A Novel Composite Hydrogel Material for Sodium Removal and Potassium Provision
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Hydrogel
2.3. Swelling Properties of Hydrogels
2.3.1. Swelling Degree of Hydrogel in Sodium Chloride Solutions
2.3.2. Soil Water Holding Rate
2.4. Adsorption Experiment
2.4.1. Adsorption Thermodynamic Experiments with Different pH Values
2.4.2. pH Effect Experiment
2.4.3. Adsorption Kinetic Experiment
2.4.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics at Different Temperatures
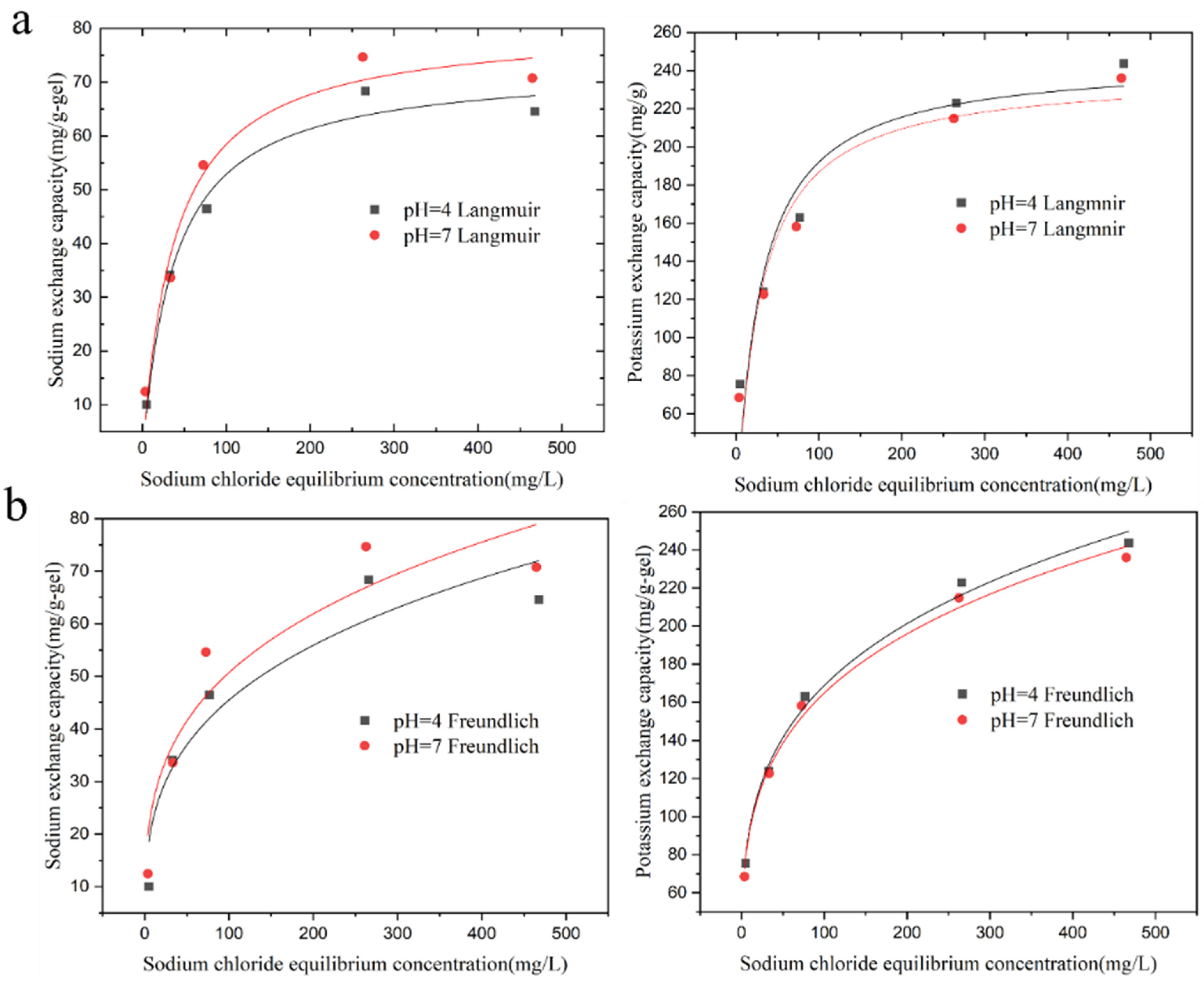
2.4.5. Adsorbent Dosage Experiment
2.5. Soil Experiment
2.5.1. Preparation of Soil Containing NaCl
2.5.2. pH Value Affects the Precipitation of Sodium and Potassium Ions in Soil
2.5.3. Amount of Hydrogel Affects Precipitation of Sodium and Potassium Ions in Soil
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Swelling Degree of Hydrogel
3.2. pH Affects the Adsorption of the Gel
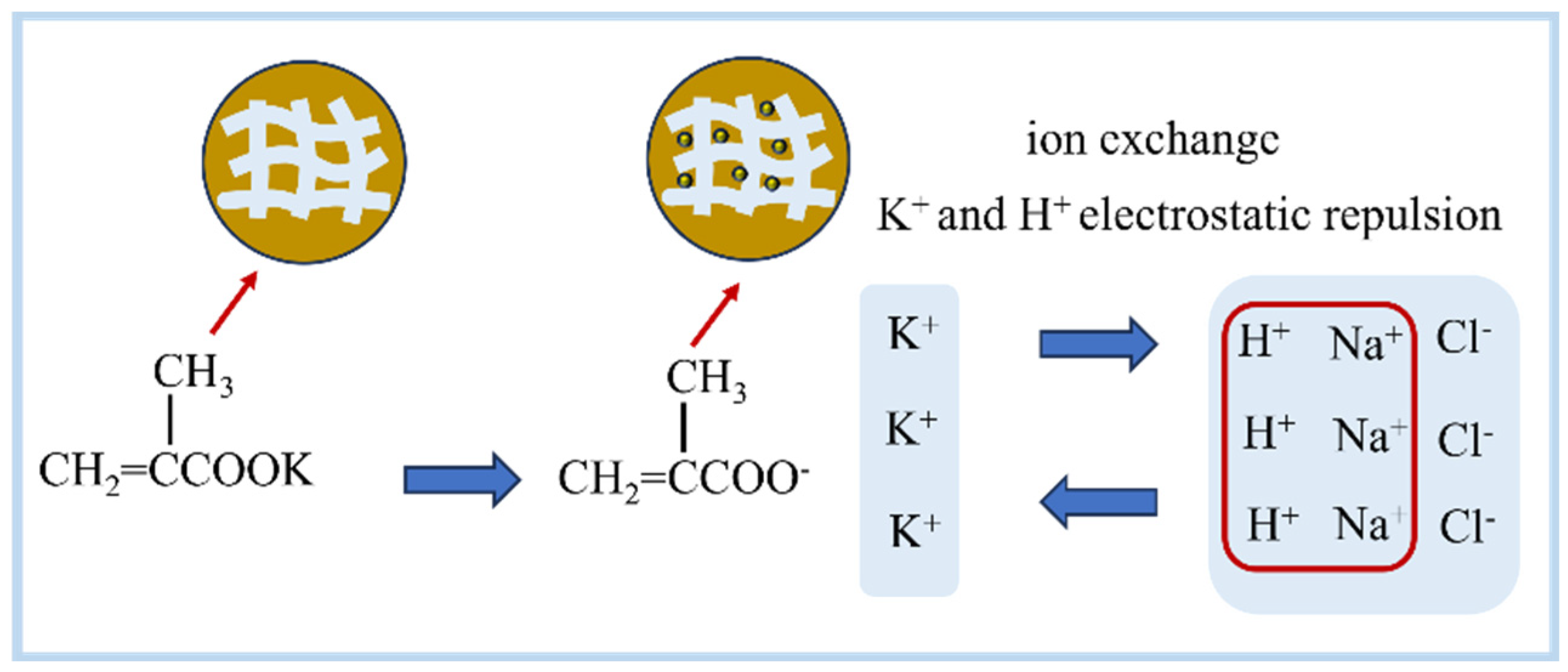
3.3. Isothermal Adsorption
3.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
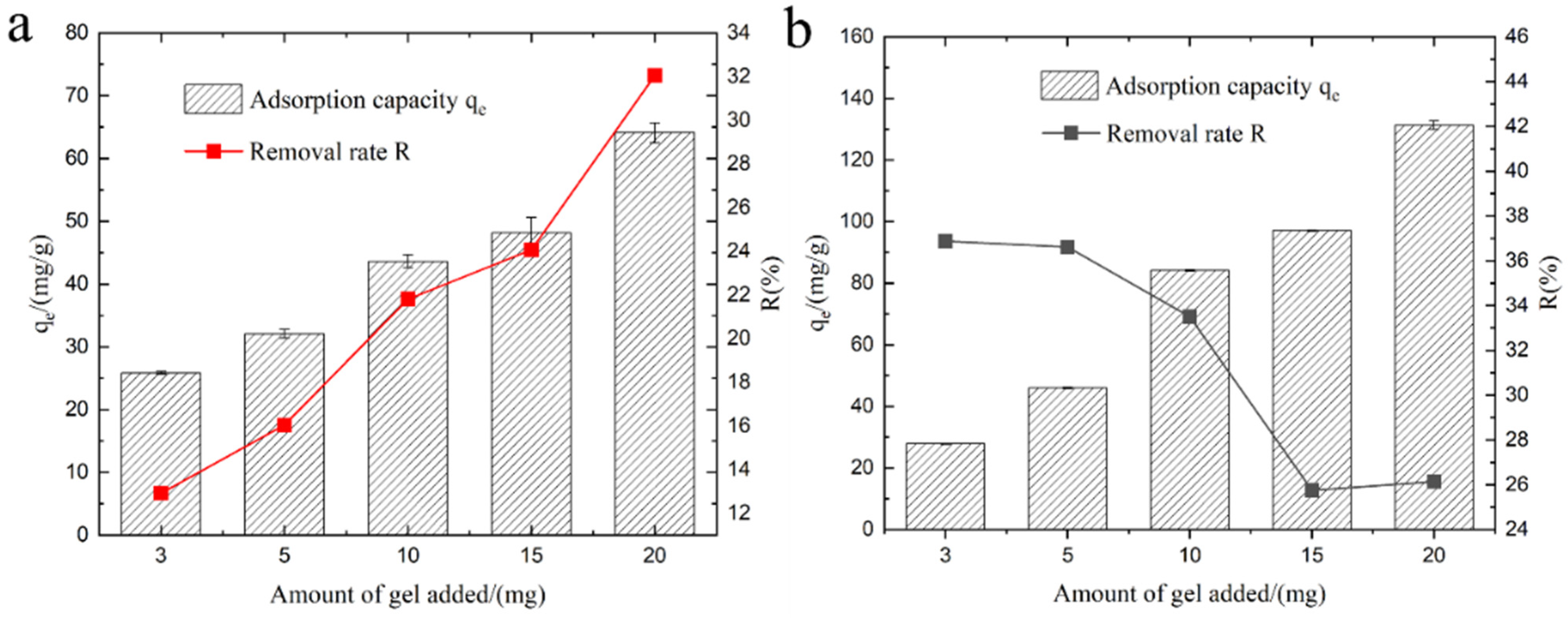
3.6. The Effect of Hydrogel Dosage
3.7. Hydrogel Applied Soil Experiments
3.7.1. Soil Precipitation Liquid Experiment
3.7.2. Effect of Different Gel Amounts on Precipitate
3.8. Structural Characteristics of Hydrogel
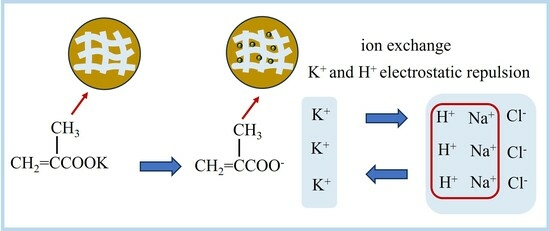
3.9. Mechanism of KMAA Hydrogel Adsorbing Sodium and Exchanging Potassium
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bobowski, N.; Rendahl, A.; Vickers, Z. Preference for salt in a food may be alterable without a low sodium diet. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 39, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Song, H.; Zou, T.; Raza, A.; Li, P.; Li, K.; Xiong, J. Reduction of sodium chloride: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 3931–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, T.G.; Santos, J.; Silva, M.A.; Oliveira, M.; Costa, H.S. An update on processed foods: Relationship between salt, saturated and trans fatty acids contents. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, B. Study on the Harm of Saline Alkali Land and Its Improvement Technology in China. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Qingdao, China, 26–27 December 2020; Volume 692, p. 042053. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pu, L.; Han, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R.; Xiang, Y. Soil salinization research in China: Advances and prospects. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.E.; Farrag, A.M.; El-Bindary, A.A.; El-Bindary, M.A.; Kiwaan, H.A. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B dye using low-cost pyrofabricated titanium dioxide quantum dots-kaolinite nanocomposite. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2023, 37, e7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cui, W.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T. Removal of iodine from the salt water used for caustic soda production by ion-exchange resin adsorption. Desalination 2019, 458, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrazek, R.V.; Hill, S.D. Vacuum Evaporation of Salt from Titanium Sponge. Metall. Trans. 1974, 5, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sedighi, M.; Behvand Usefi, M.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Ghasemi, M. Environmental sustainability and ions removal through electrodialysis desalination: Operating conditions and process parameters. Desalination 2023, 549, 116319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopeeva, E.L.; Panova, G.G.; Yakimansky, A.V. Agricultural Applications of Superabsorbent Polymer Hydrogels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, J.; Lu, X.; Tian, W. Carbohydrate polymers exhibit great potential as effective elicitors in organic agriculture: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, K.; Omidian, H.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Doroudiani, S. Superabsorbent hydrogel composites and nanocomposites: A review. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.; Blokhus, A.M.; Skauge, A. Viscosity study of salt tolerant polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, R.; Shi, X.; Lian, S.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, W. Synthesis of cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogel with high salt tolerance for soil conditioning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; García Meza, J.V.; Zhou, K.; Liu, J.; Song, S.; Zhang, M.; Meng, D.; Chen, J.; Xia, L.; Xiheng, H. Superabsorbent polymer used for saline-alkali soil water retention. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 145, 104830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Peng, H.; Ye, X.e.; Kong, Y.; Wang, N.; Yang, F.; Meni, B.-H.; Lei, Z. High salt tolerance hydrogel prepared of hydroxyethyl starch and its ability to increase soil water holding capacity and decrease water evaporation. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 222, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Cheng, S.; Zhen, J.; Lei, Z. Superabsorbent Polymer With Excellent Water/Salt Absorbency And Water Retention, And Fast Swelling Properties For Preventing Soil Water Evaporation. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Shao, J.; Deng, S.; Wang, R.; Li, N.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effects of Stockosorb and Luquasorb polymers on salt and drought tolerance of Populus popularis. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 124, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Mohammad, F.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Kalaji, H.M. Salicylic acid and trehalose attenuate salt toxicity in Brassica juncea L. by activating the stress defense mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 326, 121467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathy, M.; Moghny, T.A.; Ahmed, E.A.; Moaz, M.A.; Abdel-Hameed, A.A.E.B. Development of Sulfonated Nanocomposites Ion Exchange Resin for Removal of Sodium Ions from Saline Water. Int. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 4, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Holback, H.; Yeo, Y.; Park, K. Hydrogel swelling behavior and its biomedical applications. In Biomedical Hydrogels; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Arens, L.; Weissenfeld, F.; Klein, C.O.; Schlag, K.; Wilhelm, M. Osmotic Engine: Translating Osmotic Pressure into Macroscopic Mechanical Force via Poly(Acrylic Acid) Based Hydrogels. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Chao, H.-P. Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: A comparison study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2671–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revellame, E.D.; Fortela, D.L.; Sharp, W.; Hernandez, R.; Zappi, M.E. Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws: A review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic Radic, M.M.; Filipovic, V.V.; Vukovic, J.S.; Vukomanovic, M.; Ilic-Tomic, T.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Tomic, S.L. 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate/Gelatin/Alginate Scaffolds Reinforced with Nano TiO(2) as a Promising Curcumin Release Platform. Polymers 2023, 15, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Bindary, M.A.; El-Desouky, M.G.; El-Bindary, A.A. Metal–organic frameworks encapsulated with an anticancer compound as drug delivery system: Synthesis, characterization, antioxidant, anticancer, antibacterial, and molecular docking investigation. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2022, 36, e6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Tomita-Yokotani, K.; Hashimoto, H.; Sawaki, N.; Notoya, M. Sodium and potassium uptake of Ulva–Application of marine macro-algae for space agriculture. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Cheng, D. Environmentally friendly hydrogel: A review of classification, preparation and application in agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




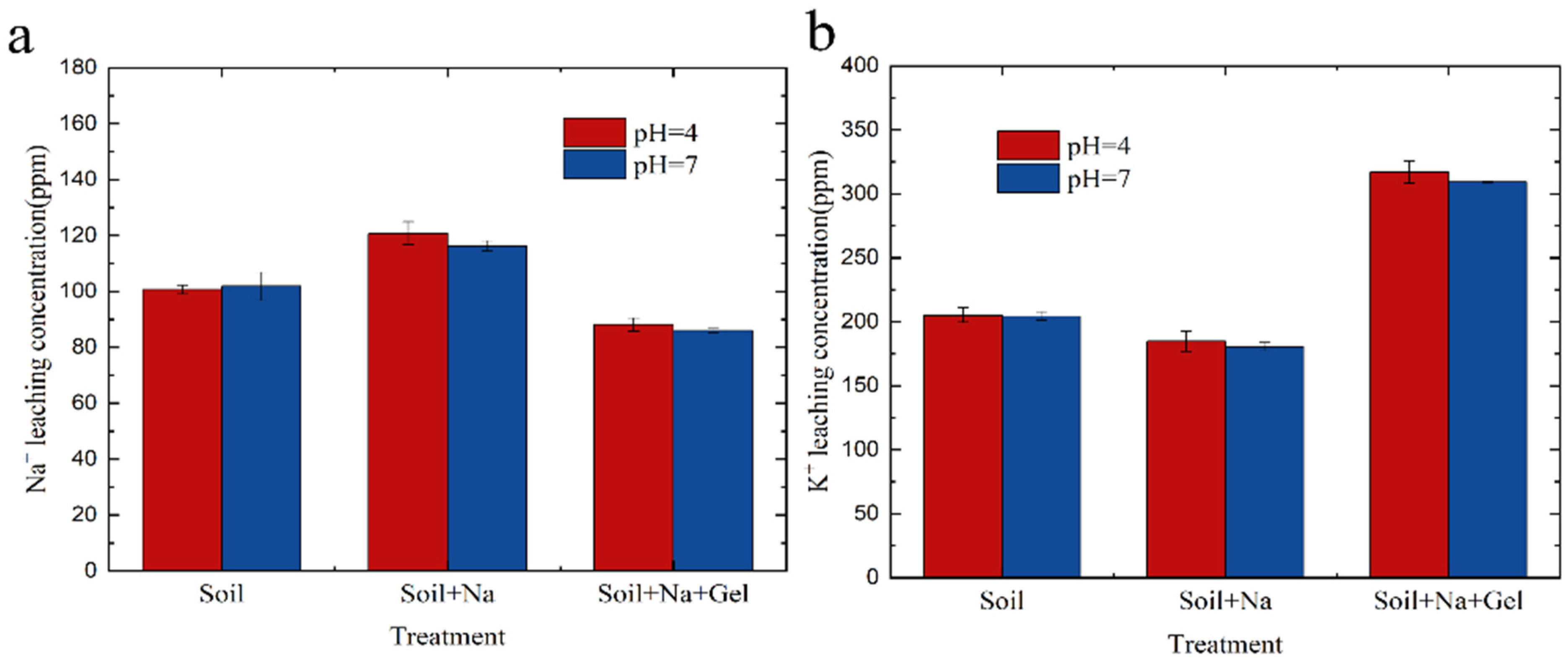
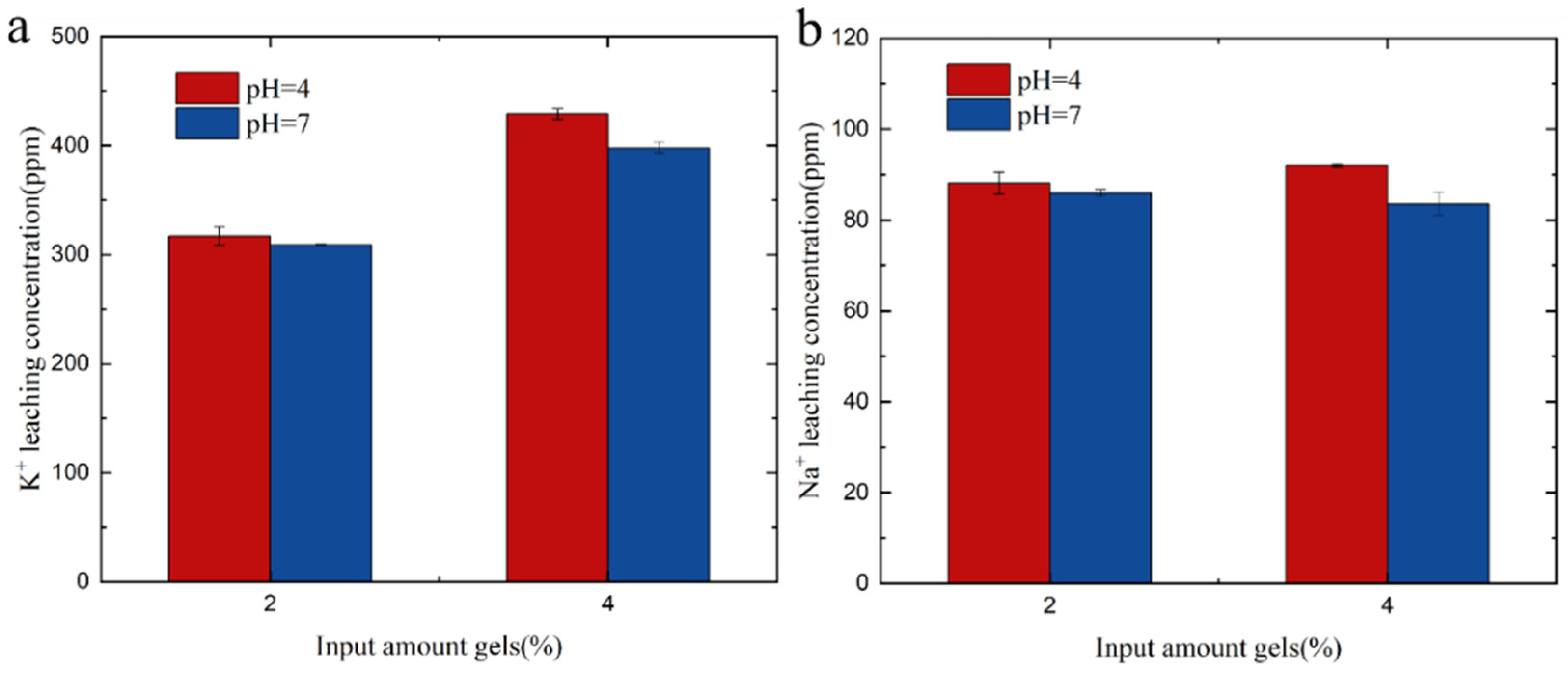
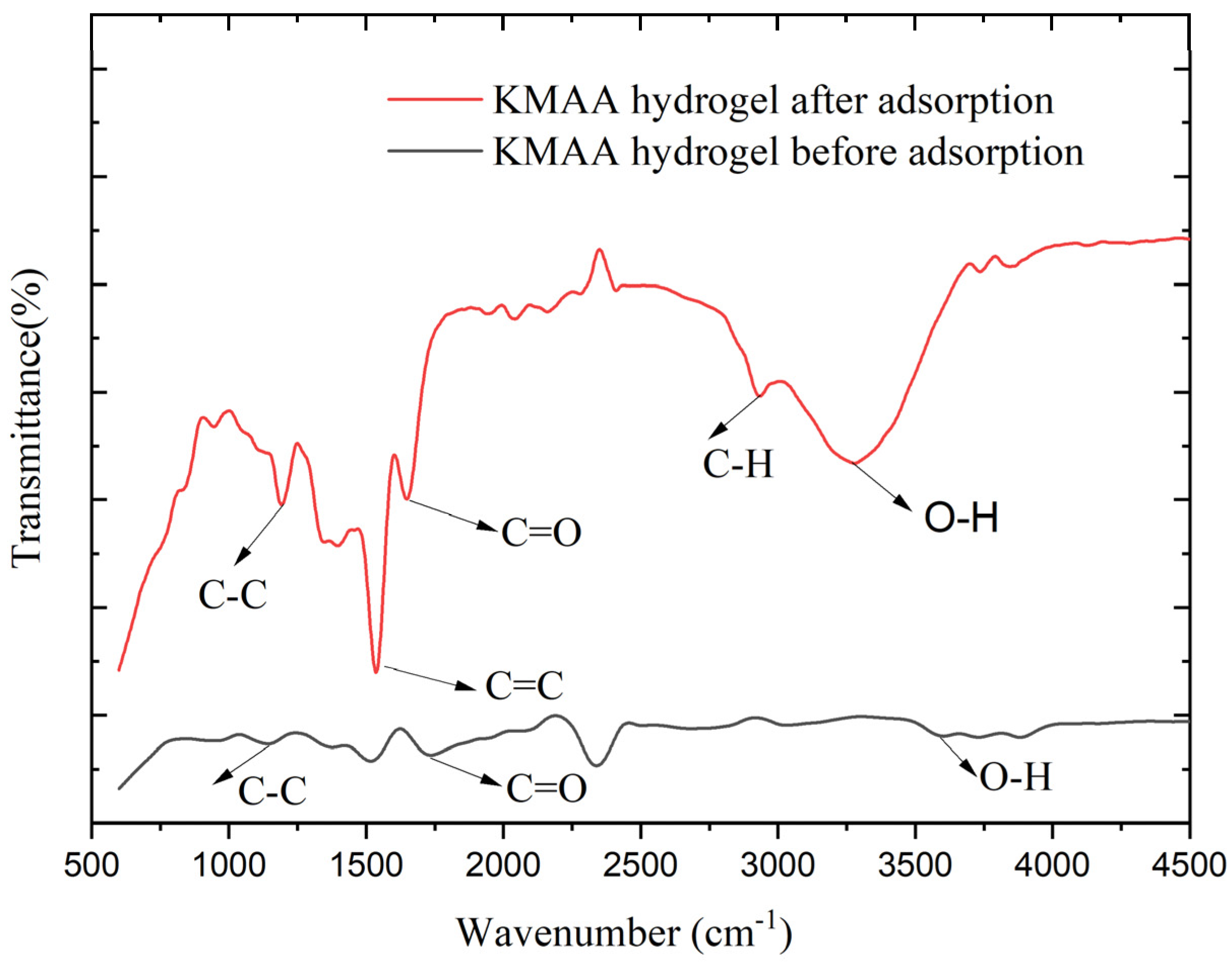
| Materials | Component Type | Molar Weight (g·mol−1) | Concentration (mol·m−3) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KMAA | Monomer | 124.18 | 1000 | 3.105 |
| MBAA | Linker | 154.17 | 50 | 0.193 |
| TEMED | Accelerator | 116.21 | 20 | 0.058 |
| APS | Initiator | 228.19 | 10 | 0.057 |
| Isotherm Model | Parameter | Initial pH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 7 | ||
| Langmuir | qmax (mg·g−1) | 72.9 | 80.5 |
| KL (L·mg−1) | 0.0264 | 0.0265 | |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.97 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg·g−1) | 11.54 | 13.47 |
| n | 3.448 | 3.571 | |
| R2 | 0.909 | 0.905 | |
| Isotherm Model | Parameter | Initial pH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 7 | ||
| Langmuir | qmax (mg·g−1) | 254.6 | 238.4 |
| KL (L·mg−1) | 0.0358 | 0.0361 | |
| R2 | 0.8964 | 0.8931 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg·g−1) | 52.37 | 52.26 |
| n | 3.937 | 4.016 | |
| R2 | 0.9934 | 0.9936 | |
| T/K | kJ·mol−1) | kJ·mol−1) | J·mol−1·K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298.15 | −2.965 | 2.762 | 19.21 |
| 308.15 | −3.157 | 2.762 | 19.21 |
| T/K | kJ·mol−1) | kJ·mol−1) | J·mol−1·K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298.15 | −1.406 | −1.589 | −44.21 |
| 308.15 | −0.964 | −1.589 | −44.21 |
| Isotherm Model | Parameter | Initial pH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 7 | ||
| Pseudo-first-order | k1 (min−1) | 0.049 | 0.084 |
| qe (mg·g−1) | 52.94 | 54.13 | |
| R2 | 0.872 | 0.631 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | k2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | 0.00133 | 0.0312 |
| qe (mg·g−1) | 55.34 | 57.31 | |
| R2 | 0.90191 | 0.714 | |
| Isotherm Model | Parameter | Initial pH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 7 | ||
| Pseudo-first-order | k1 (min−1) | 0.00044 | 0.04131 |
| qe (mg·g−1) | 136.82 | 130.28 | |
| R2 | 0.92195 | 0.935 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | k2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | 0.000467 | 0.04468 |
| qe (mg·g−1) | 150.41 | 144.08 | |
| R2 | 0.89644 | 0.89122 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Gotoh, T.; Nakai, S.; Ueda, A. A Novel Composite Hydrogel Material for Sodium Removal and Potassium Provision. Polymers 2023, 15, 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173568
Huang J, Gotoh T, Nakai S, Ueda A. A Novel Composite Hydrogel Material for Sodium Removal and Potassium Provision. Polymers. 2023; 15(17):3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173568
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jin, Takehiko Gotoh, Satoshi Nakai, and Akihiro Ueda. 2023. "A Novel Composite Hydrogel Material for Sodium Removal and Potassium Provision" Polymers 15, no. 17: 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173568
APA StyleHuang, J., Gotoh, T., Nakai, S., & Ueda, A. (2023). A Novel Composite Hydrogel Material for Sodium Removal and Potassium Provision. Polymers, 15(17), 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173568