MWCNT-Coated Glass Fabric/Phenol Composite Heating Panel Fabricated by Resin Infusion Process
Abstract
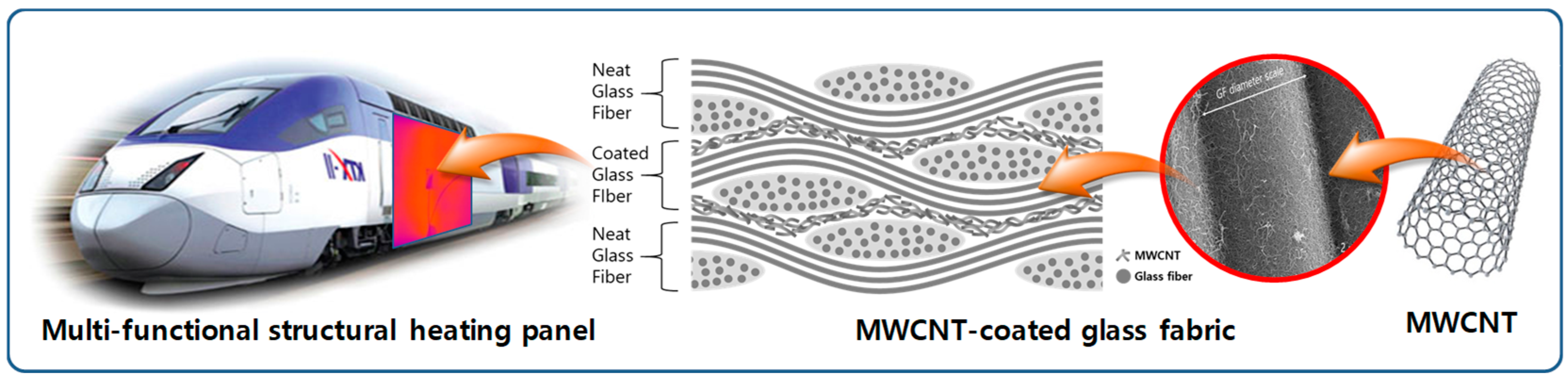
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
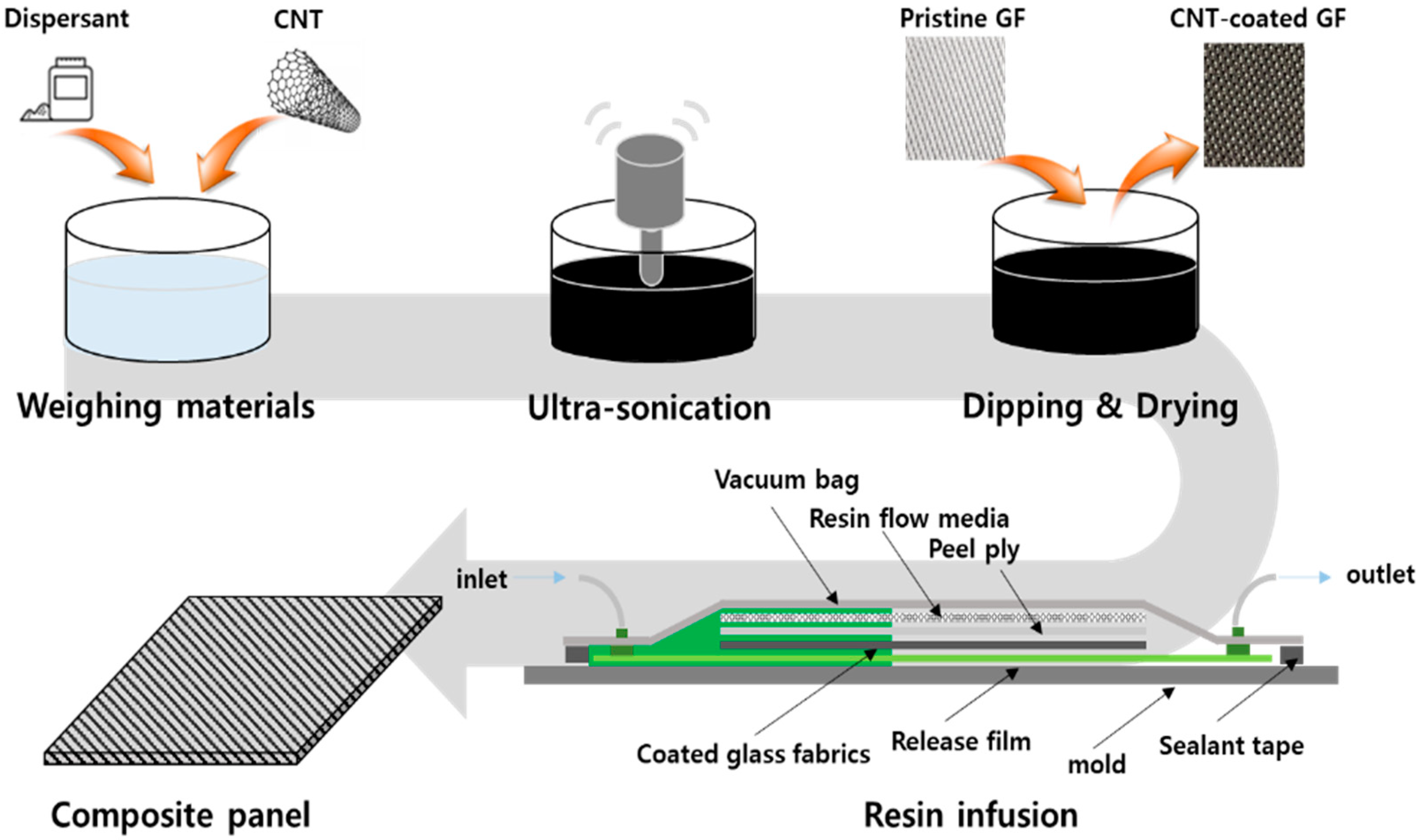
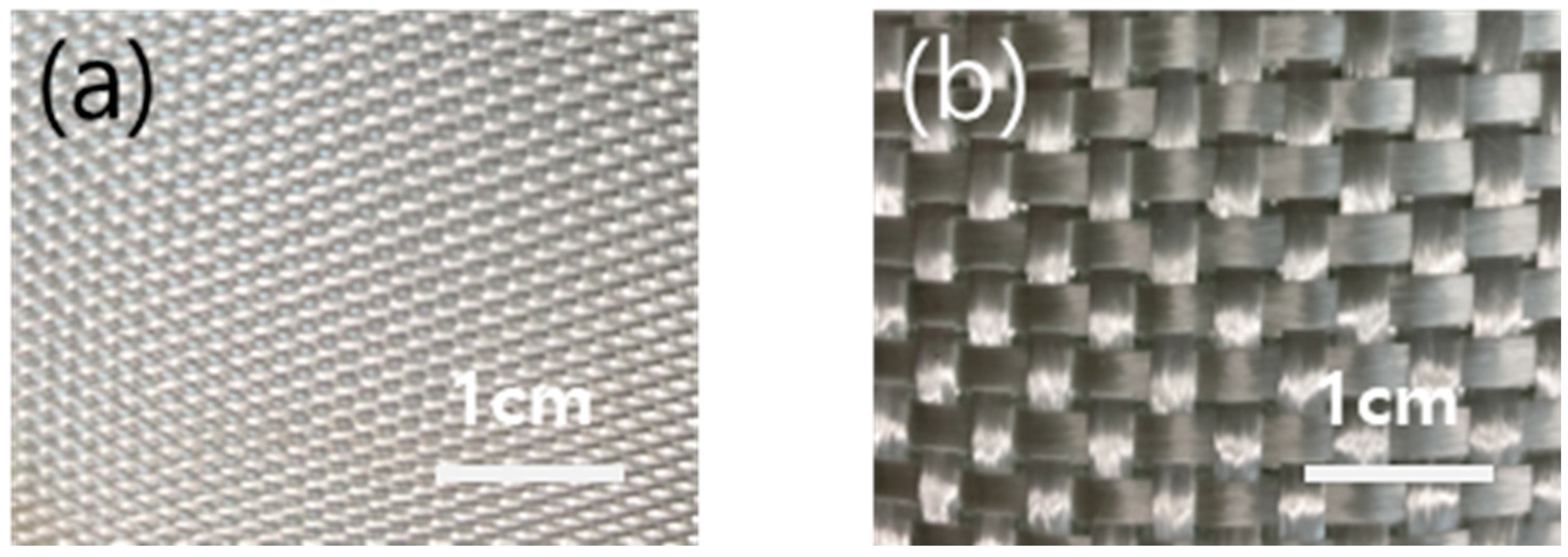
2.1. Fabrication of MWCNT-Coated GF Fabric
2.2. Fabrication of MWCNT-Coated GF Fabric/Phenolic Resin Composite
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
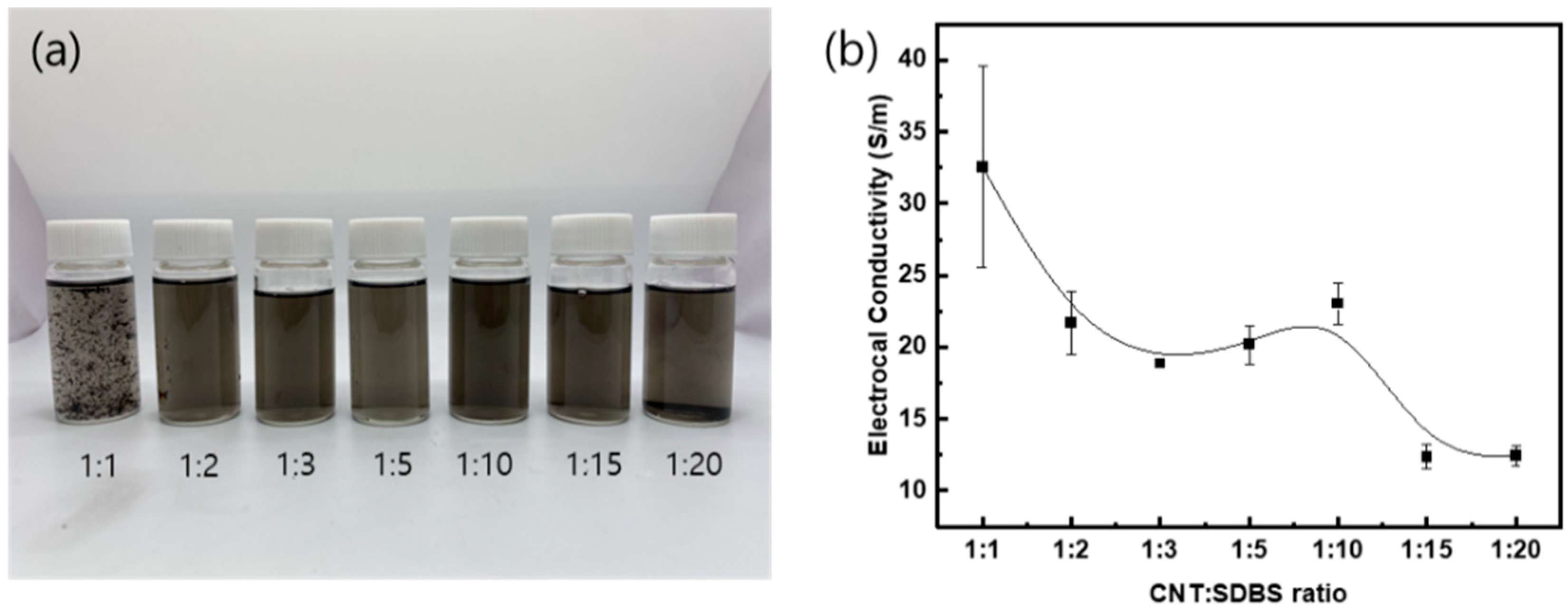
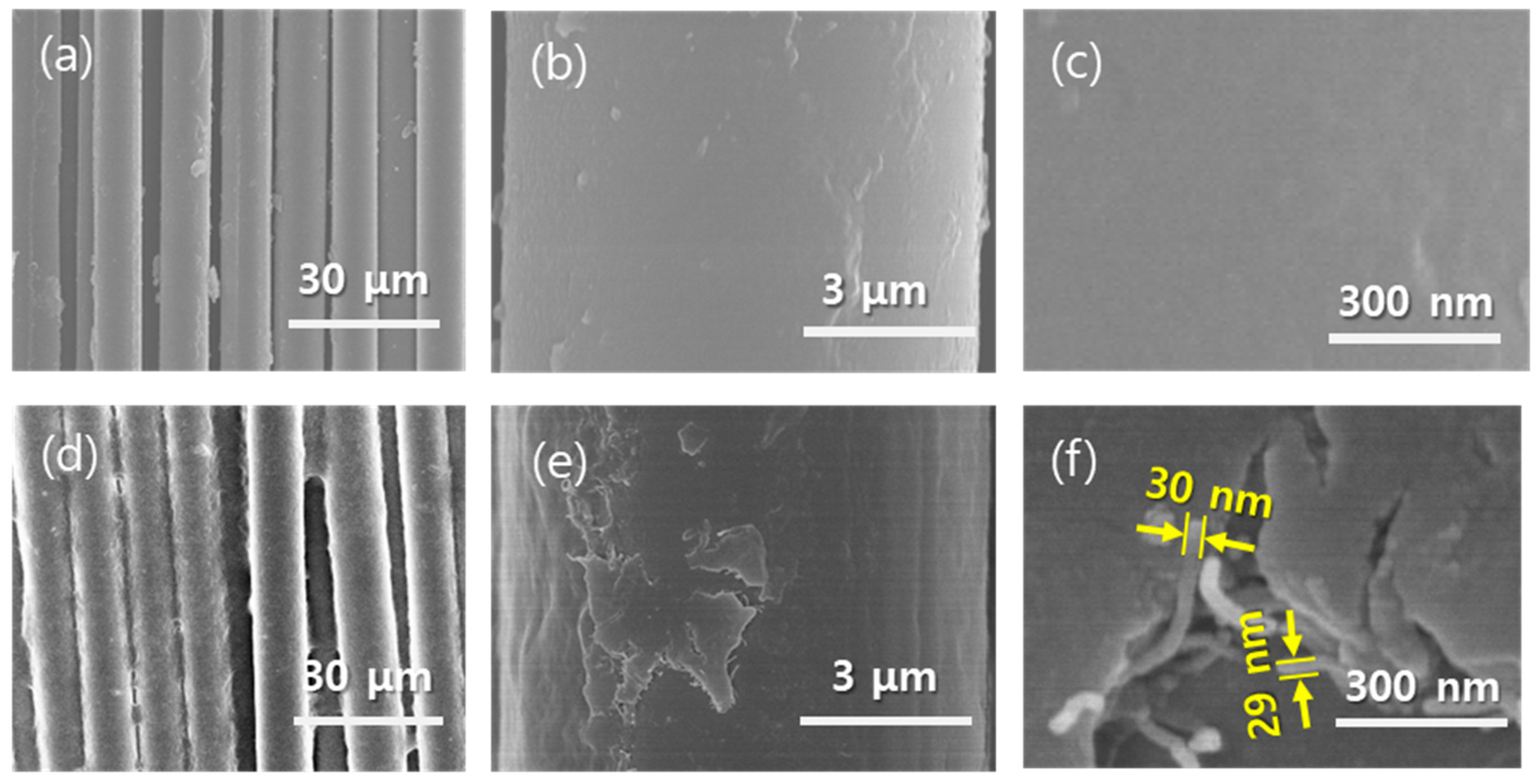
3.1. Dispersion of MWCNTs
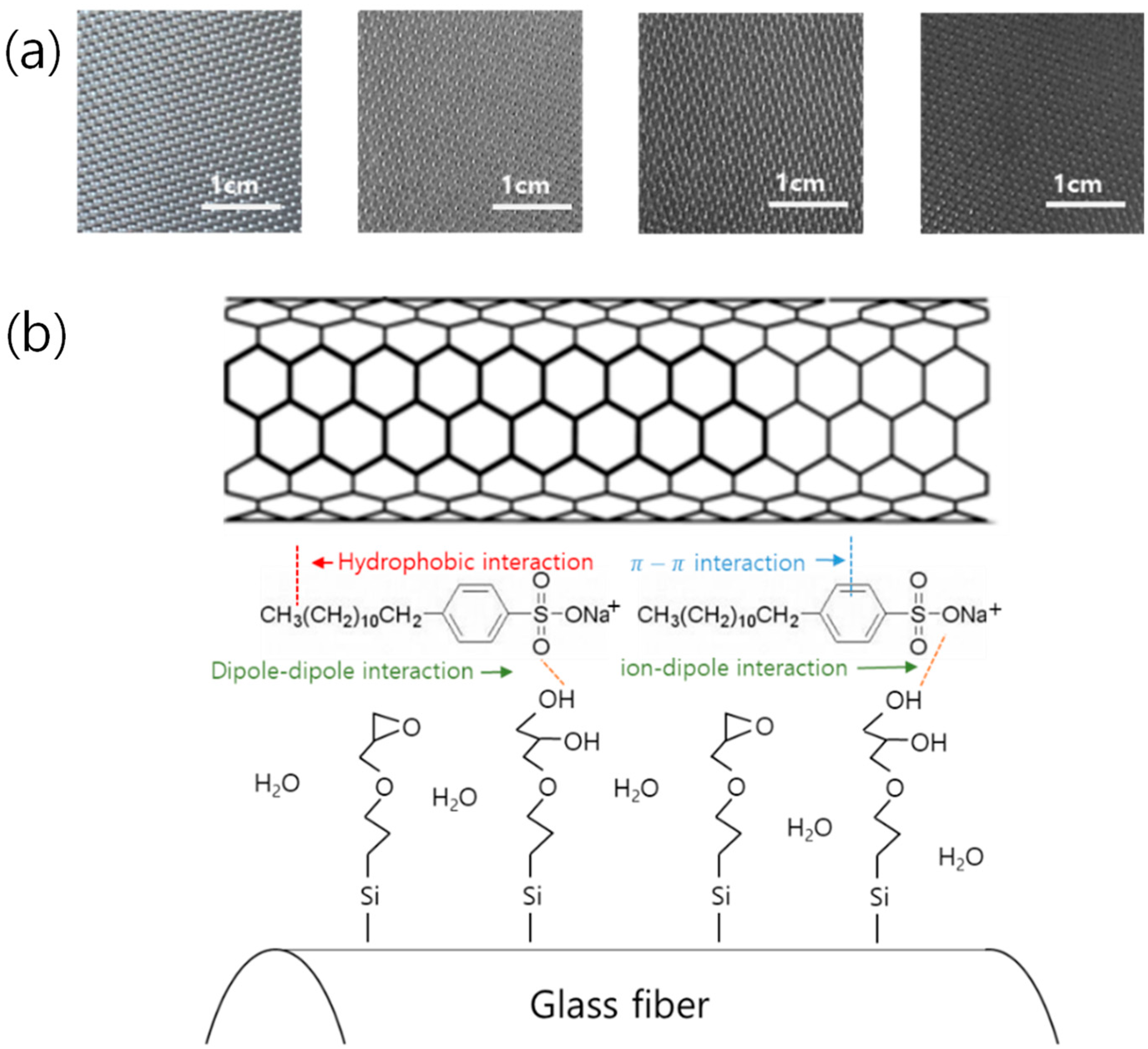
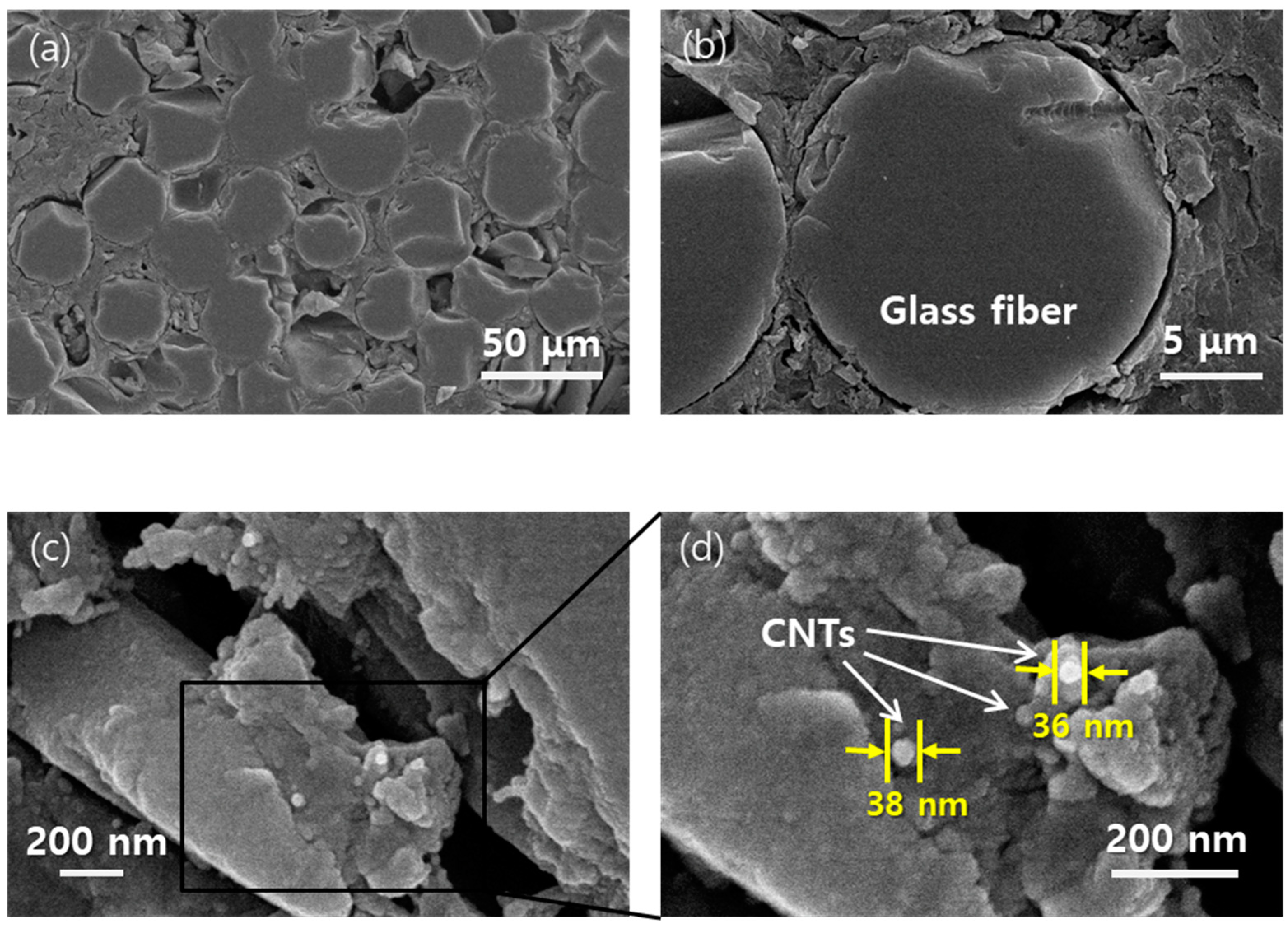
3.2. Microstructures
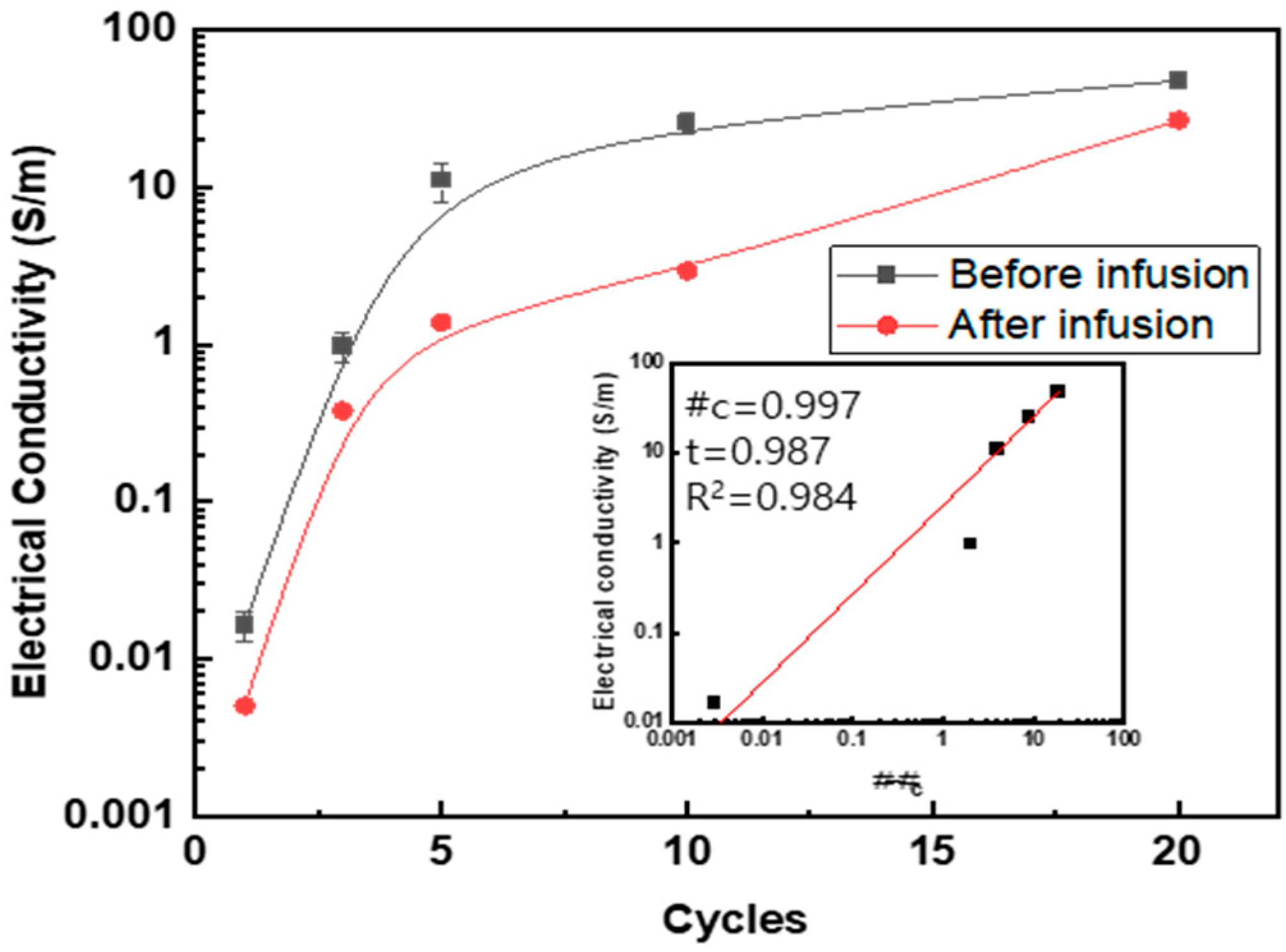
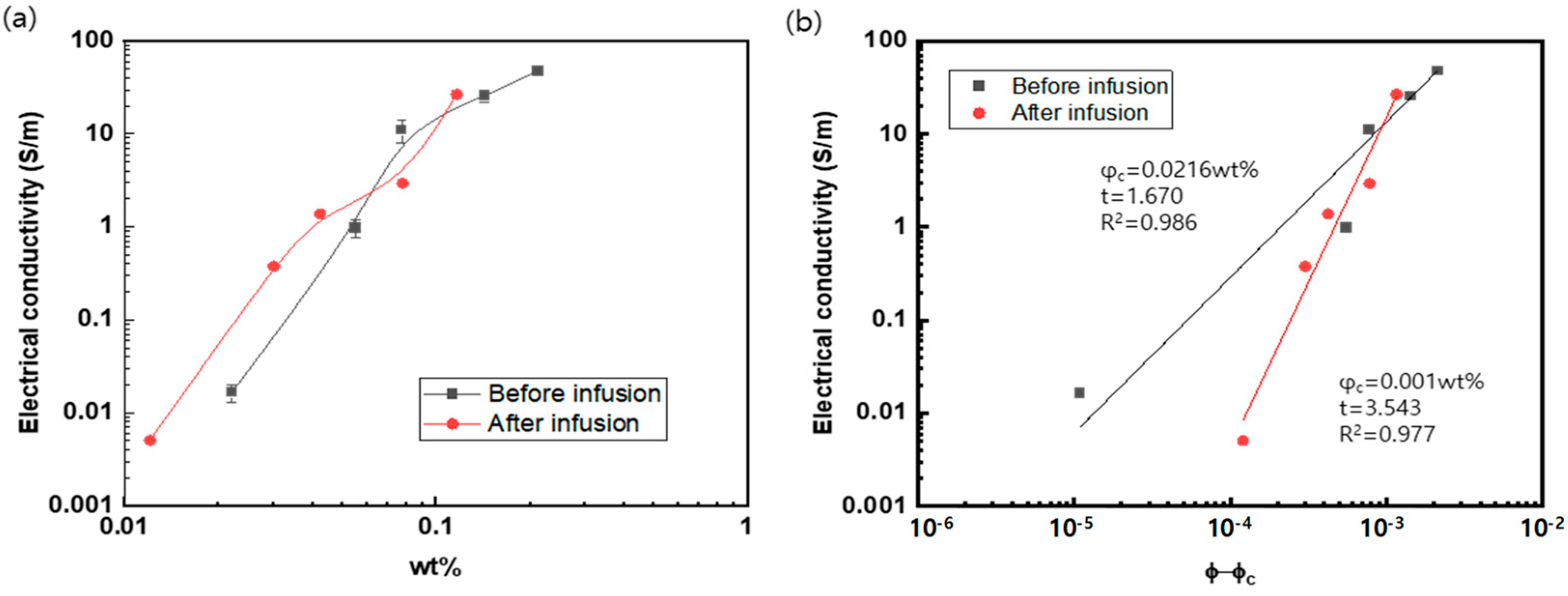
3.3. Electrical Property
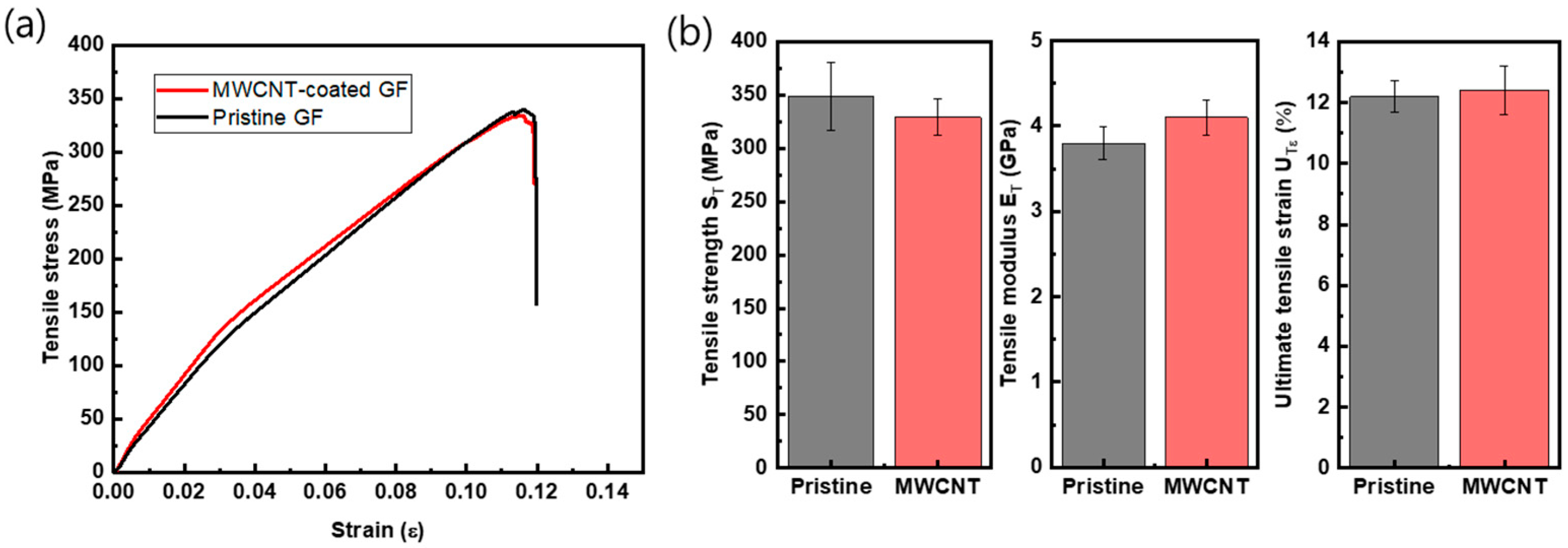
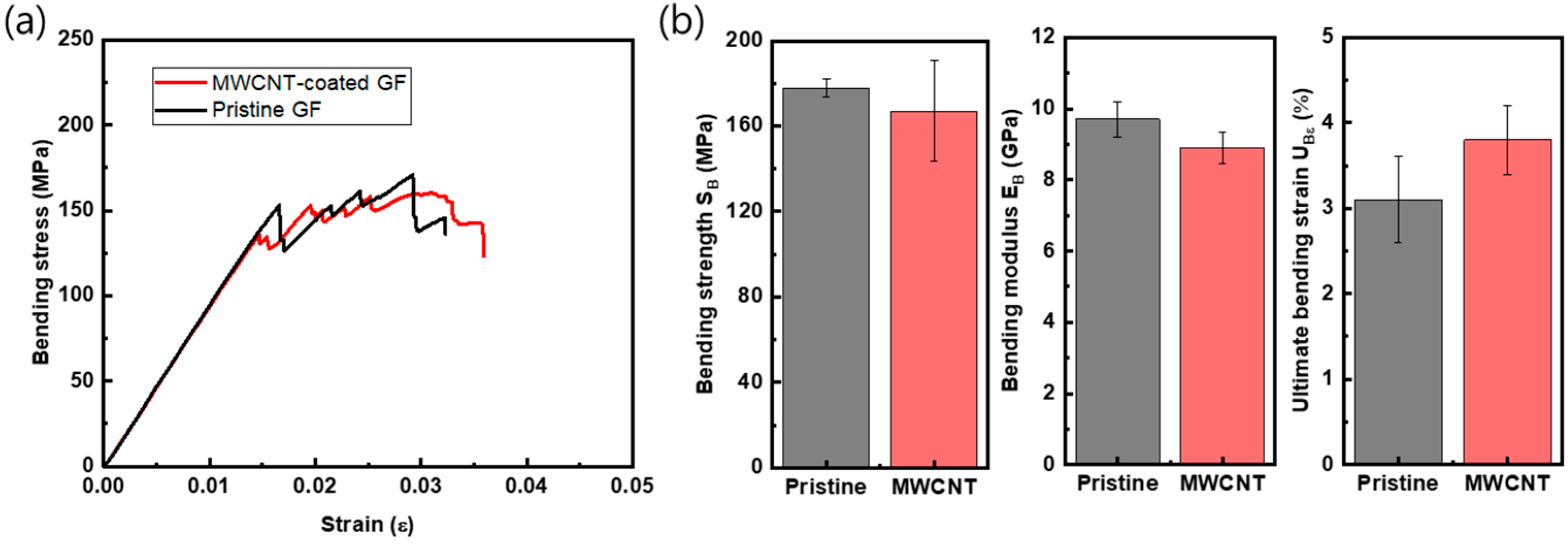
3.4. Mechanical Property
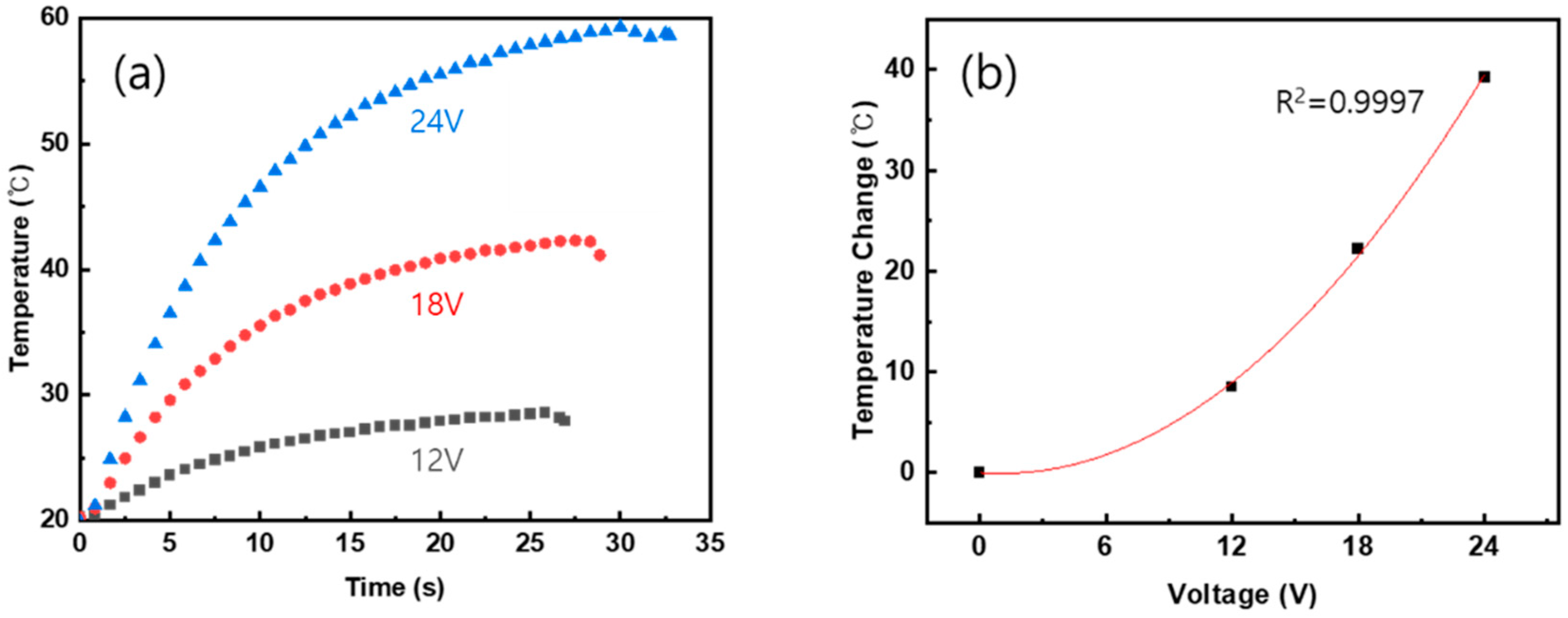
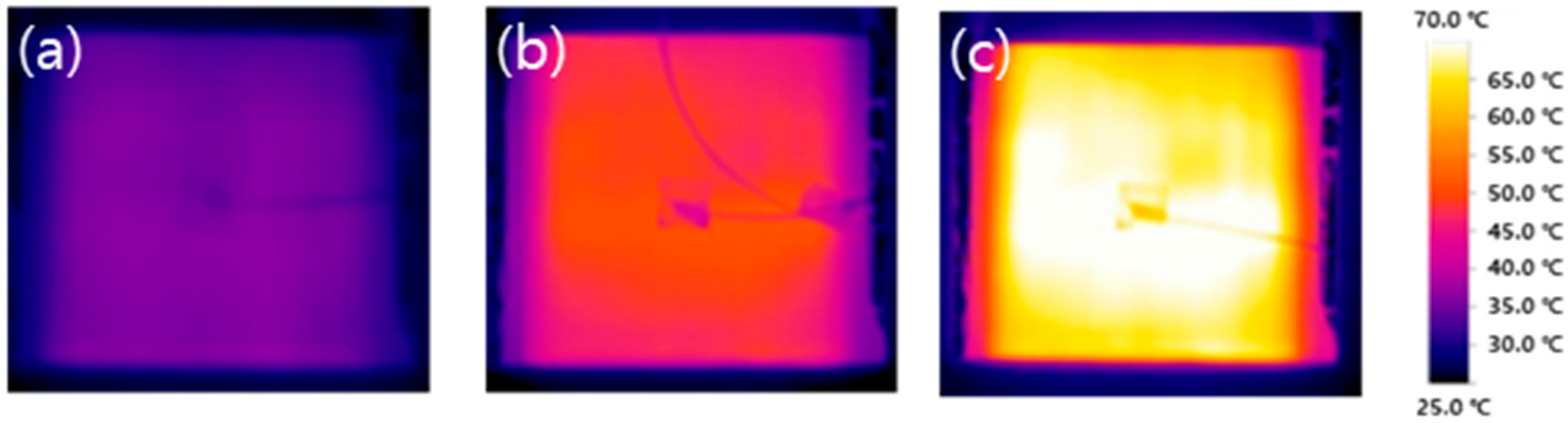
3.5. Heating Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sathishkumar, T.P.; Satheeshkumar, S.; Naveen, J. Glass fiber-reinforced polymer composites—A review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1258–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, A.; Fiedler, B.; Schulte, K. Electrical conductivity of carbon black/fibres filled glass-fibre-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2006, 37, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Haigh, A.; Soutis, C.; Gibson, A.; Sloan, R. Dielectric constant of a three-dimensional woven glass fibre composite: Analysis and measurement. Compos. Struct. 2017, 180, 853–861. [Google Scholar]
- Paz, J.; Díaz, J.; Romera, L.; Costas, M. Size and shape optimization of aluminum tubes with GFRP honeycomb reinforcements for crashworthy aircraft structures. Compos. Struct. 2015, 133, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kang, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.-K. Strain rate dependent mechanical behavior of glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composites and its effect on the performance of automotive bumper beam structure. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 166, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, B.O.; Sumaila, M.; Dan-Asabe, B. Multi-parameter optimization (grey relational analysis) and modeling of a cellulosic plant/glass fiber hybrid reinforced polymer composite (PxGyEz) for offshore pressure vessels development. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2022, 4, 305001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Shim, C.S.; Sturtevant, C.; Kim, D.-W.; Song, H.C. Mechanical properties and production quality of hand-layup and vacuum infusion processed hybrid composite materials for GFRP marine structures. Int. J. Nav. Archit. 2014, 6, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azar, K.; Graebner, J.E. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity of printed wiring boards. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Annual IEEE Semiconductor Thermal Measurement and Management Symposium. Proceedings, Austin, TX, USA, 5–7 March 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, M. Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: CNT Polymer Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.-T.; Roh, H.D.; Lee, I.-Y.; Park, Y.-B. Strain sensing and progressive failure monitoring of glass-fiber-reinforced composites using percolated carbon nanotube networks. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2020, 2, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kang, D. Cure monitoring of composites using fiber optic sensors to evaluate the molding quality of resin infusion method using heating mold. J. Korean Soc. Nondestruct. Test. 2022, 42, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, W. Enhancing SNR of thermography image for water ingress of composite materials through PCA image fusion. J. Korean Soc. Nondestruct. Test. 2021, 41, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, R.; Tian, H.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.-H. A review of the electrical and mechanical properties of carbon nanofiller-reinforced polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1036–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, D.K.; Prusty, R.K.; Kumar, D.S.; Ray, B.C. Mechanical performance of CNT-filled glass fiber/epoxy composite in in-situ elevated temperature environments emphasizing the role of CNT content. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2016, 84, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, N.; Wang, G.-D.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Shen, Y.C. The effect of rolling process on the mechanical and electrical properties of CNTs-enhanced GFRP. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.K.; Rathore, D.K.; Prusty, R.K.; Dutta, K.; Ray, B.C. Tensile behavior of MWCNT enhanced glass fiber reinforced polymeric composites at various crosshead speeds. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 178, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Santare, M.H.; Advani, S.G. Interlaminar shear strength of glass fiber reinforced epoxy composites enhanced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2008, 39, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhalchan, A.; Gspann, T.; Windle, A. Aligned carbon nanotube–epoxy composites: The effect of nanotube organization on strength, stiffness, and toughness. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 10005–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, S.; Shen, M.; Duan, P.; Lu, F.; Cheng, S.; Li, Z. Properties of MWCNT–glass fiber fabric multiscale composites: Mechanical properties, interlaminar adhesion, and thermal conductivity. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 2712–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaros, T.; Kirsten, M.; Simon, F.; Mäder, E.; Stamm, M. The interphase microstructure and electrical properties of glass fibers covalently and non-covalently bonded with multiwall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2014, 73, 310–324. [Google Scholar]
- Eskizeybek, V.; Avcı, A.; Gülce, A. Preparation and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube grafted glass fabric/epoxy multi-scale composites. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2017, 26, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnidakouong, J.R.N.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.-B. Electromagnetic interference shielding behavior of hybrid carbon nanotube/exfoliated graphite nanoplatelet coated glass fiber composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 248, 114403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Rider, A.N.; Thostenson, E.T. Hierarchical composite structures prepared by electrophoretic deposition of carbon nanotubes onto glass fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2013, 5, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Fan, B.; Zhao, H.; Lu, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J. Design of electrically conductive structural composites by modulating aligned CVD-grown carbon nanotube length on glass fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2017, 9, 2948–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulhan, T.; Kamboj, A.; Gupta, N.K.; Somani, N. Fabrication methods of glass fibre composites—A review. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2022, 4, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigolo, B.; Penicaud, A.; Coulon, C.; Sauder, C.; Pailler, R.; Journet, C.; Bernier, P.; Poulin, P. Macroscopic fibers and ribbons of oriented carbon nanotubes. Science 2000, 290, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauhofer, W.; Kovacs, J.Z. A review and analysis of electrical percolation in carbon nanotube polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, J.K.W.; Kirk, J.E.; Kinloch, I.A.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Windle, A.H. Ultra-low electrical percolation threshold in carbon-nanotube-epoxy composites. Polymer 2003, 44, 5893–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonollo, S.; Lanari, D.; Vaccaro, L. Ring-Opening of Epoxides in water. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2011, 2587–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cheng, L.; Tan, J.; Yang, W. Conductive nanocarbon-coated glass fibers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 17806–17810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriche, R.; Suárez, A.J.; Sánchez, M.; Prolongo, S.G.; Urena, A. Graphene nanoplatelets coated glass fibre fabrics as strain sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 146, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnani, B.D.; Hosseini, S.; Rahmanian, S.; Rashid, S.A.; Mustapha, S.; Balavandy, S.K. Grafting carbon nanotubes on glass fiber by dip coating technique to enhance tensile and interfacial shear strength. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 149736. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B.; Luo, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, T. CNT enabled co-braided smart fabrics: A new route for non-invasive, highly sensitive & large-area monitoring of composites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44056. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, C.D.; Palmeri, M.J.; Putz, K.W.; Ho, G.; Barto, R.; Brinson, L.C. Nanoscale structure and local mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced composites containing MWCNT-grafted hybrid glass fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Shi, B.; Doshi, S.M.; Chu, T.; Qiu, G.; Du, A.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, F.; Thostenson, E.T.; Fu, K.K. Rapid nanowelding of carbon coatings onto glass fibers by electrothermal shock. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 37722–37731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Rubio-González, C.; Soto-Cajiga, J.A. Piezoresistive response of spray-coated multiwalled carbon nanotube/glass fiber/epoxy composites under flexural loading. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Lee, S.-E.; Lee, W.-J.; Kim, C.-G. Mechanical Properties of MWNT-Loaded plain-weave glass/epoxy composites. Adv. Compos. Mat. 2009, 18, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-E.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, C.-G. Fabrication and design of multi-layered radar absorbing structures of MWNT-filled glass/epoxy plain-weave composites. Compos. Struct. 2006, 76, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Property | #823 Fabric | #580 Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Shaft satin | Plain weave |
| Thickness | 0.23 ± 0.025 mm | 0.6 ± 0.07 mm |
| Area density | 294 ± 18 g/m2 | 580 ± 58 g/m2 |
| Stacking sequence of layer | 1, 5, 9 | 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 |
| Number of Cycles | Before Infusion | After Infusion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight Fraction (wt%) | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | Weight Fraction (wt%) | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | |
| 1 | 0.022 (±0.001) | 0.0165 (±0.00343) | 0.012 (±0.001) | 0.0051 (±0.0001) |
| 3 | 0.055 (±0.003) | 0.978 (±0.206) | 0.030 (±0.002) | 0.379 (±0.017) |
| 5 | 0.078 (±0.004) | 11.0 (±3.00) | 0.042 (±0.002) | 1.38 (±0.053) |
| 10 | 0.140 (±0.007) | 25.4 (±3.70) | 0.078 (±0.004) | 2.95 (±0.12) |
| 20 | 0.210 (±0.001) | 47.5 (±1.53) | 0.116 (±0.0005) | 26.7 (±2.4) |
| Property | Pristine GF Composite | MWCNT-Coated GF Composite | Increment |
|---|---|---|---|
| (MPa) | 348.5 (±31.7) | 328.9 (±16.9) | −5.4% |
| (GPa) | 3.8 (±0.19) | 4.1 (±0.21) | +7.8% |
| 0.122 (±0.005) | 0.124 (±0.008) | +1.6% | |
| (MPa) | 177.8 (±4.2) | 167.1 (±23.4) | −5.9% |
| (GPa) | 9.7 (±0.49) | 8.9 (±0.45) | −8.3% |
| 0.031 (±0.005) | 0.038 (±0.004) | +22.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.; Park, J.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.-E. MWCNT-Coated Glass Fabric/Phenol Composite Heating Panel Fabricated by Resin Infusion Process. Polymers 2023, 15, 3353. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163353
Choi S, Park J, Kang D, Lee S-E. MWCNT-Coated Glass Fabric/Phenol Composite Heating Panel Fabricated by Resin Infusion Process. Polymers. 2023; 15(16):3353. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163353
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Seongpil, Juyeop Park, Donghoon Kang, and Sang-Eui Lee. 2023. "MWCNT-Coated Glass Fabric/Phenol Composite Heating Panel Fabricated by Resin Infusion Process" Polymers 15, no. 16: 3353. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163353
APA StyleChoi, S., Park, J., Kang, D., & Lee, S.-E. (2023). MWCNT-Coated Glass Fabric/Phenol Composite Heating Panel Fabricated by Resin Infusion Process. Polymers, 15(16), 3353. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163353






