Effect of the Coupling Agent (3-Aminopropyl) Triethoxysilane on the Structure and Fire Behavior of Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesized Silica-Epoxy Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Preparation of Silica–Epoxy Nanocomposites
2.3. Characterization and Investigation Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
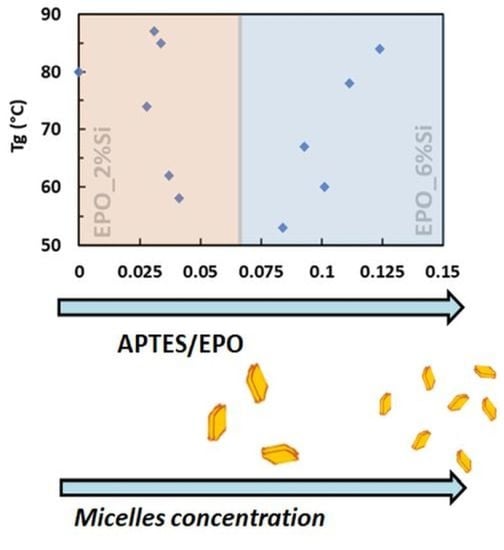
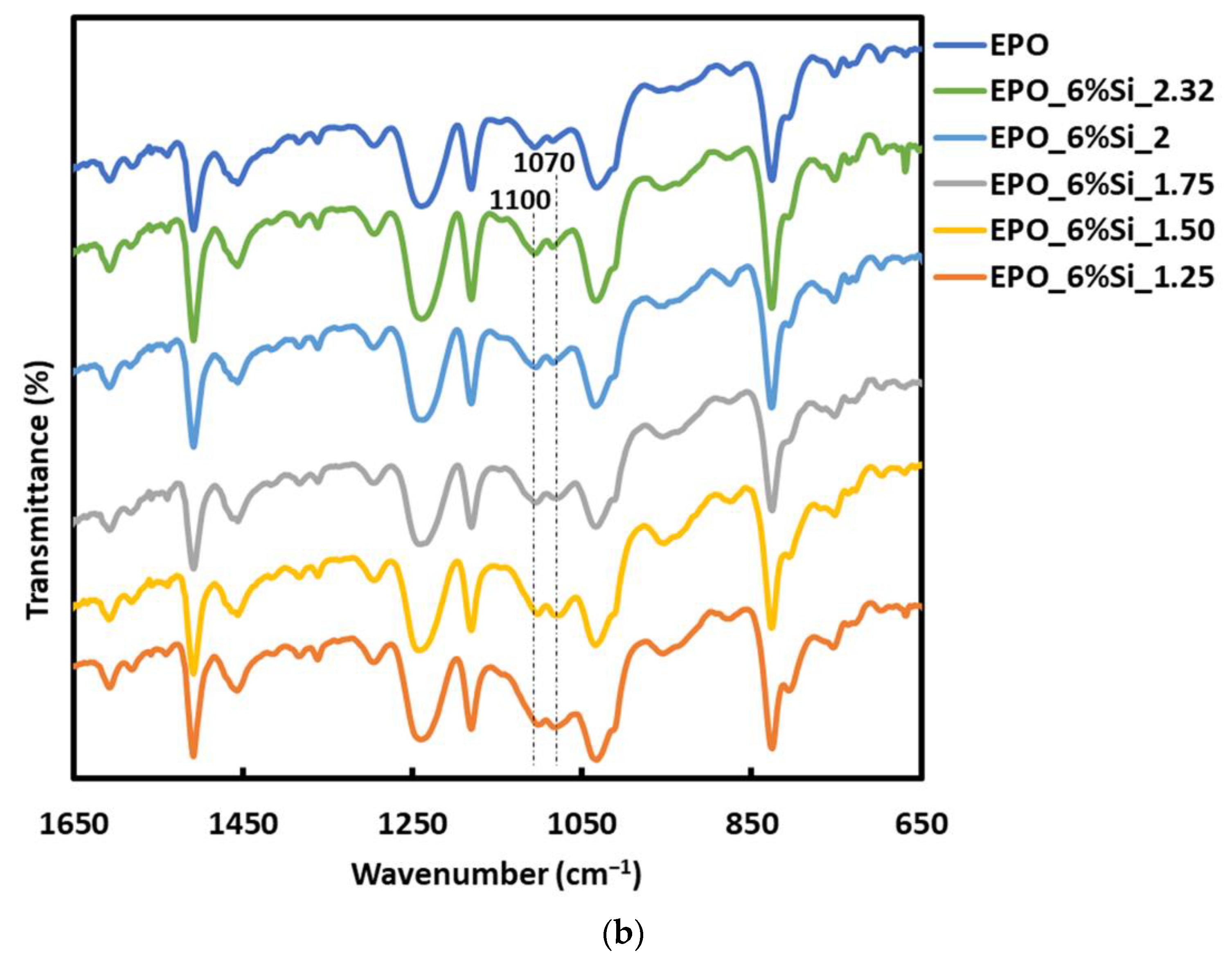
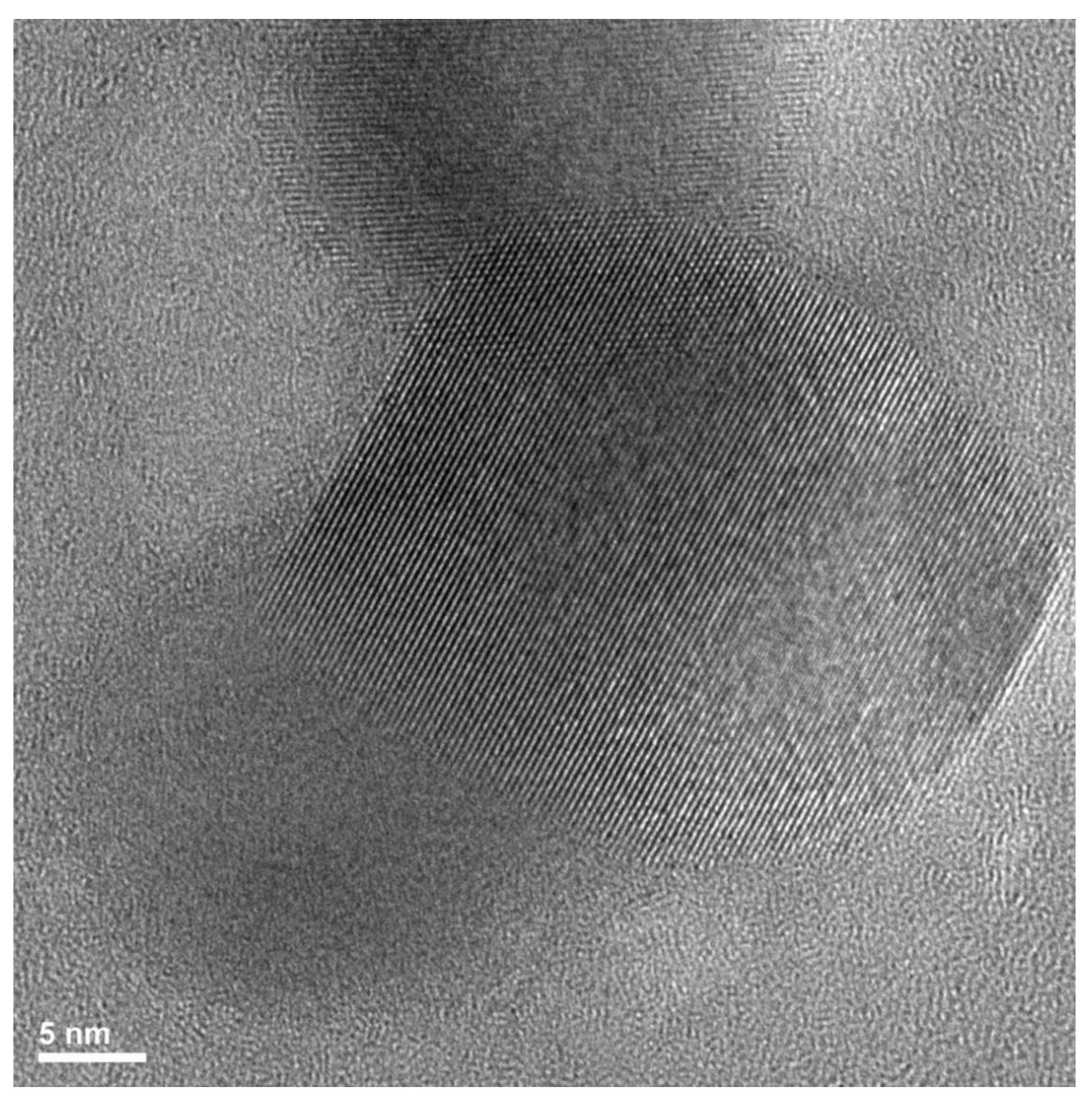
3.1. Structure and Morphology of the Nanocomposites
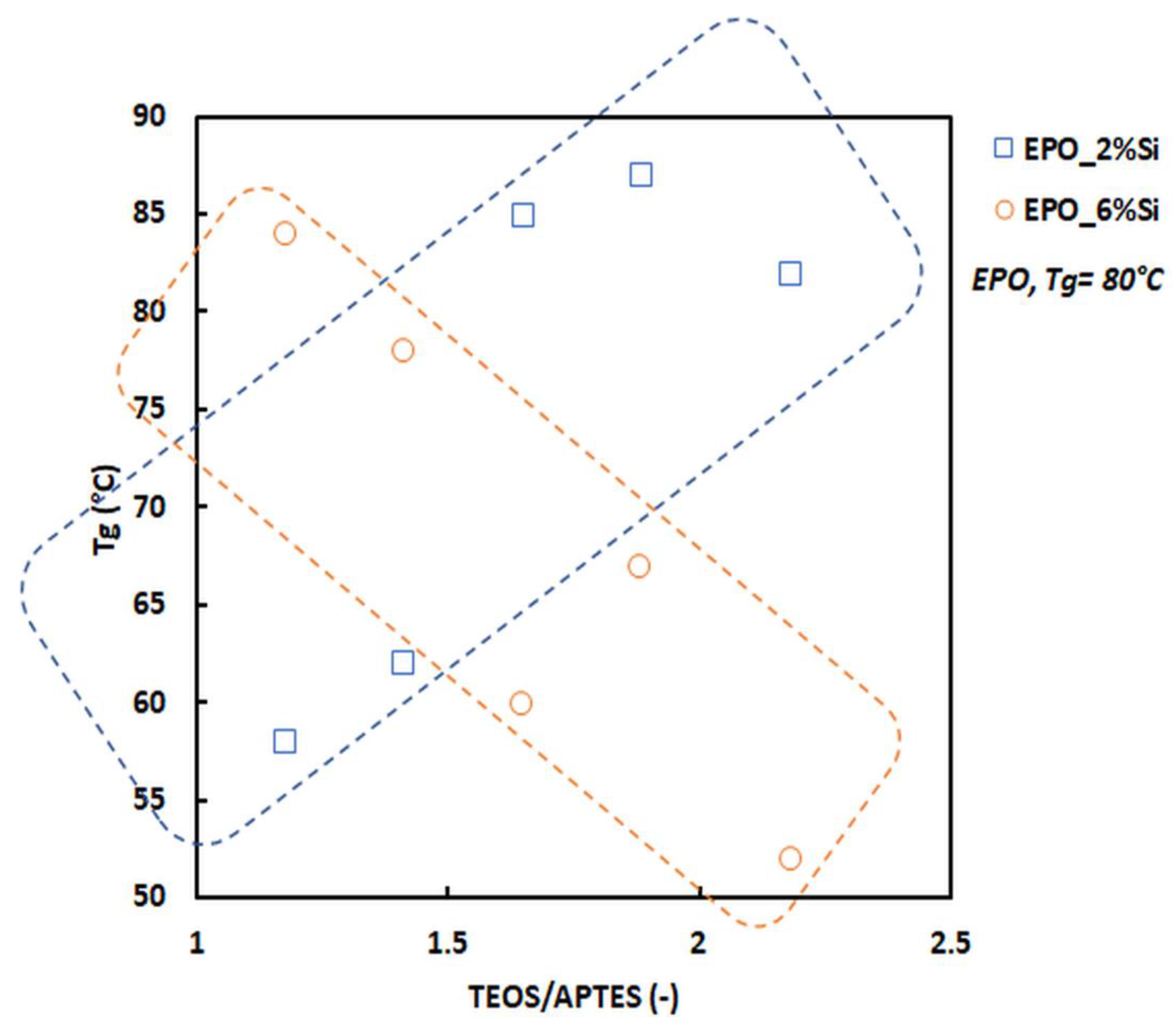
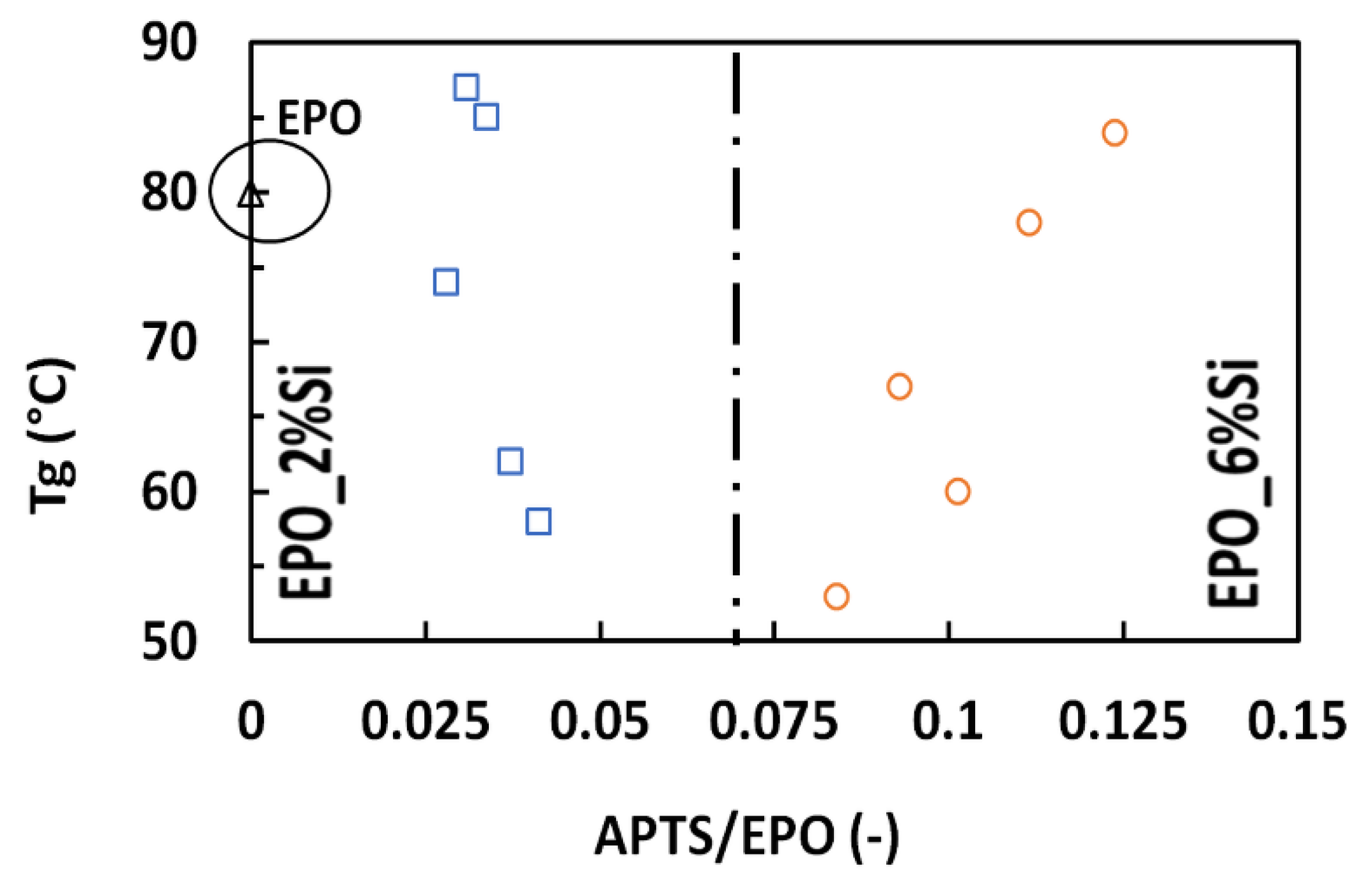
3.2. Dynamic-Mechanical Behavior
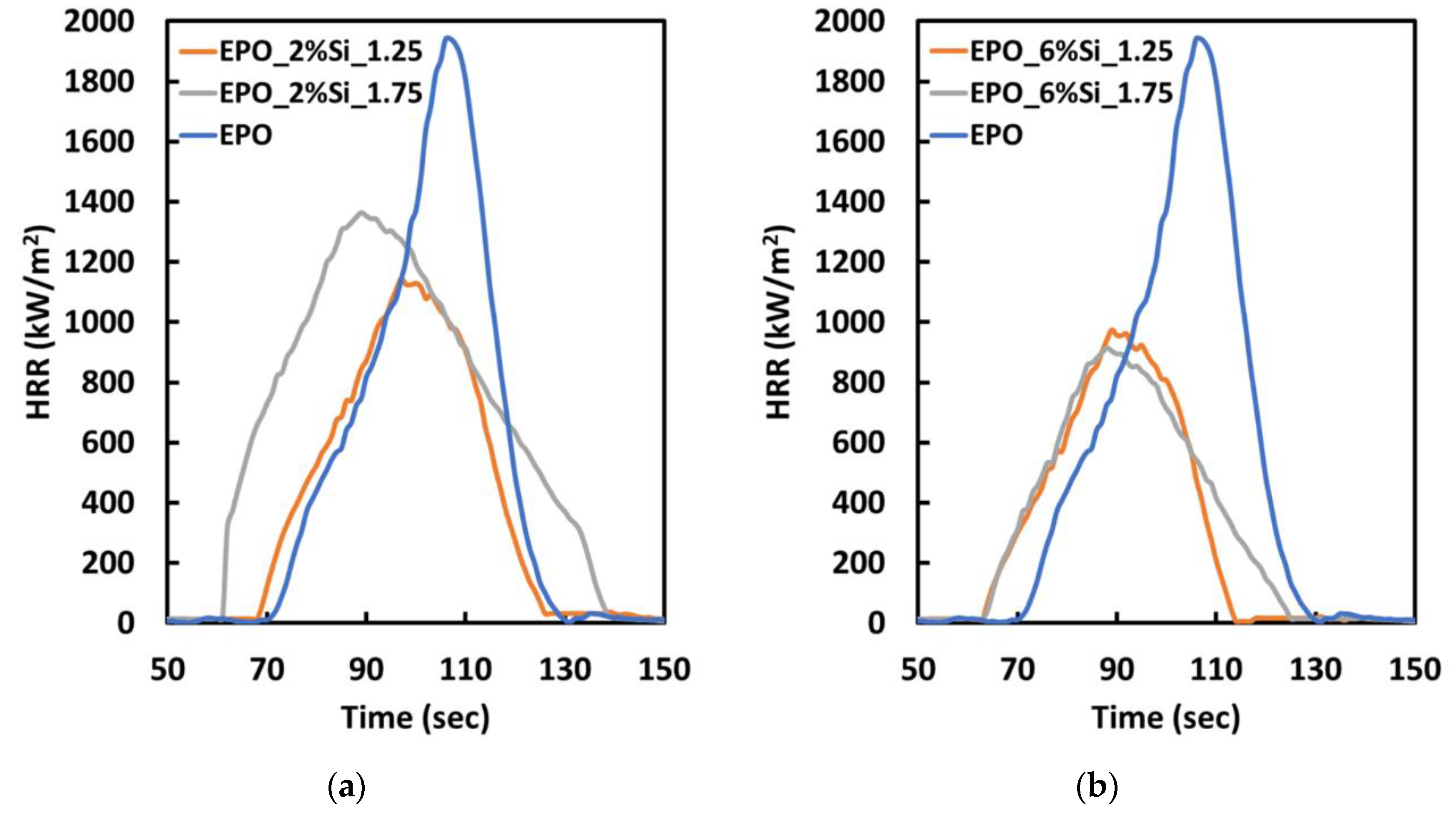
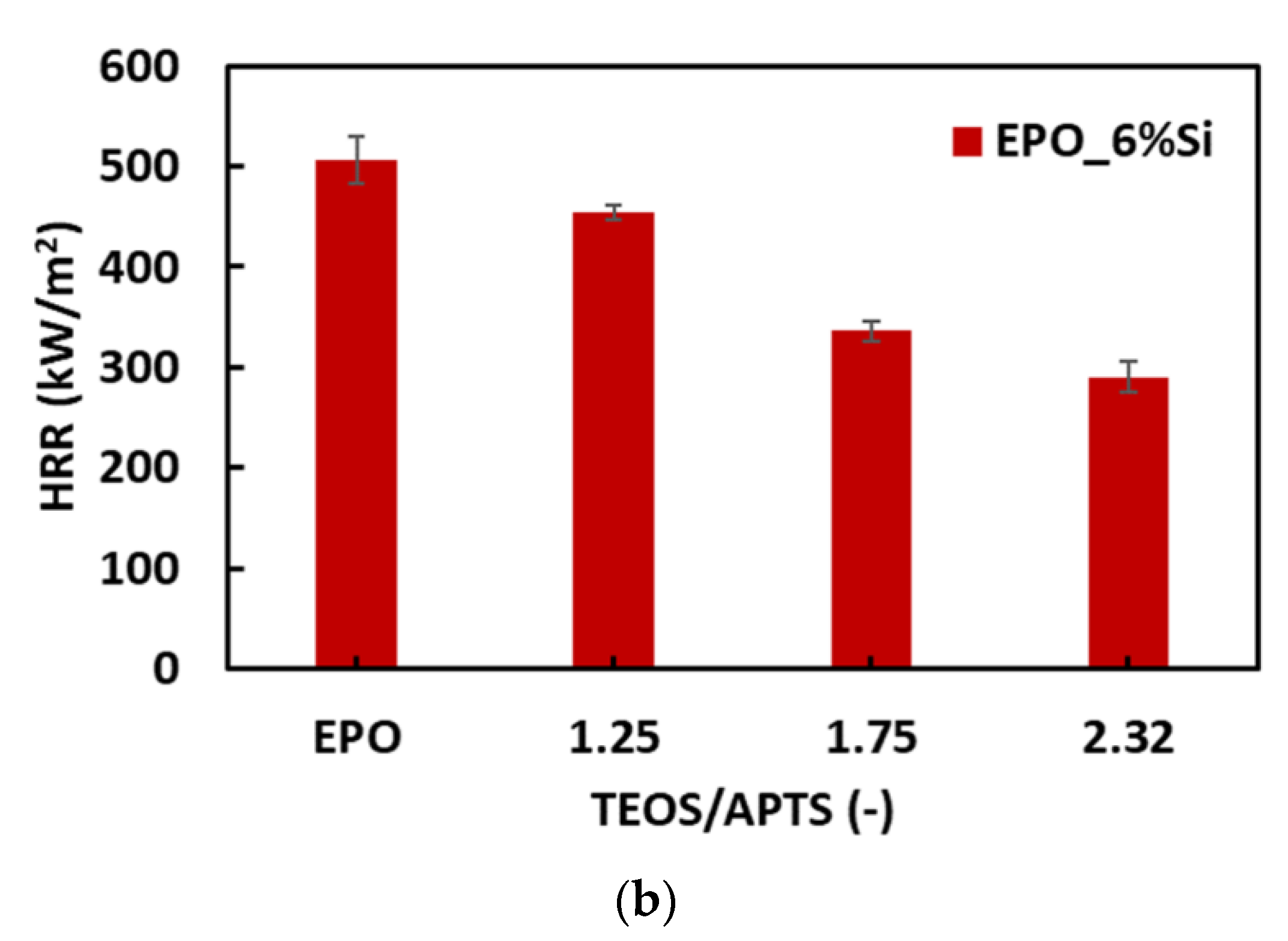
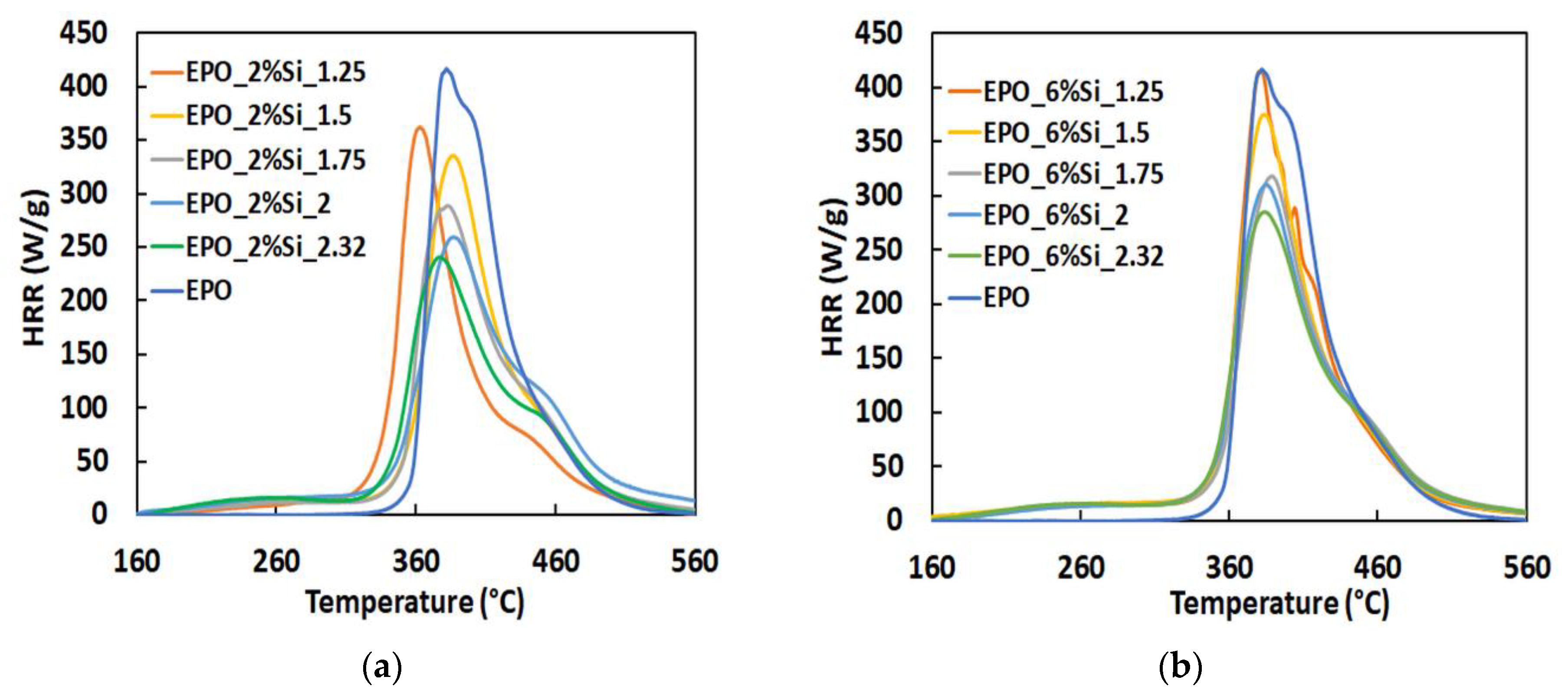
3.3. Thermal and Fire Behavior
4. Conclusions
- The APTES content affects the size distribution of the multi-sheet silica-based nanoparticles, leading to the formation of finer structures (more particles but with smaller sizes) by increasing the APTES loading.
- Despite the very low silica content, the nanocomposites exhibit an excellent flame retardance, that, depending on the composition, in the vertical frame tests, is witnessed by the absence of dripping and, in some cases, by V1 rating.
- As assessed by cone calorimetry tests, a significant decrease in the heat release rate (up to 60%) with respect to the neat epoxy network is observed. The HRR is strongly affected by TEOS/APTES molar ratio.
- The flame retardancy index values are within 1 and 10, thus indicating that all the investigated nanocomposites can be classified as “good”.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Zoubi, W.; Kamil, M.P.; Fatimah, S.; Nashrah, N.; Ko, Y.G. Recent advances in hybrid organic-inorganic materials with spatial architecture for state-of-the-art applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 112, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Mishra, S.B. Sol–gel derived organic–inorganic hybrid materials: Synthesis, characterizations and applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 59, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Ma, C.; Gu, J.; Guo, J.; Yan, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Z. An overview of multifunctional epoxy nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 5890–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, T.; Yuan, C.H.; Song, C.F.; Chang, Y.; Chen, G.R.; Xu, Y.T.; Dai, L.Z. Modification of epoxy resin through the self-assembly of a surfactant-like multi-element flame retardant. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3462–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Parkin, I.P.; Zhang, Z. Modifying epoxy resins to resist both fire and water. Langmuir 2019, 35, 14332–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Cao, A.; Yu, Z.Z. High-performance epoxy nanocomposites reinforced with three-dimensional carbon nanotube sponge for electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. Mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of graphene-epoxy nanocomposites—A review. Polymers 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Lebeau, B. Design and properties of hybrid organic–inorganic nanocomposites for photonics. Mrs Bull. 2001, 26, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Julián, B.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M. Applications of hybrid organic–inorganic nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3559–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gon, M.; Tanaka, K.; Chujo, Y. Creative Synthesis of Organic–Inorganic Molecular Hybrid Materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 90, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, C.; Galo, J.; Ribot, F.; Grosso, D. Design of functional nano-structured materials through the use of controlled hybrid organic–inorganic interfaces. C. R. Chim. 2003, 6, 1131–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Ribot, F.; Rozes, L.; Alonso, B. Design of Hybrid organic-inorganic nanocomposites synthesized via sol-gel chemistry. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol. Sect. A Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2000, 354, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Ribot, F.; Lebeau, B. Molecular design of hybrid organic-inorganic nanocomposites synthesized via sol-gel chemistry. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Romero, P.; Sanchez, C. Functional Hybrid Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Seraj, S.; Ranjbar, Z.; Jannesari, A. Synthesis and characterization of an anticratering agent based on APTES for cathodic electrocoatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, A.C. Hybrid Organic–Inorganic and Composite Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 421–455. [Google Scholar]
- Matějka, L.; Dušek, K.; Pleštil, J.; Kříž, J.; Lednický, F. Formation and structure of the epoxy-silica hybrids. Polymer 1999, 40, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, L.; Prezzi, L.; Lavorgna, M. Peculiarities in the solvent absorption characteristics of epoxy-siloxane hybrids. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, L.; Prezzi, L.; Haworth, B. Substantiating the role of phase bicontinuity and interfacial bonding in epoxy-silica nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezzi, L.; Mascia, L. Network density control in epoxy--silica hybrids by selective silane functionalization of precursors. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2005, 24, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonthamachai, N.; Chia, H.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Tjiu, W.W.; He, C. Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesis of high performance silica/epoxy nanocomposites. Polymer 2010, 51, 5377–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Siddiqi, H.M. A comprehensive study of the bicontinuous epoxy-silica hybrid polymers: I. Synthesis, characterization and glass transition. Polymer 2011, 52, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Siddiqi, H.M.; Iqbal, N.; Ahmad, Z. The effect of SiO2 filler content and its organic compatibility on thermal stability of epoxy resin. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, L.; Cai, Y. One-step synthesis of improved silica/epoxy nanocomposites with inorganic-organic hybrid network. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli, F.; Buonocore, G.G.; Lavorgna, M.; Verdolotti, L.; Pricl, S.; Gentile, G.; Mascia, L. Peculiarities in the structure--Properties relationship of epoxy-silica hybrids with highly organic siloxane domains. Polymer 2015, 63, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli, F.; Lavorgna, M.; Buonocore, G.G.; Verdolotti, L.; Galy, J.; Mascia, L. Plasticizing and Reinforcing Features of Siloxane Domains in Amine-Cured Epoxy/Silica Hybrids. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshandeh, E.; Jannesari, A.; Ranjbar, Z.; Sobhani, S.; Saeb, M.R. Anti-corrosion hybrid coatings based on epoxy--silica nano-composites: Toward relationship between the morphology and EIS data. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshandeh, E.; Sobhani, S.; Jannesari, A.; Pakdel, A.S.; Sari, M.G.; Saeb, M.R. Structure--property relationship in epoxy-silica hybrid nanocomposites: The role of organic solvent in achieving silica domains. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2015, 21, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 97–228. [Google Scholar]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, G.H.; Zukoski Iv, C.F. Uniform silica particle precipitation: An aggregative growth model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 142, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branda, F. The Sol-Gel Route to Nanocomposites. In Advances in Nanocomposites—Synthesis, Characterization and Industrial Applications, 1st ed.; Reddy, B., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2011; pp. 324–340. [Google Scholar]
- Plumeré, N.; Ruff, A.; Speiser, B.; Feldmann, V.; Mayer, H.A. Stöber silica particles as basis for redox modifications: Particle shape, size, polydispersity, and porosity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.; Ungerer, J.; Klinge, M.; Nirschl, H. Synthesis of nanometric silica particles via a modified Stöber synthesis route. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, A.; Tescione, F.; Capasso, A.; Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A.; Durante, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Malucelli, G.; Branda, F. Effects of post cure treatment in the glass transformation range on the structure and fire behavior of in situ generated silica/epoxy hybrids. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, A.; Parida, D.; Salmeia, K.A.; Nazir, R.; Lehner, S.; Stämpfli, R.; Markus, H.; Malucelli, G.; Branda, F.; Gaan, S. Fire and mechanical properties of DGEBA-based epoxy resin cured with a cycloaliphatic hardener: Combined action of silica, melamine and DOPO-derivative. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, A.; Parida, D.; Salmeia, K.; Lehner, S.; Stämpfli, R.; Markus, H.; Malucelli, G.; Branda, F.; Gaan, S. Improving Flame Retardancy of in-situ Silica-Epoxy Nanocomposites cured with Aliphatic Hardener: Combined effect of DOPO-based flame-retardant and Melamine. Compos. Part C Open Access 2020, 2, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branda, F.; Bifulco, A.; Jehnichen, D.; Parida, D.; Pauer, R.; Passaro, J.; Gaan, S.; Pospiech, D.; Durante, M. Structure and Bottom-up Formation Mechanism of Multisheet Silica-Based Nanoparticles Formed in an Epoxy Matrix through an In Situ Process. Langmuir 2021, 37, 8886–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branda, F.; Passaro, J.; Pauer, R.; Gaan, S.; Bifulco, A. Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesis of Epoxy Nanocomposites Containing Mg(OH)2 Nanocrystal–Nanoparticle Formation Mechanism. Langmuir 2022, 38, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, H.; Kandola, B.K.; Saeb, M.R. Flame retardancy index for thermoplastic composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedifar, E.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R.; Thomas, S. Flame retardant epoxy composites on the road of innovation: An analysis with flame retardancy index for future development. Molecules 2019, 24, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F.; Solar, L.; Puchol, V.; Latorre, J.; Abad, C.; Campos, A. Incorporation of silica nanospherical particles into epoxy-amine crosslinked materials. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2008, 16, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimon, I.; McMahon, H.O. Study of some binary silicate glasses by means of reflection in infrared. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1953, 36, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urnes, S. Modern Aspects of the Vitreous State; Butterworths: London, UK, 1960; pp. 10–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Kirkpatrick, R.J.; Poe, B.; McMillan, P.F.; Cong, X. Structure of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H): Near-, Mid-, and Far-infrared spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, P.; Maier, M.; Reisinger, M.; Hannebauer, B.; Weinand, R. Physical boundaries within aggregates–differences between amorphous, para-crystalline, and crystalline Structures. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2015, 50, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, R.; Rainosalo, E.; Thomas, S.P.; Ramamoorthy, S.K.; Zavašnik, J.; Vuorinen, J.; Skrifvars, M. Modification of epoxy resin by silane-coupling agent to improve tensile properties of viscose fabric composites. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 167–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, M.D.; Trung, T.H.; Thai, N.T.; Van Cong, D.; Tung, N.H.; Giang, N.V. Effect of (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane coupling agent on characteristics and mechanical properties of polylactic acid/jute fiber biocomposite. Vietnam J. Chem. 2019, 57, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mao, S. A study on the glass transition behavior and morphology of semi-interpenetrating polymer networks. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1996, 34, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G. Ueber die Abhängigkeit der Zahl der Kerne, welche sich in verschiedenen unterkühlten Flüssigkeiten bilden, von der Temperatur. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1898, 25, 441–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhnevich, G.L.; Browko, J.F. Stability of the crystallization centers of an organic liquid at various temperatures and conclusions to be drawn therefrom concerning Tammann’s method. Phys. Z. Der Sowjetunion 1938, 13, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fokin, V.M.; Zanotto, E.D.; Yuritsyn, N.S.; Schmelzer, J.W.P. Homogeneous crystal nucleation in silicate glasses: A 40 years perspective. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 2681–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.L.F.; Fokin, V.M.; Zanotto, E.D.; Abyzov, A.S. Dynamic processes in a silicate liquid from above melting to below the glass transition. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 194703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassie, N.; Guy, M.I.; Tennent, N.H. Degradation of epoxy polymers: Part 1—Products of thermal degradation of bisphenol-A diglycidyl ether. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1985, 12, 65–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musto, P. Two-Dimensional FTIR spectroscopy studies on the thermal-oxidative degradation of epoxy and epoxy−bis (maleimide) networks. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 3210–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, J.W.; Harris Jr, R.H.; Shields, J.R.; Kashiwagi, T.; Morgan, A.B. A study of the flammability reduction mechanism of polystyrene-layered silicate nanocomposite: Layered silicate reinforced carbonaceous char. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, P.; Su, Z.; Wei, P.; Wang, G.; Tang, X. Synergistic effect of phosphorus, nitrogen, and silicon on flame-retardant properties and char yield in polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartel, B.; Perret, B.; Dittrich, B.; Ciesielski, M.; Kraemer, J.; Mueller, P.; Altstaedt, V.; Zang, L.; Doering, M. Flame Retardancy of Polymers: The Role of Specific Reactions in the Condensed Phase. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, A.; Varganici, C.D.; Rosu, L.; Mustata, F.; Rosu, D.; Gaan, S. Recent advances in flame retardant epoxy systems containing non-reactive DOPO based phosphorus additives. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 200, 109962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezia, V.; Matta, S.; Lehner, S.; Vitiello, G.; Costantini, A.; Gaan, S.; Malucelli, G.; Branda, F.; Luciani, G.; Bifulco, A. Detailed Thermal, Fire, and Mechanical Study of Silicon-Modified Epoxy Resin Containing Humic Acid and Other Additives. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5969–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varganici, C.D.; Rosu, L.; Lehner, S.; Hamciuc, C.; Jovic, M.; Rosu, D.; Mustata, F.; Gaan, S. Semi–interpenetrating networks based on epoxy resin and oligophosphonate: Comparative effect of three hardeners on the thermal and fire properties. Mater. Des. 2021, 212, 110237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Gilman, J.W.; Butler, K.M.; Harris, R.H.; Shields, J.R.; Asano, A. Flame retardant mechanism of silica gel/silica. Fire Mater. 2000, 24, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R.E.; Walters, R.N. Pyrolysis combustion flow calorimetry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2004, 71, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeia, K.A.; Gaan, S. An overview of some recent advances in DOPO-derivatives: Chemistry and flame retardant applications. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 113, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Epoxy (g) | Hardner (g) | APTS (g) | TEOS (g) | APTS/EPO (-) | EtOH (g) | Water (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPO | 15 | 3.9 | - | - | 0.000 | - | - |
| Series a | |||||||
| EPO_2%Si_1.25 | 15 | 3.9 | 0.619 | 0.728 | 0.041 | 0.081 | 0.403 |
| EPO_2%Si_1.50 | 15 | 3.9 | 0.557 | 0.786 | 0.037 | 0.087 | 0.408 |
| EPO_2%Si_1.75 | 15 | 3.9 | 0.506 | 0.834 | 0.034 | 0.092 | 0.412 |
| EPO_2%Si_2.00 | 15 | 3.9 | 0.464 | 0.874 | 0.031 | 0.097 | 0.415 |
| EPO_2%Si_2.32 | 15 | 3.9 | 0.420 | 0.916 | 0.028 | 0.101 | 0.419 |
| Series b | |||||||
| EPO_6%Si_1.25 | 15 | 3.9 | 1.857 | 2.185 | 0.124 | 0.242 | 1.208 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.50 | 15 | 3.9 | 1.671 | 2.359 | 0.111 | 0.261 | 1.223 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.75 | 15 | 3.9 | 1.519 | 2.502 | 0.101 | 0.277 | 1.235 |
| EPO_6%Si_2.00 | 15 | 3.9 | 1.393 | 2.621 | 0.093 | 0.290 | 1.246 |
| EPO_6%Si_2.32 | 15 | 3.9 | 1.259 | 2.748 | 0.084 | 0.304 | 1.257 |
| Sample | UL 94/Dripping |
|---|---|
| EPO | Not classifiable (NC)/Yes |
| EPO_2%Si_1.25 | NC/No |
| EPO_2%Si_1.75 | NC/No |
| EPO_2%Si_2.32 | NC/No |
| EPO_6%Si_1.25 | V1/No |
| EPO_6%Si_1.75 | V1/No |
| EPO_6%Si_2.32 | NC/No |
| Sample | TTI (s) | HRR (kW/m2) | pkHRR (kW/m2) | THR (MJ/m2) | Residue (wt.%) | FRI (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPO | 70 ± 3.2 | 506 ± 23.3 | 1941 ± 384 | 83 ± 3.1 | 3 ± 0.7 | - |
| EPO_2%Si_1.25 | 68 ± 5.1 | 413 ± 10.2 | 1114 ± 108 | 92 ± 6.9 | 7 ± 0.7 | 2.1 |
| EPO_2%Si_1.75 | 61 ± 4.5 | 398 ± 9.3 | 1353 ± 98 | 106 ± 5.7 | 7 ± 0.6 | 1.7 |
| EPO_2%Si_2.32 | 37 ± 4.1 | 311 ± 12.1 | 991 ± 73 | 67 ± 9.2 | 6 ± 0.5 | 2.3 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.25 | 63 ± 7.3 | 454 ± 7.6 | 923.3 ± 106 | 107 ± 8.2 | 10 ± 0.6 | 2.4 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.75 | 59 ± 8.1 | 336 ± 10.2 | 902.3 ± 107 | 98 ± 6.9 | 9 ± 0.7 | 2.5 |
| EPO_6%Si_2.32 | 32 ± 2.1 | 290 ± 15.2 | 1231 ± 228 | 57 ± 6.2 | 10 ± 0.6 | 1.9 |
| Sample | TSR (m2/m2) | SEA (m2/kg) | CO Yield (kg/kg) | CO2 Yield (kg/kg) | CO/CO2 (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPO | 3066 ± 206 | 940 ± 36 | 0.061 ± 0.03 | 2.08 ± 0.06 | 0.029 |
| EPO_2%Si_1.25 | 3306 ± 223 | 887 ± 11 | 0.059 ± 0.02 | 2.07 ± 0.04 | 0.028 |
| EPO_2%Si_1.75 | 3851 ± 157 | 875 ± 15 | 0.053 ± 0.01 | 1.97 ± 0.03 | 0.026 |
| EPO_2%Si_2.32 | 2604 ± 291 | 941 ± 38 | 0.060 ± 0.04 | 1.94 ± 0.03 | 0.031 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.25 | 4053 ± 178 | 932 ± 18 | 0.054 ± 0.02 | 1.93 ± 0.02 | 0.027 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.75 | 4310 ± 125 | 967 ± 10 | 0.047 ± 0.03 | 1.89 ± 0.04 | 0.024 |
| EPO_6%Si_2.32 | 2087 ± 355 | 895 ± 31 | 0.063 ± 0.01 | 1.95 ± 0.05 | 0.032 |
| Sample | THR (kJ/g) | HRC (J/g-K) | pkHRR (W/g) | Residue (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPO | 26.7 ± 0.61 | 427 ± 12.2 | 431 ± 12.2 | 5.05 ± 0.87 |
| EPO_2%Si_1.25 | 26.3 ± 0.52 | 424 ± 1.80 | 364 ± 0.54 | 12.6 ± 1.39 |
| EPO_2%Si_1.50 | 25.7 ± 0.78 | 381 ± 7.76 | 336 ± 7.31 | 14.2 ± 2.27 |
| EPO_2%Si_1.75 | 25.1 ± 0.36 | 336 ± 5.15 | 298 ± 6.66 | 16.3 ± 0.17 |
| EPO_2%Si_2.00 | 24.7 ± 0.39 | 299 ± 3.40 | 263 ± 4.89 | 16.4 ± 0.38 |
| EPO_2%Si_2.32 | 24.3 ± 0.12 | 284 ± 11.4 | 255 ± 9.28 | 17.3 ± 0.91 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.25 | 28.9 ± 0.21 | 460 ± 14.8 | 417 ± 14.6 | 9.66 ±0.77 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.50 | 27.1 ± 0.62 | 436 ± 4.03 | 373 ± 3.13 | 11.1 ± 2.04 |
| EPO_6%Si_1.75 | 25.1 ± 0.33 | 345 ± 15.2 | 304 ± 11.4 | 14.8 ± 0.46 |
| EPO_6%Si_2.00 | 24.8 ± 0.57 | 324 ± 26.5 | 283 ± 19.8 | 14.6 ± 0.66 |
| EPO_6%Si_2.32 | 25.1 ± 0.16 | 332 ± 4.64 | 291 ± 4.94 | 13.9 ± 0.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Branda, F.; Parida, D.; Pauer, R.; Durante, M.; Gaan, S.; Malucelli, G.; Bifulco, A. Effect of the Coupling Agent (3-Aminopropyl) Triethoxysilane on the Structure and Fire Behavior of Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesized Silica-Epoxy Nanocomposites. Polymers 2022, 14, 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183853
Branda F, Parida D, Pauer R, Durante M, Gaan S, Malucelli G, Bifulco A. Effect of the Coupling Agent (3-Aminopropyl) Triethoxysilane on the Structure and Fire Behavior of Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesized Silica-Epoxy Nanocomposites. Polymers. 2022; 14(18):3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183853
Chicago/Turabian StyleBranda, Francesco, Dambarudhar Parida, Robin Pauer, Massimo Durante, Sabyasachi Gaan, Giulio Malucelli, and Aurelio Bifulco. 2022. "Effect of the Coupling Agent (3-Aminopropyl) Triethoxysilane on the Structure and Fire Behavior of Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesized Silica-Epoxy Nanocomposites" Polymers 14, no. 18: 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183853
APA StyleBranda, F., Parida, D., Pauer, R., Durante, M., Gaan, S., Malucelli, G., & Bifulco, A. (2022). Effect of the Coupling Agent (3-Aminopropyl) Triethoxysilane on the Structure and Fire Behavior of Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesized Silica-Epoxy Nanocomposites. Polymers, 14(18), 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183853