Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Blends with Poly(caprolactone) and Poly(lactic acid): A Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization of the Samples
2.4. Degradation Assays
2.5. Antibacterial Testing
3. Results
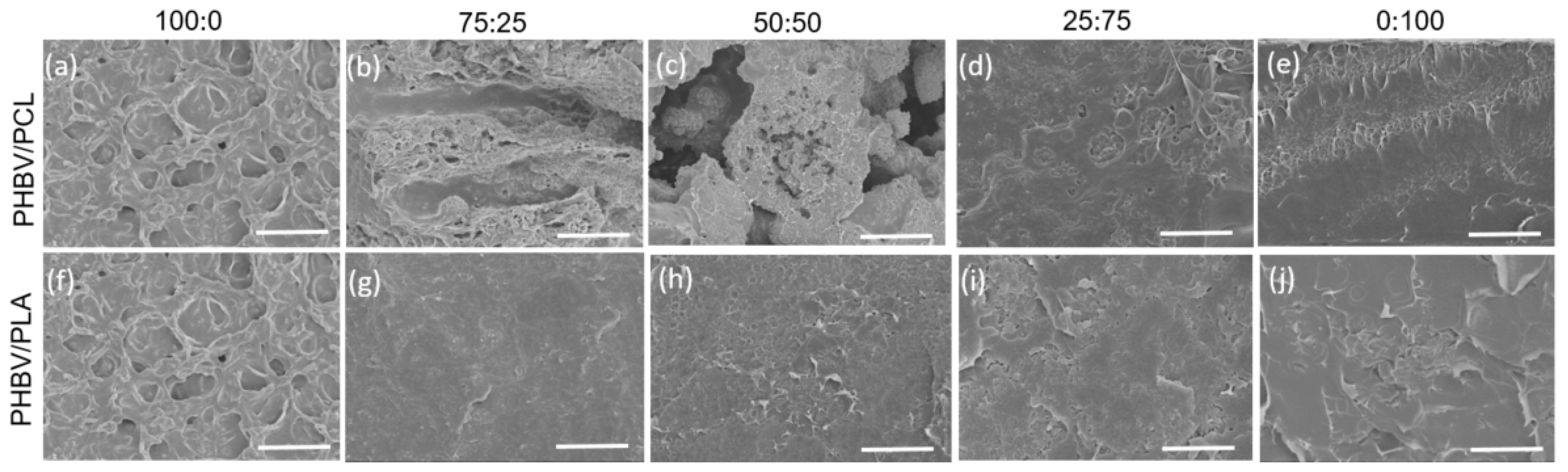
3.1. Morphological Analysis and Wettability
3.2. Vibrational Spectra
3.3. Thermal Properties
3.4. Mechanical Properties
3.5. Dielectrics Response
3.6. Degradability Testing
3.7. Antibacterial Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarrahi, R.; Fathi, Z.; Seydibeyoğlu, M.Ö.; Doustkhah, E.; Khataee, A. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): From production to nanoarchitecture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.-Y.A.; Chen, C.-L.; Li, L.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Razaad, I.M.N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Mo, Y.; Wang, J.-Y. Start a Research on Biopolymer Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): A Review. Polymers 2014, 6, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Loh, X.J. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Opening doors for a sustainable future. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 84, e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miu, D.M.; Eremia, M.C.; Moscovici, M. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) as Biomaterials in Tissue Engineering: Production, Isolation, Characterization. Materials 2022, 15, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasim-Anuar, T.A.T.; Norrrahim, M.N.F.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ilyas, R.A.; Jenol, M.A.; Razali, N.A.M.; Hakimi, M.I.; Rahim, N.F.A.; Najmuddin, S.U.F.S. Polyhydroxyalkanoates for Packaging Application. In Bio-Based Packaging; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, T.S.M.; Govindasamy, S.; Tamothran, A.M.; Vigneswari, S.; Bhubalan, K. Applications of PHA in Agriculture. In Biotechnological Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomietto, P.; Russo, F.; Galiano, F.; Loulergue, P.; Salerno, S.; Paugam, L.; Audic, J.-L.; De Bartolo, L.; Figoli, A. Sustainable fabrication and pervaporation application of bio-based membranes: Combining a polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) as biopolymer and CyreneTM as green solvent. J. Memb. Sci. 2022, 643, 120061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltronieri, P.; Kumar, P. Polyhydroxyalcanoates (PHAs) in Industrial Applications. Handb. Ecomater. 2019, 4, 2843–2872. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Briso, A.L.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate): Enhancement Strategies for Advanced Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.I.; Alsafadi, D.; Alamry, K.A.; Hussein, M.A. Properties and Applications of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Biocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Almeida, T.; Fernandes, L.C.; Correia, D.M.; Tubio, C.R.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Ribeiro, C. Piezoelectric biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) based electrospun fiber mats with tailored porosity. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigil Fuentes, M.A.; Thakur, S.; Wu, F.; Misra, M.; Gregori, S.; Mohanty, A.K. Study on the 3D printability of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/poly(lactic acid) blends with chain extender using fused filament fabrication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policastro, G.; Panico, A.; Fabbricino, M. Improving biological production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) co-polymer: A critical review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2021, 20, 479–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Qiang, Z.; Ren, J. In situ grafting approach for preparing PLA/PHBV degradable blends with improved mechanical properties. Polym. Bull. 2021, 79, 9543–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, B.; Wei, W.; Gu, Q.; Chen, P. Properties and structure of polylactide/poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PLA/PHBV) blend fibers. Polymer 2015, 68, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, W.; Ikehara, T. Fully biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate)/poly(ethylene succinate) blends: Phase behavior, crystallization and mechanical properties. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Delliou, B.; Vitrac, O.; Castro, M.; Bruzaud, S.; Domenek, S. Characterization of a new bio-based and biodegradable blends of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(butylene-co-succinate-co-adipate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 52124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, P.; Mohanty, A.K.; Rodriguez-Uribe, A.; Gámez-Pérez, J.; Cabedo, L.; Misra, M. Biodegradable blends from bacterial biopolyester PHBV and bio-based PBSA: Study of the effect of chain extender on the thermal, mechanical and morphological properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.S.; Kim, W.N. Thermal properties of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(ϵ-caprolactone) blends. Polymer 2000, 41, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modolo, L.P.; França, W.R.; Simbara, M.M.O.; Malmonge, S.M.; Santos, A.R. Dense, porous, and fibrous scaffolds composed of PHBV, PCL, and their 75:25 blend: An in vitro morphological and cytochemical characterization. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2022, 28, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Abad, A.; González-Ausejo, J.; Lagarón, J.M.; Cabedo, L. Biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/thermoplastic polyurethane blends with improved mechanical and barrier performance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 132, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaitescu, D.M.; Melinte, V.; Frone, A.N.; Nicolae, C.A.; Gabor, A.R.; Capră, L. Influence of Biobased Polyurethane Structure on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)—Polyurethane Blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.A.G.S.; Matos, M.; Dourado, F.; Reis, M.A.M.; Branco, P.C.; Poças, F.; Gama, M. Development of a layered bacterial nanocellulose-PHBV composite for food packaging. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 103, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten, E.; Turtle, J.; Bahr, D.; Jiang, L.; Wolcott, M. Thermal and mechanical properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/cellulose nanowhiskers composites. Polymer 2010, 51, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuraqmar, S.; Mahamud, S.; Ganesan, O.; Hanif, M.; Pisal, M.; Rabat, N.E. Effect of graphene nanoplatelet addition on the electrical conductivity of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) biocomposites. J. Phys. 2021, 2080, 12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, B.; Xin, C. Bioderived and Biodegradable Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Nanocomposites Based on Carbon Nanotubes: Microstructure Observation and EMI Shielding Property Improvement. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, M.I.; Zaloga, J.; Detsch, R.; Roether, J.A.; Unterweger, H.; Alexiou, C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Surface Modification of SPIONs in PHBV Microspheres for Biomedical Applications. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.C.; Chae, W.P.; Baek, J.Y.; Choi, M.J.; Jung, Y.; Kang, I.K. In vitro assessment of antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility of silver-containing phbv nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, R.M.; Yusoh, K. A Review on the Recent Research of Polycaprolactone (PCL). Adv. Mater. Res. 2016, 1134, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, S.; Pajnik, J.; Lukic, I. Tailoring of advanced poly(lactic acid)-based materials: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniak, K.; Masek, A. Green copolymers based on poly(Lactic acid)—Short review. Materials 2021, 14, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B. Polycaprolactones: Properties, Applications, and Selected Research; Nova Science Pub Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, C.P.; Poole, C.P., Jr. Encyclopedic Dictionary of Condensed Matter Physics; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Boyandin, A.; Nikolaeva, E.; Sukovatiy, A. Properties and Biocompatibility of Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate/Poly-Caprolactone Blends. J. Sib. Fed. Univ. Biol. 2016, 1, 63462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, M.L.; Maia, A.L.C.; Poletto, F.; de Andrade, F.V.; Soares, D.C.F. Poly(-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV): Current advances in synthesis methodologies, antitumor applications and biocompatibility. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.K.; Wang, H.M.D.; Lan, J.C.W. Investigation and Characterization of Plasma-Treated Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Biopolymers for an In Vitro Cellular Study of Mouse Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Polymers 2018, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, S.H.; Gholipour Kanani, A. Effect of changing solvents on poly(ε-Caprolactone) nanofibrous webs morphology. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 724153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Catchmark, J.M. Polylactic acid composites incorporating casein functionalized cellulose nanowhiskers. J. Biol. Eng. 2013, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Dai, J.; Li, G. Electrospun composites of PHBV/pearl powder for bone repairing. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2015, 25, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkaddour, A.; Jradi, K.; Robert, S.; Daneault, C. Grafting of Polycaprolactone on Oxidized Nanocelluloses by Click Chemistry. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofokeng, J.P.; Luyt, A.S.; Tábi, T.; Kovács, J. Comparison of injection moulded, natural fibre-reinforced composites with PP and PLA as matrices. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2012, 25, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, V.; Gupta, R.; Ghosh, T. Advances in Sustainable Polymers: Processing and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Wu, D. Effect of different solvents on poly(caprolactone) (PCL) electrospun nonwoven membranes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 107, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-G.; Song, R.-H.; Hu, G.-L.; Sun, Y.-Y. Thermal Stability and Degradation of Poly (Lactic Acid)/Hexamoll® DINCH/Montmorillonite Composites. BioResources 2014, 9, 4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.; La Rota, G.; Martuscelli, E.; Raimo, M.; Sadocco, P.; Elegir, G.; Riva, R. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and wheat straw fibre composites: Thermal, mechanical properties and biodegradation behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez-Blázquez, E.; Pérez, E.; Lorenzo, V.; Cerrada, M.L. Crystalline Characteristics and Their Influence in the Mechanical Performance in Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/High Density Polyethylene Blends. Polymers 2019, 11, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Yang, W.; Ikehara, T.; Nishi, T. Miscibility and crystallization behavior of biodegradable blends of two aliphatic polyesters. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(ε-caprolactone). Polymer 2005, 46, 11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaert, K.; Baere, I.D.; Cardon, L.; Degrieck, J. Bulk mechanical properties of thermoplastic poly-e-caprolactone. In Proceedings of the 6th Polymers & Mould Innovations International Conference, Guimaraes, Portugal, 10–12 September 2014; p. 339. [Google Scholar]
- Gérard, T.; Noto, T.; Budtova, T.; Gérard, T.; Noto, T.; Budtova, T. Tensile Properties of Pla And Phbv Blends: Anomalous Elongation and Aging. In Proceedings of the 11th European Symposium on Polymer Blends-Polyblends, San Sebastian, Spain, 25 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bal, B.; Tugluca, I.B.; Koc, N.; Isoglu, I.A. On the detailed mechanical response investigation of PHBV/PCL and PHBV/PLGA electrospun mats. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 065411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biresaw, G.; Carriere, C.J. Compatibility and mechanical properties of blends of polystyrene with biodegradable polyesters. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Forrester, M.; Wang, T.P.; Shen, L.; Liu, H.; Dileep, D.; Kuehl, B.; Li, W.; Kraus, G.; Cochran, E. Dihydroxyterephthalate—A Trojan Horse PET Counit for Facile Chemical Recycling. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2210154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Che, J.; Wu, W.; Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Ren, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Contributing Factors of Dielectric Properties for Polymer Matrix Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, M.; Kallel, A.; Serghei, A. Maxwell-Wagner-Sillars interfacial polarization in dielectric spectra of composite materials: Scaling laws and applications. J. Compos. Mater. 2022, 56, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallot-Lavallée, O.; Heux, L. Dielectric spectroscopy on a PHBV bio-polymer. In Proceedings of the 2013 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Chenzhen, China, 20–23 October 2013; p. 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, E.; Notopoulou, M.; Nakiou, E.; Kostoglou, M.; Barmpalexis, P.; Bikiaris, D.N. Branched Poly(ε-caprolactone)-Based Copolyesters of Different Architectures and Their Use in the Preparation of Anticancer Drug-Loaded Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakara Shetty, S.; Shetty, N. Investigation of mechanical properties and applications of polylactic acids—A review. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai-Prochnow, A.; Clauson, M.; Hong, J.; Murphy, A.B. Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria differ in their sensitivity to cold plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achinas, S.; Charalampogiannis, N.; Euverink, G.J.W. Brief Recap for Bacteria Adhesion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Si, Z.; Luo, Y.; Feng, P.; Wu, X.; Hou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Xu, L.; Huang, D. The Mechanisms and the Applications of Antibacterial Polymers in Surface Modification on Medical Devices. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Sample | Tm (°C) ± 1 °C | Tm (°C) ± 1 °C | Tg (°C) ± 1 °C | Tg (°C) ± 1 °C | Xc (%) ± 2% | Xc (%) ± 2% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHBV | PCL | PHBV | PCL | PHBV | PCL | |
| PHBV100 | 174 | - | - | - | 41 | 0 |
| PHBV75/PCL25 | 172 | 62 | - | - | 48 | 5 |
| PHBV50/PCL50 | 172 | 63 | - | - | 26 | 19 |
| PHBV25/PCL75 | 172 | 66 | - | - | 8 | 48 |
| PCL100 | - | 61 | - | - | 0 | 49 |
| PHBV | PLA | PHBV | PLA | PHBV | PLA | |
| PHBV100 | 174. | - | - | 41 | 0 | |
| PHBV75/PLA25 | 173 | - | - | 56 | 45 | 0 |
| PHBV50/PLA50 | 171 | 148 | - | 55 | 16 | 7 |
| PHBV25/PLA75 | 172 | 152 | - | 50 | 7 | 13 |
| PLA100 | - | 150 | - | 49 | 0 | 12 |
| Sample | Y (MPa) | εb (%) | σb (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHBV100 | 17 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 16.5 ± 0.5 |
| PHBV75/PCL25 | 5.7 ± 0.9 | 4.0 ± 1.9 | 9.2 ± 0.5 |
| PHBV50/PCL50 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 9.9 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.2 |
| PHBV25/PCL75 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 8.4 ± 0.2 |
| PCL100 | 2 ± 0.4 | 49.3 ± 0.6 | 13.2 ± 0.5 |
| PHBV100 | 17 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 16.5 ± 0.5 |
| PHBV75/PLA25 | 19.7 ± 1.5 | 3 ± 0.2 | 27.3 ± 2.3 |
| PHBV50/PLA50 | 10 ± 0.7 | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 14.3 ± 0.2 |
| PHBV25/PLA75 | 13.5 ± 1.4 | 5.2 ± 1.2 | 24.6 ± 0.7 |
| PLA100 | 20.2 ± 1.9 | 6.0 ± 1.6 | 37.4 ± 3.3 |
| Sample | ε′ at 1 kHz | Loss Tangent at 1 kHz | σ′ (S·cm−1) at 1 kHz |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHBV100 | 4.16 | 0.023 | 5.36 × 10−11 |
| PHBV75/PCL25 | 2.99 | 0.018 | 2.92 × 10−11 |
| PHBV50/PCL50 | 4.34 | 0.233 | 6.38 × 10−10 |
| PHBV25/PCL75 | 2.29 | 0.024 | 3.09 × 10−11 |
| PCL100 | 2.17 | 0.003 | 3.05 × 10−11 |
| PHBV100 | 4.16 | 0.023 | 5.36 × 10−11 |
| PHBV75/PLA25 | 3.88 | 0.019 | 4.22 × 10−11 |
| PHBV50/PLA50 | 6.69 | 0.059 | 2.21 × 10−10 |
| PHBV25/PLA75 | 3.59 | 0.015 | 2.98 × 10−11 |
| PLA100 | 3.47 | 0.006 | 1.08 × 10−11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tubio, C.R.; Valle, X.; Carvalho, E.; Moreira, J.; Costa, P.; Correia, D.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Blends with Poly(caprolactone) and Poly(lactic acid): A Comparative Study. Polymers 2023, 15, 4566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234566
Tubio CR, Valle X, Carvalho E, Moreira J, Costa P, Correia DM, Lanceros-Mendez S. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Blends with Poly(caprolactone) and Poly(lactic acid): A Comparative Study. Polymers. 2023; 15(23):4566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234566
Chicago/Turabian StyleTubio, Carmen R., Xabier Valle, Estela Carvalho, Joana Moreira, Pedro Costa, Daniela M. Correia, and Senentxu Lanceros-Mendez. 2023. "Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Blends with Poly(caprolactone) and Poly(lactic acid): A Comparative Study" Polymers 15, no. 23: 4566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234566
APA StyleTubio, C. R., Valle, X., Carvalho, E., Moreira, J., Costa, P., Correia, D. M., & Lanceros-Mendez, S. (2023). Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Blends with Poly(caprolactone) and Poly(lactic acid): A Comparative Study. Polymers, 15(23), 4566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234566











