Chitosan Oligosaccharide Prevents Afatinib-Induced Barrier Disruption and Chloride Secretion through Modulation of AMPK, PI3K/AKT, and ERK Signaling in T84 Cells
Abstract
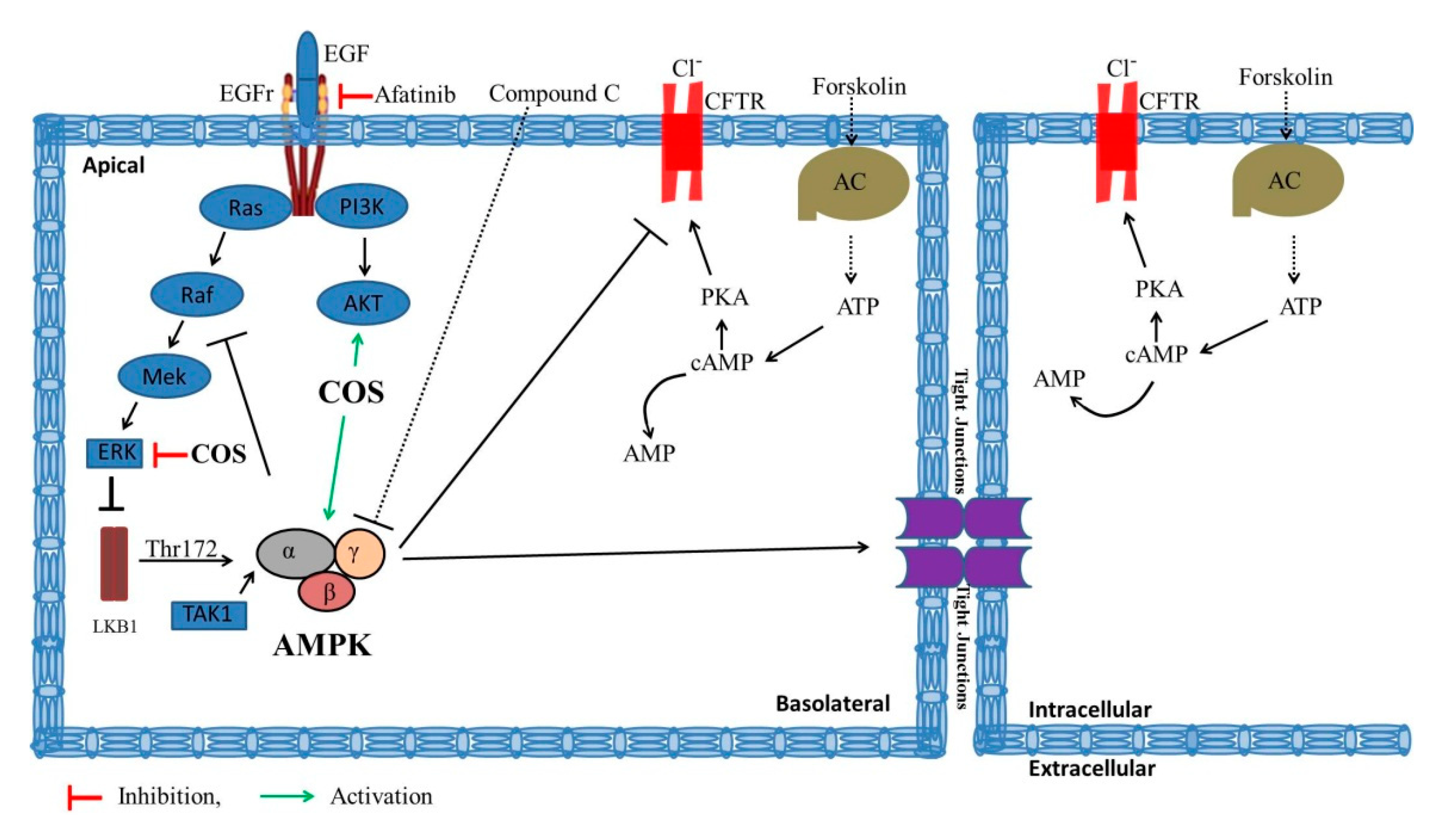
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assays
2.4. Measurement of Tight Junction Assembly
2.5. FITC-Dextran Flux Assay
2.6. Short-Circuit Current Measurement
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. COS Promotes Tight Junction Assembly
3.2. Effect of COS on Afatinib-Induced Cl− Secretion across T84 Cell Monolayers
3.3. Effect of COS and Afatinib on AMPK Signaling
3.4. Effect of COS on AKT and MAPK-ERK Signaling
3.5. Effect of COS and Afatinib on T84 Cell Viability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohmori, T.; Yamaoka, T.; Ando, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Kishino, Y.; Manabe, R.; Sagara, H. Molecular and Clinical Features of EGFR-TKI-Associated Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Attri, B.K.; Gill, R.K.; Bariwal, J. Review on EGFR Inhibitors: Critical Updates. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1134–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. Small molecule inhibitors targeting the EGFR/ErbB family of protein-tyrosine kinases in human cancers. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Wei, Y.; Ell, B.; Sheng, X.; Esposito, M.; Kang, J.; Hang, X.; Zheng, H.; Rowicki, M.; et al. Tinagl1 Suppresses Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis by Simultaneously Inhibiting Integrin/FAK and EGFR Signaling. Cancer Cell. 2019, 35, 64–80.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, G.; Phogat, D. Study of EGFR mutations in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Autops. Case Rep. 2021, 11, e2021251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamdari-Palangi, V.; Karami, Z.; Karami, H.; Baazm, M. MiRNA-7 Replacement Effect on Proliferation and Tarceva-Sensitivity in U373-MG Cell Line. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, T.; Cil, O.; Thiagarajah, J.R.; Verkman, A.S. Intestinal epithelial potassium channels and CFTR chloride channels activated in ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor diarrhea. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e126444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pessi, M.A.; Zilembo, N.; Haspinger, E.R.; Molino, L.; Di Cosimo, S.; Garassino, M.; Ripamonti, C.I. Targeted therapy-induced diarrhea: A review of the literature. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 90, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Reguart, N.; Barinoff, J.; Köhler, J.; Uttenreuther-Fischer, M.; Stammberger, U.; O’Brien, D.; Wolf, J.; Cohen, E.E. Diarrhea associated with afatinib: An oral ErbB family blocker. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2013, 13, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajah, J.R.; Donowitz, M.; Verkman, A.S. Secretory diarrhoea: Mechanisms and emerging therapies. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizzell, R.A.; Hanrahan, J.W. Physiology of epithelial chloride and fluid secretion. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009563. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, K.E.; Keely, S.J. Chloride secretion by the intestinal epithelium: Molecular basis and regulatory aspects. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000, 62, 535–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, J.E.; Sausbier, M.; Beranek, G.; Sausbier, U.; Ruth, P.; Leipziger, J. Role of cholinergic-activated KCa1.1 (BK), KCa3.1 (SK4) and KV7.1 (KCNQ1) channels in mouse colonic Cl- secretion. Acta Physiol. 2007, 189, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Quach, A.; Das, S.; Barrett, K.E. Potentiation of calcium-activated chloride secretion and barrier dysfunction may underlie EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced diarrhea. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Huang, P.; Ma, P.; Liu, Q.S.; Yu, C.; Du, Y.G. Chitosan oligosaccharides suppress LPS-induced IL-8 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through blockade of p38 and Akt protein kinases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; Qiao, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Han, B. Potential Analysis and Preparation of Chitosan Oligosaccharides as Oral Nutritional Supplements of Cancer Adjuvant Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Quan, W.; Luo, H.; Wu, K.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Q. Progress in Research of Chitosan Chemical Modification Technologies and Their Applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikušová, V.; Mikuš, P. Advances in Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Feng, J.; You, H.; Zhou, S.; Bai, Y.; He, J.; Cao, H.; Che, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The Microstructure, Antibacterial and Antitumor Activities of Chitosan Oligosaccharides and Derivatives. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Abubakar, S.; Lawal, I.M.; Abdul Latiff, A.A.; Umaru, I. Wastewater Treatment Using Alum, the Combinations of Alum-Ferric Chloride, Alum-Chitosan, Alum-Zeolite and Alum- Moringa Oleifera as Adsorbent and Coagulant. Int. J. Eng. Manag. 2018, 2, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Hayder, G.; Baloo, L.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Lawal, I.M.; Abubakar, S.; Al-dhawi, B.N.S.; Almahbashi, N.M.Y.; Umaru, I. Degradation of Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb and Zn by Moringa-oleifera, zeolite, ferric-chloride, chitosan and alum in an industrial effluent. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Phil, L.; Sohail, M.; Hasnat, M.; Baig, M.; Ihsan, A.U.; Shumzaid, M.; Kakar, M.U.; Mehmood Khan, T.; Akabar, M.D.; et al. Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS): An overview. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascuta, M.S.; Varvara, R.A.; Teleky, B.E. Polysaccharide-Based Edible Gels as Functional Ingredients: Characterization, Applicability, and Human Health Benefits. Gels 2022, 8, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, Z.B.; Yu, W.G.; Lu, X.Z. Chitosan Oligosaccharides Attenuate Amyloid Formation of hIAPP and Protect Pancreatic β-Cells from Cytotoxicity. Molecules 2020, 25, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satitsri, S.; Muanprasat, C. Chitin and Chitosan Derivatives as Biomaterial Resources for Biological and Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, P.; Cok, M.; Scognamiglio, F.; Pizzolitto, C.; Vecchies, F.; Marfoglia, A.; Marsich, E.; Donati, I. Glycosylated-Chitosan Derivatives: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muanprasat, C.; Chatsudthipong, V. Chitosan oligosaccharide: Biological activities and potential therapeutic applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 170, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muanprasat, C.; Wongkrasant, P.; Satitsri, S.; Moonwiriyakit, A.; Pongkorpsakol, P.; Mattaveewong, T.; Pichyangkura, R.; Chatsudthipong, V. Activation of AMPK by chitosan oligosaccharide in intestinal epithelial cells: Mechanism of action and potential applications in intestinal disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 96, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattaveewong, T.; Wongkrasant, P.; Chanchai, S.; Pichyangkura, R.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Muanprasat, C. Chitosan oligosaccharide suppresses tumor progression in a mouse model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer through AMPK activation and suppression of NF-κB and mTOR signaling. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 145, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Guan, S.; Woodfield, S.E.; Vasudevan, S.A.; Tao, L.; Pang, J.C.; Lu, J.; et al. Novel multi-targeted ErbB family inhibitor afatinib blocks EGF-induced signaling and induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vengoji, R.; Macha, M.A.; Nimmakayala, R.K.; Rachagani, S.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Mallya, K.; Gorantla, S.; Jain, M.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Batra, S.K.; et al. Afatinib and Temozolomide combination inhibits tumorigenesis by targeting EGFRvIII-cMet signaling in glioblastoma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Ajuwon, K.M. Butyrate modifies intestinal barrier function in IPEC-J2 cells through a selective upregulation of tight junction proteins and activation of the Akt signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehmood, T.; Maryam, A.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Khan, M.; Ma, T. Deoxyelephantopin induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells via oxidative stress, NF-κB inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction. BioFactors 2017, 43, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongkorpsakol, P.; Pathomthongtaweechai, N.; Srimanote, P.; Soodvilai, S.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Muanprasat, C. Inhibition of cAMP-activated intestinal chloride secretion by diclofenac: Cellular mechanism and potential application in cholera. PLoS Neglect. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanayindee, J.; Muanprasat, C.; Soodvilai, S.; Chatsudthipong, V. Antidiarrheal efficacy of a quinazolin CFTR inhibitor on human intestinal epithelial cell and in mouse model of cholera. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2012, 44, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhutani, J.; Sheikh, A.; Niazi, A.K. Akt inhibitors: Mechanism of action and implications for anticancer therapeutics. Infect. Agents Cancer 2013, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Hsu, C.-C.; Shiao, Y.-J.; Wang, H.-T.; Lo, Y.-L.; Lin, A.M.Y. Anti-inflammatory effect of afatinib (an EGFR-TKI) on OGD-induced neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshioka, T.; Shien, K.; Takeda, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Kurihara, E.; Ogoshi, Y.; Namba, K.; Torigoe, H.; Sato, H.; Tomida, S.; et al. Acquired resistance mechanisms to afatinib in HER2-amplified gastric cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, S.; Suzuki, T.; Taylor, W.L.; Bhargava, A.; Rao, R.K. Contrasting effects of ERK on tight junction integrity in differentiated and under-differentiated Caco-2 cell monolayers. Biochem. J. 2011, 433, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Dong, X.; Yap, J.; Hu, J. The MAPK and AMPK signalings: Interplay and implication in targeted cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, S.; Leclerc, J.; Grenier, A.; Foretz, M.; Tamburini, J.; Viollet, B. AMPK Activation Promotes Tight Junction Assembly in Intestinal Epithelial Caco-2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Cantley, L.C. Regulation of epithelial tight junction assembly and disassembly by AMP-activated protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Ji, Y.; Wu, G.; Sun, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; He, B.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, Z.; et al. l-Tryptophan Activates Mammalian Target of Rapamycin and Enhances Expression of Tight Junction Proteins in Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cells. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCole, D.F.; Truong, A.; Bunz, M.; Barrett, K.E. Consequences of direct versus indirect activation of epidermal growth factor receptor in intestinal epithelial cells are dictated by protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13303–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehmood, T.; Muanprasat, C. Deoxyelephantopin and Its Isomer Isodeoxyelephantopin: Anti-Cancer Natural Products with Multiple Modes of Action. Molecules 2022, 27, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipschutz, J.H.; Li, S.; Arisco, A.; Balkovetz, D.F. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 control claudin-2 expression in Madin-Darby canine kidney strain I and II cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 3780–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullin, J.M.; Leatherman, J.M.; Valenzano, M.C.; Huerta, E.R.; Verrechio, J.; Smith, D.M.; Snetselaar, K.; Liu, M.; Francis, M.K.; Sell, C. Ras mutation impairs epithelial barrier function to a wide range of nonelectrolytes. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005, 16, 5538–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehmood, T.; Pichyangkura, R.; Muanprasat, C. Chitosan Oligosaccharide Prevents Afatinib-Induced Barrier Disruption and Chloride Secretion through Modulation of AMPK, PI3K/AKT, and ERK Signaling in T84 Cells. Polymers 2022, 14, 4255. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204255
Mehmood T, Pichyangkura R, Muanprasat C. Chitosan Oligosaccharide Prevents Afatinib-Induced Barrier Disruption and Chloride Secretion through Modulation of AMPK, PI3K/AKT, and ERK Signaling in T84 Cells. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4255. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204255
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehmood, Tahir, Rath Pichyangkura, and Chatchai Muanprasat. 2022. "Chitosan Oligosaccharide Prevents Afatinib-Induced Barrier Disruption and Chloride Secretion through Modulation of AMPK, PI3K/AKT, and ERK Signaling in T84 Cells" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4255. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204255
APA StyleMehmood, T., Pichyangkura, R., & Muanprasat, C. (2022). Chitosan Oligosaccharide Prevents Afatinib-Induced Barrier Disruption and Chloride Secretion through Modulation of AMPK, PI3K/AKT, and ERK Signaling in T84 Cells. Polymers, 14(20), 4255. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204255




