Bioinspired Tannic Acid-Modified Coffee Grounds as Sustainable Fillers: Effect on the Properties of Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
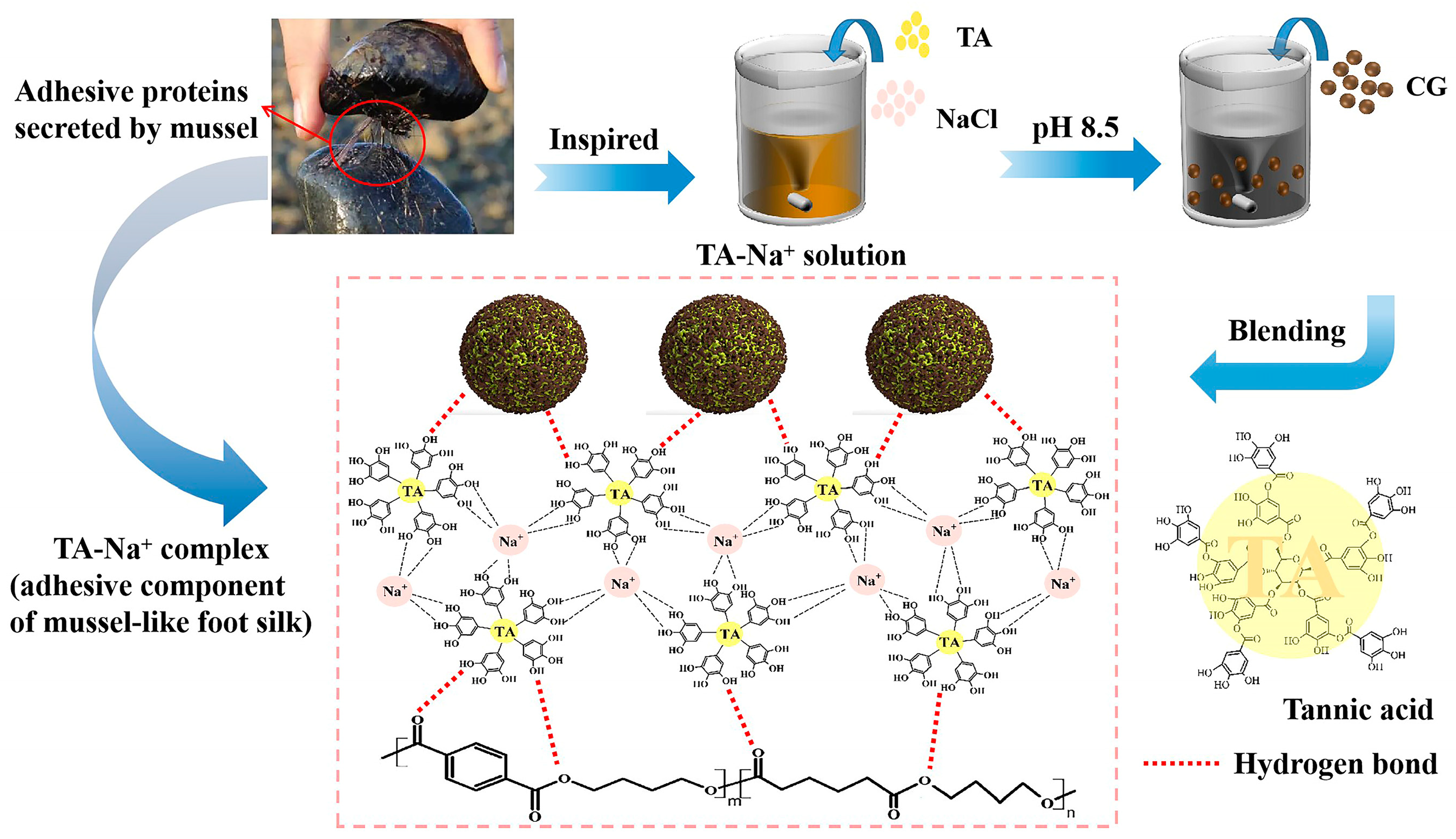
2.2.1. Preparation of CG
2.2.2. Surface Modification of CG
2.2.3. Preparation of PBAT/CG Composites
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of CG
3.2. Characterization of PBAT/CG Composites
3.2.1. Morphology
3.2.2. Rheological Properties
3.2.3. Thermal Properties
3.2.4. Tensile Properties
3.2.5. Thermal Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Coffee Organization. 2021. Available online: https://www.ico.org/prices/new-consumption-table.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Lule, Z.C.; Kim, J. Properties of economical and eco-friendly polybutylene adipate terephthalate composites loaded with surface treated coffee husk. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.J.; Zhang, K.X.; Meng, X.B.; Li, J.J.; Guan, X.T.; Sun, Q.Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.S.; Lin, M.; Liu, M.; et al. New use for spent coffee ground as an adsorbent for tetracycline removal in water. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, X.C.S.; Gallego-Schmid, A.; Najdanovic-Visak, A.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle environmental sustainability of valorisation routes for spent coffee grounds: From waste to resources. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2020, 15, 104751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejenari, V.; Marcu, A.; Ipate, A.; Rusu, D.; Tudorachi, N.; Anghel, I.; Sofran, I.; Lisa, G. Physicochemical characterization and energy recovery of spent coffee grounds. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 4437–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, F.; Barampouti, E.M.; Mai, S.; Bolzonella, D.; Malamis, D.; Moustakas, K.; Loizidou, M. Added-value molecules recovery and biofuels production from spent coffee grounds. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2020, 131, 110007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Jhou, S.Y. Integrating spent coffee grounds and silver skin as biofuels using torrefaction. Renew. Energ. 2020, 148, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.V.; Kim, Y.-T. Spent coffee grounds and coffee silverskin as potential materials for packaging: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 2372–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhbaatar, B.; Yoo, B.; Lim, J.-H. Metal-free high-adsorption-capacity adsorbent derived from spent coffee grounds for methylene blue. RES Adv. 2021, 11, 5118–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, G.V.K.; Babu, A.N.; Kalpana, K.; Ravindhranath, K. Removal of chromium (VI) from water using adsorbent derived from spent coffee grounds. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzano, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; Lucci, P.; Nunez, O.; Fiorini, D.; Giardinieri, A.; Frega, N.G.; Pacetti, D. Spent espresso coffee grounds as a source of anti-proliferative and antioxidant compounds. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 59, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongcumpou, C.; Usapein, P.; Tuntiwiwattanapun, N. Complete utilization of wet spent coffee grounds waste as a novel feedstock for antioxidant, biodiesel, and bio-char production. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 138, 111484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panusa, A.; Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R.; Marrosu, G.; Petrucci, R. Recovery of natural antioxidants from spent coffee grounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4162–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, N.A.; Farag, A.A.; Abo-Dief, H.M.; Tayeb, A.M. Production of biodegradable plastic from agricultural wastes. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaidukova, G.; Platnieks, O.; Aunins, A.; Barkane, A.; Ingrao, C.; Gaidukovs, S. Spent coffee waste as a renewable source for the production of sustainable poly(butylene succinate) biocomposites from a circular economy perspective. Rsc Adv. 2021, 11, 18580–18589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leow, Y.; Yew, P.Y.M.; Chee, P.L.; Loh, X.J.; Kai, D. Recycling of spent coffee grounds for useful extracts and green composites. Rsc Adv. 2021, 11, 2682–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.Y.; Kuan, H.T.N.; Lee, M.C. Characterization of alkaline treatment and fiber content on the physical, thermal, and mechanical properties of ground coffee waste/oxobiodegradable HDPE biocomposites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017, 6258151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, D.M.; Nhung, V.T.; Le Do, T.C.; Ha-Thuc, C.N.; Perre, P. Effective synergistic effect of treatment and modification on spent coffee grounds for sustainable biobased composites. Waste Biomass Valori. 2022, 13, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, Y.G.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.; Ochir, D.; Park, Y.; Kim, J.; Chon, K. Single and competitive adsorptions of micropollutants using pristine and alkali-modified biochars from spent coffee grounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, R.; Jagdale, P.; Bartoli, M.; Tagliaferro, A.; Malucelli, G. Structure-property relationships in polyethylene-based composites filled with biochar derived from waste coffee grounds. Polymers 2019, 11, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Z.H.; Hou, X.Q.; Hwang, S.S.; Li, H.M. The biocomposites properties of compounded poly(lactic acid) with untreated and treated spent coffee grounds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 53092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, H.; Guizani, C.; Dufresne, A. Sustainable biodegradable coffee grounds filler and its effect on the hydrophobicity, mechanical and thermal properties of biodegradable PBAT composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essabir, H.; Raji, M.; Laaziz, S.A.; Rodrique, D.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.E.K. Thermo-mechanical performances of polypropylene biocomposites based on untreated, treated and compatibilized spent coffee grounds. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 149, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, L.H.; Zhang, J.X.; Tan, S.Z.; Cai, X.; Liao, X.Y. Effect of oil extraction on properties of spent coffee ground–plastic composite. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 10205–10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Hou, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, L. Effect of different chemical surface treatments on interfacial compatibility and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates/coffee grounds composites. Polym Compos. 2023, 44, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, H.; Guizani, C.; Dupont, C.; Martin, V.; Jeguirim, M.; Dufresne, A. Utilization of torrefied coffee grounds as reinforcing agent to produce high-quality biodegradable PBAT composites for food packaging applications. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.T.; Jiang, Z.T.; Zhao, X.; Dong, J.; Li, X.T.; Zhang, Q.H. Spent coffee grounds/poly(butylene succinate) biocomposites with robust mechanical property and heat resistance via reactive compatibilization. Compos. Commun. 2022, 29, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Q.; Chen, Z.H.; Boukhir, M.; Song, W.; Zhang, S.B. Bioinspired polydopamine deposition and silane grafting modification of bamboo fiber for improved interface compatibility of poly (lactic acid) composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 201, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.H.; Cheng, H.T.; Zhang, S.B.; Rojas, O.J. Mussel-inspired reinforcement of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester with bamboo fibers. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 296, 126587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Sun, W.; Kim, J.P.; Lu, X.L.; Li, Q.Y.; Lin, M.; Mrowczynski, O.; Rizk, E.B.; Cheng, J.G.; Qian, G.Y.; et al. Development of tannin-inspired antimicrobial bioadhesives. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.Q.; Ji, W.J.; Zhang, S.F.; Huang, Y.X.; Yu, Y.L.; Yu, W.J. Insights into the immobilization mechanism of tannic acid on bamboo cellulose fibers. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 182, 114836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.T.; Shi, M.Q.; Dong, C.X.; Liu, L.F.; Gao, C.J. Applications of tannic acid in membrane technologies: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.F.; Zhang, N.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.W.; Deng, H.N.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Lv, E.G.; Li, Z.; Qiao, M.; et al. Incorporation of silver-embedded carbon nanotubes coated with tannic acid into polyamide reverse osmosis membranes toward high permeability, antifouling, and antibacterial properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 11388–11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Ma, J.Y.; Feng, X.; Cheng, J.X.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.P.; Chen, L. An effective surface modification of uhmwpe fiber for improving the interfacial adhesion of epoxy resin composites. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.S.; Cao, D.D.; Ji, S.P.; Zhang, X.M.; Muhoza, B. Tannic acid-assisted cross-linked nanoparticles as a delivery system of eugenol: The characterization, thermal degradation and antioxidant properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinbakhsh, N.; Wang, T.; Rodriguez-Uribe, A.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Characterization of wastes and coproducts from the coffee industry for composite material production. Bioresources 2016, 11, 7637–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballesteros, L.F.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Chemical, functional, and structural properties of spent coffee grounds and coffee silverskin. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2014, 7, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moraczewski, K.; Malinowski, R.; Łączny, D.; Macko, M. Surface modification of maize stem with polydopamine and tannic acid coatings. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Shao, L.; Dong, D.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Bio-inspired natural polyphenol cross-linking poly(vinyl alcohol) films with strong integrated strength and toughness. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 69966–69972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Lin, Q.Q.; Yu, Y.L.; Yu, W.J. Functionalization of wood fibers based on immobilization of tannic acid and in situ complexation of Fe (Ⅱ) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejima, H.; Richardson, J.J.; Liang, K.; Best, J.P.; Koeverden, M.P.; Such, G.K.; Cui, J.; Caruso, F. One-step assembly of coordination complexes for versatile film and particle engineering. Science 2013, 341, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Pang, B.; Zhou, S.; Li, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, S.; Yuan, T.; Sun, R. Economically competitive biodegradable PBAT/lignin composites: Effect of lignin methylation and compatibilizer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5338–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, H.D.; Musa, L.; Abubakar, A. The mechanical and dimensional properties of rice husk-unsaturated polyester composites. Polym. Plast Technol. 2005, 44, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obasi, H.C. Peanut husk filled polyethylene composites: Effects of filler content and compatibilizer on properties. J. Polym. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, M.; Weng, Y.X. Improved properties of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/calcium carbonate films through silane modification. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Chudasama, B.; Chang, B.P.; Mekonnen, T. Robust and sustainable PBAT–Hemp residue biocomposites: Reactive extrusion compatibilization and fabrication. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 215, 109014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, L.; Titone, V.; Teresi, R.; Scarlata, M.C.; Lo Re, G.; La Mantia, F.P.; Lopresti, F. Biocomposite PBAT/lignin blown films with enhanced photo-stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkanen, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Journey to polymeric materials composed exclusively of simple lignin derivatives. Acs Sustain Chem Eng. 2016, 4, 5223–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.U.R.; Prabhakar, M.N.; Wang, H.; Song, J. The influence of particle size and surface treatment of filler on the properties of oyster shell powder filled polypropylene composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 2420–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapa, P.; Tabil, L.; Schoenau, G. Physical and frictional properties of non-treated and steam exploded barley, canola, oat and wheat straw grinds. Powder Technol. 2010, 201, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Xie, J.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Qiu, S.; Chen, K.; Li, J.; Ma, C.; et al. Biodegradable Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) composites reinforced with bio-based nanochitin: Preparation, enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 137, 48485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, R.S.; Aeinehvand, R.; Kim, K.; Otaigbe, J.U. Structure and biocompatibility of bioabsorbable nanocomposites of aliphatic-aromatic copolyester and cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2179–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniyasamy, S.; Reddy, M.M.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A. Biodegradable green composites from bioethanol co-product and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate). Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Abdelwahab, M.A.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Biobased ternary blends of lignin, poly(lactic acid), and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate): The effect of lignin heterogeneity on blend morphology and compatibility. J. Polym. Environ. 2014, 22, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Mohanty, A.; Misra, M. A new biodegradable injection moulded bioplastic from modified soy meal and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate): Effect of plasticizer and denaturant. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, F.; Lin, B.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C. High content corn starch/Poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) composites with high-performance by physical-chemical dual compatibilization. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 159, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | C | O | Na | Cl | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 70.23 | 29.63 | 0.14 | 0 | 100.00 |
| CG-TA | 66.10 | 31.42 | 0.83 | 1.65 | 100.00 |
| CG-OH | 74.47 | 25.09 | 0.44 | 0 | 100.00 |
| CG-OH-TA | 58.04 | 31.26 | 1.95 | 8.75 | 100.00 |
| Sample | Tonset/°C | ΔHm/J·g−1 | Tc/°C | ΔHc/J·g−1 | Xc/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBAT | 97.4 | 9.5 | 55.7 | 17.6 | 8.3 |
| PBAT/CG | 97.3 | 5.6 | 76.0 | 10.7 | 7.0 |
| PBAT/CG-TA | 97.2 | 5.8 | 75.6 | 10.5 | 7.3 |
| PBAT/CG-OH | 94.3 | 5.7 | 74.8 | 11.0 | 7.1 |
| PBAT/CG-OH-TA | 93.9 | 5.5 | 76.0 | 11.0 | 6.9 |
| Sample | T5%/°C | Td-max/°C | Residue/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Td-max1 | Td-max2 | |||
| PBAT | 326.9 | - | 402.2 | 4.0 |
| PBAT/CG | 272.9 | 305.0 | 398.2 | 7.2 |
| PBAT/CG-TA | 267.8 | 294.1 | 395.9 | 7.6 |
| PBAT/CG-OH | 267.0 | 311.8 | 393.7 | 7.2 |
| PBAT/CG-OH-TA | 264.1 | 303.5 | 393.2 | 8.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, G.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, T. Bioinspired Tannic Acid-Modified Coffee Grounds as Sustainable Fillers: Effect on the Properties of Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132769
Wang J, Zhao D, Jiang G, Wu Y, Shen Y, Wang T. Bioinspired Tannic Acid-Modified Coffee Grounds as Sustainable Fillers: Effect on the Properties of Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate Composites. Polymers. 2023; 15(13):2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132769
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiaxin, Dong Zhao, Guodong Jiang, Yong Wu, Yucai Shen, and Tingwei Wang. 2023. "Bioinspired Tannic Acid-Modified Coffee Grounds as Sustainable Fillers: Effect on the Properties of Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate Composites" Polymers 15, no. 13: 2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132769
APA StyleWang, J., Zhao, D., Jiang, G., Wu, Y., Shen, Y., & Wang, T. (2023). Bioinspired Tannic Acid-Modified Coffee Grounds as Sustainable Fillers: Effect on the Properties of Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate Composites. Polymers, 15(13), 2769. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15132769





