A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Our Approach
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.M.; Lv, S.; Zhang, W.; Cui, Y. Microfluidic Point-of-Care (POC) Devices in Early Diagnosis: A Review of Opportunities and Challenges. Sensors 2022, 22, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Du, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.M. Efficient Drug Screening and Nephrotoxicity Assessment on Co-culture Microfluidic Kidney Chip. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S. A More Biomimetic Cell Migration Assay with High Reliability and Its Applications. Pharm 2022, 15, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.M.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Cui, Y. Dielectrophoresis assisted high-throughput detection system for multiplexed immunoassays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 180, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Xing, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W. 3D Bioprinting of the Sustained Drug Release Wound Dressing with Double-Crosslinked Hyaluronic-Acid-Based Hydrogels. Polymers 2019, 11, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Xi, Z.; Tang, T.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W. Electrospun PLGA membrane incorporated with andrographolide-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for sustained antibacterial wound dressing. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2881–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; Achenbach, S.; Subramanian, V.; Jacobs, M.; Klymyshyn, D.; Iyer, S.; Moazed, B.; Hanson, J.; Shen, C.; Haluzan, D. SyLMAND: A microfabrication beamline with wide spectral and beam power tuning range at the Canadian Light Source. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2019, 26, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Tony, A.; Yin, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W. Tactile and Thermal Sensors Built from Carbon-Polymer Nanocomposites-A Critical Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Xiao, G.; Watts, B.R.; Xu, C. Sealing SU-8 microfluidic channels using PDMS. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 046503–465038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Park, S.W.; Yang, S.S. The optimization of PDMS-PMMA bonding process using silane primer. Biochip J. 2010, 4, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, P.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Wohl, G.R. Plasma enhanced bonding of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) with parylene. In Proceedings of the 2011 16th International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, TRANSDUCERS’11, Beijing, China, 5–9 June 2011; pp. 1340–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Cho, J. Parylene-PDMS Bilayer Coatings for Microelectronic and MEMS Packaging. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2007, 968, 0968-v07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Datta, A.; Berg, J.M.; Gangopadhyay, S. Studies on surface wettability of poly(dimethyl) siloxane (PDMS) and glass under oxygen-plasma treatment and correlation with bond strength. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2005, 14, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borók, A.; Laboda, K.; Bonyár, A. PDMS Bonding Technologies for Microfluidic Applications: A Review. Biosens 2021, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.-W. Chia-Wen Polymer Microfluidics: Simple, Low-Cost Fabrication Process Bridging Academic Lab Research to Commercialized Production. Micromachines 2016, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shakeri, A.; Khan, S.; Didar, T.F. Conventional and emerging strategies for the fabrication and functionalization of PDMS-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3053–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.B.; Hanson, R.L.; Almughamsi, H.M.; Pang, C.; Fish, T.R.; Woolley, A.T. Microfluidics: Innovations in Materials and Their Fabrication and Functionalization. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.T.; Woolley, A.T. Thermal bonding of polymeric capillary electrophoresis microdevices in water. Anal. Chem. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Kwok, Y.C.; Nguyen, N.T. Low-pressure, high-temperature thermal bonding of polymeric microfluidic devices and their applications for electrophoretic separation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abgrall, P.; Low, L.-N.; Nguyen, N.-T. Fabrication of planar nanofluidic channels in a thermoplastic by hot-embossing and thermal bonding. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lin, J.; Su, R.; Xie, Y. Vacuum-assisted thermal bonding of plastic capillary electrophoresis microchip imprinted with stainless steel template. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1038, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadpour, H.; Soper, S.A. Two-dimensional electrophoretic separation of proteins using poly(methyl methacrylate) microchips. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3519–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, T.H. Disposable integrated microfluidic biochip for blood typing by plastic microinjection moulding. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duffy, D.C.; McDonald, J.C.; Schueller, O.J.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogończyk, D.; Wgrzyn, J.; Jankowski, P.; Dąbrowski, B.; Garstecki, P. Bonding of microfluidic devices fabricated in polycarbonate. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klank, H.; Kutter, J.P.; Geschke, O. CO2-laser micromachining and back-end processing for rapid production of PMMA-based microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2002, 2, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.J.; Geist, J.; Locascio, L.E.; Gaitan, M.; Rao, M.V.; Vreeland, W.N. Surface modification of poly(methyl methacrylate) for improved adsorption of wall coating polymers for microchip electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 3788–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koesdjojo, M.T.; Tennico, Y.H.; Remcho, V.T. Fabrication of a Microfluidic System for Capillary Electrophoresis Using a Two-Stage Embossing Technique and Solvent Welding on Poly(methyl methacrylate) with Water as a Sacrificial Layer. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2311–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Koerner, T.; Horton, J.H.; Oleschuk, R.D. Fabrication and characterization of poly(methylmethacrylate) microfluidic devices bonded using surface modifications and solvents. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, D.A.; Rolandi, M.; Snauko, M.; Noroski, R.; Svec, F.; Fréchet, J.M.J. Room-Temperature Bonding for Plastic High-Pressure Microfluidic Chips. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5097–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.J.; Agirregabiria, M.; Garcia, J.; Berganzo, J.; Tijero, M.; Arroyo, M.T.; Ruano, J.M.; Aramburu, I.; Mayora, K. Novel three-dimensional embedded SU-8 microchannels fabricated using a low temperature full wafer adhesive bonding. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.J.; Teixeira, A. Enhancement of the surface free energy of PDMS for reversible and leakage-free bonding of PDMS–PS microfluidic cell-culture systems. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2018, 22, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Pallandre, A.; Miserere, S.; Weber, J.; Viovy, J.-L. Lamination-based rapid prototyping of microfluidic devices using flexible thermoplastic substrates. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; McClelland, A.A.; Chen, Z.; Lahann, J. Solventless Adhesive Bonding Using Reactive Polymer Coatings. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douville, N.J.; Tung, Y.-C.; Li, R.; Wang, J.D.; El-Sayed, M.E.H.; Takayama, S. Fabrication of Two-Layered Channel System with Embedded Electrodes to Measure Resistance Across Epithelial and Endothelial Barriers. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2505–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsao, C.W.; Hromada, L.; Liu, J.; Kumar, P.; DeVoe, D.L. Low temperature bonding of PMMA and COC microfluidic substrates using UV/ozone surface treatment. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubert, K.; Drier, T.; Beebe, D. PDMS bonding by means of a portable, low-cost corona system. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1548–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillborg, H.; Sandelin, M.; Gedde, U.W. Hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsiloxane after exposure to partial discharges as a function of crosslink density. Polymer 2001, 42, 7349–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chaudhury, M.K. Corona-discharge-induced hydrophobicity loss and recovery of silicones. In Proceedings of the 1999 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (Cat. No.99CH36319), Austin, TX, USA, 17–20 October 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Xiao, K.; Wen, W. A simple method for fabricating multi-layer PDMS structures for 3D microfluidic chips. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-A.; Batista, C.; Sarpeshkar, R.; Han, J. Rapid fabrication of microfluidic polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell in PDMS by surface patterning of perfluorinated ion-exchange resin. J. Power Sources 2008, 183, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, H.I. Hydrophilic Surface Modification of PDMS Using Atmospheric RF Plasma. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 34, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ellis, A.V.; Voelcker, N.H. Recent developments in PDMS surface modification for microfluidic devices. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Khodakov, D.A.; Ellis, A.V.; Voelcker, N.H. Surface modification for PDMS-based microfluidic devices. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechene, J. Surface Modifications of Poly(dimethylsiloxane) for Biological Application of Microfluidic Devices. Electron. Ph.D. Thesis Diss. Repos, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2010; pp. 1–194. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, K.S.; Chin, J.; Chia, J.; Chiang, C.L. Quantitative Studies on PDMS-PDMS Interface Bonding with Piranha Solution and its Swelling Effect. Micromachines 2012, 3, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiroma, L.S.; Piazzetta, M.H.O.; Duarte-Junior, G.F.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Carrilho, E.; Gobbi, A.L.; Lima, R.S. Self-regenerating and hybrid irreversible/reversible PDMS microfluidic devices. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, S.; Gruner, D.; Richter, A.; Loskill, P. Membrane integration into PDMS-free microfluidic platforms for organ-on-chip and analytical chemistry applications. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 1866–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent Compatibility of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Based Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Duong, L.H. Novel solvent bonding method for thermoplastic microfluidic chips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumens, C.V.; Ziai, M.A.; Belsey, K.E.; Batchelor, J.C.; Holder, S.J. Swelling of PDMS networks in solvent vapours; applications for passive RFID wireless sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10091–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dangla, R.; Gallaire, F.; Baroud, C.N. Microchannel deformations due to solvent-induced PDMS swelling. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes Atayde, C.; Doi, I. Highly stable hydrophilic surfaces of PDMS thin layer obtained by UV radiation and oxygen plasma treatments. Phys. Status Solidi 2010, 7, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckert, E.P.; Miller, C.J.; Fisher, E.R. The Effect of Ar/O2 and H2O Plasma Treatment of SnO2 Nanoparticles and Nanowires on Carbon Monoxide and Benzene Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15733–15743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Snoeckx, R.; Zhang, X.; Cha, M.S.; Bogaerts, A. Modeling Plasma-based CO2 and CH4 Conversion in Mixtures with N2, O2, and H2O: The Bigger Plasma Chemistry Picture. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8704–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Reis, R.; Chen, Z.; Milne, N.; Winther-Jensen, B.; Kong, L.; Dumée, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Plasma Modification and Synthesis of Membrane Materials—A Mechanistic Review. Membranes 2018, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Chen, S. Polydimethylsioxane Fluidic Interconnects for Microfluidic Systems. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2003, 26, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yuan, Y.J. Investigation on the mechanism of nitrogen plasma modified PDMS bonding with SU-8. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddings, M.A.; Johnson, M.A.; Gale, B.K. Determining the optimal PDMS-PDMS bonding technique for microfluidic devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 067001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Wu, J.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G.; Jin, M.; Shui, L. Large-Area and High-Throughput PDMS Microfluidic Chip Fabrication Assisted by Vacuum Airbag Laminator. Micromachines 2017, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezai, P.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Wohl, G.R. Plasma enhanced bonding of polydimethylsiloxane with parylene and its optimization. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 065024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrito, N.; McLachlan, J.M.; Faria, S.N.; Chan, J.; Norton, P.R. A novel metal-protected plasma treatment for the robust bonding of polydimethylsiloxane. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Chen, P.; Zhou, Q. Adhesion promotion between PDMS and glass by oxygen plasma pre-treatment. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.C.; Liao, E.; Ong, W.L.; Wong, J.D.S.; Agarwal, A.; Nagarajan, R.; Yobas, L. Evaluation of bonding between oxygen plasma treated polydimethyl siloxane and passivated silicon. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 34, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, W.J.; Akin, D.; Sedlak, M.; Ladisch, M.R.; Bashir, R. Poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) and silicon hybrid biochip for bacterial culture. Biomed. Microdevices 2003, 5, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Peng, S.; Liu, L.; Wen, W.; Sheng, P. Characterizing and patterning of PDMS-based conducting composites. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-W.; DeVoe, D.L. Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2009, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lee, N.Y. A facile route for irreversible bonding of plastic-PDMS hybrid microdevices at room temperature. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lee, N.Y. One-step surface modification for irreversible bonding of various plastics with a poly(dimethylsiloxane) elastomer at room temperature. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Liao, Y.C. Adhesive Stretchable Printed Conductive Thin Film Patterns on PDMS Surface with an Atmospheric Plasma Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11868–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Song, K.Y.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W. Effects of Hydrophilicity, Adhesion Work, and Fluid Flow on Biofilm Formation of PDMS in Microfluidic Systems. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 8386–8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.; Kang, Y.; Park, W.; Jo, E.; Kim, J. Fabrication of fine-pored polydimethylsiloxane using an isopropyl alcohol and water mixture for adjustable mechanical, optical, and thermal properties. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18061–18067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plecis, A.; Chen, Y. Fabrication of microfluidic devices based on glass-PDMS-glass technology. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.-H.; Beebe, D.J. Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Microfluidic Systems by Stacking Molded Polydimethylsiloxane(PDMS) Layers. Spie 1999, 3877, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Chua, Y.C.; Kang, T.G. Oxygen plasma treatment for reducing hydrophobicity of a sealed polydimethylsiloxane microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 032204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamberti, A.; Marasso, S.L.; Cocuzza, M. PDMS membranes with tunable gas permeability for microfluidic applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61415–61419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldorsson, S.; Lucumi, E.; Gómez-Sjöberg, R.; Fleming, R.M.T. Advantages and challenges of microfluidic cell culture in polydimethylsiloxane devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehling, M. Microfluidic cell culture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 25, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.; Uchil, A.; Kalsang, T.; Chakrabarty, S.; Ali, M.A.; Srisungsitthisunti, P.; Mahato, K.K.; Surdo, S.; Mazumder, N. The revolution of PDMS microfluidics in cellular biology. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z. Nanofabrication: Principles, Capabilities and Limits, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 9783319393612. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.Y.; Loke, W.K.; Nguyen, N.T. A reliable method for bonding polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and its application in micropumps. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 151, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Meer, B.J.; de Vries, H.; Firth, K.S.A.; van Weerd, J.; Tertoolen, L.G.J.; Karperien, H.B.J.; Jonkheijm, P.; Denning, C.; IJzerman, A.P.; Mummery, C.L. Small molecule absorption by PDMS in the context of drug response bioassays. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toepke, M.W.; Beebe, D.J. PDMS absorption of small molecules and consequences in microfluidic applications. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1484–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Schwartz, M.; Ionescu-Zanetti, C. PDMS Compound Adsorption in Context. J. Biomol. Screen. 2009, 14.2, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Facility, M. Procedure for Silanization of Su-8/Silicon Master Microfabrication Core Facility, Harvard Medical School. 2015, 3–4. Available online: https://hms.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/Departments/Microfluidics and Microfabrication Facility/files/Silanization of Photoresist Master Protocol.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Galliano, A.; Bistac, S.; Schultz, J. Adhesion and friction of PDMS networks: Molecular weight effects. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 265, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Dai, Z.; Lin, B. Multilayer poly(vinyl alcohol)-adsorbed coating on poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic chips for biopolymer separation. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.Y.; Zurawsky, W.; Ulman, A. Molecular Weight Effects in Adhesion. Langmuir 1999, 15, 8447–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, A.; Rasouli, A.; Farahinia, A.; Wells, G.; Zhang, H.; Achenbach, S.; Yang, S.M.; Sun, W.; Zhang, W. Toward a Soft Microfluidic System: Concept and Preliminary Developments. In Proceedings of the IEEE 27th International Conference on Mechatronics Machine Vision Practice (M2VIP 2021), Shanghai, China, 26–28 November 2021; pp. 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour-Tamrin, S.; Sanati-Nezhad, A.; Sen, A. A simple and low-cost approach for irreversible bonding of polymethylmethacrylate and polydimethylsiloxane at room temperature for high-pressure hybrid microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, P.; Selvaganapathy, P.; Wohl, G.; Byun, I. Irreversible bonding of polyimide and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) based on a thiol-epoxy click reaction. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Greco, G.; Cecchini, M. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) irreversible bonding to untreated plastics and metals for microfluidics applications. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 081108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


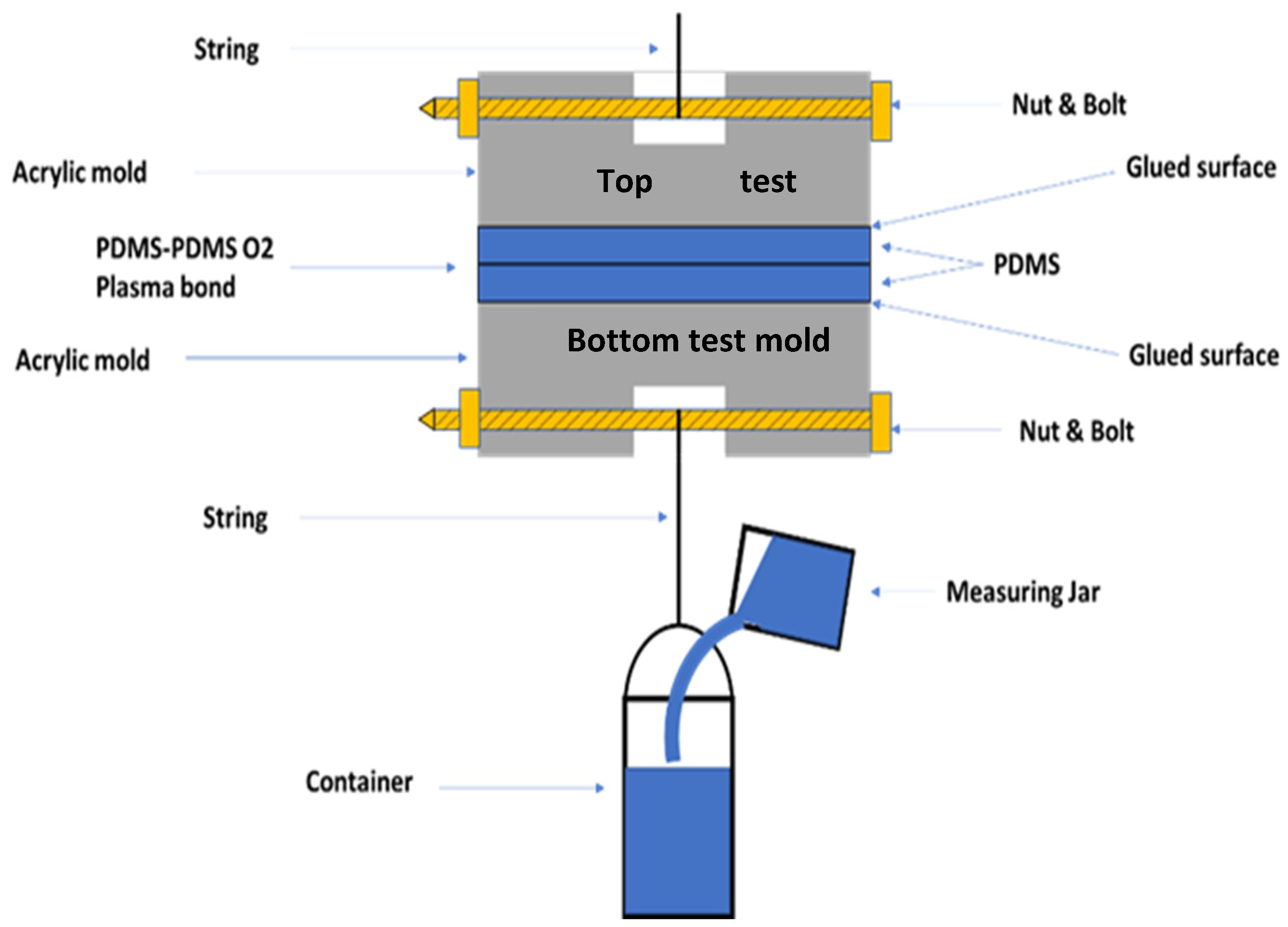
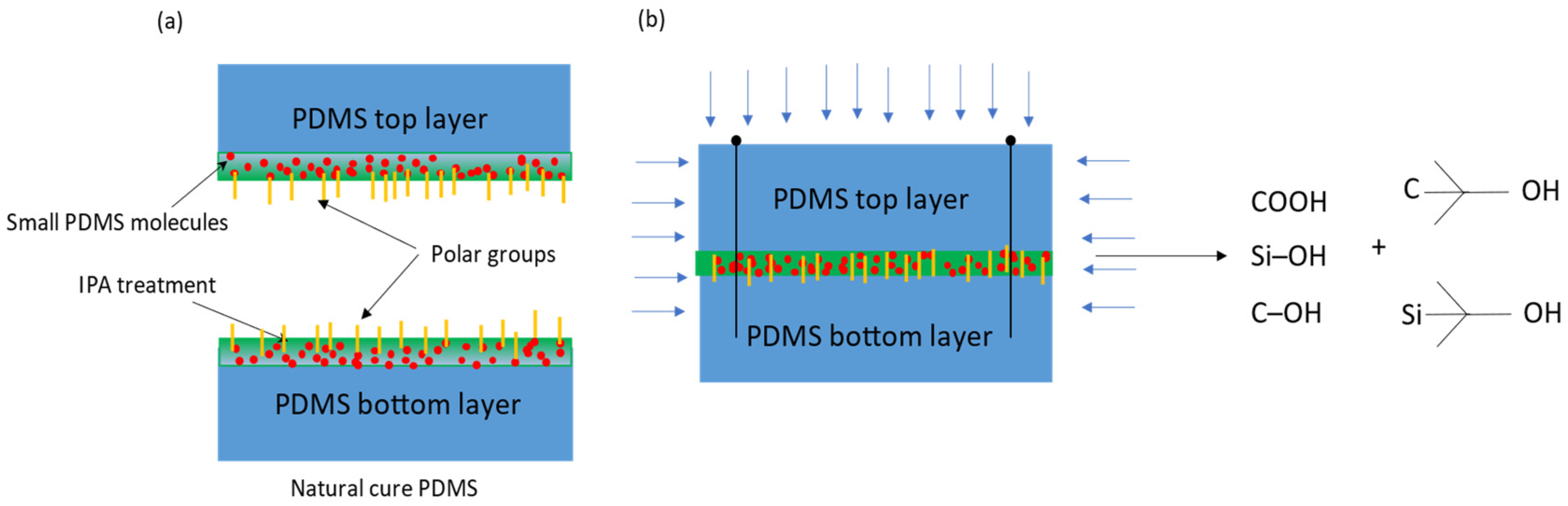
| Method | Substrate | Maximum Bond Strength | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Plasma | PDMS–PDMS | 0.510 MPa | [57] |
| Nitrogen Plasma | PDMS-SU8 | 0.428 MPa | [58] |
| Corona Discharge | PDMS–PDMS | 0.290 MPa | [59] |
| Partial Curing of PDMS | PDMS–PDMS | 0.651 MPa | [59] |
| Vacuum Airbag Lamination (VAL) | PDMS-Glass | 0.739 MPa | [60] |
| Plasma Enhanced | PDMS-PARYLENE | 1.4 MPa | [61] |
| Argon Plasma | PDMS–PDMS | 1.9 MPa | [62] |
| Type of Treatment | Type of Curing | Load (MPa) | Failure Mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | With IPA | Natural | 2.821 | PDMS–PDMS |
| Oven | 1.373 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Without IPA | Natural | 0.392 | PDMS–PDMS | |
| Oven | 0.235 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Sample 2 | With IPA | Natural | 2.668 | Glue Failure |
| Oven | 0.686 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Without IPA | Natural | 0.372 | PDMS–PDMS | |
| Oven | 0.247 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Sample 3 | With IPA | Natural | 2.786 | Glue Failure |
| Oven | 0.941 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Without IPA | Natural | 0.239 | PDMS–PDMS | |
| Oven | 0.215 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Sample 4 | With IPA | Natural | 3.060 | PDMS–PDMS |
| Oven | 1.020 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Without IPA | Natural | 0.353 | PDMS–PDMS | |
| Oven | 0.400 | PDMS–PDMS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tony, A.; Badea, I.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, S.-M.; Zhang, W. A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol. Polymers 2023, 15, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15041006
Tony A, Badea I, Yang C, Liu Y, Wang K, Yang S-M, Zhang W. A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol. Polymers. 2023; 15(4):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15041006
Chicago/Turabian StyleTony, Anthony, Ildiko Badea, Chun Yang, Yuyi Liu, Kemin Wang, Shih-Mo Yang, and Wenjun Zhang. 2023. "A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol" Polymers 15, no. 4: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15041006
APA StyleTony, A., Badea, I., Yang, C., Liu, Y., Wang, K., Yang, S.-M., & Zhang, W. (2023). A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol. Polymers, 15(4), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15041006








