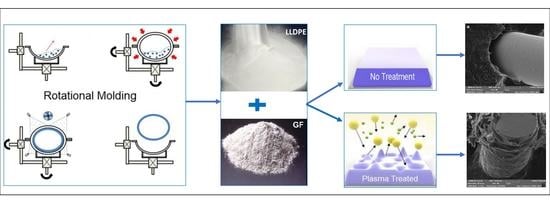
The Effect of Plasma Treatment of Polyethylene Powder and Glass Fibers on Selected Properties of Their Composites Prepared via Rotational Molding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plasma Treatment
2.3. Samples Preparation
2.4. Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Different Factors on the Selected Mechanical Properties of the Composites
3.1.1. Effect of Plasma Treatment of Polyethylene Powder
3.1.2. Effect of Oven Temperature and Holding Time
3.1.3. Effect of Plasma Treatment of Glass Fibers
3.1.4. Effect of Glass Fibers Content
3.1.5. The Effect of Plasma Treatment of the Powder and the Fibers on the Stress-Strain Behavior of the Composites
3.2. Morphology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crwaford, R.J.; Throne, J.L. Rotational Moulding Technology, 1st ed.; William Andrew: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 1-884207-85-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ogila, K.O.; Shao, M.; Yang, W.; Tan, J. Rotational molding: A review of the models and materials. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 778–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, B.I.; Takács, E.; Vlachopoulos, J. Processing enhancers for rotational molding of polyethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.Z.; Bickerton, S.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Crawford, R.J.; Harkin-Jones, E. Rotational Molding Cycle Time Reduction Using a Combination of Physical Techniques. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-W.; Crawford, R.J. Analysis of the effects of internal heating and cooling during the rotational molding of plastics. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1993, 33, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, A.G.; Crawford, R.J. Removal of pinholes and bubbles from rotationally moulded products. J. Eng. Manuf. 1996, 210, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogos, G. Bubble Removal in Rotational Molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Fu, K.H. Effect of enhancing fins on the heating/cooling efficiency of rotational molding and the molded product qualities. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.G.; Aguirre, M. Rotational Moulding and Powder Processing of Natural Fibre Reinforced Thermoplastics. Int. Polym. Process. 2003, 18, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Panigrahi, S.; Tabil, L.; Crerar, W. Pre-treatment of Flax Fibers for use in Rotationally Molded Biocomposites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2007, 26, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, Z.; Monzón, M.D.; Benítez, A.N.; Kearns, M.; Mccourt, M.; Hornsby, P.R. Banana and Abaca Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Composites Obtained by Rotational Molding Process Banana and Abaca Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Composites Obtained by Rotational Molding Process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-lópez, E.O.; González-lópez, M.E.; Pérez-fonseca, A.A.; González-núñez, R.; Rodrigue, D.; Robledo-ortíz, J.R.; González-lópez, M.E.; Pérez-fonseca, A.A. Effect of fiber content and surface treatment on the mechanical properties of natural fiber composites produced by rotomolding. Compos. Interfaces 2016, 6440, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-López, E.O.; Pérez-Fonseca, A.A.; González-García, Y.; Ramírez-Arreola, D.E.; González-Núñez, R.; Rodrigue, D.; Robledo-Ortíz, J.R. Polylactic acid–agave fiber biocomposites produced by rotational molding: A comparative study with compression molding. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 2528–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.R.R.; Rodrigue, E.G.D. Improving the Compatibility and Mechanical Properties of Natural Fibers / Green Polyethylene Biocomposites Produced by Rotational Author’s personal copy. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, P.S.; Thomas, S.; Spatenka, P.; Ghanam, Z.; Jenikova, Z. Effect of plasma modification of polyethylene on natural fibre composites prepared via rotational moulding. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 177, 107344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanana, F.E.; Rodrigue, D. Rotational Molding of Self-Hybrid Composites Based on Linear Low-Density Polyethylene and Maple Fibers. Polym. Compos. 2017, 39, 4094–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanana, F.E.; Chimeni, D.Y.; Rodrigue, D. Morphology and mechanical properties of maple reinforced LLDPE produced by rotational moulding: Effect of fibre content and surface treatment. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2018, 26, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczewski, M.; Szostak, M.; Nowak, D.; Piasecki, A. Effect of wood flour addition and modification of its surface on the properties of rotationally molded polypropylene composites. Polimery 2018, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribasplata-seguin, A.; Quispe-dominguez, R.; Tupia-anticona, W.; Acosta-sullcahuam, J. Rotational molding parameters of wood-plastic composite materials made of recycled high density polyethylene and wood particles. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewski, J.; Krawczak, A.; Weso, K.; Szostak, M. Rotational molding of biocomposites with addition of buckwheat husk filler. Structure-property correlation assessment for materials based on polyethylene (PE) and poly (lactic acid) PLA. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.C.; Harkin-Jones, E.; Kearns, M.; McCourt, M. Multilayered glass fibre-reinforced composites in rotational moulding. AIP Conf. Proc. 2011, 1353, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfler, G.; Jayaraman, K.; Lin, R. Rotational moulding and mechanical characterisation of micron-sized and nano-sized reinforced high density polyethylene. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 809, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Lin, R.J.T.; Bickerton, S.; Bhattacharyya, D. Rotational Moulding of Particulate Reinforced Polymeric Shell Structures. Mater. Sci. Forum 2003, 437–438, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Lin, R.J.T.; Bhattacharyya, D. Particulate reinforced rotationally moulded polyethylene composites-Mixing methods and mechanical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2080–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumer, M.I.; Leite, J.L.; Becker, D. Influence of calcium carbonate and slip agent addition on linear medium density polyethylene processed by rotational molding. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calò, E.; Massaro, C.; Terzi, R.; Cancellara, A.; Pesce, E.; Re, M.; Greco, A.; Maffezzoli, A.; Gonzalez-Chi, P.I.; Salomi, A. Rotational molding of polyamide-6 nano composites with improved flame retardancy. Int. Polym. Process. 2012, 27, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish Chandran, V.; Waigaonkar, S.D. Mechanical Properties and Creep Behavior of Rotationally Moldable Linear Low Density Polyethylene-Fumed Silica Nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhike, W.; Focke, W.W.; Asante, J.K.O. Rotomolded antistatic and flame-retarded graphite nanocomposites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2018, 31, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Höfler, G.; Lin, R.J.T.; Jayaraman, K. Rotational moulding and mechanical characterisation of halloysite reinforced polyethylenes. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda-Rodríguez, Z.; Arellano-Martínez, M.R.; Cruz-Barba, E.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A.; Rodrigue, D.; Vázquez-Lepe, M.; González-Núñez, R. Mechanical and thermal properties of polyethylene/carbon nanofiber composites produced by rotational molding. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.G.Ã.; Aragon, C.L. Final product testing of rotational moulded natural fibre-reinforced polyethylene. Polym. Test. 2006, 25, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlatová, M.; Horáková, M.; Hladík, J.; Špatenka, P. Plasma surface treatment of powder materials-Process and application. Acta Polytech. 2012, 52, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, V.; Prikryl, R.; Balkova, R.; Grycova, A.; Vanek, J. Plasma surface treatment and modification of glass fibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2002, 33, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, A. Effect of Plasma Treatment on Glass Fiber / Epoxy Resin Composite. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress of Innovative Textiles (ICONTEX2019), Çorlu, Turkey, 17–18 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Trejbal, J.; Šmilauer, V.; Kromka, A.; Potocký, Š.; Kopecký, L. Wettability enhancement of polymeric and glass micro fiber reinforcement by plasma treatment. In Proceedings of the NANOCON 2015-7th International Conference on Nanomaterials-Research and Application, Brno, Czech Republic, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, J.; De Farias, G.; Cordeiro, R.; Rodrigues, B.; Magalhães, H.; Scholz, S.; Antoun, R. Surface lignin removal on coir fibers by plasma treatment for improved adhesion in thermoplastic starch composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciso, B.; Abenojar, J. Influence of plasma treatment on the adhesion between a polymeric matrix and natural fibres. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Yang, H. The effect of surface treatment on the performance improvement of carbon fiber / polybenzoxazine composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 5, 2297–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Fu, Y.F.; Xu, K.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.Q.; Chen, D.M.; Fu, Y.F.; Xu, K.; Li, J.; et al. The Influence of Plasma Surface Treatment of Carbon Fibers on the Interfacial Adhesion Properties of UHMWPE Composite. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xin, D.; Cao, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, L.; Ji, F.; Qiu, Y. Improving carbon fi ber adhesion to polyimide with atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šourková, H.; Špatenka, P. Plasma activation of polyethylene powder. Polymers 2020, 12, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weberová, Z.; Šourková, H.; Antoň, J.; Vacková, T.; Špatenka, P. New method for optimization of polymer powder plasma treatment for composite materials. Polymers 2021, 13, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
























Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghanem, Z.; Šourkova, H.J.; Sezemsky, J.; Špatenka, P. The Effect of Plasma Treatment of Polyethylene Powder and Glass Fibers on Selected Properties of Their Composites Prepared via Rotational Molding. Polymers 2022, 14, 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132592
Ghanem Z, Šourkova HJ, Sezemsky J, Špatenka P. The Effect of Plasma Treatment of Polyethylene Powder and Glass Fibers on Selected Properties of Their Composites Prepared via Rotational Molding. Polymers. 2022; 14(13):2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132592
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhanem, Zoya, Hana Jelinek Šourkova, Jan Sezemsky, and Petr Špatenka. 2022. "The Effect of Plasma Treatment of Polyethylene Powder and Glass Fibers on Selected Properties of Their Composites Prepared via Rotational Molding" Polymers 14, no. 13: 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132592
APA StyleGhanem, Z., Šourkova, H. J., Sezemsky, J., & Špatenka, P. (2022). The Effect of Plasma Treatment of Polyethylene Powder and Glass Fibers on Selected Properties of Their Composites Prepared via Rotational Molding. Polymers, 14(13), 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132592