Effect of Squid Cartilage Chitosan Molecular Structure on the Properties of Its Monofilament as an Absorbable Surgical Suture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan
2.3. Wet Spinning to Produce Chitosan Monofilaments
2.4. Characterization of Chitosan Monofilaments
2.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Test of AS-85
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Parameters of Chitosan and Specifications of Their Monofilaments
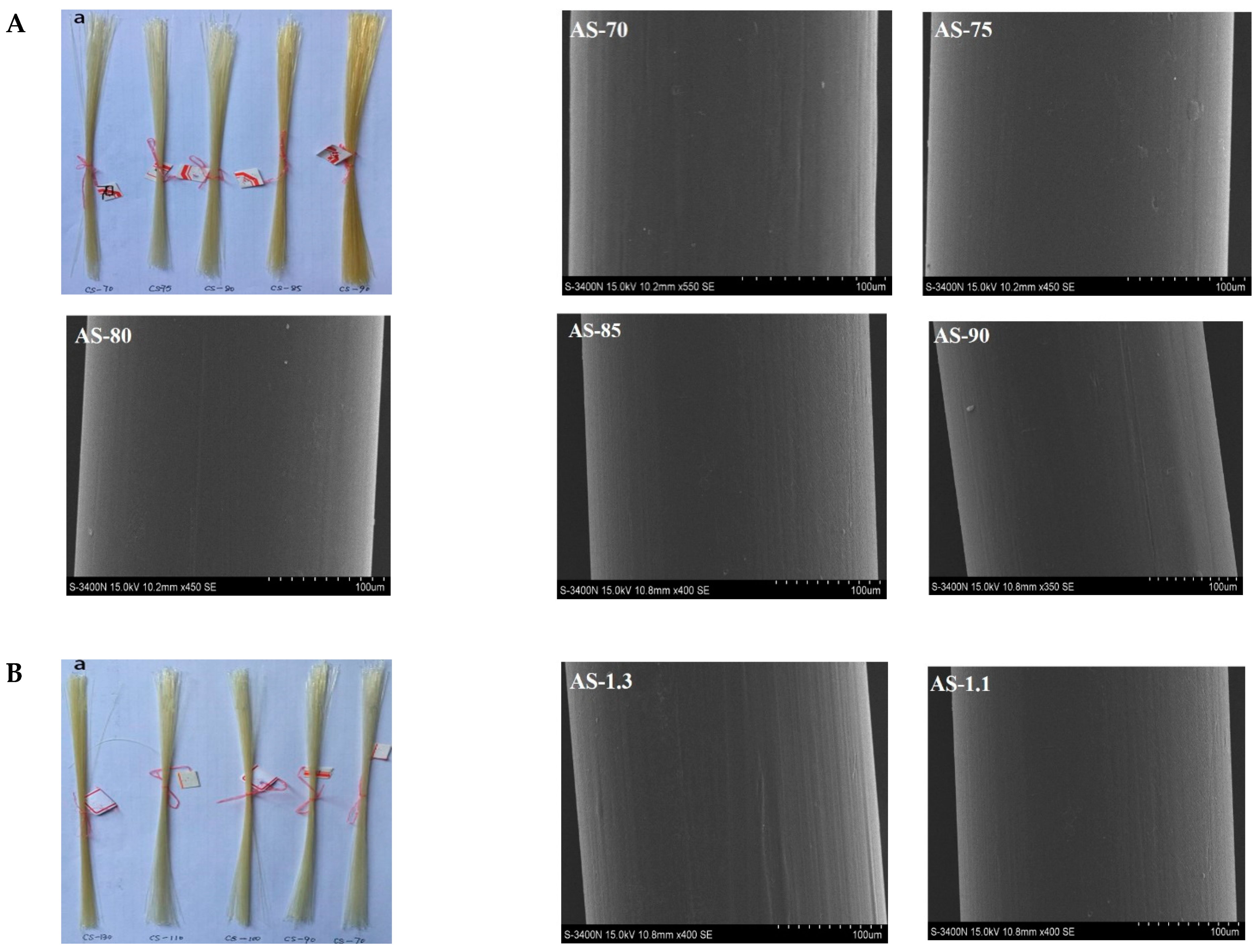
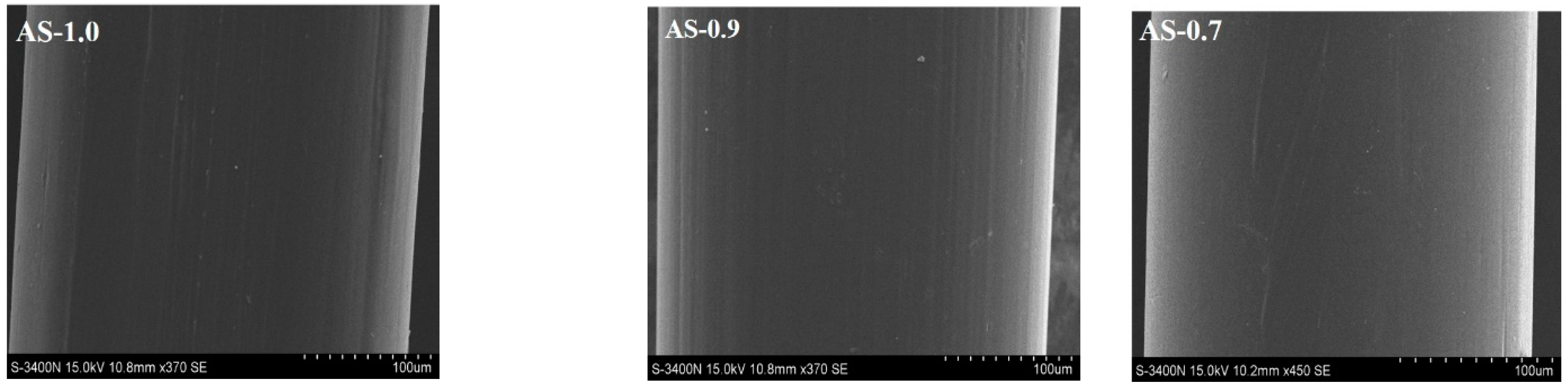
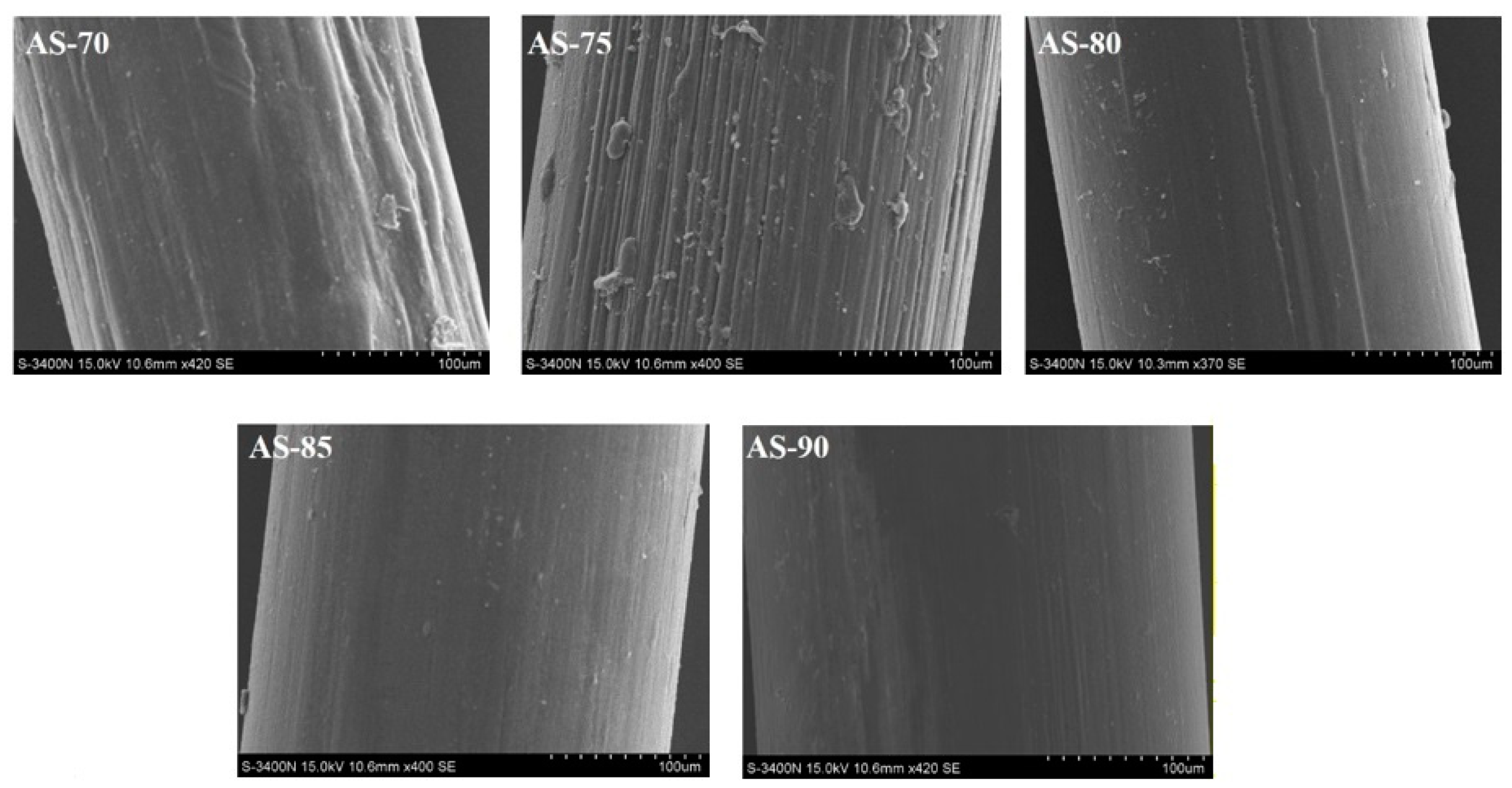
3.2. Appearance and Morphology of Monofilaments
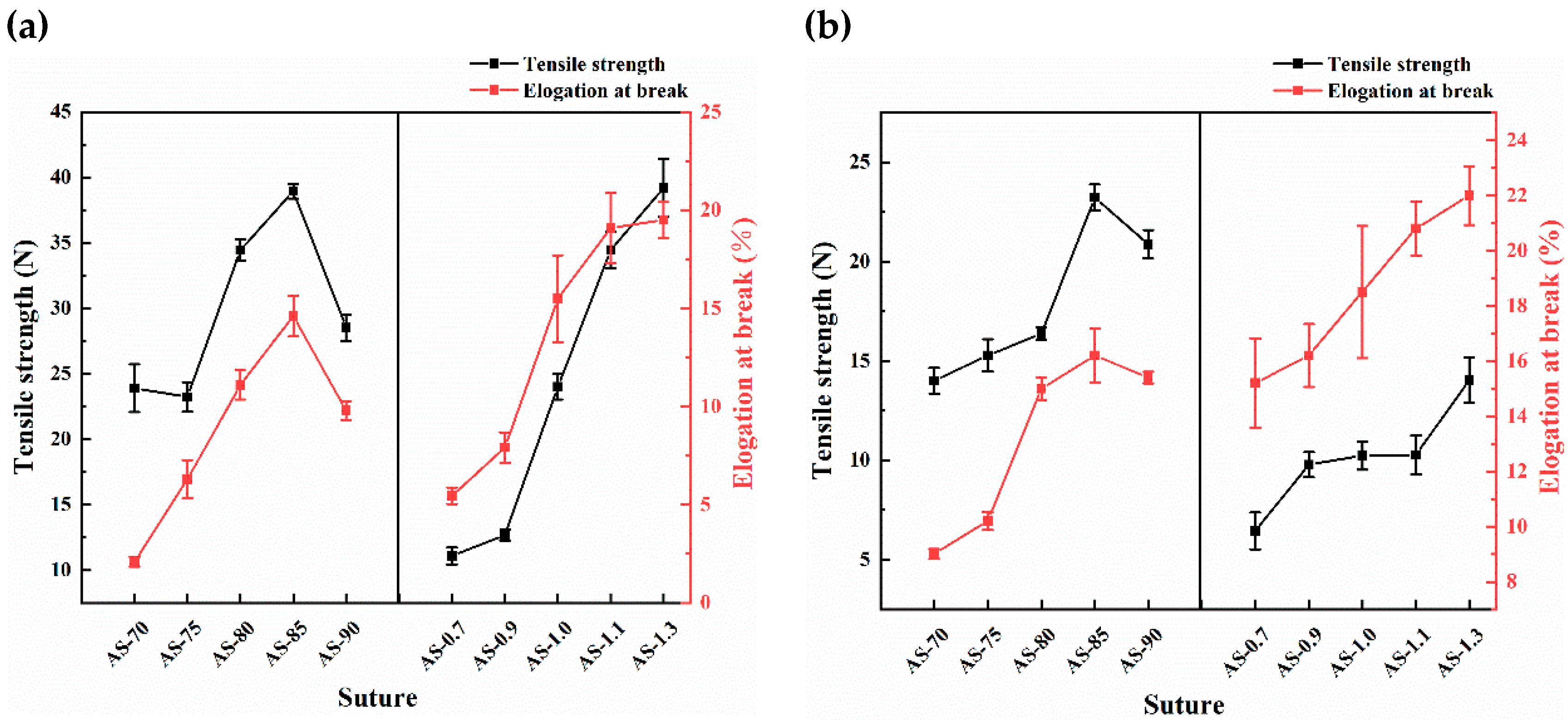
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Monofilaments
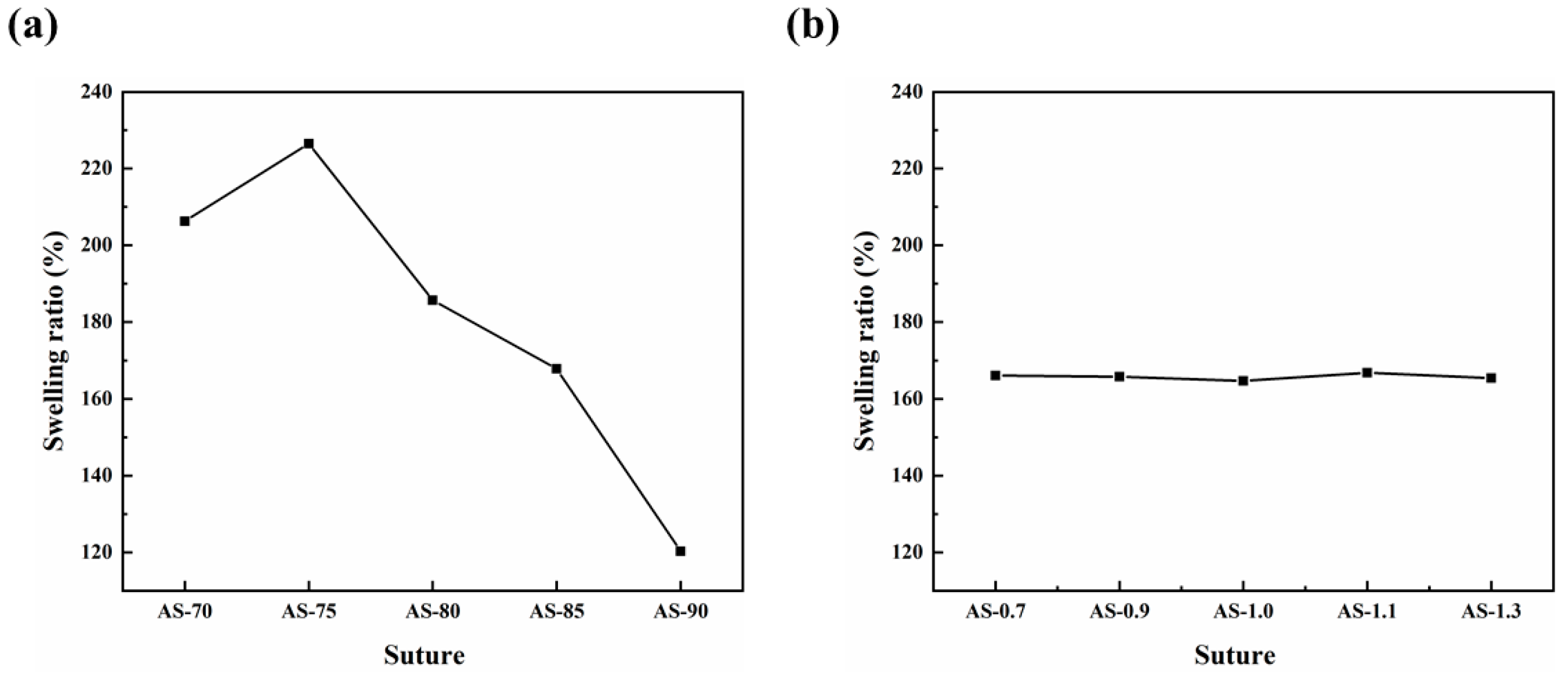
3.4. Swelling Performance of Monofilaments
3.5. Ash Contents of Monofilaments
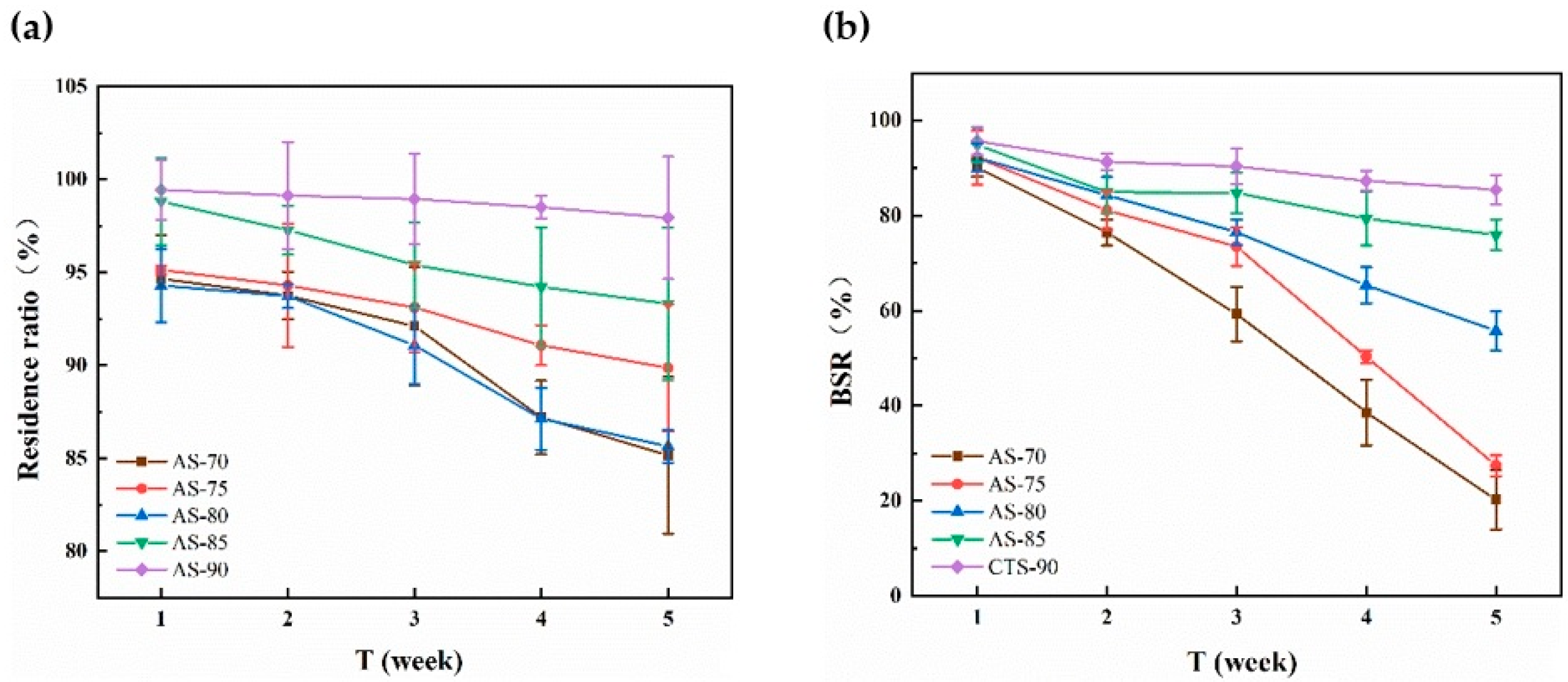
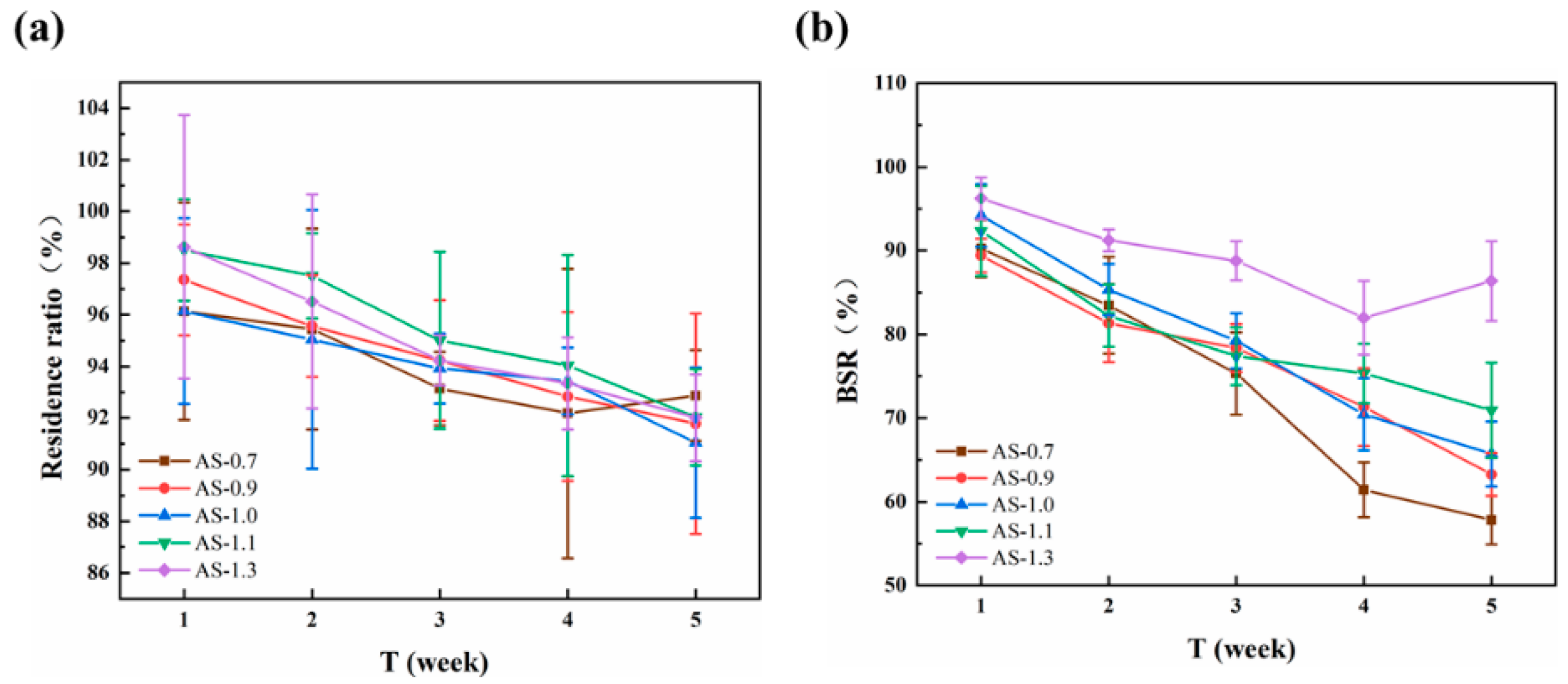
3.6. In Vitro Enzymatic Degradation of Monofilaments
3.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of AS-85
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Achrai, B.; Daniel Wagner, H. The red-eared slider turtle carapace under fatigue loading: The effect of rib–suture arrangement. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 53, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandimalla, R.; Kalita, S.; Choudhury, B.; Devi, D.; Kalita, D.; Kalita, K.; Dash, S.; Kotoky, J. Fiber from ramie plant (Boehmeria nivea): A novel suture biomaterial. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cheng, F.; Chávez-Madero, C.; Choi, J.; Wei, X.; Yi, X.; Zheng, T.; He, J. Manufacturing and physical characterization of absorbable oxidized regenerated cellulose braided surgical sutures. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, C.; Sethu, S.; Nayak, S.; Mohan, L.; Morsi, Y.Y.; Manivasagam, G. Suture materials—Current and emerging trends. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2016, 104, 1544–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoi, D.; Choudhury, A.J.; Chutia, J.; Pal, A.R.; Khan, M.; Choudhury, M.; Pathak, P.; Das, G.; Patil, D.S. Development of advanced antimicrobial and sterilized plasma polypropylene grafted muga (Antheraea assama) silk as suture biomaterial. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.P.; Reagan, M.R.; Bohara, R.A. Silk fibroin and silk-based biomaterial derivatives for ideal wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4613–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik-Ali, S.; Guets, W. Absorbable vs. non absorbable sutures for wound closure. Systematic review of systematic reviews. Wound Med. 2018, 23, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillanders, S.L.; Anderson, S.; Mellon, L.; Heskin, L. A systematic review and meta-analysis: Do absorbable or non-absorbable suture materials differ in cosmetic outcomes in patients requiring primary closure of facial wounds? J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2018, 71, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.S.; Parampalli, U.; Baig, M.K.; McFall, M.R. A systematic review on the effectiveness of slowly-absorbable versus non-absorbable sutures for abdominal fascial closure following laparotomy. Int. J. Surg. 2011, 9, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethinam, S.; Thotapalli Parvathaleswara, S.; Nandhagobal, G.; Alagumuthu, T.; Robert, B. Preparation of absorbable surgical suture: Novel approach in biomedical application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 47, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.C.; Vieira, J.C.; Ferra, J.M.; Magalhães, F.D.; Guedes, R.M.; Marques, A.T. Mechanical study of PLA–PCL fibers during in vitro degradation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Mehrotra, S. Is Catgut Really Obsolete? Experience with Buried Subcuticular Catgut Sutures in Operative Wounds. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2002, 58, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Holmer, C.; Praechter, C.; Mecklenburg, L.; Heimesaat, M.; Rieger, H.; Pohlen, U. Anastomotic stability and wound healing of colorectal anastomoses sealed and sutured with a collagen fleece in a rat peritonitis model. Asian J. Surg. 2014, 37, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Williams, G.R.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Niu, S.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L. Regenerated chitin fibers reinforced with bacterial cellulose nanocrystals as suture biomaterials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramot, Y.; Haim-Zada, M.; Domb, A.J.; Nyska, A. Biocompatibility and safety of PLA and its copolymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, M.K.; Knebel, P.; Kieser, M.; Schüler, P.; Schiergens, T.S.; Atanassov, V.; Neudecker, J.; Stein, E.; Thielemann, H.; Kunz, R.; et al. Effectiveness of triclosan-coated PDS Plus versus uncoated PDS II sutures for prevention of surgical site infection after abdominal wall closure: The randomised controlled PROUD trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, B.Y.; Ahn, S.K.; Choi, Y.M.; Choi, D.J.; Chang, J.H. Antimicrobial and biodegradable PLGA medical sutures with natural grapefruit seed extracts. Mater. Lett. 2013, 95, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, Y.; Cabral, T.; Lorenzetti, A.; Franco, L.; Turon, P.; Del Valle, L.J.; Puiggalí, J. Incorporation of biguanide compounds into poly(GL)-b-poly(GL-co-TMC-co-CL)-b-poly(GL) monofilament surgical sutures. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 71, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotting, J.A.; Nelson, T.J.; Banffy, M.B.; Yalamanchili, D.; Eberlein, S.A.; Chahla, J.; Metzger, M.F. Biomechanical evaluation of PCL reconstruction with suture augmentation. Knee 2020, 27, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; George, A.; Gopi, S.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Polymer sutures for simultaneous wound healing and drug delivery—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naleway, S.E.; Lear, W.; Kruzic, J.J.; Maughan, C.B. Mechanical properties of suture materials in general and cutaneous surgery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Profyris, C.; Tziotzios, C.; Do Vale, I. Cutaneous scarring: Pathophysiology, molecular mechanisms, and scar reduction therapeutics Part I. The molecular basis of scar formation. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, J.M.; Durisin, M.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Recent advances in biodegradable metals for medical sutures: A critical review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1915–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negm, N.A.; Hefni, H.H.H.; Abd-Elaal, A.A.A.; Badr, E.A.; Abou Kana, M.T.H. Advancement on modification of chitosan biopolymer and its potential applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 681–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, E. Progresses in targeted drug delivery systems using chitosan nanoparticles in cancer therapy: A mini-review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudin, V.E.; Dobrovolskaya, I.P.; Neelov, I.M.; Dresvyanina, E.N.; Popryadukhin, P.V.; Ivan’kova, E.M.; Elokhovskii, V.Y.; Kasatkin, I.A.; Okrugin, B.M.; Morganti, P. Wet spinning of fibers made of chitosan and chitin nanofibrils. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y.; Rajoka, M.S.R. Insights on the ultra high antibacterial activity of positionally substituted 2′-O-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan: A joint interaction of -NH2 and -N+(CH3)3 with bacterial cell wall. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz Rajoka, M.S.; Mehwish, H.M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Arfat, Y.; Majeed, K.; Anwaar, S. Chitin/chitosan derivatives and their interactions with microorganisms: A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz Rajoka, M.S.; Zhao, L.; Mehwish, H.M.; Wu, Y.; Mahmood, S. Chitosan and its derivatives: Synthesis, biotechnological applications, and future challenges. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1557–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, X.; Ding, T.; Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D. Ultrasound effects on the degradation kinetics, structure and rheological properties of apple pectin. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Yui, T. Crystallinity of Partially N-Acetylated Chitosans. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993, 57, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, E.F.; Freitas, L.C.; Lins, R.D. Chitosan molecular structure as a function of N-acetylation. Biopolymers 2011, 95, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Neau, S.H. In vitro degradation of chitosan by a commercial enzyme preparation: Effect of molecular weight and degree of deacetylation. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Yi, H.; Wang, W.; Ma, X. The enzymatic degradation and swelling properties of chitosan matrices with different degrees of N-acetylation. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Suture | Ash Content (%) | Suture | Ash Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS-70 | 0.038 | AS-1.3 | 0.036 |
| AS-75 | 0.037 | AS-1.1 | 0.037 |
| AS-80 | 0.038 | AS-1.0 | 0.039 |
| AS-85 | 0.039 | AS-0.9 | 0.037 |
| AS-90 | 0.038 | AS-0.7 | 0.038 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Y.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Ke, Z.; Mehwish, H.M.; Deng, W.; Li, J.; Qin, W.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y. Effect of Squid Cartilage Chitosan Molecular Structure on the Properties of Its Monofilament as an Absorbable Surgical Suture. Polymers 2022, 14, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071306
Tan Y, Rajoka MSR, Ke Z, Mehwish HM, Deng W, Li J, Qin W, Zhao L, Wu Y. Effect of Squid Cartilage Chitosan Molecular Structure on the Properties of Its Monofilament as an Absorbable Surgical Suture. Polymers. 2022; 14(7):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071306
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Yongxin, Muhammad Shahid Riaz Rajoka, Zekai Ke, Hafiza Mahreen Mehwish, Wenjing Deng, Jiaying Li, Wenqian Qin, Liqing Zhao, and Yiguang Wu. 2022. "Effect of Squid Cartilage Chitosan Molecular Structure on the Properties of Its Monofilament as an Absorbable Surgical Suture" Polymers 14, no. 7: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071306
APA StyleTan, Y., Rajoka, M. S. R., Ke, Z., Mehwish, H. M., Deng, W., Li, J., Qin, W., Zhao, L., & Wu, Y. (2022). Effect of Squid Cartilage Chitosan Molecular Structure on the Properties of Its Monofilament as an Absorbable Surgical Suture. Polymers, 14(7), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071306








