Electro-Responsive Conductive Blended Hydrogel Patch
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel
2.2. Characterization of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel
2.3. Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel
2.4. Electro-Responsive Drug Release of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel Patch
2.5. Biocompatibility of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel Patch
2.6. Drug Release of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel Patch
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
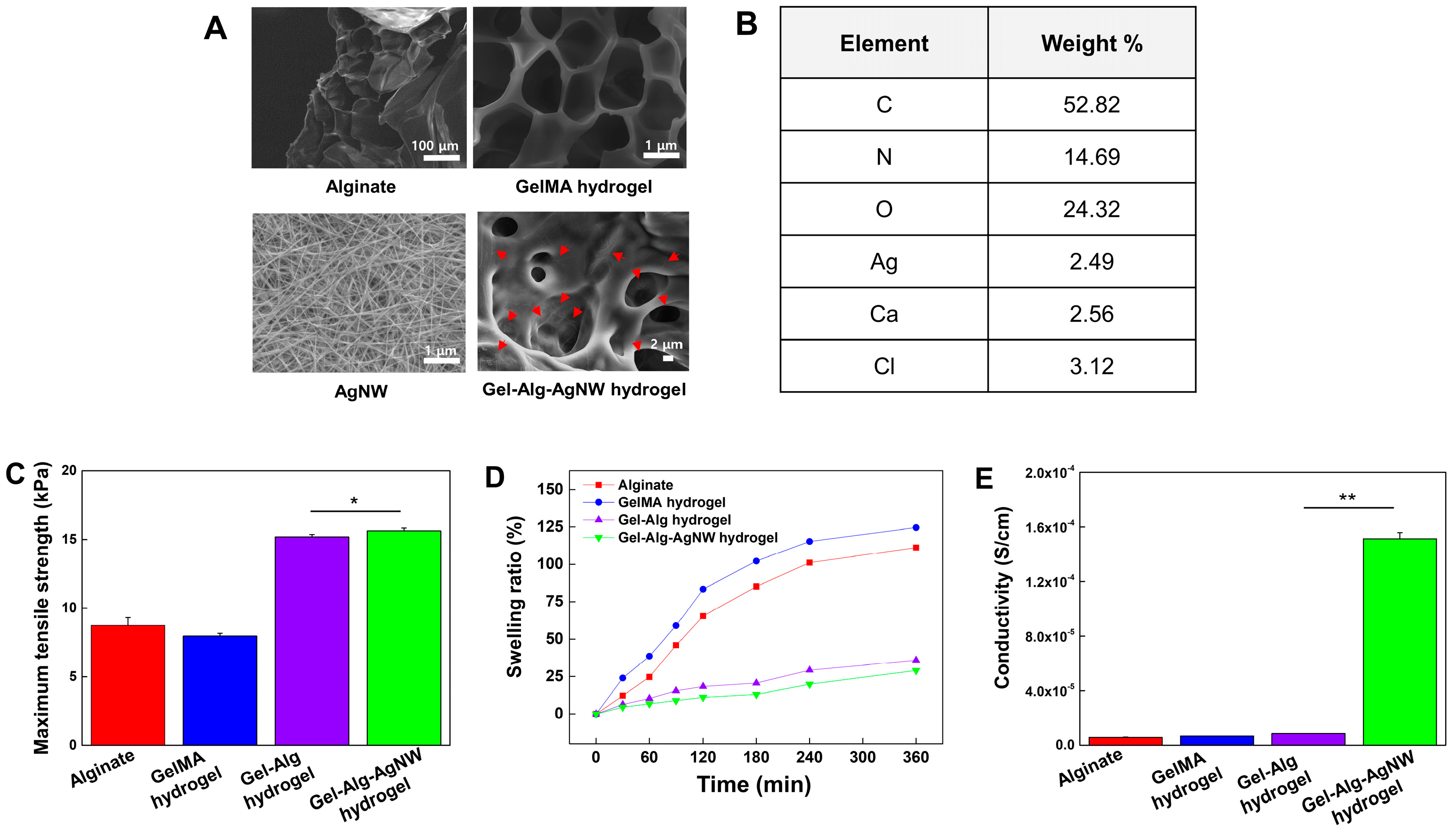
3.1. Characterization of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel
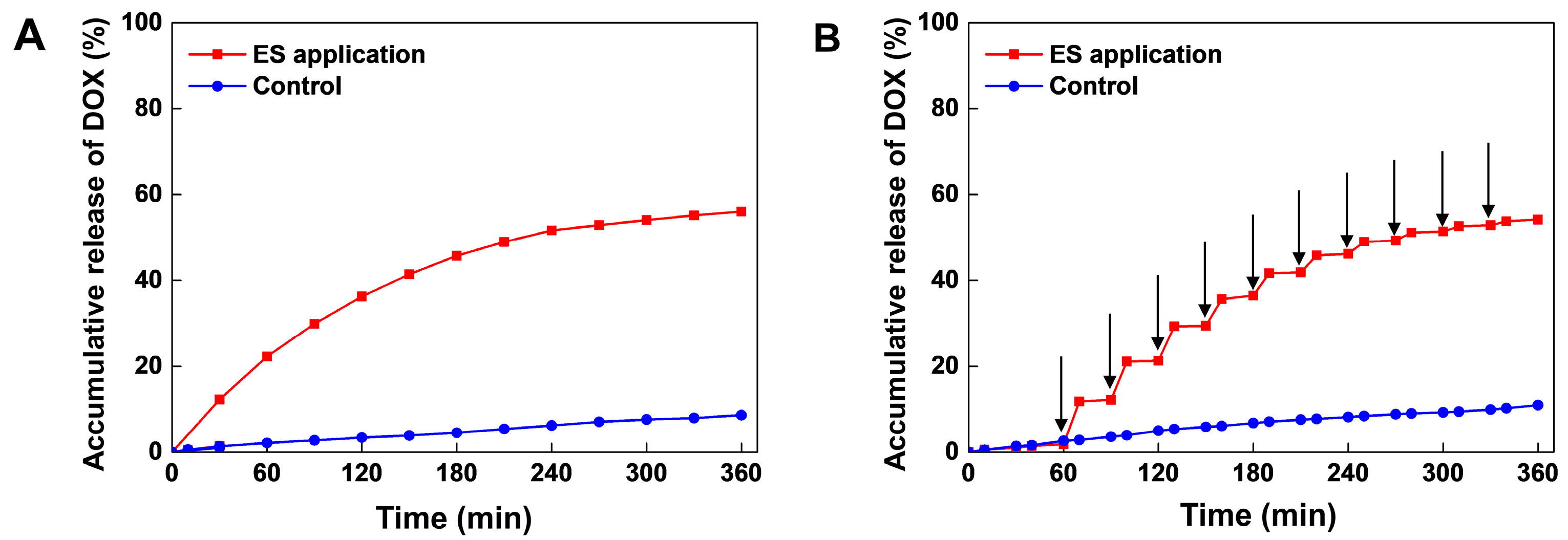
3.2. Electrical Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel Patch
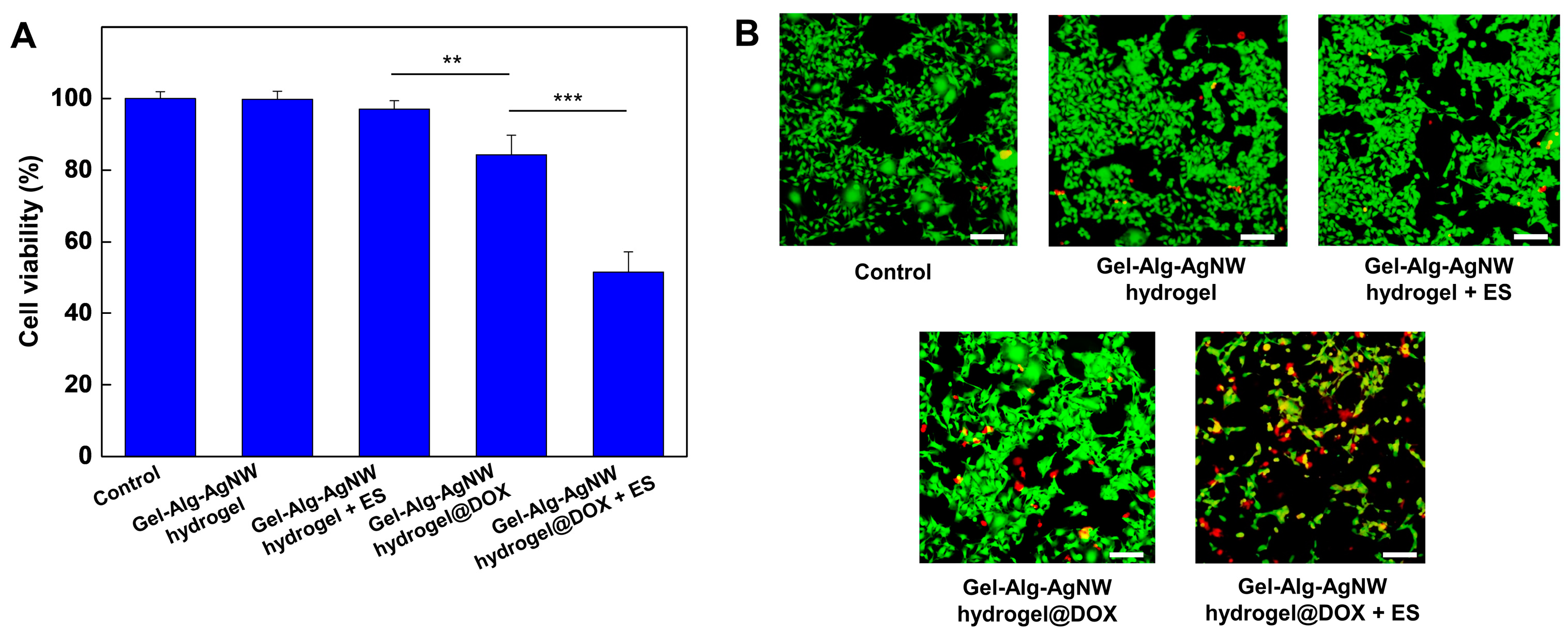
3.3. Biocompatibility and Drug Release of Gel-Alg-AgNW Blended Hydrogel
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Y.; Ramey-Ward, A.N.; Salaita, K. Programmable Mechanically Active Hydrogel-Based Materials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Ma, Y.; Shen, S.; He, B.; Mo, R. Enhanced transdermal drug delivery by transfersome-embedded oligopeptide hydrogel for topical chemotherapy of melanoma. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9693–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-H.; Lee, J.; Son, D.U.; Kang, D.H.; Park, M.J.; Cho, K.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Ko, J.; Jang, M.-H. Facilitated transdermal drug delivery using nanocarriers-embedded electroconductive hydrogel coupled with reverse electrodialysis-driven iontophoresis. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4523–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, J. Adhesive hydrogel patch with enhanced strength and adhesiveness to skin for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mela, A.; Poniatowski, Ł.A.; Drop, B.; Furtak-Niczyporuk, M.; Jaroszyński, J.; Wrona, W.; Staniszewska, A.; Dąbrowski, J.; Czajka, A.; Jagielska, B. Overview and Analysis of the Cost of Drug Programs in Poland: Public Payer Expenditures and Coverage of Cancer and Non-Neoplastic Diseases Related Drug Therapies from 2015–2018 Years. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.B.; Liu, T.Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.H. Ionic liquid transdermal delivery system: Progress, prospects, and challenges. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.B.; Martin, G.P.; Jones, S.A.; Akomeah, F.K. Dermal and transdermal drug delivery systems: Current and future prospects. Drug Deliv. 2006, 13, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.S.; Sun, Y.Y.; Qin, Z.C.; Zhang, S.Y.; Chen, W.B.; Liu, Y.Q. Losartan Potassium and Verapamil Hydrochloride Compound Transdermal Drug Delivery System: Formulation and Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, A.P.; Wright, O.R.L.; Benson, H.A.; Prow, T.W. Recent advances in physical delivery enhancement of topical drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2830–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.Y.; Kwon, M.; Choi, H.E.; Kim, K.S. Recent advances in transdermal drug delivery systems: A review. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHINGADE, G.M. Review on: Recent trend on transdermal drug delivery system. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2012, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Kim, B.S. Recent advances in polymeric transdermal drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wokovich, A.M.; Prodduturi, S.; Doub, W.H.; Hussain, A.S.; Buhse, L.F. Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) adhesion as a critical safety, efficacy and quality attribute. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong, J.S.; Yun, M.E.; Park, S.N. Surfactant-stable and pH-sensitive liposomes coated with N-succinyl-chitosan and chitooligosaccharide for delivery of quercetin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.; Nair, A.S. Temperature and ultrasound sensitive gatekeepers for the controlled release of chemotherapeutic drugs from mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.H.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, D. A transformable and biocompatible polymer series using ring-opening polymerization of cyclic silane for more effective transdermal drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 440, 135989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, M.W.; Appiah-Ntiamoah, R.; Kim, H. Gallic acid modified alginate self-adhesive hydrogel for strain responsive transdermal delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Li, P. A Porous Hydrogel with High Mechanical Strength and Biocompatibility for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.; Marshall, L.R.; Yoon, J.; Kulesha, A.; Edirisinghe, D.I.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Rathee, P.; Prabhakar, R.; Makhlynets, O.V. Peptide hydrogel with self-healing and redox-responsive properties. Nano Converg. 2022, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wat, E.; Hui, P.C.; Chan, B.; Ng, F.S.; Kan, C.-W.; Wang, X.; Hu, H.; Wong, E.C.; Lau, C.B. Dual-functional transdermal drug delivery system with controllable drug loading based on thermosensitive poloxamer hydrogel for atopic dermatitis treatment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.; Sun, M.; Bu, Y.; Luo, F.; Lin, C.; Lin, Z.; Weng, Z.; Yang, F.; Wu, D. Microcapsule-embedded hydrogel patches for ultrasound responsive and enhanced transdermal delivery of diclofenac sodium. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2330–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Gao, J.; Hu, Z.; John, J.V.S.; Ponder, B.C.; Moro, D. Controlled drug release from hydrogel nanoparticle networks. J. Control Release 2004, 94, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.-Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y.-C.; Xiao, C.; Du, J.-Z. An injectable nanocomposite hydrogel improves tumor penetration and cancer treatment efficacy. Acta Biomater. 2022, 147, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, M.; Davoodi, J.; Dehghan, R.; Zahiri, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Thermosensitive composite hydrogel incorporated with curcumin-loaded nanopolymersomes for prolonged and localized treatment of glioma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mela, A.; Rdzanek, E.; Tysarowski, A.; Sakowicz, M.; Jaroszyński, J.; Furtak-Niczyporuk, M.; Żurek, G.; Poniatowski, Ł.A.; Jagielska, B. The impact of changing the funding model for genetic diagnostics and improved access to personalized medicine in oncology. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2023, 23, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.-R.; Chun, C.; Ahn, S.-W.; Ki, M.-H.; Cho, C.-S.; Song, S.-C. Sustained delivery of human growth hormone using a polyelectrolyte complex-loaded thermosensitive polyphosphazene hydrogel. J. Control Release 2010, 147, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, E.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Ding, X.; Chen, J.; Xi, Q.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Injectable and biodegradable chitosan hydrogel-based drug depot contributes to synergistic treatment of tumors. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 5339–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treenate, P.; Monvisade, P. In vitro drug release profiles of pH-sensitive hydroxyethylacryl chitosan/sodium alginate hydrogels using paracetamol as a soluble model drug. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straccia, M.C.; d’Ayala, G.G.; Romano, I.; Laurienzo, P. Novel zinc alginate hydrogels prepared by internal setting method with intrinsic antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, N.; Xue, H. A novel controlled drug delivery system based on alginate hydrogel/chitosan micelle composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdhan, T.; Ching, S.H.; Prakash, S.; Bhandari, B. Physical and mechanical properties of alginate based composite gels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalitangkoon, J.; Wongkittisin, M.; Monvisade, P. Silver loaded hydroxyethylacryl chitosan/sodium alginate hydrogel films for controlled drug release wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Biofabrication of three-dimensional cellular structures based on gelatin methacrylate-alginate interpenetrating network hydrogel. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 33, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W.; Zuo, D.; Shi, C.; Yu, X.; Chen, R. Alendronate-functionalized double network hydrogel scaffolds for effective osteogenesis. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 977419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Injectable antibacterial conductive hydrogels with dual response to an electric field and pH for localized “smart” drug release. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krathumkhet, N.; Imae, T.; Paradee, N. Electrically controlled transdermal ibuprofen delivery consisting of pectin-bacterial cellulose/polypyrrole hydrogel composites. Cellulose 2021, 28, 11451–11463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, S.; Alemdar, N. Electrically controlled release of 5-fluorouracil from conductive gelatin methacryloyl-based hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 46914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tunesi, M.M.; Soomro, R.A.; Han, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Xu, B. Application of MXenes in environmental remediation technologies. Nano Converg. 2021, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Hu, L.; Xie, J.; He, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, D.; Yao, D.; Su, F. Biosafe, self-adhesive, recyclable, tough, and conductive hydrogels for multifunctional sensors. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5884–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Kang, W.S.; Lee, K.G.; Cho, H.-Y.; Conley, B.; Ahrberg, C.D.; Lim, J.H.; Mo, S.J.; Mun, S.G.; Kim, E.-J. Combinatorial biophysical cue sensor array for controlling neural stem cell fate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, X.; Kim, H.-J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Ling, H.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qu, M. Flexible patch with printable and antibacterial conductive hydrogel electrodes for accelerated wound healing. Biomaterials 2022, 285, 121479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, A.H.; Clare, T.L. Synthesis and characterization of flexible hydrogel electrodes for electrochemical impedance measurements of protective coatings on metal sculptures. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Du, S.; Zhong, W.; Liu, K.; Qu, L.; Chu, F.; Yang, J.; Han, X. Accurate delivery of pristimerin and paclitaxel by folic acid-linked nano-micelles for enhancing chemosensitivity in cancer therapy. Nano Converg. 2022, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Rhim, W.-K.; Cha, S.-G.; Woo, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, C.G.; Han, D.K. Bolstering the secretion and bioactivities of umbilical cord MSC-derived extracellular vesicles with 3D culture and priming in chemically defined media. Nano Converg. 2022, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, R.; Bacharouch, J.; Elkhoury, K.; Messaoud, G.B.; Kahn, C.; Desobry, S.; Linder, M.; Tamayol, A.; Francius, G.; Mano, J. Role of active nanoliposomes in the surface and bulk mechanical properties of hybrid hydrogels. Mater. Today Bio 2020, 6, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, X.; Guo, B. Nanocomposite conductive tough hydrogel based on metal coordination reinforced covalent Pluronic F-127 micelle network for human motion sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 625, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasiński, A.; Zielińska-Pisklak, M.; Oledzka, E.; Sobczak, M. Smart hydrogels-synthetic stimuli-responsive antitumor drug release systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4541–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, Y.M.; Murthy, P.K.; Sreeramulu, J.; Raju, K.M. Swelling behavior of semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels composed of poly (vinyl alcohol) and poly (acrylamide-co-sodium methacrylate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, S.; Chen, X.; Yung, A.; Naderi, A.; Ghovvati, M.; Liu, Y.; Farzad, A.; Mostafavi, A.; Dana, R.; Annabi, N. Development and optimization of an ocular hydrogel adhesive patch using definitive screening design (DSD). Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 1318–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsuriyonk, K.; Paradee, N.; Sirivat, A. Electrically controlled release of anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil from carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ji, Y.; Sun, Q.; Fu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jin, L. Fabrication of cellulose nanocrystal/chitosan hydrogel for controlled drug release. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Xie, S.; Kang, Y.; Shan, X.; Li, Q.; Cai, Z. Biocompatibility evaluation of a 3D-bioprinted alginate-GelMA-bacteria nanocellulose (BNC) scaffold laden with oriented-growth RSC96 cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 129, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadri, R.; Messaoud, G.B.; Tamayol, A.; Aliakbarian, B.; Zhang, H.; Hasan, M.; Sánchez-González, L.; Arab-Tehrany, E. Preparation and characterization of nanofunctionalized alginate/methacrylated gelatin hybrid hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27879–27884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B.; Du, Y.; Han, X. pH-responsive injectable hydrogels with mucosal adhesiveness based on chitosan-grafted-dihydrocaffeic acid and oxidized pullulan for localized drug delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, F.; Browne, D.; Asuri, P. Role of polymer concentration and crosslinking density on release rates of small molecule drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, M.; Guo, B.; Gao, Y.; Yin, Z. Biocompatible conductive hydrogels based on dextran and aniline trimer as electro-responsive drug delivery system for localized drug release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Neofytou, E.; Cahill III, T.J.; Beygui, R.E.; Zare, R.N. Drug release from electric-field-responsive nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, H.; Cheng, S.; Yao, M.; Ji, X.; Zhong, H.; Wang, D.; Fan, X.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. A pH-response chemotherapy synergistic photothermal therapy for tumor suppression and bone regeneration by mussel-inspired Mg implant. Regen. Biomater. 2021, 8, rbab053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, D.; Nayak, S.K.; Maji, S.; Anis, A.; Kim, D.; Pal, K. Environment sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 120, 109220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, M.; Dravid, A.; Aqrawe, Z.; Montgomery, J.; Wu, Z.; Svirskis, D. Conducting polymer hydrogels for electrically responsive drug delivery. J. Control Release 2020, 328, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, M.S.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; Malmström, J. Modulation of hydrogel stiffness by external stimuli: Soft materials for mechanotransduction studies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7578–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Doroudian, M. Synthesis and characterization of semi-conductive nanocomposite based on hydrolyzed collagen and in vitro electrically controlled drug release study. Polymer 2015, 76, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Luo, Y.; Ning, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, H.; Fu, C. Thermo-sensitive electroactive hydrogel combined with electrical stimulation for repair of spinal cord injury. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.-S.; Pillay, V.; Choonara, Y.E.; Du Toit, L.C.; Modi, G.; Naidoo, D.; Kumar, P. A polyvinyl alcohol-polyaniline based electro-conductive hydrogel for controlled stimuli-actuable release of indomethacin. Polymers 2011, 3, 150–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, J.H.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Chung, B.G. Electro-Responsive Conductive Blended Hydrogel Patch. Polymers 2023, 15, 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122608
Ha JH, Lim JH, Lee JM, Chung BG. Electro-Responsive Conductive Blended Hydrogel Patch. Polymers. 2023; 15(12):2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122608
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Jang Ho, Jae Hyun Lim, Jong Min Lee, and Bong Geun Chung. 2023. "Electro-Responsive Conductive Blended Hydrogel Patch" Polymers 15, no. 12: 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122608
APA StyleHa, J. H., Lim, J. H., Lee, J. M., & Chung, B. G. (2023). Electro-Responsive Conductive Blended Hydrogel Patch. Polymers, 15(12), 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122608







