One-Step Low Temperature Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles Stabilized by Carboxymethylcellulose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Nanoparticle Synthesis Procedure
2.3. Research Methods for Cerium-Containing Nanocomposites
2.3.1. UV Spectroscopy
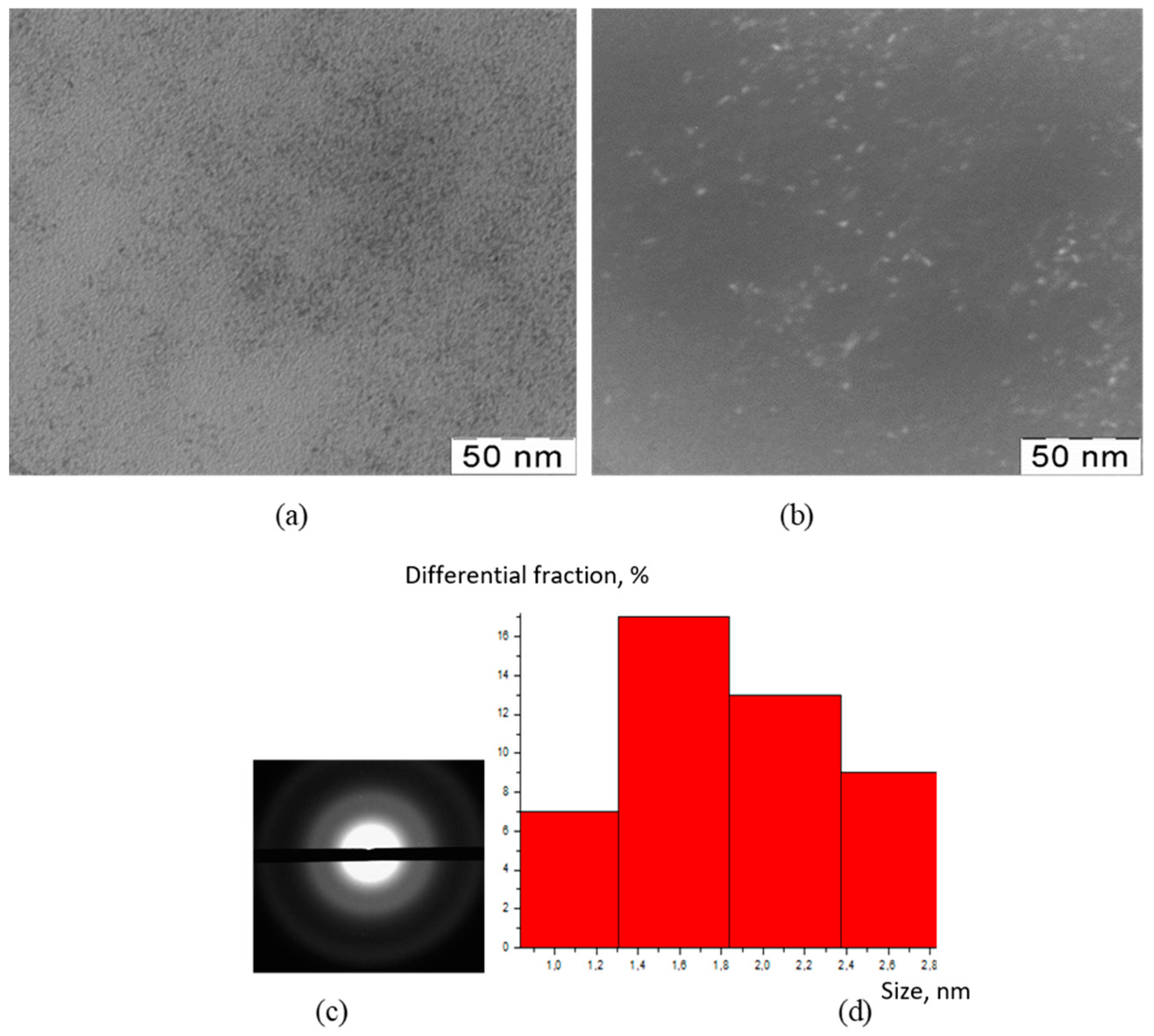
2.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
2.3.4. IR Spectroscopy
2.3.5. Raster (Scanning) Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.H.; Zuo, J.C.; Ren, X.F. Synthesis and character of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles by the precipitation method. Metalurgija 2019, 53, 463–465. [Google Scholar]
- Farahmandjou, M.; Zarinkamar, M.; Firoozabadi, T.P. Synthesis of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles using simple CO-precipitation method. Rev. Mex. Fis. 2016, 62, 496–499. [Google Scholar]
- Ketzial, J.; Jasmine, A.; Nesaraj, S. Synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles by chemical precipitation and the effect of a surfactant on the distribution of particle sizes. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2011, 12, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Soren, S.; Jena, S.R.; Samanta, L.; Parhi, P. Antioxidant Potential and Toxicity Study of the Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Microwave-Mediated Synthesis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 177, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinjari, D.V.; Pandit, A.B. Room temperature synthesis of crystalline CeO2 nanopowder: Advantage of sonochemical method over conventional method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, T.; Hirari, H.; Imanaka, N.; Adachi, G.; Sakata, T.; Mori, H. Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles by hydrothermal crystallization with citric acid. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2002, 21, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, T.; Hirari, H.; Hamada, R.; Imanaka, N.; Adachi, G.; Sakata, T.; Mori, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Coated With Turbostratic Boron Nitride. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilpour, M.; Fathalilou, M. Effect of aging time and calcination temperature on the cerium oxide nanoparticles synthesis via reverse co-precipitation method. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2012, 7, 944–948. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Lu, Q.; Komarneni, S. Fast synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles and nanorods. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2006, 6, 3812–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.; Amjadi, I.; Mohajeri, M.; Mozafari, M. Sol–Gel Synthesis, Physico-Chemical and Biological Characterization of Cerium Oxide/Polyallylamine Nanoparticles. Polymers 2020, 12, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujar, M.S.; Hunagund, S.M.; Desai, V.R.; Patil, S.; Sidarai, A.H. One-step synthesis and characterizations of cerium oxide nanoparticles in an ambient temperature via Co-precipitation method. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1942, 050026. [Google Scholar]
- Kockrick, E.; Schrage, C.; Grigas, A.; Geiger, D.; Kaskel, S. Synthesis and catalytic properties of microemulsion-derived cerium oxide nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annis, J.W.; Fisher, J.M.; Thompsett, D.; Walton, R.I. Solvothermal Synthesis Routes to Substituted Cerium Dioxide Materials. Inorganics 2021, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumkur, P.P.; Gunasekaran, N.K.; Lamani, B.R.; Nazario Bayon, N.; Prabhakaran, K.; Hall, J.C.; Ramesh, G.T. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization for Biosafe Applications. Nanomanufacturing 2021, 1, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumajdad, A.; Eastoe, J.; Mathew, A. Cerium oxide nanoparticles prepared in self-assembled systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, B.; Mirzaee, M.; Darroudi, M.; Oskuee, R.K.; Sadri, K.; Amiri, M.S. Preparation of cerium oxide nanoparticles in Salvia Macrosiphon Boiss seeds extract and investigation of their photo-catalytic activities. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Manna, P.; Das, J. Synthesis and biomedical applications of nanoceria, a redox active nanoparticle. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saifi, M.A.; Seal, S.; Godugu, C. Nanoceria, the versatile nanoparticles: Promising biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 164–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Naik, P. Synthesis and biomedical applications of Cerium oxide nanoparticles—A Review. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, M.S.; Berret, J.F.; Singh, S.; Vinu, A.; Karakoti, A.S. Redox Active Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Current Status and Burning Issues. Small 2021, 17, 2102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Fayyad, E.; Nawaz, M.; Khan, A.; Shakoor, R.A.; Kahraman, R.; Abdullah, A. Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles as Smart Carriers for Self-Healing Coatings. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, C.A.; Ni, D.; Rosenkrans, Z.T.; Cai, W. Scavenging of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species with nanomaterials. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4955–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, B.; Johnson, M.; Walker, M.; Riley, K.; Sims, C. Antioxidant Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alpaslan, E.; Yazici, H.; Golshan, N.H.; Ziemer, K.S.; Webster, T.J. pH-Dependent Activity of Dextran-Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Prohibiting Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation. ACS Biomat. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, S.; Price, E.; Connors, L.; Dettman, A.; Koh, A.S. Study of n-Alkanethiol Self-Assembly Behavior on Iron Particles: Effect of Alkyl Chain Length and Adsorption Solvent on Resulting Iron-Based Magnetorheological Fluids. Langmuir 2022, 38, 13506–13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridonov, V.V.; Liu, X.Y.; Zezin, S.B.; Panova, I.G.; Sybachin, A.V.; Yaroslavov, A.A. Hybrid nanocomposites of carboxymethyl cellulose cross-linked by in-situ formed Cu2O nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications. J. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 914, 121180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8204–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Mikhaylova, M.; Zhang, Y.; Muhammed, M. Protective Coating of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkrtchyan, K.V.; Pigareva, V.A.; Zezina, E.A.; Kuznetsova, O.A.; Semenova, A.A.; Yushina, Y.K.; Tolordava, E.R.; Grudistova, M.A.; Sybachin, A.V.; Klimov, D.I.; et al. Preparation of Biocidal Nanocomposites in X-ray Irradiated Interpolyelectolyte Complexes of Polyacrylic Acid and Polyethylenimine with Ag-Ions. Polymers 2022, 14, 4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivya, P.; Akalya, S.; Sinija, V.R. A comprehensive review on cellulose-based hydrogel and its potential application in the food industry. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Shi, S.; Qi, J.; Cai, S.; Yu, Y.; O’Carroll, D.M.; He, F. Carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized and sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron: Characterization and trichloroethene dechlorination. Appl. Cat. B 2020, 262, 118303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Hashem, A.H.; Sallam, A.-A.M.; Doghish, A.S.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Arishi, A.A.; Shehabeldine, A.M. Synthesis of Silver Nanocomposite Based on Carboxymethyl Cellulose: Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticancer Activities. Polymers 2022, 14, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altam, A.A.; Zhu, L.; Huang, W.; Huang, H.; Yang, S. Polyelectrolyte complex beads of carboxymethylcellulose and chitosan: The controlled formation and improved properties. Carbohyd. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridonov, V.V.; Panova, I.G.; Makarova, L.V.; Afanasov, M.I.; Zezin, S.B.; Sybachin, A.V.; Yaroslavov, A.A. The one-step synthesis of polymer-based magnetic γ-Fe2O3/carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposites. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 177, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimov, D.I.; Zezina, E.A.; Lipik, V.C.; Abramchuk, S.S.; Yaroslavov, A.A.; Feldman, V.I.; Sybachin, A.V.; Spiridonov, V.V.; Zezin, A.A. Radiation-induced preparation of metal nanostructures in coatings of interpolyelectrolyte complexes. Rad. Phys. Chem. 2019, 162, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavee, G.N.; Klabunde, K.J.; Sorensen, C.M.; Hadjapanayis, G.C. Borohydride reductions of metal ions. A new understanding of the chemistry leading to nanoscale particles of metals, borides, and metal borates. Langmuir 1992, 8, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvache-Muñoz, J.; Prado, F.A.; Rodríguez-Páez, J.E. Cerium oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and tentative mechanism of particle formation. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 529, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba-Chiem, L.T.; Huynh, L.; Ralston, J.; Beattie, D.A. In Situ Particle Film ATR FTIR Spectroscopy of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Adsorption on Talc: Binding Mechanism, pH Effects, and Adsorption Kinetics. Langmuir 2008, 24, 8036–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| [CMC], Base-Mole/L | (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6, mM | [CMC]/[Ce4+] | Ce4+ in Composite, wt.% * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.08 | 0.002 | 20:1 | 6.4 |
| 0.08 | 0.0053 | 15:1 | 7.1 |
| 0.08 | 0.008 | 10:1 | 9.0 |
| 0.08 | 0.011 | 7:1 | 11.0 |
| 0.08 | 0.016 | 5:1 | 14.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spiridonov, V.V.; Sybachin, A.V.; Pigareva, V.A.; Afanasov, M.I.; Musoev, S.A.; Knotko, A.V.; Zezin, S.B. One-Step Low Temperature Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles Stabilized by Carboxymethylcellulose. Polymers 2023, 15, 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061437
Spiridonov VV, Sybachin AV, Pigareva VA, Afanasov MI, Musoev SA, Knotko AV, Zezin SB. One-Step Low Temperature Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles Stabilized by Carboxymethylcellulose. Polymers. 2023; 15(6):1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061437
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpiridonov, Vasily V., Andrey V. Sybachin, Vladislava A. Pigareva, Mikhail I. Afanasov, Sharifjon A. Musoev, Alexander V. Knotko, and Sergey B. Zezin. 2023. "One-Step Low Temperature Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles Stabilized by Carboxymethylcellulose" Polymers 15, no. 6: 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061437
APA StyleSpiridonov, V. V., Sybachin, A. V., Pigareva, V. A., Afanasov, M. I., Musoev, S. A., Knotko, A. V., & Zezin, S. B. (2023). One-Step Low Temperature Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles Stabilized by Carboxymethylcellulose. Polymers, 15(6), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061437







