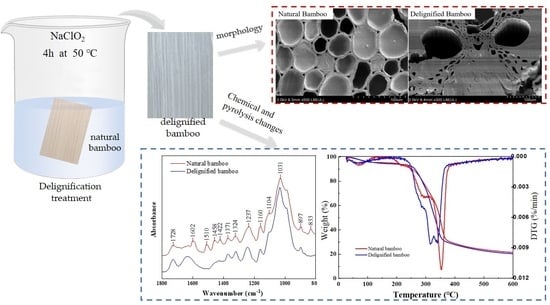
Changes in Chemical and Thermal Properties of Bamboo after Delignification Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Delignification Treatment
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
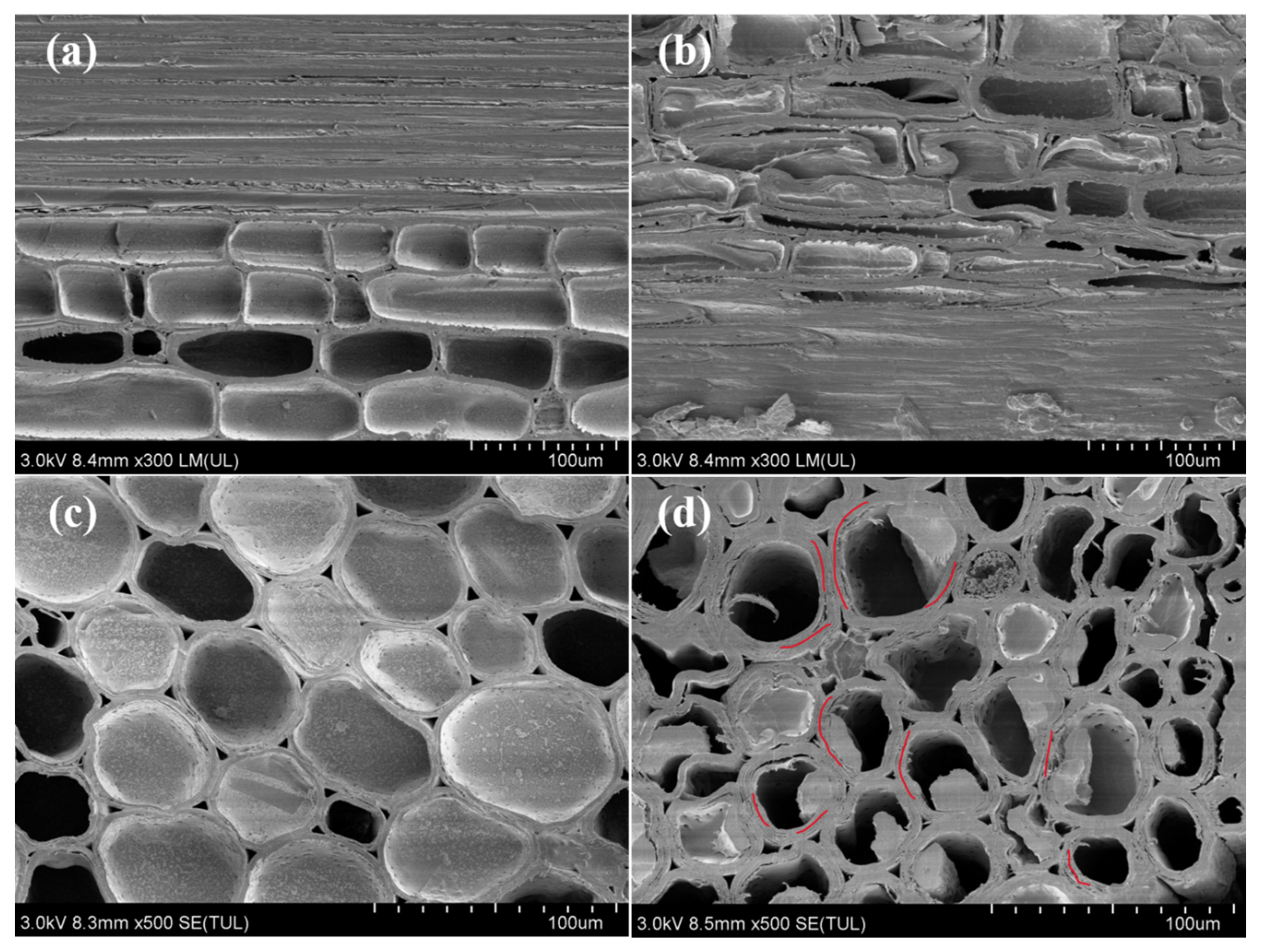
3.1. Surface Microstructure Morphology
3.2. Chemical Functional Groups
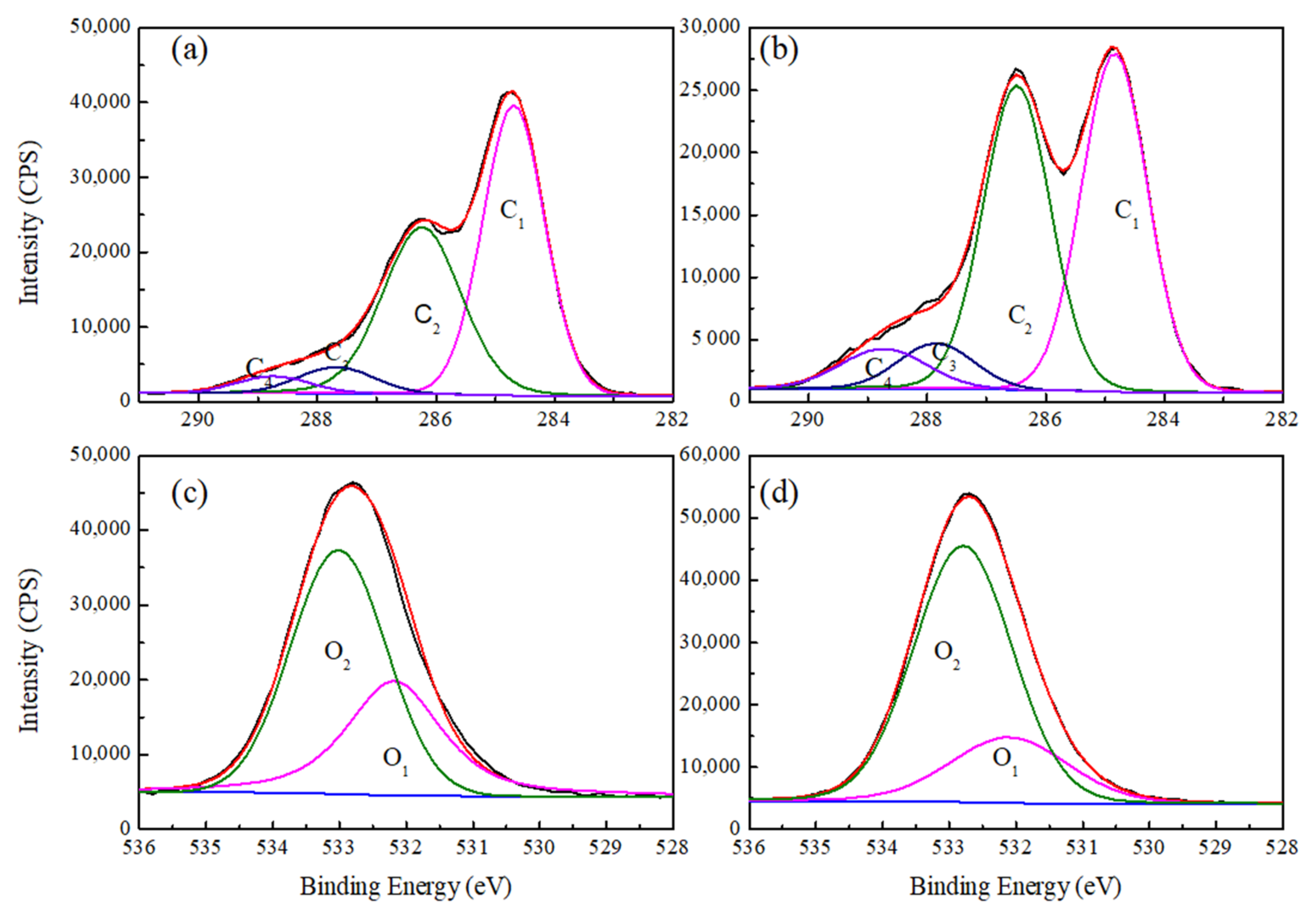
3.3. Chemical Composition
3.4. Crystalline Structure
3.5. Pyrolysis Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takatani, M.; Ito, H.; Ohsugi, S.; Kitayama, T.; Saegusa, M.; Kawai, S.; Okamoto, T. Effect of Lignocellulosic Materials on the Properties of Thermoplastic Polymer/Wood Composites. Holzforschung 2000, 54, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Yu, S.; Yan, M.; Berglund, L. Optically Transparent Wood from a Nanoporous Cellulosic Template: Combining Functional and Structural Performance. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, R.; Chen, C.; Keplinger, T.; Pei, Y.; He, S.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Dai, J.; Hitz, E.; Yang, B.; et al. Scalable Aesthetic Transparent Wood for Energy Efficient Buildings. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanadpour, M.; Carosio, F.; Larsson, P.T.; Wågberg, L. Phosphorylated Cellulose Nanofibrils: A Renewable Nanomaterial for the Preparation of Intrinsically Flame-Retardant Materials. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3399–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X. Highly Compressible Wood Sponges with a Spring-like Lamellar Structure as Effective and Reusable Oil Absorbents. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10365–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Duan, G.; Yang, H.; Cheong, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Ahn, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, S.; Han, J.; et al. Wood-Derived, Conductivity and Hierarchical Pore Integrated Thick Electrode Enabling High Areal/Volumetric Energy Density for Hybrid Capacitors. Small 2021, 17, 2102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Li, H.Y.; Li, J.; Lü, B.; Song, G.; Gong, X.; Qin, M.; Yao, C.L.; et al. Scalable, Strong and Water-Stable Wood-Derived Bioplastic. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beims, R.F.; Arredondo, R.; Sosa Carrero, D.J.; Yuan, Z.; Li, H.; Shui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Leitch, M.; Xu, C.C. Functionalized Wood as Bio-Based Advanced Materials: Properties, Applications, and Challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, L.A.; Burgert, I. Bioinspired Wood Nanotechnology for Functional Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, L. Nanoscale ion regulation in wood-based structures and their device applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 33, 2002890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Xia, C.; Zuo, S.; Ge, S.; Yang, R.; Ma, X.; Fei, B.; Li, J.; Cheng, C.K.; et al. Synthesis of ultra-high strength structured material from steam-modified delignification of wood. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 351, 131531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Song, J.; Li, T.; Gong, A.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Yao, Y.; Luo, W.; Henderson, D.; Hu, L. Henderson, and L-B. Hu: Highly anisotropic, highly transparent wood composites. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.; Widner, D.; Segmehl, J.S.; Casdorff, K.; Keplinger, T.; Burgert, I. Delignified and densified cellulose bulk materials with excellent tensile properties for sustainable engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. Biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol. J. Biotechnol. 1997, 56, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, J.S.; Ko, J.K.; Choi, I.G.; Park, Y.C.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, K.H. Fungal pretreatment of lignocellulose by Phanerochaete chrysosporium to produce ethanol from rice straw. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 104, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Mi, R.; Dai, J.; Xie, H.; Pei, Y.; Li, J.; Qiao, H.; Tang, H.; Yang, B.; et al. Rapid Processing of Whole Bamboo with Exposed, Aligned Nanofibrils toward a High-Performance Structural Material. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5194–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Li, Y.Q.; Huang, P.; Yang, B.; Hu, N.; Fu, S.Y. High-Performance Bamboo Steel Derived from Natural Bamboo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shan, S.; Shi, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, L.; Smith, L.M. Optically Transparent Bamboo with High Strength and Low Thermal Conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Julianri, I.; Wang, S.; Chan, S.H.; Li, M.; Long, Y. Transparent Bamboo with High Radiative Cooling Targeting Energy Savings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 3, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yu, W. Effects of Extraction Methods on Morphology, Structure and Properties of Bamboo Cellulose. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchessault, R. Wood Chemistry, Fundamentals and Applications. 2nd Edn., by Ero Sjöström, Academic Press, NY, 1993, 250 Pages of Text and 42 Pages of Bibliography and Index (ISBN 0-12-647481-8). Carbohydr. Res. 1994, 252, C1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhan, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Pan, X.; Zhuang, X. Wei Surface Characterization and Biodegradability of Sodium Hydroxide-Treated Moso Bamboo Substrates. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2021, 79, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.B.; Hong, Y.M.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.P.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Xu, Z.K. Delignified Wood with Unprecedented Anti-Oil Properties for the Highly Efficient Separation of Crude Oil/Water Mixtures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16735–16741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhong, T.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Fei, B. Effect of Alkali Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Individual Bamboo Fibres. Cellulose 2017, 24, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Tang, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, J. Impact of Delignification on Morphological, Optical and Mechanical Properties of Transparent Wood. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 117, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. FTIR and XPS Analysis of the Changes in Bamboo Chemical Structure Decayed by White-Rot and Brown-Rot Fungi. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, H. Comparative Study of the Photo-Discoloration of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys Pubescens Mazel) and Two Wood Species. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 7029–7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Kapu, N.S.; Beatson, R.; Chang, X.F.; Martinez, D.M. Effect of Alkaline Pre-Extraction of Hemicelluloses and Silica on Kraft Pulping of Bamboo (Neosinocalamus Affinis Keng). Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 91, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguila Inari, G.; Petrissans, M.; Lambert, J.; Ehrhardt, J.J.; Gérardin, P. XPS Characterization of Wood Chemical Composition after Heat-Treatment. Surf. Interface Anal. 2006, 38, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Guanben, Application of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy in Wood Science and Technology. China Wood Ind. 1999, 13, 17–20+29. [CrossRef]
- Watling, K.M.; Parr, J.F.; Rintoul, L.; Brown, C.L.; Sullivan, L.A. Raman, infrared and XPS study of bamboo phytoliths after chemical digestion. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 80, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Ren, H.Q.; Zhao, R.J.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, Y.P. FTIR and XPS spectroscopic studies of photodegradation of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys Pubescens Mazel). Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2009, 29, 1864–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérardin, P.; Petrič, M.; Petrissans, M.; Lambert, J.; Ehrhrardt, J.J. Evolution of Wood Surface Free Energy after Heat Treatment. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kocaefe, D.; Kocaefe, Y.; Boluk, Y.; Pichette, A. Study of the Degradation Behavior of Heat-Treated Jack Pine (Pinus Banksiana) under Artificial Sunlight Irradiation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1197–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguila Inari, G.; Pétrissans, M.; Dumarcay, S.; Lambert, J.; Ehrhardt, J.J.; Šernek, M.; Gérardin, P. Limitation of XPS for Analysis of Wood Species Containing High Amounts of Lipophilic Extractives. Wood Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaefe, D.; Huang, X.; Kocaefe, Y.; Boluk, Y. Quantitative Characterization of Chemical Degradation of Heat-Treated Wood Surfaces during Artificial Weathering Using XPS. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.D.; Yu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yu, W.J.; Gao, J.M. Surface Chemical Composition Analysis of Heat-Treated Bamboo. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Kaliaguine, S.; Kokta, B.; Adnot, A. Surface Analysis of Explosion Pulps by ESCA Part 1. Carbon (1s) Spectra and Oxygen-to-Carbon Ratios. Wood Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdem, D.P.; Riedl, B.; Adnot, A.; Kaliaguine, S. ESCA Spectroscopy of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Grafted onto Wood Fibres. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 43, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubaa, A.; Riedl, B.; Koran, Z. Surface analysis of press dried-CTMP paper samples by electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, H. X-ray diffraction study of bamboo fibres treated with NaOH. Fibres Polym. 2009, 9, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Fei, B.; Cai, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X. The Pyrolysis Characteristics of Moso Bamboo. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 94, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.H.; Li, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, R.G.; Qiao, J.Z. Effects of high temperature heat treatment on FTIR and XRD characteristics of bamboo bundles. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2013, 33, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, W. Study on the Preparation Process and Performance of a Conductive, Flexible, and Transparent Wood. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 5396–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Xue, S.S.; Zhu, W.B.; Wang, X.Q.; Huang, P.; Fu, S.Y. Superstrong, Lightweight, and Exceptional Environmentally Stable SiO2@GO/Bamboo Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 7311–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yang, Z.; Hu, X.; Hong, G.; Zhang, S.; Song, W. The Effect of Alkali Treatment on Properties of Dopamine Modification of Bamboo Fibre/Polylactic Acid Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raveendran, K. Pyrolysis Characteristics of Biomass and Biomass Components. Fuel 1996, 75, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Lu, J.; Wei, M.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, P. Combustion Behavior and Thermal Degradation Properties of Wood Impregnated with Intumescent Biomass Flame Retardants: Phytic Acid, Hydrolyzed Collagen, and Glycerol. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3921–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of Hemicellulose, Cellulose and Lignin Pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Functional Group | Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| 1728 | C=O | Non-conjugated C=O in hemicellulose (xylans) |
| 1602 | C=C | C=C unsaturated linkages, aromatic skeletal vibration in lignin |
| 1510 | C=C | Aromatic skeletal vibration (C=C) in lignin |
| 1458 | C–H, O–H | Asymmetric bending in CH3 (lignin) |
| 1422 | CH2 | Aromatic skeletal vibrations (lignin) and C–H deformation in plane (cellulose) |
| 1371 | C–H | C–H deformation in cellulose and hemicellulose |
| 1324 | O–H | phenol group (cellulose) |
| 1237 | C–O | Syringyl ring and C–O stretch in lignin and xylan |
| 1160 | C–O–C | C–O–C vibration in cellulose and hemicellulose |
| 1104 | C–H | Guaiacyl and syringyl (lignin) |
| 1031 | C–O, C–H | C–O stretch in cellulose and hemicelluloseC–H stretch in lignin |
| 897 | C–H | C–H deformation in cellulose |
| 833 | C–H | C–H vibration in guaiacyl derivatives |
| Element Component | Binding Energy (eV) | Binding Type | Main Resources |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 284.5 | C–C, C–H | Lignin and extracts |
| C2 | 285.5 | C–O | Cellulose and hemicellulose |
| C3 | 286.5 | O–C–O, C=O | Cellulose |
| C4 | 288.3 | O–C=O | Hemicellulose and extracts |
| O1 | 532.8 | O–C=O | Lignin |
| O2 | 534.1 | C–O | Cellulose and hemicellulose |
| Samples | O/C Atomic Ratios | C (%) | O (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | O1 | O2 | ||
| Natural bamboo | 0.34 | 51.71 | 39.22 | 5.59 | 3.48 | 37.48 | 62.52 |
| Delignified bamboo | 0.45 | 44.88 | 41.65 | 6.73 | 6.73 | 23.96 | 76.04 |
| Sample | Tmax (°C) | Rmax (%/(°C) | Residues | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | (wt.%) | |
| Natural bamboo | 70.12 | 353.78 | 8.39 × 10−4 | 111.71 × 10−4 | 21.68 |
| Delignified bamboo | 69.11 | 315.62 | 6.02 × 10−4 | 86.42 × 10−4 | 20.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Gui, C.; Ji, Y.; Li, X.; Rao, F.; Huan, W.; Li, L. Changes in Chemical and Thermal Properties of Bamboo after Delignification Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132573
Yu H, Gui C, Ji Y, Li X, Rao F, Huan W, Li L. Changes in Chemical and Thermal Properties of Bamboo after Delignification Treatment. Polymers. 2022; 14(13):2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132573
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Huiling, Chengsheng Gui, Yaohui Ji, Xiaoyan Li, Fei Rao, Weiwei Huan, and Luming Li. 2022. "Changes in Chemical and Thermal Properties of Bamboo after Delignification Treatment" Polymers 14, no. 13: 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132573
APA StyleYu, H., Gui, C., Ji, Y., Li, X., Rao, F., Huan, W., & Li, L. (2022). Changes in Chemical and Thermal Properties of Bamboo after Delignification Treatment. Polymers, 14(13), 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132573