Compressive Yield Stress of Flocculated Kaolin Suspensions in Seawater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
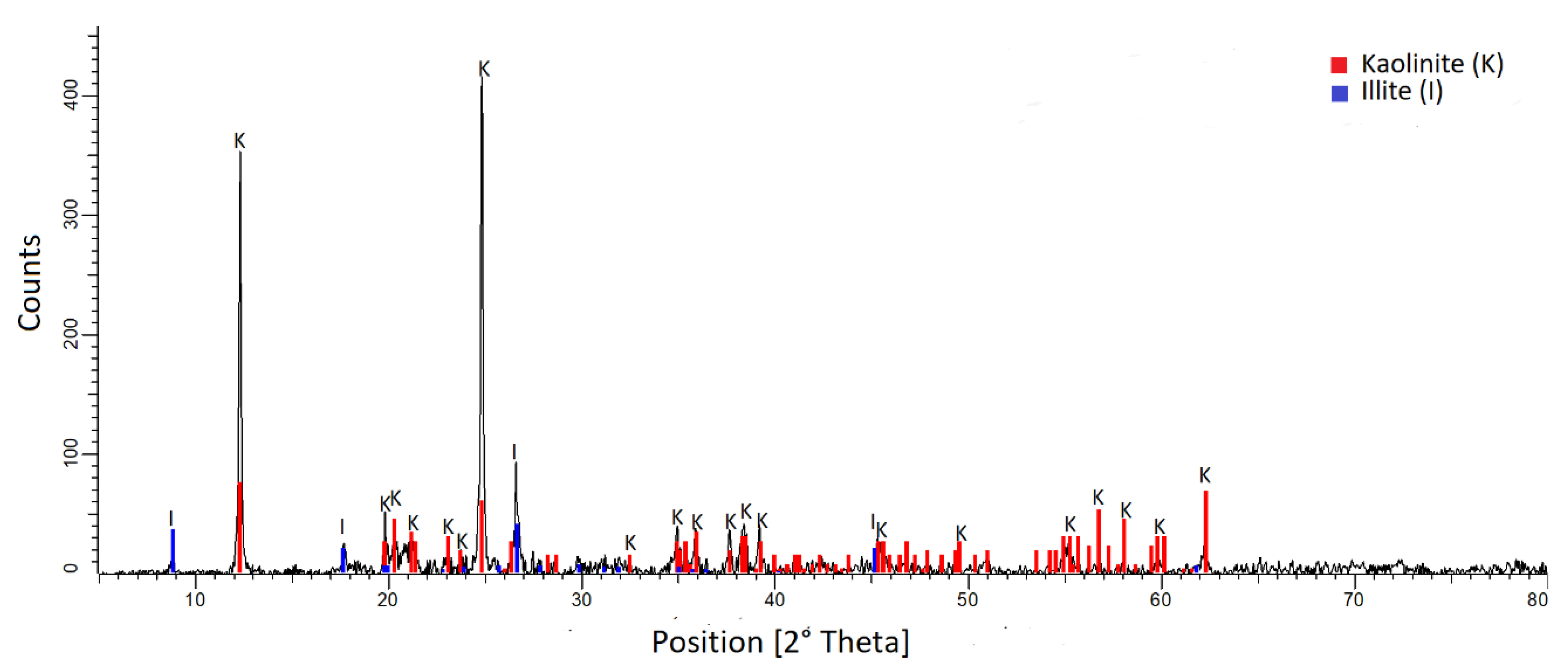
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemicals Analyses
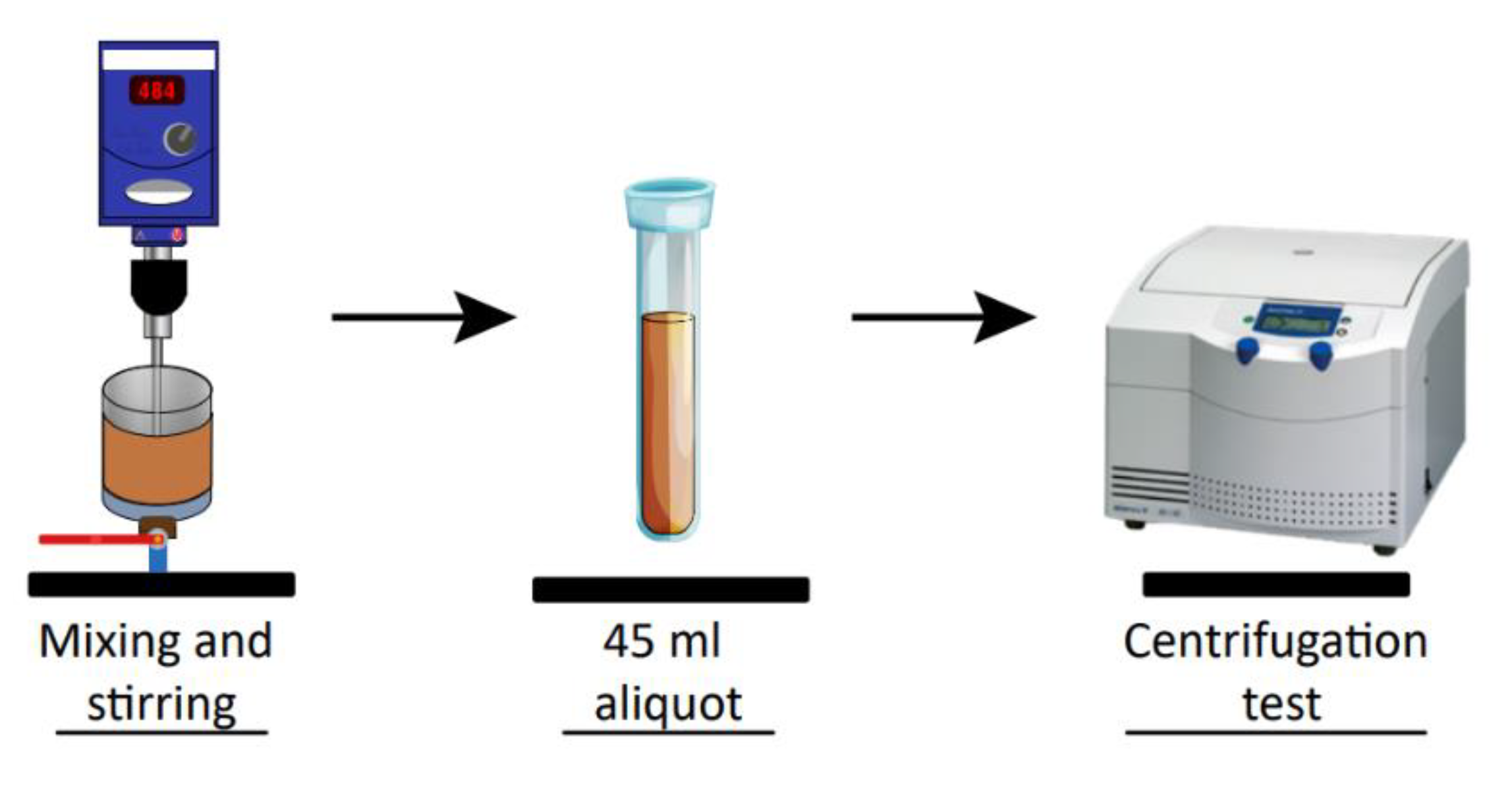
2.3. Flocculation-Sedimentation Tests and Size of Aggregates
2.4. Sediment Yield Stress
2.5. Fractal Dimension
2.6. Compressive Yield Stress
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Analyses
3.2. Initial Settling Rate
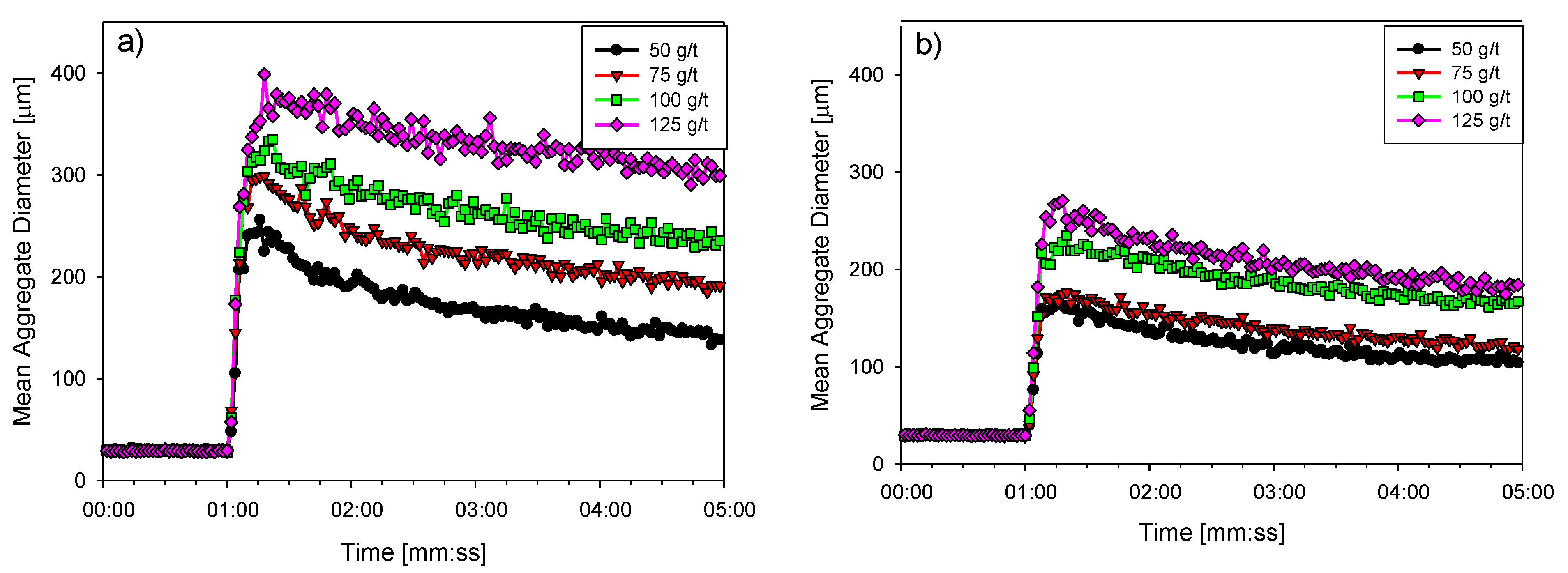
3.3. Flocculation Kinetics
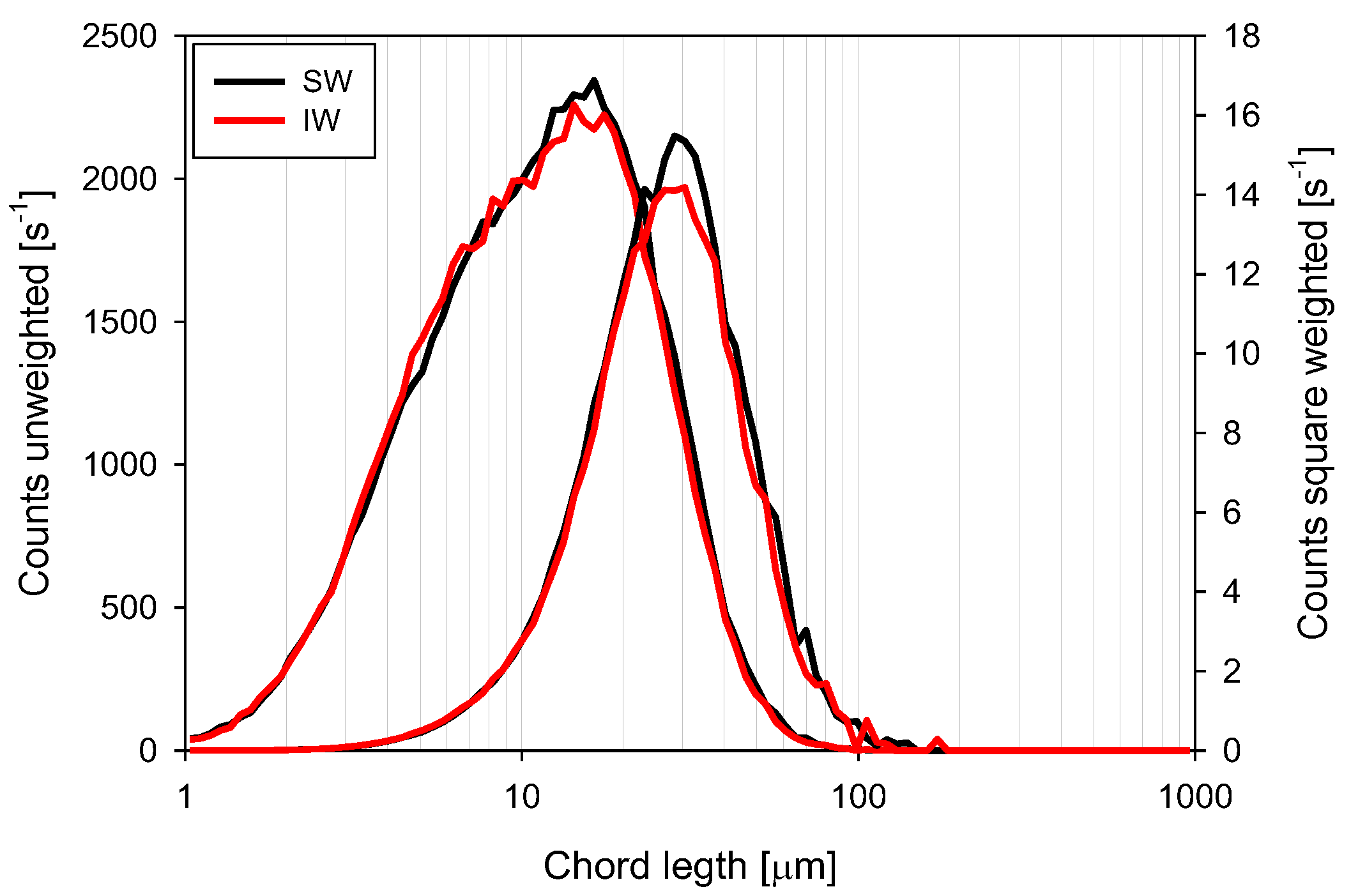
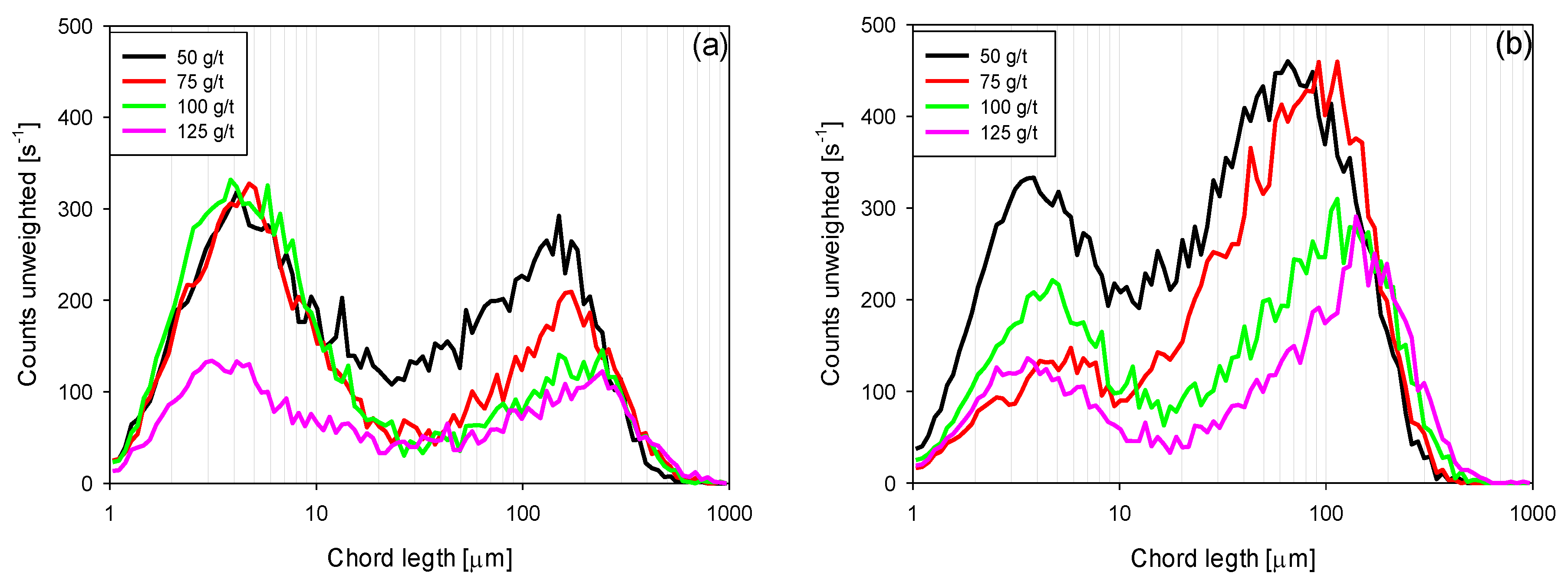
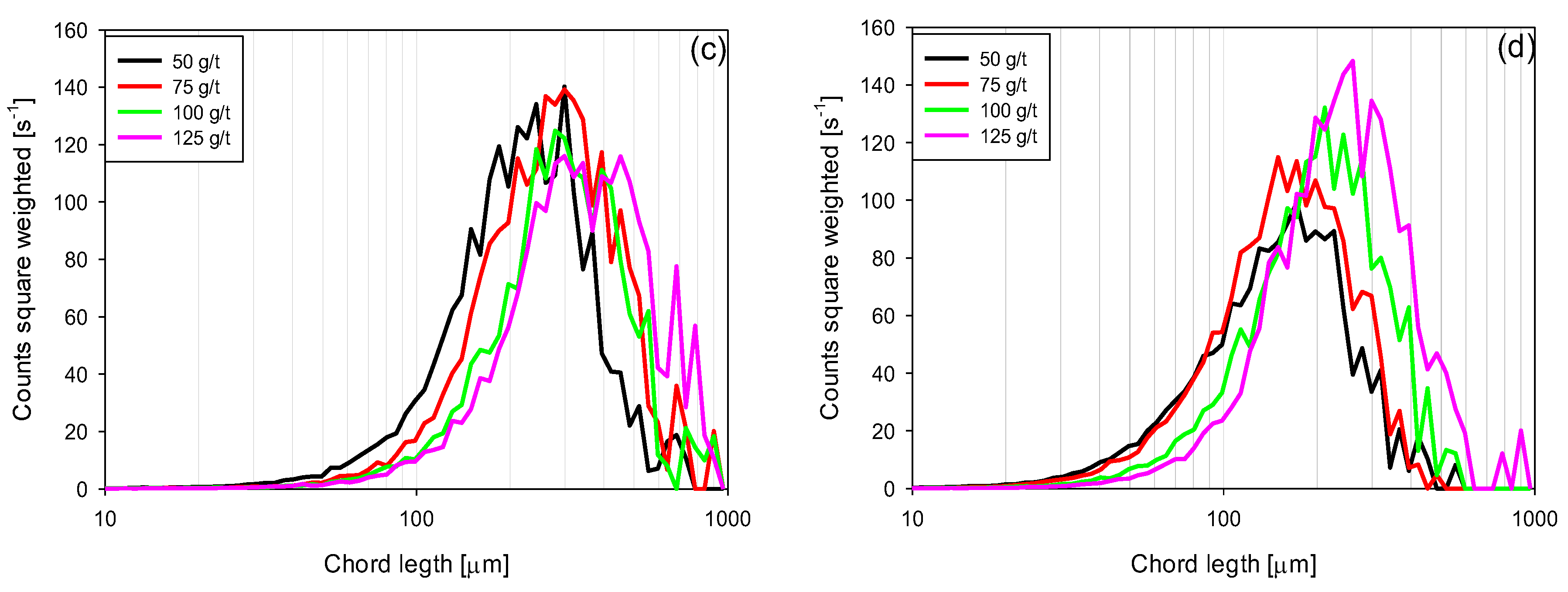
3.4. Chord Length Distributions (CLD)
3.5. Yield Stress
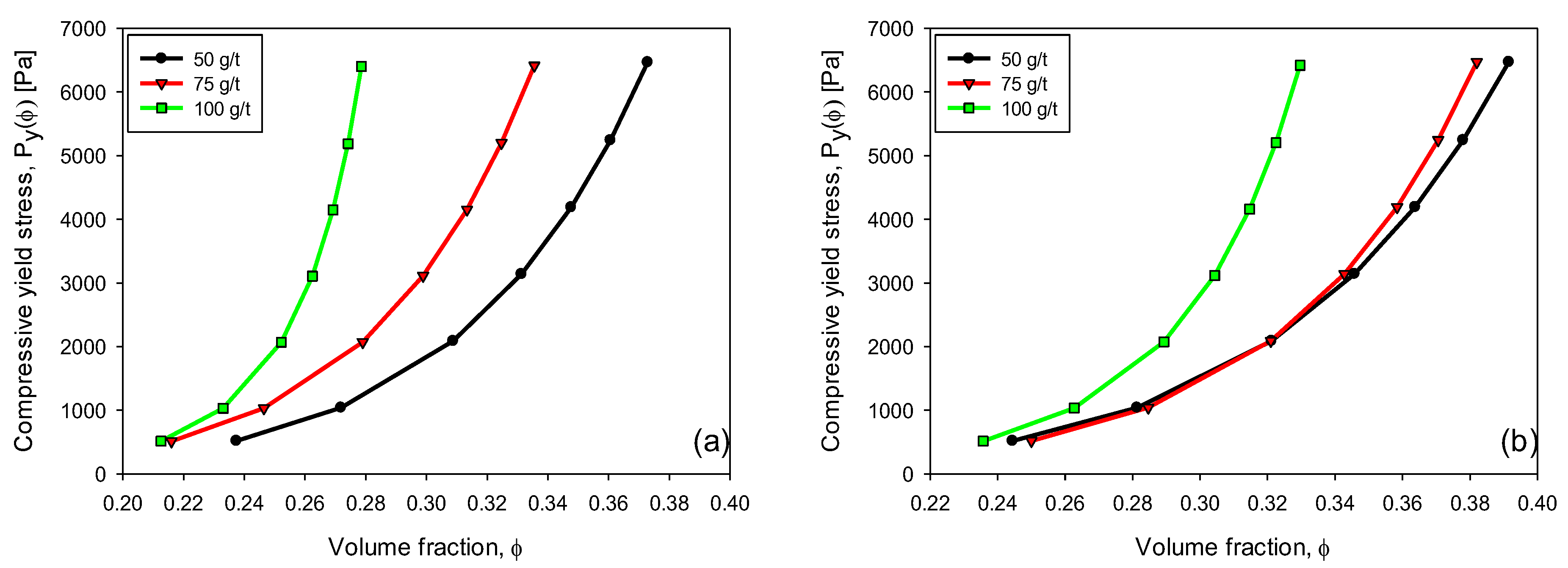
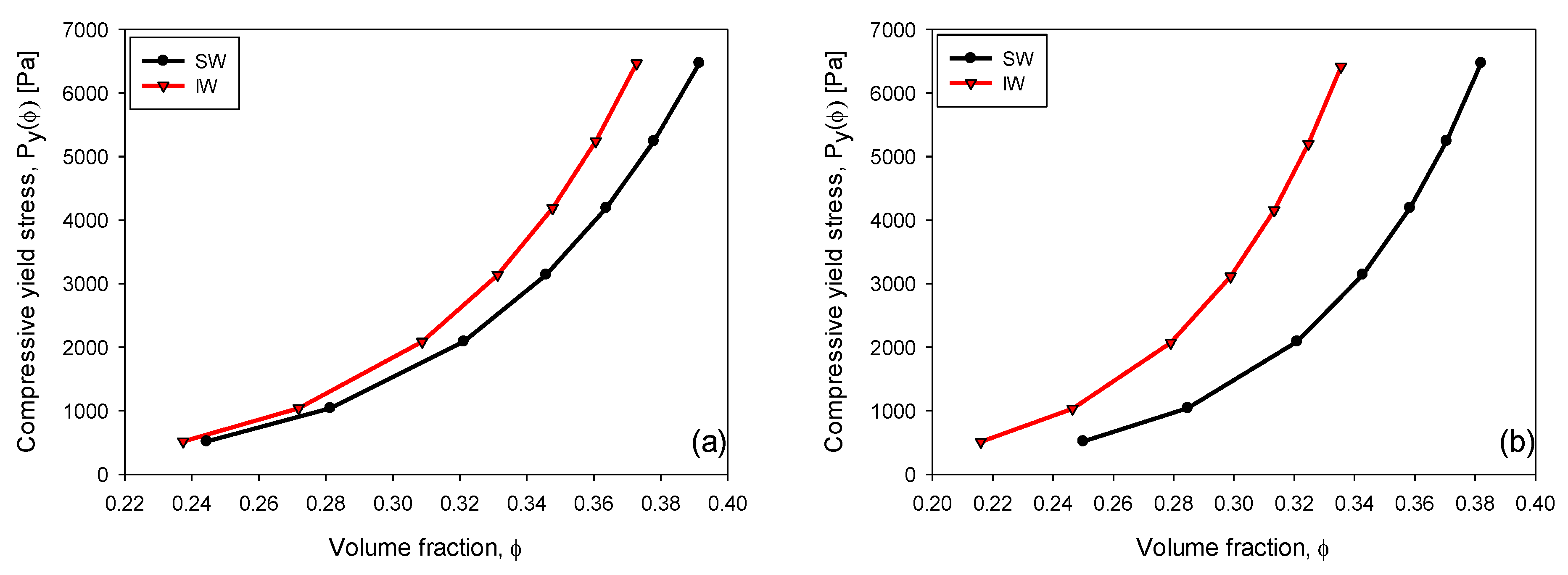
3.6. Compressive Yield Stress
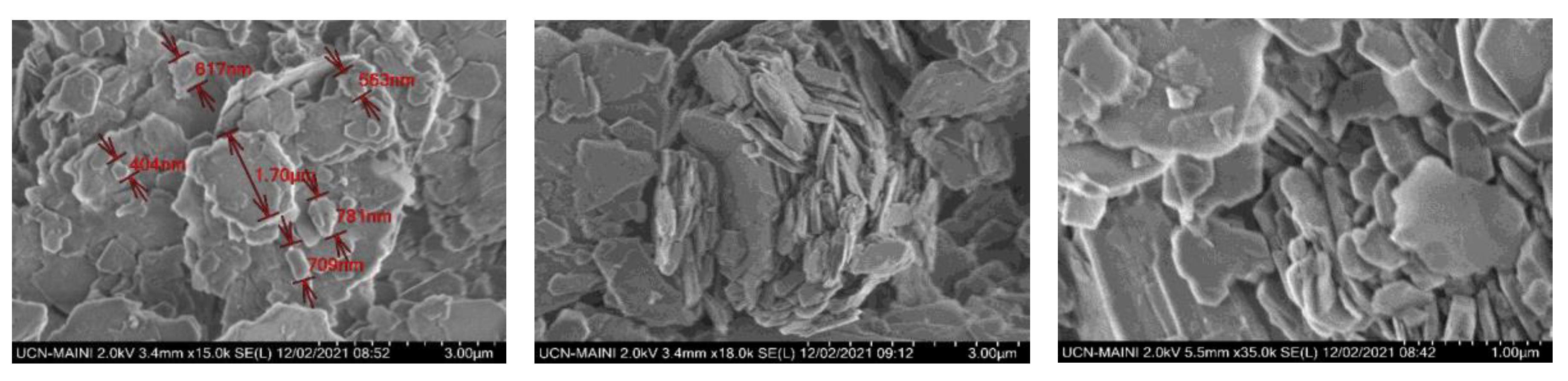
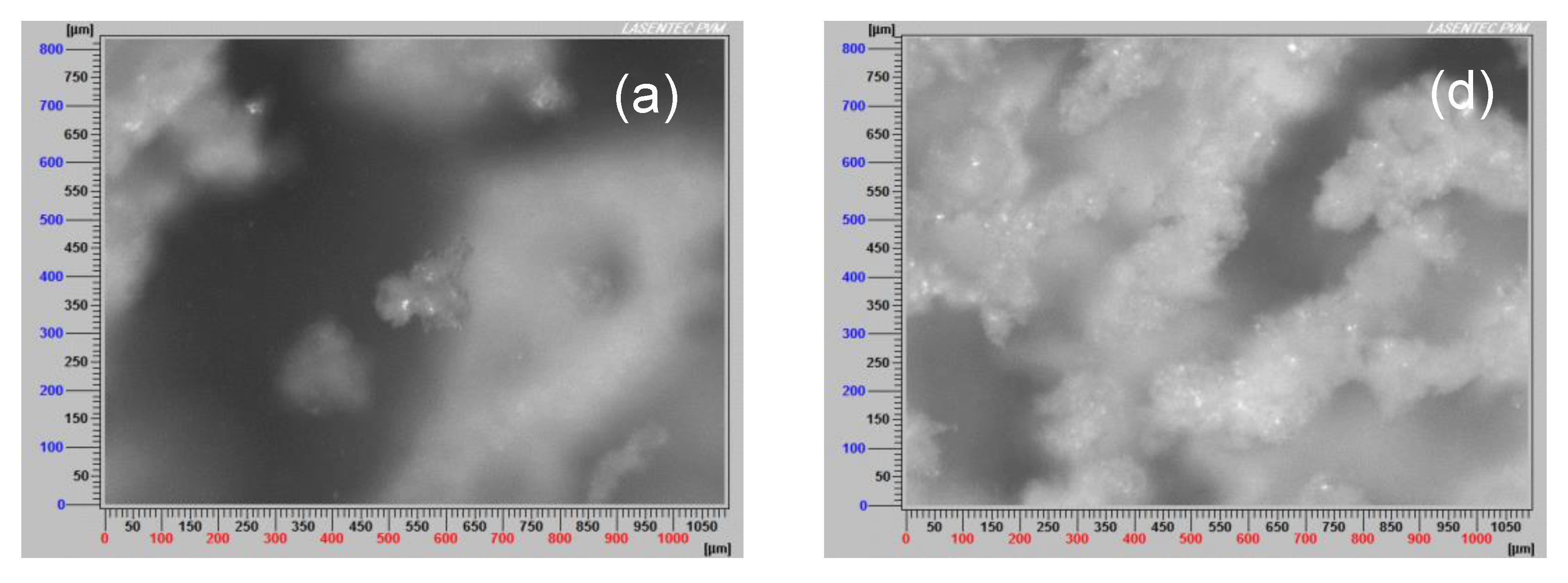
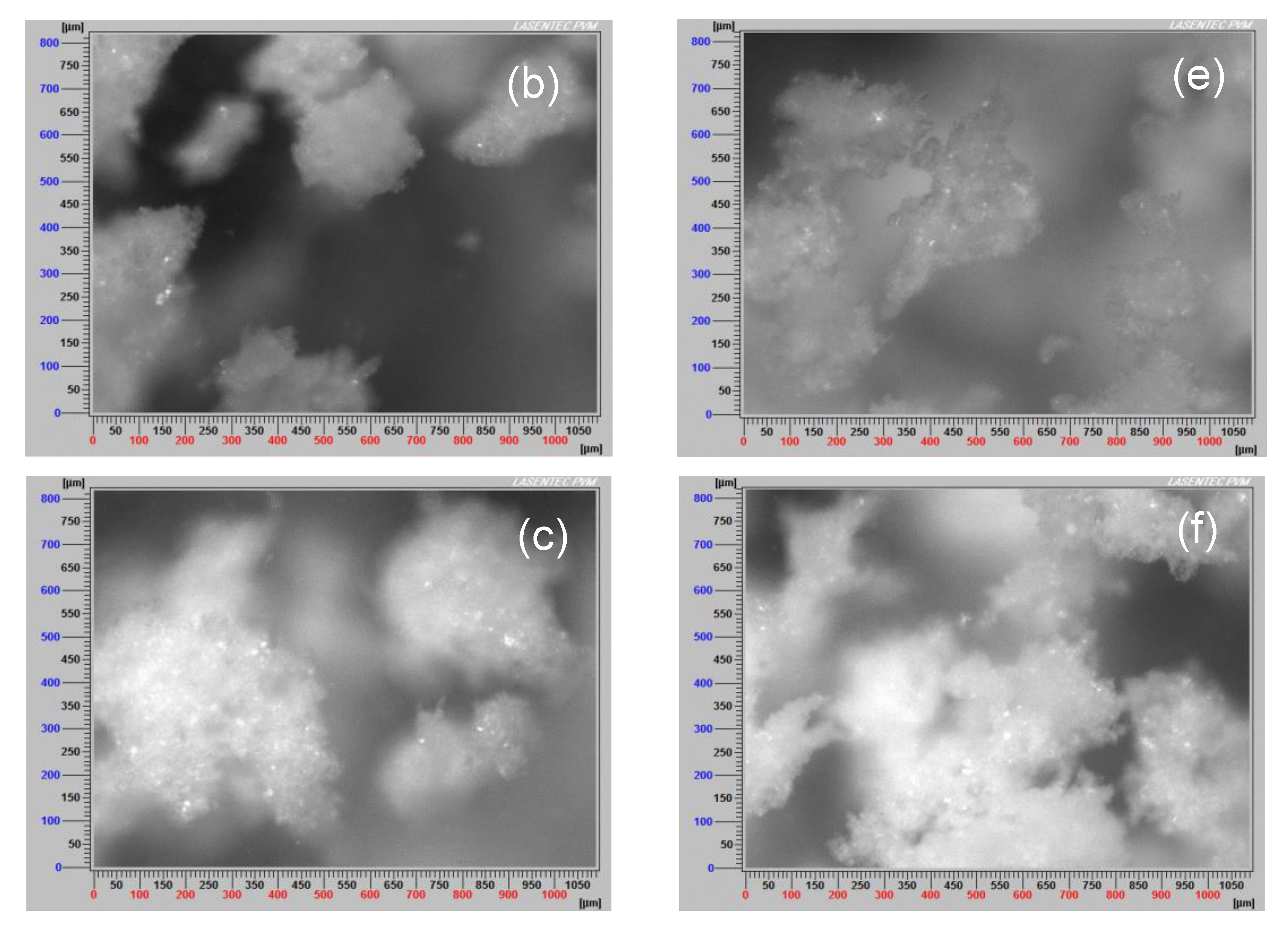
3.7. Aggregate Images
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Northey, S.A.; Mudd, G.M.; Werner, T.T.; Jowitt, S.M.; Haque, N.; Yellishetty, M.; Weng, Z. The exposure of global base metal resources to water criticality, scarcity and climate change. Glob. Environ. Change 2017, 44, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihle, C.F.; Kracht, W. The relevance of water recirculation in large scale mineral processing plants with a remote water supply. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landman, K.A.; White, L.R.; Buscall, R. The continuous-flow gravity thickener: Steady state behavior. AIChE J. 1988, 34, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, G.V.; Zhou, Y.; De Yan, Y.; Jameson, G.J.; Biggs, S. Effect of aggregate size on sediment bed rheological properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 4490–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscall, R.; Mills, P.D.A.; Stewart, R.F.; Sutton, D.; White, L.R.; Yates, G.E. The rheology of strongly-flocculated suspensions. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 1987, 24, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kretser, R.G.; Boger, D.V.; Scales, P.J. Compressive Rheology: An Overview. Rheol. Rev. 2003, 2003, 125–165. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.T.; Shi, W.; Struble, L.J.; Zukoski, C.F. Compressive yield stress of cement paste. Mater. Res. Soc. 1995, 370, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.K.; Samson, H.R. Flocculation of kaolinite due to the attraction of oppositely charged crystal faces. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1954, 18, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olphen, H. An Introduction to Clay Colloid Chemistry for Clay Technologists, Geologists and Soil Scientists An Introduction to Clay Colloid Chemistry for Clay Technologists, Geologists and Soil Scientists, 1977. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1995, 32, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Ndlovu, B.; Becker, M.; Forbes, E.; Deglon, D.; Franzidis, J.P. The influence of phyllosilicate mineralogy on the rheology of mineral slurries. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Herbert, C.M.; Yeneneh, A.M.; Sen, T.K. Rheological characteristics of mixed kaolin–sand slurry, impacts of pH, temperature, solid concentration and kaolin–sand mixing ratio. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2629–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, B.; Melton, I.E. Particle interactions in aqueous kaolinite suspensions: I. Effect of pH and electrolyte upon the mode of particle interaction in homoionic sodium kaolinite suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1977, 60, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Swartzen-allen, S.; Matijevic, E. Surface and Colloid Chemistry of Clays. Chem. Rev. 1974, 74, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Szekeres, M. Surface charge heterogeneity of kaolinite in aqueous suspension in comparison with montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 34, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, M.S.; James, A.E. Settling and sediment bed behaviour of kaolinite in aqueous media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Hampton, M.A.; Stokes, J.R.; Nguyen, A.V.; Miller, J.D. Particle interactions in kaolinite suspensions and corresponding aggregate structures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costine, A.; Cox, J.; Travaglini, S.; Lubansky, A.; Fawell, P.; Misslitz, H. Variations in the molecular weight response of anionic polyacrylamides under different flocculation conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 176, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshrouyeh Ghandashtani, M.; Costine, A.; Edraki, M.; Baumgartl, T. The impacts of high salinity and polymer properties on dewatering and structural characteristics of flocculated high-solids tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 342, 130726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, S.; Toro, N.; Robles, P.; Gálvez, E.; Gallegos, S.; Jeldres, R.I. Flocculation of Clay-Based Tailings: Differences of Kaolin and Sodium Montmorillonite in Salt Medium. Material 2022, 15, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, G.R.; Jeldres, M.; Toro, N.; Robles, P.; Toledo, P.G.; Jeldres, R.I. Understanding the flocculation mechanism of quartz and kaolinite with polyacrylamide in seawater: A molecular dynamics approach. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 608, 125576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, M.S.; James, A.E. Compressive and shear properties of flocculated kaolinite–polyacrylamide suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeldres, M.; Piceros, E.C.; Toro, N.; Torres, D.; Robles, P.; Leiva, W.H.; Jeldres, R.I. Copper tailing flocculation in seawater: Relating the yield stress with fractal aggregates at varied mixing conditions. Metals 2019, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakantan, R.; Vaezi, G.F.; Sanders, R.S. Effect of shear on the yield stress and aggregate structure of flocculant-dosed, concentrated kaolinite suspensions. Miner. Eng. 2018, 123, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.R.; Bahri, P.A.; Fawell, P.D.; Farrow, J.B. Polymer flocculation of calcite: Relating the aggregate size to the settling rate. AIChE J. 2006, 52, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, M.S.; James, A.E. The effect of polyacrylamide charge density and molecular weight on the flocculation and sedimentation behaviour of kaolinite suspensions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, M.S.; James, A.E. Effect of polyacrylamide polymers on floc size and rheological behaviour of kaolinite suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 301, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.D.; Eberl, M.; Landman, K.A. Compressive Yield Stress of Flocculated Suspensions: Determination via Experiment. AIChE J. 1996, 42, 2308–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeldres, R.I.; Piceros, E.C.; Leiva, W.H.; Toledo, P.G.; Herrera, N. Viscoelasticity and yielding properties of flocculated kaolinite sediments in saline water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoda, Y.; Costine, A.D.; Fawell, P.D.; Bellwood, J.; Das, G.K. Using focused beam reflectance measurement (FBRM) to monitor aggregate structures formed in flocculated clay suspensions. Miner. Eng. 2019, 138, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, C.; Ihle, C.F.; Jeldres, R.I. Chemometric Optimisation of a Copper Sulphide Tailings Flocculation Process in the Presence of Clays. Minerals 2019, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motta, F.L.; Gaikwad, R.; Botha, L.; Soares, J.B.P. Quantifying the effect of polyacrylamide dosage, Na+ and Ca2+ concentrations, and clay particle size on the flocculation of mature fine tailings with robust statistical methods. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Davé, R.N. Breakage of fractal agglomerates. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 161, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, K.; Stainton, C. Adhesion and aggregation of fine particles. Powder Technol. 2001, 121, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K. Exploitation of interparticle forces in the processing of colloidal ceramic materials. Mater. Des. 1994, 15, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, A.S.; Bolger, J.C. Settling Rates and Sediment Volumes of Flocculated Kaolin Suspensions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1962, 1, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Amirtharajah, A.; Sturm, T.W.; Dennett, K.E. A micromechanics approach for attachment and detachment of asymmetric colloidal particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 177, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Salt | Concentration [g/L] |
|---|---|
| NaCl | 24.53 |
| MgCl2·6H2O | 11.10 |
| Na2SO4 | 4.09 |
| CaCl2 | 1.16 |
| KCl | 0.69 |
| NaHCO3 | 0.20 |
| KBr | 0.10 |
| H3BO3 | 0.03 |
| [Mg2+] Total | [Ca2+] Total | [Na+] Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SW | 1338 | 339 | 11,130 |
| IW | 0 | 0 | 232 |
| K-SW | 1305 | 396 | 10,840 |
| K-IW | 0.8 | 1.1 | 254 |
| Water | 50 g/t | 75 g/t | 100 g/t | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW | 0.95 | 5.36 | 0.9987 | 2 | 5.95 | 0.9977 | 20 | 7.50 | 0.994 |
| IW | 2 | 5.59 | 0.9985 | 3 | 5.73 | 0.9986 | 800 | 9.28 | 0.9883 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nieto, S.; Piceros, E.; Toledo, P.G.; Robles, P.; Jeldres, R. Compressive Yield Stress of Flocculated Kaolin Suspensions in Seawater. Polymers 2023, 15, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030530
Nieto S, Piceros E, Toledo PG, Robles P, Jeldres R. Compressive Yield Stress of Flocculated Kaolin Suspensions in Seawater. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030530
Chicago/Turabian StyleNieto, Steven, Eder Piceros, Pedro G. Toledo, Pedro Robles, and Ricardo Jeldres. 2023. "Compressive Yield Stress of Flocculated Kaolin Suspensions in Seawater" Polymers 15, no. 3: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030530
APA StyleNieto, S., Piceros, E., Toledo, P. G., Robles, P., & Jeldres, R. (2023). Compressive Yield Stress of Flocculated Kaolin Suspensions in Seawater. Polymers, 15(3), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030530







