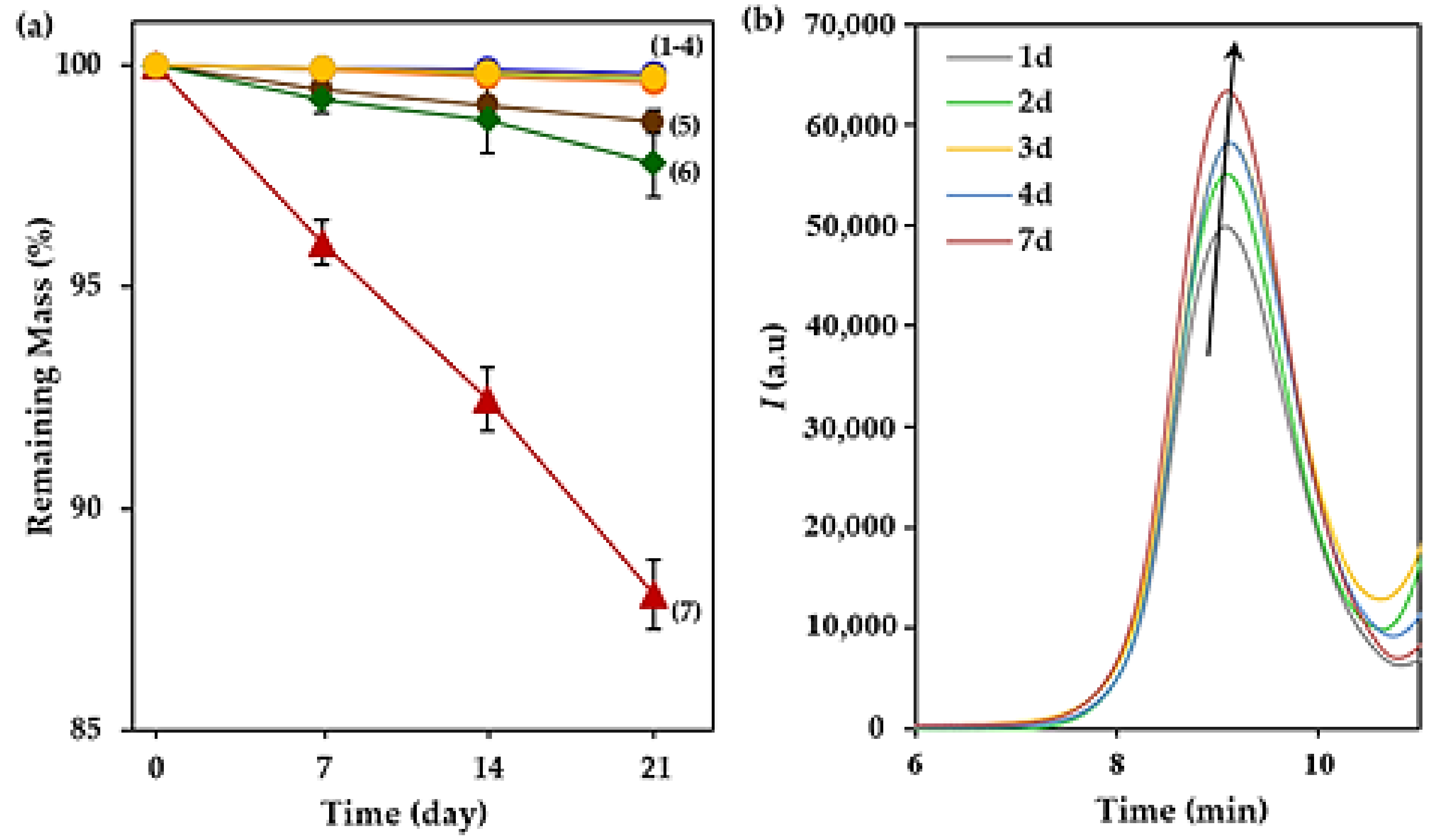
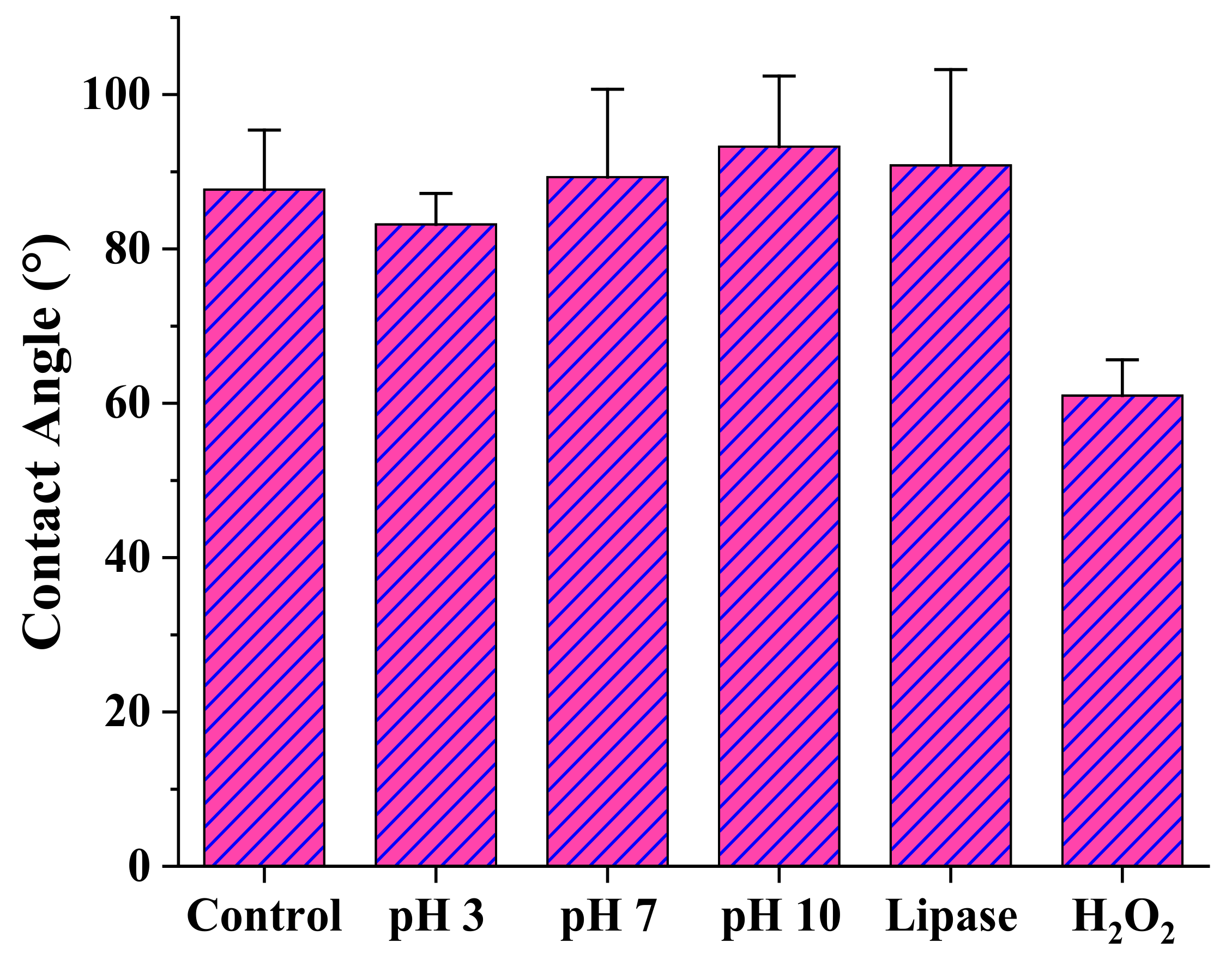
3.4. Degradability of the Selected Terpene Derivatives
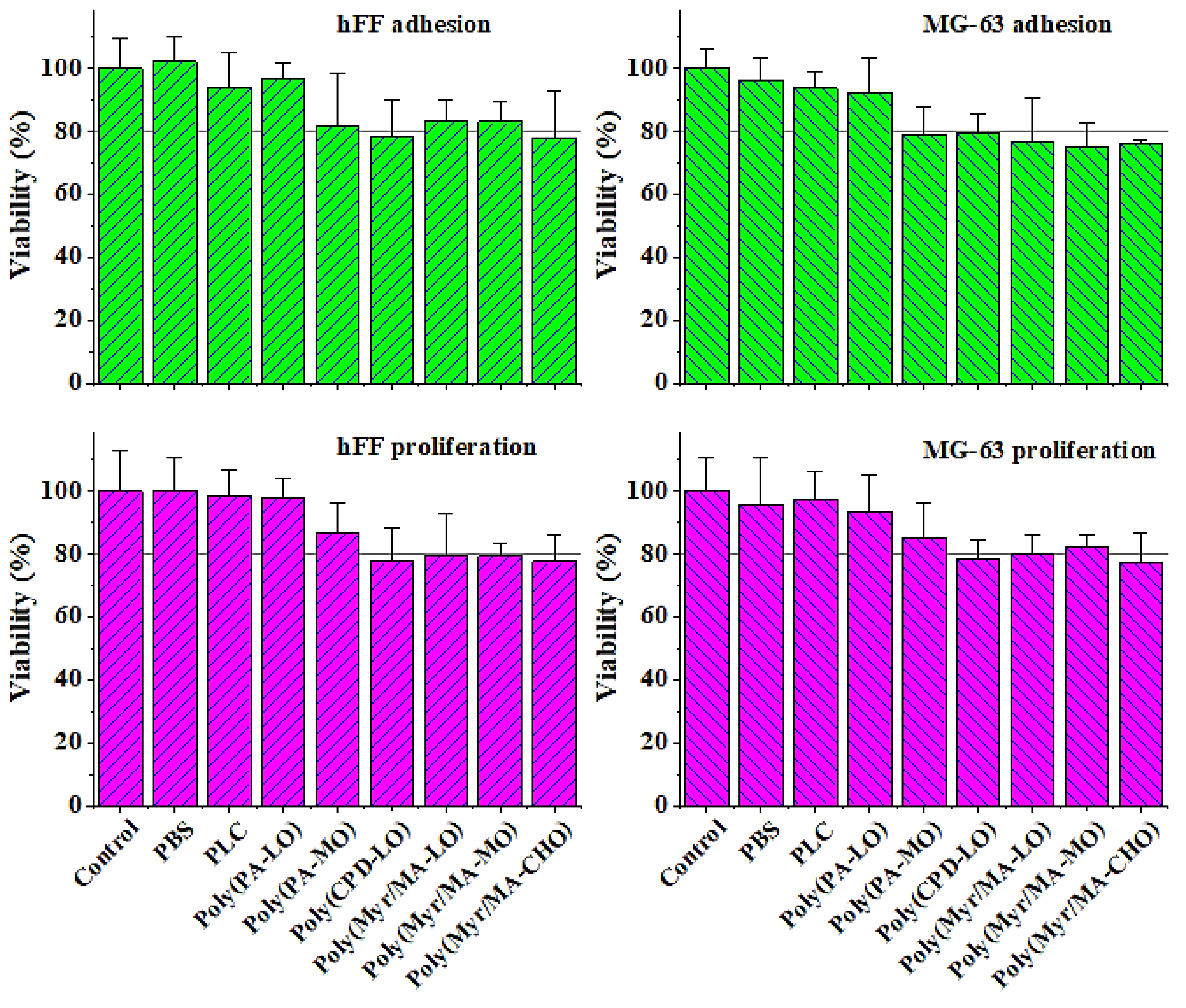
3.5. Biocompatibility of the Studied Biobased Polymers
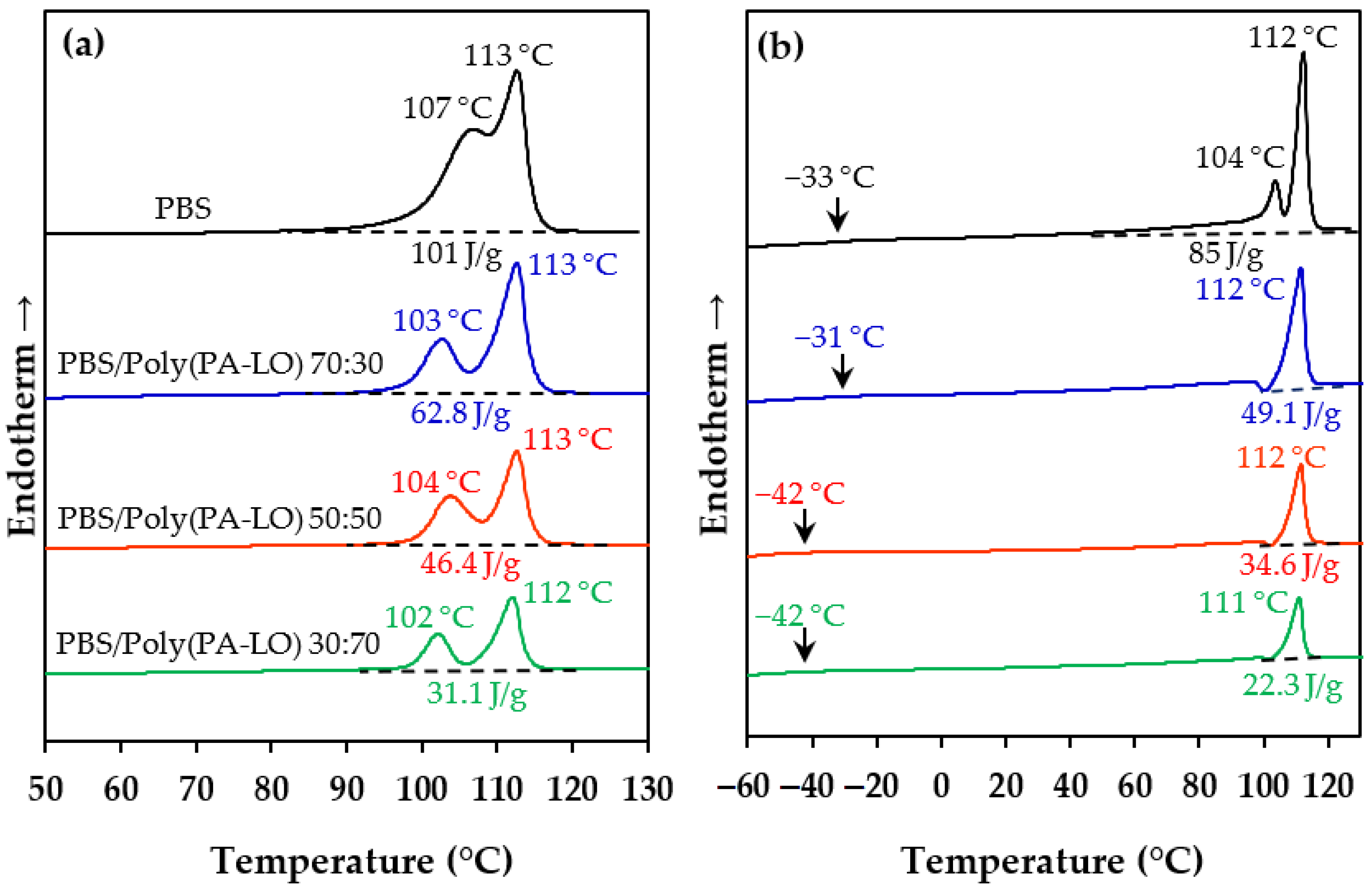
3.6. Blending of PBS with Poly(PA-LO)
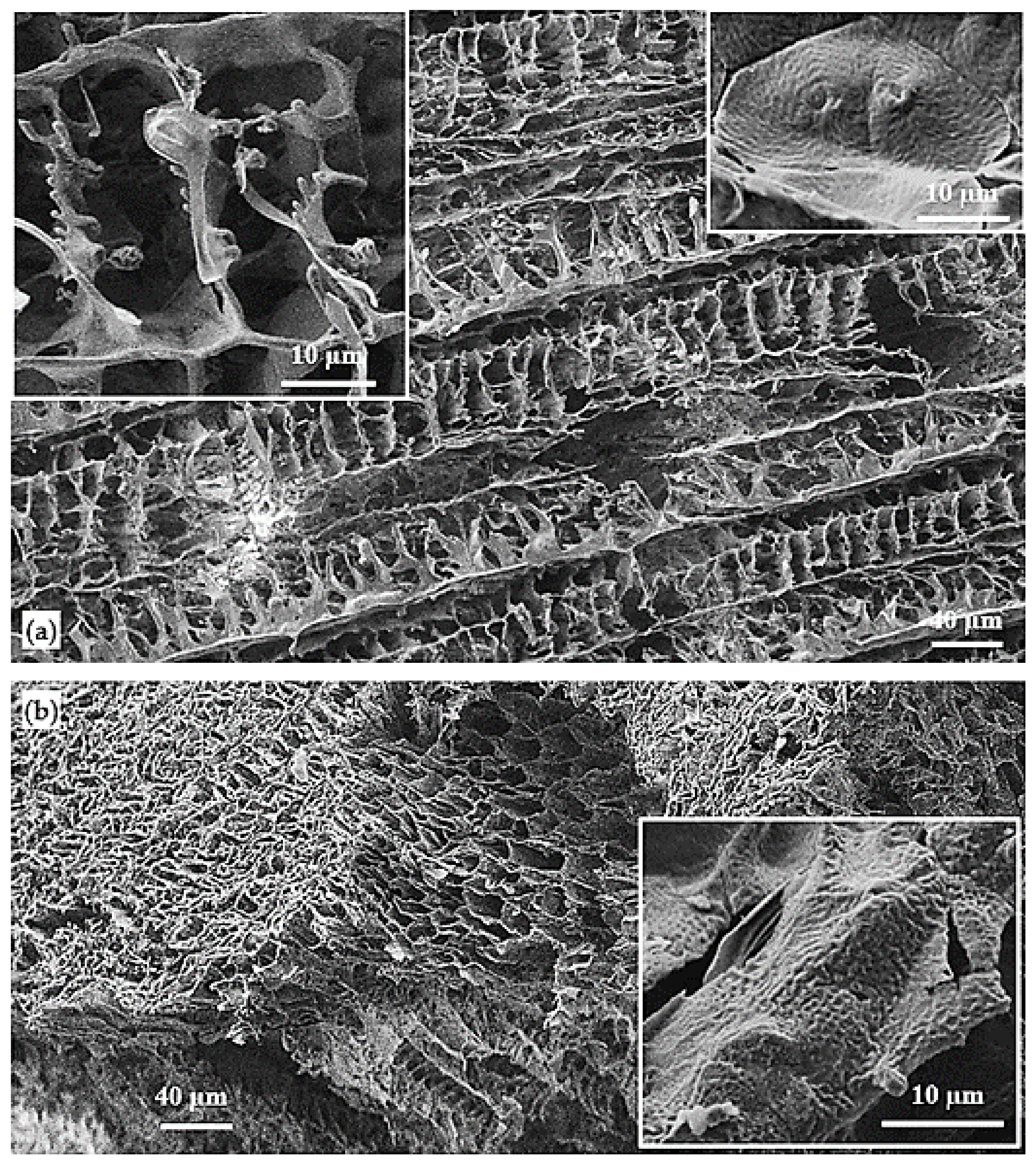
3.7. PBS/Poly(PA-LO) Blend Scaffolds from TIPS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jasinska, L.; Koning, C.E.J. Waterborne polyesters partially based on renewable resources. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 5907–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, H.W.; Pirkl, H.G.; Albers, R.; Albach, R.W.; Krause, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Casselmann, H.; Dormish, J. Polyurethanes: Versatile materials and sustainable problem solvers for today’s challenges. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9422–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Ma, S.; Wang, B.; Chen, Q.; Huang, K.; Xu, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Lu, N.; Zhu, J. High-performance biobased epoxies from ferulic acid and furfuryl alcohol: Synthesis and properties. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Cho, S.-K.; Saratale, G.D.; Kadam, A.A.; Ghodake, G.S.; Kumar, M.; Bharagava, E.N.; Kumar, G.; Kim, D.S.; Mulla, S.I.; et al. A comprehensive overview and recent advances on polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production using various organic waste streams. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbon, P.A.; Chu, F.; Tang, C. Progress in renewable polymers from natural terpenes, terpenoids, and rosin. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 8–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, C.; Kleij, A.W. Terpolymers derived from Limonene Oxide and Carbon Dioxide: Access to Cross-Linked Polycarbonates with Improved Thermal Properties. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 6285–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriemma, F.; De Rosa, C.; Di Caprio, M.R.; Di Girolamo, R.; Ellis, W.C.; Coates, G.W. Stereocomplexed poly(limonene carbonate): A unique example of the cocrystallization of amorphous enantiomeric polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darensbourg, D.J.; Poland, R.R.; Escobedo, C. Kinetic studies of the alternating copolymerization of cyclic acid anhydrides and epoxides, and the terpolymerization of cyclic acid anhydrides, epoxides, and CO2 Catalyzed by (Salen)CrIIICl. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2242–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Zhang, L.; Han, B.; Duan, Z.; Li, B.; Dong, J.; Li, X.; Liu, B. Novel chromium complexes with a [OSSO]-type bis(phenolato) dianionic ligand mediate the alternating ring-opening copolymerization of epoxides and phthalic anhydride. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 6372–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggiola, G.; Stempvoort, S.V.; Bustamante, J.; Barbero, J.M.V.; Hunt, A.J.; Clark, J.H. Can bio-based chemicals meet demand? Global and regional case-study around citrus waste-derived limonene as a solvent for cleaning applications. Biofuel. Bioprod. Biorefin. 2016, 10, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Monica, F.; Kleij, A.W. From terpenes to sustainable and functional polymers. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 5109–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; de Montigny, F.; Thomas, C.M. Tandem synthesis of alternating polyesters from renewable resources. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejad, E.H.; Paoniasari, A.; van Melis, C.G.W.; Koning, C.E.; Duchateau, R. Catalytic ring-opening copolymerization of limonene oxide and phthalic anhydride: Toward partially renewable polyesters. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, C.; Yu, H. Poly (propylene carbonate)-based polymer electrolyte with an organic cathode for stable all-solid-state sodium batteries. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2020, 36, 1905015. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquel, N.; Freyermouth, F.; Fenouillot, F.; Rousseau, A.; Pascault, J.P.; Fuertes, P.; Saint-Loup, R. Synthesis and properties of poly(butylene succinate): Efficiency of different transesterification catalysts. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 5301–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiqah, S.A.; Khalina, A.; Harmaen, A.S.; Tawakkal, I.A.; Zaman, K.; Asim, M.; Nurrazi, M.N.; Lee, C.H. A Review on properties and application of biobased poly(butylene succinate). Polymers 2021, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doug, S. Bioplastics: Technologies and Global Markets; Report Overview. BCC Research. 2010. PLS050A. Available online: www.bccresearch.com/market-research/plastics/bioplastics-technologies-markets-pls050a.html (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Ravenstijn, J.T.J. The State-of-the-Art on Bioplastics: Products, Markets, Trends, and Technologies; Polymedia Publisher GmbH: Mönchengladbach, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, R.P.; O’Connor, K.; Seeram, R. Current progress on biobased polymers and their future trends. Prog. Biomater. 2013, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gigli, M.; Fabbri, M.; Lotti, N.; Gamberini, R.; Rimini, B.; Munari, A. Poly(butylene succinate)-based polyesters for biomedical applications: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 431–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weraporn, P.A.; Sorapong, P.; Narongchai, O.C.; Ubon, I.; Puritud, J.; Sommai, P.A. Preparation of polymer blends between poly (L-lactic acid), poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) for blown film industrial application. Energy Procedia 2011, 9, 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Han, L.; Wang, X.; Wen, X.; Han, C.; Wang, S.; Dong, L. Nonisothermal crystallization behavior and mechanical properties of poly(butylene succinate)/silica nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, E.D.; Funabashi, M.; Kunioka, M. Mechanical properties and biomass carbon ratios of poly(butylene succinate) composites filled with starch and cellulose filler using furfural as plasticizer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 3410–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, R.; del Valle, L.; Torras, J.; Puiggalí, J. Recent progress on biodegradable tissue engineering scaffolds prepared by thermally-induced phase separation (TIPS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinali, R.; del Valle, L.; Franco, L.; Puiggalí, J. Poly(butylene succinate) matrices obtained by thermally-induced phase separation: Porosity orientation affects drug release. Molecules 2021. in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Sanford, M.J.; Carrodeaguas, L.P.; van Zee, N.J.; Kleij, A.W.; Coates, G.W. Alternating copolymerization of propylene oxide and cyclohexene oxide with tricyclic anhydrides: Access to partially renewable aliphatic polyesters with high glass transition temperatures. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 6394–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decortes, A.; Haak, R.M.; Martín, C.; Belmonte, M.M.; Martin, E.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Kleij, A.W. Copolymerization of CO2 and cyclohexene oxide mediated by Yb(salen)-based complexes. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 8197–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Carrodeguas, L.; Martín, C.; Kleij, A.W. Semiaromatic polyesters derived from renewable terpene oxides with high glass transitions. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 5337–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monica, F.D.; Kleij, A.W. Synthesis and characterization of biobased polyesters with tunable Tg by ROCOP of beta-elemene oxides and phthalic anhydride. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 2619–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrodeguas, L.P.; González-Fabra, J.; Castro-Gómez, F.; Bo, C.; Kleij, A.W. AlIII-catalysed formation of poly(limonene)carbonate: DFT analysis of the origin of stereoregularity. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 6115–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindermann, N.; Cristòfol, A.; Kleij, A.W. Access to biorenewable polycarbonates with unusual glass transition temperature (Tg) modulation. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3860–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongay, C.; Cerdà, V.A. Britton-Robinson buffer of known ionic strength. Ann. Chim. 1974, 64, 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Llorens, E.; del Valle, L.J.; Díaz, A.; Casas, M.C.; Puiggalí, J. Polylactide nanofibers loaded with vitamin B6 and polyphenols as bioactive platform for tissue engineering. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.M.; Allen, S.D.; Lobkovsky, E.B.; Coates, G.W. Alternating copolymerization of limonene oxide and carbon dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auriemma, F.; De Rosa, C.; Di Caprio, M.R.; Di Girolamo, R.; Coates, G.W. crystallization of alternating limonene oxide/carbon dioxide copolymers: Determination of the crystal structure of stereocomplex poly(limonene carbonate). Macromolecules 2015, 48, 2534–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barham, P.J.; Keller, A.; Otun, E.L.; Holmes, P.A. Crystallization and morphology of a bacterial thermoplastic: Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. J. Mater. Sci. 1984, 19, 2781–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.M.; Kinloch, D.R. Transverse screw dislocations: A source of twist in crystalline polymer ribbons. Polymer 1969, 10, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Gan, Z. Structural analysis of poly(butylene adipate) banded spherulites from their biodegradation behavior. Polymer 2007, 48, 6152–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyu, T.; Chiu, H.W.; Guenthner, A.J.; Okabe, Y.; Saito, H.; Inoue, T. Rhythmic growth of target and spiral spherulites of crystalline polymer blends. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 2749–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, G.; Liu, J. Morphological varieties and kinetic behaviors of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) spherulites crystallized isothermally from thin melt film. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, L.; Yan, S. Depletion-induced nonbirefringent banding in thin isotactic polystyrene thin films. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9283–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, H.D.; Padden, F.J. A phenomenological theory of spherulitic crystallization. J. Appl. Phys 1963, 34, 2409–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planellas, M.; Puiggalí, J. Synthesis and properties of poly(L-lactide)-b-poly(L-phenylalanine) hybrid copolymers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 13247–13266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawashima, K.; Kawano, R.; Miyagi, T.; Umemoto, S.; Okui, N. Morphological changes in flat-on and edge-on lamellae of poly(ethylene succinate) crystallized from molten thin films. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2003, 42, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, H.D. On the relation between different morphological forms in high polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Gen. Pap. 1964, 2, 4339–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geil, P.H. Polymer Single Crystals; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Bassett, D.C. Principles of Polymer Morphology; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zwenger, S.; Basu, C. Plant terpenoids: Applications and future potentials. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, M.J.; Chung, B.Y.; Bang, D.Y.; Lim, S.K.; Choi, S.M.; Lim, D.S.; Cho, M.C.; Yoon, K.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Safety evaluation and risk assessment of d-limonene. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2013, 16, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NTP (National Toxicology Program). Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of d-limonene (CAS No. 5989-27-5) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (Gavage studies). Natl. Toxicol. Program Tech. Rep. Ser. 1990, 347, 1–165. [Google Scholar]
- NTP (National Toxicology Program). Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of β-myrcene (CAS No. 123-35-3) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (Gavage studies). Natl. Toxicol. Program Tech. Rep. Ser. 2010, 557, 1–169. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, J.B.; Silva, B.O.; Pires-Cunha, C.L.; Hiruma-Lima, C.A.; Gaivão, I.O.N.d.M.; Maistro, E.L. Genotoxic effects induced by beta-myrcene following metabolism by liver HepG2/C3A human cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2019, 82, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinali, R.; Khorasani, M.T.; Behnamghader, A.; Atai, M.; del Valle, L.J.; Puiggalí, J. Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) porous matrices from thermally induced phase separation. Polymers 2020, 12, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.J.; Ma, P.X. Polymer phase separation. In Scaffolding in Tissue Engineering; Williams, C.G., Elisseeff, J.H., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Ma, P.X. Poly(α-hydroxyl acids)/hydroxyapatite porous composites for bone-tissue engineering. I. Preparation and morphology. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 44, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conoscenti, G.; Carrubba, V.; Brucato, V. A versatile technique to produce porous polymeric scaffolds: The thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) method. Arch. Chem. Res. 2017, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavia, F.C.; La Carrubba, V.; Piccarolo, S.; Brucato, V. Polymeric scaffolds prepared via thermally induced phase separation: Tuning of structure and morphology. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 86A, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, D.R.; Kinzer, K.E.; Tseng, H.S. Microporous membrane formation via thermally induced phase separation. I. Solid-liquid phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 52, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Witte, P.; Dijkstra, P.J.; van den Berg, J.W.A.; Feijen, J. Phase separation processes in polymer solutions in relation to membrane formation. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Solvent 1 | Poly (PA-LO) | PLC | Poly (PA-MO) | Poly (Myr/MA-LO) | Poly (Myr/MA-MO) | Poly (CPD-LO) | Poly (Myr/MA-CHO) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHCl3 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| TFA | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| HFIP | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| 1,4 dioxane | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| THF | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| DMF | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| DMSO | + | + | - | ++ | - | + | -- |
| Formic Acid | + | - | -- | + | -- | + | -- |
| Formamide | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Methanol | -- | -- | -- | ++ | -- | - | -- |
| Ethanol | -- | -- | -- | ++ | + | -- | ++ |
| Poly (PA-LO) | PLC | Poly (PA-MO) | Poly (Myr/MA-LO) | Poly (Myr/MA-MO) | Poly (CPD–LO) | Poly (Myr/MA-CHO) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn (g/mol) | 4000 | 3600 | 3900 | 4000 | 3900 | 3800 | 4100 |
| Mw (g/mol) | 9200 | 7600 | 9000 | 9600 | 9700 | 8800 | 9100 |
| PDI | 2.3 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeinali, R.; del Valle, L.J.; Franco, L.; Yousef, I.; Rintjema, J.; Alemán, C.; Bravo, F.; Kleij, A.W.; Puiggalí, J. Biobased Terpene Derivatives: Stiff and Biocompatible Compounds to Tune Biodegradability and Properties of Poly(butylene succinate). Polymers 2022, 14, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010161
Zeinali R, del Valle LJ, Franco L, Yousef I, Rintjema J, Alemán C, Bravo F, Kleij AW, Puiggalí J. Biobased Terpene Derivatives: Stiff and Biocompatible Compounds to Tune Biodegradability and Properties of Poly(butylene succinate). Polymers. 2022; 14(1):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010161
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeinali, Reza, Luis J. del Valle, Lourdes Franco, Ibraheem Yousef, Jeroen Rintjema, Carlos Alemán, Fernando Bravo, Arjan W. Kleij, and Jordi Puiggalí. 2022. "Biobased Terpene Derivatives: Stiff and Biocompatible Compounds to Tune Biodegradability and Properties of Poly(butylene succinate)" Polymers 14, no. 1: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010161
APA StyleZeinali, R., del Valle, L. J., Franco, L., Yousef, I., Rintjema, J., Alemán, C., Bravo, F., Kleij, A. W., & Puiggalí, J. (2022). Biobased Terpene Derivatives: Stiff and Biocompatible Compounds to Tune Biodegradability and Properties of Poly(butylene succinate). Polymers, 14(1), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010161








