Core/Shell Pigments with Polyaniline Shell: Optical and Physical–Technical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Dyes made from aniline;
- Dyes that include other compounds, apart from aniline;
- Dyes based on intermediate products made from aniline.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stepanov, B.I. Introduction to Chemistry and Technology of Organic Dyes, 3rd ed.; Chemistry: Moscow, Russia, 1984; pp. 280–378. [Google Scholar]
- Bibik, E.E. New Handbook of Chemist and Technologist. General Information. The Structure of Matter; NPO “Professional”: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2006; p. 1464. [Google Scholar]
- Chekalin, M.A.; Passet, B.V.; Ioffe, B.A. Technology of Organic Dyes and Intermediate Products, 3rd ed.; Chemistry: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2013; pp. 225–260. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-El-Khalek, D.E.; Hassan, H.H.A.M.; Ramadan, S.R. Water-Soluble Sulfonated Polyaniline as Multifunctional Scaling Inhibitor for Crystallization Control in Industrial Applications. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 169, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packiaraj, M.; Kumar, K.K.S. High Corrosion Protective Behavior of Water-Soluble Conducting Polyaniline–Sulfonated Naphthalene Formaldehyde Nanocomposites on 316L SS. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 864, 158345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Kawabata, K.; Goto, H. Water Soluble Polyaniline/Polysaccharide Composite: Polymerization, Carbonization to Yield Carbon Micro-Bubbles. Synth. Met. 2014, 194, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Qiu, J.; Liu, M.; Feng, H.; Lei, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, C.; Qin, L. Synthesis and Characterization of Water-Soluble Polyaniline Films. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bıçak, N.; Şenkal, B.F.; Sezer, E. Preparation of Organo-Soluble Polyanilines in Ionic Liquid. Synth. Met. 2005, 155, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahy, A.; Rguig, T.; Cho, S.J.; Bunker, C.E.; Yang, D.J. Polar Solvent Soluble and Hydrogen Absorbing Polyaniline Nanofibers. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, S.; Amarnath, C.A. A Novel Polyaniline–Maleicacid–Dodecylhydrogensulfate Salt: Soluble Polyaniline Powder. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, S.; Gul, S.; Ali, K.; Shah, A.-H.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Completely Soluble and Highly Thermally Stable PANI-DBSA Salts. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.-H.A.; Kamran, M.; Bilal, S.; Ullah, R. Cost Effective Chemical Oxidative Synthesis of Soluble and Electroactive Polyaniline Salt and Its Application as Anticorrosive Agent for Steel. Materials 2019, 12, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ermilov, P.I.; Indeikin, E.A.; Tolmachev, I.A. Pigments and Pigmented Paint and Varnish Materials; Khimiya: Leningrad, Russia, 1987; pp. 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zarras, P.; Stenger-Smith, J.D.; Wei, Y. (Eds.) Electroactive Polymers for Corrosion Control; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 843, pp. 18–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kinlen, P.J.; Menon, V.; Ding, Y. A Mechanistic Investigation of Polyaniline Corrosion Protection Using the Scanning Reference Electrode Technique. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 3690–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinlen, P.J.; Ding, Y.; Silverman, D.C. Corrosion Protection of Mild Steel Using Sulfonic and Phosphonic Acid-Doped Polyanilines. Corrosion 2002, 58, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, T.; Yin, H.; Hu, L.; Tang, J.; Ren, K. Preparation and Corrosion Protection of Three Different Acids Doped Polyaniline/Epoxy Resin Composite Coatings on Carbon Steel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 612, 126069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalendová, A.; Veselý, D.; Sapurina, I.; Stejskal, J. Anticorrosion Efficiency of Organic Coatings Depending on the Pigment Volume Concentration of Polyaniline Phosphate. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 63, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarinezhad, E.; Ebrahimi, M.; Faridi, H.R. Corrosion Inhibition of Steel in Sodium Chloride Solution by Undoped Polyaniline Epoxy Blend Coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 64, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbatov, V.G.; Indeikin, E.A. Anticorrosion Pigments with a Shell of Doped Polyaniline. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2017, 53, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugacheva, T.A.; Kurbatov, V.G.; Golikov, I.V.; Il’in, A.A.; Indeikin, E.A. Polymer Coatings Containing Core-Shell Pigments with Polyaniline Shell. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2019, 92, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagani, M.B. Electrical and Mechanical Properties of a Fully Hydrogenated Two-Dimensional Polyaniline Sheet. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2018, 153, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhadra, J.; Al-Thani, N.J.; Madi, N.K.; Al-Maadeed, M.A. Effects of Aniline Concentrations on the Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Polyaniline Polyvinyl Alcohol Blends. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arteshi, Y.; Aghanejad, A.; Davaran, S.; Omidi, Y. Biocompatible and Electroconductive Polyaniline-Based Biomaterials for Electrical Stimulation. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 108, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; Gouda, M.E. Electrical and Optical Properties of Nickel Ferrite/Polyaniline Nanocomposite. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabur, A.R. Effect of Polyaniline on the Electrical Conductivity and Activation Energy of Electrospun Nylon Films. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, U.; Kanbeş, Ç.; Torul, H.; Ertaş, N. Preparation, Characterization and Electrical Properties of Polyaniline Nanofibers Containing Sulfonated Cyclodextrin Group. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Wang, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, C. The Synthesis and Antistatic, Anticorrosive Properties of Polyaniline Composite Coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 122, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Oviedo, M.A.; Araújo, O.A.; Faez, R.; Rezende, M.C.; De Paoli, M.-A. Antistatic Coating and Electromagnetic Shielding Properties of a Hybrid Material Based on Polyaniline/Organoclay Nanocomposite and EPDM Rubber. Synth. Met. 2006, 156, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, F.X.; Oueiny, C. Polyaniline Thermoset Blends and Composites. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 114, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, D.; Wu, M.; Ni, H. Enhanced Electrical Conductivity and Competent Mechanical Properties of Polyaniline/Polyacrylate (PANI/PA) Composites for Antistatic Finishing Prepared at the Aid of Polymeric Stabilizer. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 125, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, F. Conductive Hybrid Film from Polyaniline and Polyurethane–Silica. Polymer 2007, 48, 4368–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 787-5:1980; General Methods of Test for Pigments and Extenders—Part 5: Determination of Oil Absorption Value. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1980.
- Gorlovskiy, I.A.; Indeikin, E.A.; Tolmachev, I.A. Laboratory Practice on Pigments and Pigmented Paint and Varnish Materials: Textbook; Manual for Universities; Chemistry: Leningrad, Russia, 1990; pp. 120–150. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM-D344-2016; Standard Test Method for Relative Hiding Power of Paints by the Visual Evaluation of Brushouts. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- DIN EN ISO/CIE 11664-4:2020-03; Colorimetry—Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour Space. (ISO/CIE 11664-4:2019). German Version EN ISO/CIE 11664-4:2019. German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 2020.
- DIN 55979:1989-04; Testing of Pigments; Determination of the Black Value of Carbon Black Pigments. German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 1989.
- Calheiros, L.F.; Soares, B.G.; Barra, G.M.O. DBSA-CTAB Mixture as the Surfactant System for the One Step Inverse Emulsion Polymerization of Aniline: Characterization and Blend with Epoxy Resin. Synth. Met. 2017, 226, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyanarayanan, S.; Devi, S.; Venkatachari, G. Corrosion Protection of Stainless Steel by Electropolymerised Pani Coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2006, 56, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabuddin, S.; Sarih, N.; Afzal Kamboh, M.; Rashidi Nodeh, H.; Mohamad, S. Synthesis of Polyaniline-Coated Graphene Oxide@SrTiO3 Nanocube Nanocomposites for Enhanced Removal of Carcinogenic Dyes from Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2016, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Kaner, R.B. A General Chemical Route to Polyaniline Nanofibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Kaner, R.B. Nanofiber Formation in the Chemical Polymerization of Aniline: A Mechanistic Study. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5817–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
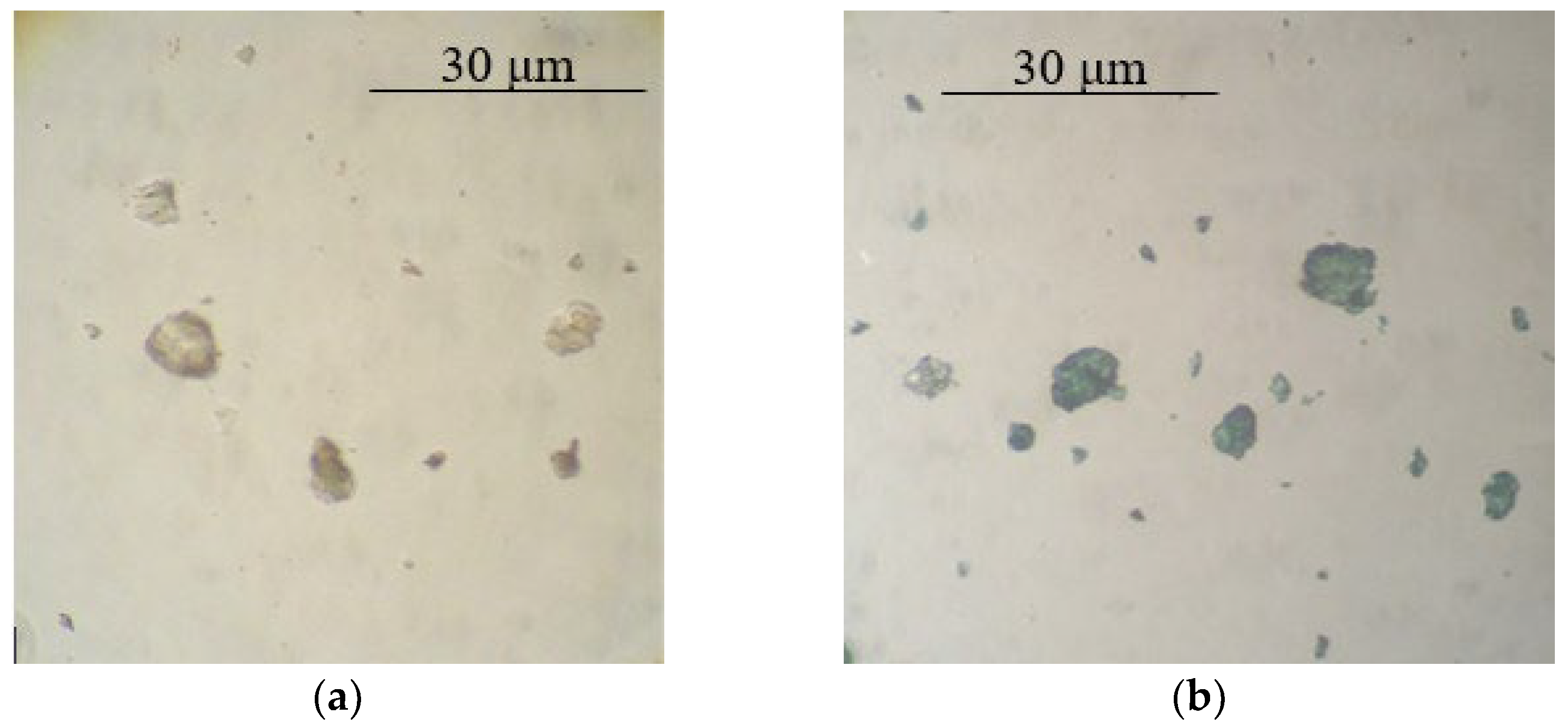


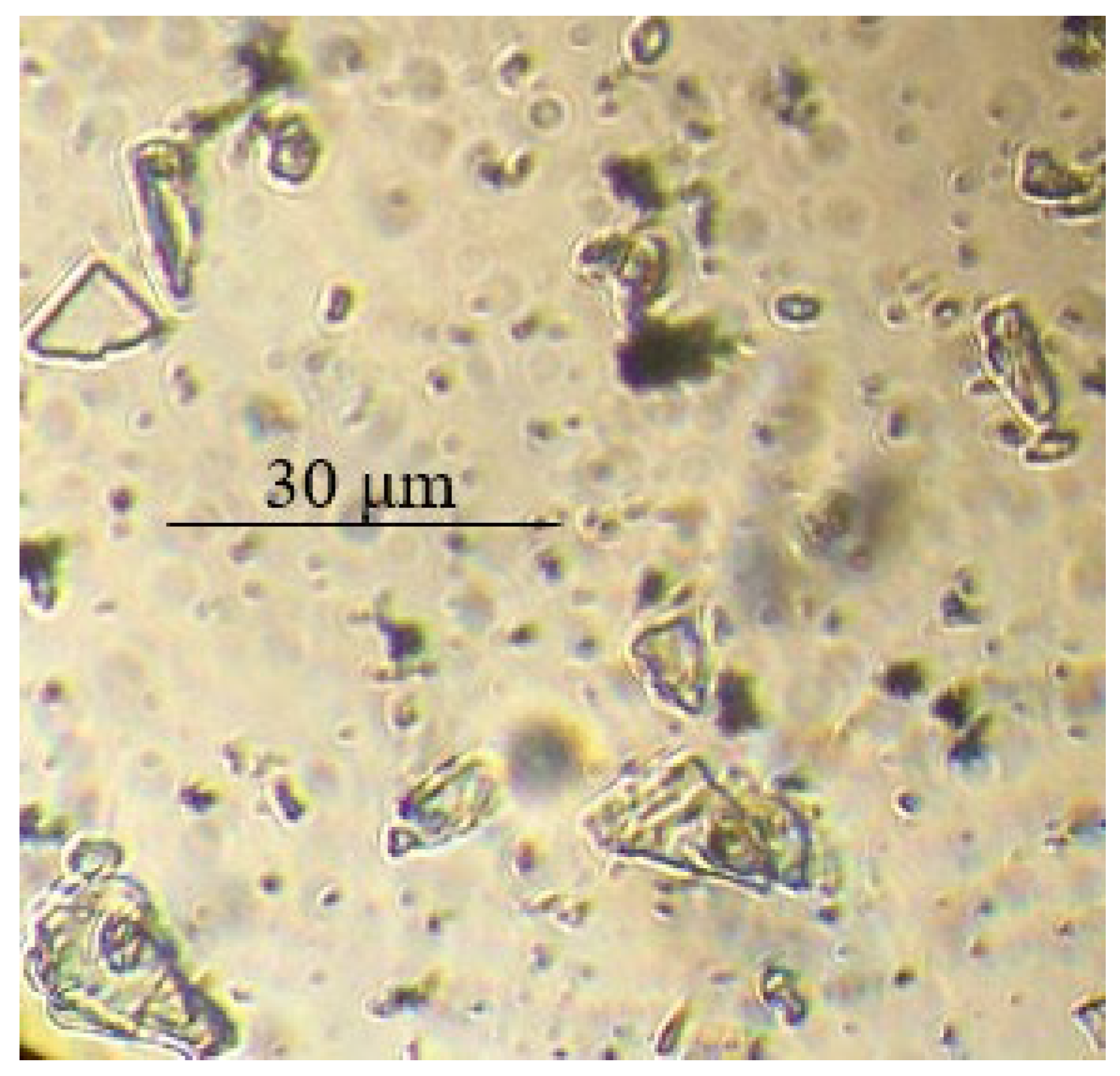
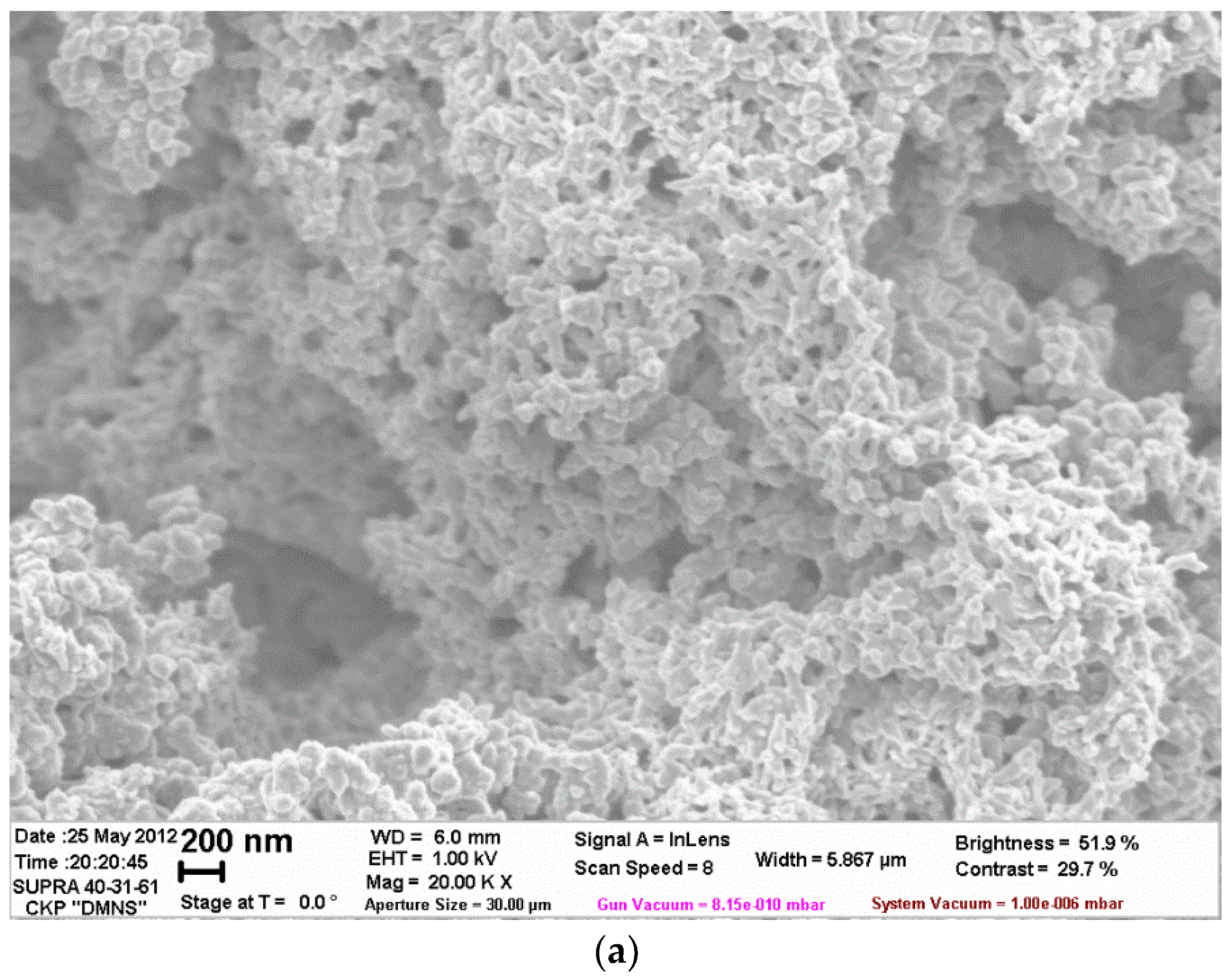
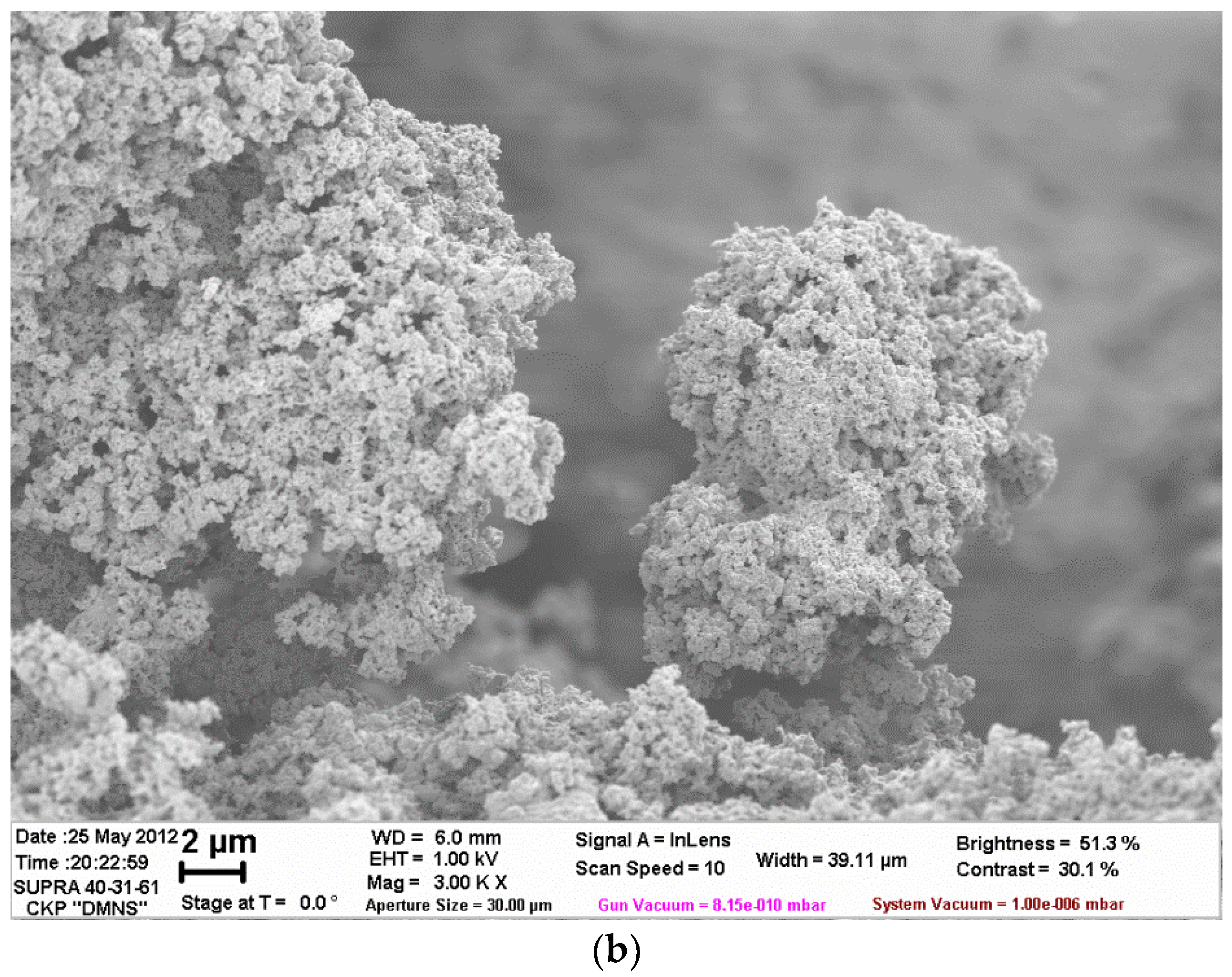

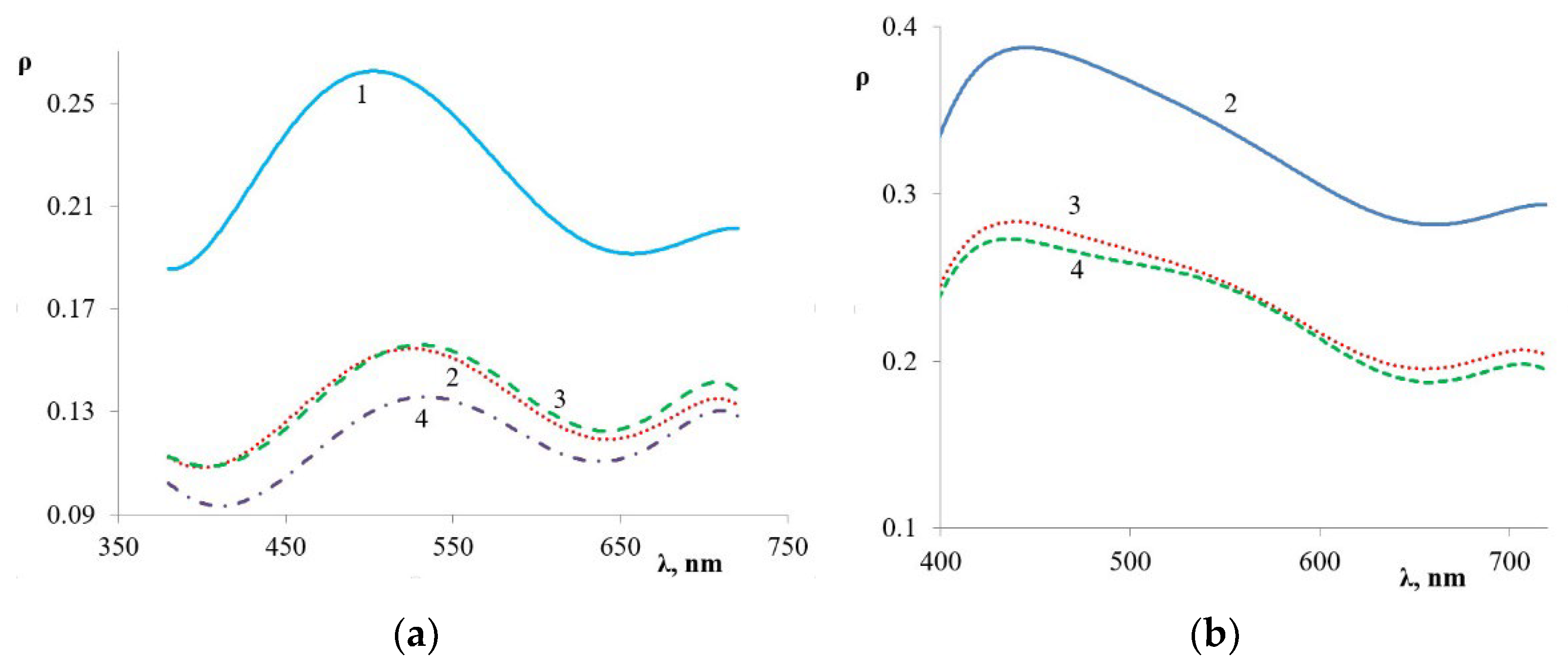
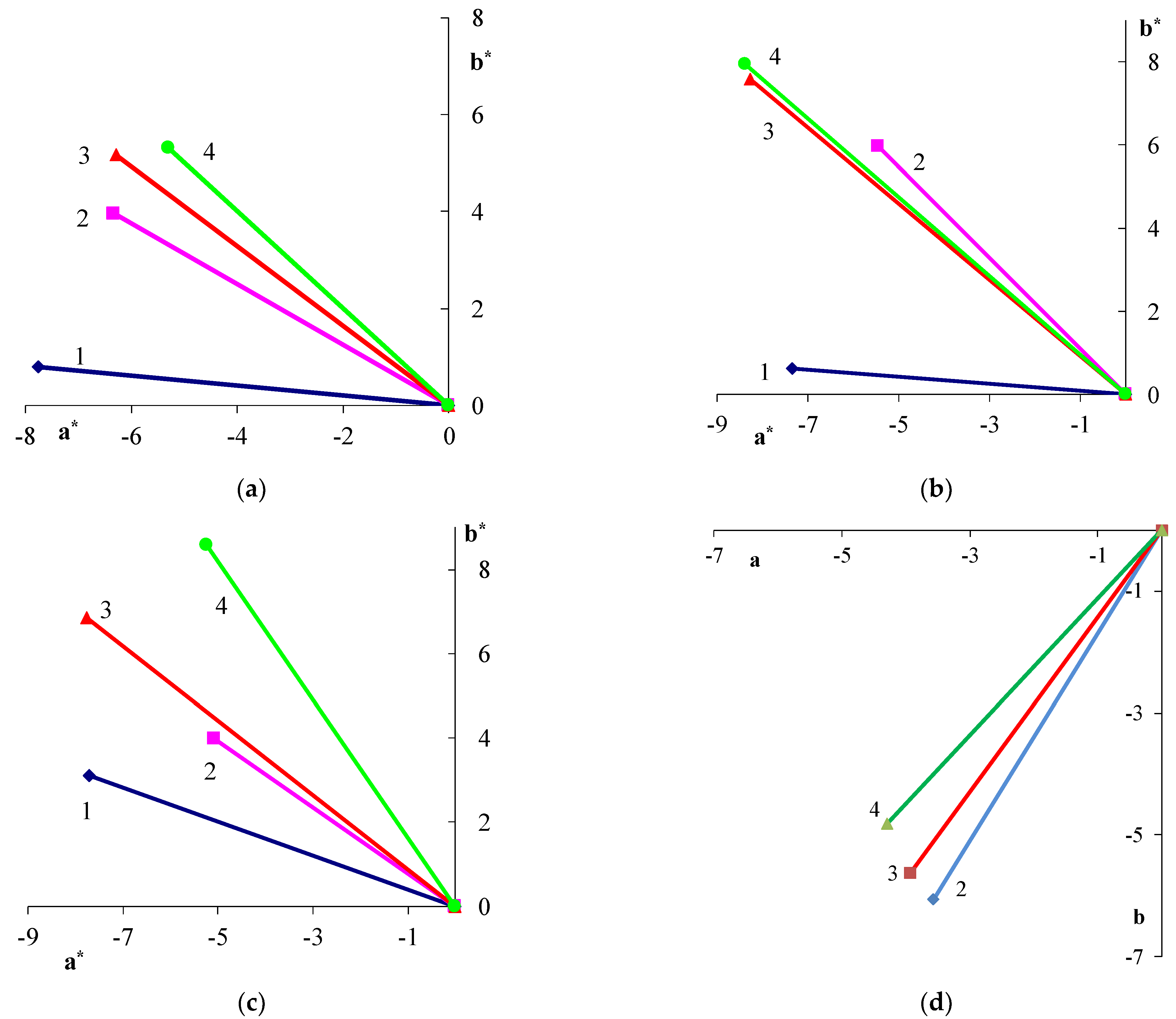

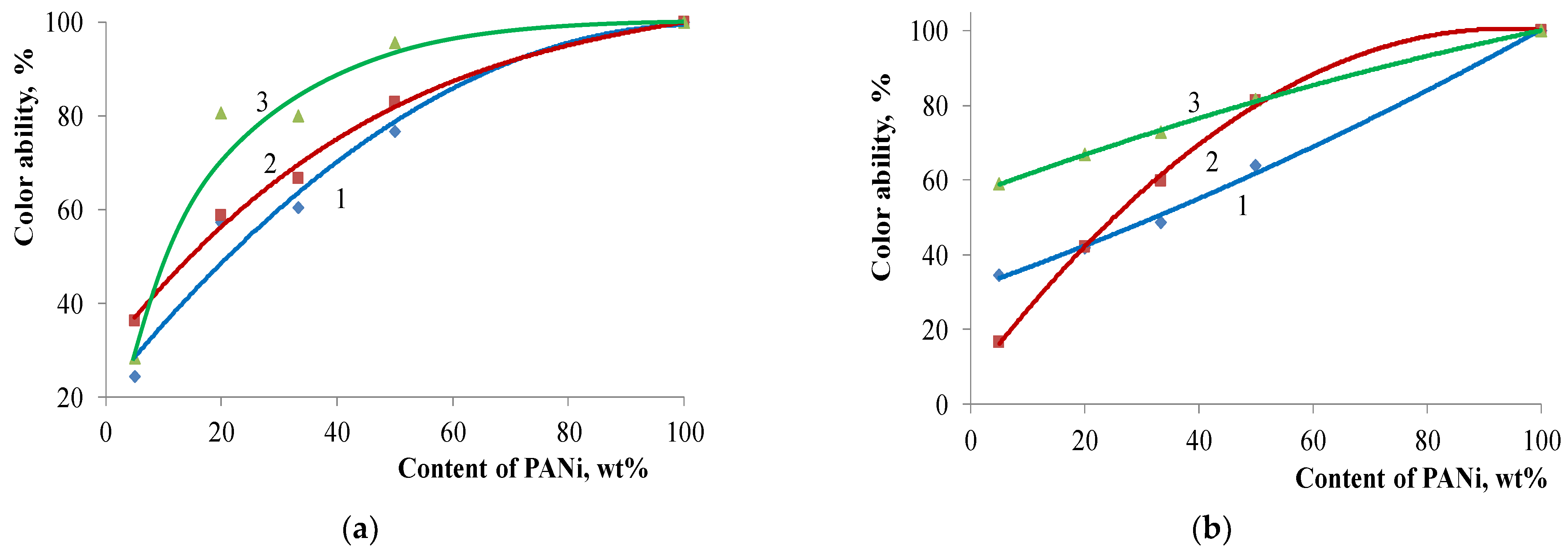
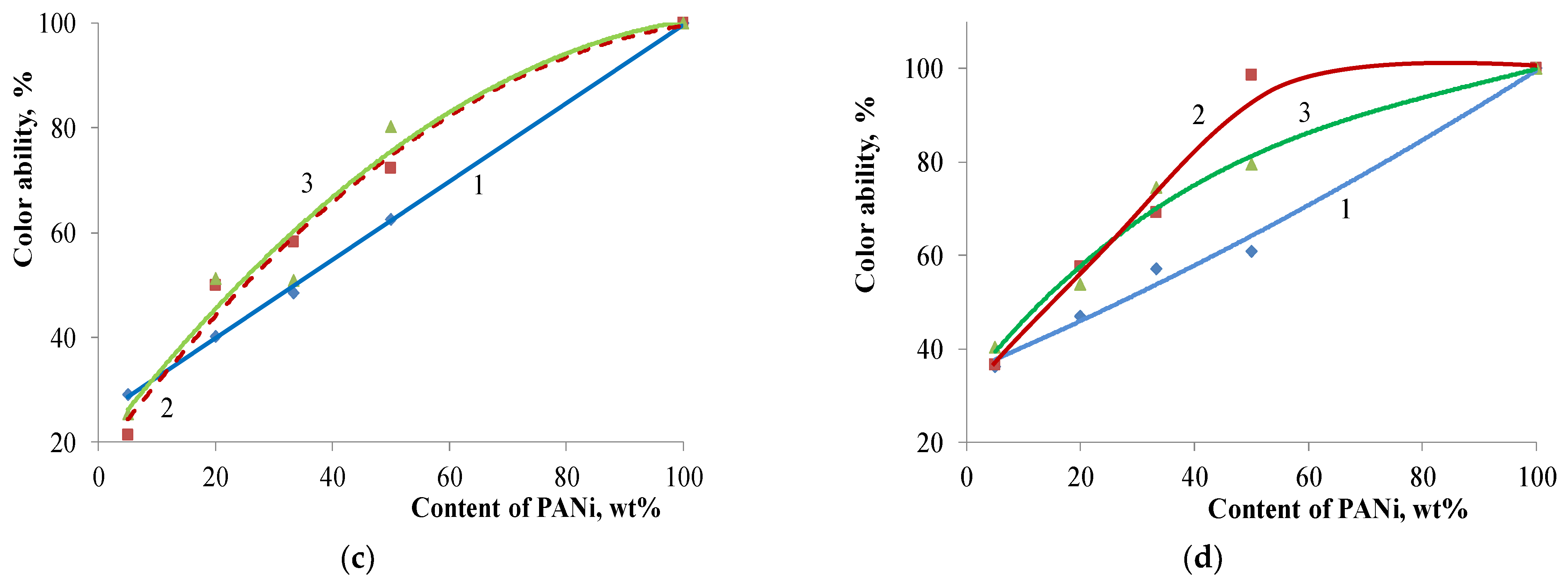

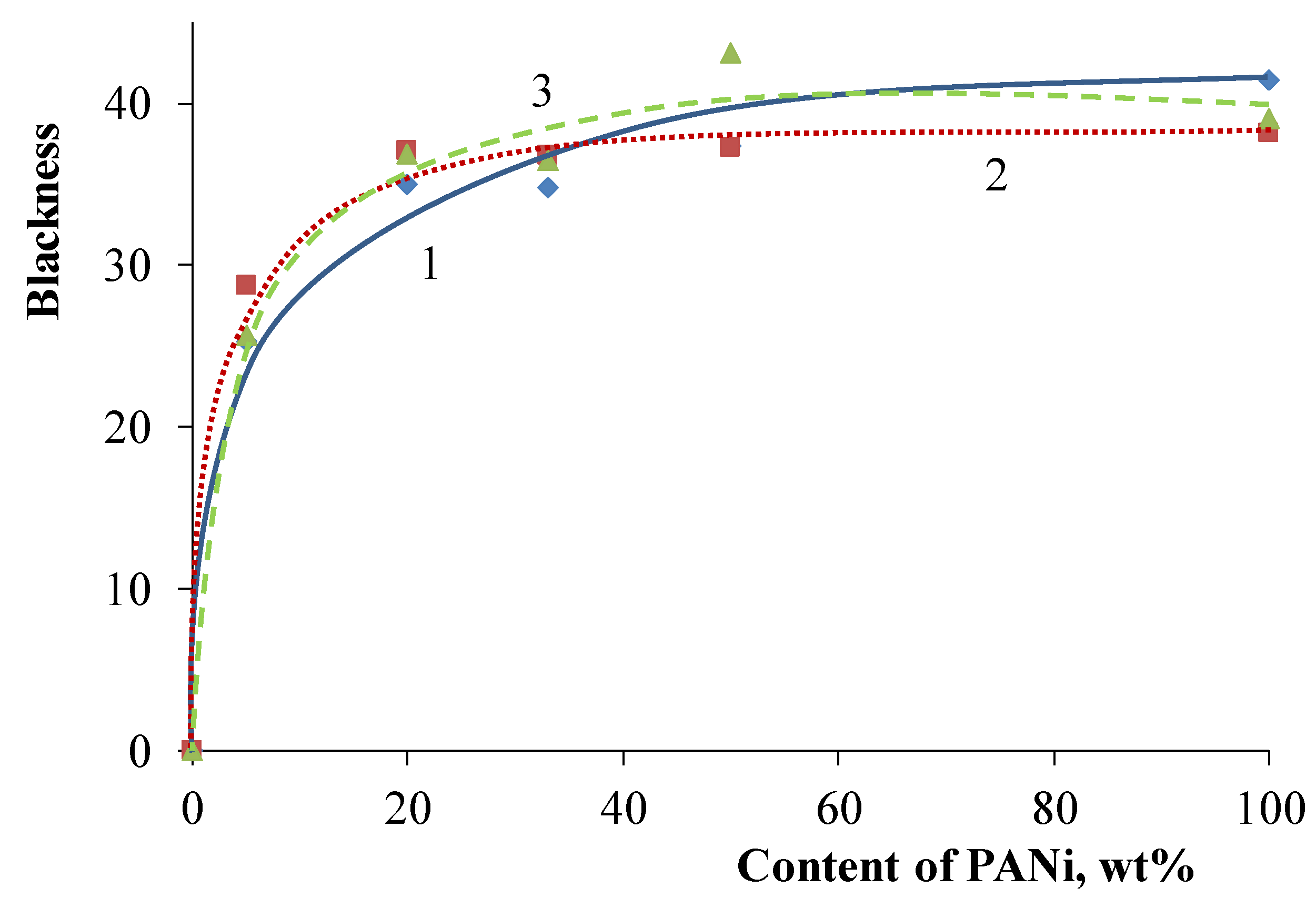
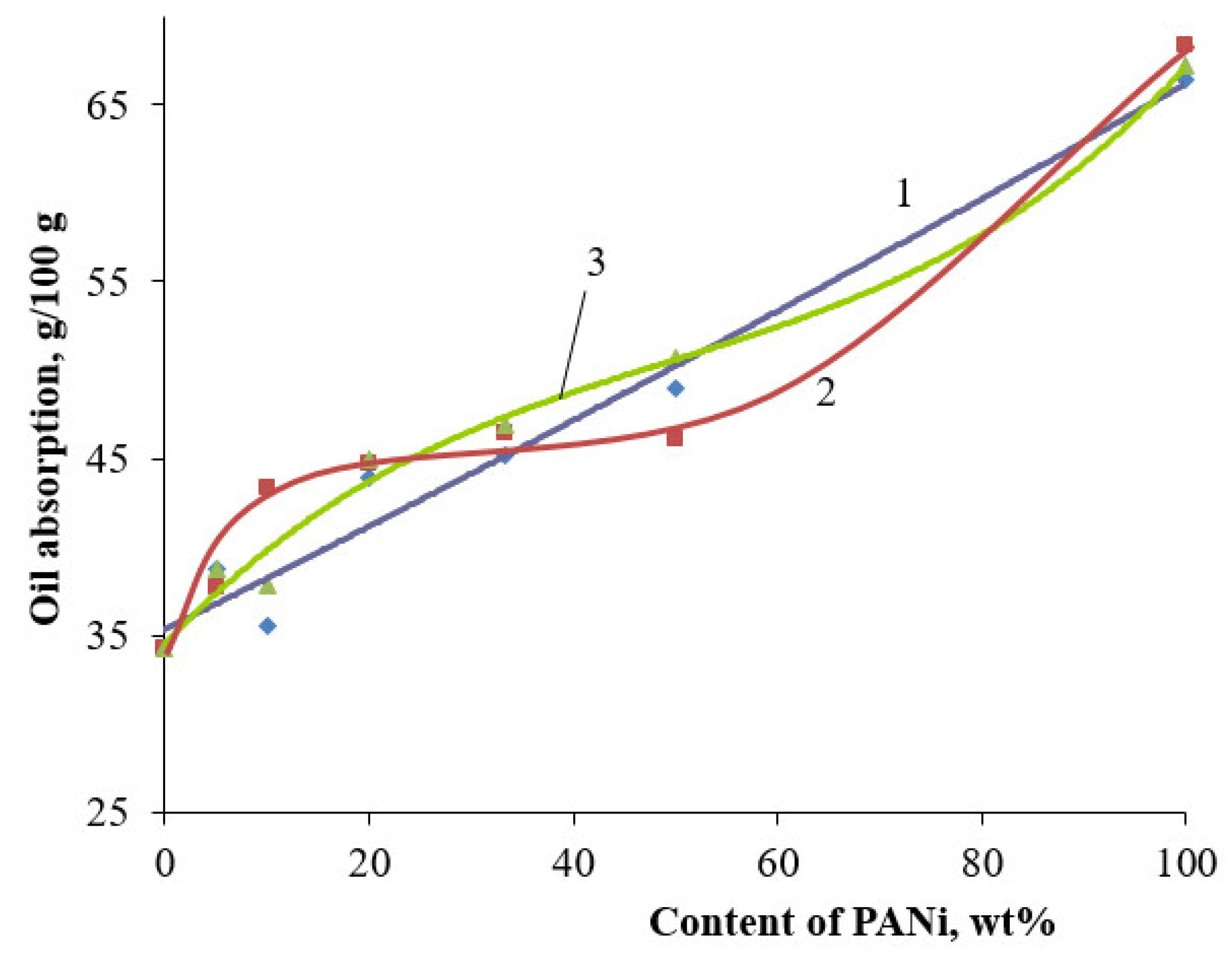
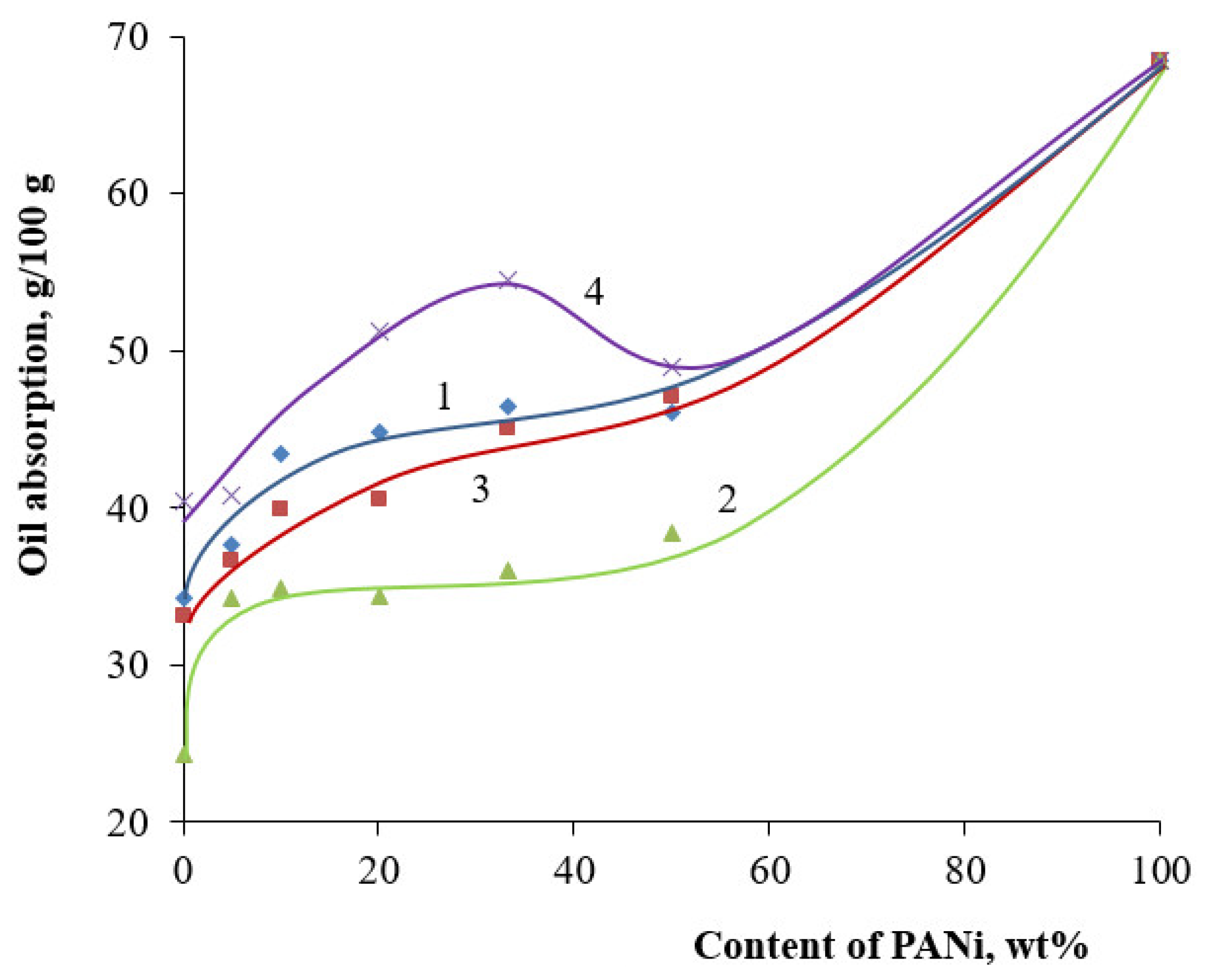
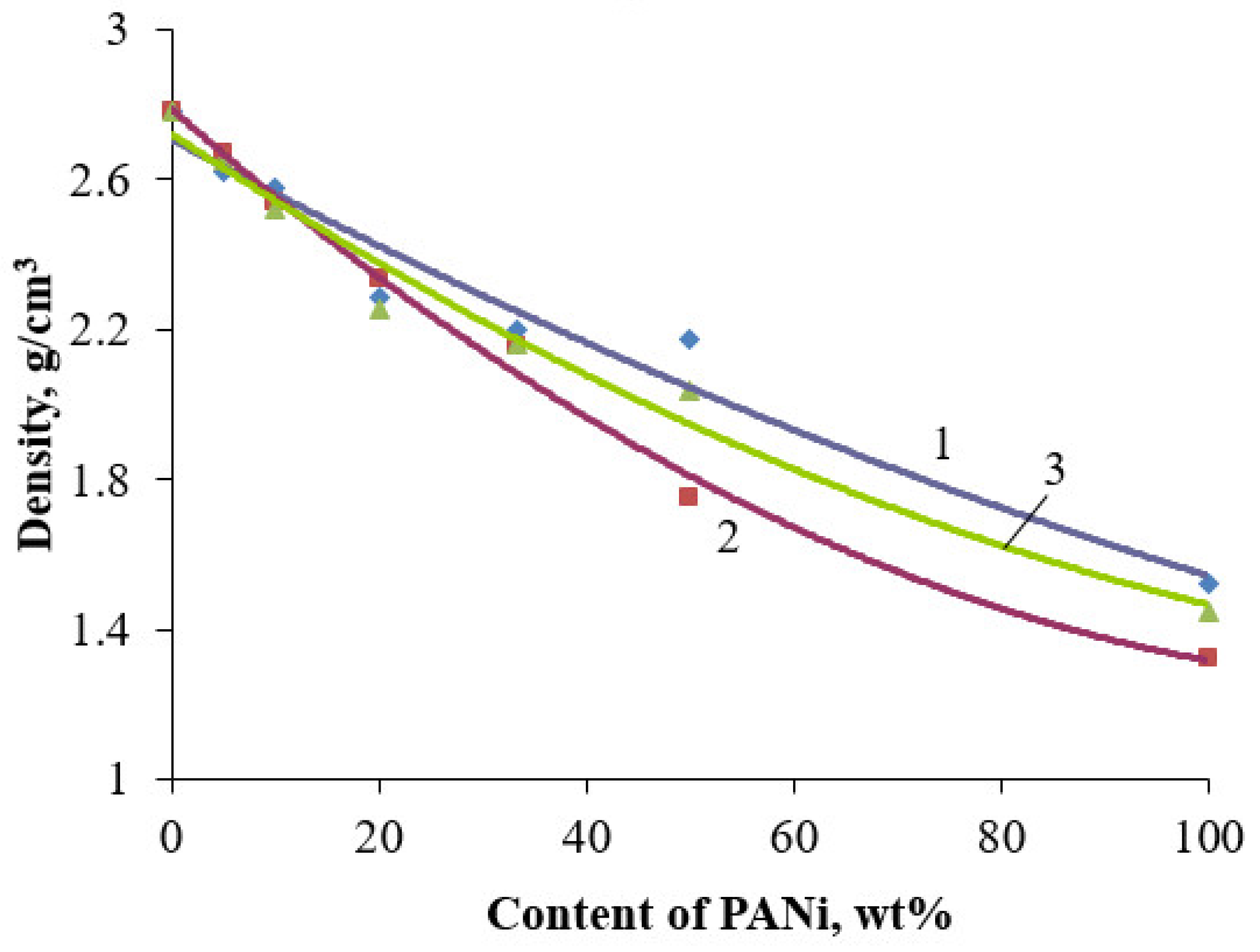
| Filler | Kaolin | Bentonite | Talc | Muscovite | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | |||||
| Refractive index | 1.6 | - | 1.58 | 1.59 | |
| Density, kg/m3 | 2600 | 2450 | 2950 | 2900 | |
| pH of water extract | 5–8 | 4–6 | 8–10 | 3.6–4.3 | |
| Oil absorption, g/100 g | 34.3 | 33.0 | 24.5 | 40.5 | |
| Pigment | Hiding Power, m2/g | Coloring Ability, % |
|---|---|---|
| Core/shell pigment (20% of doped PANi, kaolin-based, H3PO4 as a dopant) | 0.102 | 106 |
| Iron black | 0.132 | 100 |
| Doped PANi | 0.224 | 131 |
| Dopant | kd | t0.5, min |
|---|---|---|
| 5 wt.% PANi | ||
| H2SO4 | 0.012 | 3.53 |
| HCl | 0.015 | 3.11 |
| H3PO4 | 0.009 | 4.73 |
| 20 wt.% PANi | ||
| H2SO4 | 0.028 | 2.79 |
| HCl | 0.039 | 3.72 |
| H3PO4 | 0.008 | 20.3 |
| 33.3 wt.% PANi | ||
| H2SO4 | 0.020 | 12.54 |
| HCl | 0.030 | 5.66 |
| H3PO4 | 0.026 | 7.74 |
| 50 wt.% PANi | ||
| H2SO4 | 0.135 | 1.91 |
| HCl | 0.145 | 2.00 |
| H3PO4 | 0.027 | 15.21 |
| Pigment Core | kd | t0.5, min |
|---|---|---|
| Kaolin | 0.123 | 1.68 |
| Talc | 0.028 | 2.79 |
| Bentonite | 0.037 | 3.30 |
| Muscovite | 0.042 | 3.70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pugacheva, T.A.; Malkov, G.V.; Ilyin, A.A.; Indeikin, E.A.; Kurbatov, V.G. Core/Shell Pigments with Polyaniline Shell: Optical and Physical–Technical Properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14102005
Pugacheva TA, Malkov GV, Ilyin AA, Indeikin EA, Kurbatov VG. Core/Shell Pigments with Polyaniline Shell: Optical and Physical–Technical Properties. Polymers. 2022; 14(10):2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14102005
Chicago/Turabian StylePugacheva, Tatyana A., Georgiy V. Malkov, Alexander A. Ilyin, Eugene A. Indeikin, and Vladimir G. Kurbatov. 2022. "Core/Shell Pigments with Polyaniline Shell: Optical and Physical–Technical Properties" Polymers 14, no. 10: 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14102005
APA StylePugacheva, T. A., Malkov, G. V., Ilyin, A. A., Indeikin, E. A., & Kurbatov, V. G. (2022). Core/Shell Pigments with Polyaniline Shell: Optical and Physical–Technical Properties. Polymers, 14(10), 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14102005






