High Multi-Environmental Mechanical Stability and Adhesive Transparent Ionic Conductive Hydrogels Used as Smart Wearable Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis of the Hydrogel and Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Mechanical Test
2.4. Anti-Freezing Property and Moisturizing Property Tests
2.5. Adhesion Performance Test
2.6. Electrical Properties Testing
3. Results and Discussion
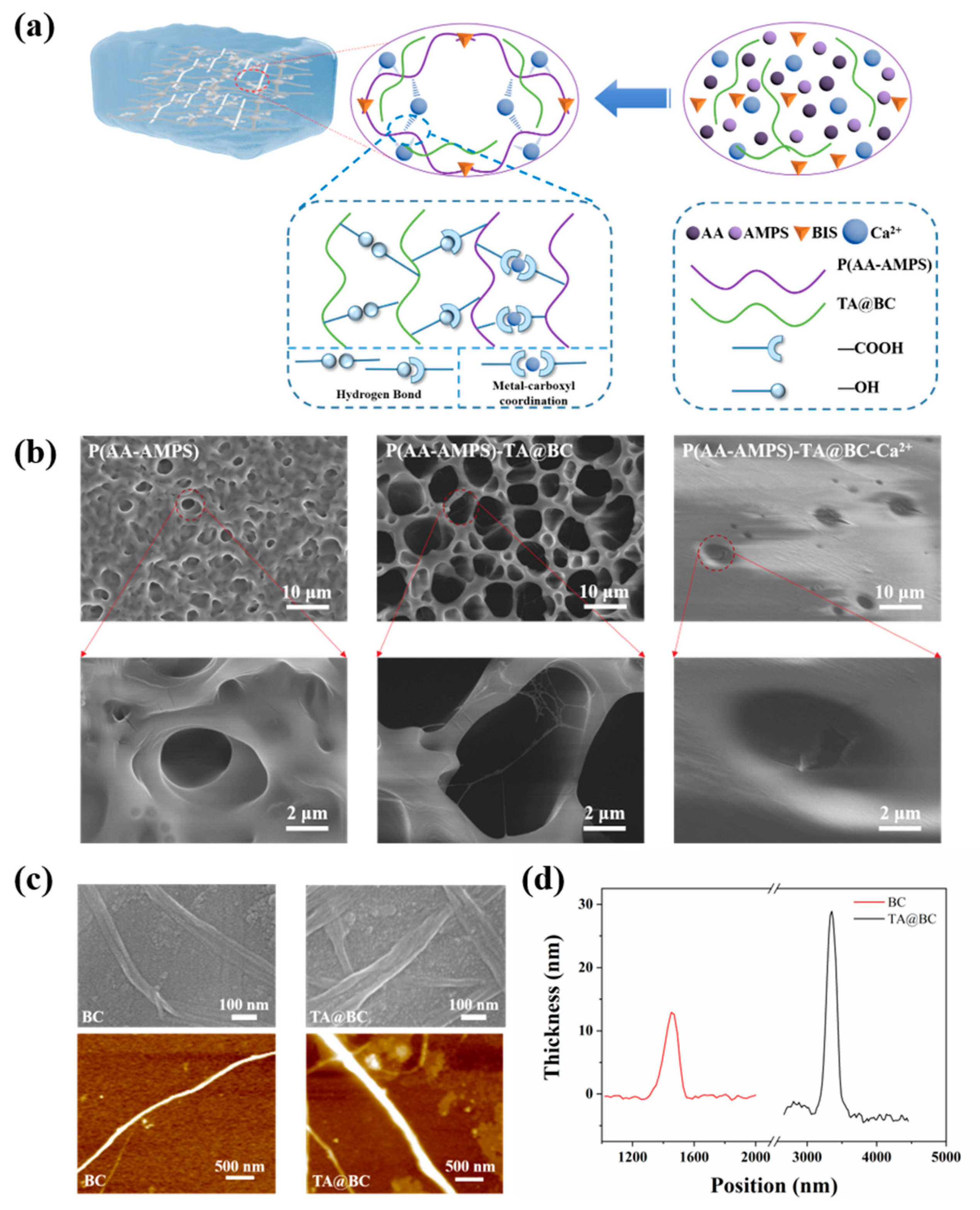
3.1. Design and Fabrication of Hydrogel
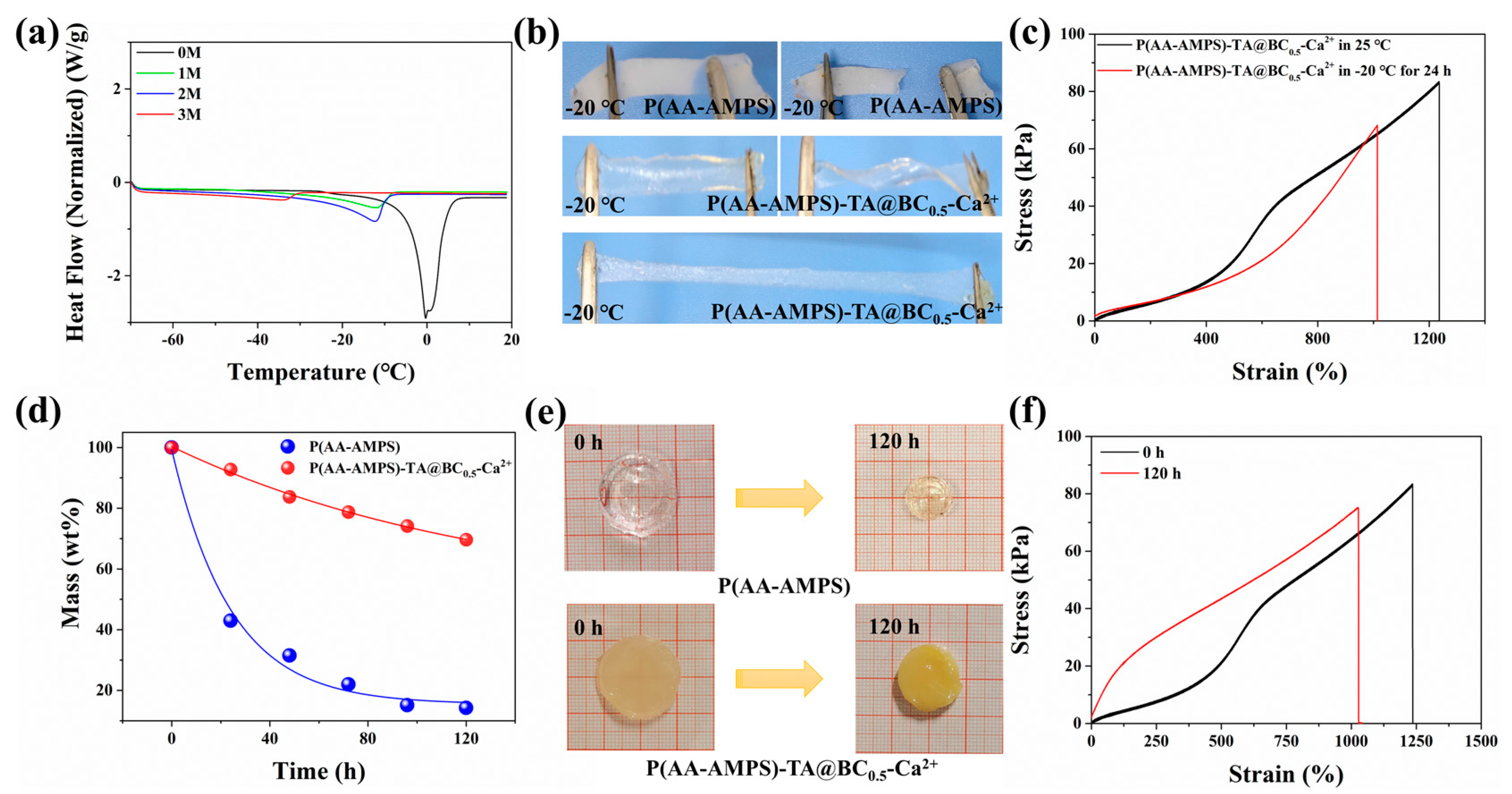
3.2. Mechanical Properties of Hydrogel
3.3. Mechanical and Conductive Stability of the Hydrogel in Freezing and Arid Environments
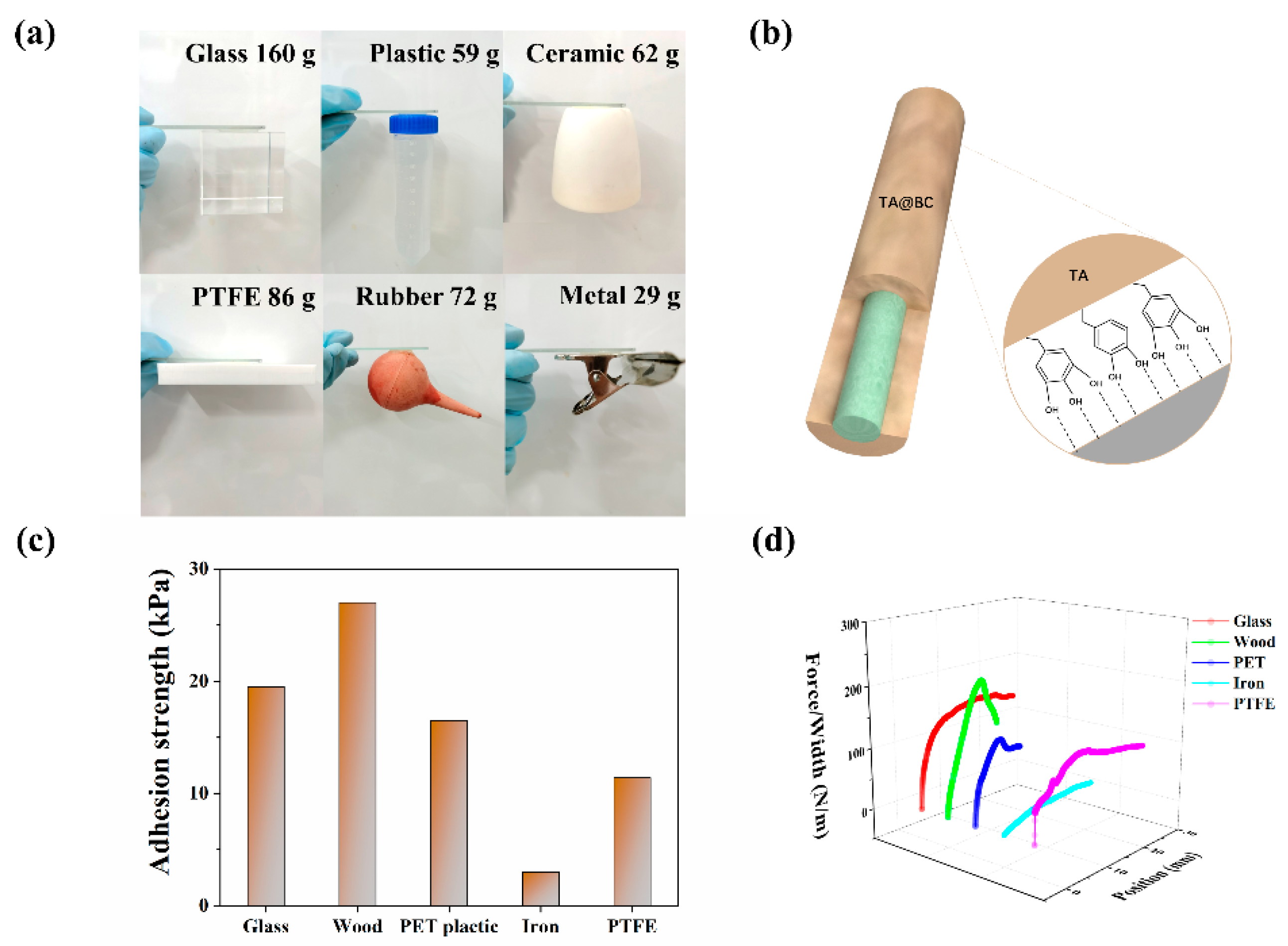
3.4. Adhesion Properties of Hydrogel
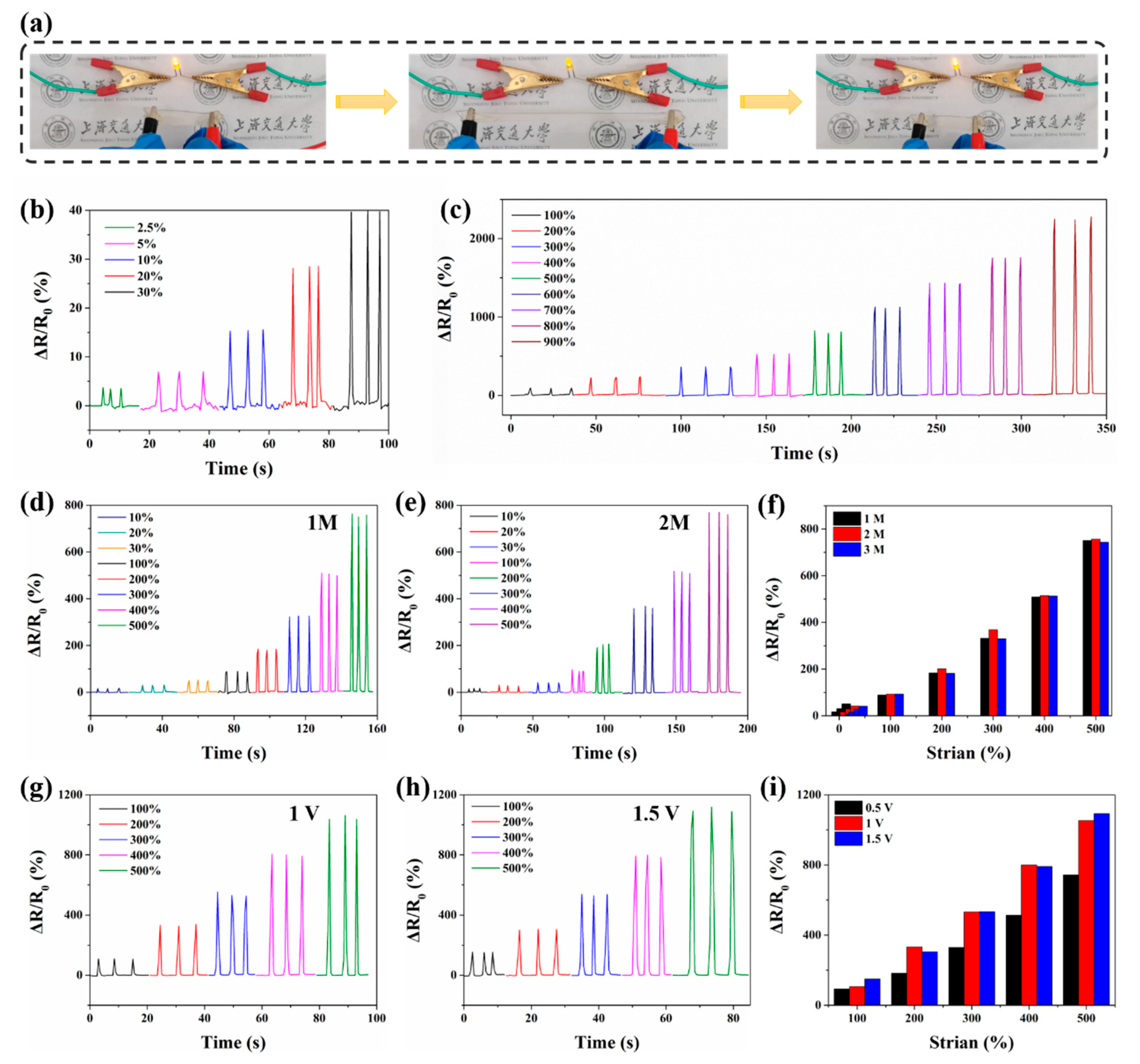
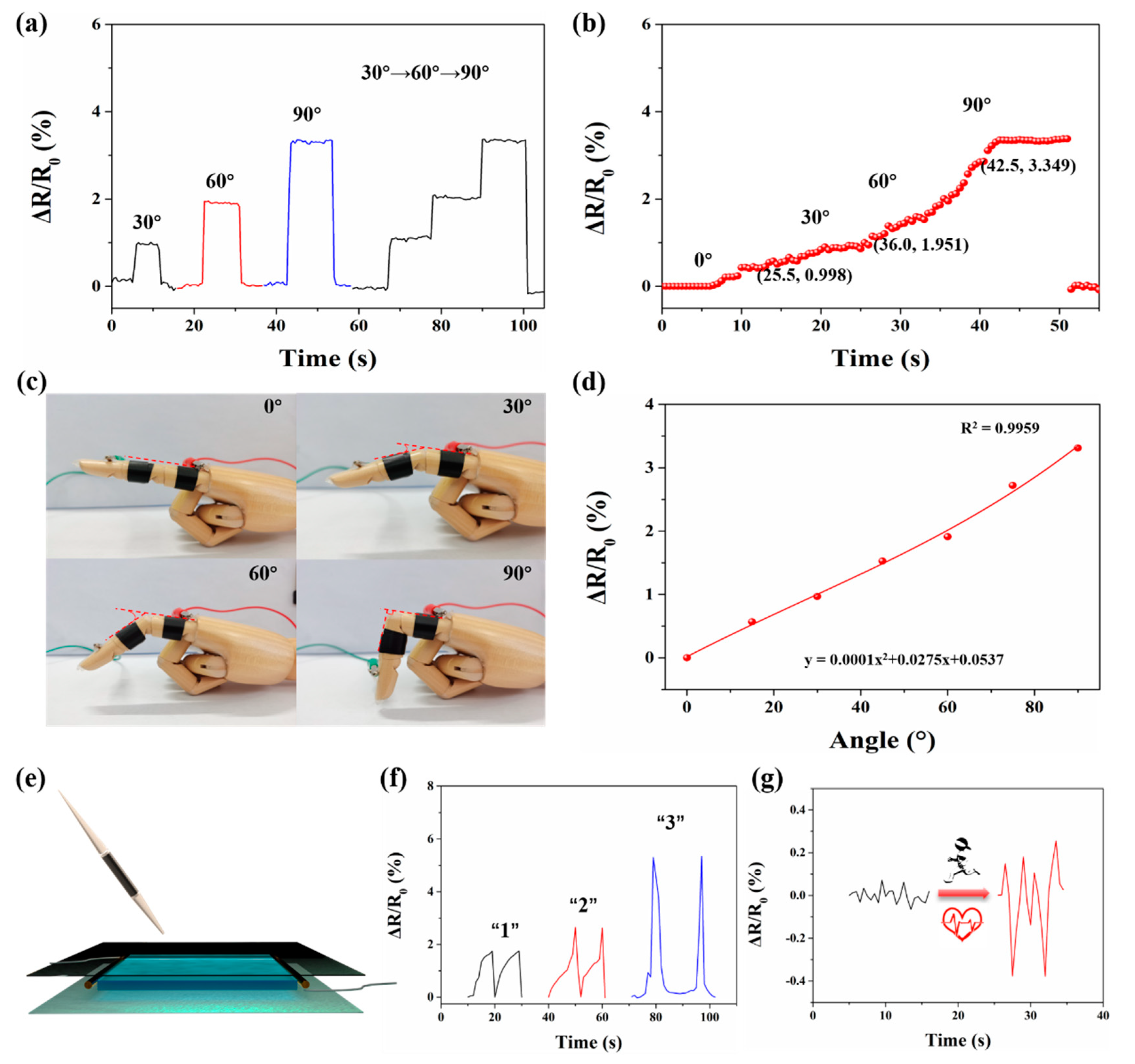
3.5. Electrical Sensing Properties of Hydrogel
3.6. Behavioral Monitoring of Human Movement and Physiological Signals by Hydrogel
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le, X.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T. Recent Progress in Biomimetic Anisotropic Hydrogel Actuators. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Liu, M.; Ishida, Y.; Ebina, Y.; Osada, M.; Sasaki, T.; Hikima, T.; Takata, M.; Aida, T. Thermoresponsive actuation enabled by permittivity switching in an electrostatically anisotropic hydrogel. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, L.; Xie, M.; Jian, Y.; Wu, B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, C. Multiple-Responsive and Amphibious Hydrogel Actuator Based on Asymmetric UCST-Type Volume Phase Transition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43641–43648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; An, T.; Yap, L.W.; Zhu, B.; Gong, S.; Cheng, W. Disruptive, Soft, Wearable Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1904664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cong, Y.; Fu, J. Stretchable and tough conductive hydrogels for flexible pressure and strain sensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3437–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Wang, H. Shape changing hydrogels and their applications as soft actuators. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Li, S.; Gao, L. Dispersed Association of Single-Component Short-Alkyl Chains toward Thermally Programmable and Malleable Multiple-Shape Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43622–43630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Du, X. Bio-inspired sensing and actuating materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 6493–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, R.; Matsuhisa, N.; Jiang, Z.; Nayeem, M.O.G.; Yokota, T.; Someya, T. A Highly Sensitive Capacitive-type Strain Sensor Using Wrinkled Ultrathin Gold Films. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5610–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Nilghaz, A.; Su, B.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, W.; Shen, W. Stretchable-Fiber-Confined Wetting Conductive Liquids as Wearable Human Health Monitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4511–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipomi, D.J.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Tee, B.C.K.; Hellstrom, S.L.; Lee, J.A.; Fox, C.H.; Bao, Z. Skin-like pressure and strain sensors based on transparent elastic films of carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Q.; Nguyen, D.H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T. Ultra-stretchable, self-healable, and reprocessable ionic conductive hydrogels enabled by dual dynamic networks. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2817–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Jiang, F. Cellulose Nanofibrils Enhanced, Strong, Stretchable, Freezing-Tolerant Ionic Conductive Organohydrogel for Multi-Functional Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplinger, C.; Sun, J.-Y.; Foo Choon, C.; Rothemund, P.; Whitesides George, M.; Suo, Z. Stretchable, Transparent, Ionic Conductors. Science 2013, 341, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Paper-Structure Inspired Multiresponsive Hydrogels with Solvent-Induced Reversible Information Recording, Self-Encryption, and Multidecryption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Feng, X.; Zhang, C.; Kang, J.; Qi, H. Highly Strong and Transparent Ionic Conductive Hydrogel as Multifunctional Sensors. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wan, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Dai, Z.; Ji, K.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Long, Y. Highly Stretchable, Elastic, and Ionic Conductive Hydrogel for Artificial Soft Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Han, L.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Pan, L.; Xu, M. Multiple Stimuli Responsive and Identifiable Zwitterionic Ionic Conductive Hydrogel for Bionic Electronic Skin. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Sheng, N.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Liang, Q.; Wang, H. Anisotropic bacterial cellulose hydrogels with tunable high mechanical performances, non-swelling and bionic nanofluidic ion transmission behavior. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8126–8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Briffa, S.M.; Swingler, S.; Gibson, H.; Kannappan, V.; Adamus, G.; Kowalczuk, M.; Martin, C.; Radecka, I. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Curcumin-Cyclodextrins Loaded into Bacterial Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing Applications. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Jin, Z. Tough, Swelling-Resistant, Self-Healing, and Adhesive Dual-Cross-Linked Hydrogels Based on Polymer–Tannic Acid Multiple Hydrogen Bonds. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Wang, M.; Meng, L.; Chang, H.; Wang, B.; Xu, F.; Yang, J.; Wan, P. Mussel-Inspired Cellulose Nanocomposite Tough Hydrogels with Synergistic Self-Healing, Adhesive, and Strain-Sensitive Properties. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3110–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Rehman, H.U.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Ionic Conductive Organohydrogels with Dynamic Pattern Behavior and Multi-Environmental Stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, C. Strong, tough, ionic conductive, and freezing-tolerant all-natural hydrogel enabled by cellulose-bentonite coordination interactions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, P.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, C.; Gao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Zwitterionic Osmolyte-Based Hydrogels with Antifreezing Property, High Conductivity, and Stable Flexibility at Subzero Temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, K.; Gao, H.; Wu, H.; Cao, S.; Huang, L.; Ni, Y. Anti-freezing and moisturizing conductive hydrogels for strain sensing and moist-electric generation applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 3109–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelle, X.P.; Illeperuma, W.R.; Tian, K.; Bai, R.; Suo, Z.; Vlassak, J.J. Highly Stretchable and Tough Hydrogels below Water Freezing Temperature. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H. Mechanisms and applications of bioinspired underwater/wet adhesives. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 2911–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord Forooshani, P.; Lee, B.P. Recent approaches in designing bioadhesive materials inspired by mussel adhesive protein. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H. Conductive nerve guide conduits based on wet-adhesive hydrogel to accelerate peripheral nerve repair. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 27, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, H.; Li, H. Multiple-Stimuli-Responsive and Cellulose Conductive Ionic Hydrogel for Smart Wearable Devices and Thermal Actuators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gu, S.; Jia, F.; Wang, Q.; Gao, G. “All-in-one” hydrolyzed keratin protein-modified polyacrylamide composite hydrogel transducer. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Xiang, L.; Ou, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Hao, L.; Diao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, P.; et al. MXene-based conductive organohydrogels with Long-Term Environmental Stability and Multifunctionality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, L. Skin-inspired cellulose conductive hydrogels with integrated self-healing, strain, and thermal sensitive performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, L. Preparation of High-Performance Ionogels with Excellent Transparency, Good Mechanical Strength, and High Conductivity. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1704253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Wu, B.; Le, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T. Antifreezing and Stretchable Organohydrogels as Soft Actuators. Research 2019, 2019, 2384347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Shi, L.; Lu, S.; Zhu, T.; Da, X.; Li, Y.; Bu, H.; Gao, G.; Ding, S. Highly Stretchable Organogel Ionic Conductors with Extreme-Temperature Tolerance. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 3257–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, C.; Lin, X.; Zheng, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, C. Dual Conductive Network Hydrogel for a Highly Conductive, Self-Healing, Anti-Freezing, and Non-Drying Strain Sensor. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbinghaus, S.; Meister, K.; Born, B.; DeVries, A.L.; Gruebele, M.; Havenith, M. Antifreeze Glycoprotein Activity Correlates with Long-Range Protein−Water Dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12210–12211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H.; Tanzer, M.L. Polyphenolic Substance of Mytilus edulis: Novel Adhesive Containing L-Dopa and Hydroxyproline. Science 1981, 212, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Liu, H. High Multi-Environmental Mechanical Stability and Adhesive Transparent Ionic Conductive Hydrogels Used as Smart Wearable Devices. Polymers 2022, 14, 5316. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235316
Wu Y, Liu J, Chen Z, Chen Y, Chen W, Li H, Liu H. High Multi-Environmental Mechanical Stability and Adhesive Transparent Ionic Conductive Hydrogels Used as Smart Wearable Devices. Polymers. 2022; 14(23):5316. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235316
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuxuan, Jing Liu, Zhen Chen, Yujie Chen, Wenzheng Chen, Hua Li, and Hezhou Liu. 2022. "High Multi-Environmental Mechanical Stability and Adhesive Transparent Ionic Conductive Hydrogels Used as Smart Wearable Devices" Polymers 14, no. 23: 5316. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235316
APA StyleWu, Y., Liu, J., Chen, Z., Chen, Y., Chen, W., Li, H., & Liu, H. (2022). High Multi-Environmental Mechanical Stability and Adhesive Transparent Ionic Conductive Hydrogels Used as Smart Wearable Devices. Polymers, 14(23), 5316. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235316








