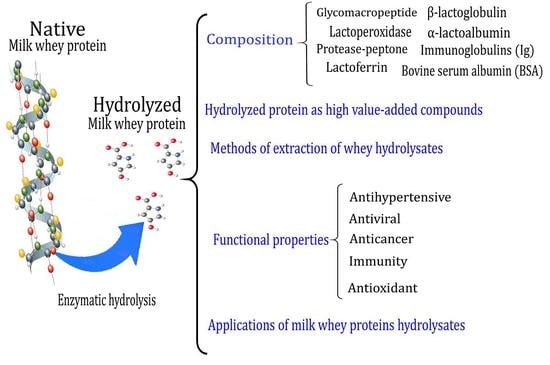
Milk Whey Hydrolysates as High Value-Added Natural Polymers: Functional Properties and Applications
Abstract
Share and Cite
León-López, A.; Pérez-Marroquín, X.A.; Estrada-Fernández, A.G.; Campos-Lozada, G.; Morales-Peñaloza, A.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Milk Whey Hydrolysates as High Value-Added Natural Polymers: Functional Properties and Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061258
León-López A, Pérez-Marroquín XA, Estrada-Fernández AG, Campos-Lozada G, Morales-Peñaloza A, Campos-Montiel RG, Aguirre-Álvarez G. Milk Whey Hydrolysates as High Value-Added Natural Polymers: Functional Properties and Applications. Polymers. 2022; 14(6):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061258
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón-López, Arely, Xóchitl Alejandra Pérez-Marroquín, Ana Guadalupe Estrada-Fernández, Gieraldin Campos-Lozada, Alejandro Morales-Peñaloza, Rafael G. Campos-Montiel, and Gabriel Aguirre-Álvarez. 2022. "Milk Whey Hydrolysates as High Value-Added Natural Polymers: Functional Properties and Applications" Polymers 14, no. 6: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061258
APA StyleLeón-López, A., Pérez-Marroquín, X. A., Estrada-Fernández, A. G., Campos-Lozada, G., Morales-Peñaloza, A., Campos-Montiel, R. G., & Aguirre-Álvarez, G. (2022). Milk Whey Hydrolysates as High Value-Added Natural Polymers: Functional Properties and Applications. Polymers, 14(6), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061258