A Proprioceptive Soft Robot Module Based on Supercoiled Polymer Artificial Muscle Strings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel proprioceptive soft robot module is proposed based on a 3D-printed soft body and SCPAM strings;
- (2)
- Both the actuation and sensing properties of the SCPAM strings are utilized to realize the bending deformation, as well shape estimation, of the soft robot module;
- (3)
- Based upon the soft robot module, a crawling robot and a robotic gripper are presented, and more soft robotic applications could be achieved.
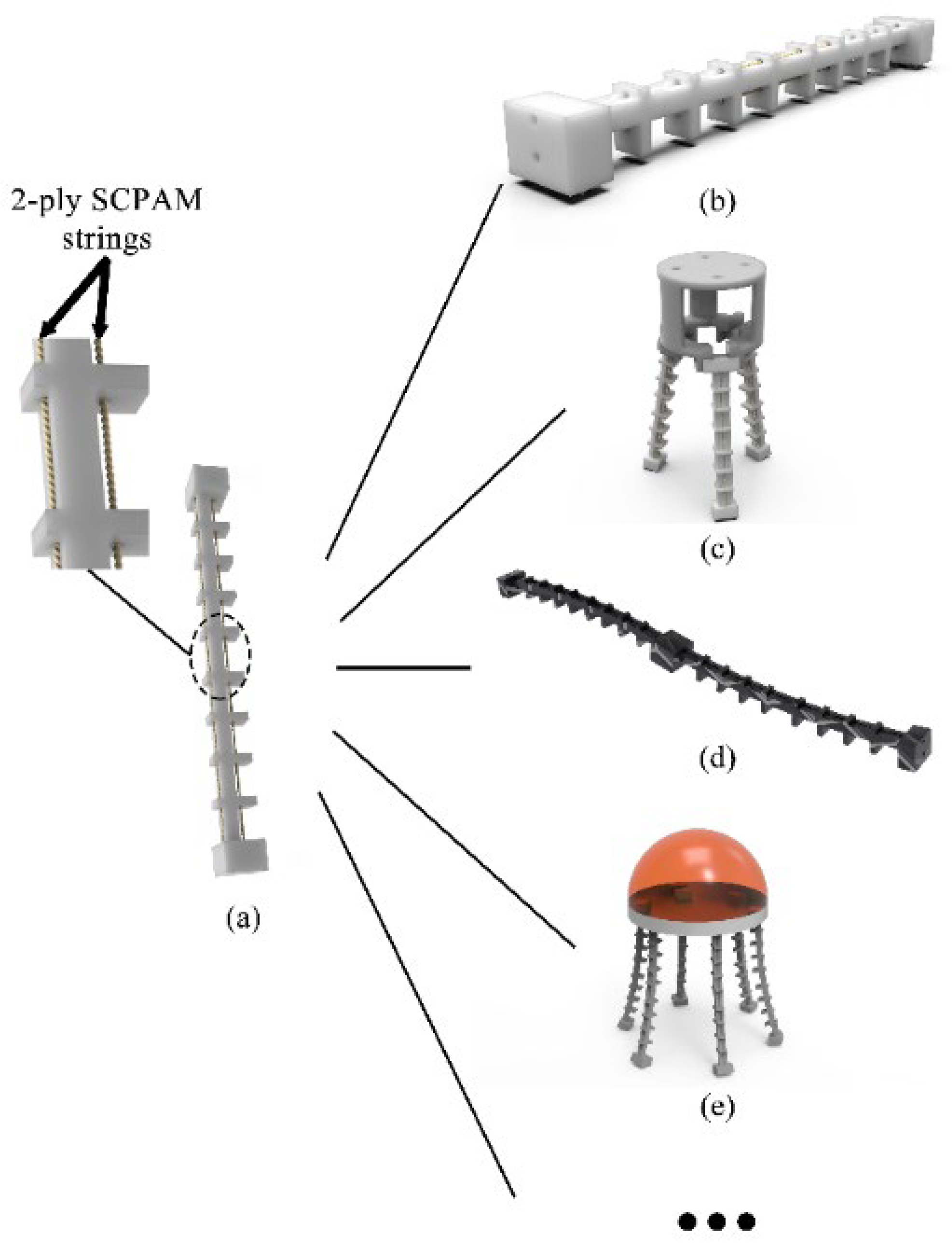
2. Design and Fabrication
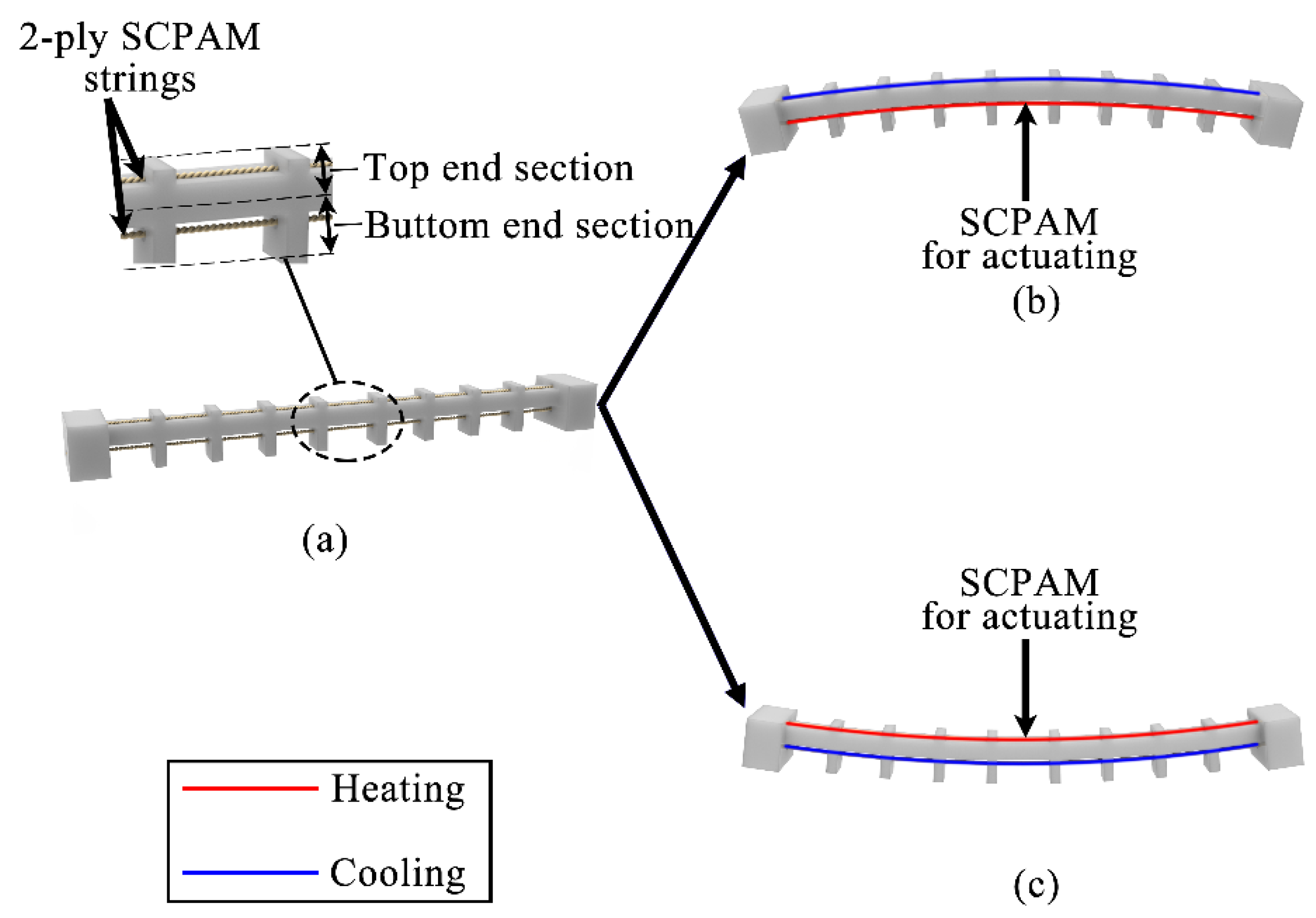
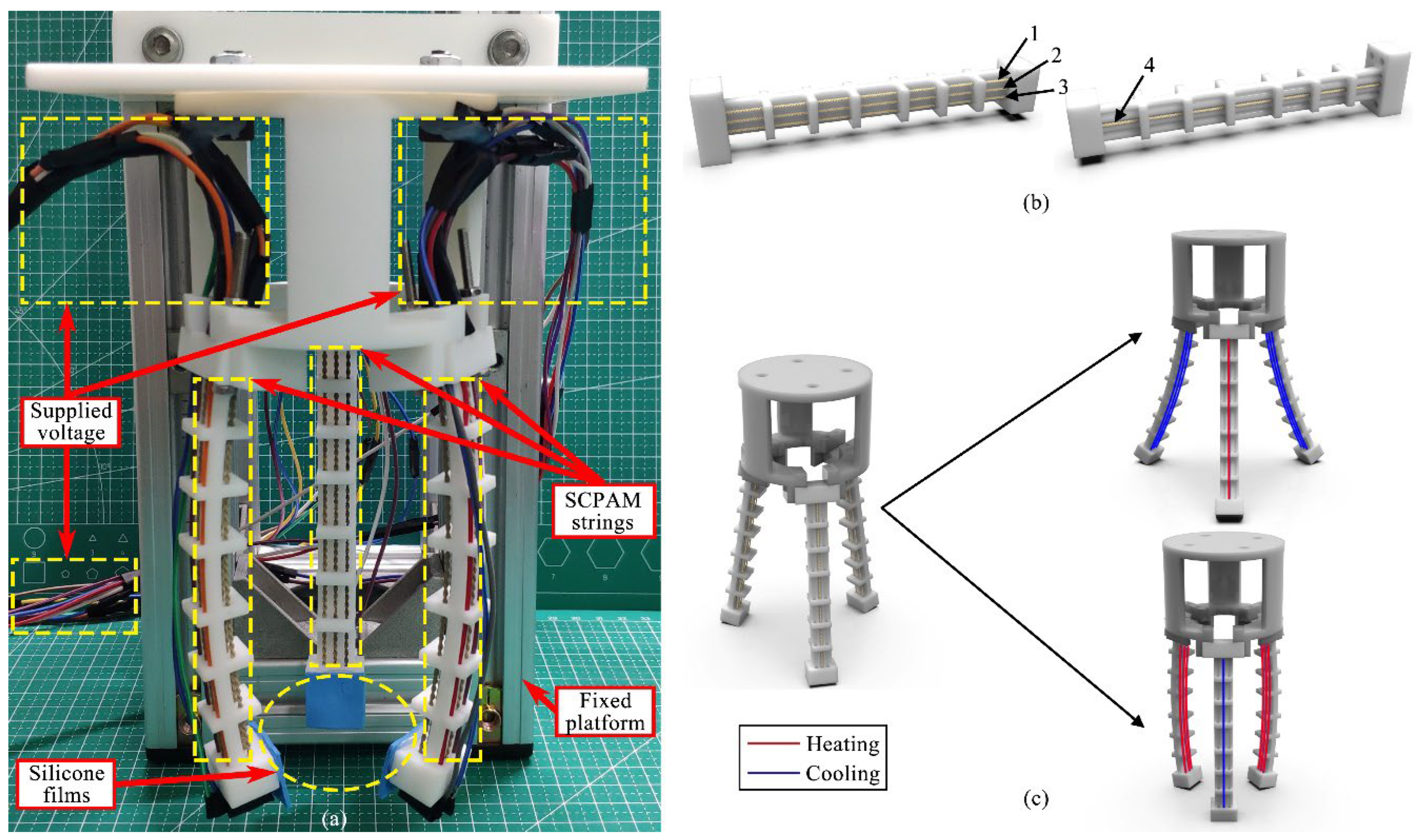
2.1. Design and Fabrication of the Soft Robot Module
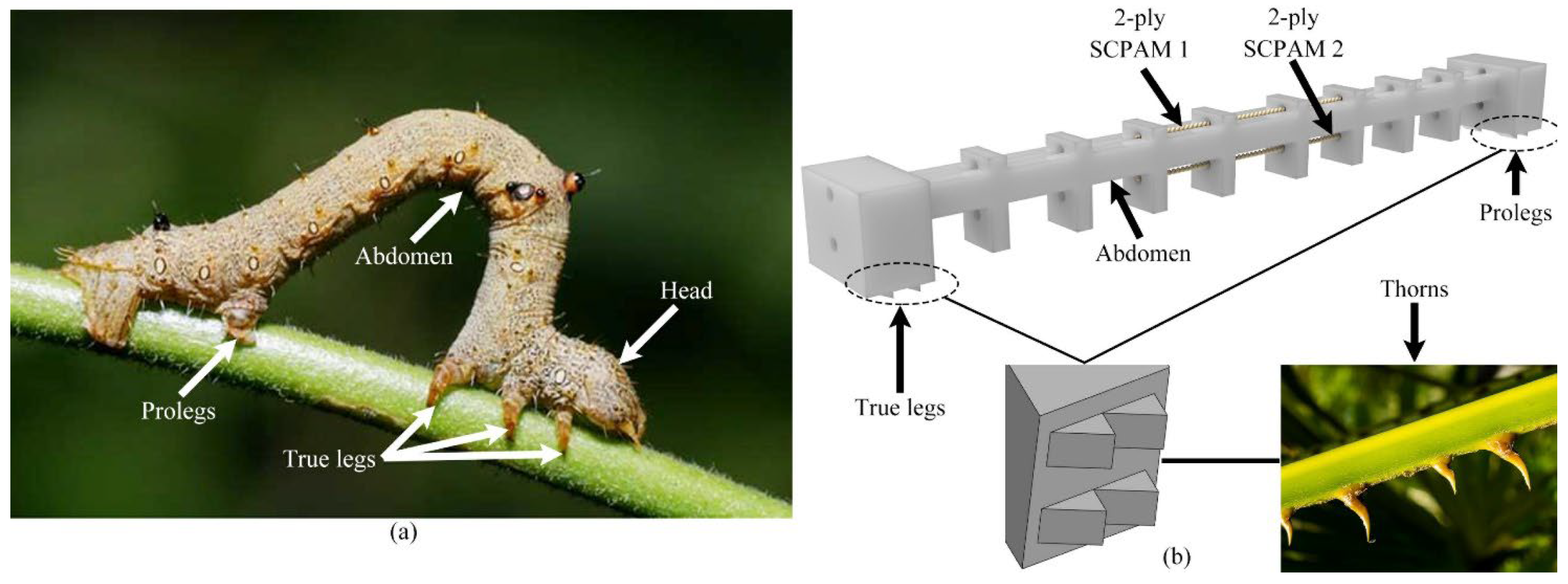
2.2. Configuration of the Crawling Robot
2.3. Configuration of the Soft Gripper
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. SCPAM Characterization
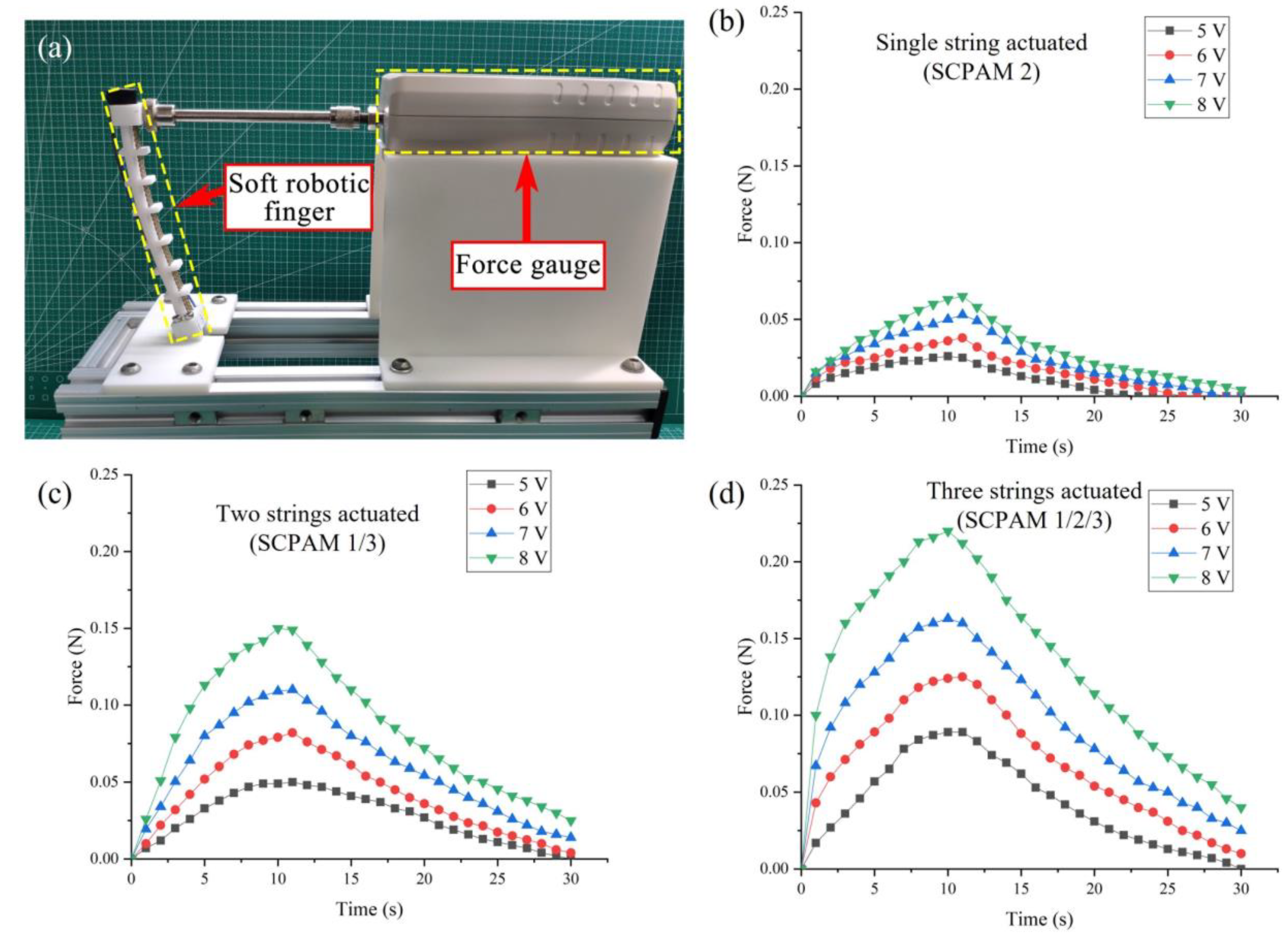
3.1.1. Force Characterization
3.1.2. Strain Characterization
3.2. Locomotion Velocity Test of the Crawling Robot
- Mode A: Insert the actuator through eight guides, then fix the actuator’s ends at the first and eighth guides, respectively. The total length of the actuator is 111 mm.
- Mode B: Insert the actuator through the middle six guides, then fix the actuator’s ends at the second and seventh guides, respectively. The total length of the actuator is 81 mm.
- Mode C: Insert the actuator through the middle four guides, then fix the actuator’s ends at the third and sixth guides, respectively. The total length of the actuator is 51 mm.
- Mode D: Fix the actuator at the two middlemost guides, with a total length of 21 mm.
3.3. Locomotion Efficiency Analysis of the Crawling Robot
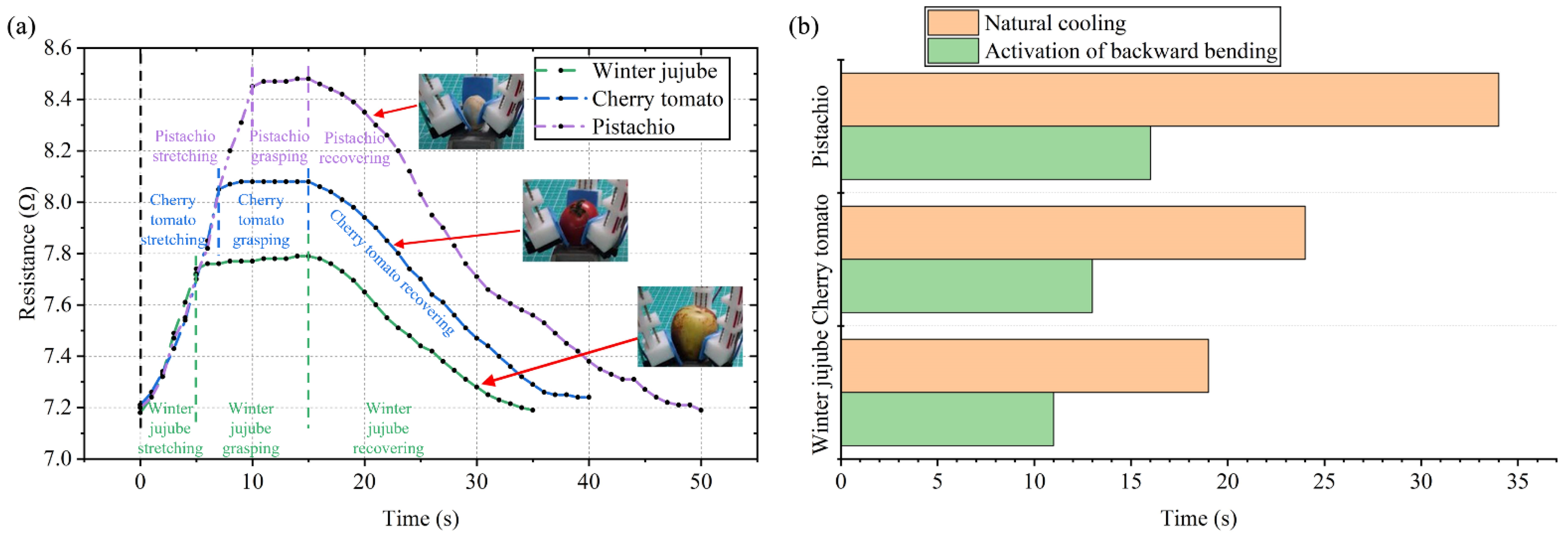
3.4. Sensing Test of the Crawling Robot
- (1)
- Modeling error generated by the hysteresis behavior of the SCPAM string;
- (2)
- Potential creep of resistance measurements over many cycles due to inherent nylon material properties and the estimation of the resistance value;
- (3)
- Deviation of the camera position in the bending test;
- (4)
- The static bending resistance relationship is used to predict the dynamic bending angle.
3.5. Output Force Test of the Finger
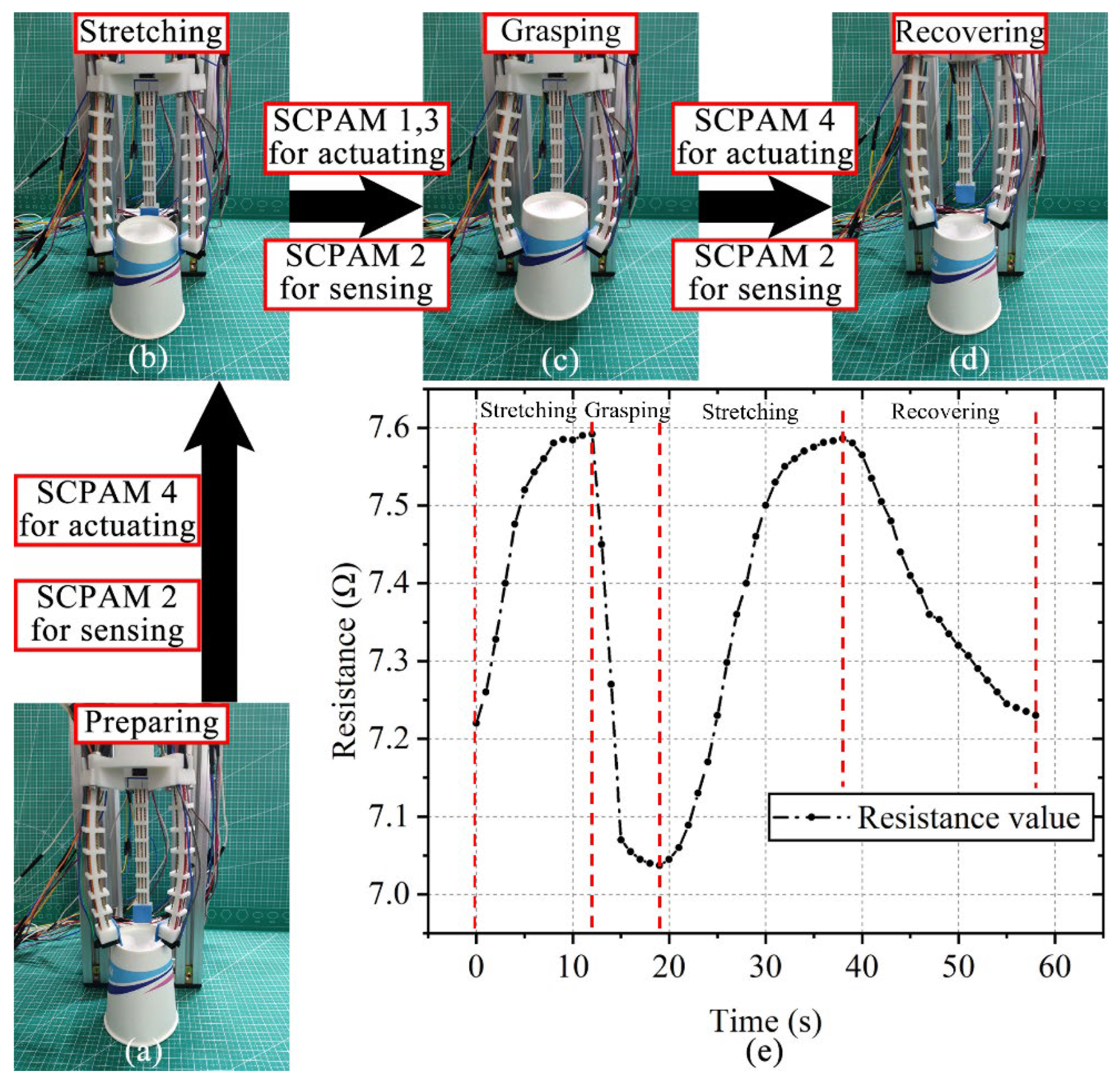
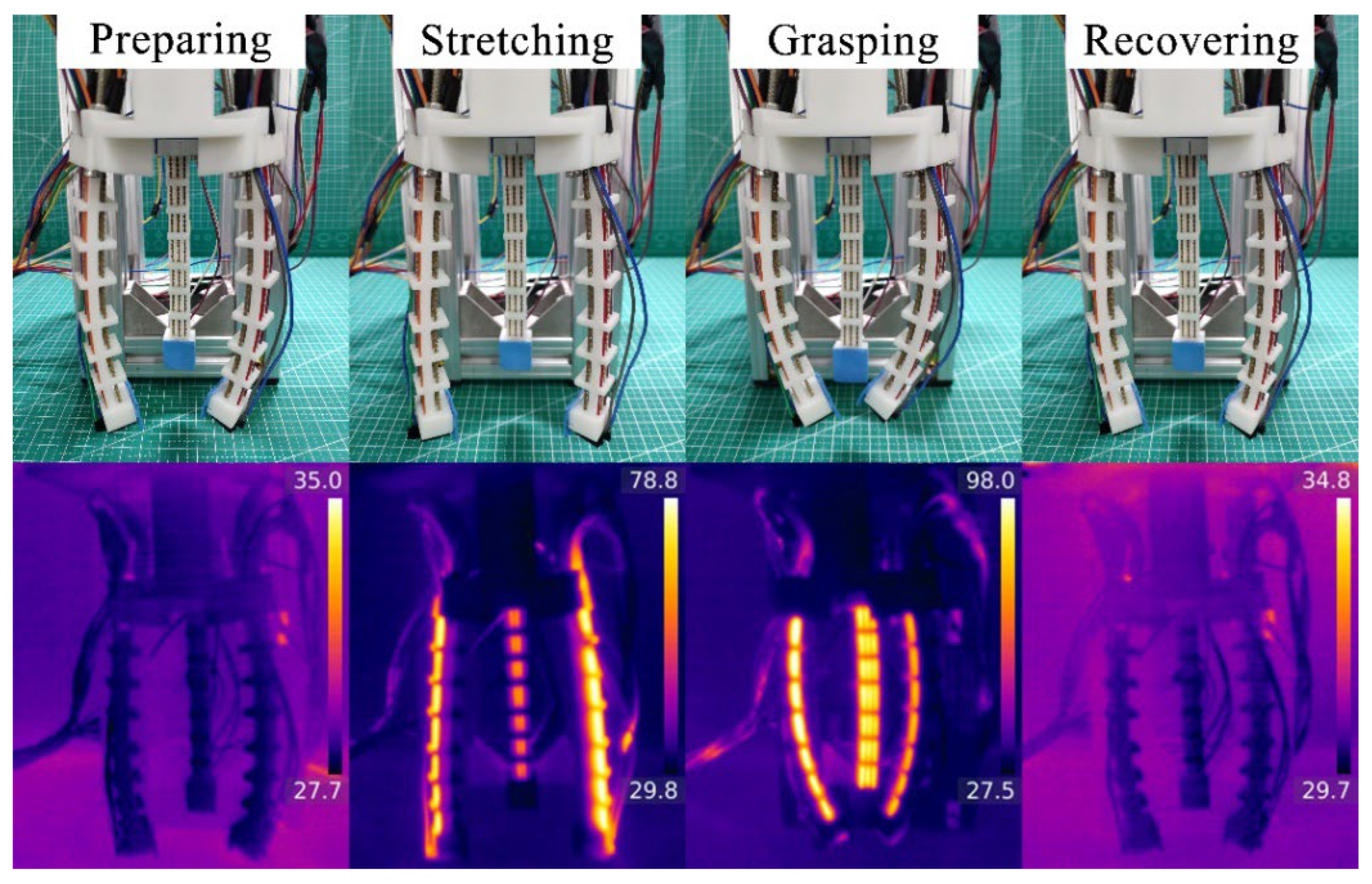
3.6. Actuation–Sensing Integration Test of the Gripper
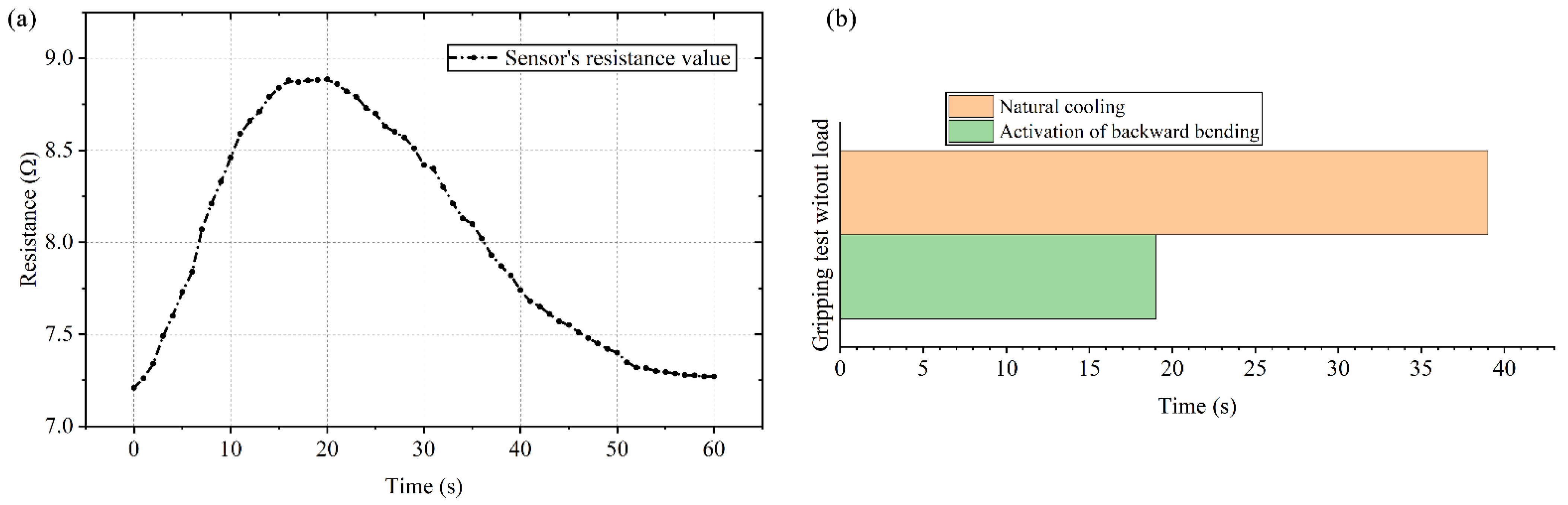
3.7. Gripping Test
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Majidi, C. Soft-matter engineering for soft robotics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umedachi, T.; Vikas, V.; Trimmer, B.A. Highly deformable 3-D printed soft robot generating inching and crawling locomotions with variable friction legs. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 4590–4595. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Ahn, S.-H. Shape memory alloy-based soft gripper with variable stiffness for compliant and effective grasping. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Design and implementation of a soft robotic arm driven by SMA coils. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 6108–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F.; Mosadegh, B.; Galloway, K.C.; Wehner, M.; Karpelson, M.; Wood, R.J.; Whitesides, G.M. A resilient, untethered soft robot. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Pre-charged pneumatic soft gripper with closed-loop control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.Z.; Wei, Y. Bioinspired robotic fingers based on pneumatic actuator and 3D printing of smart material. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liang, W.; Ren, Q.; Gupta, U.; Chen, F.; Zhu, J. Modelling and control of a novel soft crawling robot based on a dielectric elastomer actuator. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 4188–4193. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Gu, G. Bioinspired Venus flytrap: A dielectric elastomer actuated soft gripper. In Proceedings of the 2017 24th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP), Auckland, New Zealand, 21–23 November 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Liu, K.; Pan, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhu, X. An Integrated Design and Fabrication Strategy for Planar Soft Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 2629–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, J.D.; Kim, K.J.; Leang, K.K. 3D-printed ionic polymer-metal composite soft crawling robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 4313–4320. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Kim, W. Aquatic ionic-polymer-metal-composite insectile robot with multi-DOF legs. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 18, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hou, P.; Ye, Z. Robotic fish propelled by a servo motor and ionic polymer-metal composite hybrid tail. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2019, 141, 071001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vikas, V.; Cohen, E.; Grassi, R.; Sözer, C.; Trimmer, B. Design and locomotion control of a soft robot using friction manipulation and motor–tendon actuation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, T.; Manti, M.; Passetti, G.; d’Elia, N.; Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C. Design and development of a bio-inspired, under-actuated soft gripper. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 3619–3622. [Google Scholar]
- Castledine, N.P.; Boyle, J.H.; Kim, J. Design of a modular continuum robot segment for use in a general purpose manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 4430–4435. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Hu, X.; Zuo, B.; Huang, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, H. Liquid crystal elastomer actuator with serpentine locomotion. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7597–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palagi, S.; Mark, A.G.; Reigh, S.Y.; Melde, K.; Qiu, T.; Zeng, H.; Parmeggiani, C.; Martella, D.; Sanchez-Castillo, A.; Kapernaum, N. Structured light enables biomimetic swimming and versatile locomotion of photoresponsive soft microrobots. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, Q.; Iyer, P.; Cai, S. Electrically Controlled Soft Actuators with Multiple and Reprogrammable Actuation Modes. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y. 3D printing of shape memory polymer for functional part fabrication. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 84, 2079–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linghu, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Yu, K.; Li, C.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Jin, X.; You, Z.; Song, J. Universal SMP gripper with massive and selective capabilities for multiscaled, arbitrarily shaped objects. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Kumar, K.; Jawed, M.K.; Nasab, A.M.; Ye, Z.; Shan, W.; Majidi, C. Chasing biomimetic locomotion speeds: Creating untethered soft robots with shape memory alloy actuators. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaau7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Dong, E.; Xu, M.; Liu, C.; Alici, G.; Jie, Y. Soft and smart modular structures actuated by shape memory alloy (SMA) wires as tentacles of soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 085026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, M.A.; Paik, J. New soft robots really suck: Vacuum-powered systems empower diverse capabilities. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaan6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ji, C.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.; Pan, M. Vacuum-powered soft pneumatic twisting actuators to empower new capabilities for soft robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Zou, H.; Peng, Z.; Meng, G. Multisegment annular dielectric elastomer actuators for soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 115024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Cai, S. Recyclable and self-repairable fluid-driven liquid crystal elastomer actuator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35464–35474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minori, A.F.; He, Q.; Glick, P.E.; Adibnazari, I.; Stopol, A.; Cai, S.; Tolley, M.T. Reversible actuation for self-folding modular machines using liquid crystal elastomer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, C.Y.; Serrano, P.A.A.; Ahn, S.-H. Soft grasping mechanisms composed of shape memory polymer based self-bending units. Compos. B. Eng. 2019, 164, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, J. A general soft robot module driven by twisted and coiled actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 035019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfagharian, A.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Khoo, S.Y.; Moghadam, A.A.A.; Gibson, I.; Kaynak, A. Evolution of 3D printed soft actuators. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2016, 250, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Cacucciolo, V.; Shea, H.; Floreano, D. Soft biomimetic fish robot made of dielectric elastomer actuators. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, G.; Zou, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, X. Soft wall-climbing robots. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Atab, N.; Mishra, R.B.; Al-Modaf, F.; Joharji, L.; Alsharif, A.A.; Alamoudi, H.; Diaz, M.; Qaiser, N.; Hussain, M.M. Soft actuators for soft robotic applications: A review. Adv. Intell. Syst 2020, 2, 2000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Liu, X.; Cacucciolo, V.; Imboden, M.; Civet, Y.; El Haitami, A.; Cantin, S.; Perriard, Y.; Shea, H. An autonomous untethered fast soft robotic insect driven by low-voltage dielectric elastomer actuators. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaaz6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, L.; Petersen, K.; Lum, G.Z.; Sitti, M. Soft actuators for small-scale robotics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Shi, Z.; Meng, Q.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, X. Toward Application of Liquid Crystalline Elastomer for Smart Robotics: State of the Art and Challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tse, Y.A.; Zhang, Y.; Kan, Z.; Wang, M.Y. A low-cost inchworm-inspired soft robot driven by supercoiled polymer artificial muscle. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Korea, 14–18 April 2019; pp. 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, J. A soft crawling robot driven by single twisted and coiled actuator. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2019, 291, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.Y. A compact and low-cost robotic manipulator driven by supercoiled polymer actuators. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 1827–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, A.; Almubarak, Y.; Rupawat, Y.M.; Warren, J.; Tadesse, Y. Poly-Saora robotic jellyfish: Swimming underwater by twisted and coiled polymer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 045039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Zhao, J. Twisted and coiled sensor for shape estimation of soft robots. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 482–487. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, H. Study on the twisted and coiled polymer actuator with strain self-sensing ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 15716–15725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombara, D.; Fowzer, S.; Zhang, J. Compliant, large-strain, and self-sensing twisted string actuators. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombara, D.; Mansurov, V.; Konda, R.; Fowzer, S.; Zhang, J. Self-sensing for twisted string actuators using conductive supercoiled polymers. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, Louisville, KY, USA, 9–11 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Totaro, M.; Beccai, L. Toward perceptive soft robots: Progress and challenges. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. A proprioceptive bellows (PB) actuator with position feedback and force estimation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Novel variable-stiffness robotic fingers with built-in position feedback. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuc, N.H.; Thuy, D.V.; Park, J.; Kim, D.; Koo, J.; Lee, Y.; Nam, J.-D.; Choi, H.R. A dielectric elastomer actuator with self-sensing capability. In Proceedings of the 2008 Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD), San Diego, CA, USA, 10 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rosset, S.; O’Brien, B.M.; Gisby, T.; Xu, D.; Shea, H.R.; Anderson, I.A. Self-sensing dielectric elastomer actuators in closed-loop operation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 104018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzello, G.; Naso, D.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Closed loop control of dielectric elastomer actuators based on self-sensing displacement feedback. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 035034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffstadt, T.; Griese, M.; Maas, J. Online identification algorithms for integrated dielectric electroactive polymer sensors and self-sensing concepts. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäder, T.; Heusinger, J.V.; Senf, B.; Zoch, M.; Winkler, A.; Drossel, W.-G. Calibration of piezoresistive shape-memory alloy strain sensors. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2022, 33, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, E.J.; Soriano, J.; Fernández de Bastida Garrido, I.; Abdul Majid, D.L. Accurate position control of shape memory alloy actuation using displacement feedback and self-sensing system. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 2553–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, C.S.; Lima, M.D.; Li, N.; Spinks, G.M.; Foroughi, J.; Madden, J.D.; Kim, S.H.; Fang, S.; De Andrade, M.J.; Göktepe, F. Artificial muscles from fishing line and sewing thread. Science 2014, 343, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, M.C.; Niemeyer, G. On the control and properties of supercoiled polymer artificial muscles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonov, A.; Henderson, T.; Lan, Z.; Sundar, G.; Factor, A.; Zhang, J.; Yip, M. Bundled super-coiled polymer artificial muscles: Design, characterization, and modeling. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-T.; Slate, D.J.; Paetsch, C.R.; Dorfmann, A.L.; Trimmer, B.A. Scaling of caterpillar body properties and its biomechanical implications for the use of a hydrostatic skeleton. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Scaraggi, M.; Yan, C.; Wang, X.; Gorb, S.N.; Dini, D.; Zhou, F. Bioinspired 3D printed locomotion devices based on anisotropic friction. Small 2019, 15, 1802931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Z.; Yan, C.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F. Biomimetic surface with tunable frictional anisotropy enabled by photothermogenesis-induced supporting layer rigidity variation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1801460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lee, J.-Y.; Rodrigue, H.; Song, S.-H.; Chu, W.-S.; Ahn, S.-H. Locomotion of inchworm-inspired robot made of smart soft composite (SSC). Bioinspir. Biomim. 2014, 9, 046006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, R.; Zhang, J. The Effects of Nylon Polymer Threads on Strain-Loading Hysteresis Behavior of Supercoiled Polymer (SCP) Artificial Muscles. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, Park City, UT, USA, 9–11 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, F.; Wu, L.; Tadesse, Y. Modeling of One-Ply and Two-Ply Twisted and Coiled Polymer Artificial Muscles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 26, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
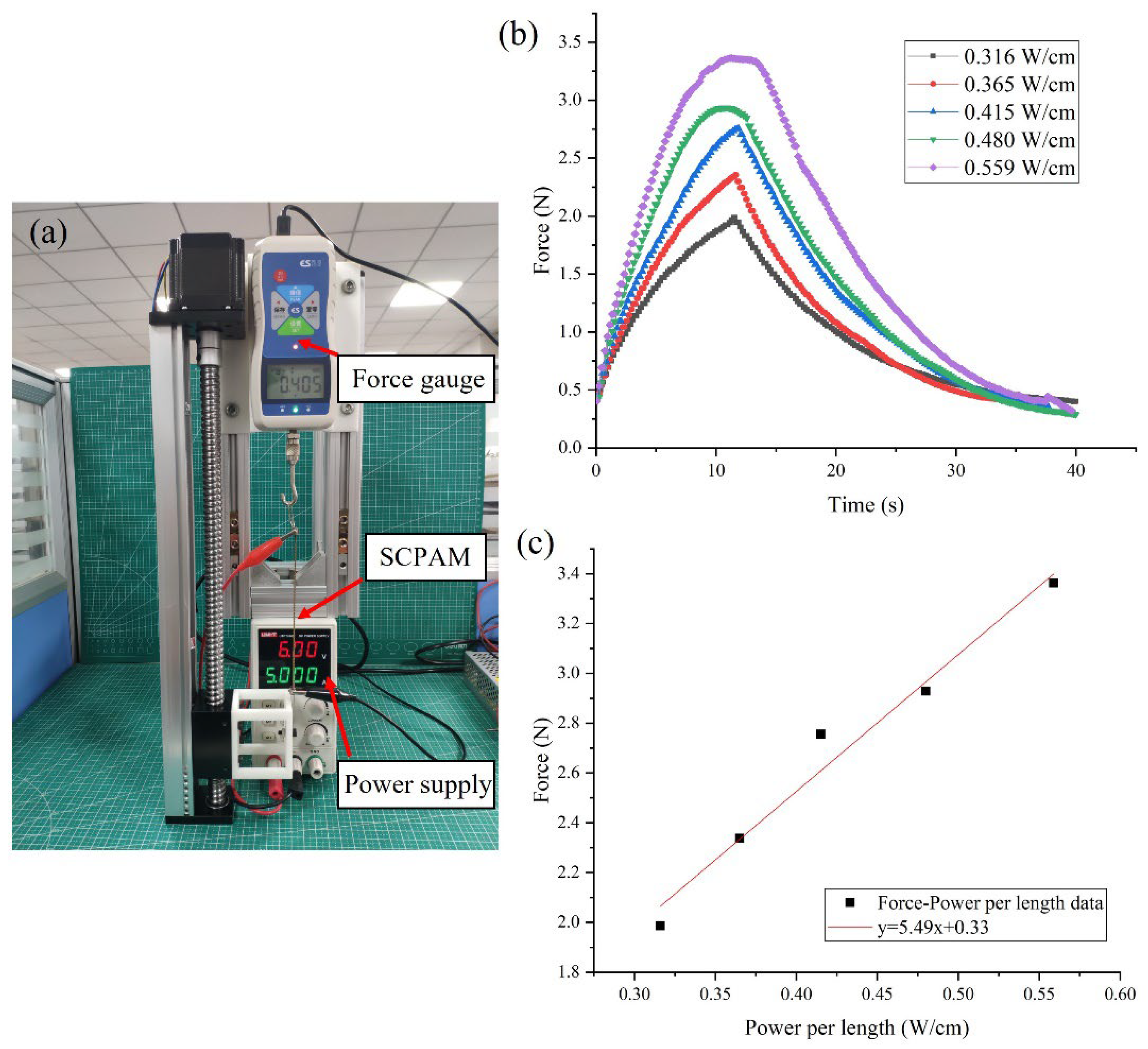
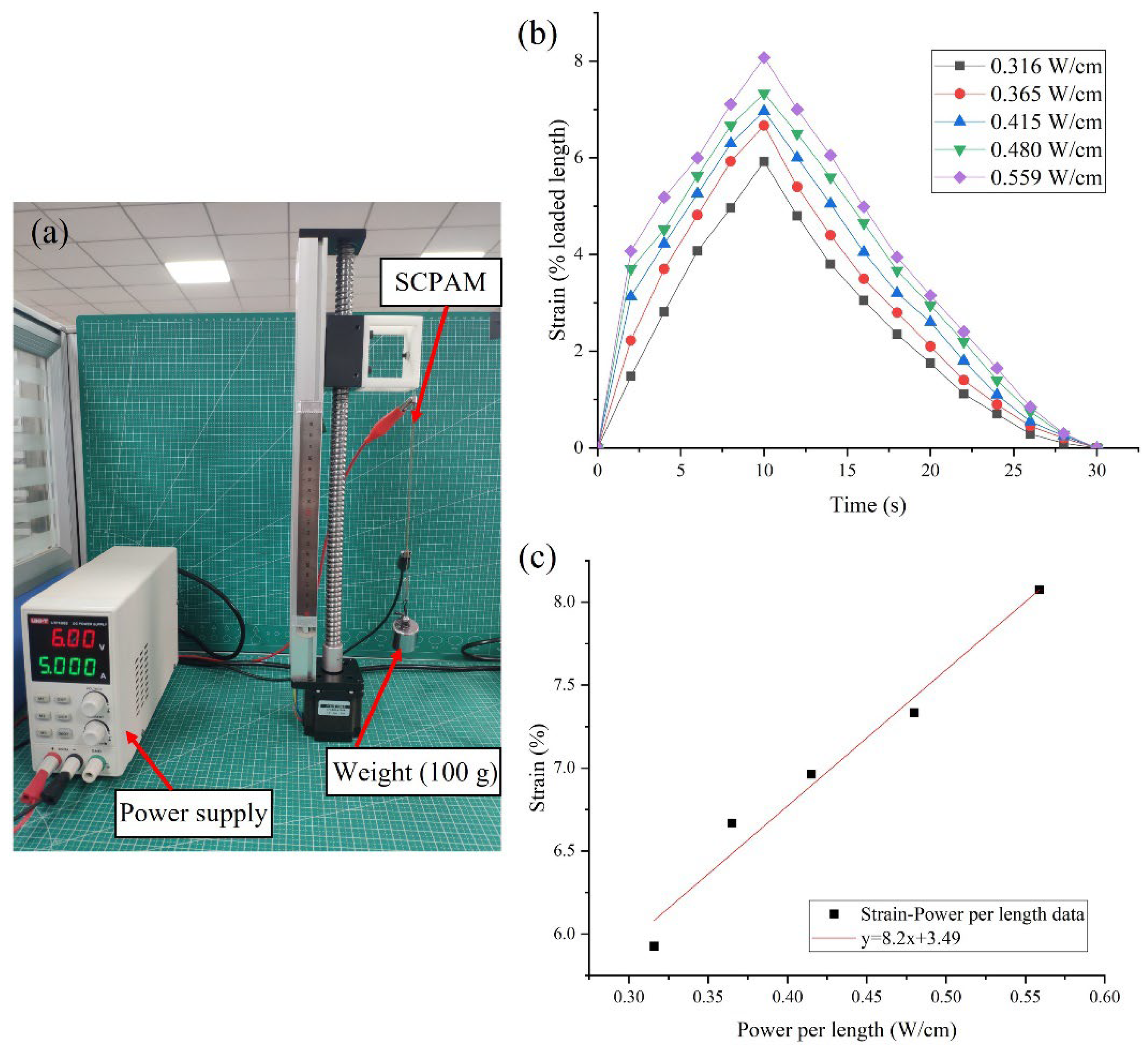
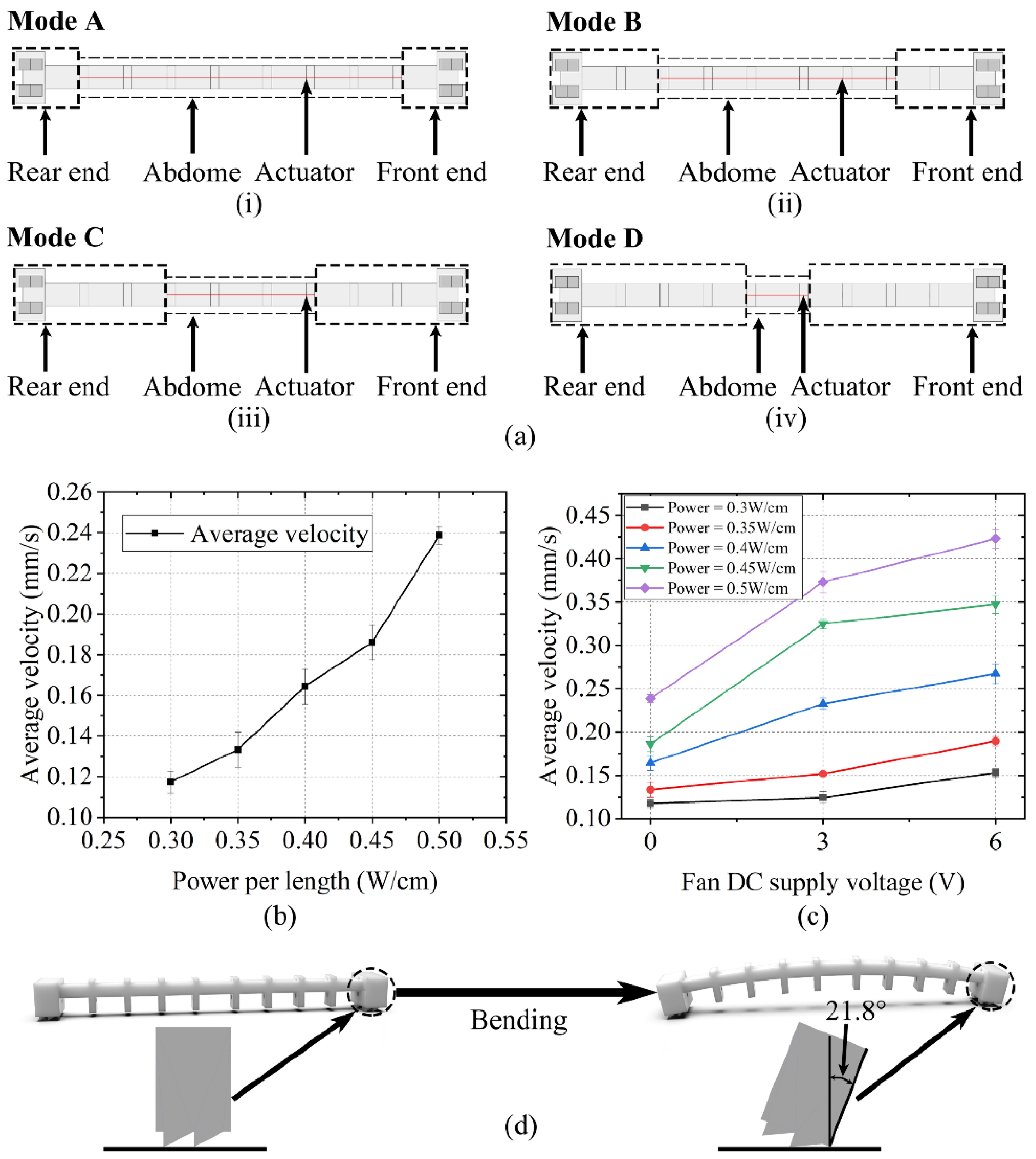

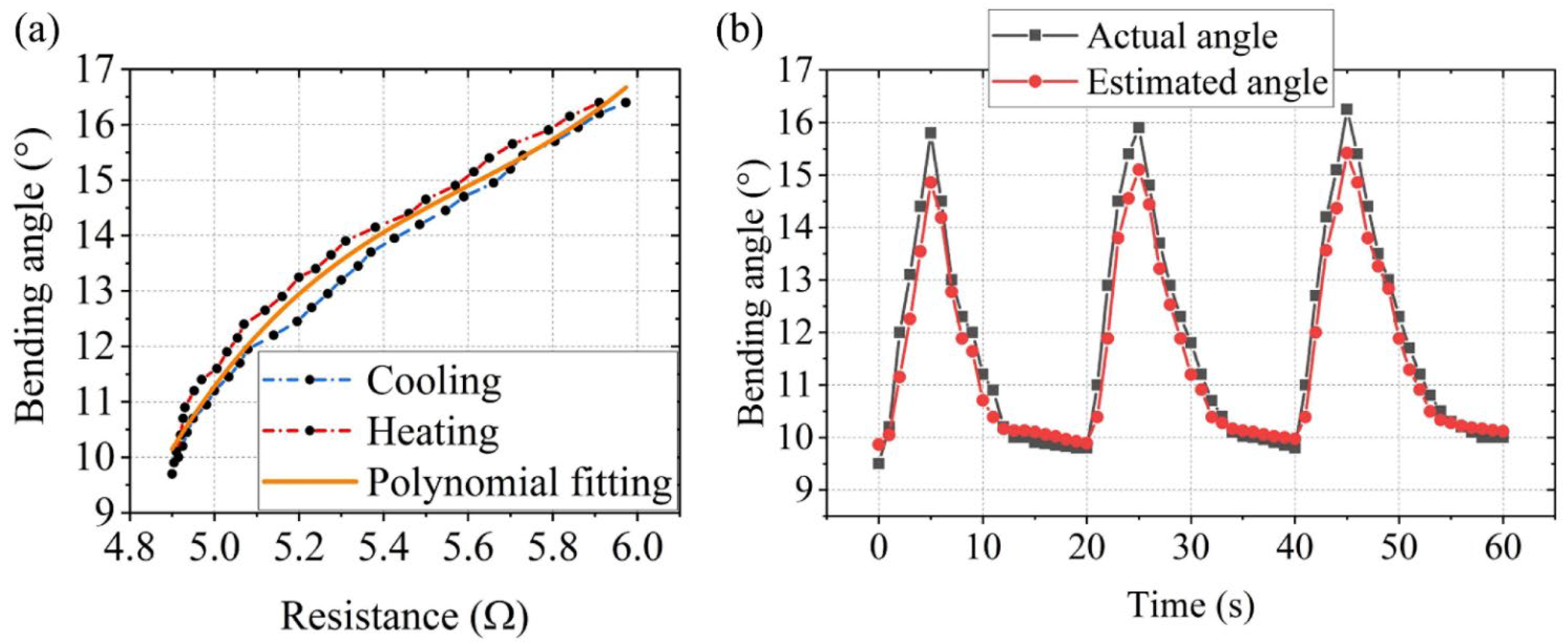
| Reference | Actuation Method | Pros | Cons | Soft Robot Applications | Future Work (Envisioned Applications) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huang et al. [22] | SMA | High power density, high reversibility, low operating voltage | Not soft material, hysteresis in phase transformation | Jumping, walking, rolling | -- |
| Jin et al. [23] | Crawling, swimming, gripping | -- | |||
| Robertson et al. [24] | Pneumatic | Light weight, soft, biocompatible | Needs bulky accessories, difficulty in controlling force | Gripping (suctioning), crawling, rolling, vertical climbing | -- |
| Jiao et al. [25] | Gripping, manipulating, crawling, climbing, driving | -- | |||
| Li et al. [26] | DEA | High elastic energy density, high strain, low Young’s modulus | High operating voltage | Rolling, creeping, crawling | -- |
| He et al. [27] | LCE | Good mechanical properties, good flexibility, anisotropic behavior | Single stimulus response, hard to control deformation accurately, difficulty in remote control | Gripping, crawling | -- |
| Minori et al. [28] | Lifting, crawling | -- | |||
| Wang et al. [29] | SMP | High strain recovery, biocompatibility, biodegradability | Fatigue, high response time, low-medium power density | Gripping (three different grasping mechanisms) | -- |
| Castledine et al. [16] | Motor & tendon | Easy to control, fast response velocity | Needs affiliated transmission mechanisms, adds rigid components | -- | Manipulating, crawling |
| Tang et al. [30] | SCPAM | High power-to-weight ratio, inherent compliance, low-cost, small hysteresis. good customizability, long cycle life | Difficulty in controlling accurately, long cooling time, break at high temperature | Gripping | Swimming, crawling |
| Our work | Crawling, gripping | Manipulating, swimming |
| p0 | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| −1017.79 | 545.29 | −96.66 | 5.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Ren, Y.; Wang, M.Y. A Proprioceptive Soft Robot Module Based on Supercoiled Polymer Artificial Muscle Strings. Polymers 2022, 14, 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112265
Yang Y, Zhu H, Liu J, Lu H, Ren Y, Wang MY. A Proprioceptive Soft Robot Module Based on Supercoiled Polymer Artificial Muscle Strings. Polymers. 2022; 14(11):2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112265
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Honghui Zhu, Jia Liu, Haojian Lu, Yi Ren, and Michael Yu Wang. 2022. "A Proprioceptive Soft Robot Module Based on Supercoiled Polymer Artificial Muscle Strings" Polymers 14, no. 11: 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112265
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhu, H., Liu, J., Lu, H., Ren, Y., & Wang, M. Y. (2022). A Proprioceptive Soft Robot Module Based on Supercoiled Polymer Artificial Muscle Strings. Polymers, 14(11), 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112265








