Oil Adsorption Kinetics of Calcium Stearate-Coated Kapok Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
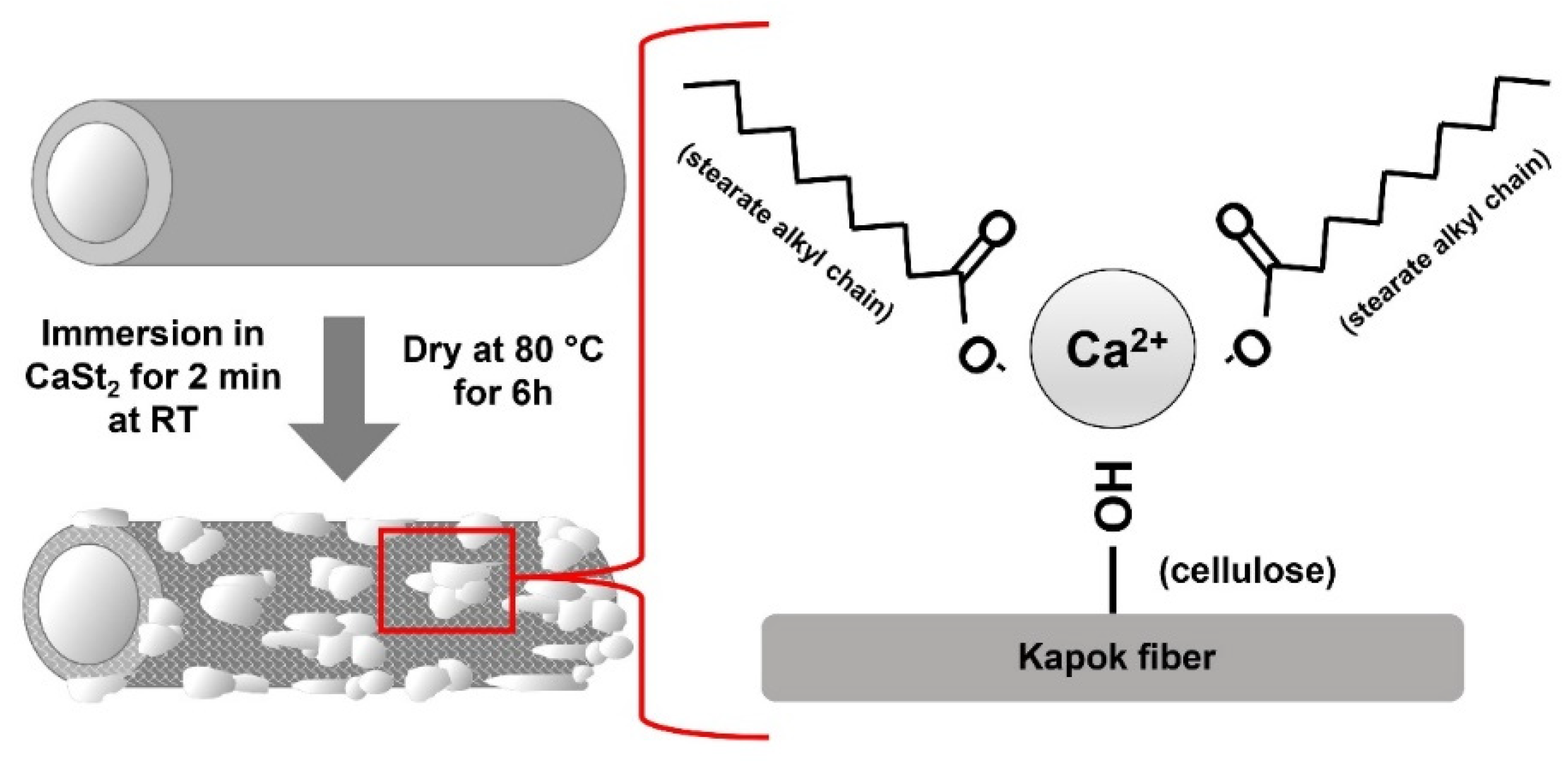
2.2. Preparation of CaSt2-Coated Kapok Fibers
2.3. Material Characterizations
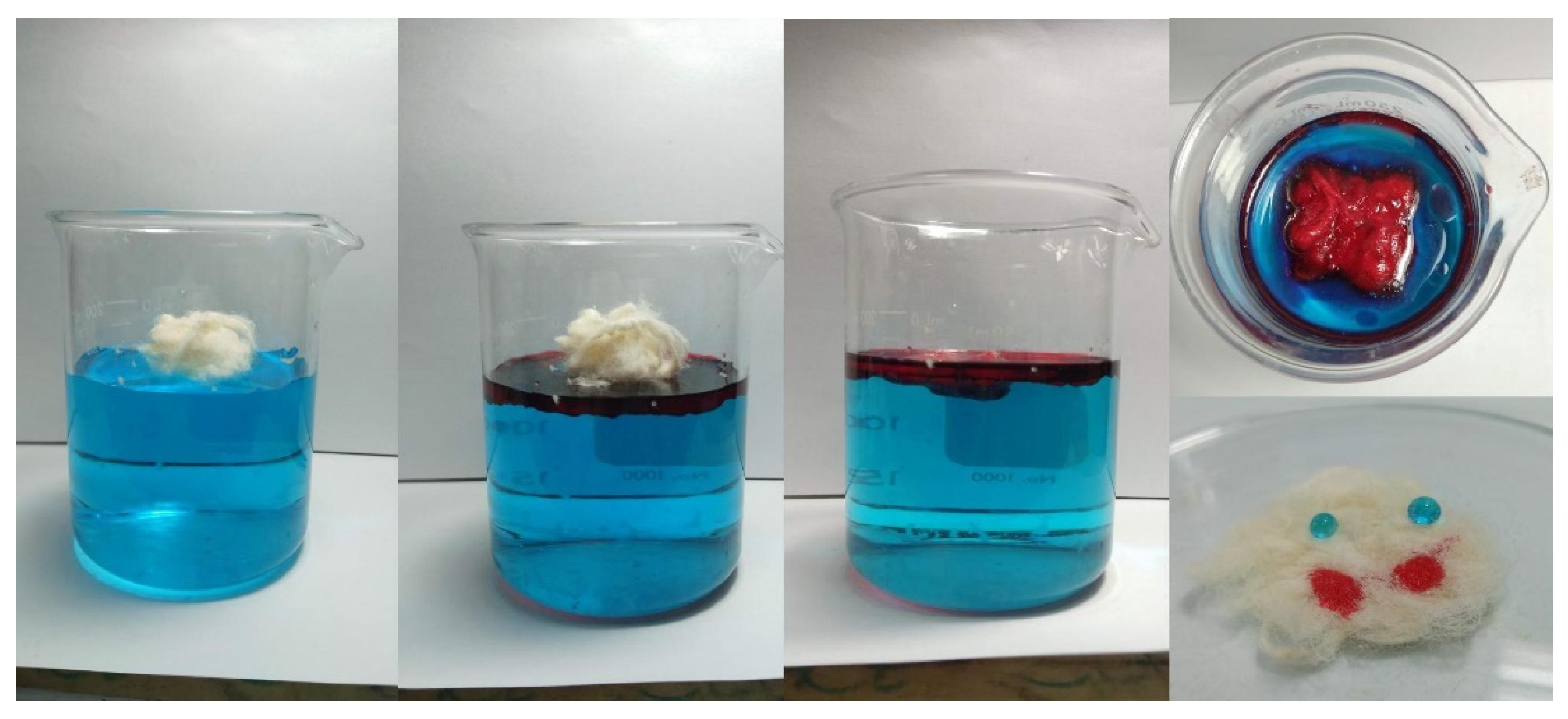
2.4. Oil Sorption and Reusability Experiments
2.5. Sorption Kinetic Studies
2.5.1. Pure Oil Sorption
2.5.2. Oil-In-Water Sorption
2.5.3. Kinetic Models
3. Results and Discussion
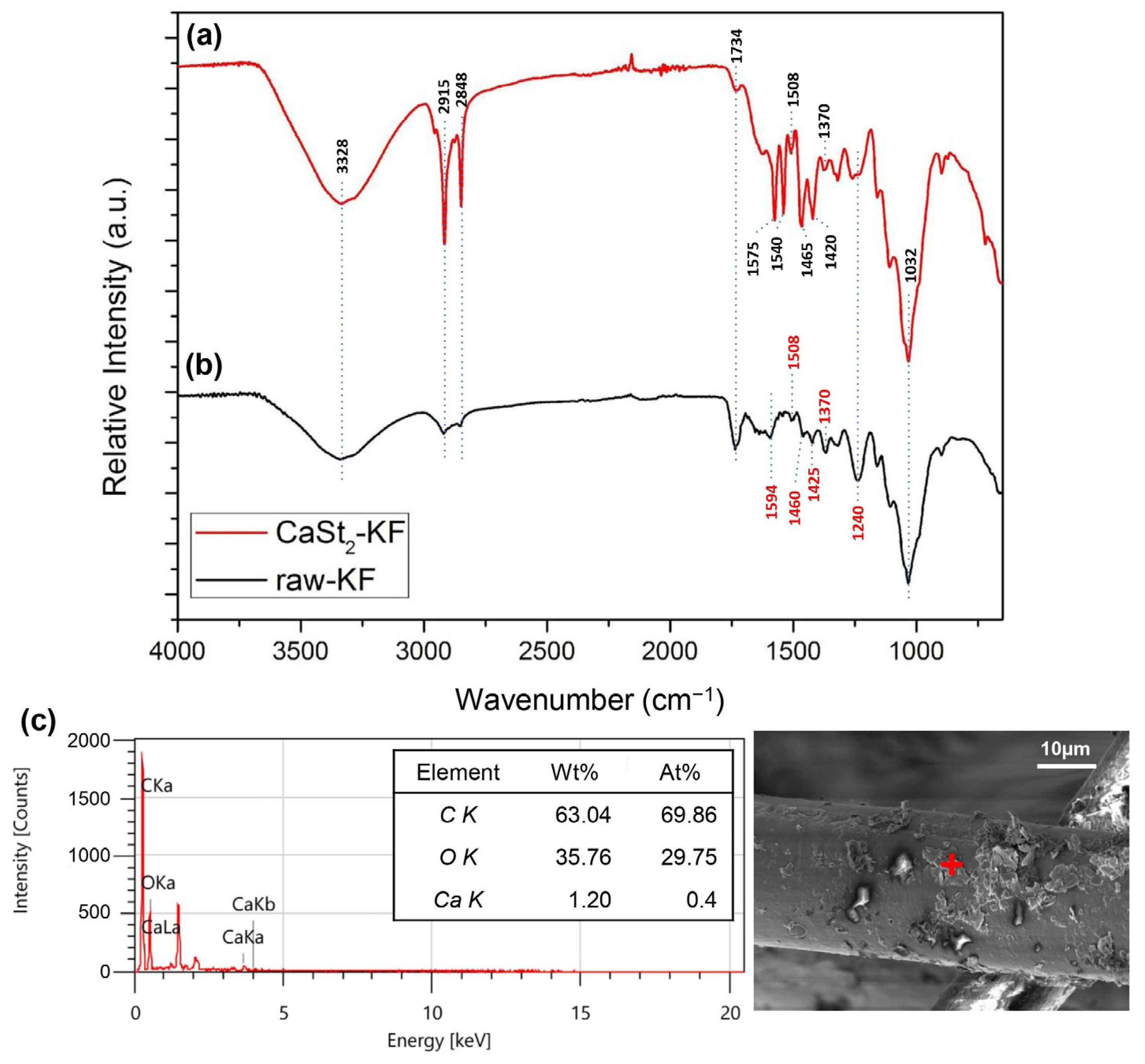
3.1. Modification of Kapok Fibers with Calcium Stearate
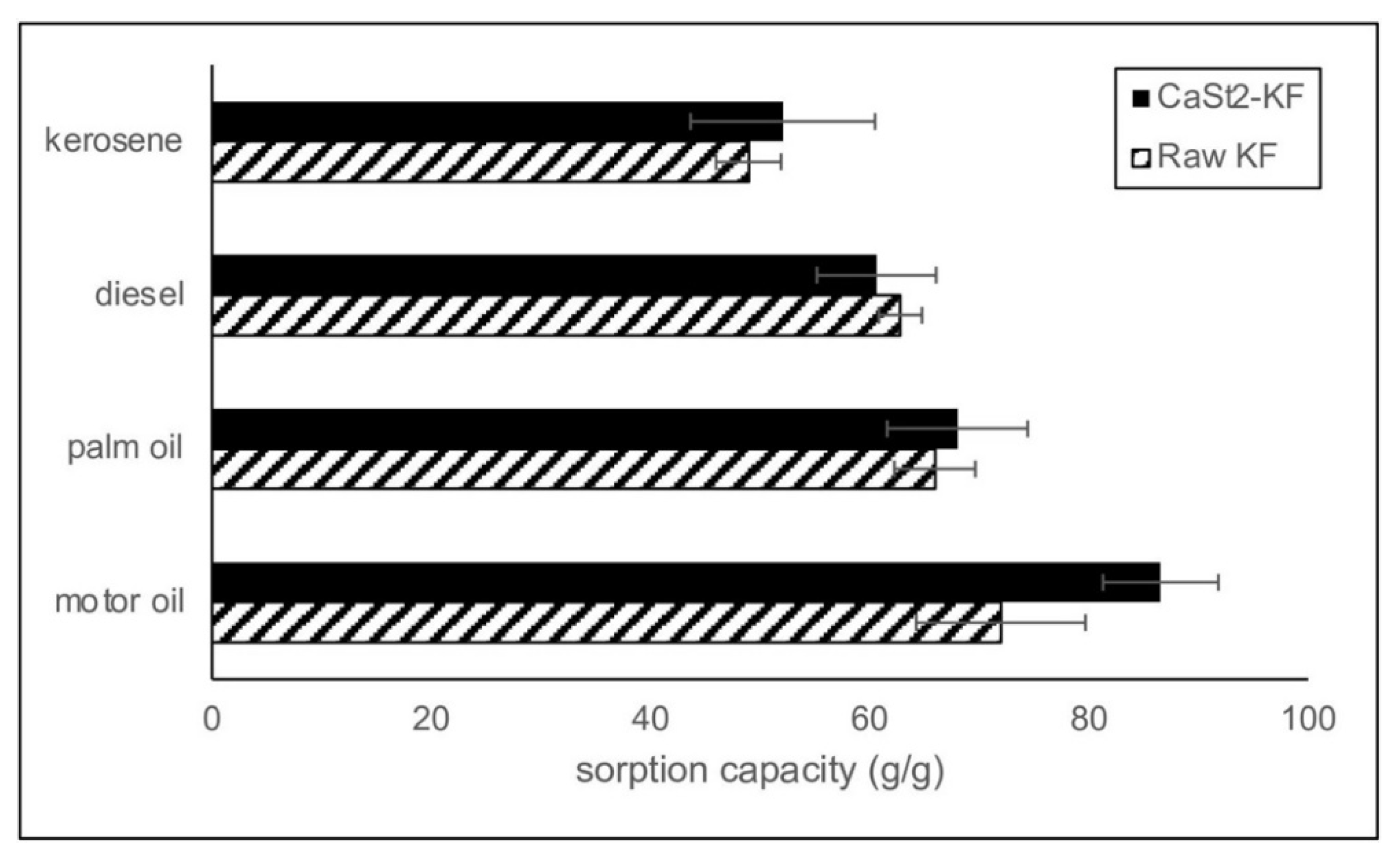
3.2. Oil Sorption Capacity
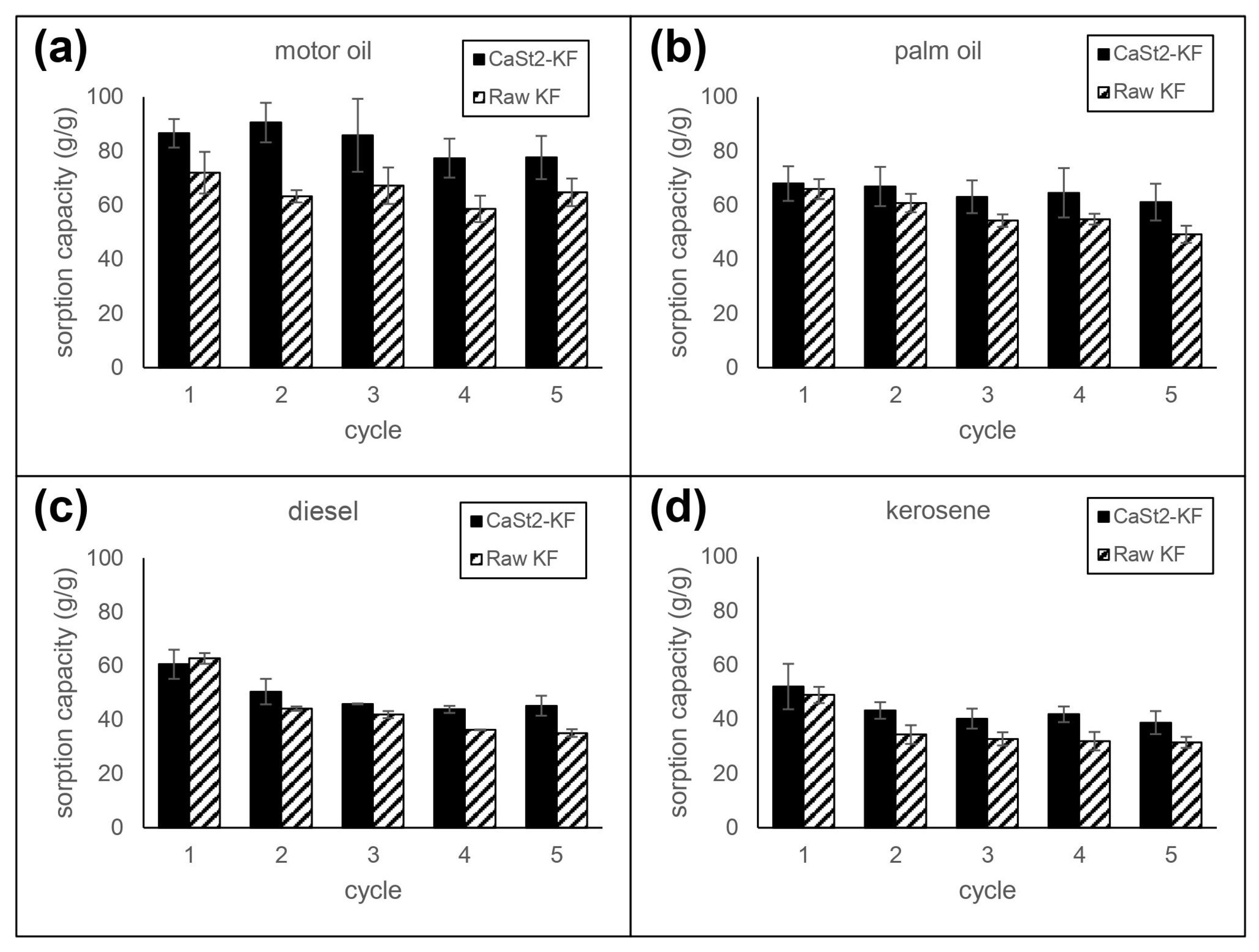
3.3. Reusability
3.4. Kinetic Modeling
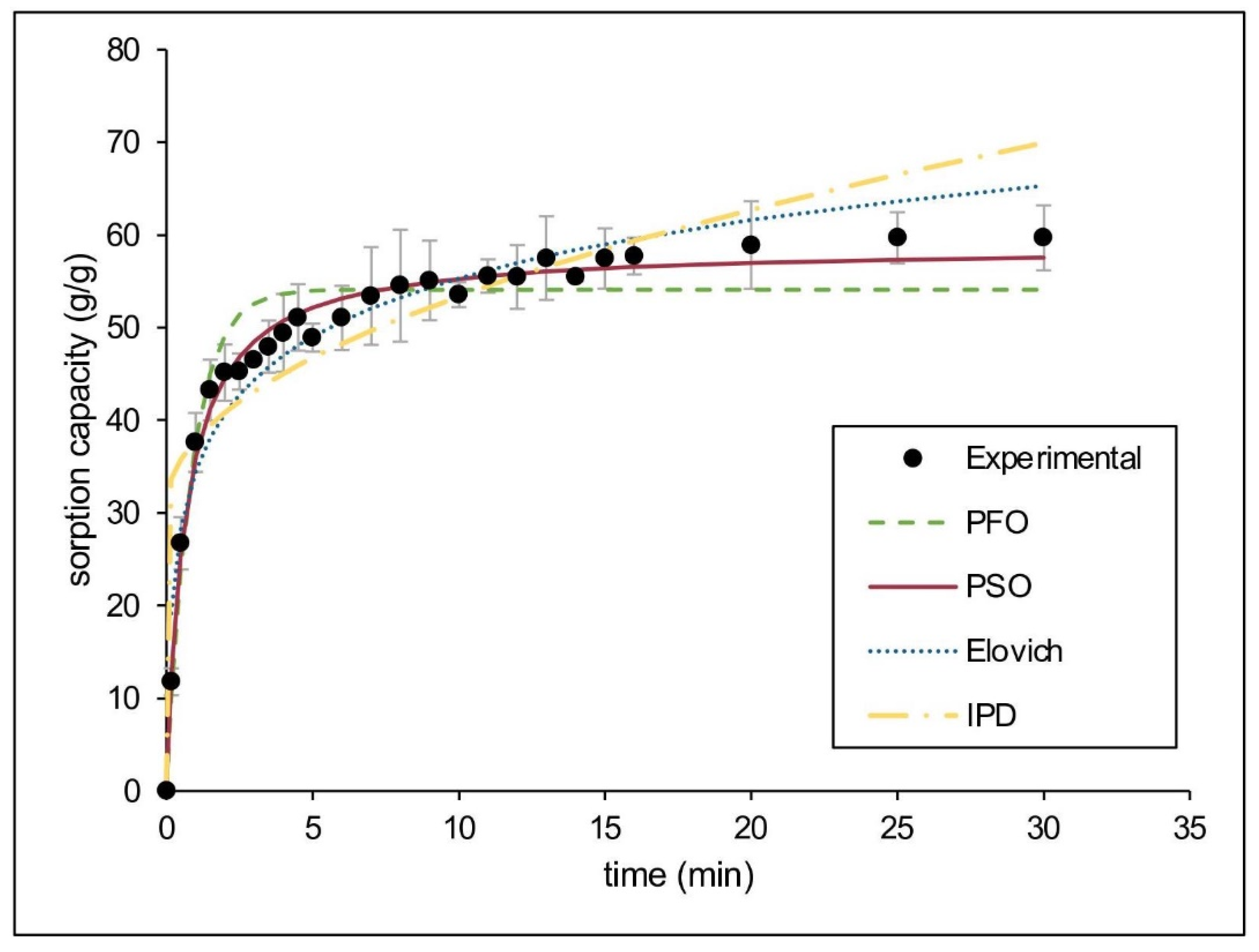
3.4.1. Pure Oil Sorption
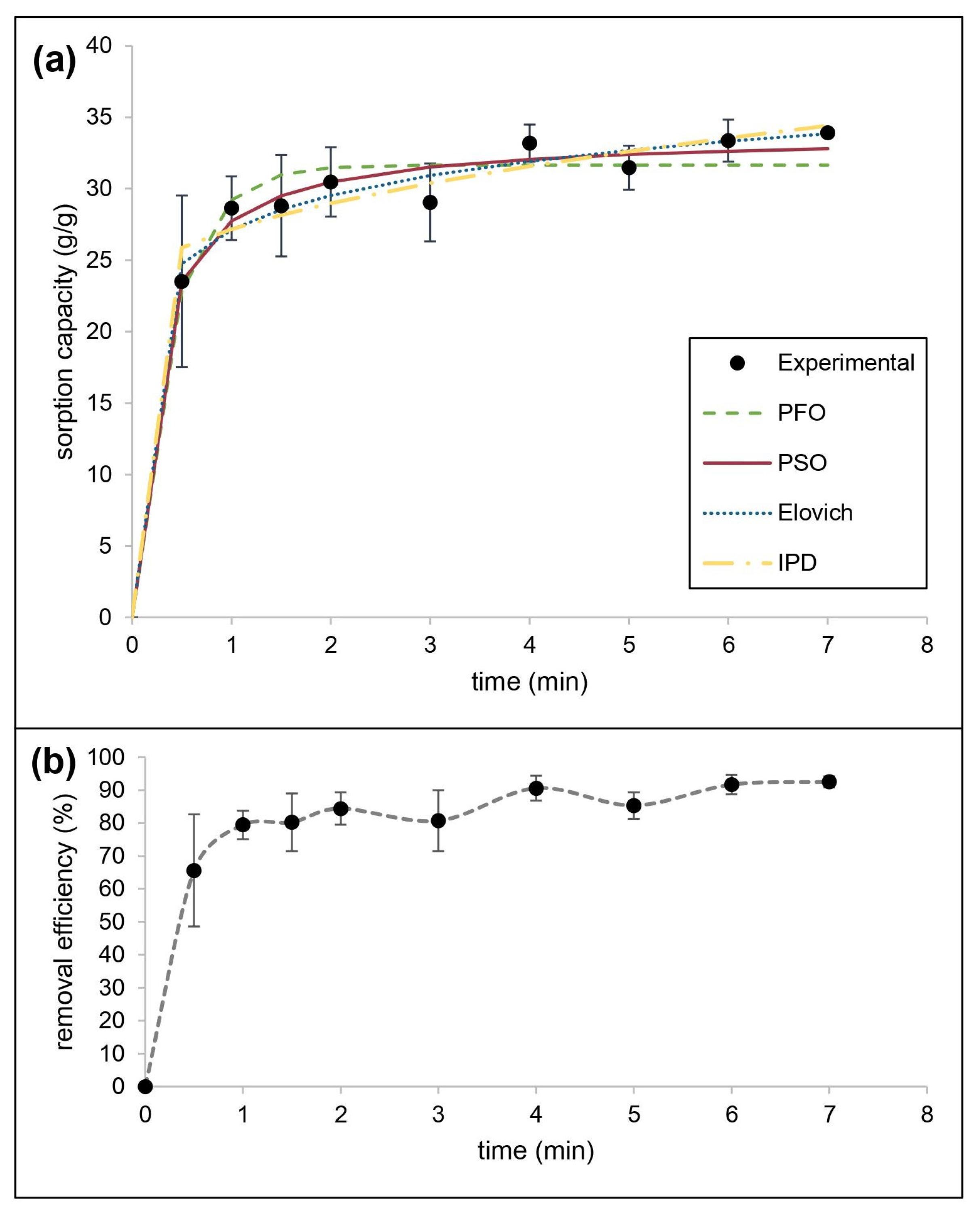
3.4.2. Oil-In-Water Sorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, D.; Wang, T.; Hu, S.; Wu, W.; Lu, B.; Huang, X.; Yu, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, G.G.; Zhang, J. Solvent-free processing of eco-friendly magnetic and superhydrophobic absorbent from all-plant-based materials for efficient oil and organic solvent sorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, K.; Tian, W.; Bai, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Du, Z.; Gong, X. Application of magnetic adsorbents based on iron oxide nanoparticles for oil spill remediation: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Tzivras, D.; Dracopoulos, V.; Ioannides, T. Application of sorbents for oil spill cleanup focusing on natural-based modified materials: A review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Li, M.C.; Wu, Q.; Pojman, J.; Kuroda, D.G. Synthesis-free phase-selective gelator for oil-spill remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33549–33553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurell, J.; Holder, A.; Gullett, B.; Lamie, N.; Arsava, K.; Conmy, R.; Sundaravadivelu, D.; Mitchell, W.; Stone, K. Analysis of emissions and residue from methods to improve efficiency of at-sea, in situ oil spill burns. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2021, 173, 113016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Homaei, A.; Patil, S.; Daverey, A. Microbial biosurfactants for oil spill remediation: Pitfalls and potentials. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, A.; Chattopadhyay, P. A review on physical remediation techniques for treatment of marine oil spills. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, R.F.; Lee, C.L.; Hsieh, P.Y.; Chen, C.S.; Kang, Y.Y.; Chin, W.C.; Tai, N.H. Superhydrophobic Graphene-Based Sponge as a Novel Sorbent for Crude Oil Removal under Various Environmental Conditions. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadpour, R.; Sapari, N.; Tuan, Z.; Jusoh, H.; Riahi, A.; Uka, O. Application of sorbent materials in oil spill management: A review. Casp. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nguyen, X.P.; Duong, X.O.; Huynh, T.T. Sorbent-based devices for the removal of spilled oil from water: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 28876–28910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb, A.M.; Farouq, R.; Mohamed, O.A.; Tony, M.A. Oil spill clean-up using combined sorbents: A comparative investigation and design aspects. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 100, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaa El-Din, G.; Amer, A.A.; Malsh, G.; Hussein, M. Study on the use of banana peels for oil spill removal. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbodo, N.O.; Asadu, C.O.; Ezema, C.A.; Onoh, M.I.; Elijah, O.C.; Ike, I.S.; Onoghwarite, O.E. Preparation and Characterization of activated carbon from agricultural waste (Musa-paradisiaca peels) for the remediation of crude oil contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, M.A.; Rojas, O.J.; Fingas, M.; Gupta, B.S. Cellulosic oil-spill sorbents. Bioresources 2013, 8, 3038–3097. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Yao, Z.; Wang, X.; Crombeen, M.; Sweeney, D.G.; Tam, K.C. Cellulose-based materials in wastewater treatment of petroleum industry. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Su, Q.; Shen, H.; Xu, G. Physicochemical and sorption characteristics of poplar seed fiber as a natural oil sorbent. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 4186–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viju, S.; Thilagavathi, G.; Vignesh, B.; Brindha, R. Oil sorption behavior of acetylated nettle fiber. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittinun, A.; Pisitsak, P. Ummartyotin, Improving the oil sorption capability of porous polyurethane composites by the incorporation of cellulose fibers extracted from water hyacinth. Compos. Commun. 2020, 20, 100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilamian, M.; Noroozi, B. Rice straw agri-waste for water pollutant adsorption: Relevant mesoporous super hydrophobic cellulose aerogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S. Remodeling of raw cotton fiber into flexible, squeezing-resistant macroporous cellulose aerogel with high oil retention capability for oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Chai, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, S. Kapok fiber as a natural source for fabrication of oil absorbent. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, P.B.; Godinho, M.; Zattera, A.J. Oils sorption on hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogel obtained from the wood furniture industry waste. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3105–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datiles, W.C.P.; Sy, S.M.; Balela, M.D.L. Synthesis of Kapok (Ceiba pentandra) Carbon Sponges for Recovery of Oil and Organic Solvents. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 880, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mones, E.S.; Balela, M.D.L.; Futalan, C.C.M.; Manalo, R.D.; Herrera, M.U. Fabrication of zinc oxide-embedded kapok (Ceiba pentandra) paper. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 201, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quek, C.S.; Ngadi, N.; Ahmad Zaini, M.A. The oil-absorbing properties of kapok fibre—A commentary. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2020, 14, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tigno, S.D.; Herrera, M.U.; Balela, M.D.L. Hydrophobicity of functionalized TiO2-based kapok nanocomposite. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datiles, W.C.P.; Herrera, M.U.; Manalo, R.D.; Maguyon-Detras, M.C.; Futalan, C.C.M.; Balela, M.D.L. Kapok-cotton Carbon Sponges for Oil Recovery. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 812, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugito, G.; Kustiana, A.; Martuani, R.; Wenten, I.G. Kapok fibre as potential oil-absorbing material: Modification mechanism and performance evaluation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 823, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Geng, G.; Liu, X.; Han, F.; Xu, J. Magnetically superhydrophobic kapok fiber for selective sorption and continuous separation of oil from water. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 115, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Chai, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Kapok Fiber Using CeO2 and Octadecyltrimethoxysilane. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017, 35, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, H. Ultralight, hydrophobic, sustainable, cost-effective and floating kapok/microfibrillated cellulose aerogels as speedy and recyclable oil superabsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Cui, J.; Di, J.; Liu, D.; Xu, M.; Tang, B.; Zeng, Q.; Xiong, J.; Wang, C.; He, Q.; et al. Carbon Microtube Aerogel Derived from Kapok Fiber: An Efficient and Recyclable Sorbent for Oils and Organic Solvents. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Du, E.; He, Y.; Fan, Y.; Ye, Y.; Tang, B. Preparation of Carbonized Kapok Fiber/Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel for Oil-Water Separation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2020, 43, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, S.; Kokushi, E.; Añasco, N.C.; Iwai, T.; Ito, K.; Koyama, J. Oil spill off the coast of Guimaras Island, Philippines: Distributions and changes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in shellfish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammouda, S.; Chen, Z.; An, C.; Lee, K. Recent advances in developing cellulosic sorbent materials for oil spill cleanup: A state-of-the-art review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, C.S.; Ngadi, N.; Zaini, M.A.A. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Dispersed Oil Sorption by Kapok Fiber. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2019, 26, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, T.; Wang, F.; Xu, G. Sorption kinetics and mechanism of various oils into kapok assembly. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, C.G.; Meili, L.; Soletti, J.I.; Oliveira, L.M.T.D.M.; Filho, J.M.E.; Lacerda, A.F.; Lourenço, R.D.O. Comparative study of diesel sorption performance between chorisia speciosa fibers and a commercial polyurethane foam. Rev. Mater. 2021, 26, e12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.T.M.; Oliveira, L.F.A.M.; Sonsin, A.F.; Duarte, J.L.S.; Soletti, J.I.; Fonseca, E.J.S.; Ribeiro, L.M.O.; Meili, L. Ultrafast diesel oil spill removal by fibers from silk-cotton tree: Characterization and sorption potential evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaković-Ognjanović, V.; Aleksić, G.; Rajaković, L. Governing factors for motor oil removal from water with different sorption materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperopoulos, E.; Calabrese, L.; Mastronardo, E.; Abdul Rahim, S.H.; Proverbio, E.; Milone, C. Assessment of sorption kinetics of carbon nanotube-based composite foams for oil recovery application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A. Oil spill cleanup by raw flax fiber: Modification effect, sorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5553–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Alazba, A.A.; Amin, M.T. Kinetic and Isotherm Studies of Ni2+ and Pb2+ Adsorption from Synthetic Wastewater Using Eucalyptus camdulensis—Derived Biochar. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwadiogbu, J.O.; Ajiwe, V.I.E.; Okoye, P.A.C. Removal of crude oil from aqueous medium by sorption on hydrophobic corncobs: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2016, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelle, H.I. Comparative analysis of removal of crude oil and some refined petroleum products from the environment using rice husk: Adsorption isotherm and kinetic studies. Niger. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2019, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Fu, J. Dual-templating synthesis of compressible and superhydrophobic spongy polystyrene for oil capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, A. Effect of kapok fiber treated with various solvents on oil absorbency. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 40, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Mu, B.; Wang, A. Facile fabrication of well-defined microtubular carbonized kapok fiber/NiO composites as electrode material for supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 194, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacuesta, A.C.; Herrera, M.U.; Manalo, R.; Balela, M.D.L. Fabrication of kapok paper-zinc oxide-polyaniline hybrid nanocomposite for methyl orange removal. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gönen, M.; Öztürk, S.; Balköse, D.; Okur, S.; Ülkü, S. Preparation and characterization of calcium stearate powders and films prepared by precipitation and Langmuir-Blodgett techniques. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balela, M.D.L.; Intila, N.M.; Salvanera, S.R. Adsorptive removal of lead ions in aqueous solution by kapok-polyacrylonitrile nanocomposites. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 17, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H. Eco-friendly construction of oil collector with superhydrophobic coating for efficient oil layer sorption and oil-in-water emulsion separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapusan, R.B.; Balela, M.D.L. Adsorption of anionic methyl orange dye and lead(II) heavy metal ion by polyaniline-kapok fiber nanocomposite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 243, 122682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Rahmah, A.U.; Man, Z. Physicochemical and sorption characteristics of Malaysian Ceiba pentandra (L.) Gaertn. as a natural oil sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, M.; Jana, S. Fabrication and multifunctional properties of fluorine-free durable nickel stearate based superhydrophobic cotton fabric. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2022, 19, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, A. Superhydrophobic kapok fiber oil-absorbent: Preparation and high oil absorbency. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 213, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Wang, F.; Xu, G. Theoretical and experimental study on the oil sorption behavior of kapok assemblies. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 61, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaneva, Z.L.; Koumanova, B.K.; Allen, S.J. Applicability comparison of different kinetic/diffusion models for 4-nitrophenol sorption on Rhizopus oryzae dead biomass. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2013, 45, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Asadpour, R.; Yavari, S.; Kamyab, H.; Ashokkumar, V.; Chelliapan, S.; Yuzir, A. Study of oil sorption behaviour of esterified oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB) fibre and its kinetics and isotherm studies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G.; Hong, T.; Bay, W.; Kong, H.; Hong, T. Separation & Purification Reviews Kinetics of Pollutant Sorption by Biosorbents: Review. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2000, 29, 189–232. [Google Scholar]
- Oyelude, E.O.; Awudza, J.A.M.; Twumasi, S.K. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study of Removal of Eosin Yellow from Aqueous Solution Using Teak Leaf Litter Powder. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, L.M.T.M.; Saleem, J.; Bazargan, A.; da S. Duarte, J.L.; McKay, G.; Meili, L. Sorption as a rapidly response for oil spill accidents: A material and mechanistic approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Model Oil | Viscosity (cSt) |
|---|---|
| kerosene | <54 |
| diesel | <54 |
| palm oil | 54–69 |
| motor oil | 302–335 |
| Kinetic Model | Linear Form | Nonlinear Form | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-First Order (PFO) | k1 [min−1] qe [g g−1] | ||
| Pseudo-Second Order (PSO) | k2 [g g−1 min−1] qe [g g−1] h [g g−1 min−1] | ||
| Elovich | 𝛼 [g g−1 min−1] 𝛽 [g g−1] | ||
| Intraparticle Diffusion (IPD) | kd [g g−1 min−1/2] I [g g−1] | ||
| Liquid Film Diffusion (LFD) | N/A | kfd [min−1] |
| Kinetic Models | Linear | Nonlinear | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | R2 | 0.9236 | 𝜒2 | 6.5209 |
| k1 | 0.1641 | k1 | 1.1979 | |
| qe | 24.3785 | qe | 54.0882 | |
| PSO | R2 | 0.9987 | 𝜒2 | 1.1399 |
| k2 | 0.0186 | k2 | 0.0268 | |
| qe | 60.6061 | qe | 58.7719 | |
| h | 68.4932 | h | 92.4950 | |
| Elovich | R2 | 0.9318 | 𝜒2 | 6.3266 |
| 𝛼 | 501.3912 | 𝛼 | 393.3614 | |
| 𝛽 | 0.1152 | 𝛽 | 0.1097 | |
| IPD | R2 | 0.7139 | 𝜒2 | 22.7360 |
| kd | 7.5790 | kd | 7.1616 | |
| I | 29.5970 | I | 30.7190 | |
| LFD | R2 | 0.9236 | N/A* | |
| kfd | 0.1641 | |||
| Kinetic Models | Linear | Nonlinear | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | R2 | 0.7344 | 𝜒2 | 0.7585 |
| k1 | 0.4410 | k1 | 2.5566 | |
| qe | 10.2420 | qe | 31.6637 | |
| PSO | R2 | 0.9959 | 𝜒2 | 0.3625 |
| k2 | 0.0932 | k2 | 0.1350 | |
| qe | 34.7222 | qe | 33.8150 | |
| h | 112.3596 | h | 154.3231 | |
| Elovich | R2 | 0.8659 | 𝜒2 | 0.3880 |
| 𝛼 | 9685.2331 | 𝛼 | 8977.4790 | |
| 𝛽 | 0.2929 | 𝛽 | 0.2898 | |
| IPD | R2 | 0.8073 | 𝜒2 | 0.5762 |
| kd | 4.3519 | kd | 4.4024 | |
| I | 22.8190 | I | 22.7643 | |
| LFD | R2 | 0.7344 | N/A* | |
| kfd | 0.4410 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blaquera, A.L.M.; Herrera, M.U.; Manalo, R.D.; Maguyon-Detras, M.C.; Futalan, C.C.M.; Balela, M.D.L. Oil Adsorption Kinetics of Calcium Stearate-Coated Kapok Fibers. Polymers 2023, 15, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020452
Blaquera ALM, Herrera MU, Manalo RD, Maguyon-Detras MC, Futalan CCM, Balela MDL. Oil Adsorption Kinetics of Calcium Stearate-Coated Kapok Fibers. Polymers. 2023; 15(2):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020452
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlaquera, Aimee Lorraine M., Marvin U. Herrera, Ronniel D. Manalo, Monet Concepcion Maguyon-Detras, Cybelle Concepcion M. Futalan, and Mary Donnabelle L. Balela. 2023. "Oil Adsorption Kinetics of Calcium Stearate-Coated Kapok Fibers" Polymers 15, no. 2: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020452
APA StyleBlaquera, A. L. M., Herrera, M. U., Manalo, R. D., Maguyon-Detras, M. C., Futalan, C. C. M., & Balela, M. D. L. (2023). Oil Adsorption Kinetics of Calcium Stearate-Coated Kapok Fibers. Polymers, 15(2), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15020452







