Chitosan-Based Therapeutic Systems for Superficial Candidiasis Treatment. Synergetic Activity of Nystatin and Propolis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
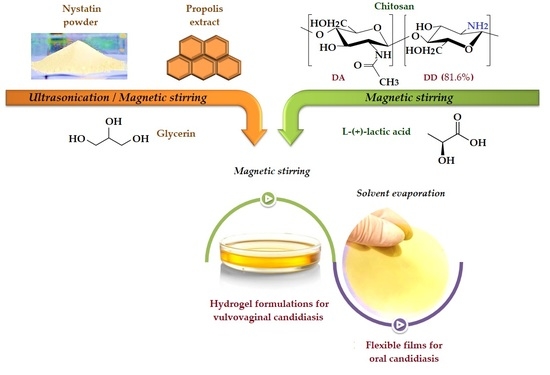
2.2. Preparation of Chitosan Antifungal Therapeutic Formulations
2.3. Methods of Characterization
2.3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization of Film Formulations
2.3.2. Mechanical Properties of the Films
2.3.3. Swelling Behavior of Film Formulations in Simulated Conditions
2.3.4. In Vitro Nystatin/Propolis Release from Film Formulations
2.3.5. Dynamic Vapor Sorption Measurements
2.3.6. Rheological Properties of the Hydrogels
2.3.7. Antifungal Activity of the Hydrogel
2.3.8. Time–Kill Assay
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Therapeutic Formulations Design and Preparative Protocol
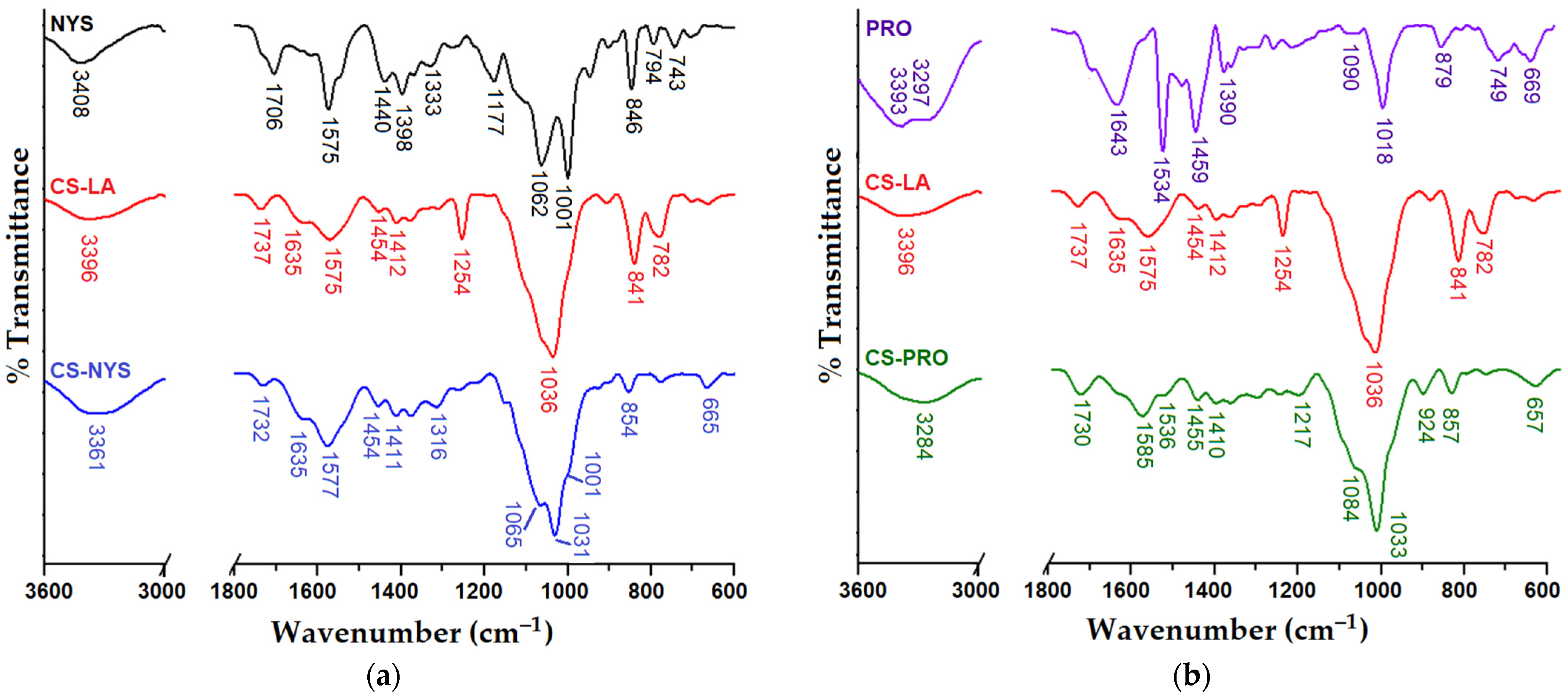
3.2. Structural Characterization
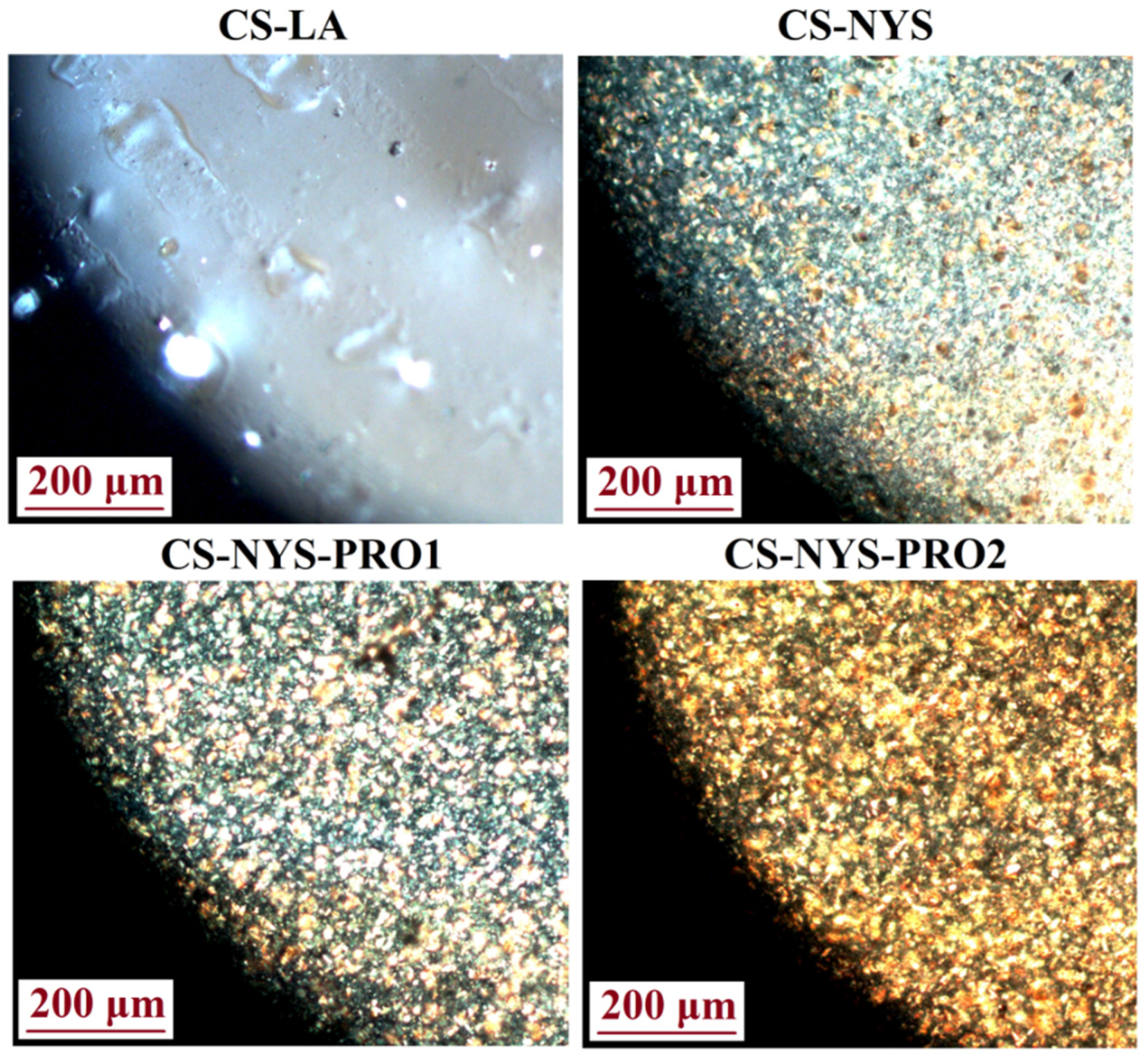
3.3. Films Morphology
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Films
3.5. Swelling Capacity of Films
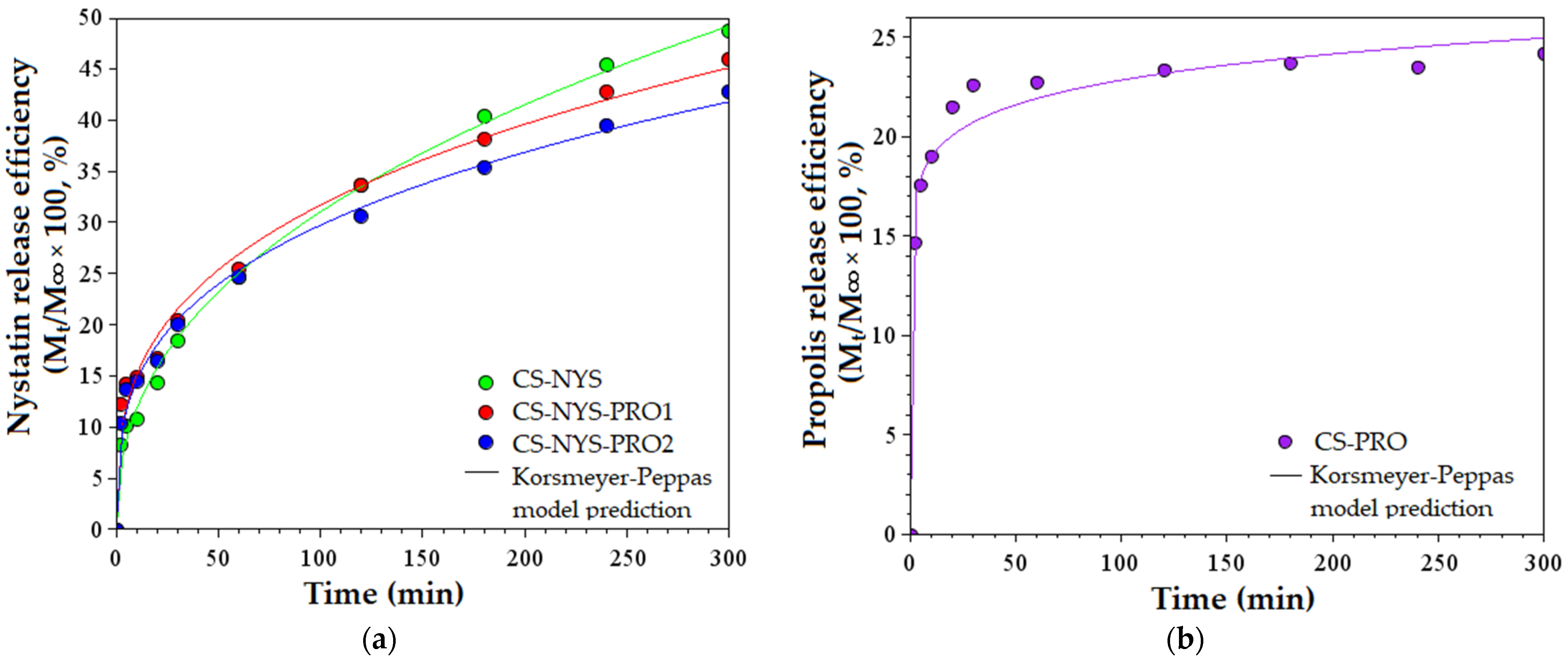
3.6. In Vitro NYS and PRO Release from Antifungal Films
3.7. Dynamic Vapor Sorption onto the Hydrogels
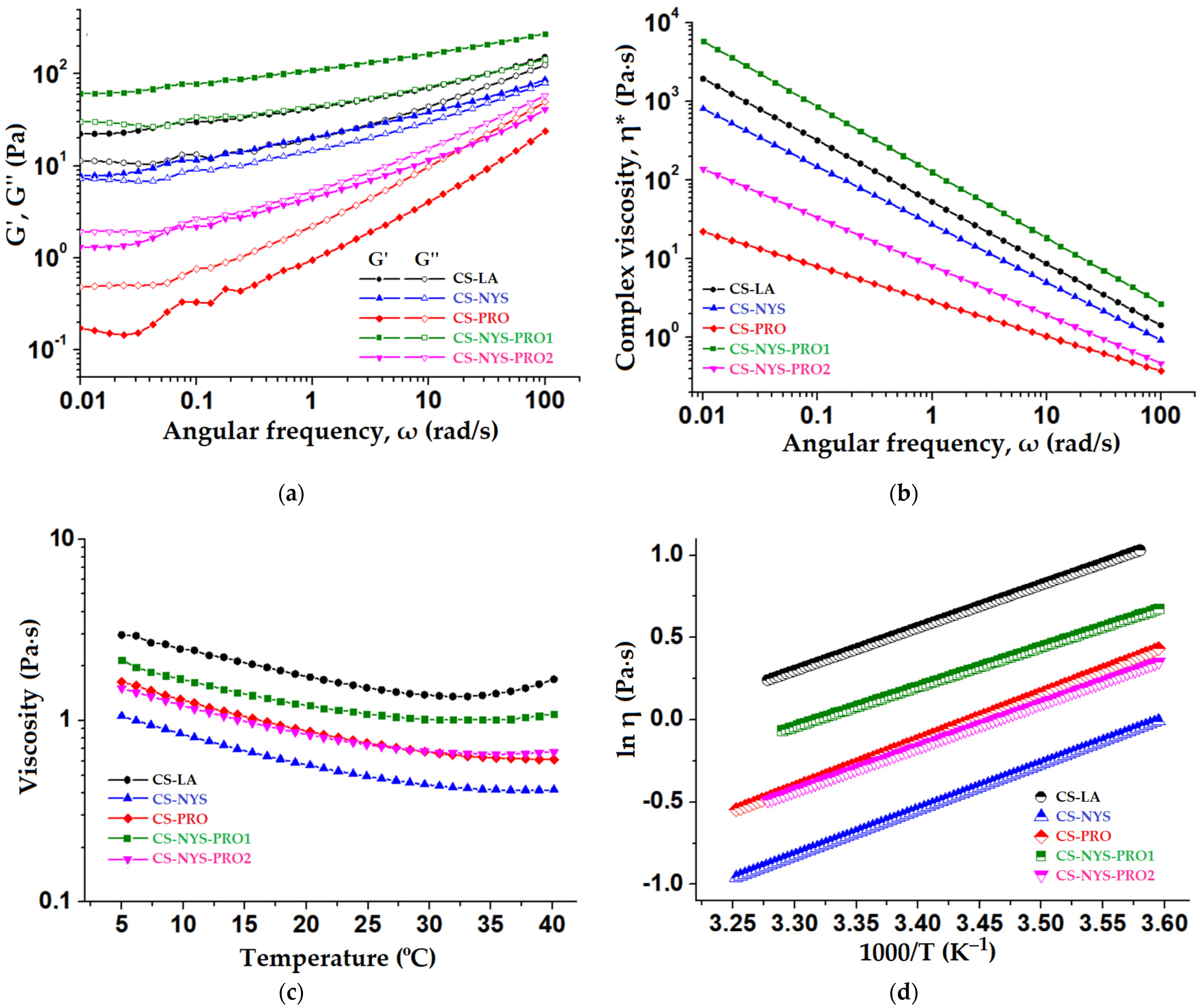
3.8. Rheological Properties of Chitosan Hydrogel Formulations
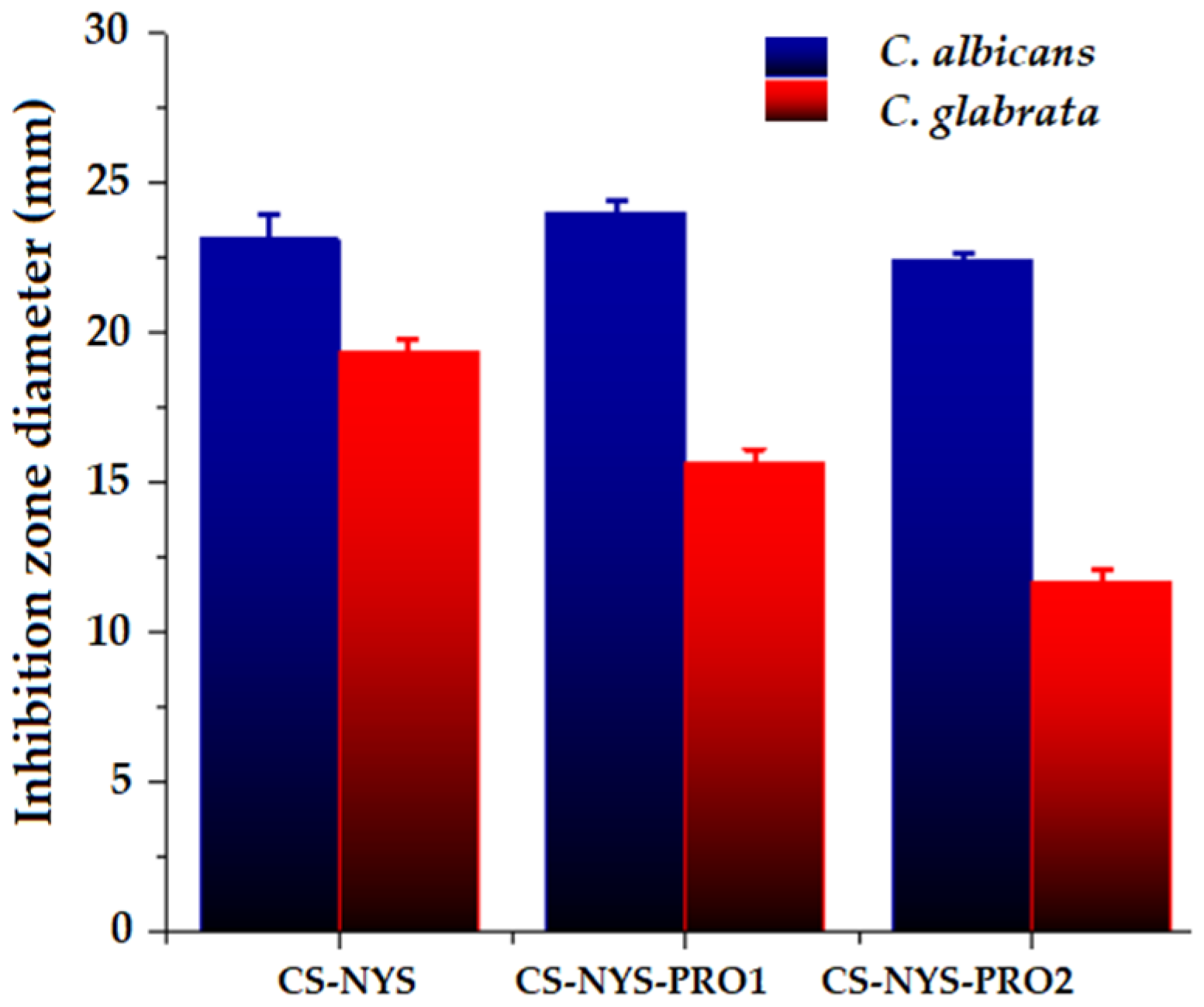
3.9. Antifungal Activity of Hydrogel Formulations
3.10. Time–Kill Assay Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spampinato, C.; Leonardi, D. Candida infections, causes, targets, and resistance mechanisms: Traditional and alternative antifungal agents. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 204237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.; Denning, D. Global and multi-national prevalence of fungal diseases—Estimate precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhaneni, S.; Mody, R.K.; Walker, T.; Chiller, T. The global burden of fungal diseases. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2016, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mareković, I.; Pleško, S.; Rezo Vranješ, V.; Herljević, Z.; Kuliš, T.; Jandrlić, M. Epidemiology of candidemia: Three-year results from a croatian tertiary care hospital. Fungi 2021, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederhold, N. Antifungal resistance: Current trends and future strategies to combat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 10, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peptu, C.; Humelnicu, A.-C.; Rotaru, R.; Fortuna, M.E.; Patras, X.; Teodorescu, M.; Tamba, B.I.; Harabagiu, V. chitosan-based drug delivery systems. In Chitin and Chitosan: Properties and Applications, 1st ed.; Van den Broek, L.A.M., Boeriu, C.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2020; pp. 259–289. [Google Scholar]
- Shelke, N.B.; James, R.; Laurencin, C.T.; Kumbar, S.G. Polysaccharide bio-materials for drug delivery and regenerative engineering. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Alcántara, A.R.; Civera, M.C.; Arias, C.; Elorza, B.; Heras Caballero, A.; Acosta, N. Chitosan: An overview of its properties and applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Geetha, N.; Khawar, K.M.; Jogaiah, S.; Mujtaba, M. Current trends and challenges in the synthesis and applications of chitosan-based nanocomposites for plants: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Gupta, A.; Agrawal, G. Recent advances in polysaccharides based bio-materials for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Villena, M.J.; Fernández-Campos, F.; Calpena-Campmany, A.C.; Bozal-de Febrer, N.; Ruiz-Martínez, M.A.; Clares-Naveros, B. Novel microparticulate systems for the vaginal delivery of nystatin: Development and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.J.; Calpena, A.C.; Fernández, F.; Mallandrich, M.; Gálvez, P.; Clares, B. Development of alginate microspheres as nystatin carriers for oral mucosa drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentefria, A.M.; Pippi, B.; Dalla Lana, D.F.; Donato, K.K.; de Andrade, S.F. Antifungals discovery: An insight into new strategies to combat antifungal resistance. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Revie, N.M.; Iyer, K.R.; Robbins, N.; Cowen, L.E. Antifungal drug resistance: Evolution, mechanisms and impact. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.S. Major Antifungal Drugs. In Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry II, 8th ed.; Taylor, J.B., Triggle, D.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2006; Volume 7, pp. 445–468. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, M.S.; Alnazzawi, A.; Habib, S.R.; Lone, M.A.; Zafar, M.S. Therapeutic role of nystatin added to tissue conditioners for treating denture-induced stomatitis: A systematic review. Prosthesis 2021, 3, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zager, R.A. Polyene antibiotics: Relative degrees of in vitro cytotoxicity and potential effects on tubule phospholipid and ceramide content. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 36, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, S.S.; Ramakishnan, J.; Raman, T. Recent advancement in combinational antifungal therapy and immunotherapy. In Recent Trends in Antifungal Agents, 1st ed.; Basak, A., Chakraborty, R., Mandal, S., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 75–95. [Google Scholar]
- Humelnicu, A.-C.; Samoila, P.; Asandulesa, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Bele, A.; Marinoiu, A.T.; Saccà, A.; Harabagiu, V. Chitosan-sulfated titania composite membranes with potential applications in fuel cell: Influence of cross-linker nature. Polymers 2020, 12, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Meth. Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Ye, Y.; Peng, S.; Deng, M.; Jiang, B. A novel ph- and salt-responsive n-succinyl-chitosan hydrogel via a one-step hydrothermal process. Molecules 2019, 24, 4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budianto, E.; Amalia, A. Swelling behavior and mechanical properties of chitosan-poly(n-vinyl-pyrrolidone) hydrogels. J. Polym. Eng. 2020, 40, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipcak, A.S.; Ismail, O.; Doymaz, I.; Piskin, S. Modeling and investigation of the swelling kinetics of acrylamide-sodium acrylate hydrogel. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peppas, N. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Peppas, N.A. Effect of the morphology of hydrophilic polymeric matrices on the diffusion and release of water soluble drugs. J. Membr. Sci. 1981, 9, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Q.; Hamid Akash, M.S.; Rasool, M.F.; Rehman, K. Role of kinetic models in drug stability. In Drug Stability and Chemical Kinetics; Akash, M.S.H., Rehman, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Castillo, D.J.; de la Cruz Hernández, E.N.; Frías Márquez, D.M.; Tilley, R.D.; Gloag, L.; Owen, P.Q.; López González, R.; Alvarez Lemus, M.A. Albendazole release from silica-chitosan nanospheres. In vitro study on cervix cancer cell lines. Polymers 2021, 13, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Sánchez-Soto, M.; Schiraldi, D. The Relation between the rheological properties of gels and the mechanical properties of their corresponding aerogels. Gels 2018, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malkin, A.Y.; Isayev, A. Viscoelasticicty. In Rheology: Concepts, Methods, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Malkin, A.Y., Isayev, A., Eds.; ChemTec Publishing: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2017; pp. 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, T.U.; Shah, L.A. Rheological investigation of go doped p(aptmacl) composite hydrogel. Z. Phys. Chem. 2021, 235, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canton, E.; Peman, J.; Gobernado, M.; Viudes, A.; Espinel-Ingroff, A. Patterns of amphotericin b killing kinetics against seven candida species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moosa, M.-Y.S.; Sobel, J.D.; Elhalis, H.; Du, W.; Akins, R.A. Fungicidal Activity of fluconazole against candida albicans in a synthetic vagina-simulative medium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 48, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, M.R.; Loebenberg, R.; Almukainzi, M. Simulated biological fluids with possible application in dissolution testing. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perchyonok, V.T.; Zhang, S.; Oberholzer, T. Alternative chitosan based drug delivery system to fight oral mucositis: Synergy of conventional and bioactives towards the optimal solution. Curr. Nanosci. 2012, 8, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perchyonok, V.T.; Zhang, S.; Grobler, S.; Oberholzer, T. Insights into and relative effect of chitosan-H, chitosan-H-propolis, chitosan-H-propolis-nystatin and chitosan-H-nystatin on dentine bond strength. Eur. J. Dent. 2013, 7, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perchyonok, V.T.; Zhang, S.; Basson, N.; Grobler, S.; Oberholzer, T.; Massey, W. Insights into chitosan based gels as functional restorative biomaterials prototypes: In vitro approach. Open J. Stomat. 2013, 3, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perchyonok, V.-T.; Zhang, S.; Oberholzer, T. Novel melatonin-chitosan hydrogels as suitable oral bio-drug delivery systems to fight oral mucositis: Synergy of antioxidants and bioactives in action. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 2430–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D.I. Stable Oil-in-Glycerin Emulsion. European Patent EP1077713A1, 28 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dallan, P.R.M.; da Luz Moreira, P.; Petinari, L.; Malmonge, S.M.; Beppu, M.M.; Genari, S.C.; Moraes, A.M. Effects of chitosan solution concentration and incorporation of chitin and glycerol on dense chitosan membrane properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 80B, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Xin, L.; Tan, H.; Fan, M.; Li, J.; Jia, Y.; Ling, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X. Chitosan membrane dressings toughened by glycerol to load antibacterial drugs for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 81, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, K.; Khan, T.; Ch’ng, H. Mechanical, bioadhesive strength and biological evaluations of chitosan films for wound dressing. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 3, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Niamsa, N.; Baimark, Y. Preparation and characterization of highly flexible chitosan films for use as food packaging. Am. J. Food Technol. 2009, 4, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwarc, K.; Płosiński, M.; Czerniejewska, K.; Laskowski, T.; Leniak, A.; Czub, J.; Kubica, P.; Sowiński, P.; Pawlaka, J.; Borowski, E. Intramolecular transformation of an antifungal antibiotic nystatin A1 into its isomer, iso -nystatin A1 structural and molecular modeling studies. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2016, 54, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpon, L.; Lancelin, J.-M. Solution NMR structure of five representative glycosylated polyene macrolide antibiotics with a sterol-dependent antifungal activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 4533–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sletta, H.; Borgos, S.E.F.; Bruheim, P.; Sekurova, O.N.; Grasdalen, H.; Aune, R.; Ellingsen, T.E.; Zotchev, S.B. Nystatin biosynthesis and transport: nysH and nysG genes encoding a Putative ABC transporter system in Streptomyces noursei ATCC 11455 are required for efficient conversion of 10-deoxynystatin to nystatin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4576–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benavent, C.; Torrado-Salmerón, C.; Torrado-Santiago, S. Development of a solid dispersion of nystatin with maltodextrin as a carrier agent: Improvements in antifungal efficacy against Candida spp. biofilm infections. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandru, M.; Ciobanu, C.; Ignat, M.E.; Popa, M.; Verestiuc, L.; Vlad, S. Sustained release of nystatin from polyurethane membranes for biomedical applications. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2011, 6, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Rajczak, E.; Tylkowski, B.; Constantí, M.; Haponska, M.; Trusheva, B.; Malucelli, G.; Giamberini, M. Preparation and characterization of uv-curable acrylic membranes embedding natural antioxidants. Polymers 2020, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Svečnjak, L.; Marijanović, Z.; Okińczyc, P.; Marek Kuś, P.; Jerković, I. Mediterranean propolis from the adriatic sea islands as a source of natural antioxidants: Comprehensive chemical biodiversity determined by GC-MS, FTIR-ATR, UHPLC-DAD-QqTOF-MS, DPPH and FRAP assay. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villalobos, K.; Rojas, H.; González-Paz, R.; Granados, D.B.; González-Masís, J.; Baudrit, J.V.; Corrales-Ureña, Y.R. Production of starch films using propolis nanoparticles as novel bioplasticizer. J. Renew. Mater. 2017, 5, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Cock, J.; Ramírez, E.; Betancourt, S.; Putaux, J.-L.; Osorio, M.; Castro, C.; Ganán, P.; Zuluaga, R. Influence of the acid type in the production of chitosan films reinforced with bacterial nanocellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R. Composite poly(lactic acid)/chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Miao, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Tang, H.; Yang, H. Preparation and characterization of a novel positively charged composite hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane based on chitosan lactate. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 4361–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattarai, N.; Ramay, H.R.; Chou, S.H.; Zhang, M. Chitosan and lactic acid-grafted chitosan nanoparticles as carriers for prolonged drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio-Martín, J.; Fabra, M.J.; Lopez-Rubio, A.; Lagaron, J.M. An effect of lactic acid oligomers on the barrier properties of polylactide. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.G.N.; Mei, L.H.I.; Santos, A.R., Jr. Sorbitol-plasticized and neutralized chitosan membranes as skin substitutes. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gleadall, A.; Ruiz-Cantu, L. Transplantable scaffolds. In 3D Printing in Medicine and Surgery-Applications in Healthcare, 1st ed.; Thomas, D.J., Singh, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Kidlington, UK, 2021; pp. 199–222. [Google Scholar]
- Koland, M.; Vijayanarayana, K.; Charyulu, R.; Prabhu, P. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of chitosan buccal films of ondansetron hydrochloride. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2011, 1, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ipate, A.-M.; Serbezeanu, D.; Bargan, A.; Hamciuc, C.; Ochiuz, L.; Gherman, S. Poly(vinylpyrrolidone)-chitosan hydrogels as matrices for controlled drug release. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2021, 55, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnaru, E.; Stoleru, E.; Brebu, M.; Darie-Nita, R.; Bargan, A.; Vasile, C. Chitosan-based bionanocomposite films prepared by emulsion technique for food preservation. Materials 2019, 12, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.T.B.; Hein, S.; Ng, C.-H.; Stevens, W.F. Molecular stability of chitosan in acid solutions stored at various conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 107, 2588–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljoen, J.M.; Steenekamp, J.H.; Marais, A.F.; Kotzé, A.F. Effect of moisture content, temperature and exposure time on the physical stability of chitosan powder and tablets. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 40, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Hydrogel/Film Code | NYS (mg) | PRO (mL Solution/mg Solid Compound) | Films Thickness (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS-LA | - | - | 49 |
| CS-NYS | 15 | - | 53 |
| CS-PRO | - | 0.30/90 | 210 |
| CS-NYS-PRO1 | 15 | 0.15/45 | 166 |
| CS-NYS-PRO2 | 15 | 0.30/90 | 220 |
| Film Code | σb (MPa) | εb (%) | Y (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS-LA | 73.3 | 7.7 | 9.310 |
| CS-NYS | 8.6 | 113.9 | 0.044 |
| CS-PRO | 7.5 | 88.1 | 0.031 |
| CS-NYS-PRO1 | 5.4 | 74.8 | 0.036 |
| CS-NYS-PRO2 | 3.0 | 68.9 | 0.025 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Humelnicu, A.-C.; Samoilă, P.; Cojocaru, C.; Dumitriu, R.; Bostănaru, A.-C.; Mareș, M.; Harabagiu, V.; Simionescu, B.C. Chitosan-Based Therapeutic Systems for Superficial Candidiasis Treatment. Synergetic Activity of Nystatin and Propolis. Polymers 2022, 14, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040689
Humelnicu A-C, Samoilă P, Cojocaru C, Dumitriu R, Bostănaru A-C, Mareș M, Harabagiu V, Simionescu BC. Chitosan-Based Therapeutic Systems for Superficial Candidiasis Treatment. Synergetic Activity of Nystatin and Propolis. Polymers. 2022; 14(4):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040689
Chicago/Turabian StyleHumelnicu, Andra-Cristina, Petrișor Samoilă, Corneliu Cojocaru, Raluca Dumitriu, Andra-Cristina Bostănaru, Mihai Mareș, Valeria Harabagiu, and Bogdan C. Simionescu. 2022. "Chitosan-Based Therapeutic Systems for Superficial Candidiasis Treatment. Synergetic Activity of Nystatin and Propolis" Polymers 14, no. 4: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040689
APA StyleHumelnicu, A.-C., Samoilă, P., Cojocaru, C., Dumitriu, R., Bostănaru, A.-C., Mareș, M., Harabagiu, V., & Simionescu, B. C. (2022). Chitosan-Based Therapeutic Systems for Superficial Candidiasis Treatment. Synergetic Activity of Nystatin and Propolis. Polymers, 14(4), 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040689