Effect of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Modified by Citric and Oleic Acids on the Physicochemical and Magnetic Properties of Hybrid Electrospun P(VDF-TrFE) Scaffolds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
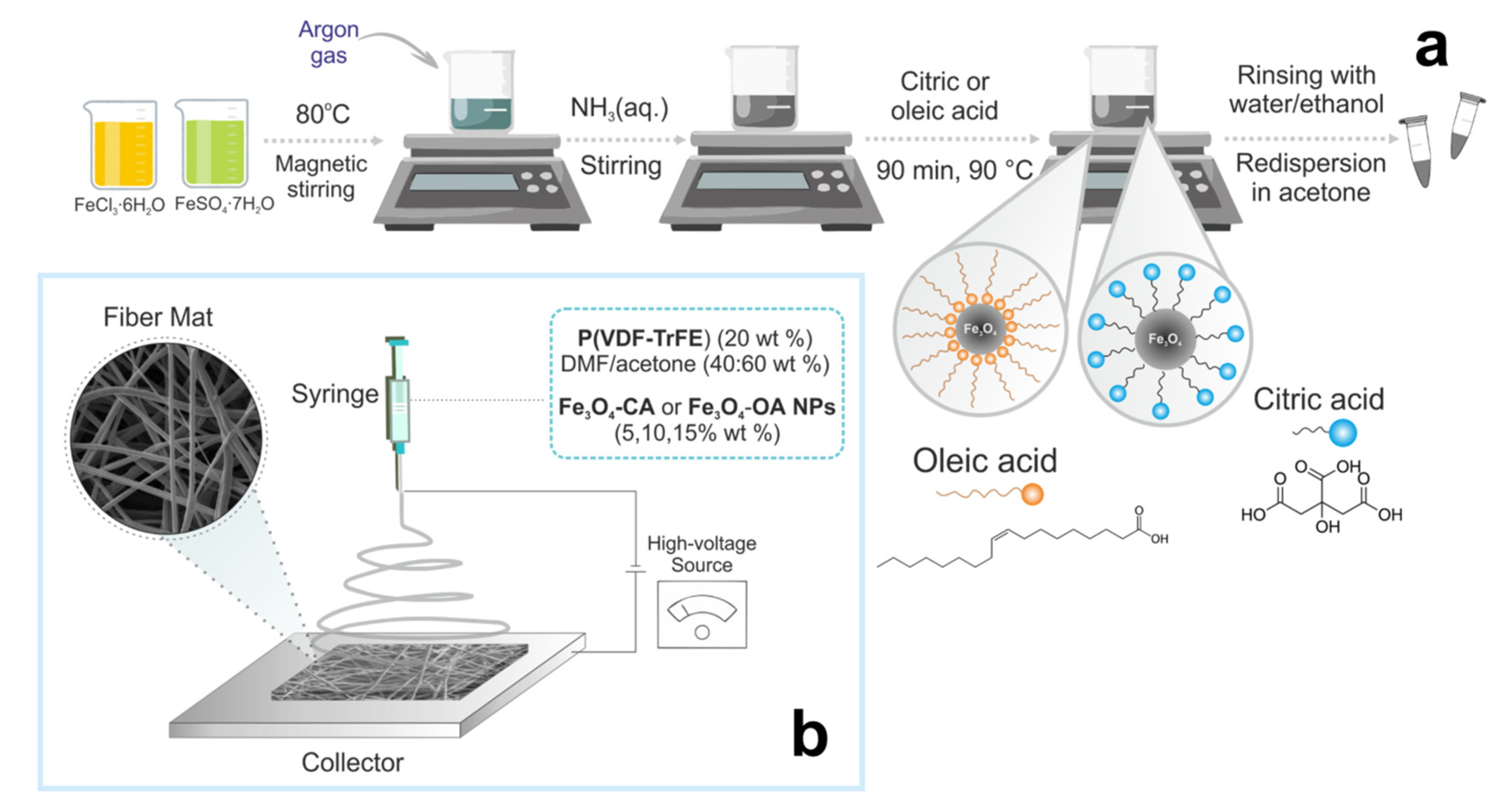
2.2. Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles Modified by Citric and Oleic Acids
2.3. Preparation of Electrospinning Solutions
2.4. Electrospinning Parameters
2.5. Characterization of the Samples
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narita, F.; Fox, M. A review on piezoelectric, magnetostrictive, and magnetoelectric materials and device technologies for energy harvesting applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapat, K.; Shubhra, Q.T.; Zhou, M.; Leeuwenburgh, S. Piezoelectric nano-biomaterials for biomedicine and tissue regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, J.; Oliveira, H.; Sandre, O.; Lecommandoux, S. Magnetic responsive polymer composite materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7099–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, N.X. Magnetoelectric materials and devices. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 041114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, S.; Nagar, H.; Singh, I.; Sehgal, S. Smart materials types, properties and applications: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Spinks, G.M.; Fay, C.; Cheng, Z.; Raad, R.; Xi, J.; Foroughi, J. Wearable electronic textiles from nanostructured piezoelectric fibers. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopyl, S.; Surmenev, R.; Surmeneva, M.; Fetisov, Y.; Kholkin, A. Magnetoelectric effect: Principles and applications in biology and medicine—A review. Mater. Today Bio. 2021, 12, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.; Lima, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Martins, P. Magnetoelectrics: Three centuries of research heading towards the 4.0 industrial revolution. Materials 2020, 13, 4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palneedi, H.; Annapureddy, V.; Priya, S.; Ryu, J. Status and perspectives of multiferroic magnetoelectric composite materials and applications. Actuators 2016, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Q. Design, synthesis and processing of PVDF-based dielectric polymers. IET Nanodielectrics 2018, 1, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Magnetite nanoparticles: Synthesis methods–A comparative review. Methods 2022, 199, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.M.; Chou, M.H. Polymorphism, piezoelectricity and sound absorption of electrospun PVDF membranes with and without carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 127, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, L.L.; Soleimani, H.; Yahya, N.; Abbas, Z.; Ridwan, A.T.; Wahaab, F.A. Investigation of the broadband microwave absorption of citric acid coated Fe3O4/PVDF composite using finite element method. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, W.; Luo, L.; Zhu, Y. Ultrahigh dielectric constant composites based on the oleic acid modified ferroferric oxide nanoparticles and polyvinylidene fluoride. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 092904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, N.; Tambe, P.; Panda, B. Surface modified iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanosheets reinforced PVDF nanocomposites: Influence on morphology, thermal and magnetic properties. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2022, 51, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, I.; Gul, B.Y.; Esmaeili, M.S.; Pekgenc, E.; Teber, O.O.; Tuncay, G.; Karimi, H.; Parvaz, S.; Maleki, A.; Vatanpour, V. Modification of PVDF membranes by incorporation Fe3O4@ Xanthan gum to improve anti-fouling, anti-bacterial, and separation performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Simple synthesis of smart magnetically driven fibrous films for remote controllable oil removal. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, A.; Cespedes, O.; Russell, S. Controlling dielectric and magnetic properties of PVdF/magnetite nanocomposite fibre webs. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 2014, 102946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, M.; Li, F.; Weng, K.; Qi, K.; Liu, C.; Ni, Q.; Tao, X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, W. Preparation and properties of PVDF/Fe3O4 nanofibers with magnetic and electret effects and their application in air filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 1900856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ning, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, N. Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 1386–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvin, V.V.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Mukhortova, Y.R.; Belyakova, E.O.; Wagner, D.V.; Chelobanov, B.P.; Laktionov, P.P.; Sukhinina, E.V.; Pershina, A.G.; Kholkin, A.L. Magnetoactive electrospun hybrid scaffolds based on poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) and magnetite particles with varied sizes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhortova, Y.R.; Pryadko, A.S.; Chernozem, R.V.; Pariy, I.O.; Akoulina, E.A.; Demianova, I.V.; Zharkova, I.I.; Ivanov, Y.F.; Wagner, D.V.; Bonartsev, A.P. Fabrication and characterization of a magnetic biocomposite of magnetite nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide for biomedical applications. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2022, 29, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhu, H. Effect of calcination temperature of TiO2 on the crystallinity and the permittivity of PVDF-TrFE/TiO2 composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.V.; Kareva, K.V.; Zhuravlev, V.A.; Dotsenko, O.A.; Minin, R.V. Investigation of BaFe12O19 Hexaferrites Manufactured by Various Synthesis Methods Using a Developed Pulsed Magnetometer. Inventions 2023, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favela-Camacho, S.E.; Samaniego-Benítez, E.J.; Godínez-García, A.; Avilés-Arellano, L.M.; Pérez-Robles, J.F. How to decrease the agglomeration of magnetite nanoparticles and increase their stability using surface properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 574, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, E.; Botvin, V.; Galstenkova, M.; Mukhortova, Y.; Wagner, D.; Gerasimov, E.; Surmeneva, M.; Kholkin, A.; Surmenev, R. A Comprehensive Study of Synthesis and Analysis of Anisotropic Iron Oxide and Oxyhydroxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhou, L.; Lu, Y. Direct Continuous Synthesis of Oleic Acid-Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in a Microflow System. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 4320–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Noqta, O.A.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Simple rapid stabilization method through citric acid modification for magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebanova, O.N.; Lazor, P. Raman spectroscopic study of magnetite (FeFe2O4): A new assignment for the vibrational spectrum. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 174, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Suh, C.-Y.; Cho, S.-W.; Roh, K.-M.; Kwon, H.; Song, K.; Shon, I.-J. A new method for the identification and quantification of magnetite–maghemite mixture using conventional X-ray diffraction technique. Talanta 2012, 94, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.I.; Laia, C.A.; Carvalho, A.; Pereira, L.C.; Coutinho, J.T.; Ferreira, I.M.; Novo, C.M.; Borges, J.P. Iron oxide nanoparticles stabilized with a bilayer of oleic acid for magnetic hyperthermia and MRI applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 383, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dai, C.; Hu, Y. Aqueous aggregation behavior of citric acid coated magnetite nanoparticles: Effects of pH, cations, anions, and humic acid. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharuddin, A.A.; Ang, B.C.; Hussein, N.A.A.; Andriyana, A.; Wong, Y.H. Mechanisms of highly stabilized ex-situ oleic acid-modified iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized with 4-pentynoic acid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, J.; Wijn, H.P.J. Ferrites; Philips Technical Library: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 1959; Volume 278. [Google Scholar]
- Arefi, M.; Kazemi Miraki, M.; Mostafalu, R.; Satari, M.; Heydari, A. Citric acid stabilized on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for transamidation of carboxamides, phthalimide, urea and thiourea with amines under neat conditions. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R. Magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamie, S.; Parseh, B.; Ahadian, M.M.; Naghdabadi, F.; Saber, R.; Soleimani, M. Heat transfer of PEGylated cobalt ferrite nanofluids for magnetic fluid hyperthermia therapy: In vitro cellular study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 462, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.; Barick, K.; Bahadur, D. Development of citrate-stabilized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Conjugation and release of doxorubicin for therapeutic applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryadko, A.A.S.; Mukhortova, Y.R.; Chernozem, R.V.; Pariy, I.; Alipkina, S.I.; Zharkova, I.I.; Dudun, A.A.; Zhuikov, V.A.; Moisenovich, A.M.; Bonartseva, G.A. Electrospun Magnetic Composite Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate/Magnetite Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications: Composition, Structure, Magnetic Properties, and Biological Performance. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 3999–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15382–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.; De Saja, J.; Constantino, C. Tailoring the structural properties of PVDF and P (VDF-TrFE) by using natural polymers as additives. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeen, A.; Kala, M.; Jayalakshmy, M.; Thomas, S.; Philip, J.; Rouxel, D.; Bhowmik, R.; Kalarikkal, N. Flexible and self-standing nickel ferrite–PVDF-TrFE cast films: Promising candidates for high-end magnetoelectric applications. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 16961–16973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigoni, A.; Brambilla, L.; Bertarelli, C.; Serra, G.; Tommasini, M.; Castiglioni, C. P(VDF-TrFE) nanofibers: Structure of the ferroelectric and paraelectric phases through IR and Raman spectroscopies. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37779–37796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; He, Q.; Sun, J.; Xia, G.; Song, R. Crystallization behavior and electroactive properties of PVDF, P(VDF-TrFE) and their blend films. Polym. Test. 2017, 57, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Cebe, P. Crystal polymorphism in electrospun composite nanofibers of poly(vinylidene fluoride) with nanoclay. Polymer 2009, 50, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Zhang, L.; Su, R.; Wang, K.; Fong, H.; Zhu, L. Understanding polymorphism formation in electrospun fibers of immiscible poly(vinylidene fluoride) blends. Polymer 2011, 52, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, A.; Li, J.; Han, C.C. Polymorphism control of poly(vinylidene fluoride) through electrospinning. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 2159–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Hu, X.; Zheng, G.; Lv, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Sun, D. Spectroscopic evidence for a high fraction of ferroelectric phase induced in electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fibers. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 24952–24958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Xia, W.; Zhu, X.; Sun, T.; Cao, C.; Zhang, L. Enhanced piezoelectric and acoustic performances of poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) films for hydroacoustic applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 5711–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, R., Jr.; Botta, M.M. Effect of crystallization temperature on the phase transitions of P(VDF/TrFE) copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1998, 36, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryadko, A.S.; Mukhortova, Y.R.; Chernozem, R.V.; Shlapakova, L.E.; Wagner, D.V.; Romanyuk, K.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Kholkin, A.; Surmenev, R.A.; Surmeneva, M.A. Comprehensive Study on the Reinforcement of Electrospun PHB Scaffolds with Composite Magnetic Fe3O4–rGO Fillers: Structure, Physico-Mechanical Properties, and Piezoelectric Response. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 41392–41411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Xing, J. PVDF-based and its Copolymer-Based Piezoelectric Composites: Preparation Methods and Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 5528–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shui, L.; Shen, S.; Yang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F. P(VDF-TrFE)/PMMA blended films with enhanced electrowetting responses and superior energy storage performance. Polymers 2019, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.-L.; Mai, Z.-H.; Xie, Q.; Bao, R.-Y.; Yang, W.; Xie, B.-H.; Yang, M.-B. Induced formation of dominating polar phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Positive ion–CF2 dipole or negative ion–CH2 dipole interaction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 9104–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Tang, M.; Wang, Y.; Hou, D.; Li, X.; Wang, J. A novel Cu-BTC@ PVA/PVDF Janus membrane with underwater-oleophobic/hydrophobic asymmetric wettability for anti-fouling membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
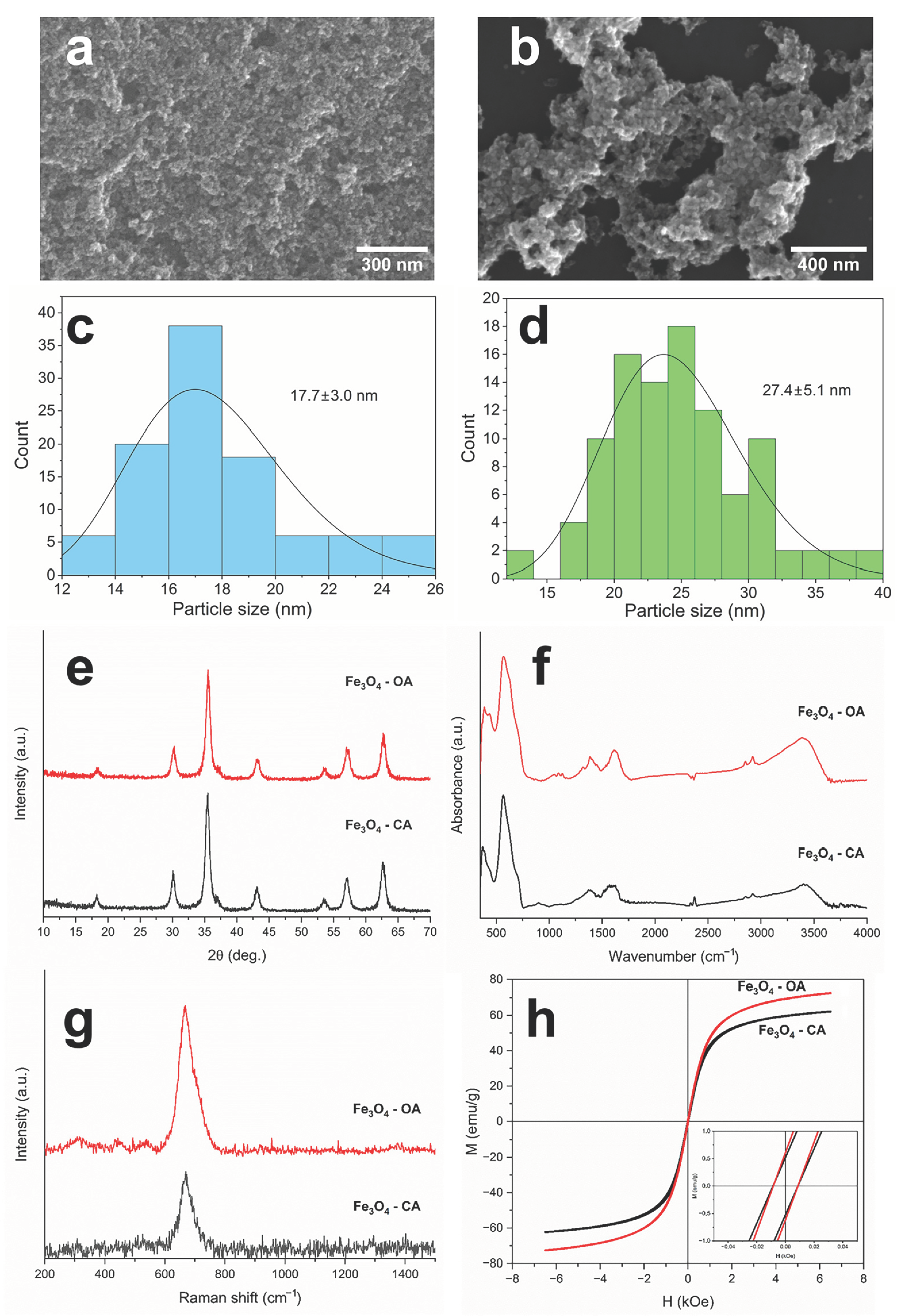



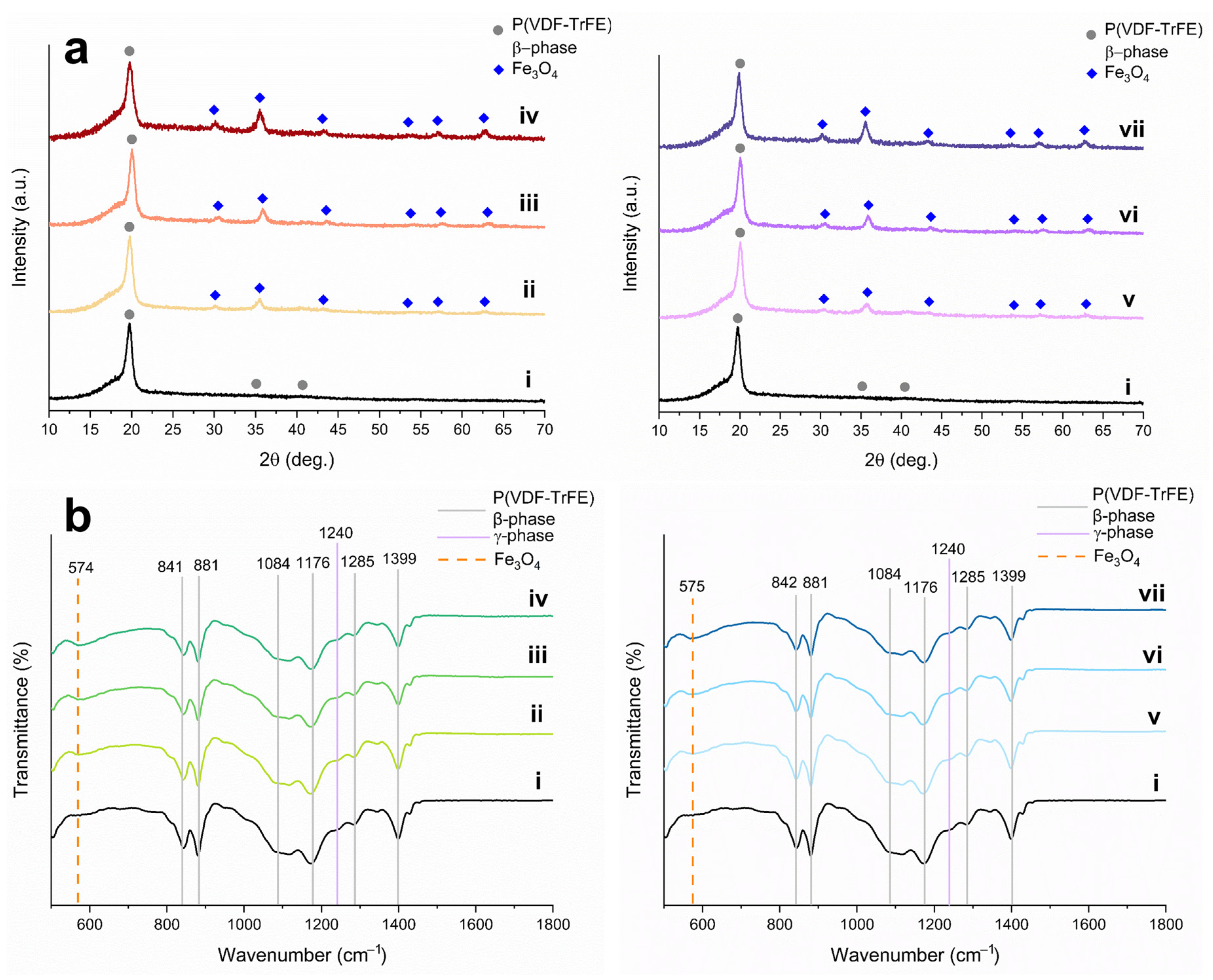


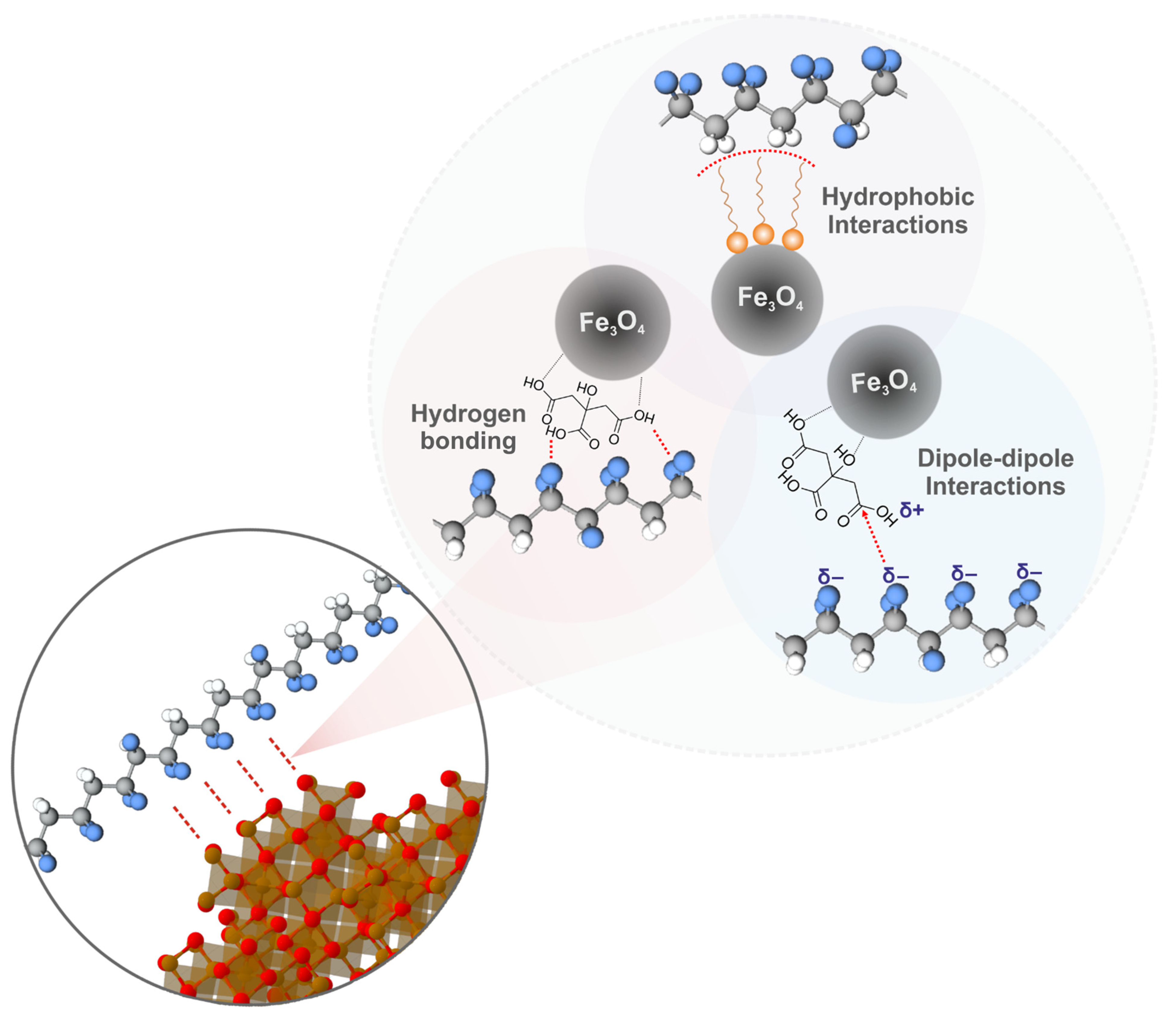
| Sample | Ms, emu/g | Mra, emu/g | Hc, Oe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4-CA | 61.9 ± 1.9 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 10.0 ± 0.5 |
| Fe3O4-OA | 72.6 ± 3.6 | 0.6 ± 0.03 | 8.0 ± 0.4 |
| Sample | Tm, °C | ΔHm, J/g | Xc,% |
|---|---|---|---|
| P(VDF-TrFE) | 147.4 | 27.30 | 60.7 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-CA 5% | 147.7 | 25.58 | 59.8 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-CA 10% | 147.8 | 22.80 | 56.3 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-CA 15% | 148.4 | 29.04 | 75.9 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-OA 5% | 148.2 | 32.00 | 74.8 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-OA 10% | 148.4 | 26.68 | 65.9 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-OA 15% | 147.9 | 29.42 | 76.9 |
| Sample | Ms, emu/g | Mra, emu/g | Hc, Oe |
|---|---|---|---|
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-CA (5 wt.%) | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 0.14 | 28 ± 1 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-CA (10 wt.%) | 7.9 ± 0.4 | 0.18 | 22 ± 1 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-CA (15 wt.%) | 10.0 ± 0.5 | 0.26 | 24 ± 1 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-OA (5 wt.%) | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 0.16 | 35 ± 2 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-OA (10 wt.%) | 6.8 ± 0.3 | 0.23 | 30 ± 2 |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Fe3O4-OA (15 wt.%) | 8.8 ± 0.4 | 0.16 | 17 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Botvin, V.; Fetisova, A.; Mukhortova, Y.; Wagner, D.; Kazantsev, S.; Surmeneva, M.; Kholkin, A.; Surmenev, R. Effect of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Modified by Citric and Oleic Acids on the Physicochemical and Magnetic Properties of Hybrid Electrospun P(VDF-TrFE) Scaffolds. Polymers 2023, 15, 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143135
Botvin V, Fetisova A, Mukhortova Y, Wagner D, Kazantsev S, Surmeneva M, Kholkin A, Surmenev R. Effect of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Modified by Citric and Oleic Acids on the Physicochemical and Magnetic Properties of Hybrid Electrospun P(VDF-TrFE) Scaffolds. Polymers. 2023; 15(14):3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143135
Chicago/Turabian StyleBotvin, Vladimir, Anastasia Fetisova, Yulia Mukhortova, Dmitry Wagner, Sergey Kazantsev, Maria Surmeneva, Andrei Kholkin, and Roman Surmenev. 2023. "Effect of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Modified by Citric and Oleic Acids on the Physicochemical and Magnetic Properties of Hybrid Electrospun P(VDF-TrFE) Scaffolds" Polymers 15, no. 14: 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143135
APA StyleBotvin, V., Fetisova, A., Mukhortova, Y., Wagner, D., Kazantsev, S., Surmeneva, M., Kholkin, A., & Surmenev, R. (2023). Effect of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Modified by Citric and Oleic Acids on the Physicochemical and Magnetic Properties of Hybrid Electrospun P(VDF-TrFE) Scaffolds. Polymers, 15(14), 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143135












