Immobilization and Release of Platelet-Rich Plasma from Modified Nanofibers Studied by Advanced X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Nanofibers
2.2. Plasma-Coated COOH
2.3. Sample Characterization
2.4. Preparation of PRP
2.5. PRP Immobilization
2.6. Testing the Stability of PCL-COOH-PRP
3. Results
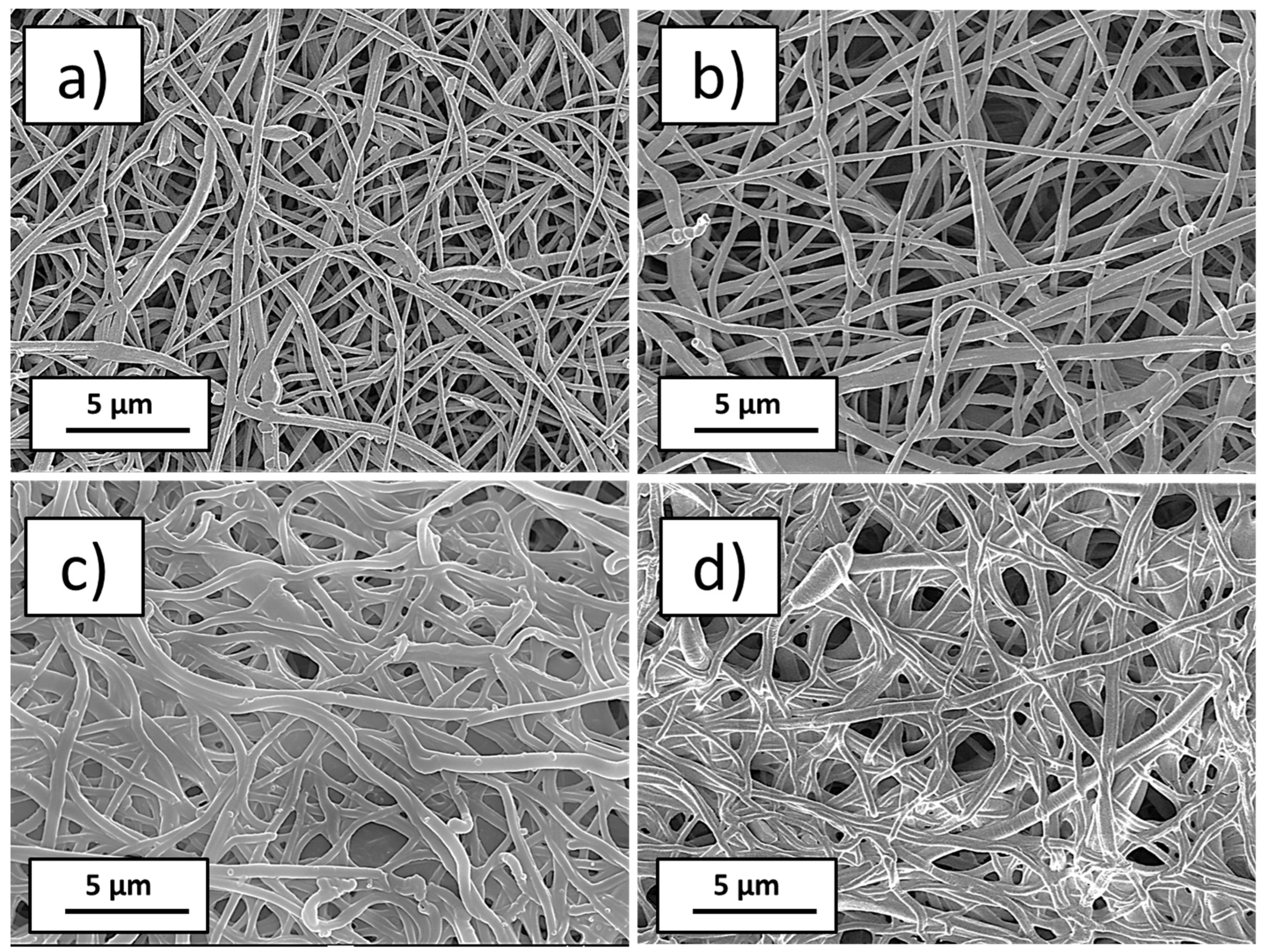
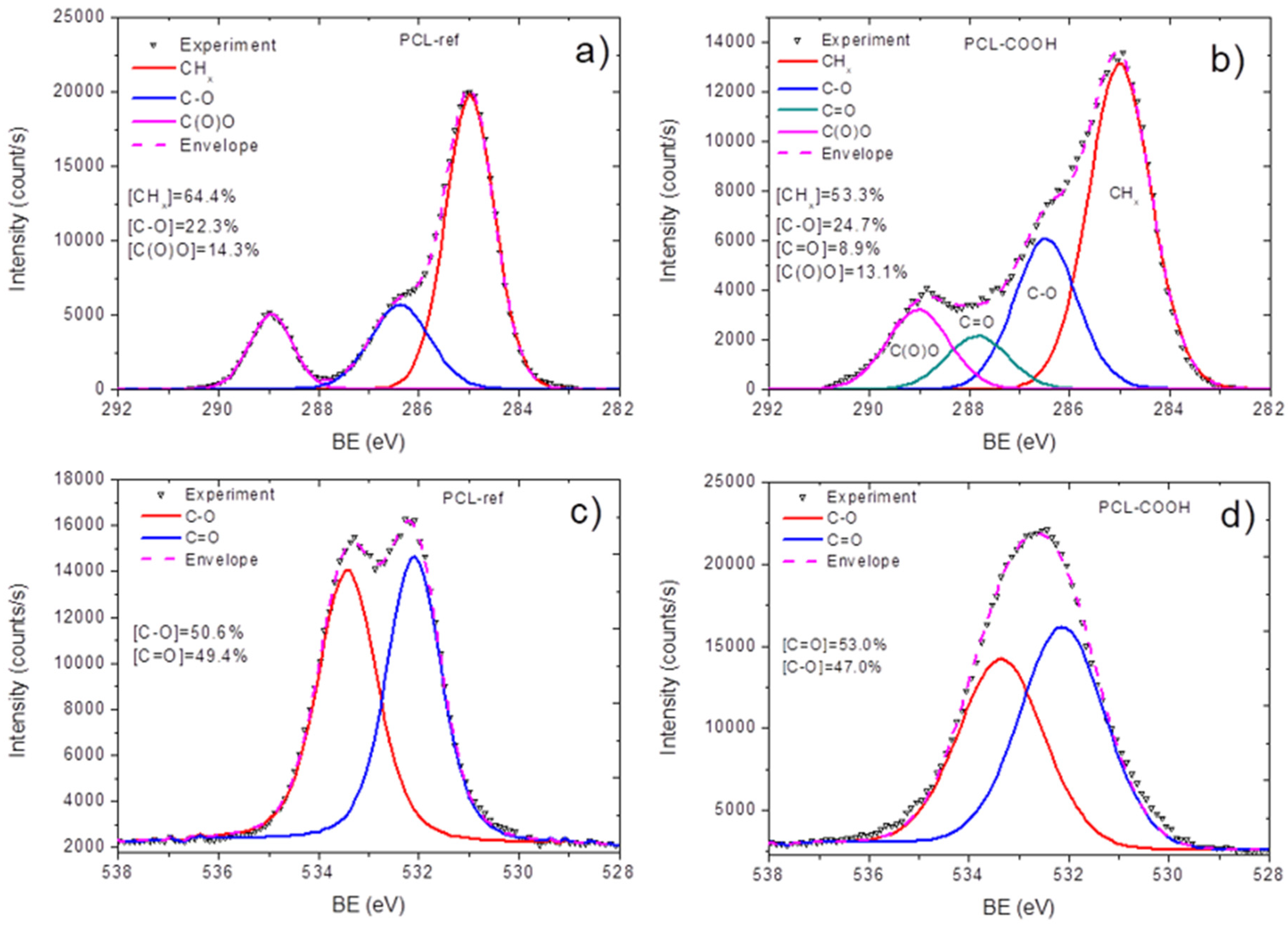
3.1. Plasma-Modified PCL Nanofibers
3.2. Quantification of Immobilized PRP
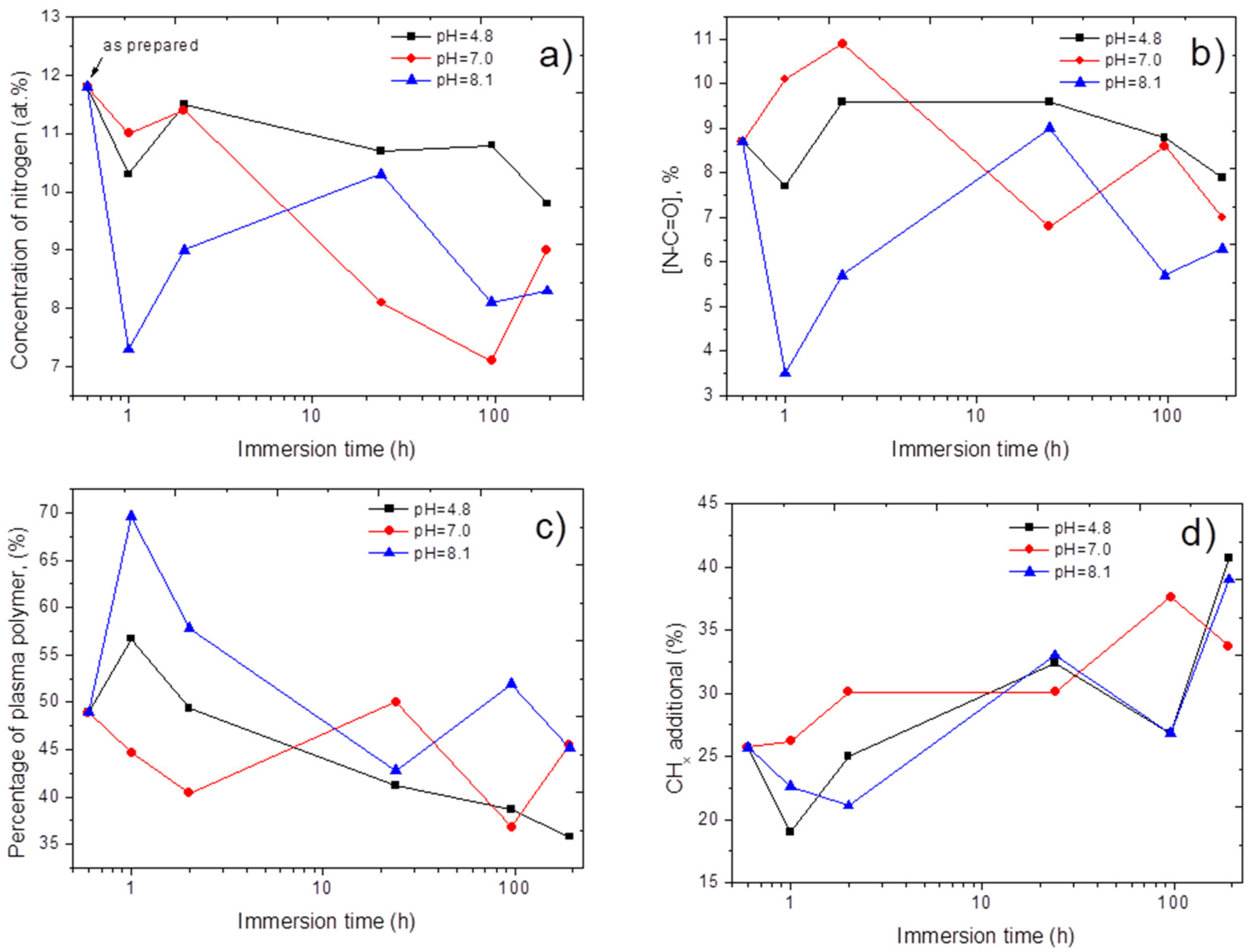
3.3. Stability of Immobilized PRP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, R.A.F.; Ghosh, K.; Tonnesen, M.G. Tissue Engineering for Cutaneous Wounds. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przekora, A. A Concise Review on Tissue Engineered Artificial Skin Grafts for Chronic Wound Treatment: Can We Reconstruct Functional Skin Tissue In Vitro? Cells 2020, 9, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badylak, S.F. The extracellular matrix as a scaffold for tissue reconstruction. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, L.E.; Minasian, R.A.; Caterson, E.J. Extracellular Matrix and Dermal Fibroblast Function in the Healing Wound. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcin, Y.M.; Dixit, V.; Gitnick, G. Extensive In Vivo Angiogenesis Following Controlled Release of Human Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor: Implications for Tissue Engineering and Wound Healing. Artif. Organs 2001, 25, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuttappan, S.; Anitha, A.; Minsha, M.G.; Menon, P.M.; Sivanarayanan, T.B.; Vijayachandran, L.S.; Nair, M.B. BMP2 expressing genetically engineered mesenchymal stem cells on composite fibrous scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration in segmental defects. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 85, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudno, Y.; Ennett-Shepard, A.B.; Chen, R.R.; Aizenberg, M.; Mooney, D.J. Enhancing microvascular formation and vessel maturation through temporal control over multiple pro-angiogenic and pro-maturation factors. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9201–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizwan, M.; Tse, J.W.; Nori, A.; Leong, K.W.; Yim, E.K.F. Cell–Substrate Interactions. In Principles of Regenerative Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 437–468. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, T.E.; Bari, A.; Bullock, A.J.; Turner, R.; Montalbano, G.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; MacNeil, S.; Shepherd, J. Multifunctional Copper-Containing Mesoporous Glass Nanoparticles as Antibacterial and Proangiogenic Agents for Chronic Wounds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitnikova, N.A.; Solovieva, A.O.; Permyakova, E.S.; Sheveyko, A.N.; Shtansky, D.V.; Manakhov, A.M. Silver Ions Incorporation into Nanofibers for Enhanced hMSC Viability. Chemistry 2022, 4, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakhov, A.M.; Permyakova, E.S.; Sitnikova, N.A.; Tsygankova, A.R.; Alekseev, A.Y.; Solomatina, M.V.; Baidyshev, V.S.; Popov, Z.I.; Blahová, L.; Eliáš, M.; et al. Biodegradable Nanohybrid Materials as Candidates for Self-Sanitizing Filters Aimed at Protection from SARS-CoV-2 in Public Areas. Molecules 2022, 27, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovold, M.; Almeida, J.I.; Pla-Palacín, I.; Sainz-Arnal, P.; Sánchez-Romero, N.; Rivas, J.J.; Almeida, H.; Dachary, P.R.; Serrano-Aulló, T.; Soker, S.; et al. Naturally-Derived Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. In Novel Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 421–449. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Florit, M.; Pardo, A.; Domingues, R.M.A.; Graça, A.L.; Babo, P.S.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E. Natural-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alven, S.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Fabrication of Hybrid Nanofibers from Biopolymers and Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (ε-Caprolactone) for Wound Dressing Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawadkar, P.; Mohanakrishnan, J.; Rajasekar, P.; Rahmani, B.; Kohli, N.; Bozec, L.; García-Gareta, E. A Synergistic Relationship between Polycaprolactone and Natural Polymers Enhances the Physical Properties and Biological Activity of Scaffolds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13587–13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedroňová, E.; Kupka, V.; Manakhov, A.; Stoica, A.; Vojtová, L.; Zajícková, L. Electrospun biodegradable PCL, PEG and PCL/PEG polyurethane nanofibers coated by amine-rich plasma polymers. In Proceedings of the NANOCON 2016—8th International Conference on Nanomaterials—Research and Application, Brno, Czech Republic, 19–21 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kedroňová, E.; Zajíčková, L.; Hegemann, D.; Klíma, M.; Michlíček, M.; Manakhov, A. Plasma Enhanced CVD of Organosilicon Thin Films on Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakhov, A.; Nečas, D.; Čechal, J.; Pavliňák, D.; Eliáš, M.; Zajíčková, L. Deposition of stable amine coating onto polycaprolactone nanofibers by low pressure cyclopropylamine plasma polymerization. Thin Solid Films 2015, 581, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Manakhov, A.; Zajíčková, L.; Thomas, S. Structural and Surface Compatibility Study of Modified Electrospun Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) Composites for Skin Tissue Engineering. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, H.S.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Cosme, J.G.L.; Xu, T.; Miszuk, J.M.; Picciani, P.H.S.; Fong, H.; Sun, H. Three dimensional electrospun PCL/PLA blend nanofibrous scaffolds with significantly improved stem cells osteogenic differentiation and cranial bone formation. Biomaterials 2017, 115, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mozaffari, A.; Parvinzadeh Gashti, M.; Mirjalili, M.; Parsania, M. Argon and Argon–Oxygen Plasma Surface Modification of Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Leong, K.W.; Yoo, H.S. In vivo wound healing of diabetic ulcers using electrospun nanofibers immobilized with human epidermal growth factor (EGF). Biomaterials 2008, 29, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovieva, A.O.; Permyakova, E.S.; Ershov, K.I.; Bakhareva, K.I.; Miroshnichenko, S.M.; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V.; Konopatsky, A.S.; Polčak, J.; Shtansky, D.V.; Manakhov, A.M.; et al. Plasma-coated PCL scaffolds with immobilized platelet-rich plasma enhance the wound healing in diabetics mice. Plasma Process. Polym. 2022, 19, 2200032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grip, J.; Engstad, R.E.; Skjæveland, I.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; Isaksson, J.; Basnet, P.; Holsæter, A.M. Beta-glucan-loaded nanofiber dressing improves wound healing in diabetic mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 121, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manakhov, A.M.; Solovieva, A.O.; Permyakova, E.S.; Sitnikova, N.A.; Klyushova, L.S.; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V.; Konopatsky, A.S.; Shtansky, D.V. Adhesion and Proliferation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Plasma-Coated Biodegradable Nanofibers. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakhov, A.; Permyakova, E.; Ershov, S.; Miroshnichenko, S.; Pykhtina, M.; Beklemishev, A.; Kovalskii, A.; Solovieva, A. XPS Modeling of Immobilized Recombinant Angiogenin and Apoliprotein A1 on Biodegradable Nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupka, V.; Dvořáková, E.; Manakhov, A.; Michlíček, M.; Petruš, J.; Vojtová, L.; Zajíčková, L. Well-Blended PCL/PEO Electrospun Nanofibers with Functional Properties Enhanced by Plasma Processing. Polymers 2020, 12, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakhov, A.; Kedroňová, E.; Medalová, J.; Černochová, P.; Obrusník, A.; Michlíček, M.; Shtansky, D.V.; Zajíčková, L. Carboxyl-anhydride and amine plasma coating of PCL nanofibers to improve their bioactivity. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakhov, A.; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.; Michlíček, M.; Permyakova, E.; Dvořáková, E.; Polčák, J.; Popov, Z.; Visotin, M.; Shtansky, D.V. Grafting of carboxyl groups using CO2/C2H4/Ar pulsed plasma: Theoretical modeling and XPS derivatization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, A.; Manakhov, A.; Polčák, J.; Ondračka, P.; Buršíková, V.; Zajíčková, R.; Medalová, J.; Zajíčková, L. Cell proliferation on modified DLC thin films prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 029520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, F.; Camporeale, G.; Yang, Y.W.; Wu, J.S.; Sardella, E.; Dilecce, G.; Calvano, C.D.; Quintieri, L.; Caputo, L.; Baruzzi, F.; et al. Direct Plasma Deposition of Lysozyme-Embedded Bio-Composite Thin Films. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhorukova, I.V.; Sheveyko, A.N.; Manakhov, A.; Zhitnyak, I.Y.; Gloushankova, N.A.; Denisenko, E.A.; Filippovich, S.Y.; Ignatov, S.G.; Shtansky, D.V. Synergistic and long-lasting antibacterial effect of antibiotic-loaded TiCaPCON-Ag films against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permyakova, E.S.; Konopatsky, A.S.; Ershov, K.I.; Bakhareva, K.I.; Sitnikova, N.A.; Shtansky, D.V.; Solovieva, A.O.; Manakhov, A.M. Ag-Contained Superabsorbent Curdlan–Chitosan Foams for Healing Wounds in a Type-2 Diabetic Mice Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manakhov, A.; Moreno-Couranjou, M.; Choquet, P.; Boscher, N.D.; Pireaux, J.-J. Diene functionalisation of atmospheric plasma copolymer thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, S466–S469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakhov, A.; Landová, M.; Medalová, J.; Michlíček, M.; Polčák, J.; Nečas, D.; Zajíčková, L. Cyclopropylamine plasma polymers for increased cell adhesion and growth. Plasma Process. Polym. 2017, 14, 1600123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Gomez, L.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A.; Silva, M.; Dominguez, F.; Sheikh, F.A.; Cantu, T.; Desai, R.; Garcia, V.L.; Macossay, J. Biodegradable electrospun nanofibers coated with platelet-rich plasma for cell adhesion and proliferation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 40, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, M.; Wei, X.; Hao, Y.; Wang, J. Evaluation of 3D-printed polycaprolactone scaffolds coated with freeze-dried platelet-rich plasma for bone regeneration. Materials 2017, 10, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarantopoulou, E.; Petrou, P.S.; Kollia, Z.; Palles, D.; Spyropoulos-Antonakakis, N.; Kakabakos, S.; Cefalas, A.-C. Protein immobilization and detection on laser processed polystyrene surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 064309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manakhov, A.M.; Sitnikova, N.A.; Tsygankova, A.R.; Alekseev, A.Y.; Adamenko, L.S.; Permyakova, E.; Baidyshev, V.S.; Popov, Z.I.; Blahová, L.; Eliáš, M.; et al. Electrospun Biodegradable Nanofibers Coated Homogenously by Cu Magnetron Sputtering Exhibit Fast Ion Release. Computational and Experimental Study. Membranes 2021, 11, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovieva, A.; Miroshnichenko, S.; Kovalskii, A.; Permyakova, E.; Popov, Z.; Dvořáková, E.; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.; Obrosov, A.; Polčak, J.; Zajíčková, L.; et al. Immobilization of Platelet-Rich Plasma onto COOH Plasma-Coated PCL Nanofibers Boost Viability and Proliferation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Polymers 2017, 9, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, M.; Ben-Josef, E.; Robb, R.; Vedaie, M.; Seum, S.; Thirumoorthy, K.; Palanichamy, K.; Harbrecht, M.; Chakravarti, A.; Williams, T.M. Caveolae-mediated endocytosis is critical for albumin cellular uptake and response to albumin-bound chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5925–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miroshnichenko, S.; Timofeeva, V.; Permyakova, E.; Ershov, S.; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.; Dvořaková, E.; Shtansky, D.; Zajíčková, L.; Solovieva, A.; Manakhov, A. Plasma-Coated Polycaprolactone Nanofibers with Covalently Bonded Platelet-Rich Plasma Enhance Adhesion and Growth of Human Fibroblasts. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polycaprolactone (PCL) Safety Profile; Report Details; U.S. FDA Center for Devices and Radiological Health: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2021.

| Sample | C | O | N | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL-ref | 77.3 | 22.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| PCL-COOH | 69.3 | 30.2 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP | 70.7 | 17.2 | 11.8 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-1h-pH7.4 | 70.1 | 18.6 | 11.0 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-2h-pH7.4 | 70.6 | 17.6 | 11.4 | 0.4 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-1d-pH7.4 | 73.6 | 18.0 | 8.1 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-4d-pH7.4 | 74.7 | 17.0 | 7.1 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-8d-pH7.4 | 73.2 | 17.5 | 9.0 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-1h-pH4.8 | 70.0 | 19.4 | 10.2 | 0.4 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-2h-pH4.8 | 69.7 | 18.5 | 11.4 | 0.4 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-1d-pH4.8 | 72.1 | 17.0 | 10.6 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-4d-pH4.8 | 72.8 | 16.2 | 10.8 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-8d-pH4.8 | 74.1 | 15.9 | 9.8 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-1h-pH8.1 | 69.0 | 23.5 | 7.3 | 0.2 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-2h-pH8.1 | 69.1 | 22.0 | 8.7 | 0.2 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-1d-pH8.1 | 69.4 | 20.0 | 10.3 | 0.3 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-4d-pH8.1 | 70.0 | 21.7 | 8.1 | 0.2 |
| PCL-COOH-PRP-8d-pH8.1 | 72.8 | 18.7 | 8.3 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manakhov, A.M.; Permyakova, E.S.; Solovieva, A.O.; Sitnikova, N.A.; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V.; Konopatsky, A.S.; Shtansky, D.V. Immobilization and Release of Platelet-Rich Plasma from Modified Nanofibers Studied by Advanced X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analyses. Polymers 2023, 15, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061440
Manakhov AM, Permyakova ES, Solovieva AO, Sitnikova NA, Kiryukhantsev-Korneev PV, Konopatsky AS, Shtansky DV. Immobilization and Release of Platelet-Rich Plasma from Modified Nanofibers Studied by Advanced X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analyses. Polymers. 2023; 15(6):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061440
Chicago/Turabian StyleManakhov, Anton M., Elizaveta S. Permyakova, Anastasiya O. Solovieva, Natalya A. Sitnikova, Philipp V. Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, Anton S. Konopatsky, and Dmitry V. Shtansky. 2023. "Immobilization and Release of Platelet-Rich Plasma from Modified Nanofibers Studied by Advanced X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analyses" Polymers 15, no. 6: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061440
APA StyleManakhov, A. M., Permyakova, E. S., Solovieva, A. O., Sitnikova, N. A., Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P. V., Konopatsky, A. S., & Shtansky, D. V. (2023). Immobilization and Release of Platelet-Rich Plasma from Modified Nanofibers Studied by Advanced X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analyses. Polymers, 15(6), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061440










