Effect of Spent Coffee Grounds on the Crystallinity and Viscoelastic Behavior of Polylactic Acid Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Preparation
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.2. Thermo-Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.3.3. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
2.3.4. Rheology
2.3.5. Impact Test
2.3.6. Density and Porosity
2.3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. DSC and TGA
3.2. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
3.3. Rheology
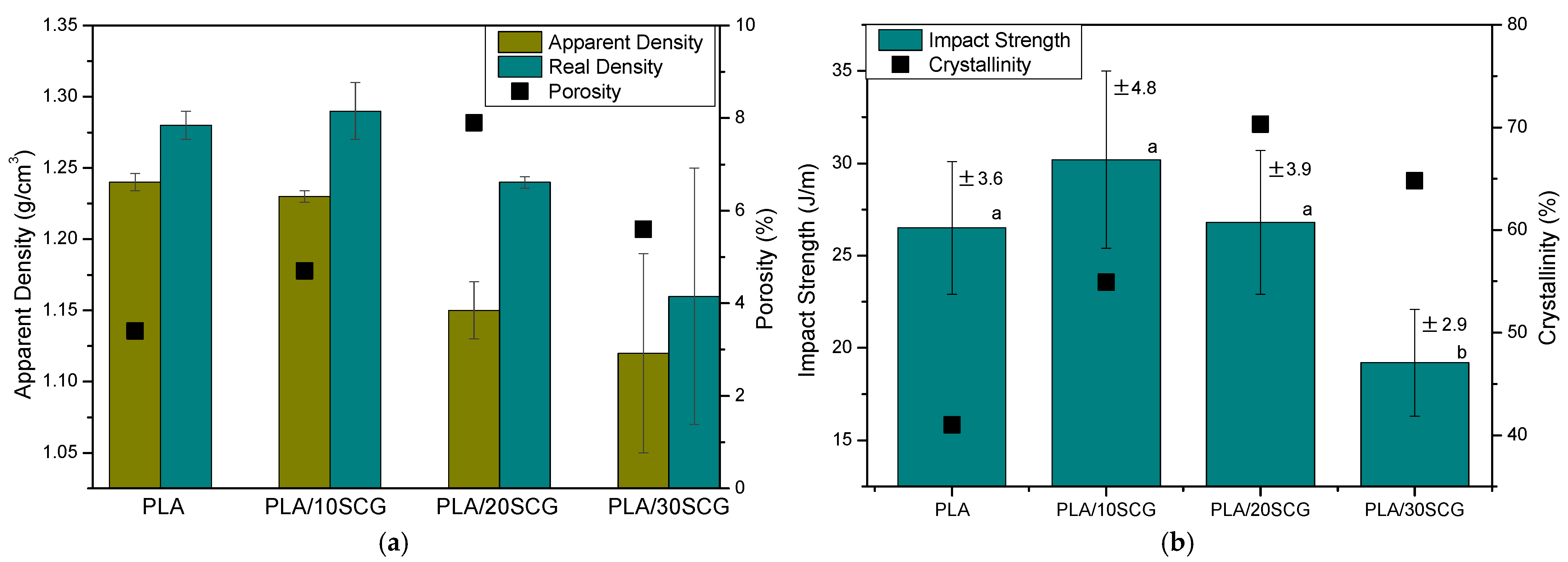
3.4. Impact Strength and Density
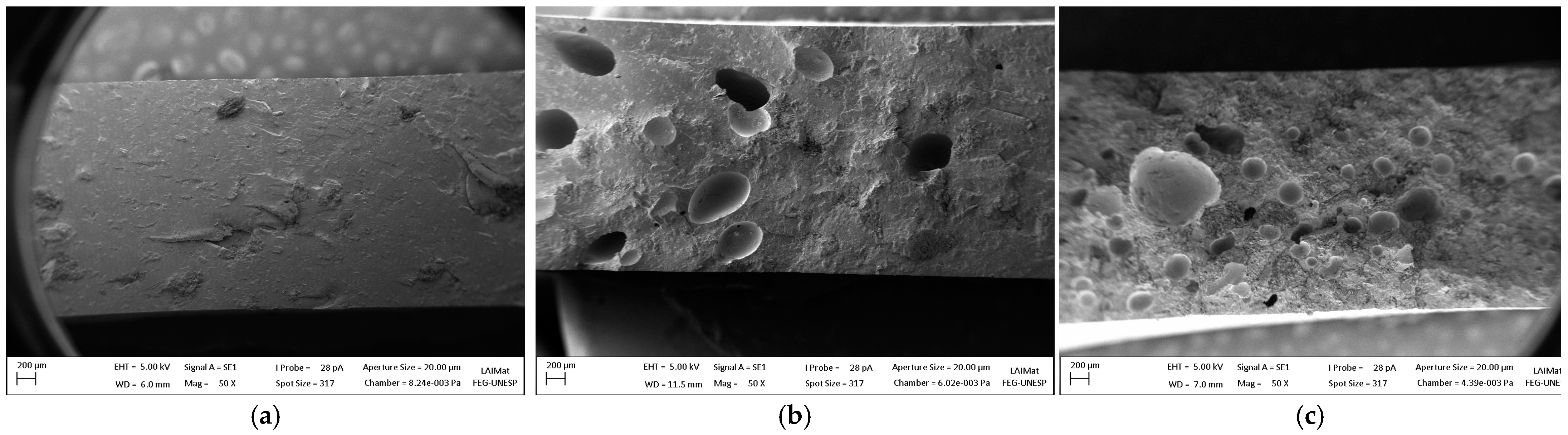
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.H.; Jang, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Park, C.; Yoo, H.Y. Statistical optimization of alkali pretreatment to improve sugars recovery from spent coffee grounds and utilization in lactic acid fermentation. Processes 2021, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkinen, S.; Hakkarainen, M.; Albertsson, A.C.; Södergård, A. From lactic acid to poly(lactic acid) (PLA): Characterization and analysis of PLA and Its precursors. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA composites: From production to properties. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suaduang, N.; Ross, S.; Ross, G.M.; Pratumshat, S.; Mahasaranon, S. Effect of spent coffee grounds filler on the physical and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid) bio-composite films. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 17, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Jiang, Z.; Fang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, M.; Pei, L.; Huang, Z. The Reinforcing Effect of Waste Corrugated Paper Fiber on Polylactic Acid. Polymers 2022, 14, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidarian, P.; Behzad, T.; Karimi, K.; Sain, M. Properties investigation of recycled polylactic acid reinforced by cellulose nanofibrils isolated from bagasse. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 3740–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaowthong, C.; Borůvka, M.; Běhálek, L.; Lenfel, P.; Švec, M.; Dangtungee, R.; Siengchin, S.; Mavinkere, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J. Recycling of sisal fiber reinforced polypropylene and polylactic acid composites: Thermo-mechanical properties, morphology, and water absorption behavior. Waste Manag. 2019, 97, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.A.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Aisyah, H.A.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Hassan, S.A.; Zainudin, E.S.; Sapuan, S.M.; Sharma, S.; Bangar, S.P.; Jumaidin, R.; et al. Natural Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid, Polylactic Acid Blends and Their Composites for Advanced Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNutt, J.; He, Q. (Sophia) Spent coffee grounds: A review on current utilization. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 71, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, A.S.C.D.; de Oliveira, D.M.; Voorwald, H.J.C.; Benini, K.C.C.d.C.; Dumont, M.-J.; Rodrigue, D. Valorization of Spent Coffee Grounds as Precursors for Biopolymers and Composite Production. Polymers 2022, 14, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, A.P.; Pereira, M.d.P.; Passador, F.R.; Montagna, L.S. PLA/Coffee Grounds Composites: A Study of Photodegradation and Biodegradation in Soil. Macromol. Symp. 2020, 394, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songtipya, L.; Limchu, T.; Phuttharak, S.; Songtipya, P.; Kalkornsurapranee, E. Poly(lactic acid)-based Composites Incorporated with Spent Coffee Ground and Tea Leave for Food Packaging Application: A Waste to Wealth. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 553, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, N.; Ferreira, A.; Evtuguin, D.V. New poly(lactic acid) composites produced from coffee beverage wastes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 139, 51434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, I.K.M.; Chan, O.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wong, K.-H.; Tsang, D.C.W. Upcycling of Spent Tea Leaves and Spent Coffee Grounds into Sustainable 3D-Printing Materials: Natural Plasticization and Low-Energy Fabrication. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6230–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopus Database. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/results/results.uri?sort=plf-f&src=s&st1=%28%28%22PLA%22+OR+%22polylactic+acid%22%29+AND+%22coffee+grounds%22%29&sid=2ee44e9e778e4ccad9588324a12431ae&sot=b&sdt=b&sl=66&s=TITLE-ABS-KEY%28%28%28%22PLA%22+OR+%22polylactic+acid%22%29+AND+%22coffee+grounds%22%29%29&origin=searchbasic&editSaveSearch=&yearFrom=Before+1960&yearTo=Present (accessed on 31 May 2023).
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly (Lactic Acid) A Literature Review of Poly (Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Tashiro, K.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Bin, Y. Crystallization behavior of poly(lactic acid)/microfibrillated cellulose composite. Polymer 2013, 54, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perić, M.; Putz, R.; Paulik, C. 3D-printed pla filaments reinforced with nanofibrillated cellulose. J. Renew. Mater. 2020, 8, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, M.; Sun, H.; Zhu, F.; Han, J.; Bhat, G. Preparation and properties of poly (lactic acid)/magnetic Fe3O4 composites and nonwovens. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41929–41935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cacciotti, I.; Mori, S.; Cherubini, V.; Nanni, F. Eco-sustainable systems based on poly(lactic acid), diatomite and coffee grounds extract for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Shi, C.; Sun, S.; Chan, H.; Lu, H.; Nilghaz, A.; Tian, J.; Cao, R. From brown to colored: Polylactic acid composite with micro/nano-structured white spent coffee grounds for three-dimensional printing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 174, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, M.; Han, W.; Li, P. Waste office paper filled polylactic acid composite filaments for 3D printing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 221, 108998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Chang, C.W.; Jahan, K.; Wu, T.M.; Shih, Y.F. Effects of the Grapevine Biochar on the Properties of PLA Composites. Materials 2023, 16, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yuan, T.; Yao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X. PLA/Coffee Grounds Composite for 3D Printing and Its Properties. Forests 2023, 14, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terroba-Delicado, E.; Fiori, S.; Gomez-Caturla, J.; Montanes, N.; Sanchez-Nacher, L.; Torres-Giner, S. Valorization of Liquor Waste Derived Spent Coffee Grains for the Development of Injection-Molded Polylactide Pieces of Interest as Disposable Food Packaging and Serving Materials. Foods 2022, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Ning, J.; Hao, C.; Rock, M.; Amer, M.; Feng, S.; Falahati, M.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, R.K.; et al. No Such Thing as Trash: A 3D-Printable Polymer Composite Composed of Oil-Extracted Spent Coffee Grounds and Polylactic Acid with Enhanced Impact Toughness. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15304–15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Hossain, N.; Qureshi, S.S.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Tanjung, F.A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Siddiqui, M.T.H.; Baloch, H.A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Griffin, G.; et al. Experimental investigation of physicochemical, thermal, mechanical and rheological properties of polylactide/rice straw hydrochar composite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, D.; Carbonell, A.; Samper, M.D.; García-Sanoguera, D.; Balart, R. Green composites based on polypropylene matrix and hydrophobized spend coffee ground (SCG) powder. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 78, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, A.S.C.d.; Voorwald, H.J.C.; Benini, K.C.C.d.C.; Oliveira, D.M.d.; Fernandes, M.F.; Cioffi, M.O.H. Sustainable application of recycled espresso coffee capsules: Natural composite development for a home composter product. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, A.T.; Cho, Y.J.; Chun, B.S. Effect of pretreatments on isolation of bioactive polysaccharides from spent coffee grounds using subcritical water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, B.S.; Park, J.W.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, H.J. Development and Application of Green Composites: Using Coffee Ground and Bamboo Flour. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gond, R.K.; Naik, T.P.; Gupta, M.K.; Singh, I. Development and characterisation of sugarcane bagasse nanocellulose/PLA composites. Mater. Technol. 2022, 37, 2942–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Khalina, A.; Lee, S.H. Importance of interfacial adhesion condition on characterization of plant-fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, M.E.; Pérez-Fonseca, A.A.; Cisneros-López, E.O.; Manríquez-González, R.; Ramírez-Arreola, D.E.; Rodrigue, D.; Robledo-Ortíz, J.R. Effect of Maleated PLA on the Properties of Rotomolded PLA-Agave Fiber Biocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlin, M.N.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Zainudin, E.S.; Ilyas, R.A. Thermal Stability, Dynamic Mechanical Analysis and Flammability Properties of Woven Kenaf/Polyester-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Hybrid Laminated Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.P.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Leng, J. Effect of silk fiber to the mechanical and thermal properties of its biodegradable composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.L.; Mathew, A.P.; Hassan, E.A.; Fadel, S.M.; Oksman, K. Improving cellulose/polypropylene nanocomposites properties with chemical modified bagasse nanofibers and maleated polypropylene. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Safwan, A.; Sanyang, M.L.; Mohammad, F.; Pervaiz, M.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Sain, M. Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of cellulose nanofibers reinforced epoxy composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, M.; Ionita, D.; Iftime, M.M. Dynamic mechanical analysis investigations of pla-based renewable materials: How are they useful? Materials 2020, 13, 5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomfim, A.S.C.D.; Oliveira, D.M.d.; Walling, E.; Babin, A.; Hersant, G.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Dumont, M.-J.; Rodrigue, D. Spent Coffee Grounds Characterization and Reuse in Composting and Soil Amendment. Waste 2022, 1, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, R.; Bartoli, M.; Malucelli, G. Poly(lactic Acid)–Biochar Biocomposites: Effect of Processing and Filler Content on Rheological, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ares, A.; Bouza, R.; Pardo, S.G.; Abad, M.J.; Barral, L. Rheological, mechanical and thermal behaviour of wood polymer composites based on recycled polypropylene. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Duarte, M.E.; Estrada-Moreno, I.A.; López-Martínez, E.I.; Vega-Rios, A. Effect of the Addition of Different Natural Waxes on the Mechanical and Rheological Behavior of PLA—A Comparative Study. Polymers 2023, 15, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriano, T.F.; Silva, A.L.N.D.; Silva, A.H.M.D.F.T.D.; Sousa, A.M.F.D.; Silva, G.M.D.; Rocha, M.G. Thermal, rheological and morphological properties of poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and talc composites. Polímeros Ciência E Tecnol. 2014, 24, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azizi, H.; Ghasemi, I. Investigation on the dynamic melt rheological properties of polypropylene/wood flour composites. Polym. Compos. 2009, 30, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, A.; Maghoolpilehrood, F.; Disfani, M.M.; Horpibulsuk, S. Spent coffee grounds as a non-structural embankment fill material: Engineering and environmental considerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 72, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Das, D. Fibrous biocomposites from nettle (Girardinia diversifolia) and poly(lactic acid) fibers for automotive dashboard panel application. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 130, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, J.F.; Martins, J.T.; Manrich, A.; Luchesi, B.R.; Dantas, A.P.S.; Vanderlei, R.M.; Claro, P.C.; Neto, A.R.d.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Martins, M.A. Thermo-physical and mechanical characteristics of composites based on high-density polyethylene (HDPE) e spent coffee grounds (SCG). J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 2888–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

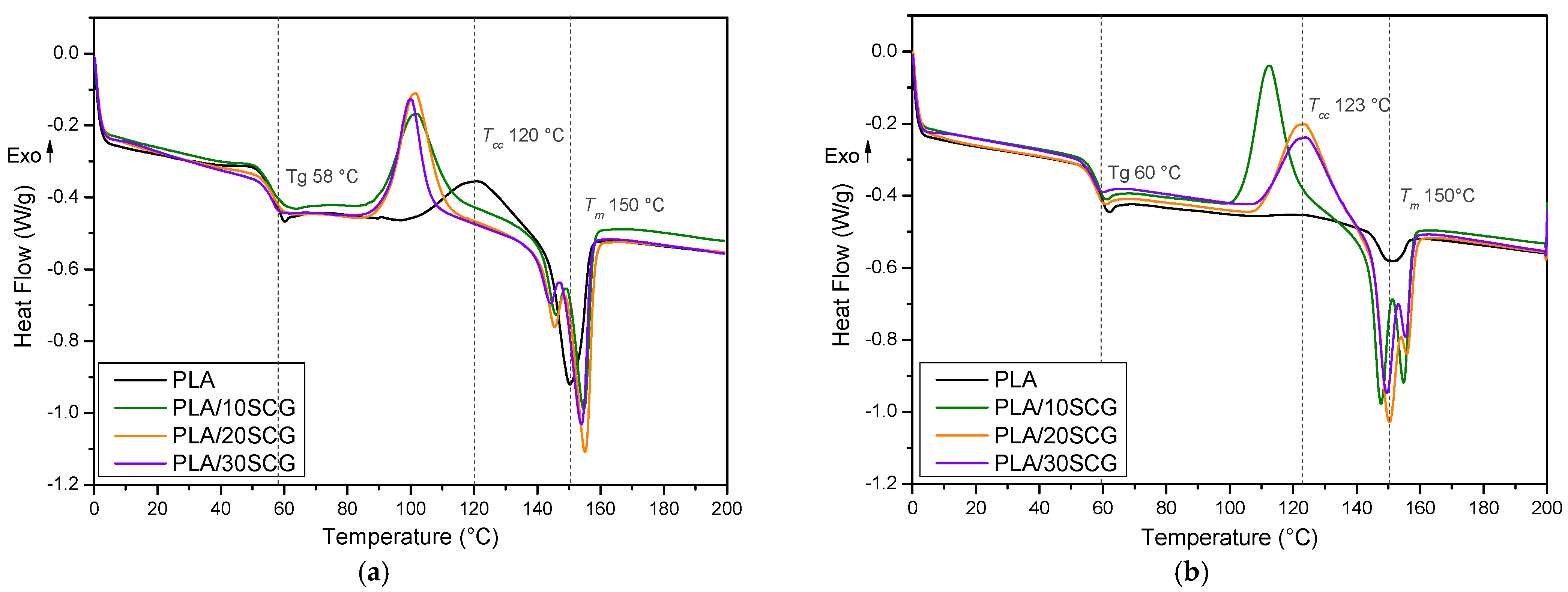

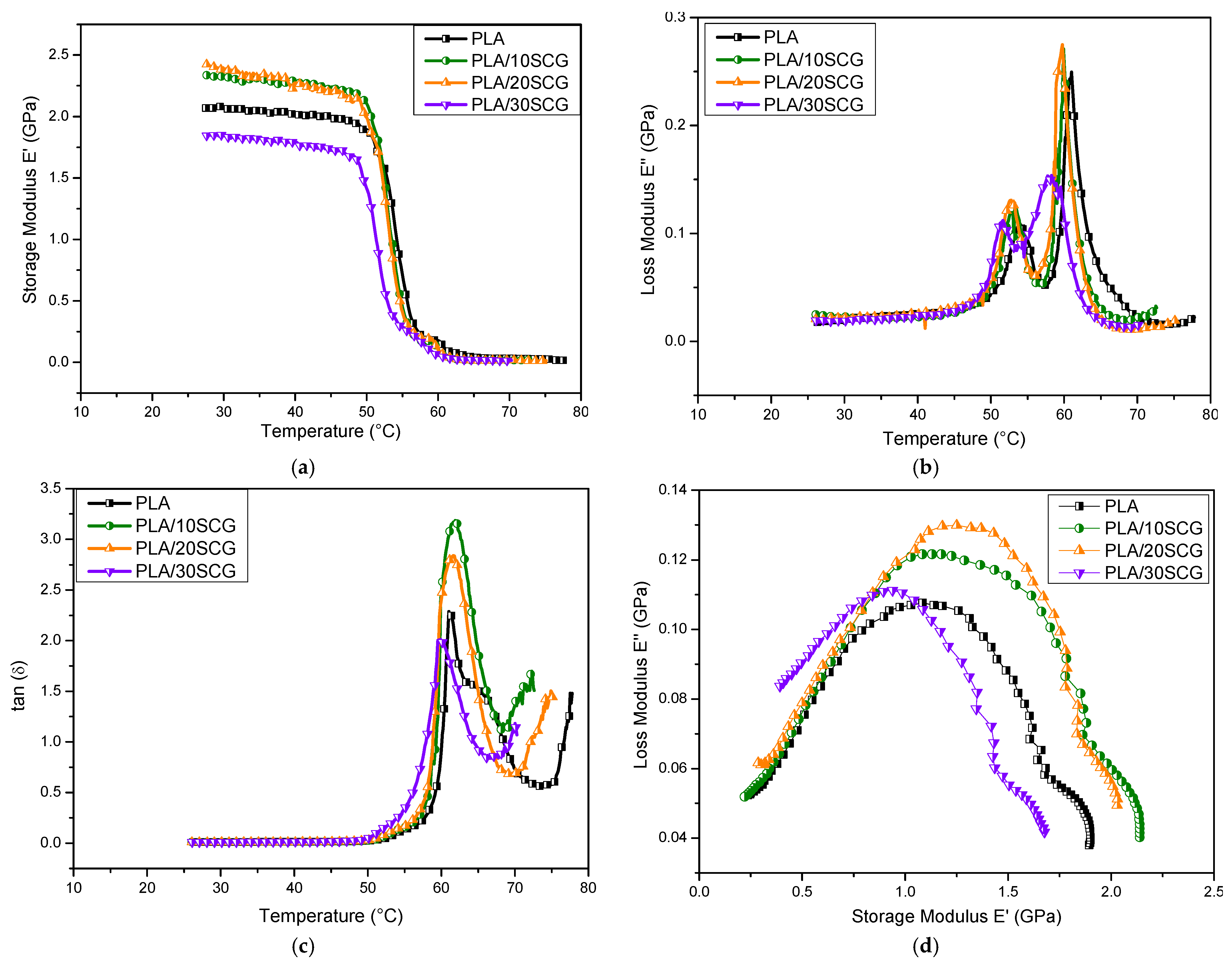
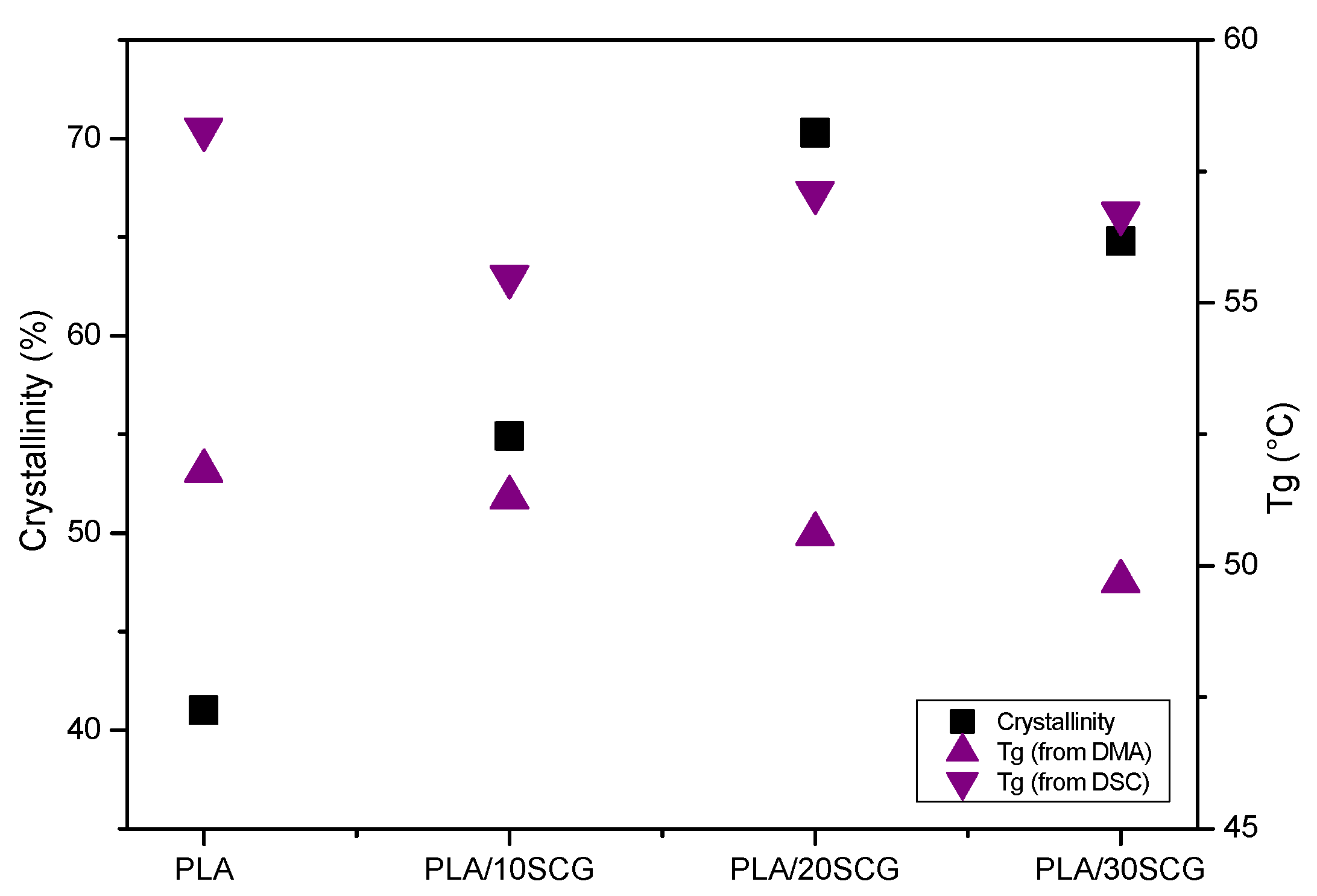

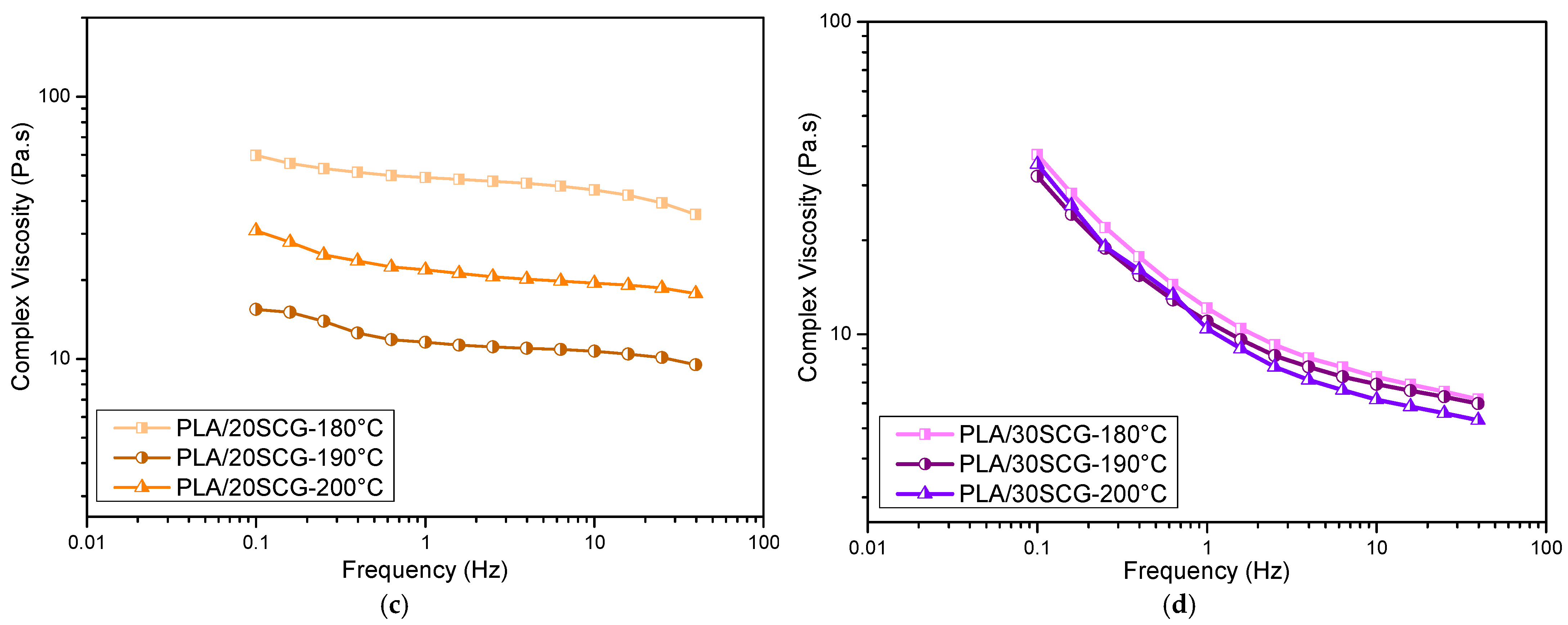


| Sample | 1st Heating | 2nd Heating | TGA | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm1 (°C) | Tm2 (°C) | Tcc (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | ΔHcc (J/g) | Tg (°C) | Xc (%) | Tm1 (°C) | Tm2 (°C) | Tcc (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | ΔHcc (J/g) | Tg (°C) | Xc (%) | Tonset (°C) | Residue600°C (%) | |
| PLA | 150.4 | - | 120.5 | 19.9 | −18.5 | 58.3 | 41.0 | 150.0 | - | - | 3.2 | - | 59.9 | 3.4 | 291.3 | 0.6 |
| PLA/10SCG | 146.0 | 154.7 | 102.1 | 25.2 | −21.1 | 55.5 | 54.9 | 147.7 | 154.9 | 112.5 | 25.6 | −24.3 | 58.9 | 59.2 | 259.3 | 2.9 |
| PLA/20SCG | 145.5 | 155.1 | 101.4 | 28.7 | −24.0 | 57.1 | 70.3 | 150.4 | 155.7 | 123.6 | 25.4 | −22.5 | 58.1 | 63.9 | 252.7 | 4.8 |
| PLA/30SCG | 144.2 | 153.9 | 100.0 | 24.8 | −17.7 | 56.7 | 64.8 | 149.5 | 155.4 | 123.9 | 20.5 | −16.6 | 57.5 | 56.6 | 230.7 | 8.4 |
| Source of Variation | SS | Df | MS | F | p-Value | Fcritical |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG | 450.254 | 3 | 150.0847 | 8.396984 | 0.000543 | 3.08787 |
| WG | 428.9673 | 24 | 17.87364 | |||
| Total | 879.2214 | 27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Bomfim, A.S.C.; de Oliveira, D.M.; Benini, K.C.C.d.C.; Cioffi, M.O.H.; Voorwald, H.J.C.; Rodrigue, D. Effect of Spent Coffee Grounds on the Crystallinity and Viscoelastic Behavior of Polylactic Acid Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122719
de Bomfim ASC, de Oliveira DM, Benini KCCdC, Cioffi MOH, Voorwald HJC, Rodrigue D. Effect of Spent Coffee Grounds on the Crystallinity and Viscoelastic Behavior of Polylactic Acid Composites. Polymers. 2023; 15(12):2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122719
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Bomfim, Anne Shayene Campos, Daniel Magalhães de Oliveira, Kelly Cristina Coelho de Carvalho Benini, Maria Odila Hilário Cioffi, Herman Jacobus Cornelis Voorwald, and Denis Rodrigue. 2023. "Effect of Spent Coffee Grounds on the Crystallinity and Viscoelastic Behavior of Polylactic Acid Composites" Polymers 15, no. 12: 2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122719
APA Stylede Bomfim, A. S. C., de Oliveira, D. M., Benini, K. C. C. d. C., Cioffi, M. O. H., Voorwald, H. J. C., & Rodrigue, D. (2023). Effect of Spent Coffee Grounds on the Crystallinity and Viscoelastic Behavior of Polylactic Acid Composites. Polymers, 15(12), 2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15122719








