Adsorption of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Microcystins by Virgin and Weathered Microplastics in Freshwater Matrices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Materials and Reagents
2.3. Microplastic Weathering
2.4. PFAS Adsorption Trials
2.5. Microcystin Adsorption Trials
2.6. Analytical Methods
2.7. Surface Roughness
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PFAS Isotherm and Kinetic Trials Using 200 and 1090 µm Virgin LDPE
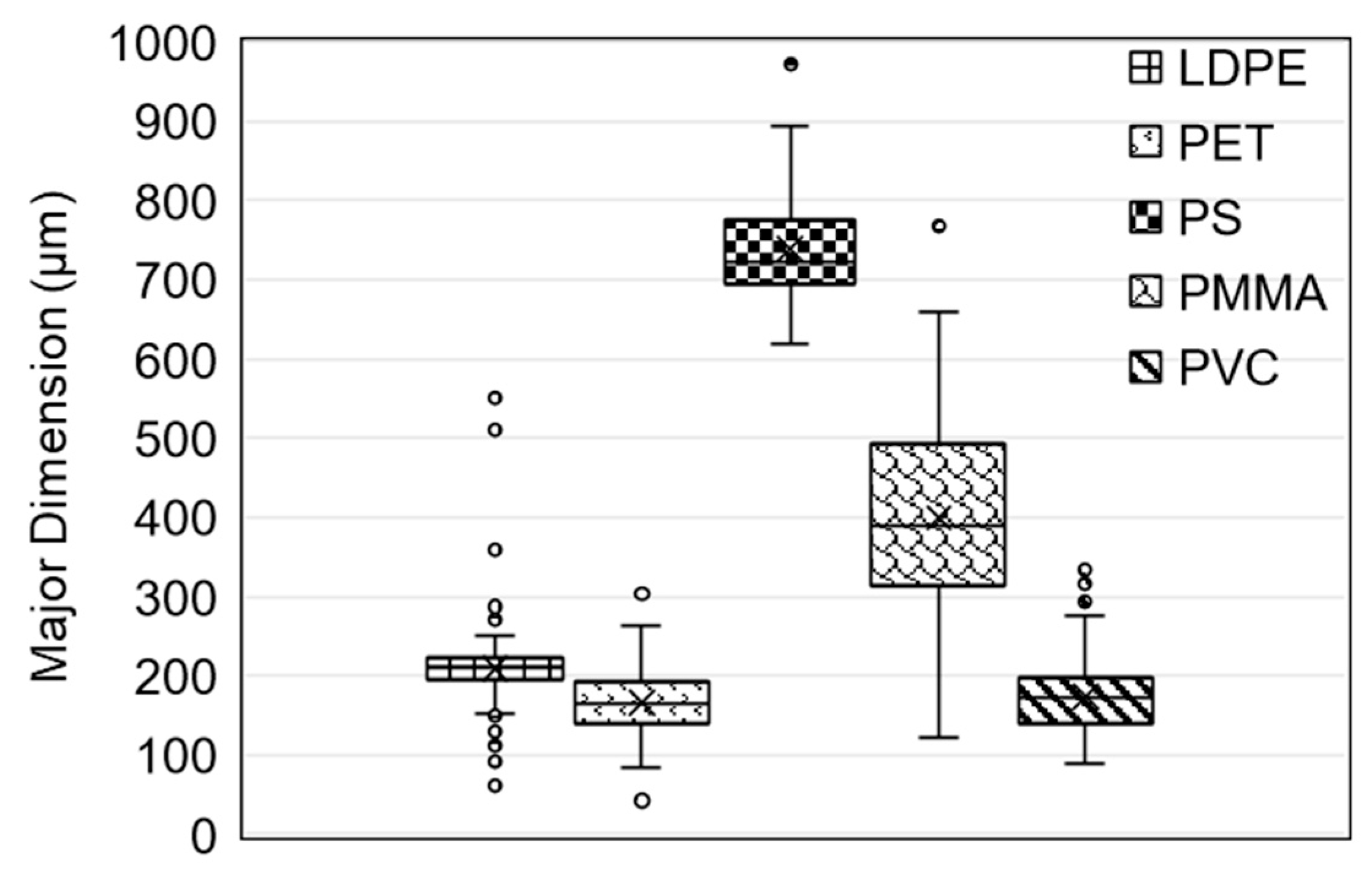
3.2. PFAS Trials Using Virgin 125–250 µm LDPE, PET, and PVC and 300–700 µm PS and PMMA
3.3. PFAS Trials Using Weathered LDPE, PET, PS, PMMA, and PVC
3.4. Microcystin Kinetic Trials Using Virgin LDPE, PET, PS, PMMA, and PVC
3.5. Microcystin Trials Using Weathered PET, PS, PMMA, and PVC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ateia, M.; Zheng, T.; Calace, S.; Tharayil, N.; Pilla, S.; Karanfil, T. Sorption Behavior of Real Microplastics (MPs): Insights for Organic Micropollutants Adsorption on a Large Set of Well-Characterized MPs. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, M.; Ortiz, D.; Nieto-Sandoval, J.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A. Adsorption of Micropollutants onto Realistic Microplastics: Role of Microplastic Nature, Size, Age, and NOM Fouling. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.D.; Elanjickal, A.I.; Mankar, J.S.; Krupadam, R.J. Assessment of Cancer Risk of Microplastics Enriched with Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, E.G.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Ma, L.; Zeng, E.Y.; Shi, H. A Review of Microplastics in Table Salt, Drinking Water, and Air: Direct Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3740–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, E.; Twiddy, M.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastic Contamination of Drinking Water: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in Freshwaters and Drinking Water: Critical Review and Assessment of Data Quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oßmann, B.E. Microplastics in Drinking Water? Present State of Knowledge and Open Questions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 41, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of Microplastics in Raw and Treated Drinking Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zeng, Z.; Wen, X.; Ren, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, R. Presence of Microplastics in Drinking Water from Freshwater Sources: The Investigation in Changsha, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 42313–42324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanpiwat, P.; Damrongsiri, S. Abundance and Characteristics of Microplastics in Freshwater and Treated Tap Water in Bangkok, Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Ball, H.; Cross, R.; Horton, A.A.; Jürgens, M.D.; Read, D.S.; Vollertsen, J.; Svendsen, C. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics in Potable Water and Their Sources within Water Treatment Works in England and Wales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12326–12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, T.; Chen, W. Occurrence and Removal of Microplastics in an Advanced Drinking Water Treatment Plant (ADWTP). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, L.M.; Moore, C.; Jones, P.R. Persistent Organic Pollutants Carried by Synthetic Polymers in the Ocean Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Manzano, C.; Hentschel, B.T.; Simonich, S.L.M.; Hoh, E. Polystyrene Plastic: A Source and Sink for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13976–13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Enhanced Desorption of Persistent Organic Pollutants from Microplastics under Simulated Physiological Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Competitive Sorption of Persistent Organic Pollutants onto Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha-Graña, E.; Moscoso-Pérez, C.M.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. Adsorption of Pesticides and Personal Care Products on Pristine and Weathered Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Comparison between Bio-Based and Conventional Plastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S. Adsorption of Three Pesticides on Polyethylene Microplastics in Aqueous Solutions: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Characterisation, Quantity and Sorptive Properties of Microplastics Extracted from Cosmetics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic Resin Pellets as a Transport Medium for Toxic Chemicals in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Hentschel, B.T.; Kaye, S. Long-Term Field Measurement of Sorption of Organic Contaminants to Five Types of Plastic Pellets: Implications for Plastic Marine Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Mai, L.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, F. Occurrence and Abundance of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) on Microplastics (MPs) in Pearl River Estuary (PRE) Region: Spatial and Temporal Variations. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 117025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca, M.; Schirinzi, G.; Martínez, M.; Barceló, D.; Farré, M. Adsorption of Perfluoroalkyl Substances on Microplastics under Environmental Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Shih, K.M.; Li, X.Y. The Partition Behavior of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanesulfonamide (FOSA) on Microplastics. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, J.-H. Sorption Capacity of Plastic Debris for Hydrophobic Organic Chemicals. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wu, X.; Song, X.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Z. Sorption and Desorption of Petroleum Hydrocarbons on Biodegradable and Nondegradable Microplastics. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolahpur Monikh, F.; Vijver, M.G.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Darbha, G.K.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M. Metal Sorption onto Nanoscale Plastic Debris and Trojan Horse Effects in Daphnia Magna: Role of Dissolved Organic Matter. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udenby, F.A.O.; Almuhtaram, H.; McKie, M.J.; Andrews, R.C. Adsorption of Fluoranthene and Phenanthrene by Virgin and Weathered Polyethylene Microplastics in Freshwaters. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, R.; Xing, B. Interaction of Microplastics with Antibiotics in Aquatic Environment: Distribution, Adsorption, and Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15579–15595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; He, G.; Liu, W. Adsorption Mechanism of Cadmium on Microplastics and Their Desorption Behavior in Sediment and Gut Environments: The Roles of Water PH, Lead Ions, Natural Organic Matter and Phenanthrene. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atugoda, T.; Wijesekara, H.; Werellagama, D.R.I.B.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Bolan, N.S.; Vithanage, M. Adsorptive Interaction of Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin on Polyethylene Microplastics: Implications for Vector Transport in Water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Kong, X.; Tao, S.; Xing, B. Sorption of Four Hydrophobic Organic Compounds by Three Chemically Distinct Polymers: Role of Chemical and Physical Composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Yu, F. Effect of Microplastic Size on the Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Triclosan on Polyvinyl Chloride. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Cai, Z.; Jin, H.; Tang, Y. Adsorption Mechanisms of Five Bisphenol Analogues on PVC Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Ge, W.; Chai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Xia, B. Sorption of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers by Microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnke, A.; Arp, H.P.H.; Escher, B.I.; Gewert, B.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Ogonowski, M.; Potthoff, A.; Rummel, C.; Schmitt-Jansen, M.; et al. Reducing Uncertainty and Confronting Ignorance about the Possible Impacts of Weathering Plastic in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhan, X.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, S. Effect of Weathering on Environmental Behavior of Microplastics: Properties, Sorption and Potential Risks. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Liu, C.; He, D.; Sun, J.; Zhang, A.; Li, J.; Pan, X. Interactions between Polypropylene Microplastics (PP-MPs) and Humic Acid Influenced by Aging of MPs. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. Laboratory Simulation of Microplastics Weathering and Its Adsorption Behaviors in an Aqueous Environment: A Systematic Review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Solla, S.R.; De Silva, A.O.; Letcher, R.J. Highly Elevated Levels of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and Other Perfluorinated Acids Found in Biota and Surface Water Downstream of an International Airport, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Environ. Int. 2012, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewurtz, S.B.; Bhavsar, S.P.; Petro, S.; Mahon, C.G.; Zhao, X.; Morse, D.; Reiner, E.J.; Tittlemier, S.A.; Braekevelt, E.; Drouillard, K. High Levels of Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Sport Fish Species Downstream of a Firefighting Training Facility at Hamilton International Airport, Ontario, Canada. Environ. Int. 2014, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareitalabad, P.; Siemens, J.; Hamer, M.; Amelung, W. Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) in Surface Waters, Sediments, Soils and Wastewater—A Review on Concentrations and Distribution Coefficients. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, B.C.; Speth, T.F.; Wahman, D.G.; Smith, S.J.; Abulikemu, G.; Kleiner, E.J.; Pressman, J.G. Occurrence of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Source Water and Their Treatment in Drinking Water. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 2359–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. Drinking Water Health Advisory for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS); US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Drinking Water Health Advisories for PFOA and PFOS. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/drinking-water-health-advisories-pfoa-and-pfos (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Scott, J.W.; Gunderson, K.G.; Green, L.A.; Rediske, R.R.; Steinman, A.D. Perfluoroalkylated Substances (PFAS) Associated with Microplastics in a Lake Environment. Toxics 2021, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempisty, D.M.; Xing, Y.; Racz, L. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in the Environment: Theory, Practice, and Innovation, 1st ed.; Series: Environmental and Occupational Health Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-429-48712-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bláha, L.; Babica, P.; Maršálek, B. Toxins Produced in Cyanobacterial Water Blooms—Toxicity and Risks. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, J.S.; Zia, A.; Clemins, P.J.; Schroth, A.W.; Winter, J.M.; Oikonomou, P.D.; Rizzo, D.M. Modeling the Sensitivity of Cyanobacteria Blooms to Plausible Changes in Precipitation and Air Temperature Variability. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meriluoto, J.A.; Spoof, L.E. Cyanotoxins: Sampling, Sample Processing and Toxin Uptake. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 483–499. ISBN 978-0-387-75865-7. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.-J.; Cheng, B.-L.; Cheng, Y.-L. Adsorption of Microcystin-LR by Three Types of Activated Carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Triantis, T.M.; Antoniou, M.G.; He, X.; Pelaez, M.; Han, C.; Song, W.; O’Shea, K.E.; de la Cruz, A.A.; Kaloudis, T.; et al. Destruction of Microcystins by Conventional and Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 91, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document—Cyanobacterial Toxins. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/publications/healthy-living/guidelines-canadian-drinking-water-quality-guideline-technical-document-cyanobacterial-toxins-document.html (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Moura, D.S.; Pestana, C.J.; Moffat, C.F.; Hui, J.; Irvine, J.T.S.; Edwards, C.; Lawton, L.A. Adsorption of Cyanotoxins on Polypropylene and Polyethylene Terephthalate: Microplastics as Vector of Eight Microcystin Analogues. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 303, 119135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, C.J.; Moura, D.S.; Capelo-Neto, J.; Edwards, C.; Dreisbach, D.; Spengler, B.; Lawton, L.A. Potentially Poisonous Plastic Particles: Microplastics as a Vector for Cyanobacterial Toxins Microcystin-LR and Microcystin-LF. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15940–15949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Duan, J.; Tian, S.; Ji, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, D. Short-Chain per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Aquatic Systems: Occurrence, Impacts and Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J. Comparative Evaluation of Sorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Pyrene onto Microplastics. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.; Fernández-González, V.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui, S. A Low-Cost System to Simulate Environmental Microplastic Weathering. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainali, N.M.; Kalaronis, D.; Kontogiannis, A.; Evgenidou, E.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Yang, X.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Microplastics in the Environment: Sampling, Pretreatment, Analysis and Occurrence Based on Current and Newly-Exploited Chromatographic Approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. Sorption Behavior and Mechanism of Hydrophilic Organic Chemicals to Virgin and Aged Microplastics in Freshwater and Seawater. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggan, T.L.; Moodie, D.; Kolobaric, A.; Szabo, D.; Shimeta, J.; Crosbie, N.D.; Lee, E.; Fernandes, M.; Clarke, B.O. An Investigation into Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Nineteen Australian Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs). Heliyon 2019, 5, e02316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtz, E.F.; Sutton, R.; Park, J.-S.; Sedlak, M. Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Wastewater: Significance of Unknown Precursors, Manufacturing Shifts, and Likely AFFF Impacts. Water Res. 2016, 95, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Method 537.1 Determination of Selected Per- and Polyflourinated Alkyl Substances in Drinking Water by Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?dirEntryId=348508&Lab=CESER&simpleSearch=0&showCriteria=2&searchAll=537.1&TIMSType=&dateBeginPublishedPresented=03%2F24%2F2018 (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- US EPA. Method 533: Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Drinking Water by Isotope Dilution Anion Exchange Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/dwanalyticalmethods/method-533-determination-and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-drinking-water-isotope (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- US EPA. Method 544. Determination of Microcystins and Nodularin in Drinking Water by Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?Lab=NERL&dirEntryId=306953 (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- McCord, J.; Lang, J.R.; Hill, D.; Strynar, M.; Chernoff, N. PH Dependent Octanol–Water Partitioning Coefficients of Microcystin Congeners. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Aggregation, Deposition, and Enhanced Contaminant Transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Mao, R.; Ma, S.; Guo, X.; Zhu, L. High Temperature Depended on the Ageing Mechanism of Microplastics under Different Environmental Conditions and Its Effect on the Distribution of Organic Pollutants. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hataley, E.K. Sorption of the Common Freshwater Cyanotoxin Microcystin to Microplastics. Master’s Thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]






| Polymer Type | Mean Roughness (µm) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin | Weathered | ||
| LDPE | 0.74 ± 0.59 | 0.47 ± 0.61 | 0.36 |
| PET | 0.78 ± 0.55 | 0.99 ± 0.89 | 0.56 |
| PS | 0.49 ± 0.47 | 0.19 ± 0.10 | 0.07 |
| PMMA | 0.32 ± 0.28 | 0.18 ± 0.11 | 0.19 |
| PVC | 1.23 ± 0.67 | 1.64 ± 2.21 | 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Almuhtaram, H.; Andrews, R.C. Adsorption of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Microcystins by Virgin and Weathered Microplastics in Freshwater Matrices. Polymers 2023, 15, 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183676
Shi Y, Almuhtaram H, Andrews RC. Adsorption of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Microcystins by Virgin and Weathered Microplastics in Freshwater Matrices. Polymers. 2023; 15(18):3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183676
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yucong, Husein Almuhtaram, and Robert C. Andrews. 2023. "Adsorption of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Microcystins by Virgin and Weathered Microplastics in Freshwater Matrices" Polymers 15, no. 18: 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183676
APA StyleShi, Y., Almuhtaram, H., & Andrews, R. C. (2023). Adsorption of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Microcystins by Virgin and Weathered Microplastics in Freshwater Matrices. Polymers, 15(18), 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183676







