Exploring the Antimicrobial and Antitumoral Activities of Naphthoquinone-Grafted Chitosans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
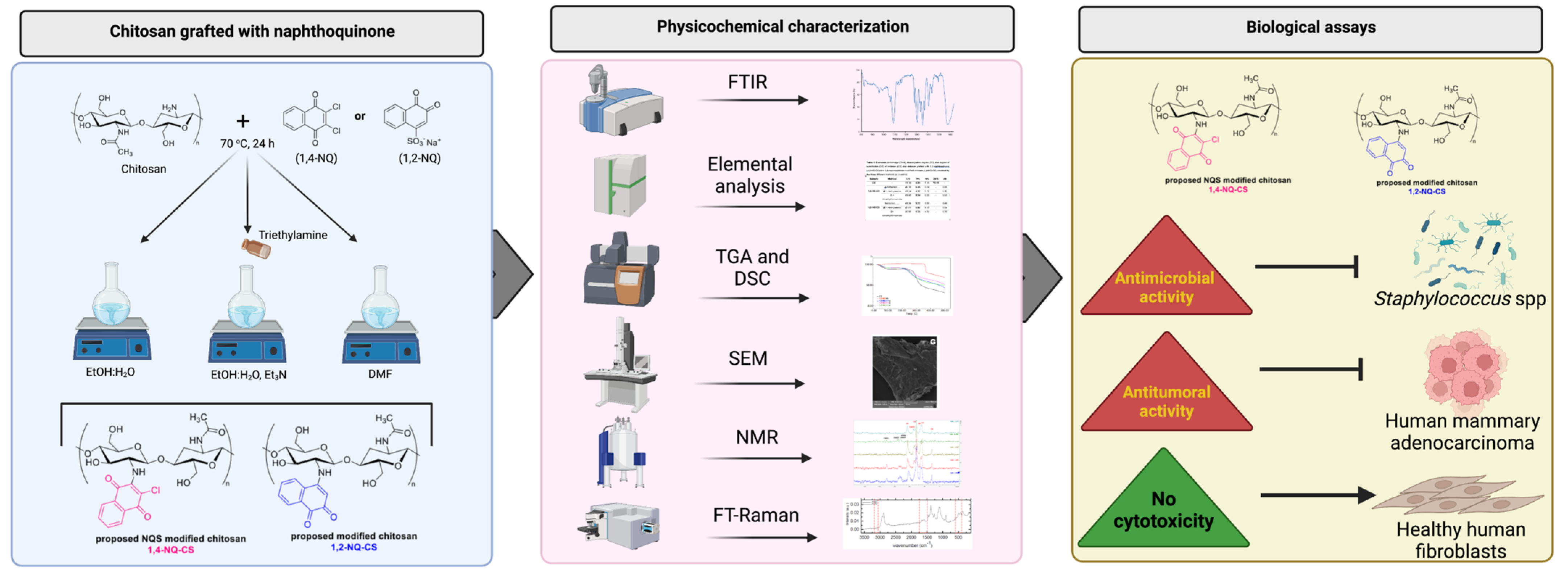
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Materials
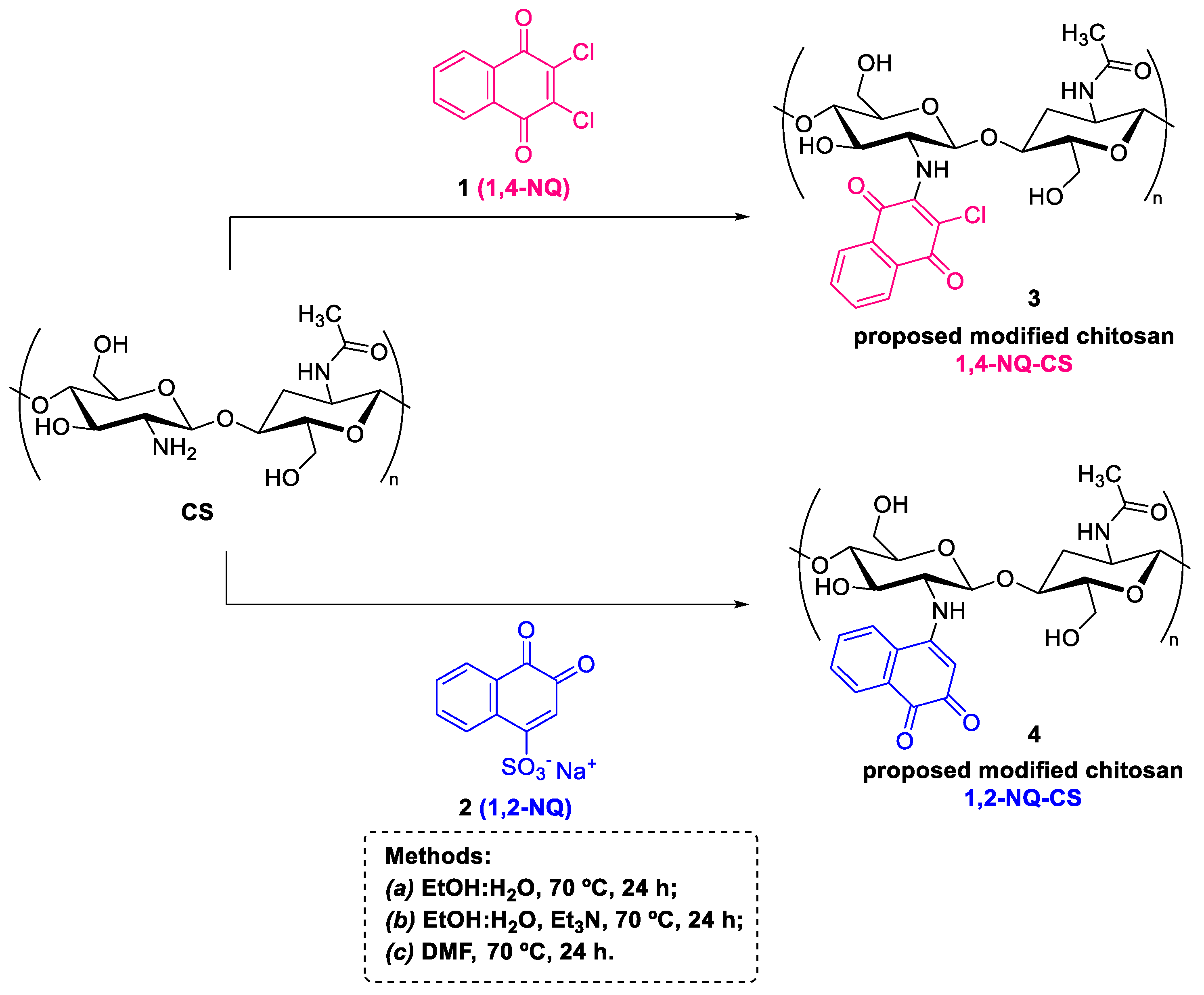
2.3. Preparation of the Modified Chitosan Naphthoquinone Derivatives
2.4. Physicochemical Characterizations
2.5. Biological Assays
2.5.1. Organisms and Human Cell Lineages
2.5.2. Antimicrobial Activity Assessments of Naphthoquinones, Chitosan and Chitosan-Grafted with Naphthoquinones
2.5.3. Cytotoxicity Evaluations of Free-Naphthoquinones, Chitosan and Chitosan Grafted with Naphthoquinones towards Healthy Human Cell Lineages
2.5.4. Assessment of In Vitro Antitumoral Activity of Free-Naphthoquinones, Chitosan and Chitosan Grafted with Naphthoquinones
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
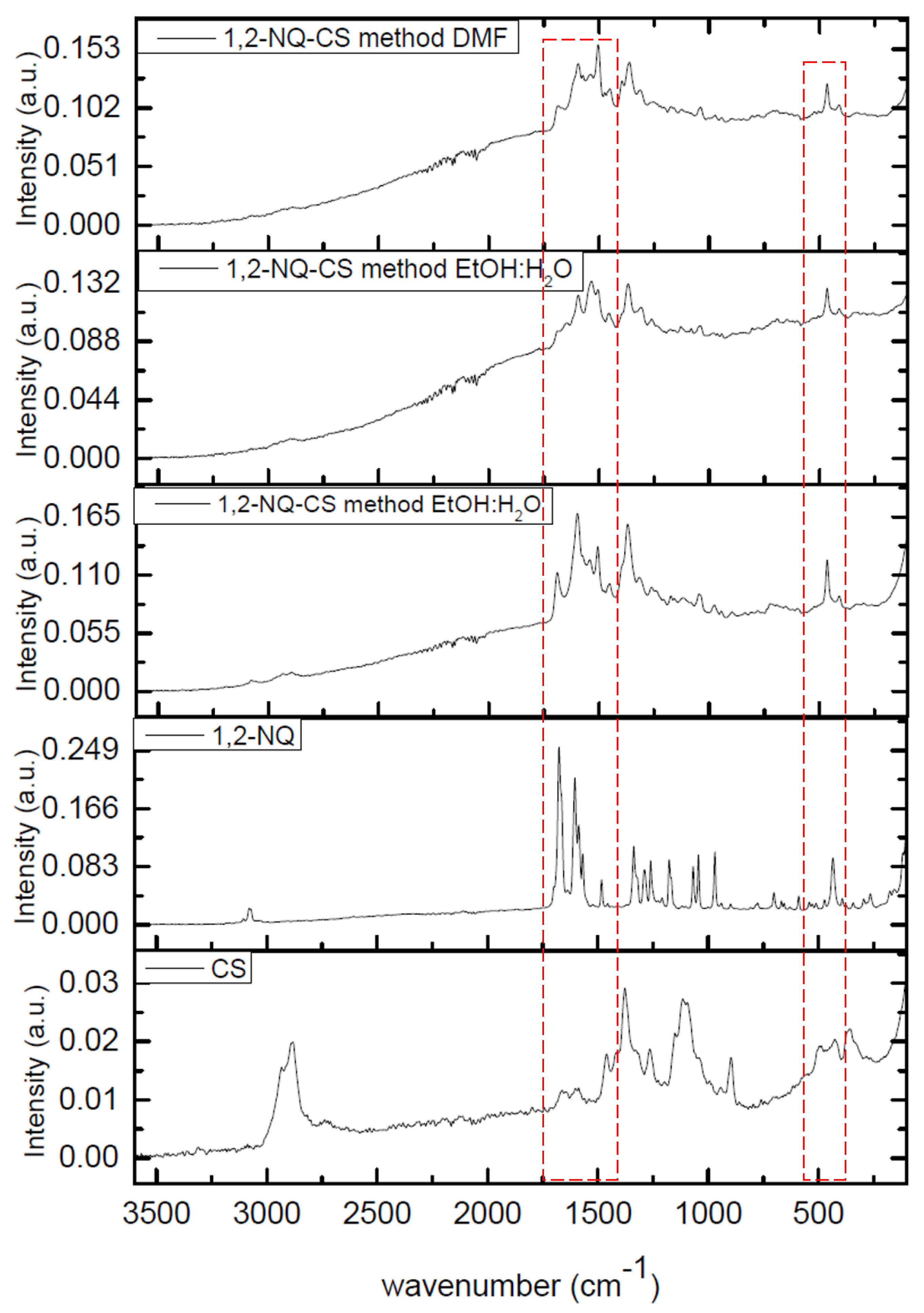
3.2. Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
3.3. Elemental Analysis
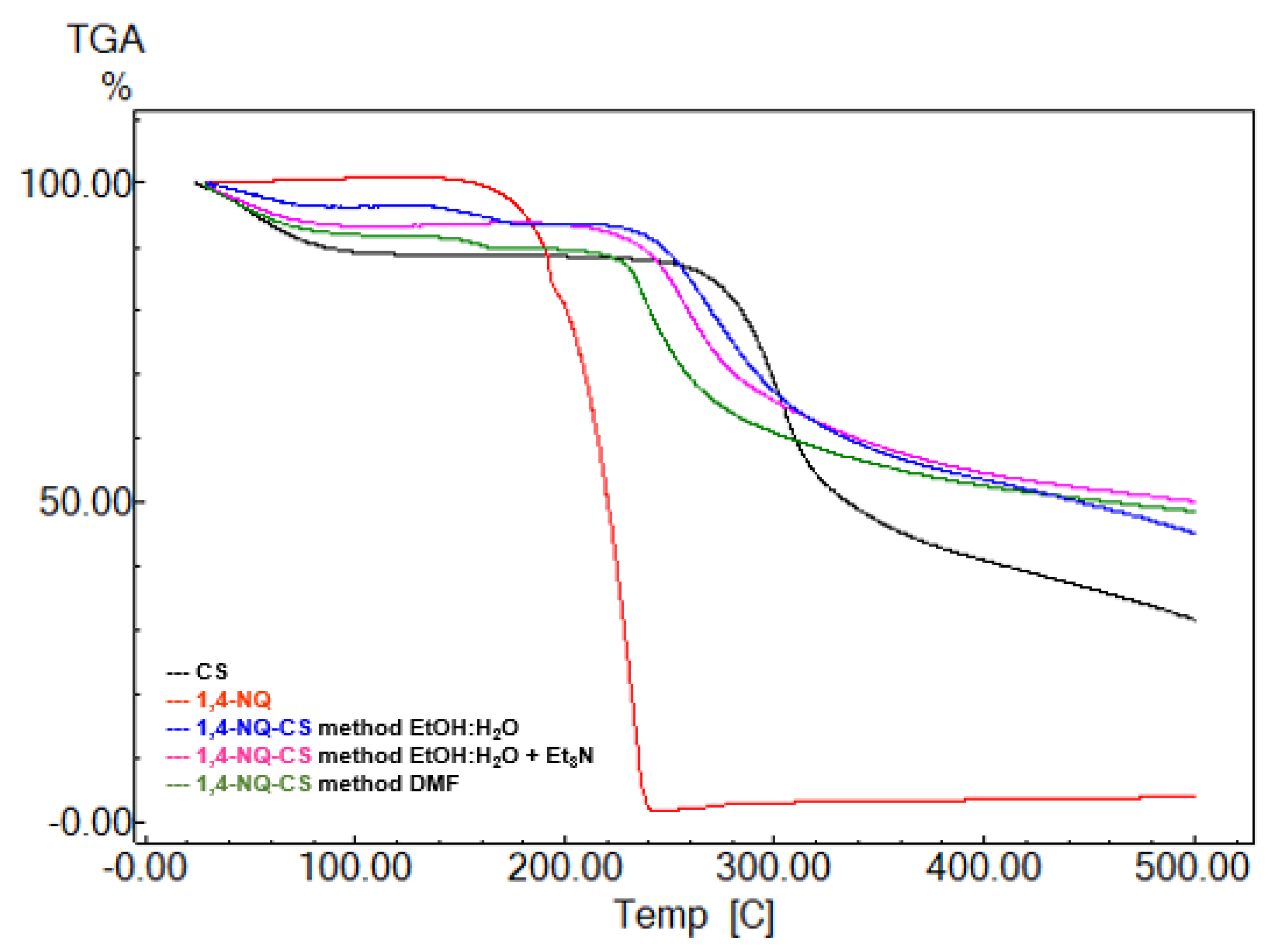
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
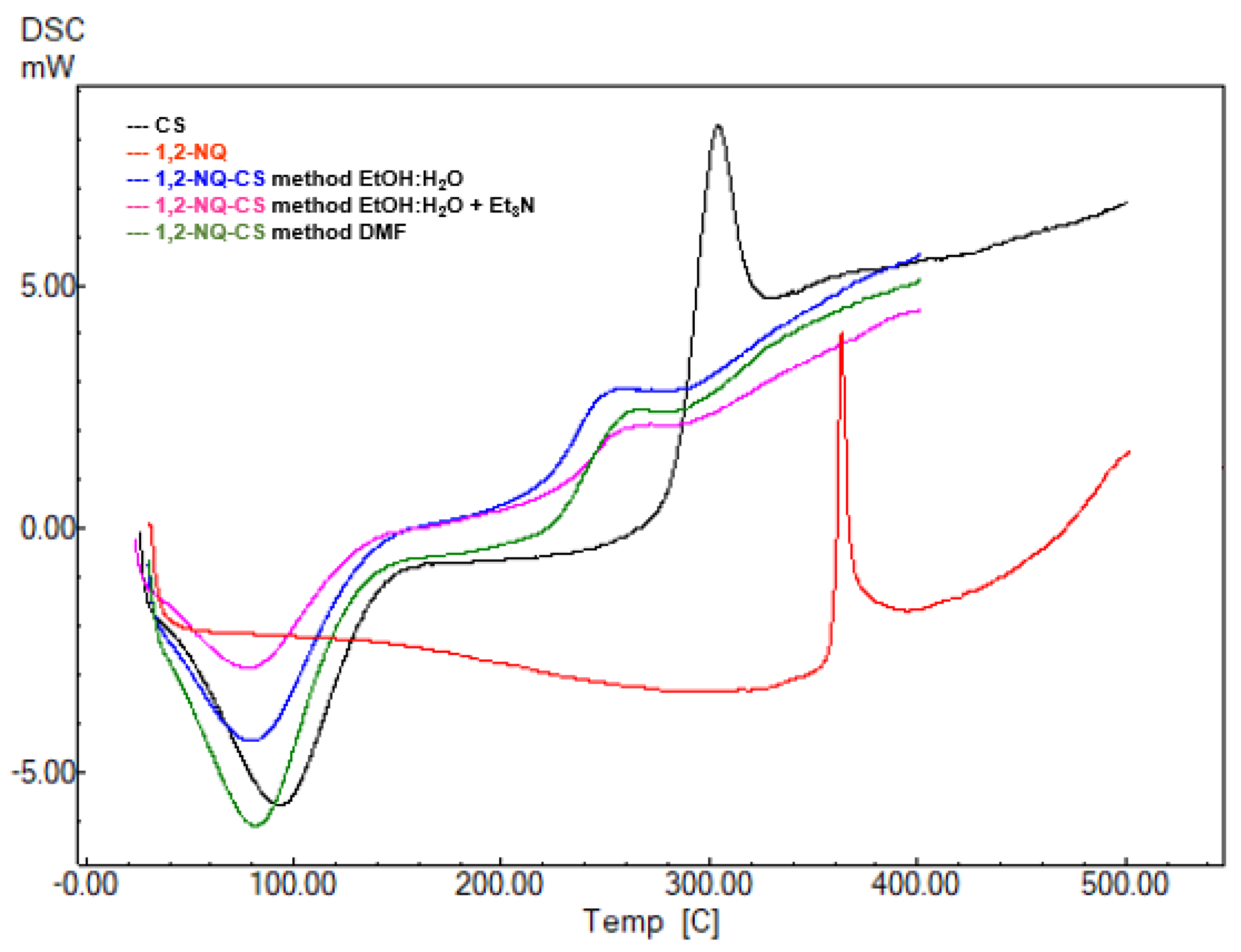
3.5. DSC Analysis
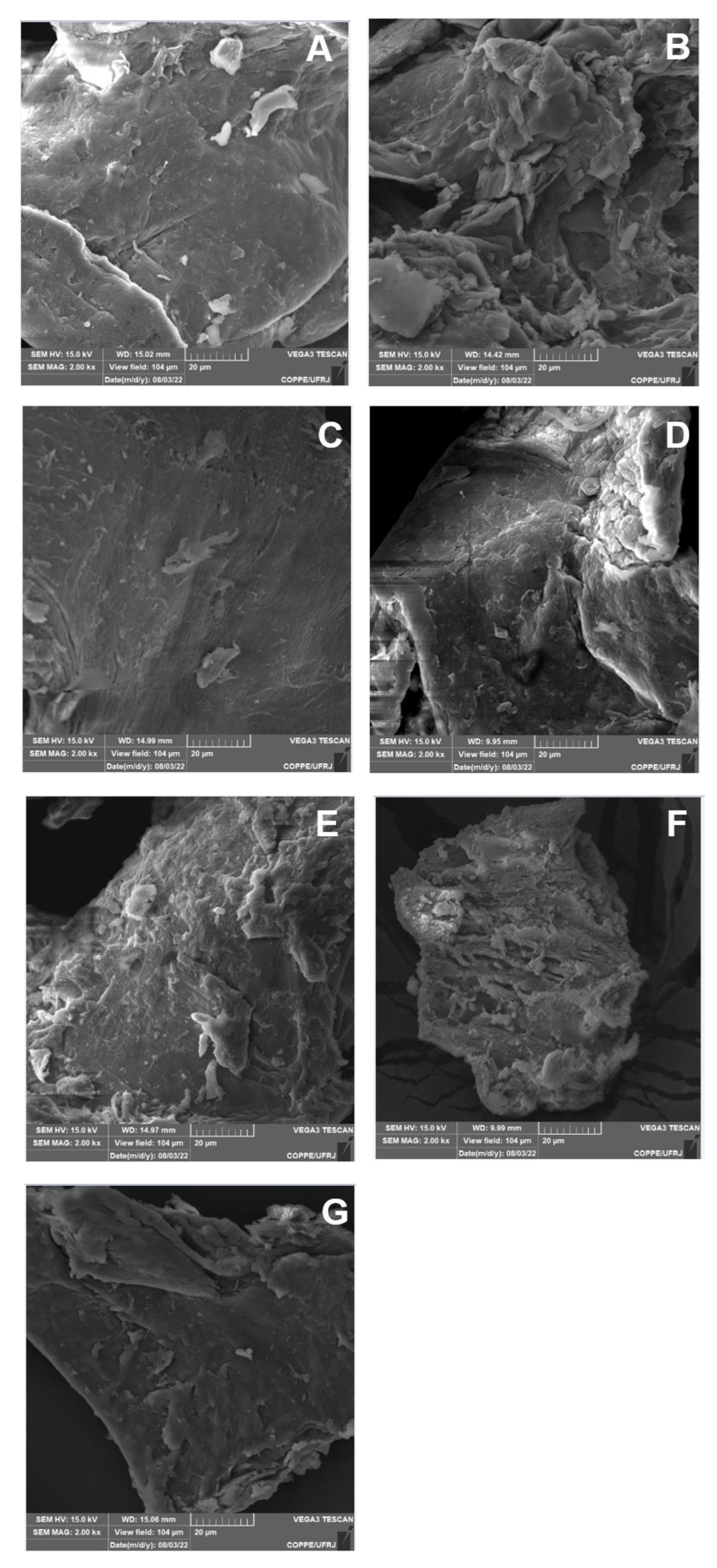
3.6. SEM Analysis
3.7. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
3.8. Raman Spectroscopy
3.9. Antibacterial Potential of Chitosan Grafted with Naphthoquinones
3.10. Anticancer Potential of Naphthoquinone-Grafted Chitosan
3.11. Toxicological Evaluation against Healthy Human Cells and Therapeutic Index
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, H.A.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Nayak, A.; Kishore, U.; Khan, A. Nanoparticles for biomedical applications: An overview. In Nanobiomaterials; Narayan, R., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 357–384. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaens, L.; Soetemans, L.; D’Hondt, E.; Elst, K. Sources of Chitin and Chitosan and their Isolation. In Chitin and Chitosan: Properties and Applications; van den Broek, L.A.M., Boeriu, C.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Elango, J.; Wu, W. Recent Advancement of Molecular Structure and Biomaterial Function of Chitosan from Marine Organisms for Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Application. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.P.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Del Aguila, E.M. Chitosan Nanoparticles: Production, Physicochemical Characteristics and Nutraceutical Applications. Rev. Virtual Química 2017, 9, 387–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana-Filho, S.P.; Sagnini, R.; Cardoso, M.R. Propriedades e Aplicações de Quitosana. Process. Químicos 2007, 1, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, S. Antibacterial activity of chitosan and its derivatives and their interaction mechanism with bacteria: Current state and perspectives. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 138, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-L.; Deng, F.-S.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Antimicrobial Actions and Applications of Chitosan. Polymers 2021, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.G.; Ferreira, V.F.; da Silva, F.d.C.; Freitas, C.S.; Pereira, P.R.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Chitosans and Nanochitosans: Recent Advances in Skin Protection, Regeneration, and Repair. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landriscina, A.; Rosem, J.; Friedman, A.J. Biodegradable chitosan nanoparticles in drug delivery for infectious disease. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.C.R.; Queda, F.; Santos, C.V.A.; Marques, M.M.B. Selective Modification of Chitin and Chitosan: En Route to Tailored Oligosaccharides. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 3468–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, C.; Mao, X. Chitosan: Structural modification, biological activity and application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4532–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahariah, P.; Másson, M. Antimicrobial Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives: A Review of the Structure–Activity Relationship. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3846–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhaveri, J.; Raichura, Z.; Khan, K.; Momin, M.; Omri, A. Chitosan Nanoparticles-Insight into Properties, Functionalization and Applications in Drug Delivery and Theranostics. Molecules 2021, 26, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Li, P. Antimicrobial Chitosan Conjugates: Current Synthetic Strategies and Potential Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braz, E.M.d.A.; Silva, S.C.C.C.; da Silva, D.A.; Carvalho, F.A.d.A.; Barreto, H.M.; Santos Júnior, L.d.S.; da Silva Filho, E.C. Modified chitosan-based bioactive material for antimicrobial application: Synthesis and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, V.K.; Kumar, S. Recent development on naphthoquinone derivatives and their therapeutic applications as anticancer agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 1087–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forezi, L.S.M.; Cardoso, M.F.C.; Costa, D.C.S.; da Silva, F.C.; Ferreira, V.F. 2,3-Dichloro-1,4-Naphthoquinone in Organic Synthesis: Recent Advances. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2017, 14, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, D.; Lande, D.N.; Chakravarty, D.; Gejji, S.P.; Das, P.; Pardesi, K.R.; Satpute, S.; Salunke-Gawali, S. Reactions of 2,3-dichloro-1,4-naphthoquinone with aminophenols: Structural proof for an intermediate hydroxy benzophenoxazine and antibacterial activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1176, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, D.W. Observations on Antimicrobial Action of 2, 3-Dichloro-l, 4-Naphthoquinone, and its Reversal by Vitamins K. Exp. Biol. Med. 1945, 60, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingaew, R.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Nantasenamat, C.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Novel 1,4-naphthoquinone-based sulfonamides: Synthesis, QSAR, anticancer and antimalarial studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 103, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.N., Jr.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S.; Pinto, M.C.F.R.; Silva, R.S.F.; Teixeira, D.V.; de Souza, M.C.B.V.; de Simone, C.A.; de Castro, S.L.; Ferreira, V.F.; Pinto, A.V. Naphthoquinoidal [1,2,3]- triazole, a new structural moiety active against Trypanosoma cruzi. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1774–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.C.B.; Ferreira, P.G.; Borges, A.A.; Forezi, L.S.M.; da Silva, F.C.; Ferreira, V.F. 1,2-Naphthoquinone-4-sulfonic acid salts in organic synthesis. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, V.R.; dos Santos, E.A.; Ferreira, V.F.; Montenegro, R.C.; de Souza, M.C.B.V.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; de Moraes, M.O.; Regufe, A.K.P.; Jordão, A.K.; Pinto, A.C.; et al. Synthesis of a new class of naphthoquinone glycoconjugates and evaluation of their potential as antitumoral agentes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 11438–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Ha, J.D.; Chu, S.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Jung, Y.S.; Baek, J.Y.; Choi, I.K.; Shin, E.Y.; Kang, S.K.; et al. Synthesis and PTP1B inhibition of 1,2-naphthoquinone derivatives as potent anti-diabetic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 12, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, M.J.; Chen, J.; Fratt, E.M.; Chi, L.; Bollinger, J.C.; Binder, R.J.; Bowling, J.; Hyatt, J.L.; Scarborough, J.; Jeffries, C.; et al. Selective Inhibitors of Human Liver Carboxylesterase Based on a β-Lapachone Scaffold: Novel Reagents for Reaction Profiling. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1568–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, P.J. Molecular mechanisms of quinone cytotoxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1991, 80, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, C.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, B.; Bae, H.-W.; Chung, I.-Y.; Kim, E.S.; Cho, Y.-H. Antibacterial strategies inspired by the oxidative stress and response networks. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, N.A.; Abu Hanifah, S.; Mobarak, N.N.; Su’ait, M.S.; Ahmad, A.; Shyuan, L.K.; Khoon, L.T. Synthesis and characterizations of o-nitrochitosan based biopolymer electrolyte for electrochemical devices. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzamly, R.A.; Mohamed, H.M.; Mohamed, M.I.; Zaky, H.T.; Harding, D.R.K.; Kandile, N.G. New sustainable chemically modified chitosan derivatives for different applications: Synthesis and characterization. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 10th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015; Volume 32, p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- McMillian, M.; Li, L.; Parker, J.; Patel, L.; Zhong, Z.; Gunnett, J.; Powers, W.; Johnson, M. An improved resazurin-based cytotoxicity assay for hepatic cells. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2002, 18, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, A.C.; Verícimo, M.A.; Dashevskiy, A.; Pereira, P.R.; Paschoalin, V.M. Liposomal Taro Lectin Nanocapsules Control Human Glioblastoma and Mamary Adenocarcinoma Cell Proliferation. Molecules 2019, 24, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, F.J.; Freitas, R.P. Modification of Chitosan by Zincke Reaction: Synthesis of a Novel Polycationic Chitosan-Pyridinium Derivative. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarmelina, M.; Daltoé, R.D.; Cerri, M.F.; Madeira, K.P.; Rangel, L.B.A.; Júnior, V.C.; Romão, W.; Taranto, A.G.; Greco, S.J. Synthesis, Antitumor Activity and Docking of 2,3-(Substituted)-1,4-Naphthoquinone Derivatives Containing Nitrogen, Oxygen and Sulfur. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madera-Santana, T.J.; Herrera-Méndez, C.H.; Rodríguez-Núñes, R.R. An overview of the chemical modifications of chitosan and their advantages. Green Mat. 2018, 6, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumari, S.; Singh, R.P.; Chavan, N.N.; Annamalai, P.K. Chitosan-based bionanocomposites for biomedical application. Bioinspired Biomim. Nanobiomaterials 2016, 7, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, R.A.; Cantuarias, L.; Cuéllar, M.; Villena, J. Microwave-Assisted Reaction of 2,3-Dichloronaphthoquinone with Aminopyridines. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishioka, T.; Endo-Umeda, K.; Ito, Y.; Shimoda, A.; Takeuchi, A.; Tode, C.; Hirota, Y.; Osakabe, N.; Makishima, M.; Suhara, Y. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists Based on Naphthoquinone Derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yıldırım, H.; Bayrak, N.; Tuyun, A.F.; Kara, E.M.; Çelik, B.O.; Gupta, G.K. 2,3-Disubstituted-1,4-naphthoquinones containing an arylamine with trifluoromethyl group: Synthesis, biological evaluation, and computational study. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 25753–25764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diogo, E.B.T.; Dias, G.G.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Guimaraes, T.T.; Valenca, W.O.; Camara, C.A.; de Oliveira, R.N.; da Silva, M.G.; Ferreira, V.F.; de Paiva, Y.G.; et al. Synthesis and anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity of naphthoquinone-containing triazoles: Electrochemical studies on the effects of the quinoidal moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6337–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, R.G.; Valença, W.O.; Rosa, L.G.; de Simone, C.A.; de Castro, S.L.; Barbosa, J.M.C.; Pinheiro, D.P.; Paier, C.R.K.; de Carvalho, G.G.C.; Pessoa, C.; et al. Synthesis of quinone imine and sulphur-containing compounds with antitumor and trypanocidal activities: Redox and biological implications. RSC Med. Chem. 2020, 11, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, A.; Mucha, M. Thermogravimetric and FTIR studies of chitosan blends. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 396, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, J.; Kaczmarek, H. Thermal treatment of chitosan in various conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafakish, B.; Wilson, L.D. Surface-Modified Chitosan: An Adsorption Study of a “Tweezer-Like” Biopolymer with Fluorescein. Surfaces 2019, 2, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, M.A.; Omer, A.M.; Abbas, E.; Baset, W.M.A.; Tamer, T.M. Preparation, physicochemical characterization and antimicrobial activities of novel two phenolic chitosan Schiff base derivatives. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baran, T.; Menteş, A. Cu(II) and Pd(II) complexes of water soluble O-carboxymethyl chitosan Schiff bases: Synthesis, characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ping, Q.; Zhang, H.; Shen, J. Synthesis and characterization of water-soluble O-succinyl-chitosan. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Deepak, V.; Kumari, M.; Dutta, P.K. Antibacterial activity of diisocyanate-modified chitosan for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 84, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber-Samandari, S.; Yilmaz, O.; Yilmaz, E. Photoinduced Graft Copolymerization onto Chitosan Under Heterogeneous Conditions. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2012, 49, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, N.L.G.D.; Salles, T.F.; Brandão, H.M.; Edward, H.G.M.; de Oliveira, L.F.C. Synthesis, Vibrational Spectroscopic and Thermal Properties of Oxocarbon Cross-Linked Chitosan. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Figueroa, M.J.; Narváez-Araya, D.; Armijo-Escalona, N.; Carrasco-Flores, E.A.; González-Aramundiz, J.V. Design of Chitosan Nanocapsules with Compritol 888 ATO® for Imiquimod Transdermal Administration. Evaluation of Their Skin Absorption by Raman Microscopy. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarmelina, M.; Ferreira, G.B.; Ferreira, V.F.; de M. Carneiro, J.W. Vibrational spectroscopy of lapachol, α- and β-lapachone: Theoretical and experimental elucidation of the Raman and infrared spectra. Vib. Spectrosc. 2016, 86, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.R.F.; Campos, V.R.; de Moraes, R.S.; Souza, N.A.; Cunha, A.C.; Lageb, M.R.; Ferreira, G.B. Theoretical and Experimental Spectroscopic Study on 2-Chloro-3-(substitutedphenylamino)-1,4-naphthoquinone Derivatives. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2023, 34, 242–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.; Miller, L.S. Host–pathogen interactions between the skin and Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Opi. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Severn, M.M.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus epidermidis and its dual lifestyle in skin health and infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Ko, H.; You, D.G.; Kataoka, K.; Park, J.H. Nanomedicines for Reactive Oxygen Species Mediated Approach: An Emerging Paradigm for Cancer Treatment. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Pan, Q.; Gao, W.; He, B. Harnessing polymer-derived drug delivery systems for combating inflammatory bowel disease. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Pan, Q.; Gao, W.; Pu, Y.; Luo, K.; He, B. Reactive oxygen species-upregulating nanomedicines towards enhanced cancer therapy. Biomat. Sci. 2023, 11, 1182–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Method | C% | H% | N% | DD% | DS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | - | 41.19 | 6.90 | 7.40 | 75.45 | - |
| 1,4-NQ-CS | EtOH:H2O | 40.12 | 6.35 | 6.54 | - | 0.06 |
| EtOH:H2O + Et3N | 41.24 | 6.32 | 6.12 | - | 0.12 | |
| DMF | 41.93 | 6.59 | 6.58 | - | 0.08 | |
| 1,2-NQ-CS | EtOH:H2O | 41.26 | 5.22 | 3.95 | - | 0.48 |
| EtOH:H2O + Et3N | 47.61 | 4.84 | 4.33 | - | 0.54 | |
| DMF | 49.90 | 5.58 | 4.82 | - | 0.39 |
| Sample | Method | T (ºC) | Weight Loss (%) | T (oC) | Weight Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | - | 93 | 7 | 304 | 38 |
| 1,4-NQ-CS | EtOH:H2O | 67 | 3 | 268 | 32 |
| EtOH:H2O + Et3N | 71 | 5 | 271 | 31 | |
| DMF | 73 | 5 | 273 | 24 | |
| 1,2-NQ-CS | EtOH:H2O | 78 | 10 | 263 | 20 |
| EtOH:H2O + Et3N | 80 | 6 | 268 | 19 | |
| DMF | 82 | 6 | 262 | 25 |
| Sample | Methods | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus (ATCC 14458) | S. epidermidis (ATCC 12228) | ||
| CS | - | 0.323 | 0.625 |
| 1,2-NQ | - | 0.625 | 0.323 |
| 1,2-NQ-CS | EtOH:H2O | 1.25 | 1.25 |
| EtOH:H2O + Et3N | NI | 1.25 | |
| DMF | NI | 1.25 | |
| 1,4-NQ | - | 0.156 | 0.156 |
| 1,4-NQ-CS | EtOH:H2O | 0.156 | 0.039 |
| EtOH:H2O + Et3N | 0.156 | 0.078 | |
| DMF | 0.156 | 0.039 | |
| Estimated Indexes | Cell Lineage or Bacteria Lineage | CS | 1,4-NQ | 1,4-NQ-CS Method a | 1,4-NQ-CS Method b | 1,4-NQ-CS Method c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC50 (mg/mL) | HFF-1 (HTB-26) | 0.59 | 0.027 | 0.81 | 1.10 | 0.65 |
| TI | MDA-MB-231 (SCRC-1041) | 1.97 | 1.58 | 2.98 | 4.03 | 2.40 |
| S. aureus ATCC 14458 | 3.47 | 0.34 | 10.25 * | 13.92 * | 8.33 | |
| S. epidermidis ATCC 12228 | 1.84 | 0.33 | 35.22 * | 31.42 * | 26.00 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pauli, F.P.; Freitas, C.S.; Pereira, P.R.; Magalhães, A.; de Carvalho da Silva, F.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Ferreira, V.F. Exploring the Antimicrobial and Antitumoral Activities of Naphthoquinone-Grafted Chitosans. Polymers 2023, 15, 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061430
Pauli FP, Freitas CS, Pereira PR, Magalhães A, de Carvalho da Silva F, Paschoalin VMF, Ferreira VF. Exploring the Antimicrobial and Antitumoral Activities of Naphthoquinone-Grafted Chitosans. Polymers. 2023; 15(6):1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061430
Chicago/Turabian StylePauli, Fernanda Petzold, Cyntia Silva Freitas, Patricia Ribeiro Pereira, Alviclér Magalhães, Fernando de Carvalho da Silva, Vania M. F. Paschoalin, and Vitor Francisco Ferreira. 2023. "Exploring the Antimicrobial and Antitumoral Activities of Naphthoquinone-Grafted Chitosans" Polymers 15, no. 6: 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061430
APA StylePauli, F. P., Freitas, C. S., Pereira, P. R., Magalhães, A., de Carvalho da Silva, F., Paschoalin, V. M. F., & Ferreira, V. F. (2023). Exploring the Antimicrobial and Antitumoral Activities of Naphthoquinone-Grafted Chitosans. Polymers, 15(6), 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061430











