A Facile Synthesis of Cellulose Nanofibers from Corn Cob and Rice Straw by Acid Hydrolysis Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Nanocellulose from Corn Cob (CC-NC) and Rice Straw (RS-NC)
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
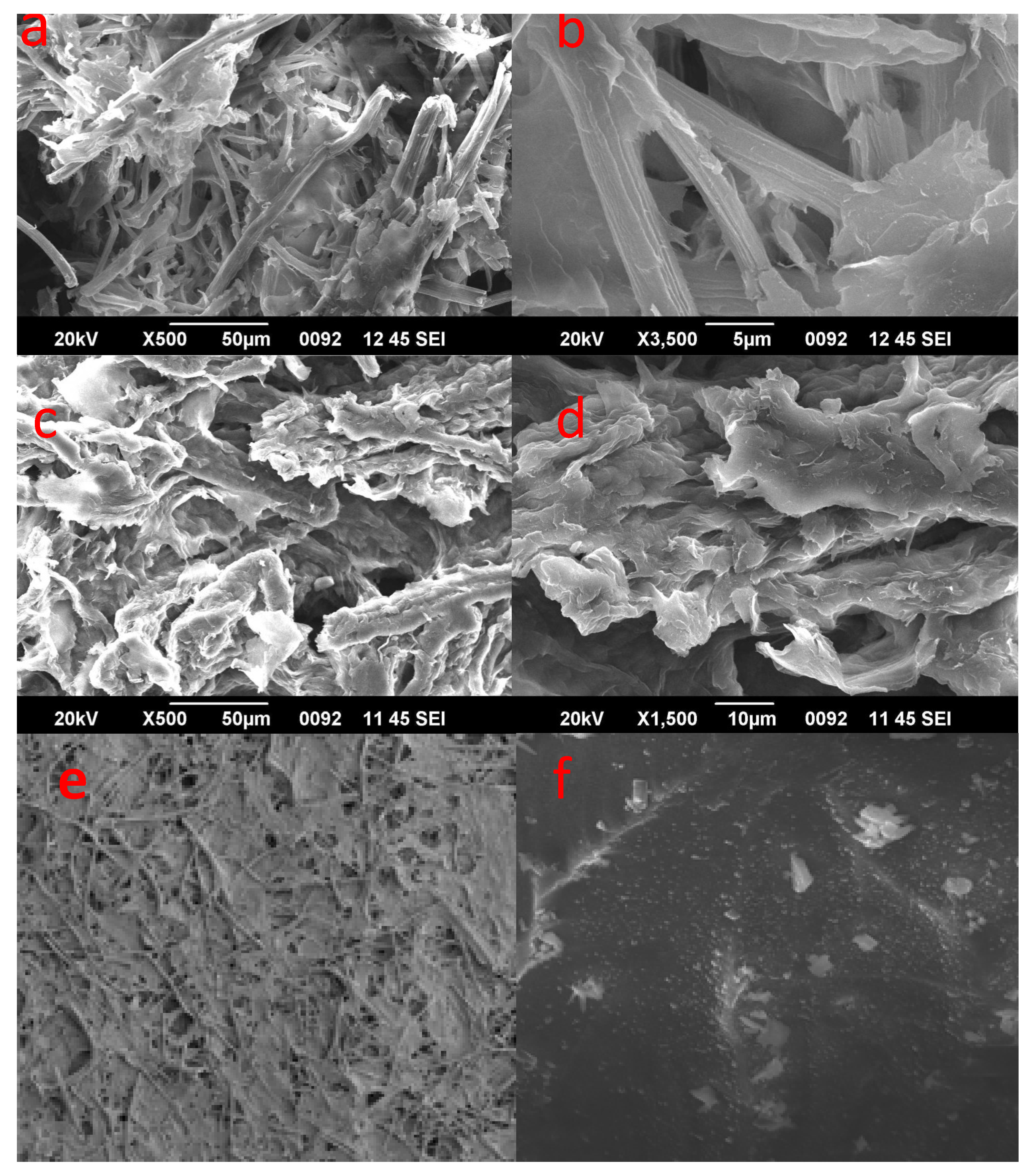
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
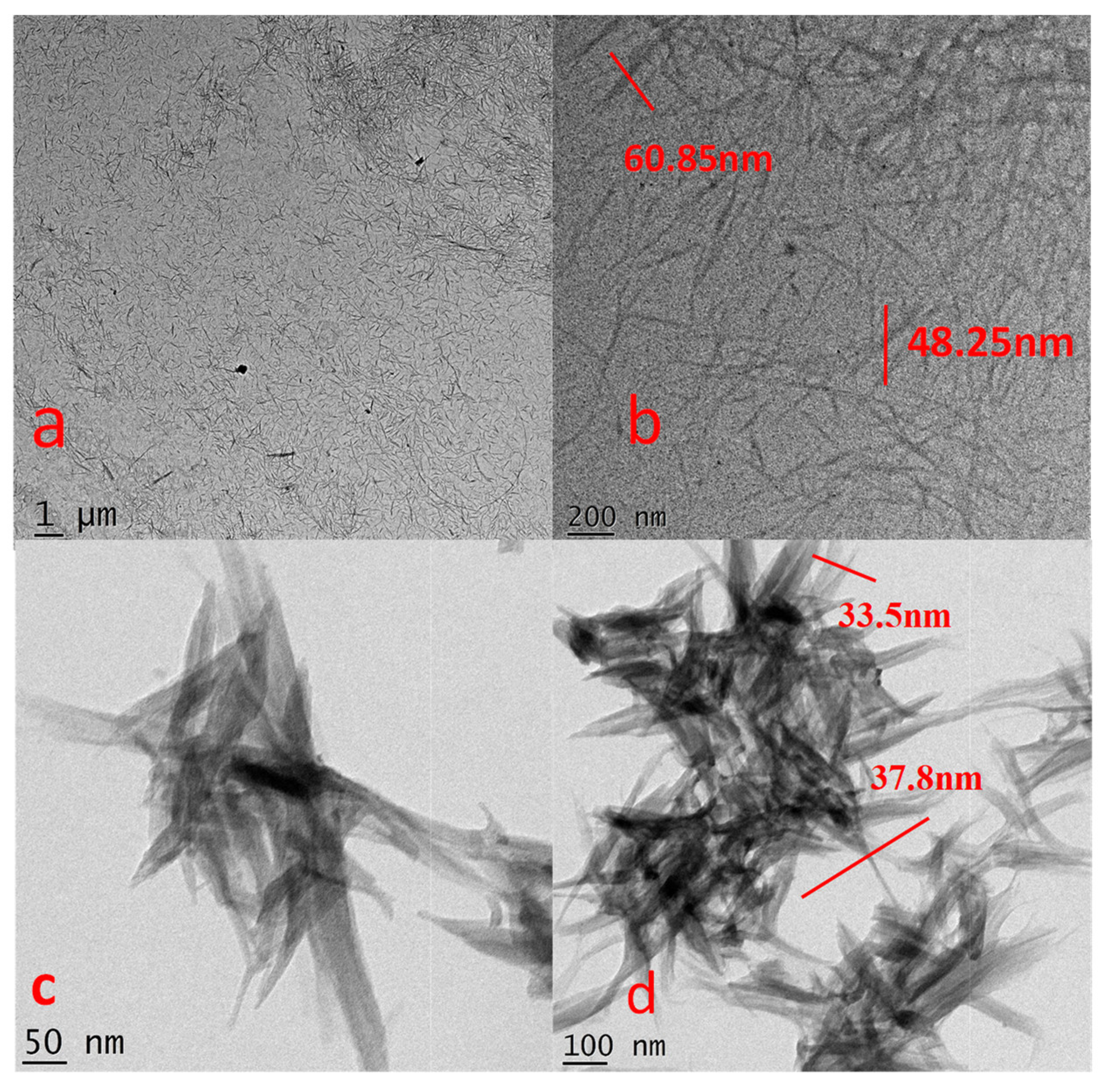
3.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
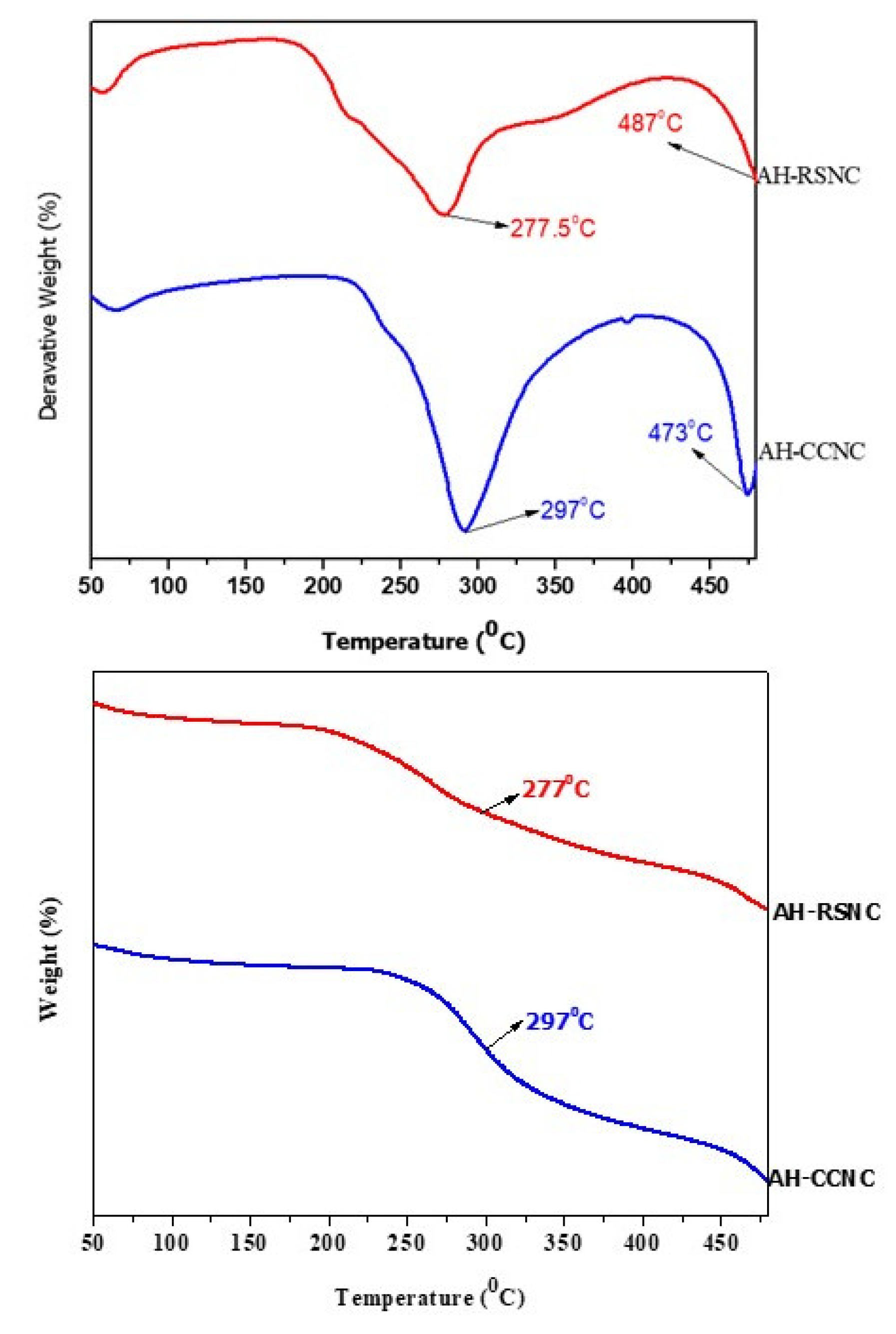
3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Differential Thermal Analysis (TGA/DTA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onkarappa, H.S.; Prakash, G.K.; Pujar, G.H.; Rajith Kumar, C.R.; Betageri, V.S. Facile synthesis and characterization of nanocellulose from Zea mays husk. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.L.; Yao, Z.L.; Wang, X.C.; Crombeen, M.; Sweeney, D.G.; Tam, K.C. Cellulose-based materials in wastewater treatment of petroleum industry. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Kamran, G. Current Trends and Future Developments on (bio-) Membranes: Microporous Membranes and Membrane Reactors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Langan, P.; Petridis, L.; O’Neill, H.M.; Pingali, S.V.; Foston, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Schulz, R.; Lindner, B.; Hanson, B.L.; Harton, S.; et al. Common processes drive the thermochemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbor, V.B.; Cicek, N.; Sparling, R.; Berlin, A.; Levin, D.B. Biomass pretreatment: Fundamentals toward application. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burhenne, L.; Messmer, J.; Aicher, T.; Laborie, M.-P. The effect of the biomass components lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose on TGA and fixed bed pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 101, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikgor, F.H.; Becer, C.R. Lignocellulosic biomass: A sustainable platform for the production of bio-based chemicals and polymers. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 4497–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, C.; Zhou, B.; He, Y. Determination of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin in Moso bamboo by near infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ruitao, C.; Pai, Z.; Huize, L.; Xingyu, J. Cellulosic Substrate materials with multi-scale building blocks: Fabrications, properties and applications in bioelectronic devices. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansary, M.A.; Pouresmaeel-Selakjani, P.; Aroon, M.A.; Hallajisani, A.; Cookman, J.; Shirazian, S. A molecular scale analysis of TEMPO-oxidation of native cellulose molecules. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babicka, M.; Magdalena, W.; Krzysztof, D.; Sławomir, B.; Izabela, R. Preparation of nanocellulose using ionic liquids: 1-propyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Molecules 2020, 25, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Dufresne, A. Nanocellulose in biomedicine: Current status and future prospect. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 59, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Nidhi, P.; Yashasvi, B.; Rawel, S.; Jitendra, K.; Thallada, B. Pyrolysis of agricultural biomass residues: Comparative study of corn cob, wheat straw, rice straw and rice husk. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 237, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, A.C.F.; Venkatachalam, S. Energy efficient process for valorization of corn cob as a source for nanocrystalline cellulose and hemicellulose production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.P.; Yongbo, P.E.N.G.; Min, Y.U.A.N.; Zhineng, H.O.N.G.; Dejian, W.A.N.G.; Renkou, X.U. Rice straw-derived biochar properties and functions as Cu (II) and cyromazine sorbents as influenced by pyrolysis temperature. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, H.K.; Patel, D.H.; Onkarappa, H.S.; Prasanna, G.D.; Prateeksha, C.C. Prasanna, Role of nanocellulose in industrial and pharmaceutical sectors—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, N.F.M.; Yusop, S.M.; Ahmad, I. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose and Nanocellulose From Pomelo (Citrus grandis) Albedo. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 5, 334. [Google Scholar]
- Adejumo, A.L.; Azeez, L.; Oyedeji, A.O.; Adetoro, R.O.; Aderibigbe, F.A. Nanostructured and surface functionalized corncob as unique adsorbents for anionic dye remediation. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Tian, X.; Sun, B.; Huang, J.; Yan, J.; Bao, Q.; Wang, X. Effect of synergistic fermentation of Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on thermal properties of wheat bran dietary fiber-wheat starch system. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, W.; Qu, L.; Chen, S.; Wu, S. Electrospun strong, bioactive, and bioabsorbable silk fibroin/poly (L-lactic-acid) nanoyarns for constructing advanced nanotextile tissue scaffolds. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 14, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.A.; Assis, D.D.J.; Gomes, G.V.; da Silva, J.B.; Fonsêca, A.F.; Druzian, J.I. Extraction and characterization of nanocellulose from corn stover. Mater. Today: Proc. 2015, 2, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from rice straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Han, F.; Xu, C.; Jiang, S.; Huang, L.; Liu, L.; Xia, Z. Effects of preparation methods on the morphology and properties of nanocellulose (NC) extracted from corn husk. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 109, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; You-Lo, H. Rice straw nanocelluloses: Process-linked structures, properties, and self-assembling into ultra-fine fibers. In Nanocelluloses: Their Preparation, Properties, and Applications; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 133–150. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Tamal, M.; Saswata, G. Cellulose nanofibers from rice straw: Process development for improved delignification and better crystallinity index. Trends Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 9, 16–27. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajanna, M.; Shivashankar, L.M.; Shivamurthy, O.H.; Ramachandrappa, S.U.; Betageri, V.S.; Shivamallu, C.; Hallur Lakshmana Shetty, R.; Kumar, S.; Amachawadi, R.G.; Kollur, S.P. A Facile Synthesis of Cellulose Nanofibers from Corn Cob and Rice Straw by Acid Hydrolysis Method. Polymers 2022, 14, 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204383
Rajanna M, Shivashankar LM, Shivamurthy OH, Ramachandrappa SU, Betageri VS, Shivamallu C, Hallur Lakshmana Shetty R, Kumar S, Amachawadi RG, Kollur SP. A Facile Synthesis of Cellulose Nanofibers from Corn Cob and Rice Straw by Acid Hydrolysis Method. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204383
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajanna, Madhuri, Latha Muglihalli Shivashankar, Onkarappa Honnebagi Shivamurthy, Shwetha Uramundina Ramachandrappa, Virupaxappa Shekarappa Betageri, Chandan Shivamallu, Raghavendra Hallur Lakshmana Shetty, Saurabh Kumar, Raghavendra G. Amachawadi, and Shiva Prasad Kollur. 2022. "A Facile Synthesis of Cellulose Nanofibers from Corn Cob and Rice Straw by Acid Hydrolysis Method" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204383
APA StyleRajanna, M., Shivashankar, L. M., Shivamurthy, O. H., Ramachandrappa, S. U., Betageri, V. S., Shivamallu, C., Hallur Lakshmana Shetty, R., Kumar, S., Amachawadi, R. G., & Kollur, S. P. (2022). A Facile Synthesis of Cellulose Nanofibers from Corn Cob and Rice Straw by Acid Hydrolysis Method. Polymers, 14(20), 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204383









