Three-Dimensional Printable Ball Joints with Variable Stiffness for Robotic Applications Based on Soft Pneumatic Elastomer Actuators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
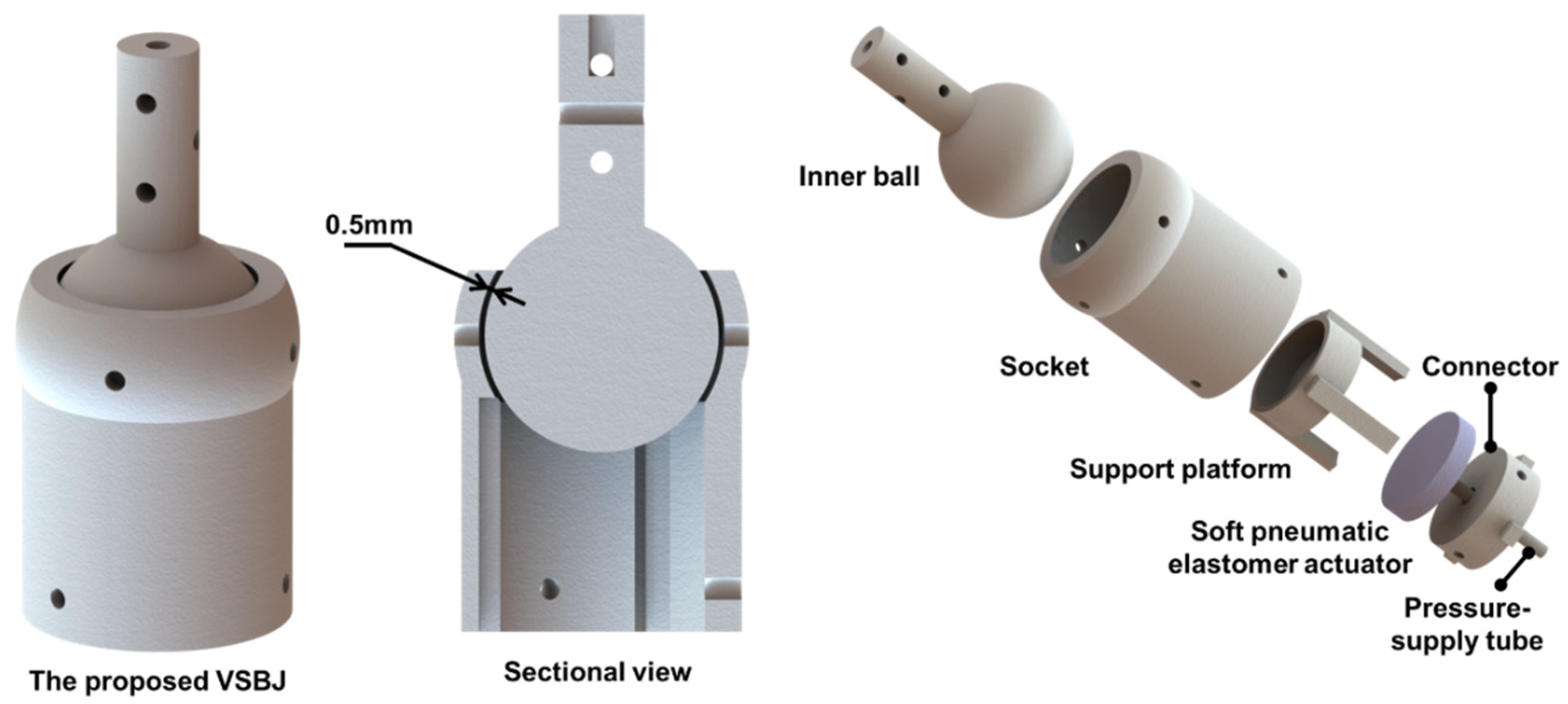
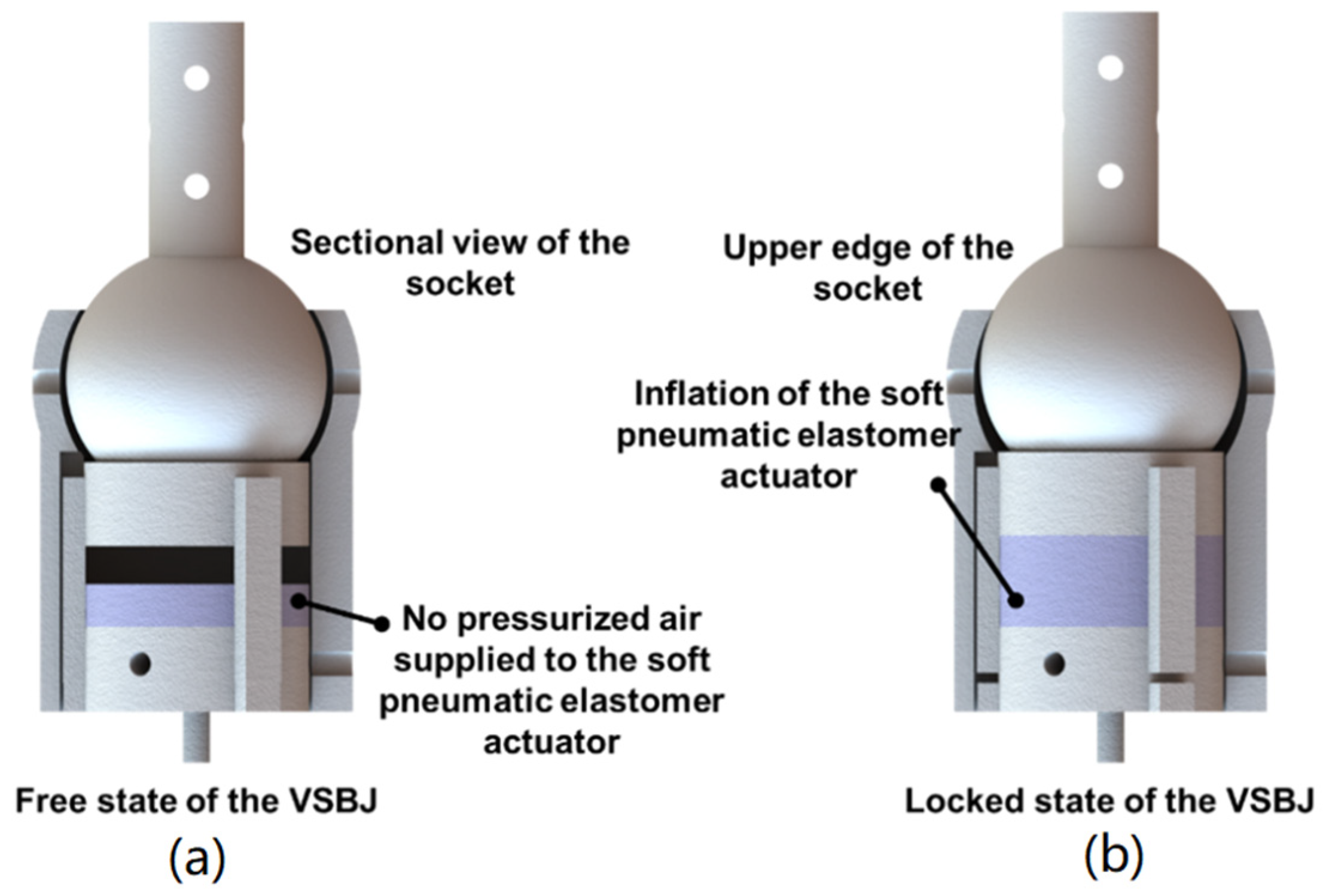
2.1. Design and Working Principle of the VSBJ
2.2. Finite Element Analysis of the Support Platform
2.3. Fabrication of the Soft Pneumatic Elastomer Actuator
3. Results
3.1. Rotating Stiffness Evaluation
3.2. Twisting Stiffness Evaluation
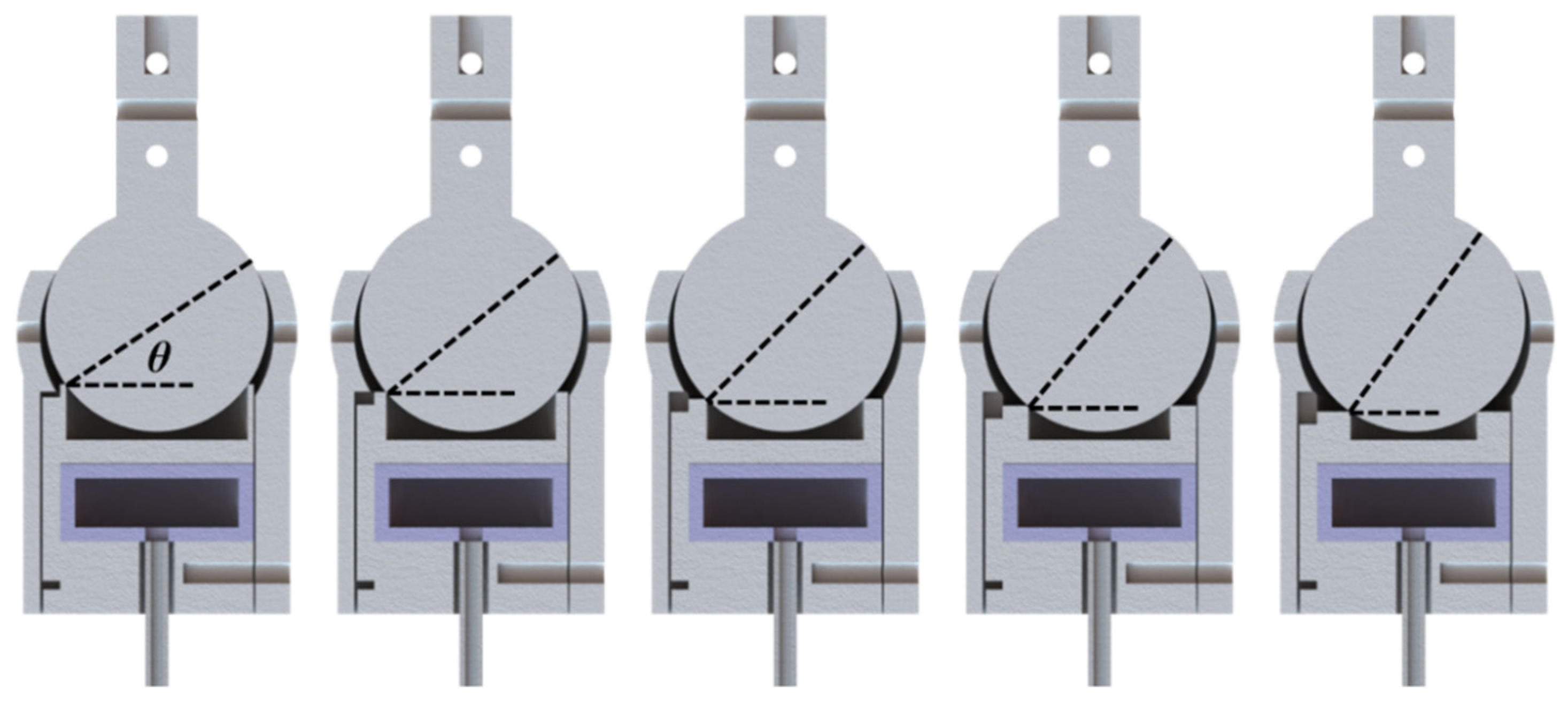
3.3. Customizations of the VSBJ
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.; Cheng, S.; Kim, S.; Iagnemma, K. A Stiffness-Adjustable Hyperredundant Manipulator Using a Variable Neutral-Line Mechanism for Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Cheng, S.; Desai, J.P. Active Stiffness Tuning of a Spring-Based Continuum Robot for MRI-Guided Neurosurgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgner-Kahrs, J.; Rucker, D.C.; Choset, H. Continuum Robots for Medical Applications: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1261–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ham, R.; Vanderborght, B.; Van Damme, M.; Verrelst, B.; Lefeber, D. MACCEPA, the mechanically adjustable compliance and controllable equilibrium position actuator: Design and implementation in a biped robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2007, 55, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderBorght, B.; Verrelst, B.; Van Ham, R.; Van Damme, M.; Beyl, P.; Lefeber, D. Development of a compliance controller to reduce energy consumption for bipedal robots. Auton. Robot. 2008, 24, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.W.; Chestnutt, J.; Rizzi, A.A. An actuator with physically variable stiffness for highly dynamic legged locomotion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; pp. 4662–4667. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, F.; Fu, Q.; Santello, M.; Polygerinos, P. Soft Robotic Haptic Interface with Variable Stiffness for Rehabilitation of Neurologically Impaired Hand Function. Front. Robot. AI 2017, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallery, H.; Veneman, J.; Van Asseldonk, E.; Ekkelenkamp, R.; Buss, M.; Van Der Kooij, H. Compliant actuation of rehabilitation robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2008, 15, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestari, M.; Sanz-Merodio, D.; Arevalo, J.C.; Garcia, E. An Adjustable Compliant Joint for Lower-Limb Exoskeletons. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S.; Robertson, M.; Ijspeert, A.; Paik, J. JammJoint: A Variable Stiffness Device Based on Granular Jamming for Wearable Joint Support. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Ishida, D.; Ogata, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Tabata, O.; Sugiyama, S. Development of passive elements with variable mechanical impedance for wearable robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 May 2002; pp. 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. 3D printing of variable stiffness hyper-redundant robotic arm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3871–3877. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, D.; Yang, H.S.; Park, J.; Shim, Y. Variable stiffness mechanism for human-friendly robots. Mech. Mach. Theory 2010, 45, 880–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ham, R.; Sugar, T.G.; Vanderborght, B.; Hollander, K.W.; Lefeber, D. Compliant actuator designs. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2009, 16, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C.; Menciassi, A.; Dario, P. Biomedical applications of soft robotics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, C.; Mazzolai, B.; Cianchetti, M. Soft robotics: Technologies and systems pushing the boundaries of robot abilities. Sci. Robot. 2016, 1, eaah3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slesarenko, V.; Engelkemier, S.; Galich, P.I.; Vladimirsky, D.; Klein, G.; Rudykh, S. Strategies to Control Performance of 3D-Printed, Cable-Driven Soft Polymer Actuators: From Simple Architectures to Gripper Prototype. Polymers 2018, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhlenko, I.D.; Farajikhah, S.; Lilley, C.; Georgis, A.; Large, M.; Fleming, S. Performance Optimization of Polymer Fibre Actuators for Soft Robotics. Polymers 2020, 12, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchetti, M.; Ranzani, T.; Gerboni, G.; Nanayakkara, T.; Althoefer, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Menciassi, A. Soft Robotics Technologies to Address Shortcomings in Today’s Minimally Invasive Surgery: The STIFF-FLOP Approach. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Principles and methods for stiffness modulation in soft robot design and development. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2018, 1, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manti, M.; Cacucciolo, V.; Cianchetti, M. Stiffening in Soft Robotics: A Review of the State of the Art. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, T.L.; Yuen, M.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Kramer-Bottiglio, R. Enhanced Variable Stiffness and Variable Stretchability Enabled by Phase-Changing Particulate Additives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Senatore, G.; Jansen, K.; Habraken, A.; Teuffel, P. Design and characterization of variable stiffness structural joints. Mater. Des. 2020, 187, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozer, C.; Paterno, L.; Tortora, G.; Menciassi, A. A Novel Pressure-Controlled Revolute Joint with Variable Stiffness. Soft Robot. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, A.; Beccai, L.; Mazzolai, B. Innovative Soft Robots Based on Electro-Rheological Fluids. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 4237–4242. [Google Scholar]
- Majidi, C.; Wood, R.J. Tunable elastic stiffness with microconfined magnetorheological domains at low magnetic field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 164104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y. Novel Design and Three-Dimensional Printing of Variable Stiffness Robotic Grippers. J. Mech. Robot. 2016, 8, 061010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xu, Z.; Shi, P.; Zhao, J. A Human-Inspired Soft Finger with Dual-Mode Morphing Enabled by Variable Stiffness Mechanism. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yu, C.Y.; Serrano, P.A.A.; Ahn, S.H. Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Finger with Changeable Bending Length Using Targeted Variable Stiffness. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hao, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z. A novel design of shape-memory alloy-based soft robotic gripper with variable stiffness. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, S. Flexible Manipulator with Low-Melting-Point Alloy Actuation and Variable Stiffness. Soft. Robot. 2021, 9, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Cheng, S.; Kim, S.; Iagnemma, K. A Novel Layer Jamming Mechanism With Tunable Stiffness Capability for Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimi, M.; Paternò, L.; Ricotti, L.; Menciassi, A. A Layer Jamming Actuator for Tunable Stiffness and Shape-Changing Devices. Soft Robot. 2021, 8, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Sun, F.; Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Huang, W.; Liu, H.; Wen, L. Multimode Grasping Soft Gripper Achieved by Layer Jamming Structure and Tendon-Driven Mechanism. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y. Passive Particle Jamming and Its Stiffening of Soft Robotic Grippers. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Meng, Y.; Tian, Y. Flexible adhesion control by modulating backing stiffness based on jamming of granular materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 115023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wockenfuß, W.R.; Brandt, V.; Weisheit, L.; Drossel, W.G. Design, Modeling and Validation of a Tendon-Driven Soft Continuum Robot for Planar Motion Based on Variable Stiffness Structures. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 3985–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.W.; Tsoi, K.H.; Vitiello, V.; Clark, J.; Chow, G.C.T.; Luk, W.; Yang, G. Dimensionality Reduction in Controlling Articulated Snake Robot for Endoscopy Under Dynamic Active Constraints. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappe, S.; Boyraz, P.; Korz, H.; Ortmaier, T. Design, Production and Integration of a Shape Sensing Robotic Sleeve for a Hyper-Redundant, Binary Actuated Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Auckland, New Zealand, 9–12 July 2018; pp. 298–303. [Google Scholar]
- Boehler, Q.; Vedrines, M.; Abdelaziz, S.; Poignet, P.; Renaud, P. Design and evaluation of a novel variable stiffness spherical joint with application to MR-compatible robot design. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 661–667. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. A soft robotic spine with tunable stiffness based on integrated ball joint and particle jamming. Mechatronics 2016, 33, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, W.; Pusch, T.P.; Siegfarth, M.; Schad, L.R.; Stallkamp, J.L. CT and MRI compatibility of flexible 3D-printed materials for soft actuators and robots used in image-guided interventions. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 5488–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păcurar, R.; Berce, P.; Petrilak, A.; Nemes, O.; Borzan, C.S.M.; Harnicárová, M.; Păcurar, A. Selective Laser Sintering of PA 2200 for Hip Implant Applications: Finite Element Analysis, Process Optimization, Morphological and Mechanical Characterization. Materials 2021, 14, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoia, D.I.; Marsavina, L.; Linul, E. Correlations between Process Parameters and Outcome Properties of Laser-Sintered Polyamide. Polymers 2019, 11, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynková, G.S.; Slíva, A.; Kratošová, G.; Barabaszová, K.C.; Študentová, S.; Klusák, J.; Brožová, S.; Dokoupil, T.; Holešová, S. Polyamide 12 Materials Study of Morpho-Structural Changes during Laser Sintering of 3D Printing. Polymers 2021, 13, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Li, Z.; Zhu, F. Effect of powder recycling on anisotropic tensile properties of selective laser sintered PA2200 polyamide. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 141, 110093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steltz, E.; Mozeika, A.; Rodenberg, N.; Brown, E.; Jaeger, H.M. JSEL: Jamming Skin Enabled Locomotion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 11–15 October 2009; pp. 5672–5677. [Google Scholar]











| θ | 35.3° | 40.3° | 45.3° | 50.3° | 55.3° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotation | 7.76 N | 7.57 N | 7.28 N | 7.15 N | 7.02 N |
| Twist | 8.21 N | 7.59 N | 7.16 N | 6.75 N | 6.46 N |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Low, J.-H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yeow, C.-H. Three-Dimensional Printable Ball Joints with Variable Stiffness for Robotic Applications Based on Soft Pneumatic Elastomer Actuators. Polymers 2022, 14, 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173542
Guo J, Low J-H, Liu J, Li Y, Liu Z, Yeow C-H. Three-Dimensional Printable Ball Joints with Variable Stiffness for Robotic Applications Based on Soft Pneumatic Elastomer Actuators. Polymers. 2022; 14(17):3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173542
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jin, Jin-Huat Low, Jun Liu, Yangfan Li, Zhuangjian Liu, and Chen-Hua Yeow. 2022. "Three-Dimensional Printable Ball Joints with Variable Stiffness for Robotic Applications Based on Soft Pneumatic Elastomer Actuators" Polymers 14, no. 17: 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173542
APA StyleGuo, J., Low, J.-H., Liu, J., Li, Y., Liu, Z., & Yeow, C.-H. (2022). Three-Dimensional Printable Ball Joints with Variable Stiffness for Robotic Applications Based on Soft Pneumatic Elastomer Actuators. Polymers, 14(17), 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173542








