Sulfated Polysaccharides from Macroalgae—A Simple Roadmap for Chemical Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
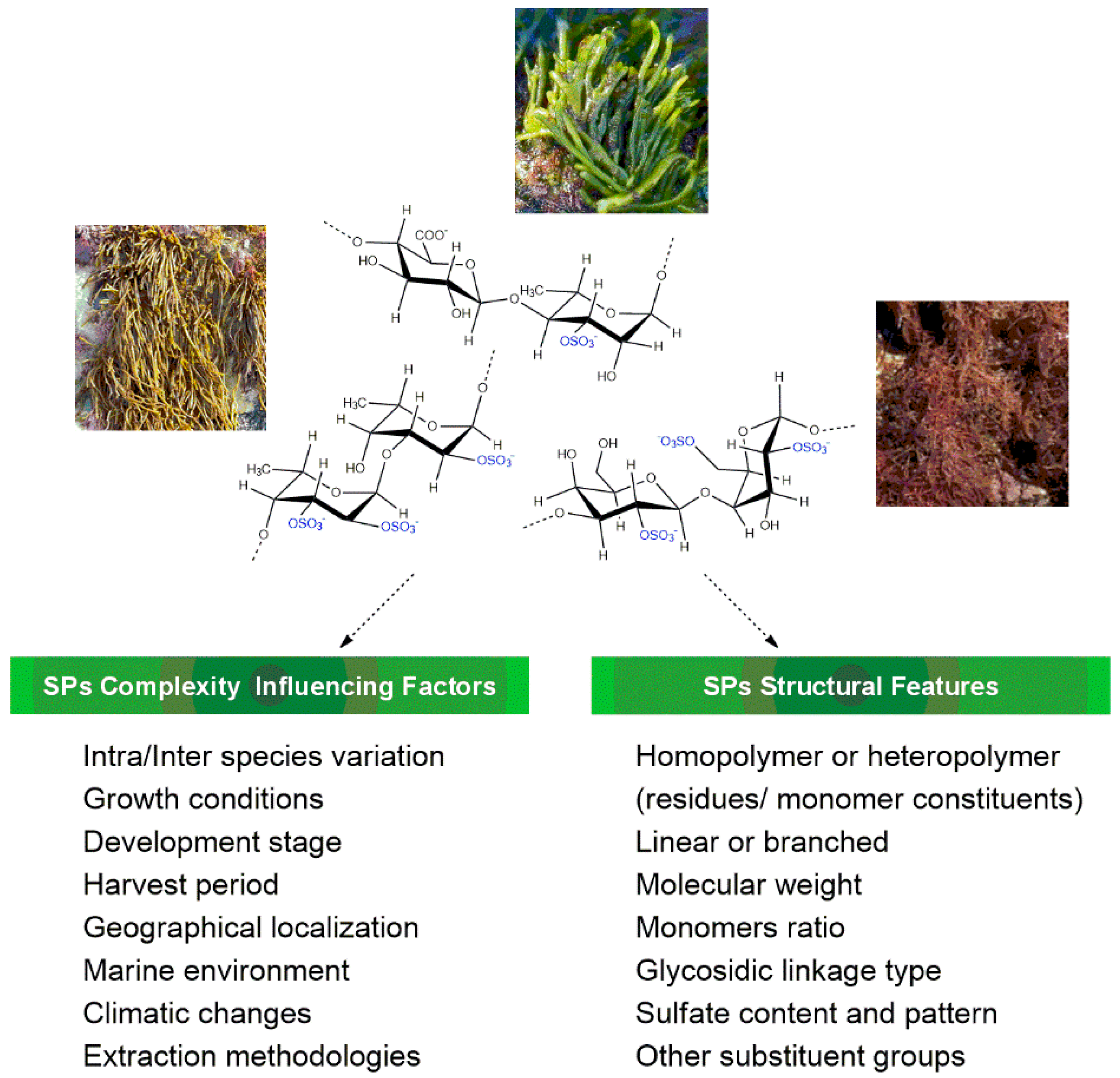
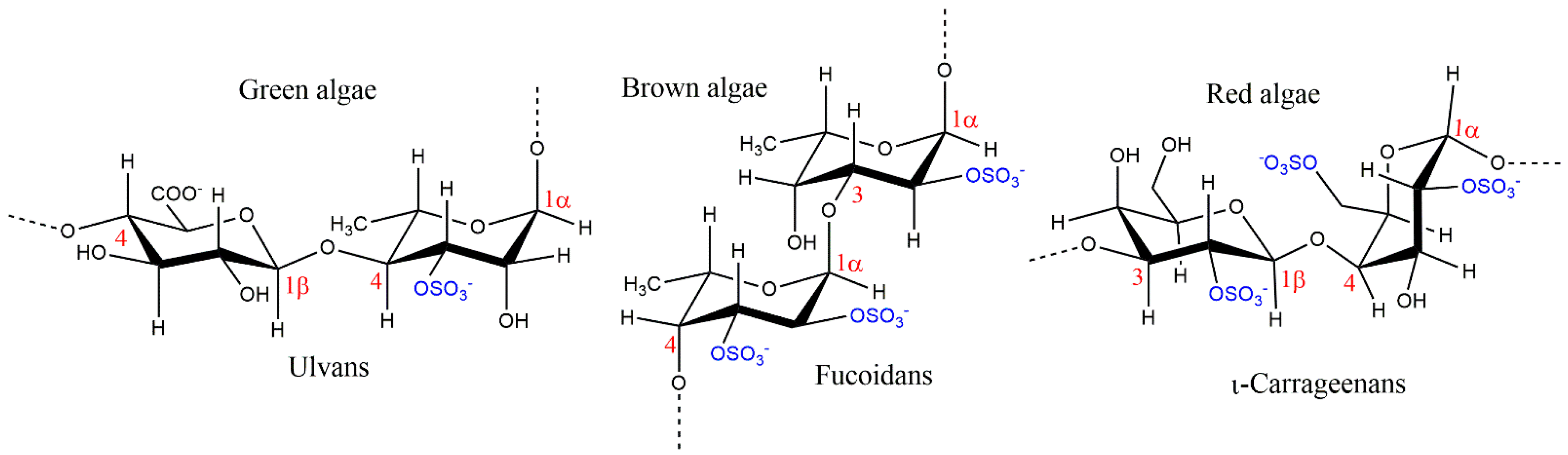
2. Chemical Features of Macroalgae Sulfated Polysaccharides
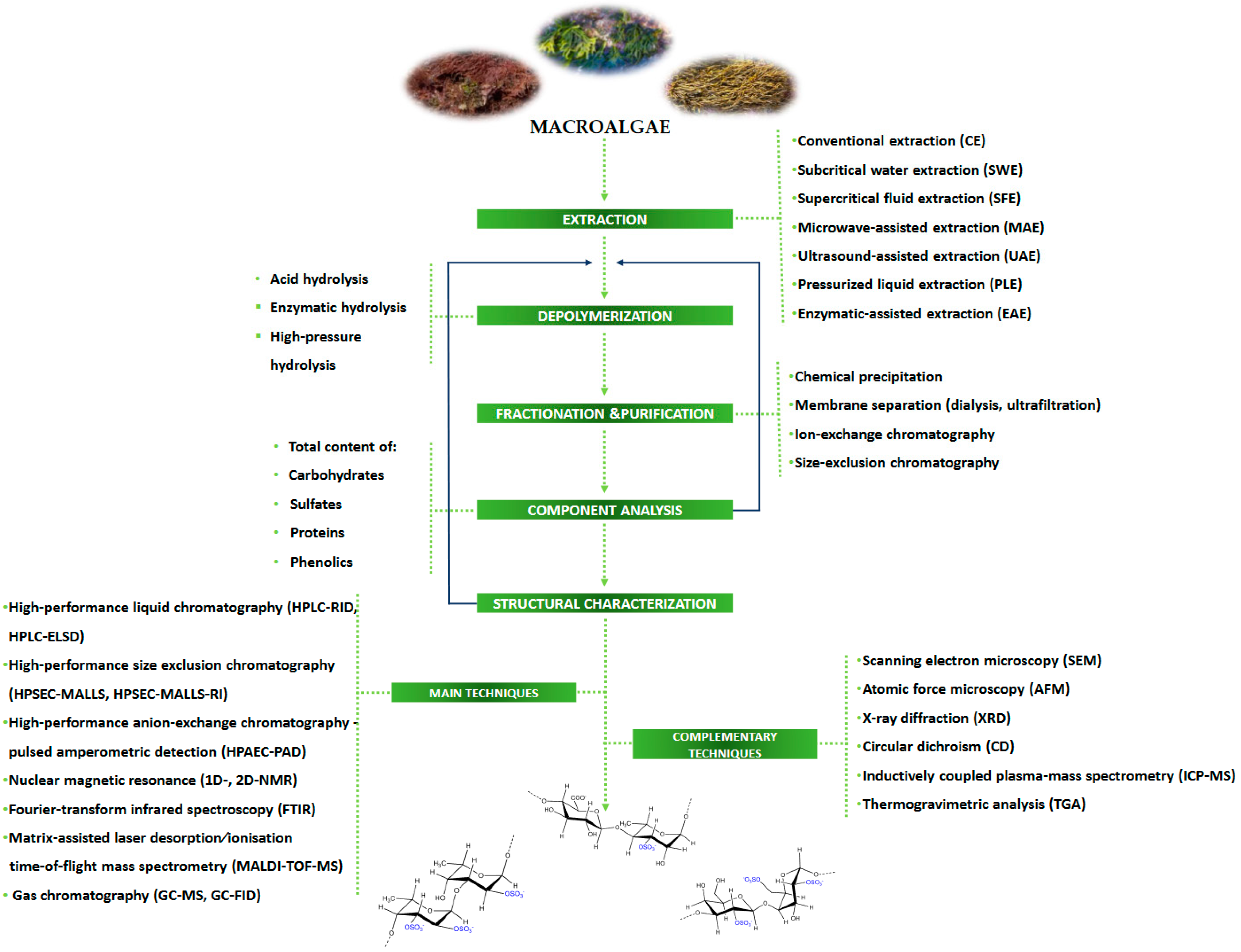
3. Extraction, Depolymerization, and Purification Processes
4. Chemical Characterization
5. Conclusions and Further Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAS | Atomic absorption spectroscopy |
| AEC | Anion-exchange chromatography |
| AGE | Agarose gel electrophoresis |
| CD | Circular dichroism |
| 13C NMR | Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance |
| 2D-NMR | Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| DEAE-Cellulose | Diethylaminoethyl-Cellulose column chromatography |
| DEAE-Sepharose | Diethylaminoethyl-Sepharose column chromatography |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| FACE | Fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| FTIR-ATR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy-attenuated total reflectance |
| GC-FID | Gas chromatography with flame ionization detection |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography with mass spectrometry detection |
| GPC | Gel permeation chromatography |
| 1H NMR | Proton nuclear magnetic resonance |
| HILIC-FT-MS | Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-Fourier transform-mass spectrometry |
| HPAEC | High-performance anion-exchange chromatography |
| HPAEC-PAD | High-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection |
| HPGPC | High-performance gel-permeation chromatography |
| HPLC-ELSD | High-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detector |
| HPLC-RID | High-performance liquid chromatography with refractive index detection |
| HPSEC | High-performance size-exclusion chromatography |
| HPSEC-ELSD | High-performance size-exclusion chromatography with evaporative light scattering detector |
| HPSEC-MALLS | High-performance size-exclusion chromatography coupled with multi-angle laser light scattering |
| HPSEC-MALS-RI | High-performance size-exclusion chromatography-multi-angle light scattering and refractive index detection |
| HPSEC-UV-MALLS-RI | High-performance size-exclusion liquid chromatography with ultraviolet-multi-angle laser light scattering-refractive index detection |
| HPTLC | High-performance thin-layer chromatography |
| ICP-MS | Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry |
| ICP-OES | Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry |
| IEC | Ion-exchange chromatography |
| LC-ESI–MS/MS | Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry |
| MALDI-TOF-MS | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| MALLS | Multi-angle laser light scattering detection |
| RP-HPLC | Reversed phase-high-performance liquid chromatography |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SEC-MALLS | Size-exclusion chromatography-multi-angle laser light scattering |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SEM-EDX | Scanning electron microscope-energy-dispersive X-ray analysis |
| SLS/DLS | Static and dynamic light scattering |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Lee, Y.E.; Kim, H.; Seo, C.; Park, T.; Lee, K.B.; Yoo, S.Y.; Hong, S.C.; Kim, J.T.; Lee, J. Marine polysaccharides: Therapeutic efficacy and biomedical applications. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2017, 40, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Coutinho, A.J.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruocco, N.; Costantini, S.; Guariniello, S.; Costantini, M. Polysaccharides from the Marine Environment with Pharmacological, Cosmeceutical and Nutraceutical Potential. Molecules 2016, 21, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Wan Aida, W.M.; Schiehser, S.; Rosenau, T.; Böhmdorfer, S. Structural elucidation of fucoidan from Cladosiphon okamuranus (Okinawa mozuku). Food Chem. 2019, 272, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, P.; Carpena, M.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Echave, J.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Cao, H.; Nie, S.; Xiao, J.; et al. Seaweed polysaccharides: Emerging extraction technologies, chemical modifications and bioactive properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.; Schütz, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Jana, S.; Ray, S.; Marschall, M. Exploiting the Amazing Diversity of Natural Source-Derived Polysaccharides: Modern Procedures of Isolation, Engineering, and Optimization of Antiviral Activities. Polymers 2021, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurpilhares, D.d.B.; Moreira, T.R.; Bueno, J.d.L.; Cinelli, L.P.; Mazzola, P.G.; Pessoa, A.; Sette, L.D. Algae’s sulfated polysaccharides modifications: Potential use of microbial enzymes. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalhal, F.; Cristelo, R.R.; Resende, D.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Sousa, E.; Correia-da-Silva, M. Antithrombotics from the Sea: Polysaccharides and Beyond. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, D.; Nah, J.-W.; Jeon, Y.-J. Advances in functionalizing fucoidans and alginates (bio)polymers by structural modifications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated Seaweed Polysaccharides as Multifunctional Materials in Drug Delivery Applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez, N.; Gonzalez-Munoz, M.J.; Ribeiro, D.; Fernandes, E.; Dominguez, H.; Freitas, M. Algae Polysaccharides’ Chemical Characterization and their Role in the Inflammatory Process. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L. Biological and therapeutic properties of the seaweed polysaccharides. Int. Biol. Rev. 2018, 2. Available online: http://journals.kei.org/index.php/IBR (accessed on 3 March 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasconcelos, A.A.; Pomin, V.H. The Sea as a Rich Source of Structurally Unique Glycosaminoglycans and Mimetics. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kidgell, J.T.; Magnusson, M.; de Nys, R.; Glasson, C.R.K. Ulvan: A systematic review of extraction, composition and function. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manlusoc, J.K.T.; Hsieh, C.L.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Salac, E.S.N.; Lee, Y.T.; Tsai, P.W. Pharmacologic Application Potentials of Sulfated Polysaccharide from Marine Algae. Polymers 2019, 11, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hentati, F.; Tounsi, L.; Djomdi, D.; Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Fendri, I.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Bioactive Polysaccharides from Seaweeds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, M.; Allahgholi, L.; Sardari, R.R.R.; Hreggviðsson, G.O.; Nordberg Karlsson, E. Extraction and Modification of Macroalgal Polysaccharides for Current and Next-Generation Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafarga, T.; Acién-Fernández, F.G.; Garcia-Vaquero, M. Bioactive peptides and carbohydrates from seaweed for food applications: Natural occurrence, isolation, purification, and identification. Algal Res. 2020, 48, 101909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Mao, J. Composition, isolation, purification, and biological activities of Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 228, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegappan, R.; Selvaprithiviraj, V.; Amirthalingam, S.; Jayakumar, R. Carrageenan based hydrogels for drug delivery, tissue engineering and wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarzadeh, M.; Golmoradizadeh, A.; Homaei, A.J.P.R. Carrageenans and carrageenases: Versatile polysaccharides and promising marine enzymes. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 535–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Vieira, H.; Gaspar, H.; Santos, S. Marketed marine natural products in the pharmaceutical and cosmeceutical industries: Tips for success. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1066–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernando, P.S.; Kim, K.N.; Kim, D.; Jeon, Y.J. Algal polysaccharides: Potential bioactive substances for cosmeceutical applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 39, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, C.; Sørensen, A.M.; Holdt, S.L.; Akoh, C.C.; Hermund, D.B. Source, Extraction, Characterization, and Applications of Novel Antioxidants from Seaweed. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 541–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, M.A.; Parvathy, K.R.K.; Balasubramanian, P.; Jayabalan, R. An overview of extraction and purification techniques of seaweed dietary fibers for immunomodulation on gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Biologically active macromolecules: Extraction strategies, therapeutic potential and biomedical perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrinčić, A.; Balbino, S.; Zorić, Z.; Pedisić, S.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Elez Garofulić, I.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. Advanced Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Brown Algal Polysaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Rajauria, G.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Sweeney, T. Polysaccharides from macroalgae: Recent advances, innovative technologies and challenges in extraction and purification. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matos, G.S.; Pereira, S.G.; Genisheva, Z.A.; Gomes, A.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rocha, C.M.R. Advances in Extraction Methods to Recover Added-Value Compounds from Seaweeds: Sustainability and Functionality. Foods 2021, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.; Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Sami, R.; Nikolova, M.P.; Chavali, M.; Sinha, S. Perspective on the Therapeutic Applications of Algal Polysaccharides. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 785–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, W.; Del Rio Flores, A. The Preparation and Structure Analysis Methods of Natural Polysaccharides of Plants and Fungi: A Review of Recent Development. Molecules 2019, 24, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quero-Jiménez, P.; Montenegro, O.; Sosa, R.; Pérez, D.L.; Rodríguez, A.S.; Méndez, R.R.; Alonso, A.C.; Corrales, A.; de la Torre, J.; Acosta, J.V.J.A. Total carbohydrates concentration evaluation in products of microbial origin. Afinidad. J. Chem. Eng. Theor. Appl. Chem. 2019, 76, 587. [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson, K.S.; Price, R.G. A note on the determination of the ester sulphate content of sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem. J. 1962, 84, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. A Simple Turbidimetric Method of Determining Total Sulfur in Plant Materials. Agron. J. 1970, 62, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.G.; Dodgson, K.S.; Price, R.G.; Rose, F.A. Polysaccharide sulphates. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 1961, 46, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torode, T.A.; Marcus, S.E.; Jam, M.; Tonon, T.; Blackburn, R.S.; Hervé, C.; Knox, J.P. Monoclonal antibodies directed to fucoidan preparations from brown algae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chemists, A.O.O.A.; Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume 222. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.; Randall, R.J.J.C. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Lee, W.W.; Kim, H.-S.; Kang, N.; Ranasinghe, P.; Lee, H.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. A fucoidan fraction purified from Chnoospora minima; a potential inhibitor of LPS-induced inflammatory responses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanniyasi, E.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; Anbalagan, M.M.; Raj, P.P.; Gopal, R.K. In Vitro anti-HIV-1 activity of the bioactive compound extracted and purified from two different marine macroalgae (seaweeds) (Dictyota bartayesiana J.V.Lamouroux and Turbinaria decurrens Bory). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daub, C.D.; Mabate, B.; Malgas, S.; Pletschke, B.I. Fucoidan from Ecklonia maxima is a powerful inhibitor of the diabetes-related enzyme, α-glucosidase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Rasin, A.B.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Zueva, A.O.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Ermakova, S.P. Modification of native fucoidan from Fucus evanescens by recombinant fucoidanase from marine bacteria Formosa algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Aparicio, I.; Martera, G.; Goñi, I.; Villanueva-Suárez, M.-J.; Redondo-Cuenca, A. Chemical structure and molecular weight influence the In Vitro fermentability of polysaccharide extracts from the edible seaweeds Himathalia elongata and Gigartina pistillata. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Yang, H.W.; Lee, H.G.; Kang, M.C.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Oh, J.Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Isolation, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of a Fucoidan from an Enzymatic Digest of the Edible Seaweed, Hizikia fusiforme. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; He, Y.; Ren, D.; Liu, S.; Wu, L. Structural characterization and antitumor effects of fucoidans from brown algae Kjellmaniella crassifolia farmed in northern China. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörschmann, P.; Kopplin, G.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Effects of Sulfated Fucans from Laminaria hyperborea Regarding VEGF Secretion, Cell Viability, and Oxidative Stress and Correlation with Molecular Weight. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M.-J.; Liu, G.-M.; Chen, Q.; Sun, L.; Chen, H. Antibacterial activity and mechanisms of depolymerized fucoidans isolated from Laminaria japonica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cai, L.; Liu, H.; Tu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, L. Chain conformation and biological activities of hyperbranched fucoidan derived from brown algae and its desulfated derivative. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, D.; Mansilla, A.; Matsuhiro, B.; Moncada-Basualto, M.; Lapier, M.; Maya, J.D.; Olea-Azar, C.; De Borggraeve, W.M. Chemical structure and biological properties of sulfated fucan from the sequential extraction of subantarctic Lessonia sp. (Phaeophyceae). Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alboofetileh, M.; Rezaei, M.; Tabarsa, M. Enzyme-assisted extraction of Nizamuddinia zanardinii for the recovery of sulfated polysaccharides with anticancer and immune-enhancing activities. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Shanura Fernando, I.P.; Wang, L.; Abetunga, D.T.U.; Kim, W.-S.; Lee, D.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Fucoidan isolated from Padina commersonii inhibit LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages blocking TLR/NF-κB signal pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, G.M.; Kurup, G.M. The efficacy of sulfated polysaccharides from Padina tetrastromatica in modulating the immune functions of RAW 264.7 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, G.M.; Raghavankutty, M.; Kurup, G.M. Sulfated polysaccharides from Padina tetrastromatica induce apoptosis in HeLa cells through ROS triggered mitochondrial pathway. Process Biochem. 2018, 68, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekshmi, V.S.; Kurup, G.M. Sulfated polysaccharides from the edible marine algae Padina tetrastromatica protects heart by ameliorating hyperlipidemia, endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in isoproterenol induced experimental myocardial infarction. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravana, P.S.; Cho, Y.-J.; Park, Y.-B.; Woo, H.-C.; Chun, B.-S. Structural, antioxidant, and emulsifying activities of fucoidan from Saccharina japonica using pressurized liquid extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Duan, D.; Jeon, Y.J.; Xu, J.; Gao, X. In Vitro and In Vivo anti-inflammatory activities of a fucose-rich fucoidan isolated from Saccharina japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sathuvan, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Tang, S.; Liu, Y.; Cheong, K.-L. Characterization of polysaccharides from different species of brown seaweed using saccharide mapping and chromatographic analysis. BMC Chem. 2021, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.G.; Lee, H.G.; Fernando, K.H.N.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ryu, B. Purification and Structural Characterization of Sulfated Polysaccharides Derived from Brown Algae, Sargassum binderi: Inhibitory Mechanism of iNOS and COX-2 Pathway Interaction. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoltseva, R.V.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Surits, V.V.; Silchenko, A.S.; Isakov, V.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Thinh, P.D.; Ermakova, S.P. Polysaccharides from brown algae Sargassum duplicatum: The structure and anticancer activity In Vitro. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usoltseva, R.V.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Surits, V.V.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Thinh, P.D.; Zadorozhny, P.A.; Ermakova, S.P. Comparison of structure and In Vitro anticancer activity of native and modified fucoidans from Sargassum feldmannii and S. duplicatum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Rasin, A.B.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Miansong, Z.; Changheng, L.; Malyarenko, O.; Zueva, A.O.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Ermakova, S.P. Structure, enzymatic transformation, anticancer activity of fucoidan and sulphated fucooligosaccharides from Sargassum horneri. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Sousa, S.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; Pintado, M.M.; Pereira, L.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Costa, J.P.; Silva, A.M.S.; Duarte, A.C.; et al. Sargassum muticum and Osmundea pinnatifida Enzymatic Extracts: Chemical, Structural, and Cytotoxic Characterization. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Wei, X.-L.; Sun, Z.-L.; Wang, C.-Y. Extraction, fractionation, and chemical characterisation of fucoidans from the brown seaweed Sargassum pallidum. Czech J. Food Sci. 2016, 34, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanavil, B.; Selvaraj, K.; Aanandhalakshmi, R.; Sri, K.U.; Arumugam, M. Bioactive and thermostable sulphated polysaccharide from Sargassum swartzii with drug delivery applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Tarafdar, A.; Kumar, D.; Verma, K.; Aggarwal, M.; Badgujar, P.C. Evaluation of Chemical, Functional, Spectral, and Thermal Characteristics of Sargassum wightii and Ulva rigida from Indian Coast. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 9133464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwarsamy, M.; Gooneratne, R.; Ravichandran, R. Effect of fucoidan from Turbinaria conoides on human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial (A549) cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, S.P.; Menshova, R.V.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Thinh, P.D.; Ly, B.M.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Structure, chemical and enzymatic modification, and anticancer activity of polysaccharides from the brown alga Turbinaria ornata. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsur, H.A.; Jaswir, I.; Simsek, S.; Amid, A.; Alam, Z. Chemical structure of sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweed (Turbinaria turbinata). Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, H.S.A.; Lu, J.; Zhou, W. Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of fucoidan isolated from Undaria pinnatifida grown in New Zealand. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaballi, I.; Sallem, I.; Feki, A.; Cherif, B.; Kallel, C.; Boudawara, O.; Jamoussi, K.; Mellouli, L.; Nasri, M.; Amara, I.B. Polysaccharide from a Tunisian red seaweed Chondrus canaliculatus: Structural characteristics, antioxidant activity and In Vivo hemato-nephroprotective properties on maneb induced toxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagas, F.; Lima, G.C.; Dos Santos, V.I.N.; Costa, L.E.C.; de Sousa, W.M.; Sombra, V.G.; de Araújo, D.F.; Barros, F.C.N.; Marinho-Soriano, E.; de Andrade Feitosa, J.P.; et al. Sulfated polysaccharide from the red algae Gelidiella acerosa: Anticoagulant, antiplatelet and antithrombotic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Yang, S.; Xiao, Z.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Qian, Z.-J. Structural Characterization of Sulfated Polysaccharide Isolated from Red Algae (Gelidium crinale) and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Macrophage Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 794818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alencar, P.O.C.; Lima, G.C.; Barros, F.C.N.; Costa, L.E.C.; Ribeiro, C.V.P.E.; Sousa, W.M.; Sombra, V.G.; Abreu, C.M.W.S.; Abreu, E.S.; Pontes, E.O.B.; et al. A novel antioxidant sulfated polysaccharide from the algae Gracilaria caudata: In Vitro and In Vivo activities. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.R.P.; Silva, C.P.M.; Carvalho-França, L.F.; Alves, E.H.P.; Santos-Carvalho, J.; Di Lenardo, D.; Brito, T.V.; Medeiros, J.-V.R.; Oliveira, J.S.; Freitas, A.L.P.; et al. Sulfated polysaccharides from the marine algae Gracilaria caudata prevent tissue damage caused by ligature-induced periodontitis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olasehinde, T.A.; Mabinya, L.V.; Olaniran, A.O.; Okoh, A.I. Chemical characterization of sulfated polysaccharides from Gracilaria gracilis and Ulva lactuca and their radical scavenging, metal chelating, and cholinesterase inhibitory activities. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belattmania, Z.; Bhaby, S.; Nadri, A.; Khaya, K.; Bentiss, F.; Jama, C.; Reani, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Sabour, B. Gracilaria gracilis (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta) from Dakhla (Southern Moroccan Atlantic Coast) as Source of Agar: Content, Chemical Characteristics, and Gelling Properties. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Yan, X.; Cheong, K.-L.; Liu, Y. Extraction, purification, and characterization of polysaccharides from marine algae Gracilaria lemaneiformis with anti-tumor activity. Process Biochem. 2018, 73, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajili, S.; Ammar, H.H.; Mzoughi, Z.; Amor, H.B.H.; Muller, C.D.; Majdoub, H.; Bouraoui, A. Characterization of sulfated polysaccharide from Laurencia obtusa and its apoptotic, gastroprotective and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannam, A.; Murad, H.; Jazzara, M.; Odeh, A.; Allaf, A.W. Isolation, Structural characterization, and antiproliferative activity of phycocolloids from the red seaweed Laurencia papillosa on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Yang, S.; Chang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zeng, H. Application of X-ray diffraction and energy dispersive spectroscopy in the isolation of sulfated polysaccharide from Porphyra haitanensis and its antioxidant capacity under In Vitro digestion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6452–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, W.M.; Silva, R.O.; Bezerra, F.F.; Bingana, R.D.; Barros, F.C.N.; Costa, L.E.C.; Sombra, V.G.; Soares, P.M.G.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; de Paula, R.C.M.; et al. Sulfated polysaccharide fraction from marine algae Solieria filiformis: Structural characterization, gastroprotective and antioxidant effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.D.S.; Sabry, D.A.; Silva, C.H.F.; Gomes, D.L.; Santana-Filho, A.P.; Sassaki, G.L.; Rocha, H.A.O. Immunostimulatory Effect of Sulfated Galactans from the Green Seaweed Caulerpa cupressoides var. flabellata. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Song, S.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, J.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Anti-inflammatory activity and structural identification of a sulfated polysaccharide CLGP4 from Caulerpa lentillifera. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajriah, S.; Rizki, I.F.; Sinurat, E. Characterization and analysis of the antidiabetic activities of sulphated polysaccharide extract from Caulerpa lentillifera. Pharmacia 2021, 68, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, G.P.C.; Sousa, A.F.G.; Viana, R.L.S.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Medeiros, S.R.B.; Moreira, S.M.G. Osteogenic activity of non-genotoxic sulfated polysaccharides from the green seaweed Caulerpa sertularioides. Algal Res. 2019, 42, 101546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Chávez-Quintal, C.; Caamal-Fuentes, E.; Vázquez-Delfín, E.; Madera-Santana, T.; Robledo, D. Valorization of the filamentous seaweed Chaetomorpha gracilis (Cladophoraceae, Chlorophyta) from an IMTA system. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, D.A.; Cordeiro, S.L.; Ferreira Silva, C.H.; Cunha Farias, E.H.; Sassaki, G.L.; Nader, H.B.; Oliveira Rocha, H.A. Pharmacological prospection and structural characterization of two purified sulfated and pyruvylated homogalactans from green algae Codium isthmocladum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, D.L.; Mazepa, E.; Biscaia, S.M.P.; Gonçalves, J.P.; Oliveira, C.C.; Rossi, G.R.; Ferreira, L.G.; Noseda, M.D.; Trindade, E.S.; Duarte, M.E.R.; et al. Non-Cytotoxic Sulfated Heterorhamnan from Gayralia brasiliensis Green Seaweed Reduces Driver Features of Melanoma Metastatic Progression. Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 22, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; He, X.; Qin, L.; He, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Mao, W. Anticoagulant and Antithrombotic Properties in Vitro and in Vivo of a Novel Sulfated Polysaccharide from Marine Green Alga Monostroma nitidum. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Hou, L.; Qin, L.; He, M.; Li, W.; Mao, W. A sulfated glucuronorhamnan from the green seaweed Monostroma nitidum: Characteristics of its structure and antiviral activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidara, M.; Yaich, H.; Amor, I.B.; Fakhfakh, J.; Gargouri, J.; Lassoued, S.; Blecker, C.; Richel, A.; Attia, H.; Garna, H. Effect of extraction procedures on the chemical structure, antitumor and anticoagulant properties of ulvan from Ulva lactuca of Tunisia coast. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El Azm, N.; Fleita, D.; Rifaat, D.; Mpingirika, E.Z.; Amleh, A.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Production of Bioactive Compounds from the Sulfated Polysaccharides Extracts of Ulva lactuca: Post-Extraction Enzymatic Hydrolysis Followed by Ion-Exchange Chromatographic Fractionation. Molecules 2019, 24, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, Y.-H.R.; Chen, G.-W.; Pan, C.-L.; Lin, H.-T.V. Production of Ulvan Oligosaccharides with Antioxidant and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Activities by Microbial Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Fermentation 2021, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.E.; Andrade, R.G.C.; Accardo, C.M.; Maia, L.F.; Oliveira, L.F.C.; Nader, H.B.; Aguiar, J.A.K.; Medeiros, V.P. Influence of sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva lactuca L. upon Xa and IIa coagulation factors and on venous blood clot formation. Algal Res. 2020, 45, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari-Chmayssem, N.; Taha, S.; Mawlawi, H.; Guégan, J.-P.; Jeftić, J.; Benvegnu, T. Extracted ulvans from green algae Ulva linza of Lebanese origin and amphiphilic derivatives: Evaluation of their physico-chemical and rheological properties. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qu, H.; Gao, Z.; Zeng, D.; Wang, J.; Baranenko, D.; Li, Y.; Lu, W. Protective effects of Ulva pertusa polysaccharide and polysaccharide-iron (III) complex on cyclophosphamide induced immunosuppression in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournière, M.; Latire, T.; Lang, M.; Terme, N.; Bourgougnon, N.; Bedoux, G. Production of Active Poly- and Oligosaccharidic Fractions from Ulva sp. by Combining Enzyme-Assisted Extraction (EAE) and Depolymerization. Metabolites 2019, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahlström, N.; Nylander, F.; Malmhäll-Bah, E.; Sjövold, K.; Edlund, U.; Westman, G.; Albers, E. Composition and structure of cell wall ulvans recovered from Ulva spp. along the Swedish west coast. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Algae | Source | Compound | Chemical Characterization | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ochrophyta (Brown Algae) | ||||
| Chnoospora minima | Southern coastal area of Sri Lanka | Fucoidan | Component analysis DEAE-Sepharose chromatography FTIR AGE HPAE-PAD NMR | [42] |
| Cladosiphon okamuranus | Ishigaki Island (Okinawa, Japan) | Fucoidan | Component analysis IEC GC-FID GC-MS Chemical modifications | [4] |
| Dictyota bartayesiana Turbinaria decurrens | Mandapam Coastal region, Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu, India | Fucoidan | Component analysis FTIR RP-HPLC DEAE-Cellulose chromatography Chemical modifications | [43] |
| Ecklonia maxima | HIK-Abalone Farm, Hermanus, South Africa | Fucoidan | Component analysis Ultracentrifugation FTIR NMR XRD | [44] |
| Fucus evanescens | - | Fucoidan | Component analysis SEC IEC NMR | [45] |
| Himanthalia elongata | Spanish Atlantic coasts (local supplier Porto-Muiños, A Coruña, Spain) | Fucoidans | FTIR HPSEC GC-FID | [46] |
| Hizikia fusiforme | - | Fucoidan | Component analysis HPGPC HPAEC-PAD FTIR NMR | [47] |
| Kjellmaniella crassifolia | Coast of Dalian, China | Fucoidans | Component analysis HPLC DEAE-Sepharose chromatography SEC FTIR 1D and 2D NMR | [48] |
| Laminaria hyperborea | Northeast Atlantic Ocean, Scandinavia | Sulfated fucans | AEC Raman spectroscopy ICP-MS HPSEC-MALLS | [49] |
| Laminaria japonica | Putian, Fujian, China | Fucoidans | DEAE-Cellulose chromatography Ultrafiltration Chemical modifications GC | [50] |
| Laminaria japonica | Crude commercial fucoidan (Rizhao Jiejing Ocean Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd., Rizhao, China) | Fucoidan | Elemental analysis Component analysis Chemical modifications 1D and 2D NMR GC-FID GC-MS SLS/DLS measurements FTIR AFM | [51] |
| Lessonia sp. | Tekenika Bay, Southern Chile | Sulfated fucan | FTIR NMR GC-FID DEAE HPLC | [52] |
| Nizamuddinia zanardinii | Rocky beaches of Chabahr at Oman Sea, South of Iran | Fucoidan | Component analysis FTIR GCMS HPSEC-UV-MALLS-RI SEM | [53] |
| Padina commersonii | Coast of Galle, Sri Lanka | Fucoidan | AEC FTIR NMR | [54] |
| Padina tetrastromatica | Vizhinjam coast of Kerala, India | SPs | 1H NMR DEAE-Cellulose chromatography | [55] |
| Padina tetrastromatica | Vizhinjam coast of Kerala, India | SPs | Elemental analysis UV-Vis GPC | [56] |
| Padina tetrastromatica | Coastal rocks of Mulloor, Vizhinjam, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India | Sulfated fucan | HPTLC LC-ESI-MS DEAE-Cellulose chromatography | [57] |
| Saccharina japonica | Guemil-eup, Wando-gun, and Jeollanam-do, Republic of Korea | Fucoidans | Component analysis Elemental analysis FTIR UV-Vis XRD TGA TLC HPSEC-ELSD HPLC-ELSD | [58] |
| Saccharina japonica | Xiapu, Fujian province, China | Fucoidan | Component analysis HPSEC-MALLS-RID FTIR NMR GC | [59] |
| Saccharina japonica Sargassum fusiforme Sargassum hemiphyllum Undaria pinnatifida | Various | SPs | AEC HPSEC-MALLS-Visc-RID FTIR HPLC | [60] |
| Sargassum binderi | Hikkaduwa southern coast of Sri Lanka | - | IEC FTIR NMR | [61] |
| Sargassum duplicatum | Nhatrang Bay (Socialist Republic of Vietnam) | Fucoidan | Component analysis Chemical modifications ESI-MS/MS MALDI-TOF NMR HPSEC DEAE-Cellulose chromatography AGE | [62] |
| Sargassum duplicatum Sargassum feldmannii | Nhatrang bay (Socialist Republic of Vietnam) | Fucoidan | ESI-MS/MS NMR HPSEC Chemical modifications | [63] |
| Sargassum horneri | - | Fucoidan and sulfated fucooligosaccharides | NMR IEC PAGE | [64] |
| Sargassum muticum | Buarcos Bay (Figueira da Foz, Portugal) | Fucoidans | Component analysis ICP-OES HPLC-UV FTIR-ATR 1H NMR | [65] |
| Sargassum pallidum | Weihai, Yellow Sea, China | Fucoidans | Component analysis HPGPC-FTIR GC-FID | [66] |
| Sargassum swartzii | Coast of Kanyakumari, India | SPs | FTIR NMR UV-Vis TLC HPSEC TGA | [67] |
| Sargassum wightii | Tamil Nadu, India | - | Elemental analysis Component analysis FTIR TGA | [68] |
| Turbinaria conoides | Coast of Mandapam, Rameswaram, Gulf of Mannar, Tamil Nadu, India | Fucoidan | GPC HPLC NMR GC-MS DEAE-Cellulose chromatography Component analysis | [69] |
| Turbinaria ornata | Nhatrang Bay (Socialist Republic of Vietnam) | Fucoidan | DEAE ESI-MS/MS GC-MS NMR | [70] |
| Turbinaria turbinata | Malaysian origin | SPs | GC-FID FTIR HPSEC-MALS-RI DEAE-Cellulose chromatography NMR TGA | [71] |
| Undaria pinnatifida | Auckland, New Zealand | Fucoidan | Component analysis FTIR 2D-NMR HPLC-RID | [72] |
| Rhodophyta (Red Algae) | ||||
| Chondrus canaliculatus | Tunisian coasts, Sfax (“Sidi Mansour, Tabaroura”) | Fractions of SPs | Component analysis HPGPC FTIR-ATR HPLC-RID Solid-state 13C NMR | [73] |
| Gelidiella acerosa | Atlantic coast, Brazil (Búzios Beach, Nísia Floresta—Rio Grande do Norte) | SPs | Elemental analysis Component analysis FTIR NMR HPSEC | [74] |
| Gelidium crinale | Naozhou Island Sea, Zhanjiang City, Guangdong Province | SPs | Chemical modifications Component analysis FTIR HPLC-UV GPC | [75] |
| Gigartina pistillata | Collected at Spanish Atlantic coasts and obtained from a local supplier (Porto-Muiños, A Coruña, Spain) | Carrageenans | Component analysis FTIR HPSEC GC-FID | [46] |
| Gracilaria caudata | Brazilian Atlantic coast (Fleixeiras Beach, Trairí—Ceará) | SP | Component analysis GPC ICP-OES FTIR NMR | [76] |
| Gracilaria caudata | Northeast Atlantic coast of Brazil (Fleixeira Beach, Trairi—CE, Brazil) | SPs | FTIR NMR | [77] |
| Gracilaria gracilis | Wild Coast Abalone, East London, South Africa | SPs | Component analysis SEM-EDX FTIR GC-MS | [78] |
| Gracilaria gracilis | Dakhala shoreline, Morocco | Agars | FTIR NMR | [79] |
| Gracilaria lemaneiformis | Nan’ao Island of China | SPs | DEAE-Sephadex chromatography HPLC-ELSD FTIR GC-FID GC-MS | [80] |
| Laurencia obtusa | Coastal region of Bizerte (Tunisia) in the Mediterranean Sea | Complex SPs | Component analysis DEAE-Sephadex chromatography SEC-MALLS FTIR NMR | [81] |
| Laurencia papillosa | East-Mediterranean coastal waters of Lattakia, Syria | Carrageenans | Component analysis FTIR-ATR NMR GPC | [82] |
| Osmundea pinnatifida | Buarcos bay (Figueira da Foz, Portugal) | Agarans | Component analysis ICP-OES HPLC FTIR-ATR NMR | [65] |
| Porphyra aitanensis | Purchased from Pingtan Island, Fujian Province, China | SPs | HPLC-SEC-MALLS-RI UV EDS XRD | [83] |
| Solieria filiformis | Northeast Atlantic coast of Brazil (Flexeiras Beach, Trairi—Ceará) | SPs | HPSEC FTIR NMR Component analysis | [84] |
| Chlorophyta (Green Algae) | ||||
| Caulerpa cupressoides var. flabellata | Nísia Floresta, southern coast of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. | Sulfated galactans | Component analysis GPC NMR IEC | [85] |
| Caulerpa lentillifera | Cultivated, Dalian, Liaoning, China | SPs | Chemical modifications NMR GC-MS | [86] |
| Caulerpa lentillifera | Takalar, South of Sulawesi, Indonesia | SPs | FTIR HPLC NMR | [87] |
| Caulerpa sertularioides | Coast of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil | SPs | Component analysis HPLC-RID GPC | [88] |
| Chaetomorpha gracilis | IMTA system Cinvestav Marine Station, Telchac | SPs | Component analysis FTIR NMR XRD TGA | [89] |
| Codium isthmocladum | Pirambuzios beach, Nisia Floresta, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil | Sulfated homogalactans | AEC AGE GPC GC-MS NMR | [90] |
| Gayralia brasiliensis | Baía de Paranaguá, Paraná State, Brasil | Sulfated heterorhamnan | Component analysis HPSEC-MALLS-RI NMR | [91] |
| Monostroma nitidum | Coast of Yantai, China | SPs | Component analysis NMR GC-MS AEC HILIC-FT-MS FTIR HPGPC | [92] |
| Monostroma nitidum | Yellow Sea of China | Sulfated glucuronorhamnan | Component analysis FTIR NMR HILIC-FT-MS HPGPC RP-HPLC | [93] |
| Ulva lactuca | Taboulba and Sayada (Monastir—Tunisia) | Ulvans | Component analysis GC-FID HPSEC FTIR NMR | [94] |
| Ulva lactuca | Mediterranean Sea in Egypt (Alexandria in Abou Kir region) | SPs | Component analysis AEC FTIR HPLC-RID | [95] |
| Ulva lactuca | Wild Coast Abalone, East London, South Africa | SPs | Component analysis SEM-EDX FTIR GC-MS | [78] |
| Ulva lactuca | Ho-Ping Island, Keelung, Taiwan | Ulvans | Component analysis FTIR HPSEC | [96] |
| Ulva lactuca L. | Seashore of Nísia Floresta, RN, Brazil | SPs | Component analysis AGE FACE FT-Raman spectroscopy | [97] |
| Ulva linza | Lebanese Mediterranean coast | Ulvans | Elemental analysis Component analysis SEC HPLC FTIR NMR | [98] |
| Ulva pertusa | China | SPs | DEAE-Cellulose chromatography HPGPC GC FTIR AAS | [99] |
| Ulva sp. | Landrézac Beach, Sarzeau, Brittany, France | Ulvans | Component analysis HPSEC HPAEC MALDI-TOF | [100] |
| Ulva spp. | Swedish West coast | Ulvans | Elemental analysis FTIR SEC TGA SEM NMR HPAEC-PAD | [101] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, A.; Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Gaspar, H.; Pedrosa, R. Sulfated Polysaccharides from Macroalgae—A Simple Roadmap for Chemical Characterization. Polymers 2023, 15, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020399
Martins A, Alves C, Silva J, Pinteus S, Gaspar H, Pedrosa R. Sulfated Polysaccharides from Macroalgae—A Simple Roadmap for Chemical Characterization. Polymers. 2023; 15(2):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020399
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Alice, Celso Alves, Joana Silva, Susete Pinteus, Helena Gaspar, and Rui Pedrosa. 2023. "Sulfated Polysaccharides from Macroalgae—A Simple Roadmap for Chemical Characterization" Polymers 15, no. 2: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020399
APA StyleMartins, A., Alves, C., Silva, J., Pinteus, S., Gaspar, H., & Pedrosa, R. (2023). Sulfated Polysaccharides from Macroalgae—A Simple Roadmap for Chemical Characterization. Polymers, 15(2), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020399











