Removal of Cationic Dyes by Iron Modified Silica/Polyurethane Composite: Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Analyses, and Regeneration via Advanced Oxidation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Iron Modified Silica/Polyurethane (FMS/PU) Composite
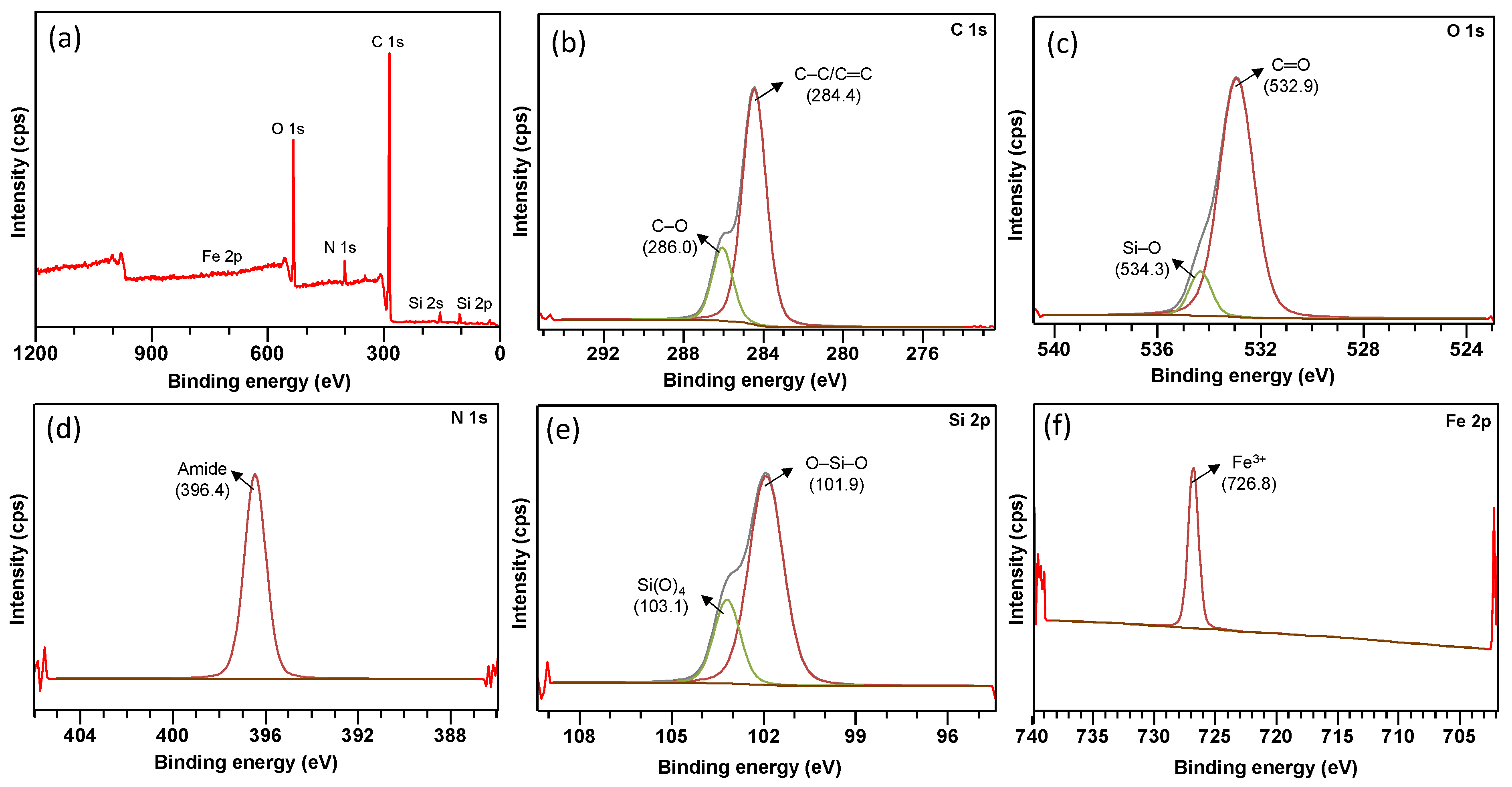
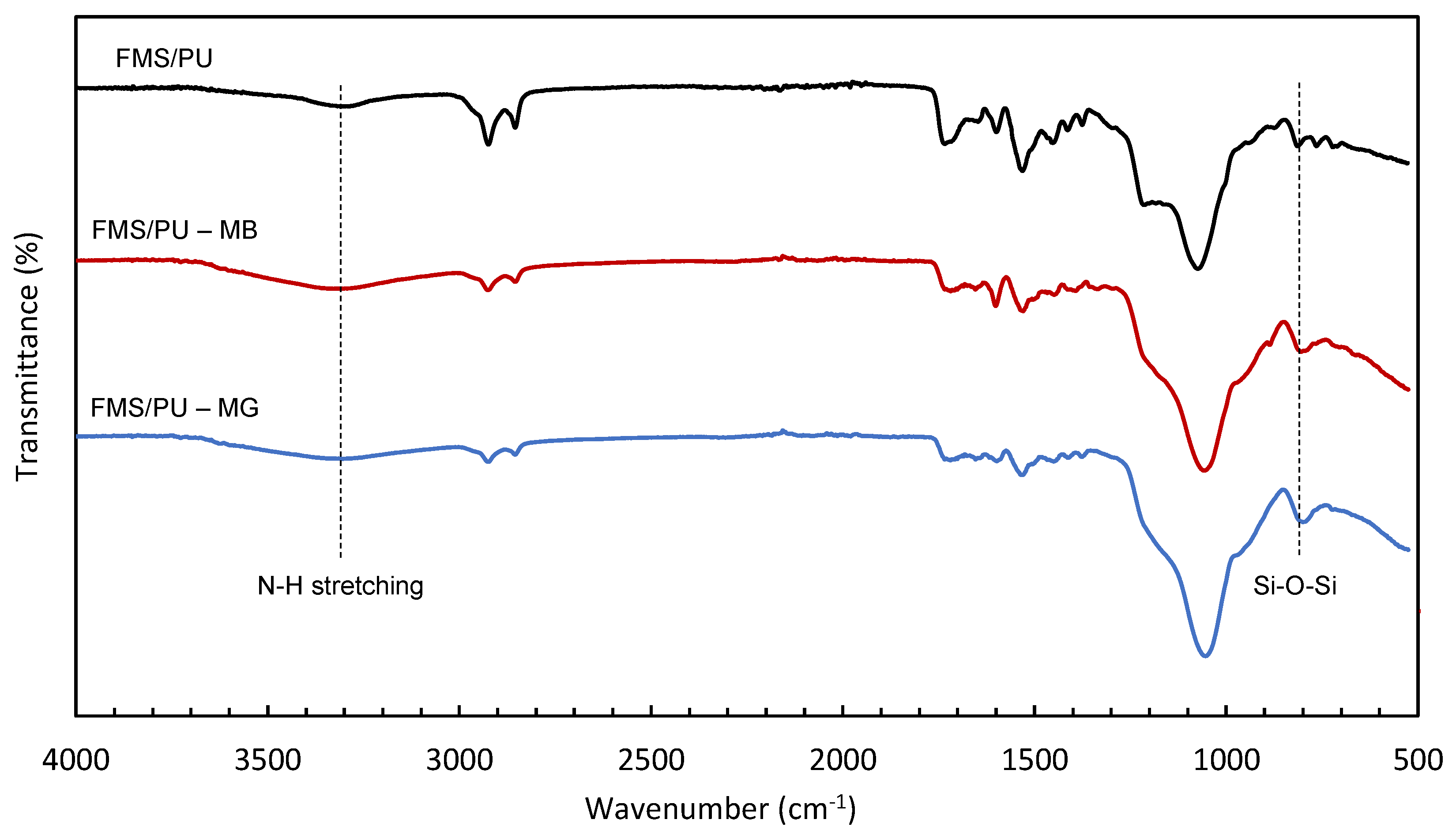
2.3. Characterisation of FMS/PU Composite
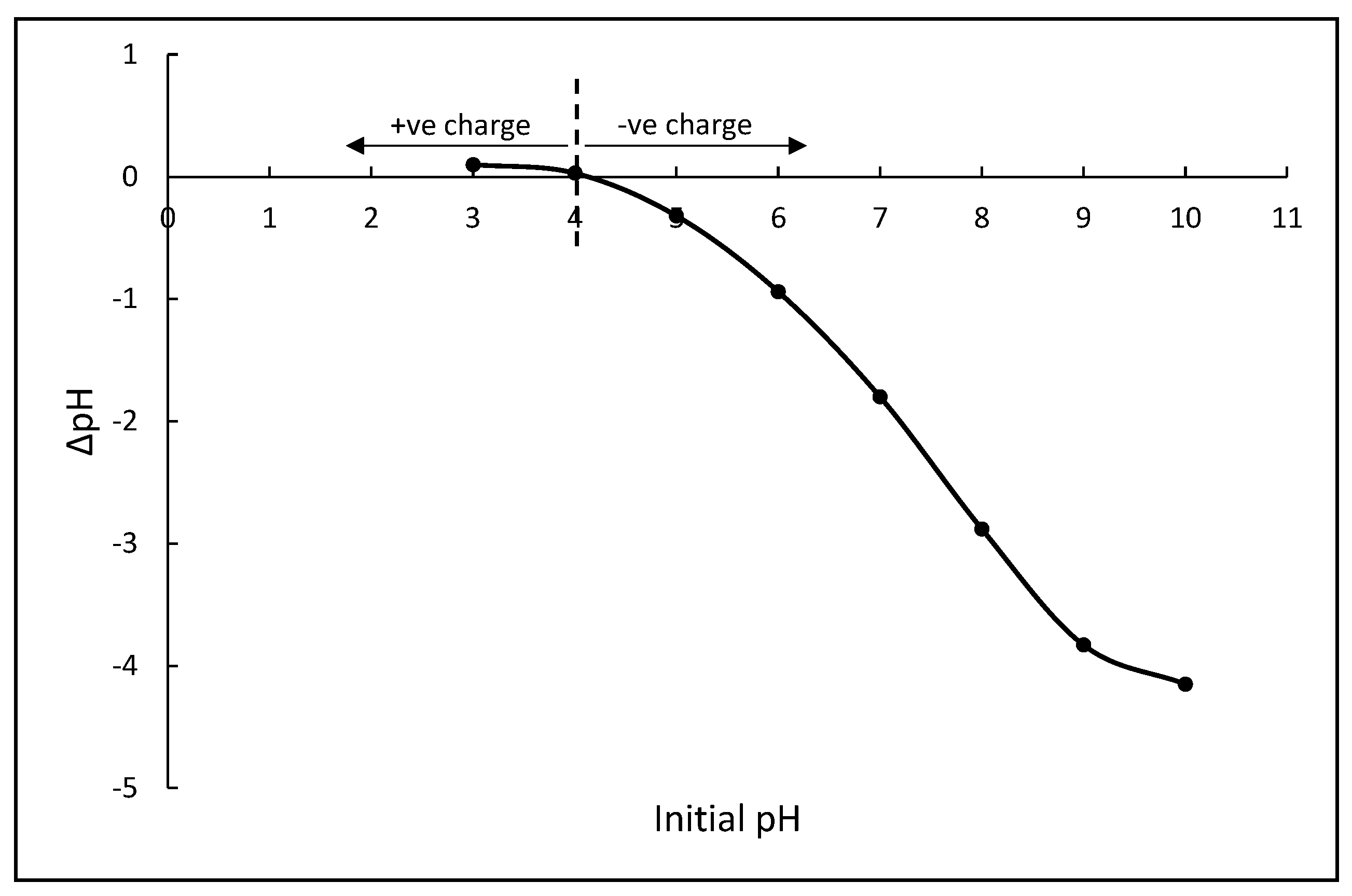
2.4. Point of Zero Charge (PZC)
2.5. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.6. Regeneration of FMS/PU
3. Results and Discussions
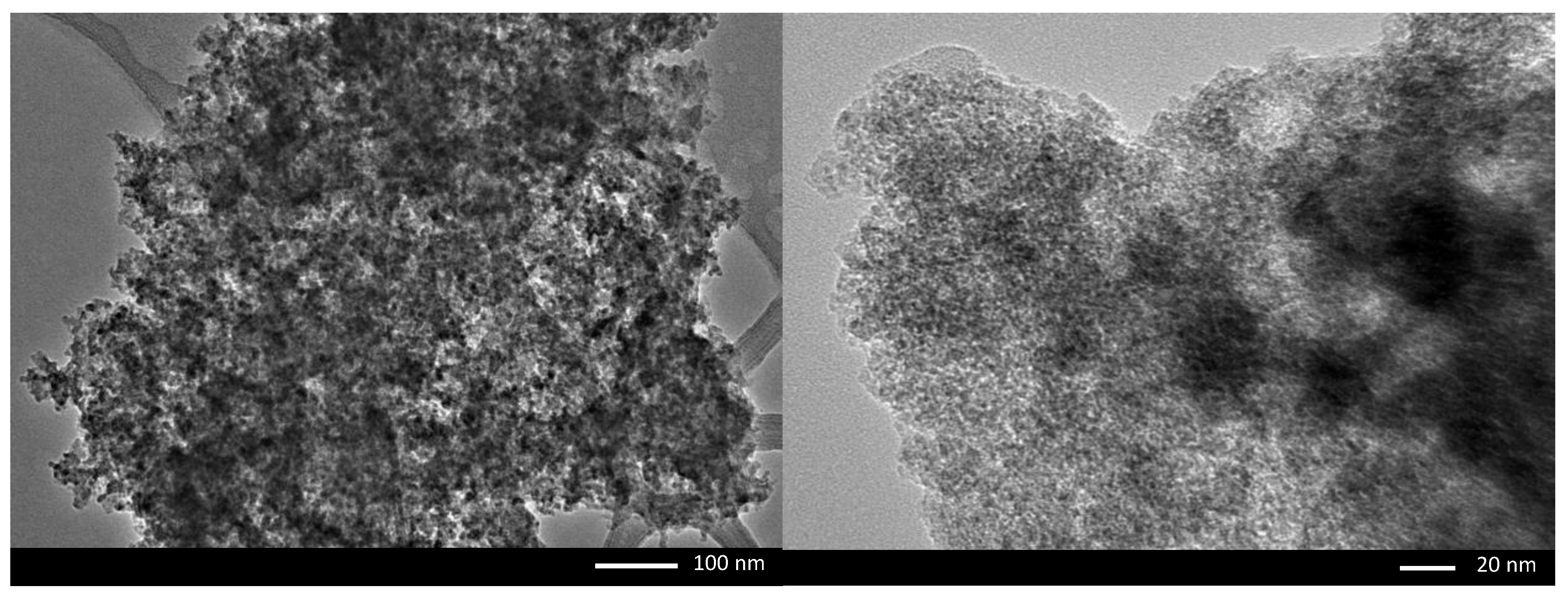
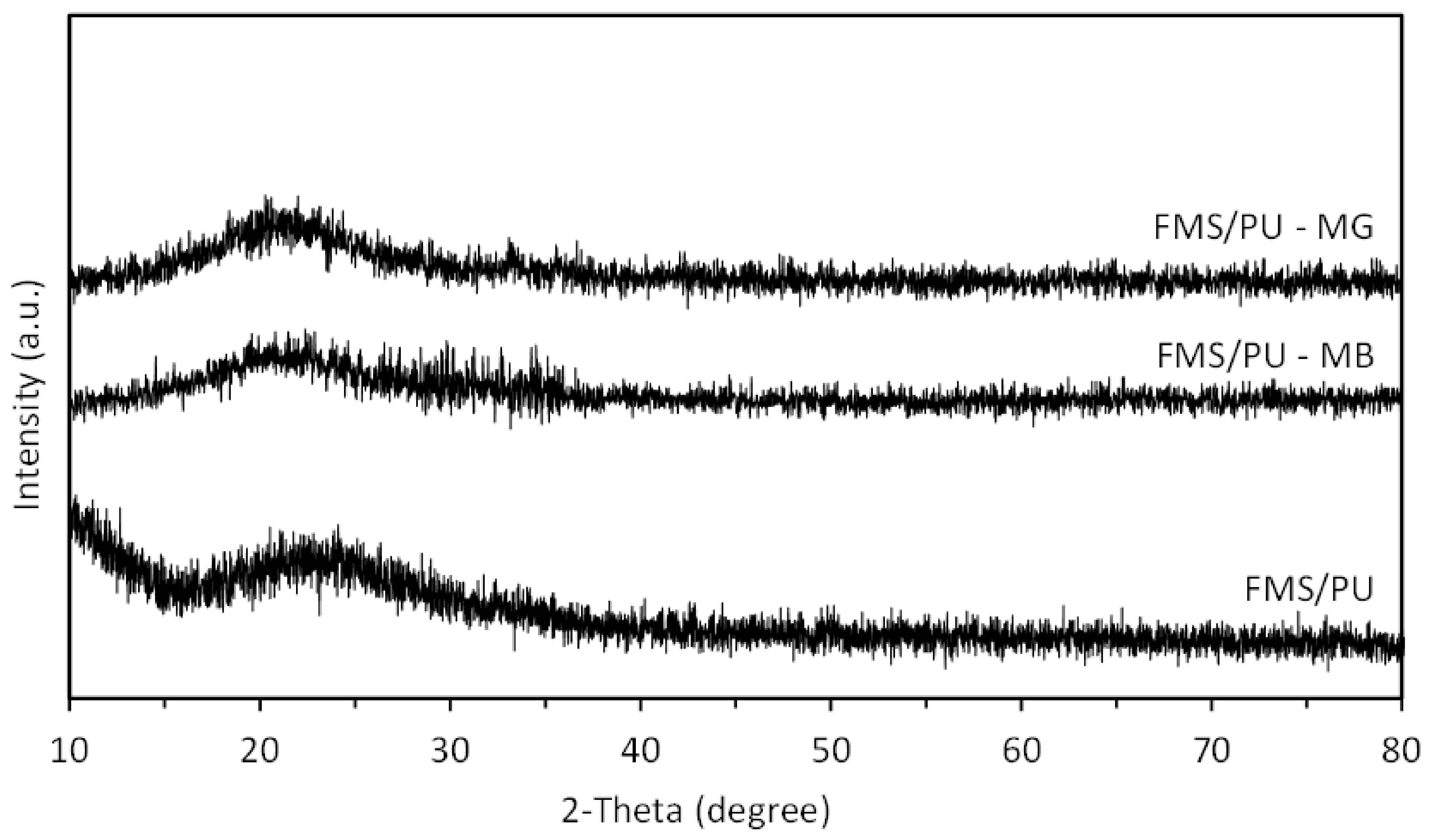
3.1. Characterisation of FMS/PU Composite Adsorbent
3.2. Batch Adsorption
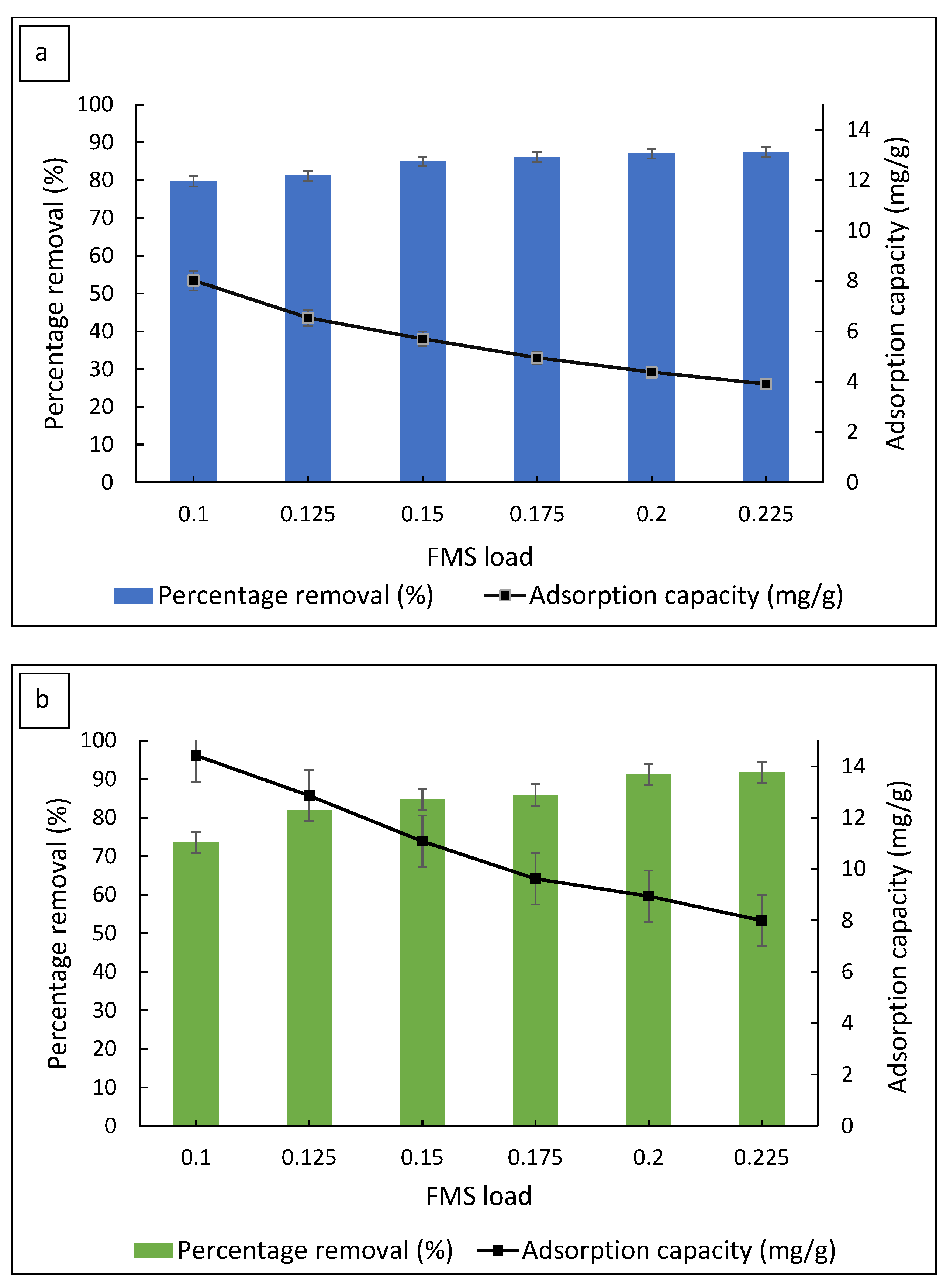
3.2.1. Effect of Adsorbent Load
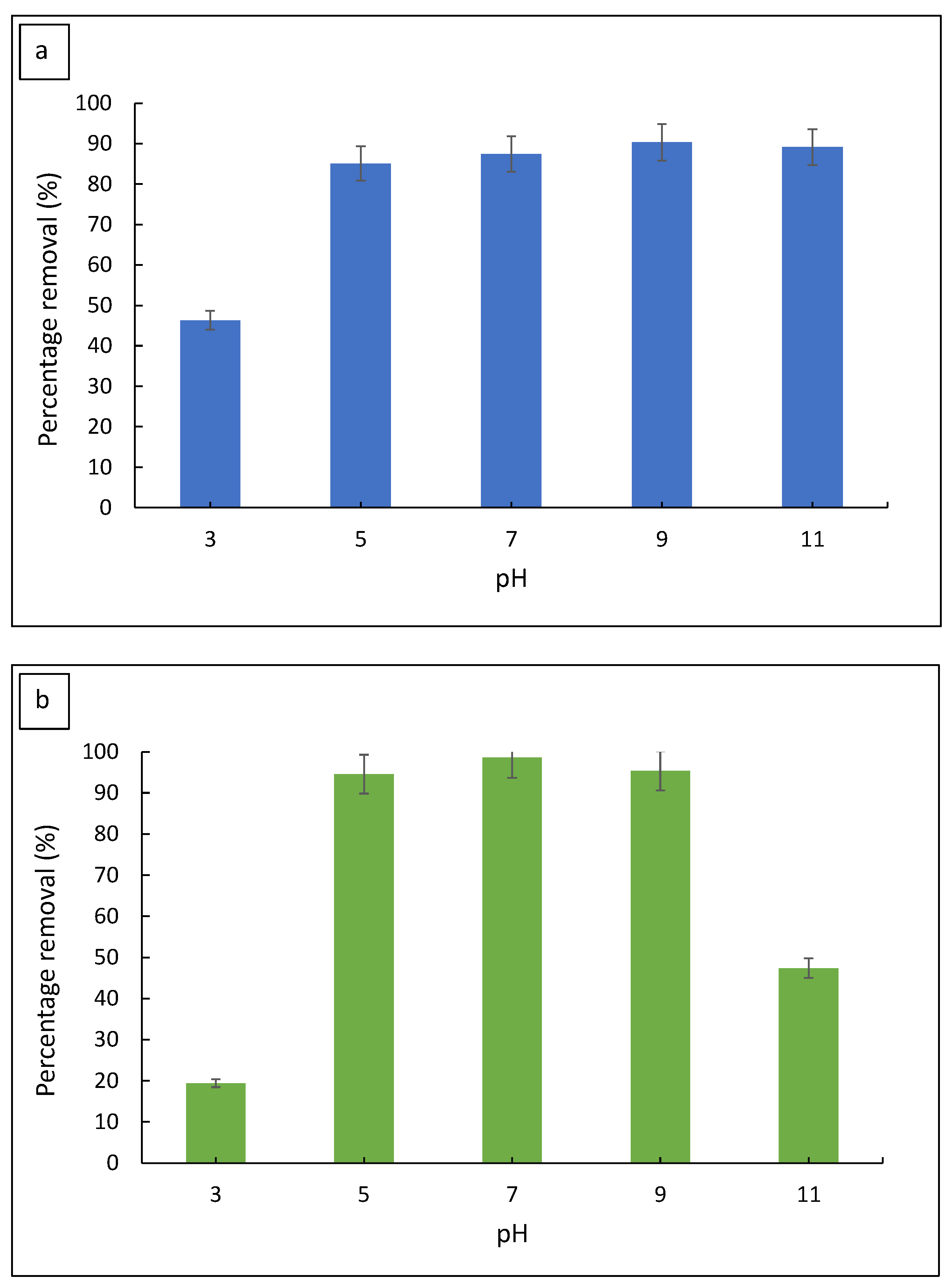
3.2.2. Effect of Initial pH
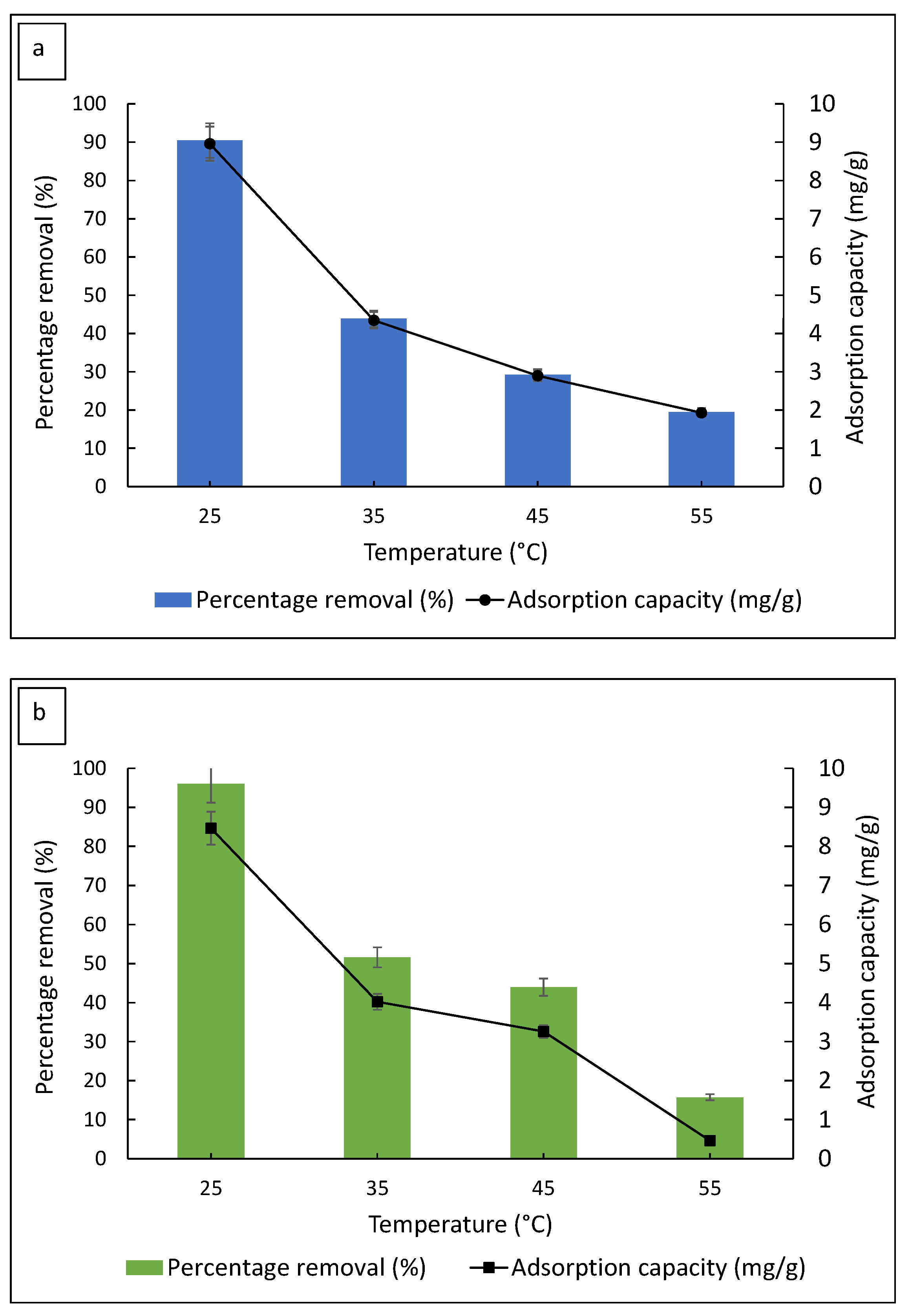
3.2.3. Effect of Solution Temperature
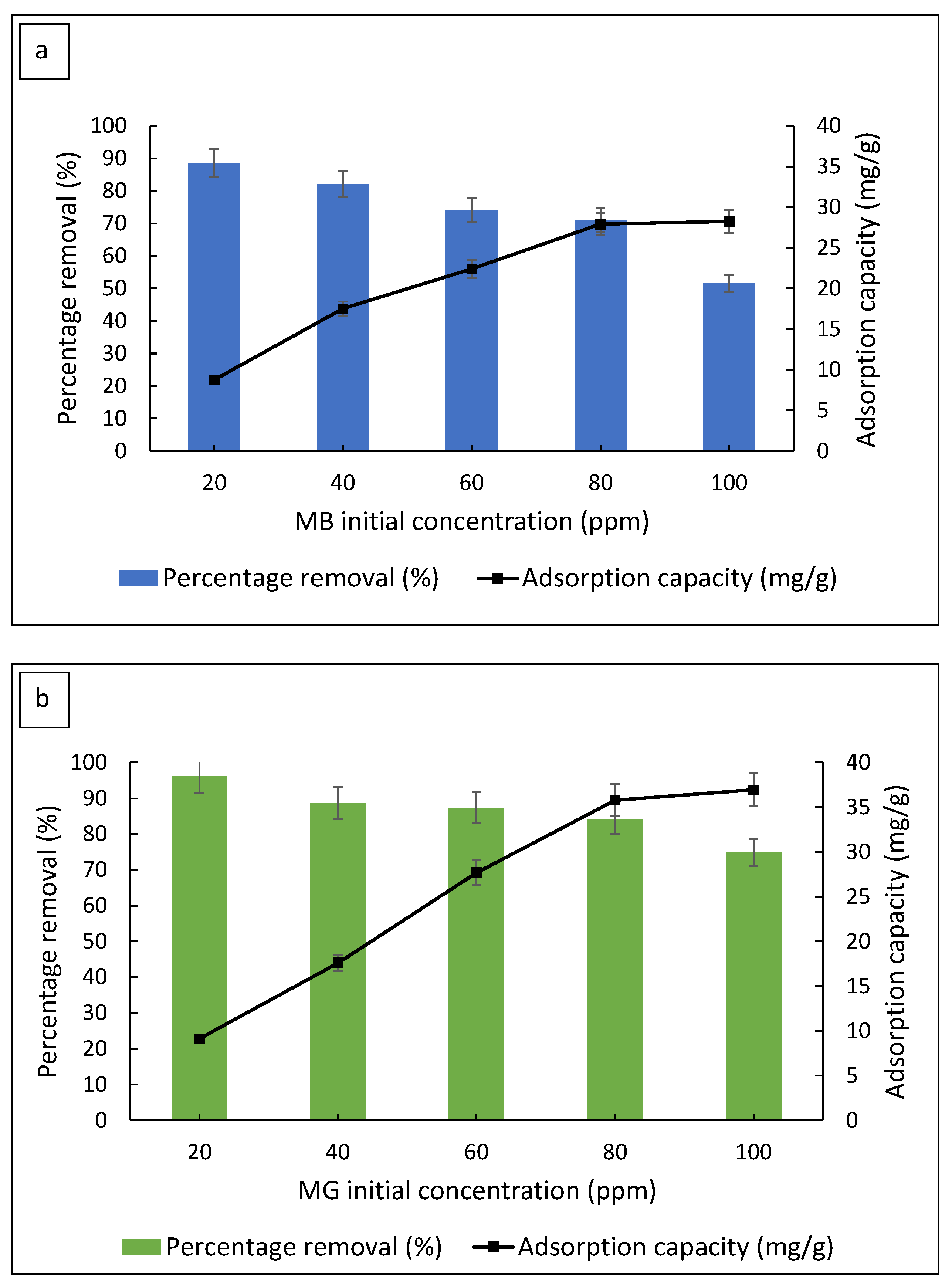
3.2.4. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
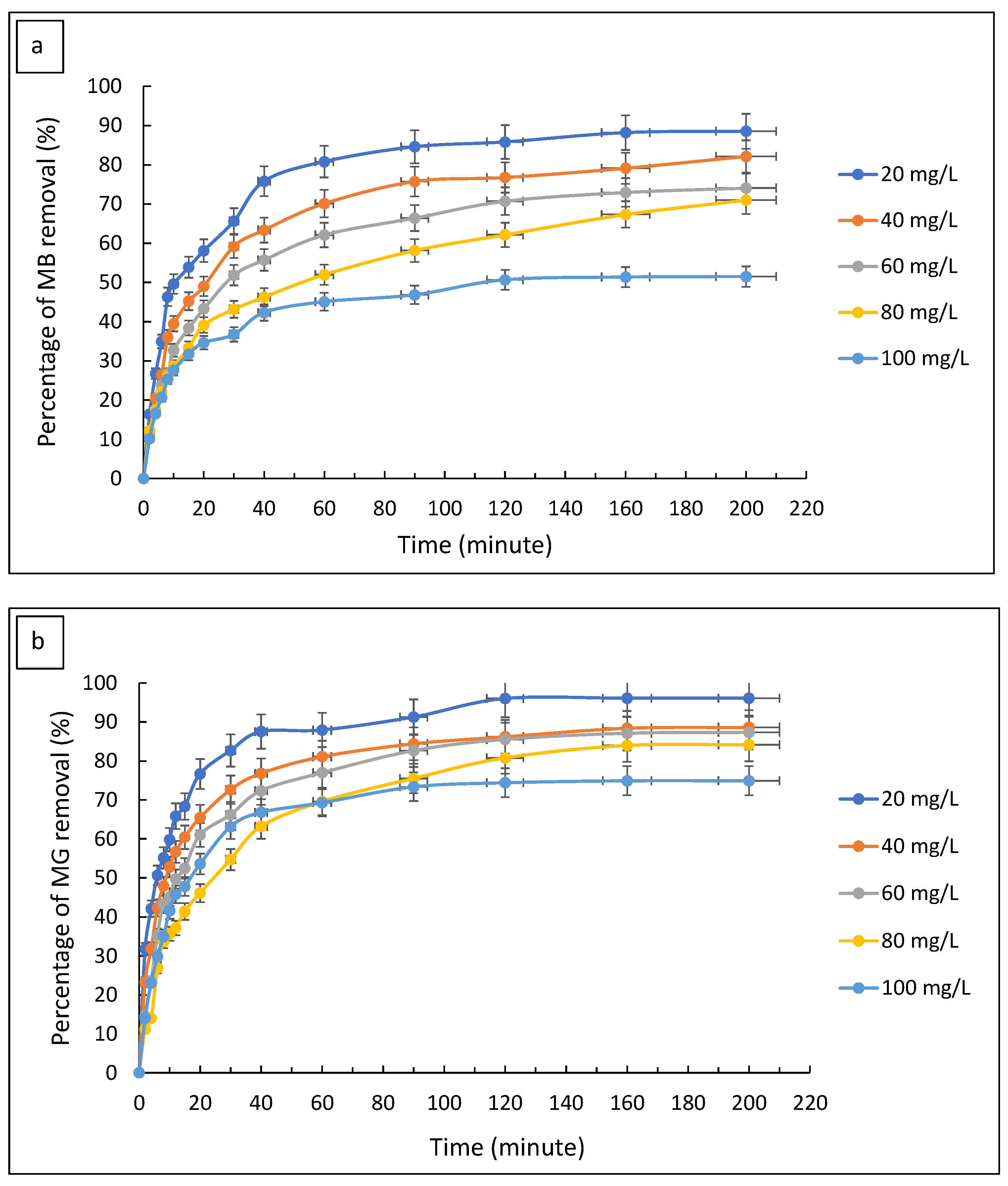
3.2.5. Effect of Contact Time
3.3. Kinetic Studies
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Thermodynamic Studies
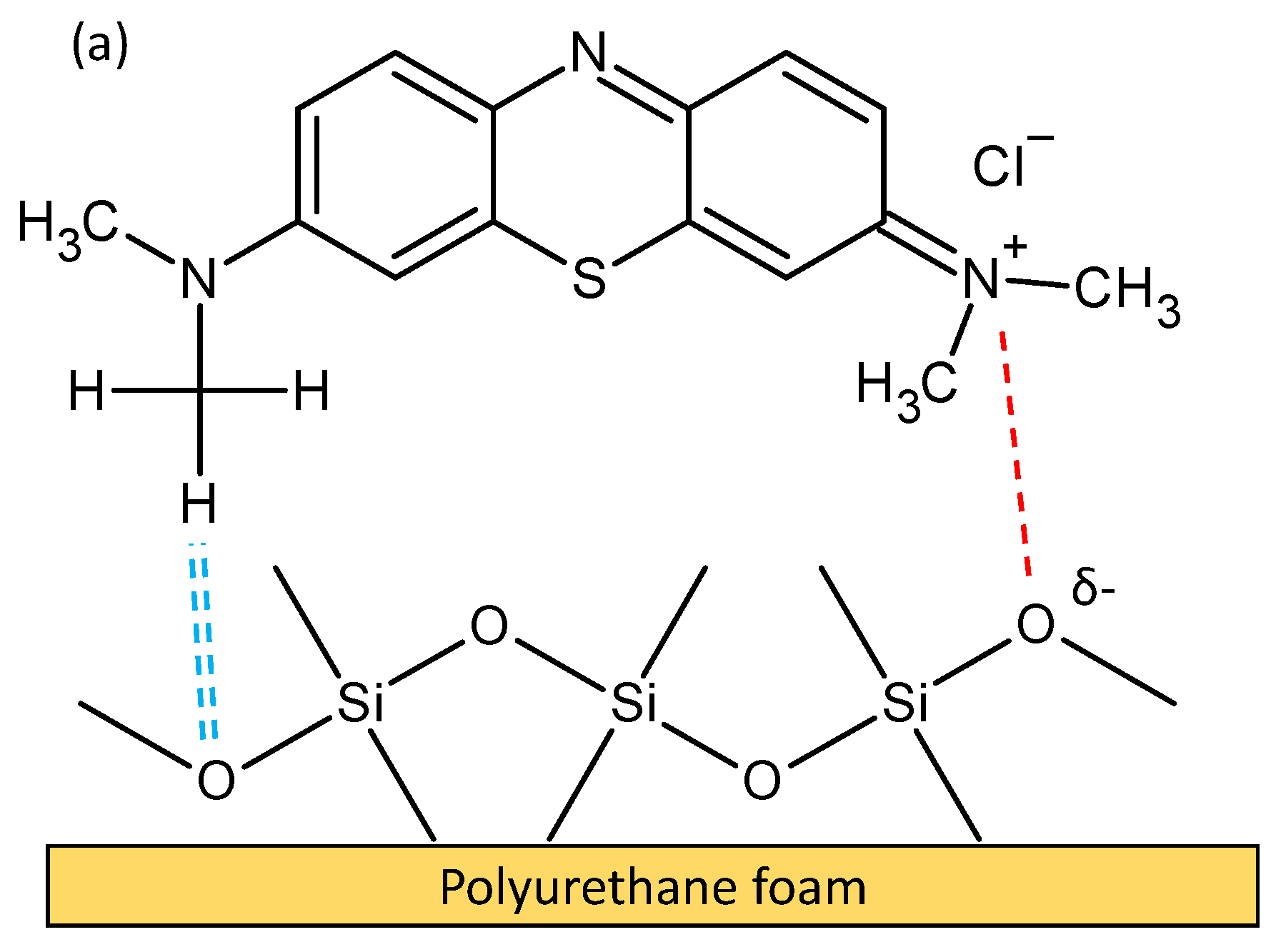
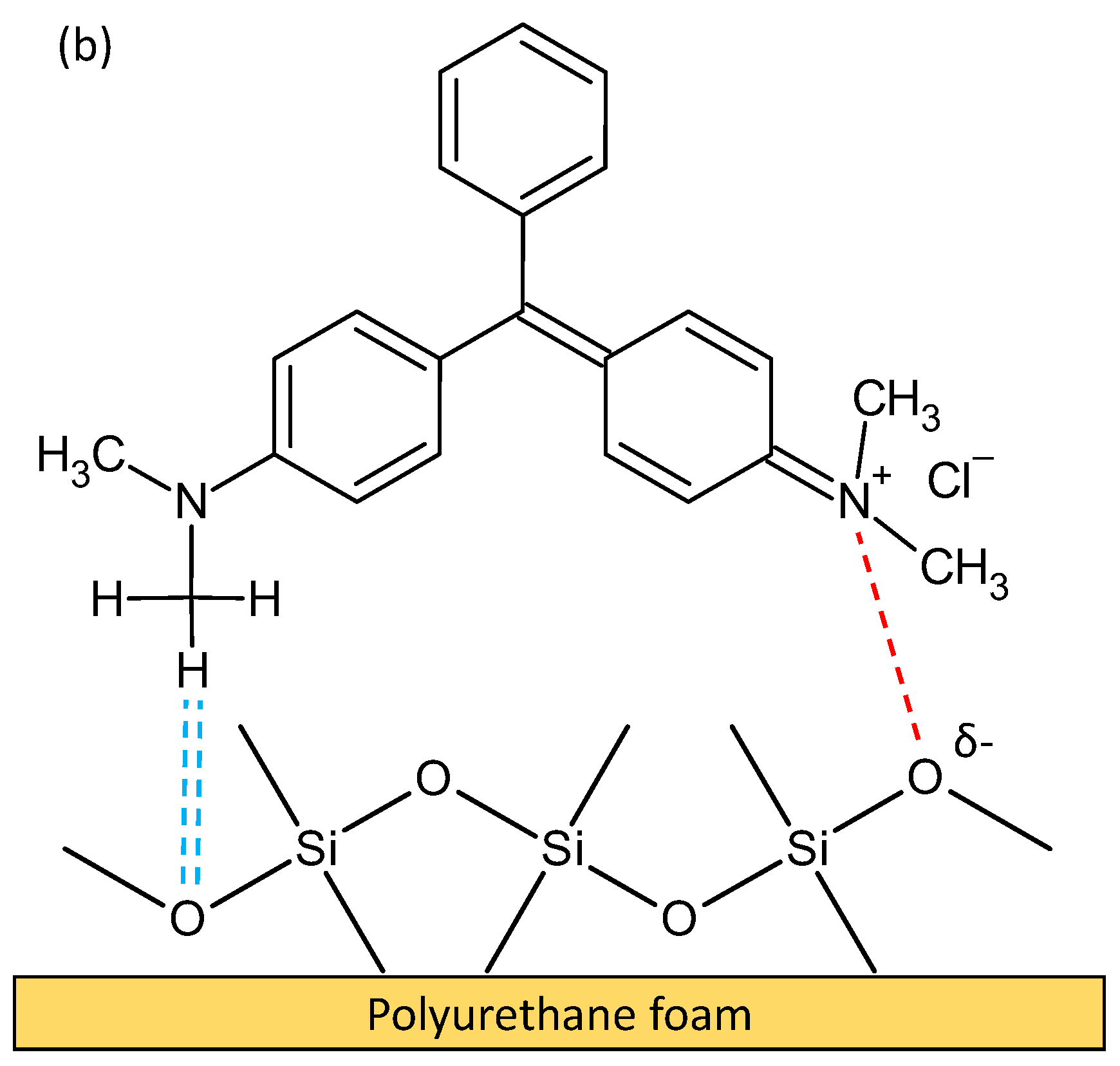
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism
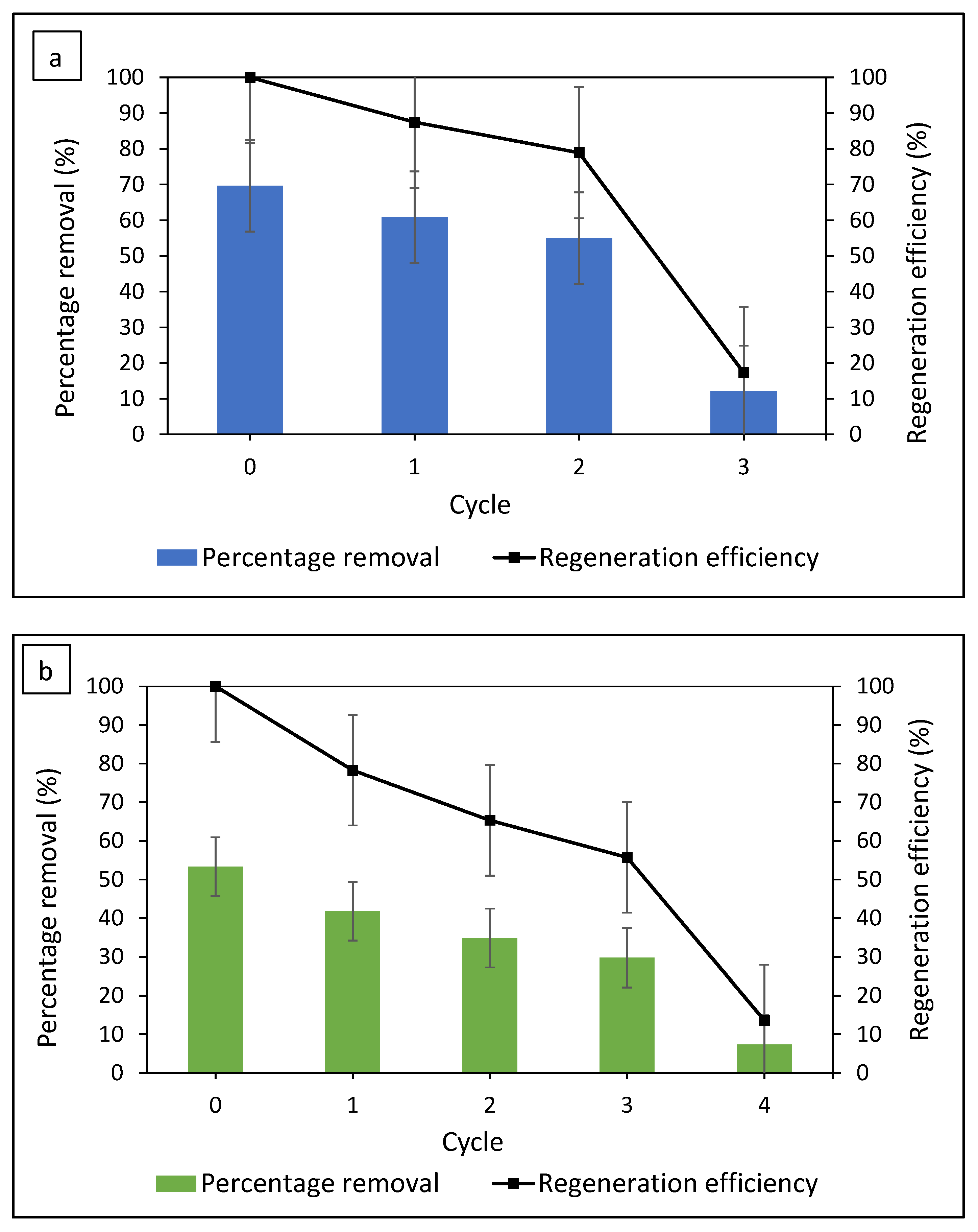
3.7. Regeneration of Adsorbent
3.8. Future Direction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ginimuge, P.R.; Jyothi, S.D. Methylene blue: Revisited. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 26, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Q.; Nie, S. High-performance liquid chromatography for food quality evaluation. In Evaluation Technologies for Food Quality; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B. Removal of dyes and industrial dye wastes by magnesium chloride. Water Res. 2000, 34, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Ramachandran, M. Adsorptive removal of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by surfactant modified bentonite clay (organoclay): Kinetic and competitive adsorption isotherm. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 95, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessier, A.P. Chytridiomycosis. In Current Therapy in Reptile Medicine and Surgery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfac-tant Modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, R.; Arivoli, S. Thermodynamic and Isotherm Analysis on the Removal of Malachite Green Dye Using Thespesia Populnea Bark. J. Chem. 2012, 9, 629089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, S.; Ali, N.; Ali, Z.; Bilal, M.; Adalat, B.; Hussain, S.; Gul, S.; Ali, F.; Khan, S.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; et al. Silica-based nanomaterials as designer adsorbents to mitigate emerging organic contaminants from water matrices. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarezadeh-Mehrizi, M.; Badiei, A.; Mehrabadi, A.R. Ionic liquid functionalized nanoporous silica for removal of anionic dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 180, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, H.S.; Kumari, S.; Chauhan, G.S.; Reddy, N.S.; Ahn, J.-H. Silica-polymer hybrid materials as methylene blue adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak, M.; Mohamed, E.A.; Selim, A.Q.; Eissa, M.F.; Seliem, M.K. Experimental results and theoreti-cal statistical modeling of malachite green adsorption onto MCM–41 silica/rice husk composite modified by beta radiation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirak, M.; Abdollahiyan, A.; Eftekhari-Sis, B.; Saraei, M. Carboxymethyl cellulose coated Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanoparticles for methylene blue removal: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Cellulose 2018, 25, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Raman, A.A.A.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Advanced oxidation processes for in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide/hydroxyl radical for textile wastewater treatment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H. Iron modified bentonite: Enhanced adsorption performance for organic pollutant and its regeneration by heterogeneous visible light photo-Fenton process at circumneutral pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, E.; Anasie, D.; Pazos, M.; Lazar, I.; Sanromán, M.A. Kaolinite adsorption-regeneration system for dyestuff treatment by Fenton based processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Wang, W.; Li, T.; Cui, Y.; Wang, B.; Yu, G.; Wang, X.; Wei, D.; Xiao, J.; Deng, S. Powdered activated coke for COD removal in the advanced treatment of mixed chemical wastewaters and regeneration by Fenton oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneš, H.; Vlčková, V.; Paruzel, A.; Trhlíková, O.; Chalupa, J.; Kanizsová, L.; Skleničková, K.; Halecký, M. Multifunctional and fully aliphatic biodegradable polyurethane foam as porous biomass carrier for biofiltration. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 176, 109156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandip, M.; Kalyanraman, V. Enhanced simultaneous nitri-denitrification in aerobic moving bed biofilm reactor containing polyurethane foam-based carrier media. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, L.; Kelber, J.; Jierry, L.; Ritleng, V.; Edouard, D. Polydopamine-coated open cell polyurethane foam as an efficient and easy-to-regenerate soft structured catalytic support (S2CS) for the reduction of dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, S.A.; Baghdadi, M.; Abdoli, M.A. Immobilization of polyaniline nanoparticles on the polyurethane foam derived from waste materials: A porous reactive fixed-bed medium for removal of mercury from contaminated waters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6612–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Shean Yaw Choong, T.; Abdullah, A.H.; Mastuli, M.S.; Othman, N.; Jiman, N. Green Flexible Polyurethane Foam as a Potent Support for Fe-Si Adsorbent. Polymers 2019, 11, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, S.; Piccaluga, G.; Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J. Sol-gel formation of γ-Fe2O3/SiO2 nanocomposites. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 2805–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, J.V.; Guedes, M.S.; Prado, R.G.; Tronto, J.; Ardisson, J.D.; Pereira, M.C.; Oliveira, L.C. Effect of iron precursor on the Fenton-like activity of Fe2O3/mesoporous silica catalysts prepared under mild conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.L.-T.; Lee, C.; Doyle, F.M.; Sedlak, D.L. A Silica-Supported Iron Oxide Catalyst Capable of Activating Hydrogen Peroxide at Neutral pH Values. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8930–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Zhou, Y.; He, M.; Xu, R.; Ding, B.; Zhong, X.; Huang, Y. Enhanced mechanical properties of silica nanoparticle-covered cross-linking graphene oxide filled thermoplastic polyurethane composite. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, N.; Cao, J.; Xiong, J. Preparation of electrospun polyurethane/hydrophobic silica gel nanofibrous membranes for waterproof and breathable application. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, X.; Xing, Z.; Mou, S.; Li, C.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Greatly Improving Electrochemical N2 Reduction over TiO2 Nanoparticles by Iron Doping. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18449–18453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhtiyarova, G.A.; Bukhtiyarov, V.I.; Sakaeva, N.S.; Kaichev, V.V.; Zolotovskii, B.P. XPS study of the silica-supported Fe-containing catalysts for deep or partial H2S oxidation. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2000, 158, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, S.J.; Beland, F.A. Malachite Green: A Toxicological Review. J. Am. Coll. Toxicol. 1996, 15, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, H.R.; Silva, L.S.; Sousa, P.A.A.; Sousa, R.R.M.; Fonseca, M.G.; Osajima, J.A.; Silva-Filho, E.C. Evaluation of methylene blue removal by plasma activated palygorskites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5432–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.R.; Santiano, B.; Kim, H.; Kan, E. Heterogeneous Oxidation of Methylene Blue with Surface-Modified Iron-Amended Activated Carbon. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 4, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.M.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Moradi, M.; Taghavi, M.; Karimyan, K. Application of Box–Behnken Design for Optimization of Malachite Green Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Modified Barley Straw. Glob. NEST J. 2020, 22, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaqi, Z.; Yimin, D.; Danyang, L.; Shengyun, W.; Liling, Z.; Yi, Z. Synthesis of carboxyl-functionalized magnetic nanoparticle for the removal of methylene blue. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 572, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muinde, V.M.; Onyari, J.M.; Wamalwa, B.; Wabomba, J.N. Adsorption of malachite green dye from aqueous solutions using mesoporous chitosan–zinc oxide composite material. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Douma, M.; Tijani, N.; Dehmani, Y.; Messaoudi, L. Adsorption process of the malachite green onto clay: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 240, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, E.C.; Slaviero, J.C.; Cunha, A.M.; Hosseini–Bandegharaei, A.; Dotto, G.L. Microwave synthesis of silica nanoparticles and its application for methylene blue adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beagan, A.M. Investigating Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solution by Cysteine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 8839864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajapara, S.J.; Patel, S.J.; Bhasin, C.P. Efficient Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Malachite Green Dye Using Bentonite Natural Adsorbent. Int. J. Nanomater. Chem. 2017, 3, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.A.; Bhatti, H.N.; Hussain, I.; Bhatti, I.A.; Asghar, M. Sol–Gel Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica–Iron Composite: Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamics Studies for the Adsorption of Turquoise-Blue X-GB Dye. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 2020, 234, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, F.; Turkyilmaz, M.; Kucukcongar, S. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by silica gel supported calix[4]arene cage: Investigation of adsorption properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 125, 109540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A. Synthesis of zeolite nanostructures from waste aluminum cans for efficient removal of malachite green dye from aqueous media. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 253, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Al-Ruwayshid, S.H.; Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles grafted with copolymer of acrylic acrylamide for ultra-removal of methylene blue from aquatic solutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 130, 109698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Hong, W.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Duan, X. A novel mesoporous Fe-silica aerogel composite with phenomenal adsorption capacity for malachite green. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, K.U.; Singh, R.; Baruah, I.; Choudhury, H.; Sharma, M.R. Equilibrium and kinetics modeling of fluoride adsorption onto activated alumina, alum and brick powder. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selçuk, N.Ç. Kinetics and Thermodynamic Studies of Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions onto Paliurus spina-christi Mill. Frutis and Seeds. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 10, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyi, A.A.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Abdullah, L.C.; Choong, T.S.Y.; Lau, K.L.; Abdullah, M. Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue from Aquatic Environments Using Thiourea-Modified Poly(Acrylonitrile-co-Acrylic Acid). Materials 2019, 12, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pholosi, A.; Naidoo, E.B.; Ofomaja, A.E. Intraparticle diffusion of Cr(VI) through biomass and magnetite coated biomass: A comparative kinetic and diffusion study. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 32, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyi, A.A.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Abdullah, L.C.; Choong, T.S.Y. Adsorption of Malachite Green Dye from Liquid Phase Using Hydrophilic Thiourea-Modified Poly(acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid): Kinetic and Isotherm Studies. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-P.; Fu, S.-Y.; Du, Y.-M.; Guo, J.-Z.; Li, B. Adsorption of methylene blue and malachite green from aqueous solution by sulfonic acid group modified MIL-101. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 237, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H. Dye adsorption on unburned carbon: Kinetics and equilibrium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 126, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Hayati, B.; Arami, M. Textile Dye Removal from Single and Ternary Systems Using Date Stones: Kinetic, Isotherm, and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4638–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonappan, L.; Rouissi, T.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. An insight into the adsorption of diclofenac on different biochars: Mechanisms, surface chemistry, and thermodynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhao, E.; Kim, T.; Wang, J.; Hableel, G.; Reardon, P.J.T.; Ananthakrishna, S.J.; WANG, T.; Arconada-Alvarez, S.; Knowles, J.C.; et al. Organosilica Nanoparticles with an Intrinsic Secondary Amine: An Efficient and Reusable Adsorbent for Dyes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15566–15576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Hayati, B.; Bahrami, H.; Arami, M. Dye adsorption and desorption properties of Mentha pulegium in single and binary systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hartono, S.B.; Jin, Y.G.; Li, Z.; (Max) Lu, G.Q.; Qiao, S.Z. A facile vesicle template route to multi-shelled mesoporous silica hollow nanospheres. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Tang, Z.; Liu, P. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with silica nano-sheets derived from vermiculite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimin, D.; Jiaqi, Z.; Danyang, L.; Lanli, N.; Liling, Z.; Yi, Z.; Xiaohong, Z. Preparation of Congo red functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticle and its application for the removal of methylene blue. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 550, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Uthappa, U.T.; Kigga, M.; Jung, H.-Y.; Altalhi, T.; Kurkuri, M.D. Xerogel activated diatom as an effective hybrid adsorbent for the efficient removal of malachite green. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3810–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, J. Adsorption of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using hydrophilic silica aerogel via ambient pressure drying. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyzi, M.; Nourozi, L.; Shariati-Rad, M.; Abdi, F. Kinetic and equilibrium isotherms of removal malachite green from aqueous solution by using Fe3O4@SiO2-CPTS magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Nanochem. 2019, 1, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, J.; Shi, H.; Li, N.; Ping, Q. Adsorption of Malachite Green by Diatomite: Equilibrium Isotherms and Kinetic Studies. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kang, S.; Qin, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Self-assembled gels of Fe-chitosan/montmorillonite nanosheets: Dye degradation by the synergistic effect of adsorption and photo-Fenton reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, Q.U.; Rasheed, U.; Yaseen, M.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Z. Superior dye degradation and adsorption capability of polydopamine modified Fe3O4-pillared bentonite composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktar, J. Batch adsorption process in water treatment. In Intelligent Environmental Data Monitoring for Pollution Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.; Chandan, M.R.; Shanthakumar, S. Fixed bed column study for pesticide removal using silver nanoparticles-embedded polyurethane foam and glass beads. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 207, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

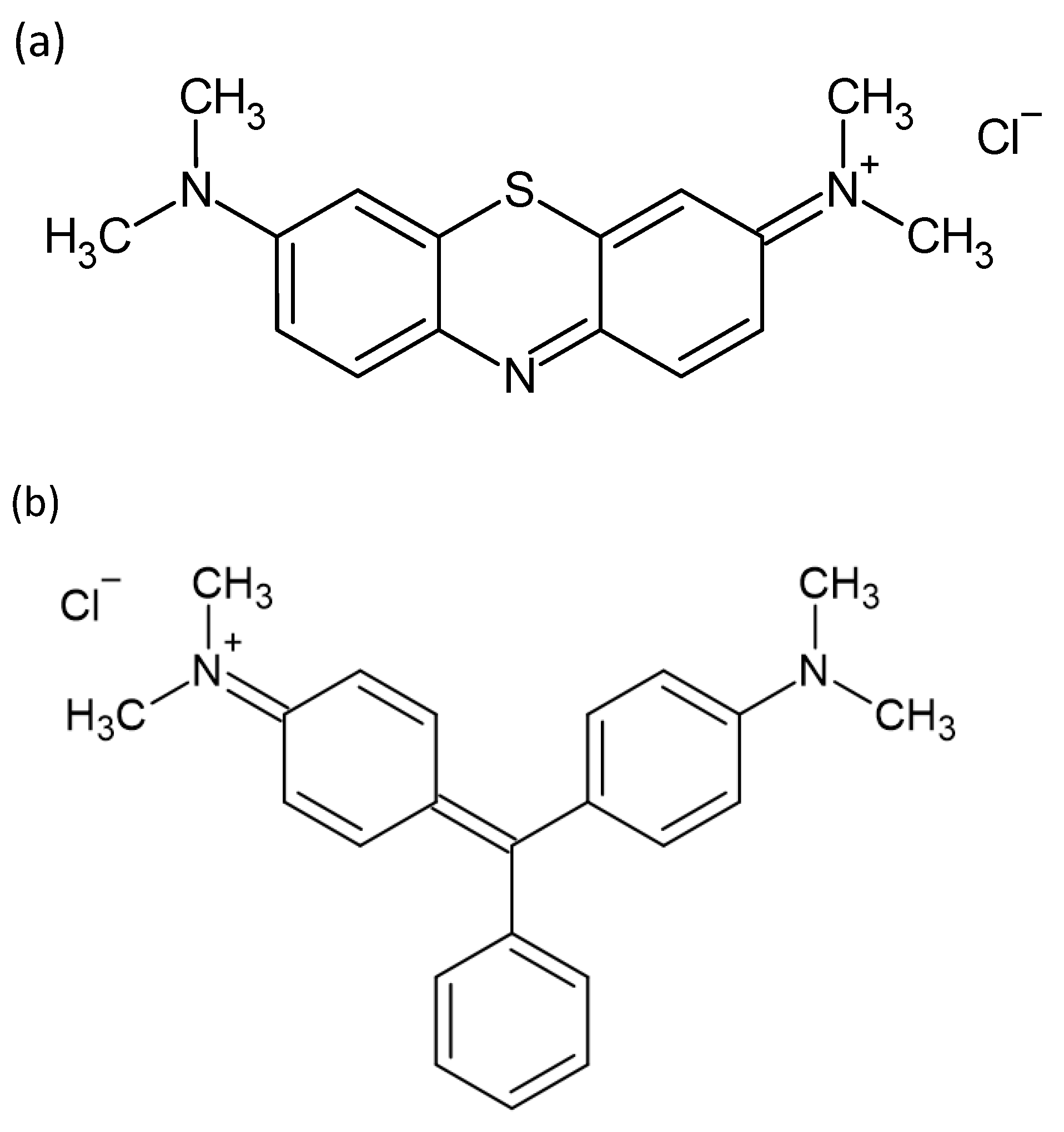
| Dye | MB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
| Pseudo First Order | |||||
| Qe experimental (mg/g) | 8.8 | 17.5 | 22.4 | 27.9 | 28.3 |
| Qe calculated (mg/g) | 6.3 | 14.1 | 18.0 | 19.7 | 21.8 |
| k1 | 0.0835 | 0.0835 | 0.0772 | 0.0778 | 0.0575 |
| R2 | 0.8953 | 0.9388 | 0.9634 | 0.8734 | 0.9371 |
| Pseudo Second Order | |||||
| Qe experimental (mg/g) | 8.8 | 17.5 | 22.4 | 27.9 | 28.3 |
| Qe calculated (mg/g) | 7.8 | 16.4 | 19.3 | 20.2 | 23.8 |
| k2 | 73.5 | 452.8 | 872.5 | 1297.0 | 2592.0 |
| R2 | 0.9859 | 0.9663 | 0.9834 | 0.9919 | 0.9949 |
| Elovich Kinetic Model | |||||
| α (mg/(g.min)) | 3.602 | 4.866 | 0.816 | 8.551 | 14.448 |
| β (g/mg) | 0.6799 | 0.3254 | 0.2548 | 0.2789 | 0.2276 |
| R2 | 0.9599 | 0.9390 | 0.9534 | 0.9353 | 0.9556 |
| Intraparticle Diffusion | |||||
| kIP (mg/(g.min1/2)) | 0.983 | 2.094 | 2.676 | 2.641 | 2.933 |
| CIP (mg/g) | 1.305 | 1.249 | 1.120 | 2.870 | 5.207 |
| R2 | 0.9641 | 0.9796 | 0.9956 | 0.9846 | 0.9571 |
| Dye | MG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
| Pseudo-First Order | |||||
| Qe experimental (mg/g) | 9.1 | 17.6 | 27.7 | 35.8 | 38.0 |
| Qe calculated (mg/g) | 5.8 | 11.7 | 20.7 | 29.9 | 28.9 |
| k1 | 0.1211 | 0.1054 | 0.0941 | 0.1229 | 0.0660 |
| R2 | 0.9671 | 0.9476 | 0.9317 | 0.9721 | 0.9348 |
| Pseudo-Second Order | |||||
| Qe experimental (mg/g) | 9.1 | 17.6 | 27.7 | 35.8 | 38.0 |
| Qe calculated (mg/g) | 8.8 | 16.4 | 26.1 | 29.0 | 39.4 |
| k2 | 166.8 | 936.7 | 2414.0 | 2909.1 | 7680.9 |
| R2 | 0.9956 | 0.9961 | 0.9827 | 0.9766 | 0.9846 |
| Elovich Kinetic Model | |||||
| α (mg/(g.min)) | 8.553 | 10.198 | 9.264 | 7.275 | 13.495 |
| β (g/mg) | 0.6768 | 0.3268 | 0.1935 | 0.1585 | 0.1324 |
| R2 | 0.9477 | 0.9765 | 0.9736 | 0.9889 | 0.9419 |
| Intraparticle Diffusion | |||||
| kIP (mg/(g.min1/2)) | 1.006 | 2.203 | 3.466 | 4.205 | 5.163 |
| CIP (mg/g) | 2.518 | 3.640 | 2.935 | 0.892 | 3.9256 |
| R2 | 0.9871 | 0.9856 | 0.9838 | 0.9870 | 0.9890 |
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | Separation Factor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dye | kL | Qmax | R2 | Qmax | kF | 1/n | R2 | RL |
| MB | 0.1761 | 31.7 | 0.9954 | 42.9 | 7.323 | 0.3838 | 0.9189 | 0.054–0.221 |
| MG | 0.4875 | 34.3 | 0.9439 | 76.1 | 10.49 | 0.4305 | 0.9591 | 0.020–0.093 |
| Adsorbent | Qmax (mg/g) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MB | FMS/PU composite | 31.7 | This work |
| Silica hollow nanosphere-3 | 25.5 | Liu et al. [55] | |
| Silica nanosheet | 12.6 | Zhao et al. [56] | |
| CMC Fe3O4@SiO2 MNP | 22.7 | Zirak et al. [12] | |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-CR | 31.4 | Yimin et al. [57] | |
| MG | FMS/PU composite | 34.3 | This work |
| Xerogel activated diatom (XDE) | 4.2 | Sriram et al. [58] | |
| Silica aerogel (HSA) | 6.7 | Liu et al. [59] | |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-CPTS | 12.5 | Feyzi et al. [60] | |
| Diatomite | 23.6 | Tian et al. [61] |
| Dye | Temperature (K) | Kd | Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J/mol K) | |||
| MB | 298 | 4.7194 | −2.55 | −95.43 | −311.69 |
| 308 | 0.3903 | 0.56 | |||
| 318 | 0.2068 | 3.68 | |||
| 328 | 0.1210 | 6.79 | |||
| MG | 298 | 12.0977 | −5.09 | −151.48 | −491.24 |
| 308 | 0.4189 | −0.18 | |||
| 318 | 0.2935 | 4.72 | |||
| 328 | 0.0277 | 9.63 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, A.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Choong, T.S.Y.; Abdullah, A.H.; Faujan, N.H.; Adeyi, A.A.; Daik, R.; Othman, N. Removal of Cationic Dyes by Iron Modified Silica/Polyurethane Composite: Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Analyses, and Regeneration via Advanced Oxidation Process. Polymers 2022, 14, 5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245416
Ahmad A, Jamil SNAM, Choong TSY, Abdullah AH, Faujan NH, Adeyi AA, Daik R, Othman N. Removal of Cationic Dyes by Iron Modified Silica/Polyurethane Composite: Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Analyses, and Regeneration via Advanced Oxidation Process. Polymers. 2022; 14(24):5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245416
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Afiqah, Siti Nurul Ain Md. Jamil, Thomas S. Y. Choong, Abdul Halim Abdullah, Nur Hana Faujan, Abel A. Adeyi, Rusli Daik, and Nurhanisah Othman. 2022. "Removal of Cationic Dyes by Iron Modified Silica/Polyurethane Composite: Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Analyses, and Regeneration via Advanced Oxidation Process" Polymers 14, no. 24: 5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245416
APA StyleAhmad, A., Jamil, S. N. A. M., Choong, T. S. Y., Abdullah, A. H., Faujan, N. H., Adeyi, A. A., Daik, R., & Othman, N. (2022). Removal of Cationic Dyes by Iron Modified Silica/Polyurethane Composite: Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Analyses, and Regeneration via Advanced Oxidation Process. Polymers, 14(24), 5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245416