DNA-Immobilized Special Conformation Recognition of L-Penicillamine Using a Chiral Molecular Imprinting Technique
Abstract
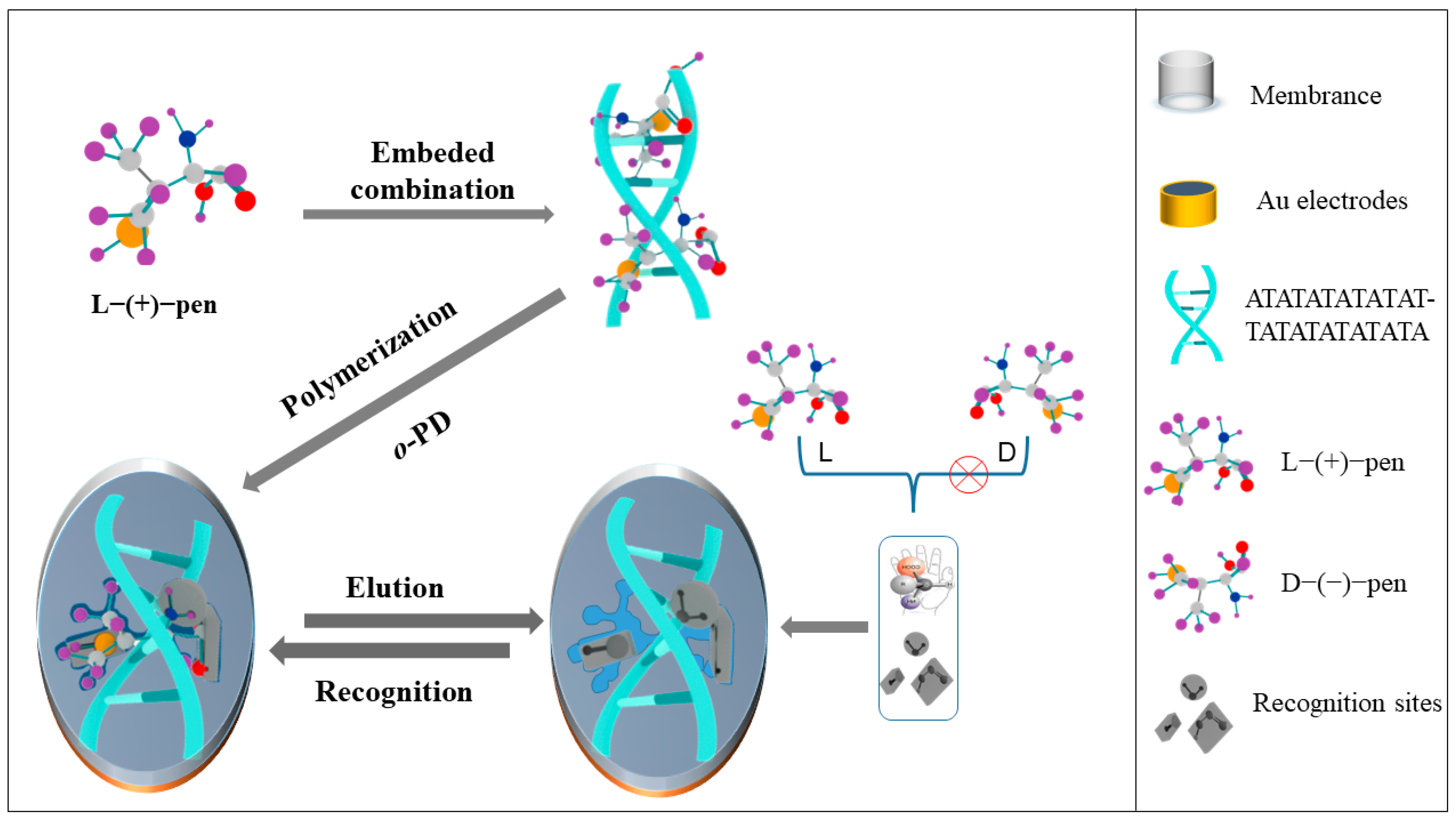
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus and Reagents
2.2. Assay Procedures
2.3. Measurement Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Interaction between L-Pen and dsDNA
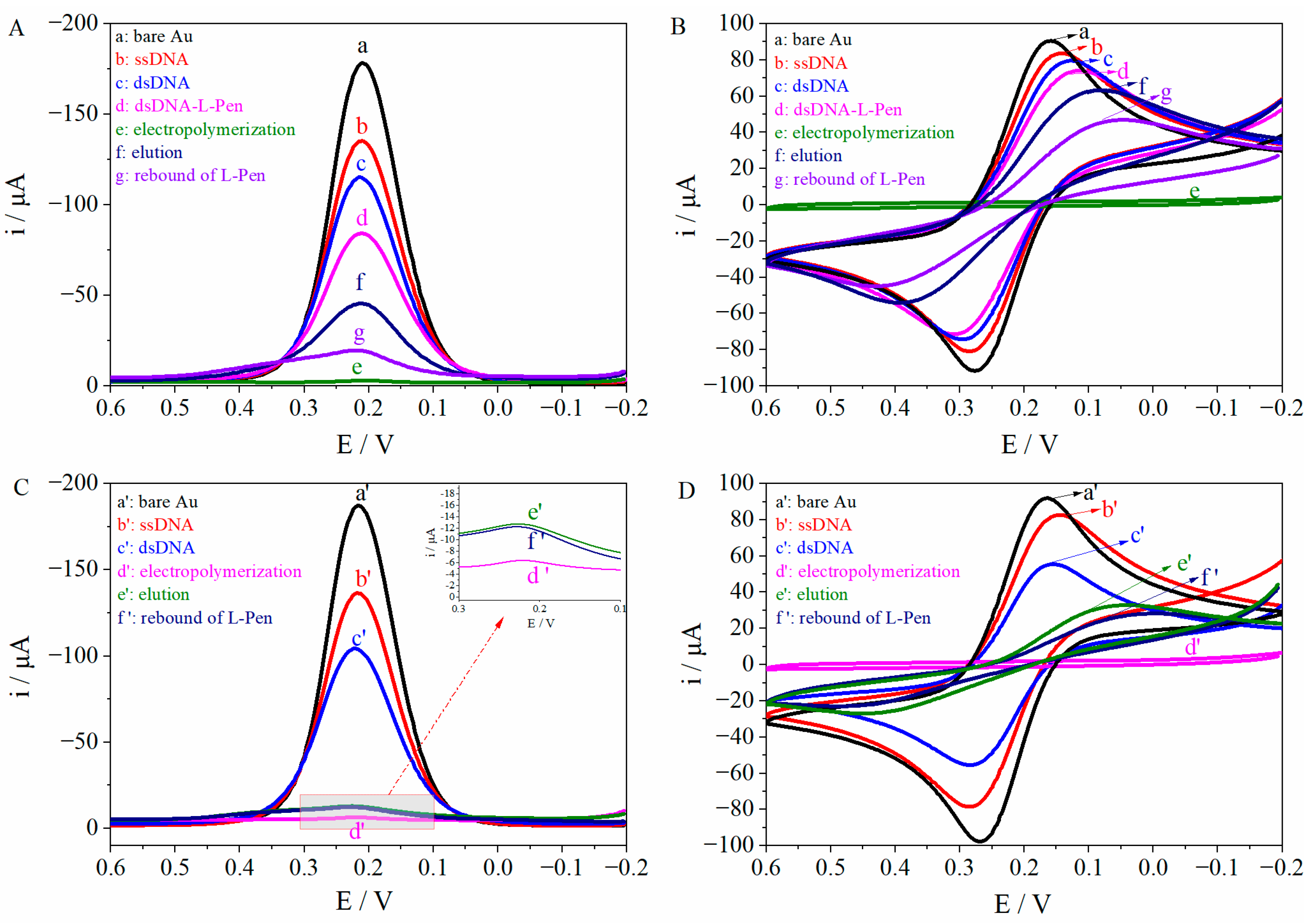
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of MIP/dsDNA and Non-MIP/dsDNA
3.3. Optimization of the MIP/dsDNA Sensor
3.4. DPV Response of the MIP/dsDNA Sensor to Identify L-Pen at Different Concentrations
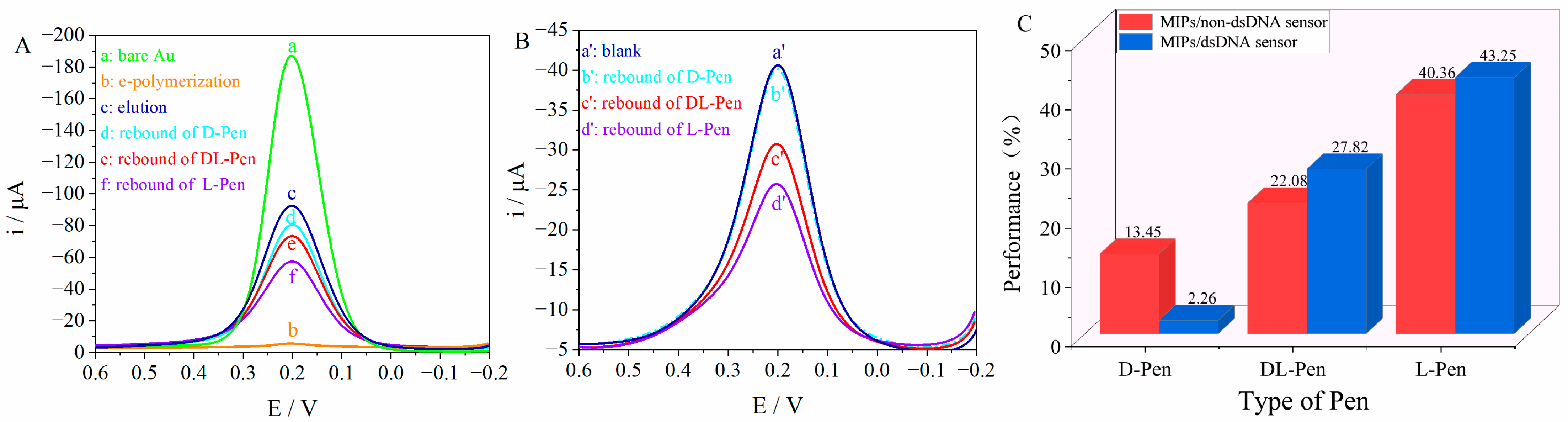
3.5. Chiral Separation and Recognition Performance of the Sensors
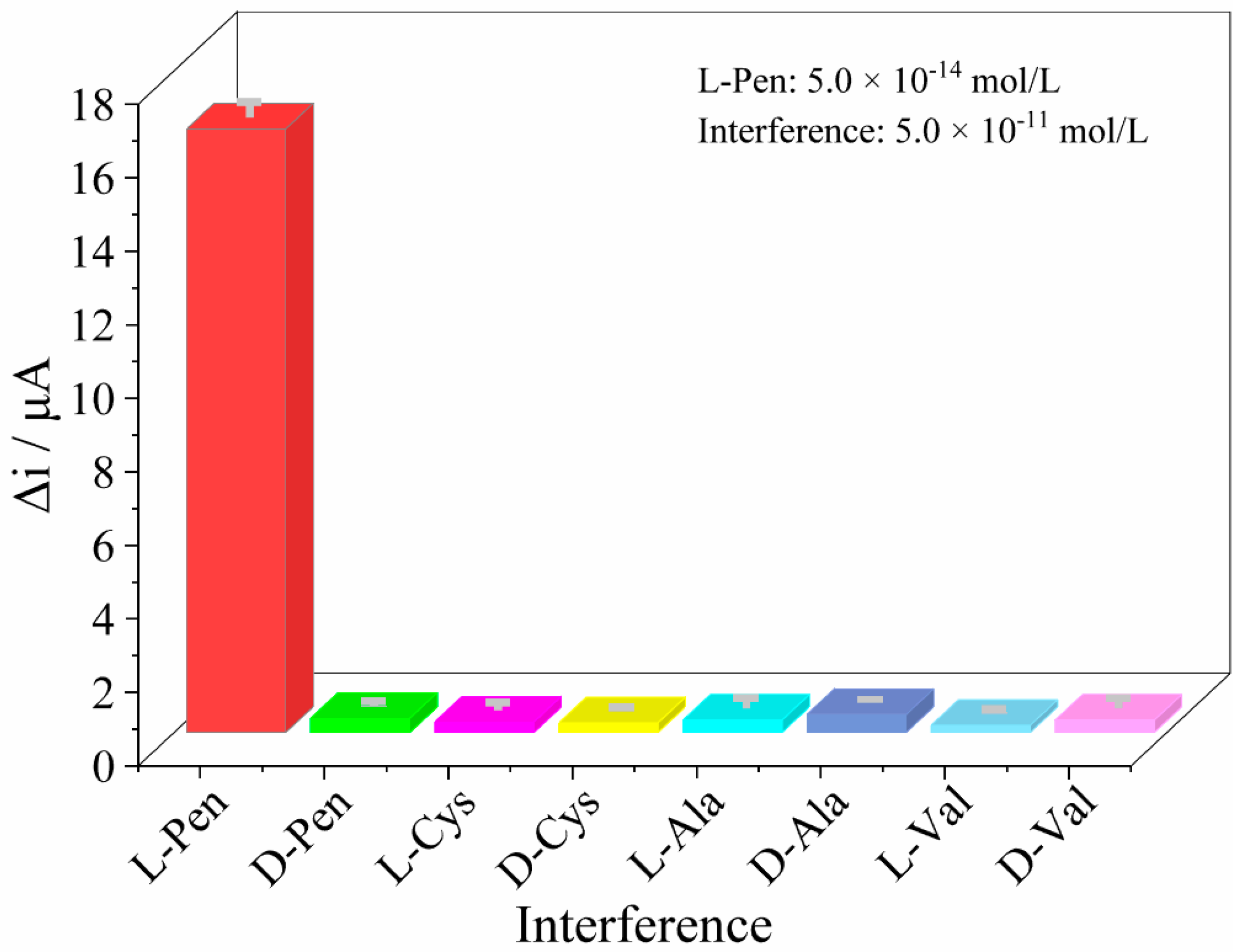
3.6. Stability and Reproducibility
3.7. Sample Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malyshko, E.V.; Tverdislov, V.A. Chirality as a physical aspect of structure formation in biological macromolecular systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser 2016, 741, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Yu, L.S.; Zeng, S. Stereoselectivity of chiral drug transport: A focus on enantiomer–transporter interaction. Drug Metab. Rev. 2014, 46, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Sharma, L. Enantioseparation of D-and L-isomers of chiral drugs for improving their bioavailability: Some techniques including micellization with gemini surfactants. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. 2018, 52, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P.F. Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: Realising their potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, M.P.; Prasad, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer based enantioselective sensing devices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Morrison, C.; Wieczorek, P.P.; Namieśnik, J.; Marć, M. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in analytical chiral separations and analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Luo, K.; Zhang, L.M.; Gao, J.X.; Liang, J.L.; Li, J.P.; Pan, H.C. Research and Application of Highly Selective Molecular Imprinting Technology in Chiral Separation Analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.D.; Li, S.; Liu, W. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the identification and separation of chiral drugs and biomolecules. Polymers 2016, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wei, X.P.; Ma, X.H.; Li, J.P. Amperometric sensing of L-phenylalanine using a gold electrode modified with a metal organic framework, a molecularly imprinted polymer, and β-cyclodextrin-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lian, H.T.; Sun, X.Y.; Yu, Y.M.; Liu, B. An L-dopa electrochemical sensor based on a graphene doped molecularly imprinted chitosan film. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Bagherzadeh, A.; Shamkhali, A.N. Synthesis of nano-sized stereoselective imprinted polymer by copolymerization of (S)-2-(acrylamido) propanoic acid and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate in the presence of racemic propranolol and copper ion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 63, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.H.; Zhang, S.B.; Shan, X.L.; Chen, Z.D. Derivative chiral copper (II) complexes as template of an electrochemical molecular imprinting sol-gel sensor for enantiorecognition of aspartic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1072, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Sarwar, T.; Husain, M.A.; Ishqi, H.M.; Tabish, M. Studying non-covalent drug–DNA interactions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 576, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feagin, T.A.; Olsen, D.P.V.; Headman, Z.C.; Heemstra, J.M. High-throughput enantiopurity analysis using enantiomeric DNA-based sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4198–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doan, P.; Pitter, D.R.G.; Kocher, A.; Wilson, J.N.; Goodson, T., III. A new design strategy and diagnostic to tailor the DNA-binding mechanism of small organic molecules and drugs. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 3202–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J.P. A Cimaterol Molecularly Imprinted Sensor Based on DNA-assisted Recognition. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 46, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, R.M.; Zheng, A.L.T. Zinc oxide/vancomycin-based electrochemical chiral sensor for the recognition of penicillamine enantiomers. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 3255–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devassy, D.E.; Harshad, S.R.; Devarbhai, H. Pompholyx-like eruptions induced by penicillamine in a patient with wilson’s disease. Indian J. Dermatol. 2019, 64, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Ubiña, S.; Jiménez-Gallo, D.; Russo-de la Torre, F.; Linares-Barrios, M. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa induced by d-penicillamine treated with cyclosporine and allopurinol. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, G.M.; Abellán, C.; Contento, A.M.; Ríos, Á. Discrimination of penicillamine enantiomers using β-cyclodextrin modified CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, S.M.; Najafzadeh, H.; Bahmei, S. Protective role of silymarin and D-penicillamine against lead-induced liver toxicity and oxidative stress. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaseth, J.; Skaug, M.A.; Cao, Y.; Andersen, O. Chelation in metal intoxication—Principles and paradigms. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 31, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisombath, N.S.; Jalilehvand, F.; Schell, A.C.; Wu, Q. Lead (II) binding to the chelating agent D-penicillamine in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 12459–12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Han, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.H.; Guo, L.J.; Fu, Y.Z. Chiral recognition of penicillamine enantiomers based on a vancomycin membrane electrode. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 5579–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.E.; Du Vigneaud, V. Inhibition of the growth of the rat by L-penicillamine and its prevention by aminoethanol and related compounds. J. Biol. Chem. 1950, 184, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukoc-Modun, L.; Biocic, M.; Radie, N. Flow-injection Determination of Glutathione, Penicillamine and Tiopronin Based on the Reduction of Copper (II)-neocuproine Reagent. Croat. Chem. Acta 2020, 93, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.J.; Guo, Z.P.; Chen, Y. Separation and determination of chiral composition in penicillamine tablets by capillary electrophoresis in a broad p H range. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgia, S.; Zinellu, A.; Forteschi, M.; Paliogiannis, P.; Deiana, G.A.; Pinna, G.A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C. A liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry study on the spirocyclization of ninhydrin with the aminothiols. Microchem. J. 2018, 141, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgia, S.; Zinellu, A.; Pinna, G.A.; Deiana, L.; Carru, C. Application of an unusual ninhydrin-based reaction for the indirect chiral resolution of D, L-penicillamine. Talanta 2011, 85, 1783–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.M.; Yang, J.D.; Yuan, H.Y.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, X.Q.; Cheng, J.W.; Zhang, Y.H. A novel competitive-displacement fluorescence assay for l-penicillamine based on the reaction between the target and N-acetyl-l-cysteine-capped CdTe quantum dots for copper ions. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamdee, K.; Puangmali, T.; Tuntulani, T.; Ngeontae, W. Circular dichroism sensor based on cadmium sulfide quantum dots for chiral identification and detection of penicillamine. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2015, 898, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Homochiral fluorescence responsive molecularly imprinted polymer: Highly chiral enantiomer resolution and quantitative detection of L-penicillamine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.J.; Liu, P.; Liu, Q.Y. Nano-scale minerals in-situ supporting CeO2 nanoparticles for off-on colorimetric detection of L–penicillamine and Cu2+ ion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Q.H.; Xia, Q.; Ran, P.Y.; Fu, Y.Z. Chiral recognition of penicillamine enantiomers using hemoglobin and gold nanoparticles functionalized graphite-like carbon nitride nanosheets via electrochemiluminescence. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 148, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Han, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.H.; Guo, L.J.; Fu, Y.Z. Enantioselective recognition of penicillamine enantiomers on bovine serum albumin-modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2013, 17, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Han, Q.; Chen, Q.; Guo, L.J.; Fu, Y.Z. Chiral Recognition of Penicillamine Enantiomers Based on DNA-MWNT Complex Modified Electrode. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Ge, Q.; Jiang, N.; Liu, M.; Cong, H.; Tao, Z. Ultrasensitive sensor for L-penicillamine with chirality-induced amplification of benzo [3] uril electrochemiluminescence via supramolecular interactions. Sens. Actuators B 2022, 362, 131801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Found 10−14 mol/L | RSD% n = 7 | Added 10−14 mol/L | Total Found 10−14 mol/L | RSD% n = 7 | Recoveries% | LC-MS 10−14 mol/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 5.82 | 4.42 | 3.00 | 8.79 | 4.04 | 98.91 | 5.79 |
| II | 6.24 | 3.56 | 6.00 | 12.00 | 3.16 | 96.20 | 6.01 |
| III | 5.45 | 4.32 | 6.00 | 11.65 | 3.98 | 103.43 | 5.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Luo, K.; Gao, J.; Li, J. DNA-Immobilized Special Conformation Recognition of L-Penicillamine Using a Chiral Molecular Imprinting Technique. Polymers 2022, 14, 4133. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194133
Zhang L, Luo K, Gao J, Li J. DNA-Immobilized Special Conformation Recognition of L-Penicillamine Using a Chiral Molecular Imprinting Technique. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):4133. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194133
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lianming, Kui Luo, Jingxia Gao, and Jianping Li. 2022. "DNA-Immobilized Special Conformation Recognition of L-Penicillamine Using a Chiral Molecular Imprinting Technique" Polymers 14, no. 19: 4133. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194133
APA StyleZhang, L., Luo, K., Gao, J., & Li, J. (2022). DNA-Immobilized Special Conformation Recognition of L-Penicillamine Using a Chiral Molecular Imprinting Technique. Polymers, 14(19), 4133. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194133







