Understanding the Flame Retardant Mechanism of Intumescent Flame Retardant on Improving the Fire Safety of Rigid Polyurethane Foam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polyurethane Foam
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
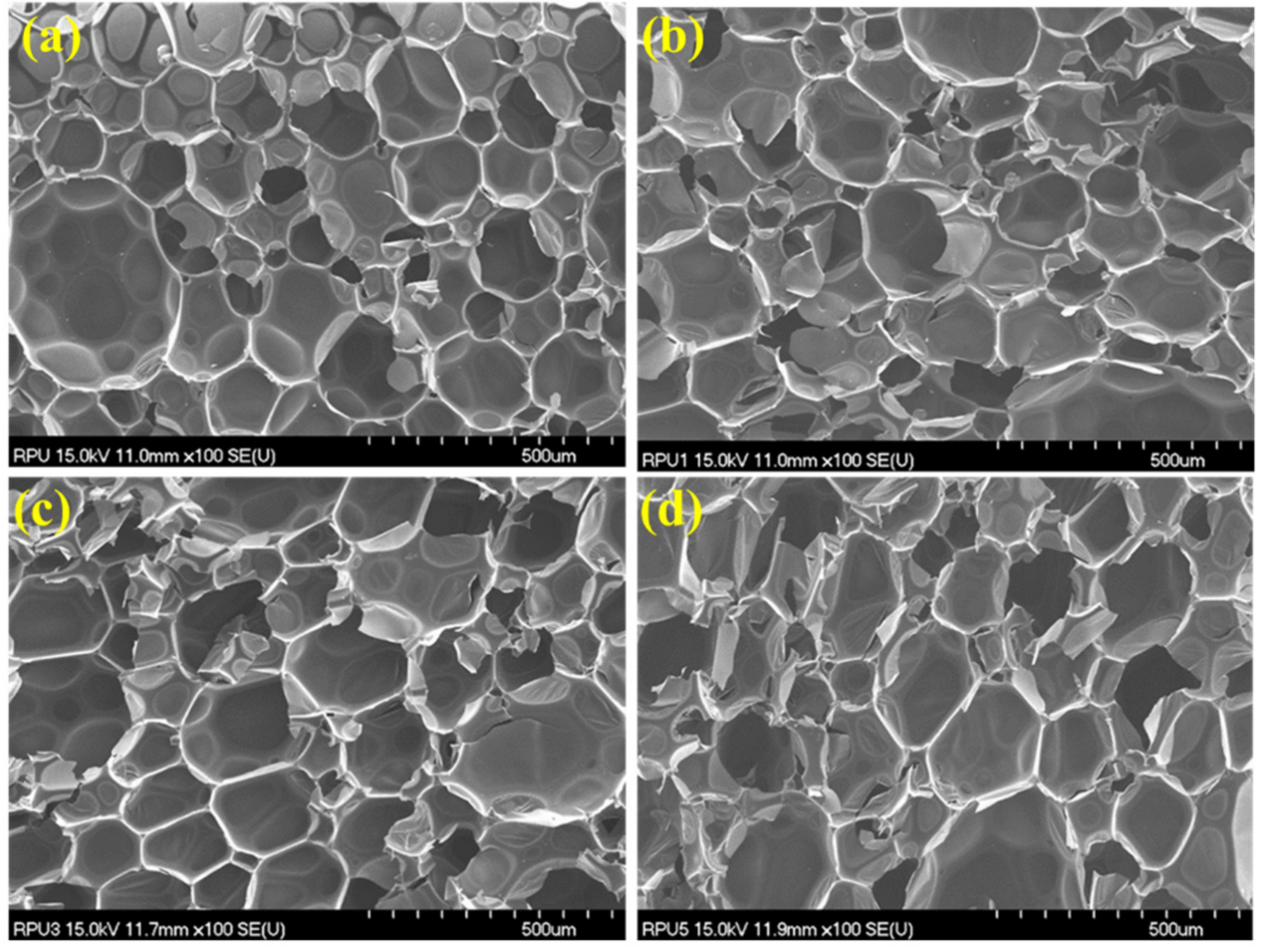
3.1. Surface Morphology
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3. Cone Calorimeter Tests
3.4. Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) Tests
3.5. Combustion Behavior and Char Residue Analysis
3.6. Char Residue Analysis
3.7. Raman Analysis
3.8. Physical Properties of RPU Foam
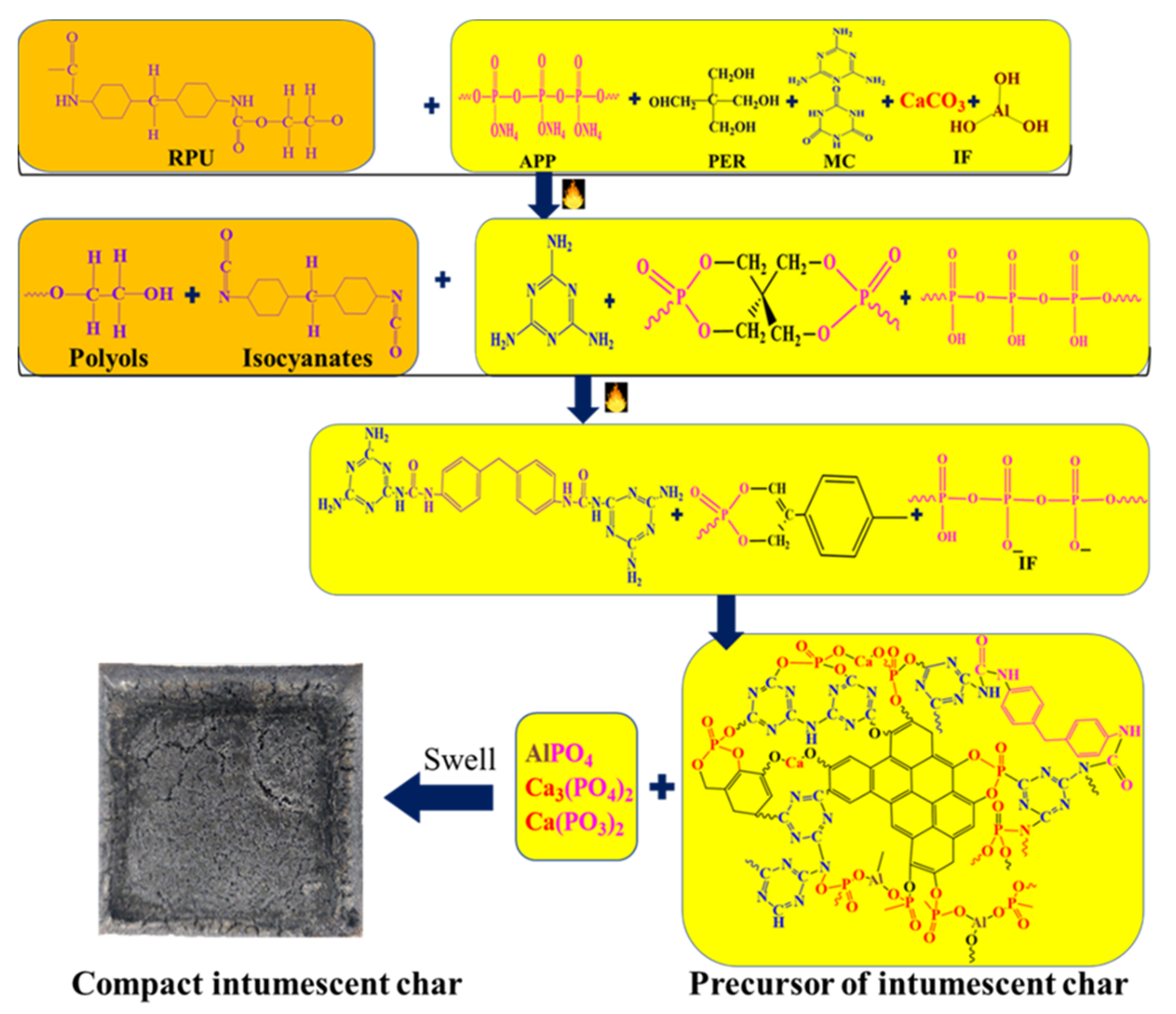
4. Possible Flame Retardant Mechanism
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demharter, A. Polyurethane rigid foam, a proven thermal insulating material for applications between +130 °C and −196 °C. Cryogenics 1998, 38, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairyte, A.; Kremensas, A.; Vaitkus, S.; Członka, S.; Strakowska, A. Fire suppression and thermal behavior of biobased rigid polyurethane foam filled with biomass incinerationwaste ash. Polymers 2020, 12, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borreguero, A.M.; Valverde, J.L.; Peijs, T.; Rodrı’guez, J.F.; Carmona, M. Characterization of rigid polyurethane foams containing microencapsulated RubithermRT27. Part I. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 4462–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Huo, S.; Song, P. Recent advances in fire-retardant rigid polyurethane foam. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 112, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, S. Synthesis and properties of rigid polyurethane foams synthesized from modified urea-formaldehyde resin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Gao, M. Thermal degradation and flame retardant mechanism of the rigid polyurethane foam including functionalized graphene oxide. Polymers 2019, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S. Flame retardant properties of polyurethane produced by the addition of phosphorous containing polyurethane oligomers (II). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 15, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Wang, D.M. Enhanced fire behavior of rigid polyurethane foam by intumescent flame retardants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, P.; Yang, H.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Functionalized lignin for halogen-free flame retardant rigid polyurethane foam: Preparation, thermal stability, fire performance and mechanical properties. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, T.; Jia, D. Structure and flame-retardant actions of rigid polyurethane foams with expandable graphite. Polymers 2019, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoite, S.P.; Kim, J.; Jo, W.; Bhoite, P.H.; Mali, S.S.; Park, K.H.; Hong, C.K. Expanded polystyrene beads coated with intumescent flame retardant material to achieve fire safety standards. Polymers 2021, 13, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, X.Z.; Yu, Z.Z.; Guo, P.; Song, H.H.; Duc, X.S. Dispersion of graphene oxide and its flame retardancy effect on epoxy nanocomposites. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2011, 29, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Y.; Zou, H.; Liang, M.; Luo, W. Effect of expandable graphite particle size on the flame retardant, mechanical, and thermal properties of water-blown semi-rigid polyurethane foam. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kalali, E.N.; Wan, J.T.; Wang, D.Y. Carbon-family materials for flame retardant polymeric materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 69, 22–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S. Intumescent fire protective coating: Toward a better understanding of their mechanism of action. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 449, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirnstein, B.; Schulze, D.; Scharte, B. Mechanical and fire properties of multicomponent flame retardant EPDM rubbers using aluminum trihydroxide, ammonium polyphosphate, and polyaniline. Materials 2019, 12, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, U.; Schartel, B. Flame retardant mechanisms of red phosphorus and magnesium hydroxide in high impact polystyrene. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D. A review of recent progress in phosphorus-based flame retardants. J. Fire Sci. 2006, 24, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperopoulos, E.; Scionti, G.; Atria, M.; Calabrese, L.; Proverbio, E.; Ingegneria, D.; Messina, U.; Sant, D. Flame—Retardant Performance Evaluation of Functional Coatings Filled with Mg(OH)2 and Al(OH)3. Polymers 2022, 14, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chu, Z.; Yan, L.; Chen, H.; Jia, H.; Tang, W. Effect of chicken eggshell on the flame-retardant and smoke suppression properties of an epoxy-based traditional APP-PER-MEL system. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 2712–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, W. Influence of expanded vermiculite on fire protection of intumescent fireproof coatings for steel structures. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2015, 12, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevda, B.T.; Ayfer, D.C.; Turgay, O. The synergistic effect of intumescent coating containing titanium dioxide and antimony trioxide onto spruce and alder wood species. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wei, P.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, X.; Yu, H. Synthesis of a novel hybrid synergistic flame retardant and its application in PP/IFR. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. Influence of nano-silica on the flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties of transparent intumescent fire-retardant coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 112, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirzadeh, M.; Yahyaei, H.; Mohseni, M. Effects of inorganic fillers on the performance of the water-based intumescent fire-retardant coating. Fire Mater. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeras, X.; Bras, M.L.; Hornsby, P.; Bourbigot, S.; Marosi, G.; Keszei, S.; Poutch, F. Effect of fillers on the fire retardancy of intumescent polypropylene compounds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 82, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, T.R.; Witkowski, A.; Hollingbery, L. Fire retardant action of mineral fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Pang, L.; Chen, M.; Xie, J.; Liu, Q. Effects of aluminum hydroxide and layered double hydroxide on asphalt fire resistance. Materials 2018, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, J. Flame-retardant effect of montmorillonite intercalation iron compounds in polypropylene/aluminum hydroxide composites system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 124, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasuney, S. Novel multi-component flame retardant system based on nanoscopic aluminium-trihydroxide (ATH). Powder Technol. 2017, 305, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Wu, K.; Lu, M. Thermal degradation and flame retardancy of microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate in rigid polyurethane foam. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 120, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J. Thermal degradation characteristics of rigid polyurethane foam and the volatile products analysis with TG-FTIR-MS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2687–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qi, L.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Li, S. Recent Advances in Halogen-Free Flame Retardants for Polyolefin Cable Sheath Materials. Polymers 2022, 14, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hao, J.; Gaan, S. Recent studies on the decomposition and strategies of smoke and toxicity suppression for polyurethane based materials. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 74742–74756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrovinci, A.; Camino, G.; Drevelle, C.; Duquesne, S.; Magniez, C.; Vouters, M. Ammonium polyphosphate–aluminum trihydroxide antagonism in fire retarded butadiene–styrene block copolymer. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 2023–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, F.; Wu, K.; Wang, Q.; Qian, Z.; Li, S.; Guo, W. Improved Flame-Retardant and Ceramifiable Properties of EVA Composites by Combination ofAmmonium Polyphosphate andAluminum Hydroxide. Polymers 2019, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, U.; Schartel, B.; Fichera, M.A.; Jäger, C. Flame retardancy mechanisms of aluminium phosphinate in combination with melamine polyphosphate and zinc borate in glass-fibre reinforced polyamide 6,6. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1528–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffendahl, C.; Fontaine, G.; Duquesne, S.; Taschner, F.; Mezger, M.; Bourbigot, S. The fire retardant mechanism of ethylene vinyl acetate elastomer (EVM) containing aluminium trihydroxide and melamine phosphate. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 20185–20199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.C. Orientation effect on cone calorimeter test results to assess fire hazard of materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.Y.; Ma, C.; Zhou, F.; Hu, Y.; Schartel, B. A liquid phosphorous flame retardant combined with expandable graphite or melamine in flexible polyurethane foam. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemła, M.; Prociak, A.; Michałowski, S. Bio-Based Rigid Polyurethane Foams Modified with Phosphorus Flame Retardants. Polymers 2021, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, J. Synergistic flame retardant effect of aluminum hydroxide and ammonium polyphosphate on epoxy resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Yan, L. Comparative study of fire resistance and char formation of intumescent fire-retardant coatings reinforced with three types of shell bio-fillers. Polymers 2021, 13, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, N.H.; Pham, D.L.; Hanh, N.T.; Oanh, H.T.; Yen Duong, T.H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tuyen, N.D.; Phan, D.L.; Trinh, H.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; et al. Influence of Organoclay on the Flame Retardancy and Thermal Insulation Property of Expandable Graphite/Polyurethane Foam. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Sun, S.; Xu, W.; Song, Y.; Deng, Z.; Qian, X. Covalently-functionalized graphene oxide via introduction of bifunctional phosphorus-containing molecules as an effective flame retardant for polystyrene. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 24993–25000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H. Comparative Study on the Flame Retardancy and Retarding Mechanism of Rare Earth (La, Ce, and Y)-Based Organic Frameworks on Epoxy Resin. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 35548–35558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Shankar, K.; Morozov, E.V. Behaviour of PU-foam/glass-fibre composite sandwich panels under flexural static load. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2015, 48, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Materials | Specification |
|---|---|
| Polyol | Stepanol PS-3152, polyester polyol, 315 mg/g Hydroxyl value, purchased from STEPAN, Anaheim, CA, USA |
| Isocyanate | 4’4-Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) |
| Catalyst | Dabco K-15, potassium-octoate obtained from EVONIC, Rheinfelden, Germany |
| Polysiloxane silicon | TEGOSTAB B-8462, surfactant, purchased from EVONIC, Rheinfelden, Germany |
| HC- Cyclopentane | Blowing agent from SK Geocentric |
| Ammonium polyphosphate (APP) | Flame retardant, acid source, purity > 98%, particle size d50 of ~8 μm, obtained from Samchun Pure Chemicals, Seoul, Korea |
| Pentaerythritol (PER) | Flame retardant, carbonizing agent, purity 98%, obtained from Samchun Pure Chemicals, Seoul, Korea |
| Melamine cyanurate (MC) | Flame retardant, blowing agent, purity 99%, particle size 1.8 μm, obtained from Samchun Pure Chemicals, Seoul, Korea |
| Expandable graphite (EG) | Flame retardant, purity 99%, particle size is 80% >50 mesh, expansion rate is over 350 cm3/g, pH 7.0, obtained from Samjung C&G, Ulsan, Korea |
| Calcium carbonate (CC) | Flame retardant filler, purity 98.5%, particle size 3.5 μm, obtained from Samchun Pure Chemicals, Seoul, Korea. |
| Aluminum hydroxide (ATH) | Flame retardant filler, purity 63% particle size ~6 μm, purchased from Daejung Chemicals, Gyeonggi, Korea and used without further purification. |
| Samples | Basic Composition (pphp) | Flame Retardant (php) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyol | Catalyst | Surfactant | Blowing Agent | MDI | APP | PER | MC | EG | CC | ATH | |
| RPU | 100 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 150 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RPU/IFR0 | 100 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 150 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 5 | - |
| RPU/IFR1 | 100 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 150 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 3 |
| RPU/IFR2 | 100 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 150 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 5 |
| Sample Code | PHRR (kW/m2) | THR (MJ/m2) | Av-EHC (MJ/kg) | MARHE (kW/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPU | 140 | 25.06 | 33.71 | 90.0 |
| RPU/IFR0 | 88.97 | 19.68 | 11.02 | 53.7 |
| RPU/IFR1 | 82.12 | 15.15 | 6.32 | 48.9 |
| RPU/IFR2 | 96.05 | 18.69 | 9.40 | 60.7 |
| Sample | Density (kg/m3) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·k) | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat RPU | 61.1 | 0.0163 | 22 |
| RPU/IFR0 | 64.2 | 0.0168 | 34 |
| RPU/IFR1 | 65.0 | 0.0169 | 36 |
| RPU/IFR2 | 65.6 | 0.0170 | 35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, J.S.; Ma, B.C. Understanding the Flame Retardant Mechanism of Intumescent Flame Retardant on Improving the Fire Safety of Rigid Polyurethane Foam. Polymers 2022, 14, 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224904
Lee SH, Lee SG, Lee JS, Ma BC. Understanding the Flame Retardant Mechanism of Intumescent Flame Retardant on Improving the Fire Safety of Rigid Polyurethane Foam. Polymers. 2022; 14(22):4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224904
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung Hun, Seul Gi Lee, Jun Seo Lee, and Byung Chol Ma. 2022. "Understanding the Flame Retardant Mechanism of Intumescent Flame Retardant on Improving the Fire Safety of Rigid Polyurethane Foam" Polymers 14, no. 22: 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224904
APA StyleLee, S. H., Lee, S. G., Lee, J. S., & Ma, B. C. (2022). Understanding the Flame Retardant Mechanism of Intumescent Flame Retardant on Improving the Fire Safety of Rigid Polyurethane Foam. Polymers, 14(22), 4904. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224904






