A Review on Fresh, Hardened, and Microstructural Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
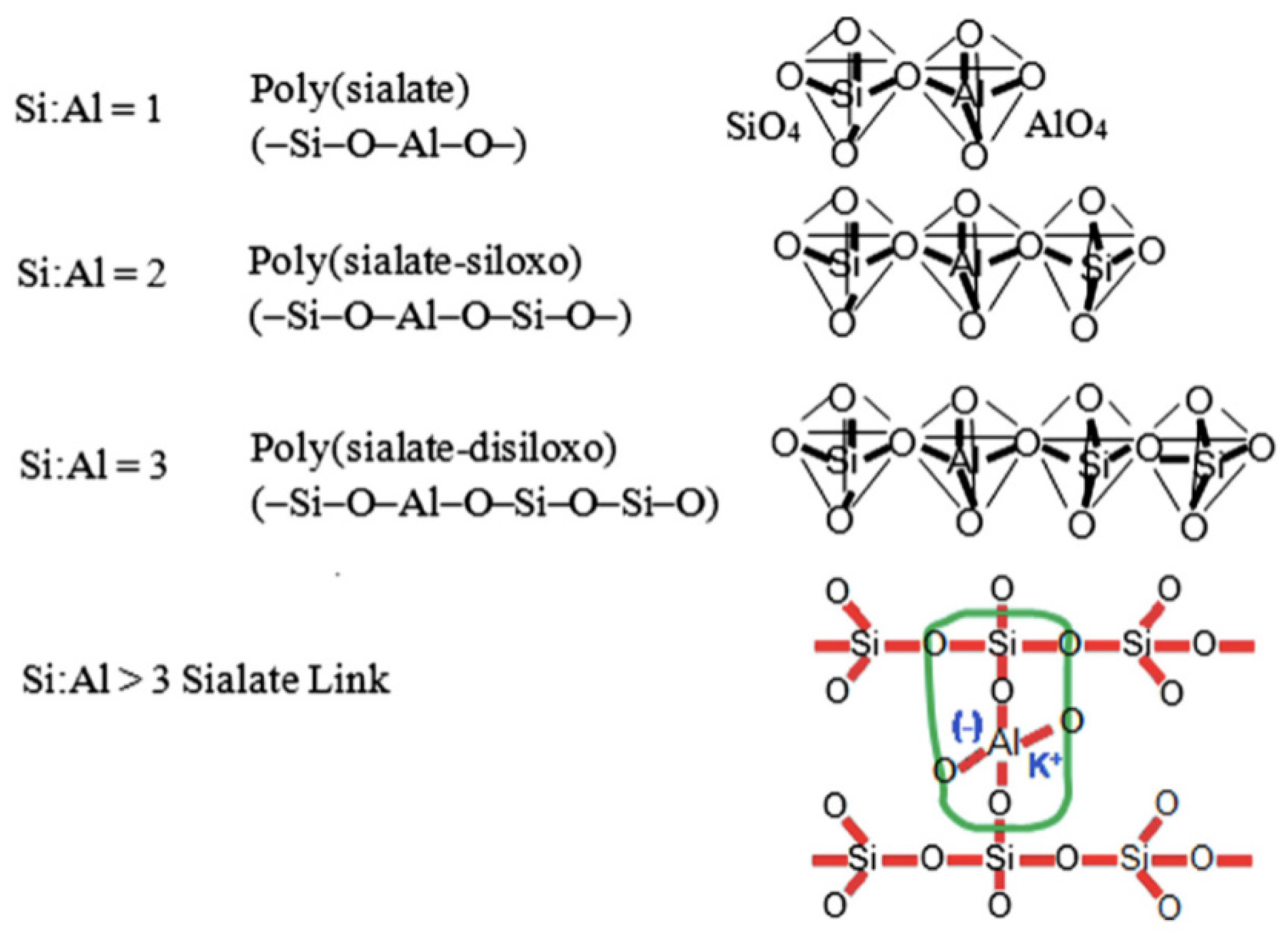
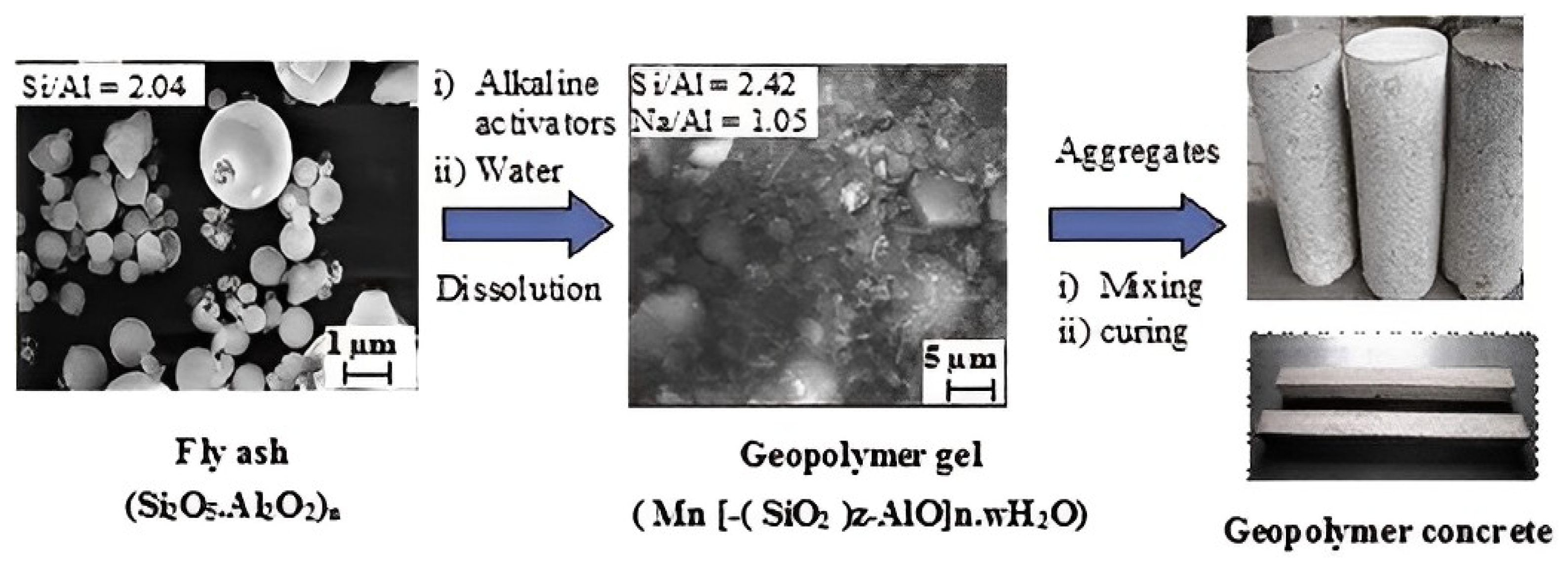
2. Geopolymerization
3. Fibre-Reinforced Concrete and Its Types
3.1. Steel Fiber
3.2. Inorganic Fiber
3.3. Glass Fiber
3.4. Al2O5Si and Al2O3 Fiber
3.5. Basalt Fiber
3.6. Other Inorganic Fiber
3.7. Plant-Inferred Fiber
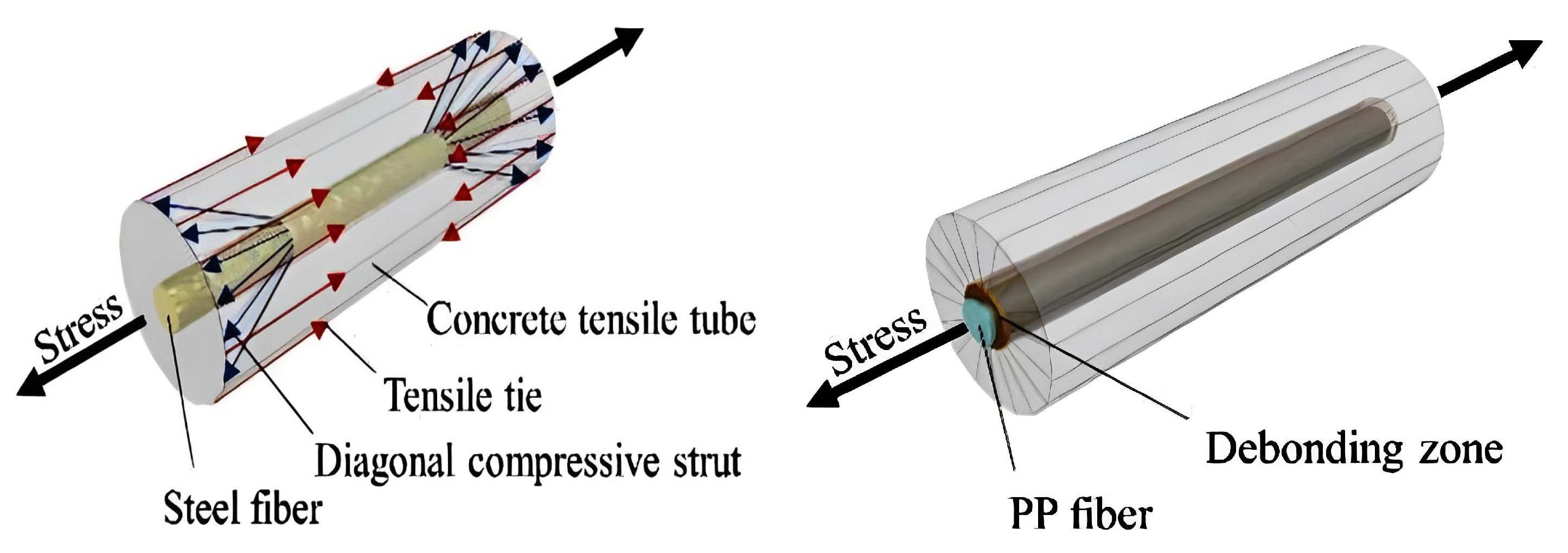
4. Mechanism and Matrix Interaction
5. Materials
5.1. Fine Aggregate
5.2. Coarse Aggregate
5.3. GGBS
5.4. Metakaolin
6. Alkaline Activator Solution
7. Specimen Preparation and Testing
8. Mixing Process
| Ref | Composition | GGBFS/CFR/m3 | FA | Metakaolin, kg/m3 | Fine Aggregate, kg/m3 | CA kg/m3 | NaOH kg/m3 | Cement kg/m3 | Na2So4 + NaOH kg/m3 | SiO2 kg/m3 | Na2Sio3 kg/m3 | Fibre kg/m3 | M | SP % | H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [87] | Liquid ratio: 0.5b | 143.32–592.41 | - | 146.84–572.3 | 1705 | - | 89.45–116.5 | - | - | 190 | - | - | - | - | - |
| GGBFS/CFR-M50 | 143.32–592.41 | - | 146.84–572.31 | 1705 | - | 89.45–116.5 | - | - | 190 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| [90] | SF0.5 NS2 | 225–22.8 | 225–22.8 | - | 859.69–865.22 | 737 742.88 | - | 450 | 225 | - | - | 0–10 (NS) 0.784 (SF) | 12 | 5 | 8 |
| [91] | - | 6000 | - | 1430 | 780 | 10 | - | - | - | 1500 | 0.5% (PF) | - | - | - | |
| [89] | F3 AR80 V0.75 | 39.4 | 354.95 | - | 554.4 | 1294 | 45.1 | - | - | - | 112.6 | 19.63–58.88 (SF) | - | 11.8 | 59.1 |
| [92] | - | 639 | - | 285 | 975 | 72 | - | - | - | 180 | - | - | - | 53 | |
| [105] | PVA1.0 + Steel 1.5 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 0.5–1 | - | 0.05 | - | 0.5–2.5 (SF) | - | - | 0.45 |
| [106] | - | 400 | - | 660 | 1230 | - | 400 | - | - | 2.5 | - | 12 | 2 | 14 | |
| [106] | SLAG 78–310 | 388–698 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0–78 | - | 0–2 (SF) | - | - | - | |
| [107] | - | 400 | - | 540 | 1260 | 57.1 | - | - | - | 143 | 0–1.25 (Glass) | - | - | - |
9. Results and Discussion
9.1. Compressive Strength of FRGC
9.2. Splitting Tensile and Flexural Strength
9.3. Impact Strength
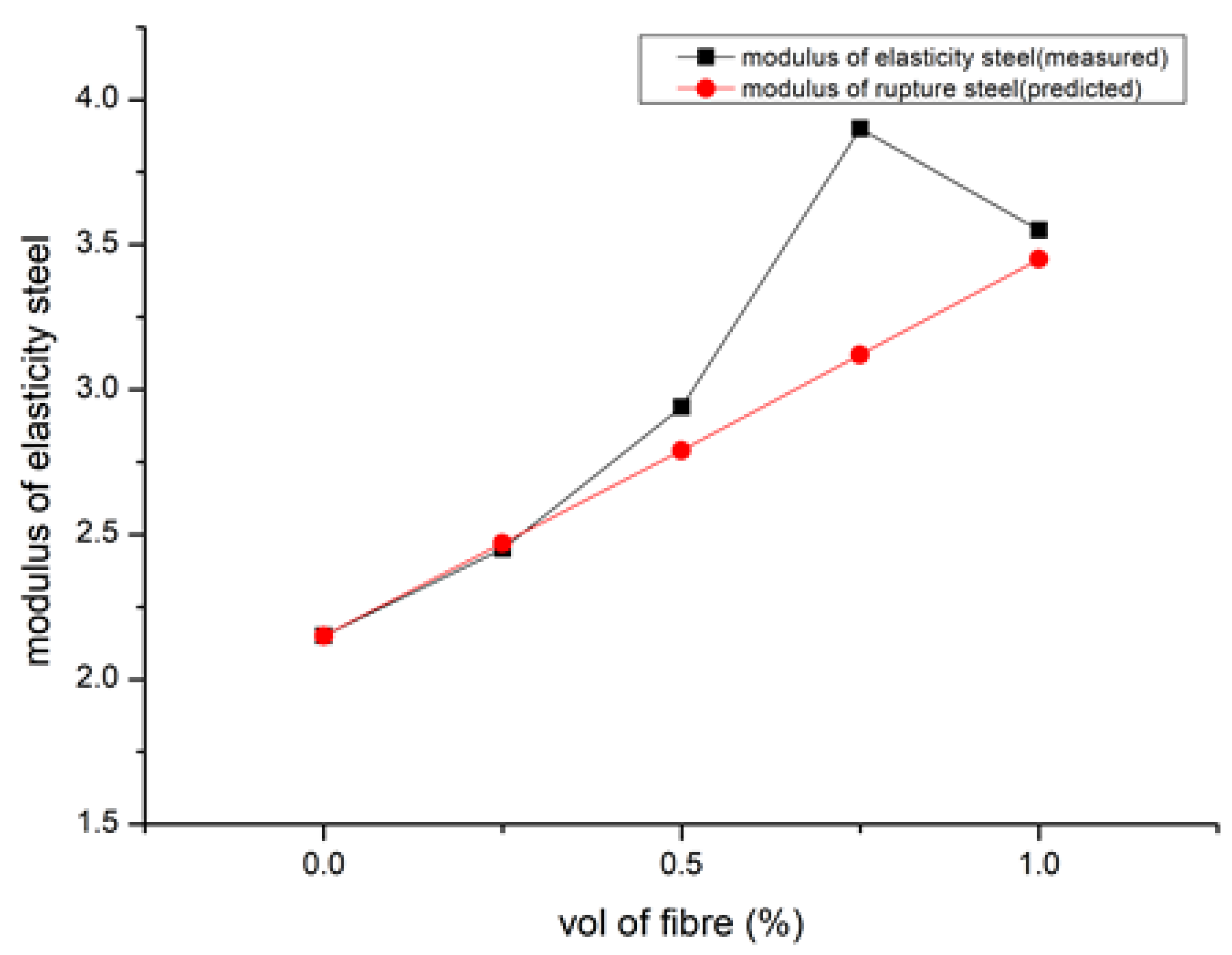
9.4. Modulus of Elasticity
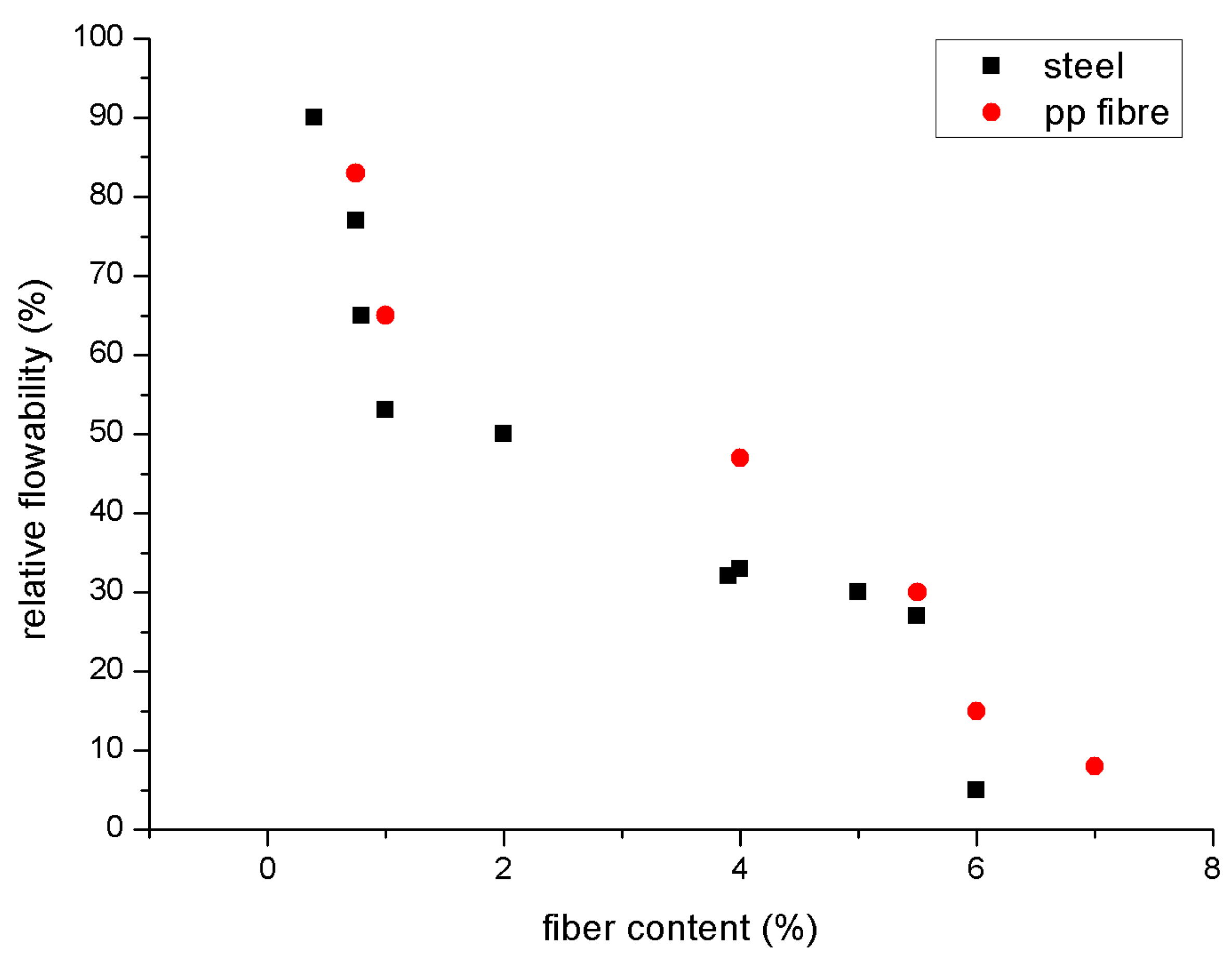
9.5. Workability
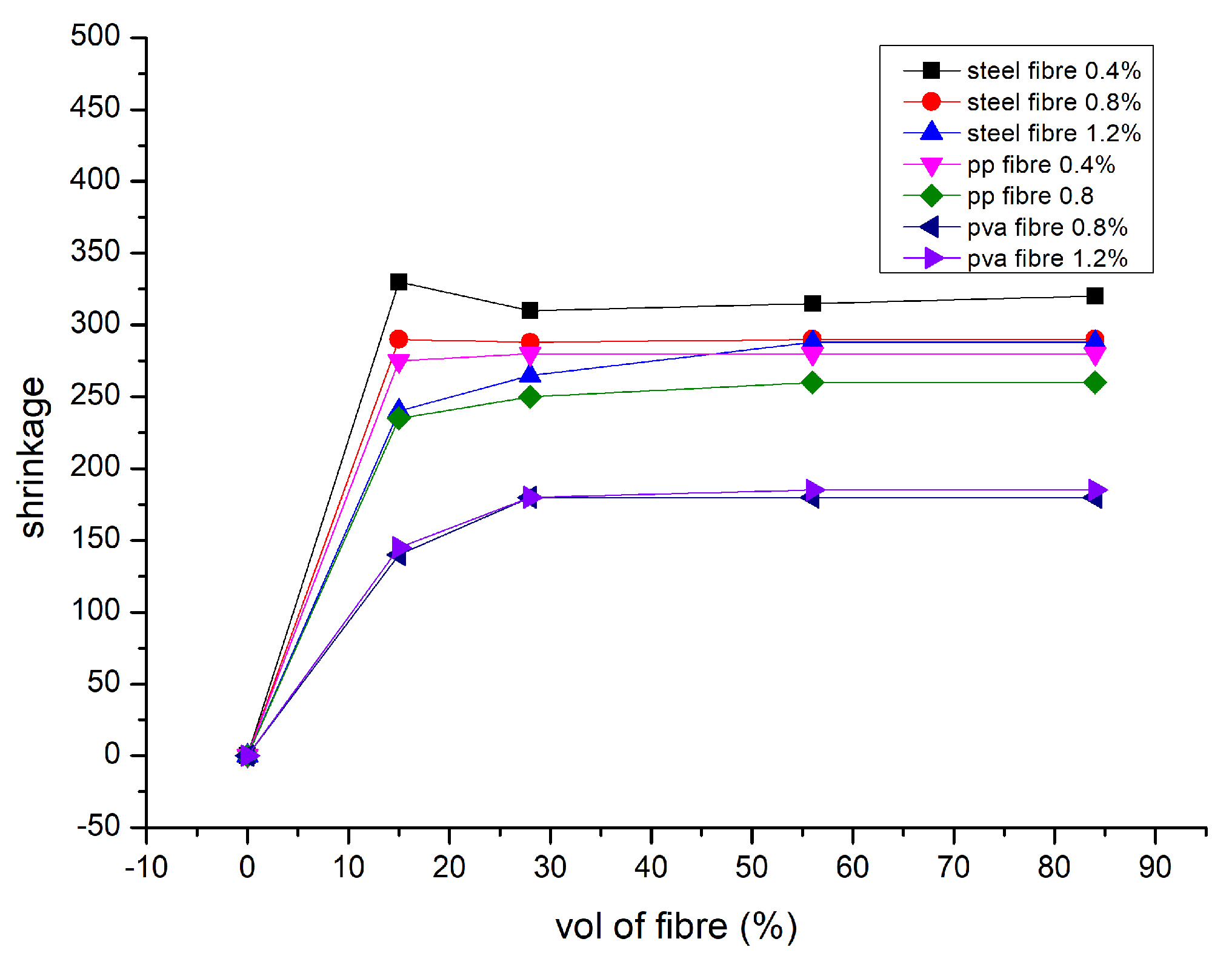
9.6. Shrinkage
9.7. Density
9.8. Water Absorption
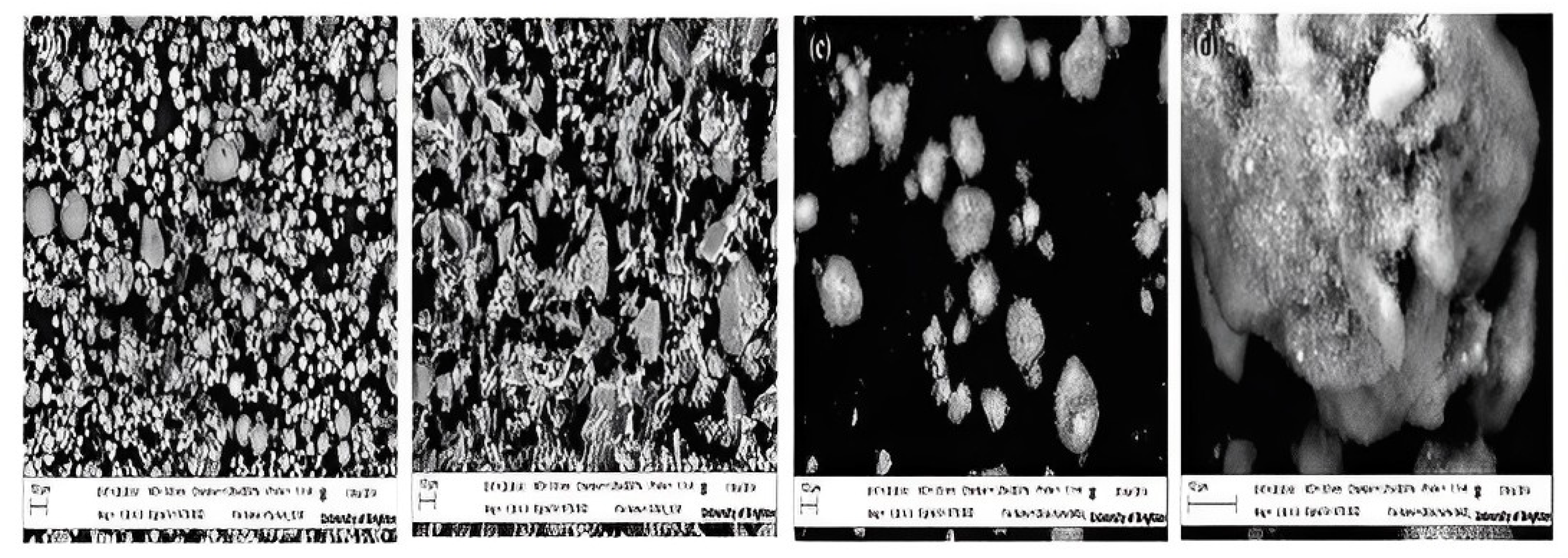
9.9. Microstructural Property
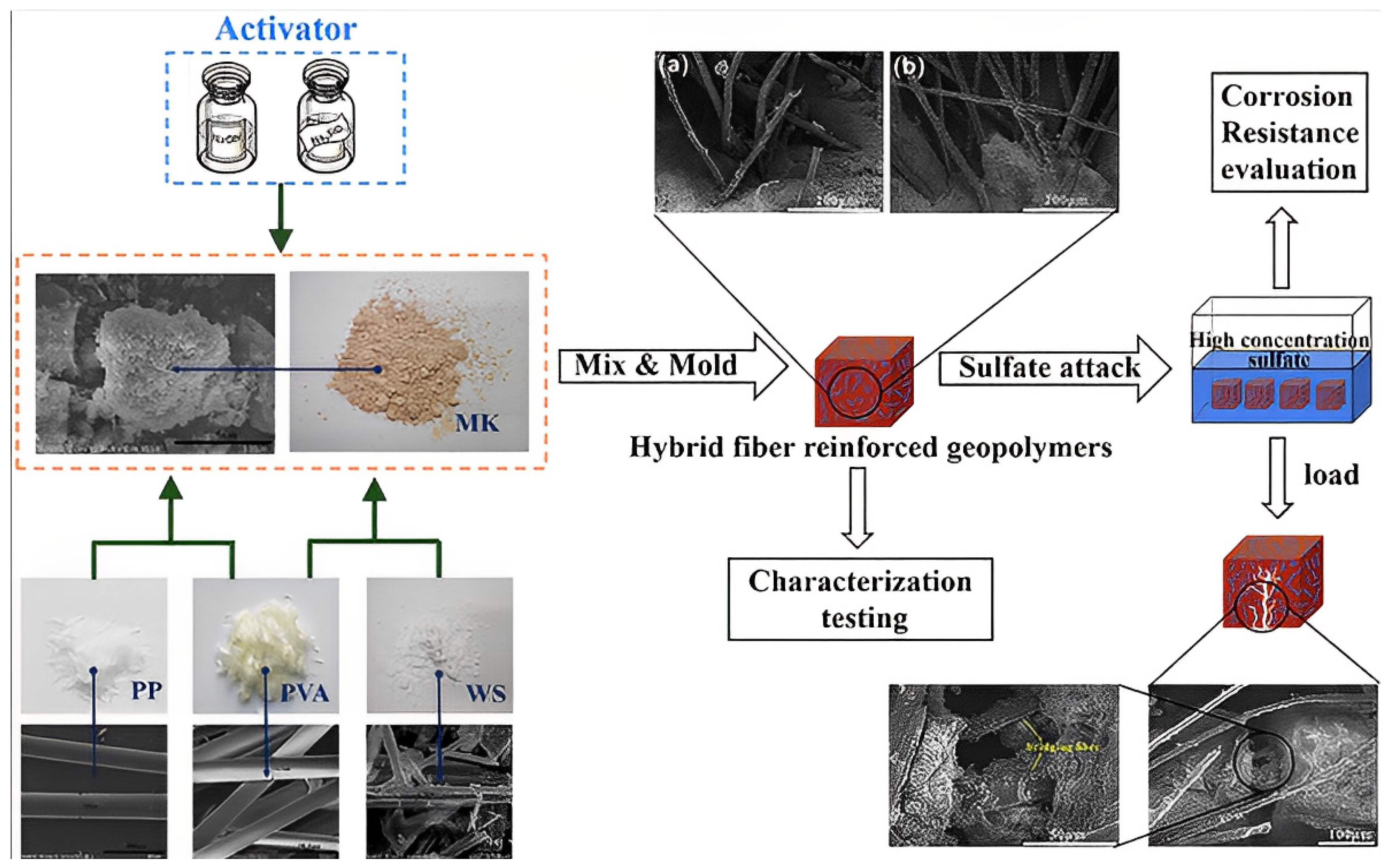
9.10. Crack Control
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-Efficient Cements: Potential Economically Viable Solutions for a Low-CO2 Cement-Based Materials Industry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrell, E.; Price, L.; Martin, N.; Hendriks, C.; Meida, L.O. Carbon Dioxide Emissions from the Global Cement Industry. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 2001, 26, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilek, V.; Sucharda, O.; Bujdos, D. Frost resistance of alkali-activated concrete—An important pillar of their sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametkaliyev, T.; Ali, M.H.; Kutugin, V.; Savinova, O.; Vereschagin, V. Influence of Mixing Order on the Synthesis of Geopolymer Concrete. Polymers 2022, 14, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Luo, S.; Xu, S.; Xing, F.; Liu, M. Pre-Treatment of Reclaimed Concrete Slurry Waste for Substituting Cementitious Materials: Effect of Treatment Approach and Substitution Content. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhou, Q.Z.; Yang, C.H.; Bai, Y. Performance and Interaction of Sodium Silicate Activated Slag with Lignosulfonate Superplasticiser Added at Different Mixing Stages. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 136, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Fediuk, R.; Murali, G.; Avudaiappan, S.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Fly ash-based eco-efficient concretes: A comprehensive review of the short-term properties. Materials 2021, 14, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliabdo, A.A.; Abd Elmoaty, A.E.M.; Salem, H.A. Effect of Cement Addition, Solution Resting Time and Curing Characteristics on Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Concrete Performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevasan, K.K.; Ranganath, R.V. Geopolymer Concrete Using Industrial Byproducts. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Constr. Mater. 2011, 164, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, M.; Butt, F.; Waqas, R.M.; Hussain, K.; Tufail, R.F.; Ahmad, N.; Usanova, K.; Musarat, M.A. Mechanical and Microstructural Characterization of Quarry Rock Dust Incorporated Steel Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete and Residual Properties after Exposure to Elevated Temperatures. Materials 2021, 14, 6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.K.; Maitra, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, S. Microstructural and Morphological Evolution of Fly Ash Based Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, V.; Komljenović, M.; Baščarević, Z.; Marjanović, N.; Miladinović, Z.; Petrović, R. The Influence of Fly Ash Characteristics and Reaction Conditions on Strength and Structure of Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Mehrali, M.; Mehrali, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Zamin, M. Graphene Nanoplatelet- Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 76, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L.; Duxson, P.; Lukey, G.C. Reaction Mechanisms in the Geopolymeric Conversion of Inorganic Waste to Useful Products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, C.A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The Mechanism of Geopolymer Gel Formation Investigated through Seeded Nucleation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 318, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, A.; Provis, J.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Effect of Alumina Release Rate on the Mechanism of Geopolymer Gel Formation. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 5199–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, A.; Provis, J.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The Effect of Silica Availability on the Mechanism of Geopolymerisation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Jiménez, A.F.; Palomo, A. New Cements for the 21st Century: The Pursuit of an Alternative to Portland Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-torgal, F. Alkali-Activated Binders: A Review. Part 2. About Materials and Binders Manufacture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, J.; Kontoleon, K.J.; Majdi, A.; Naqash, M.T.; Deifalla, A.F.; Ben Kahla, N.; Isleem, H.F.; Qaidi, S.M.A. A Comprehensive Review on the Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS) in Concrete Production. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, A.A.; Wan Ibrahim, M.H.; Othman, N.H.; Shahidan, S. The Effect of Palm Oil Clinker and Oil Palm Shell on the Compressive Strength of Concrete. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2019, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehu, I.A.; Abdul Awal, A.S.A. Mechanical Properties of Concrete Incorporating High Volume Palm Oil Fuel Ash. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 599, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Characterisation of Fly Ashes. Potential Reactivity as Alkaline Cements. Fuel 2003, 82, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.; De Gutierrez, R.; Delvasto, S.; Rodriguez, E. Performance of an Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete Reinforced with Steel Fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Van Beers, L.; Spiesz, P.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Impact Resistance of a Sustainable Ultra-High Performance Fibre Reinforced Concrete (UHPFRC) under Pendulum Impact Loadings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 107, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnahhal, M.F.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Alqedra, M.A.; Mo, K.H.; Sumesh, M. Evaluation of Industrial By-Products as Sustainable Pozzolanic Materials in Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Sustainability 2017, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumesh, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Mo, K.H.; Alnahhal, M.F. Incorporation of Nano-Materials in Cement Composite and Geopolymer Based Paste and Mortar—A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, A.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Yusuf, M.O.; Kabir, S.M.A.; Bashar, I.I. Influence of Source Materials and the Role of Oxide Composition on the Performance of Ternary Blended Sustainable Geopolymer Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, I.M.; Mcgrath, M.; Lawrence, D.; Schmidt, P. Mechanical and Fracture Properties of Cellulose-Fibre-Reinforced Epoxy Laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, I.M.; Somers, J.; Kho, H.S.; Davies, I.J.; Latella, A. Fabrication and Properties of Recycled Cellulose Fibre- Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Compos. Interfaces 2009, 16, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M.; Alothman, Z. Mechanical, Thermal and Microstructural Characteristics of Cellulose Fibre Reinforced Epoxy/Organoclay Nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulekbache, B.; Hamrat, M.; Chemrouk, M.; Amziane, S. Flowability of Fibre-Reinforced Concrete and Its Effect on the Mechanical Properties of the Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, B.; Kumutha, R.; Vijay, K. Effect of Fiber on the Mechanical Properties of fly ash and GGBS based Geopolymer Concrete under different curing conditions. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2017, 24, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Steveson, M.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K. Relationships between Composition, Structure and Strength of Inorganic Polymers: Part I Metakaolin-Derived Inorganic Polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L.; Duxson, P.; Brice, D.G. Chemical Research and Climate Change as Drivers in the Commercial Adoption of Alkali Activated Materials. Waste Biomass Valorization 2010, 1, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumajouw, D.M.J.; Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.E.; Rangan, B.V. Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete: Study of Slender Reinforced Columns. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3124–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Ishwarya, G.; Gupta, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.K. Geopolymer Concrete: A Review of Some Recent Developments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 85, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer Technology: The Current State of the Art. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers. J. Therm. Anal. 1991, 37, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Properties of Geopolymer Cements. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Alkaline Cements and Concretes, Kiev, Ukraine, October 1994; pp. 131–149. [Google Scholar]
- Jaarsveld, J.G.S.; Van Deventer, J.S.J.; Van Lukey, G.C. The Characterization of Source Materials in Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers. Fuel Energy Abstr. 2004, 45, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardjito, D.; Rangan, B.V. Development and Properties of Low-Calcium Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete; Research Report GC1; Curtin University of Technology: Singapore, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovits, P.J. 30 Years of Successes and Failures in Geopolymer Applications. In Market Trends and Potential Breakthroughs. In Proceedings of the Geopolymer 2002 Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 28–29 October 2002; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.; Sumajouw, D.M.J.; Rangan, B.V. Brief Review of Development of Geopolymer. In Proceedings of the 8th Canmet/ACI international Conference on fly ash, Silica Fume, Slag and Natural Pozzolans in Conerete, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 20 May 2004; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Khale, D.; Chaudhary, R. Mechanism of Geopolymerization and Factors Influencing Its Development: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, H.; Li, L. Cement and Concrete Research A Review: The Comparison between Alkali-Activated Slag (Si + Ca) and Metakaolin (Si + Al) Cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuder, K.G.; Ozyurt, N.; Mu, E.B.; Shah, S.P. Rheology of Fiber-Reinforced Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, D.A.; Ouyang, C.; Shah, S.P. Behavior of Cement Based Matrices Reinforced by Randomly Dispersed Microfibers. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1996, 3, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinie, L.; Rossi, P.; Roussel, N. Cement and Concrete Research Rheology of Fi Ber Reinforced Cementitious Materials: Classi Fi Cation and Prediction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Bhutta, A.; Banthia, N. Tensile Performance of Eco-Friendly Ductile Geopolymer Composites (EDGC) Incorporating Different Micro-Fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 103, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, A.; Borges, P.H.R.; Zanotti, C.; Farooq, M.; Banthia, N. Flexural Behavior of Geopolymer Composites Reinforced with Steel and Polypropylene Macro Fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, J.; Saha, A.K.; Sarker, P.K.; Pramanik, A. Workability and Flexural Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Geopolymer Using Different Mono and Hybrid Fibres. Materials 2021, 14, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, T.F. Inorganic Fibers—A Literature Review. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 2959–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Provis, J.L.; Reid, A.; Wang, H. Geopolymer Foam Concrete: An Emerging Material for Sustainable Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Mehrali, M.; Mehrali, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z. High Tensile Strength Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Composite Using Copper Coated Micro Steel Fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, M.N.; Ahmad, W.; Khan, K.; Ahmad, A. Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: A Systematic Review of the Research Progress and Knowledge Mapping. Materials 2022, 15, 6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivito, R.S.; Zuccarello, F.A. Composites: Part B An Experimental Study on the Tensile Strength of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Compos. Part B 2010, 41, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Han, G. Spatial Distribution of Steel Fibers and Air Bubbles in UHPC Cylinder Determined by X-ray CT Method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; D’Haese, C.; Nysten, B. Surface Electrical Properties of Stainless Steel Fibres: An AFM-Based Study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 330, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Jacobsen, S.; He, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Lee, S.F.; Lein, H.L. Application of Nanoindentation Testing to Study of the Interfacial Transition Zone in Steel Fiber Reinforced Mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, C.; Camões, A.; Barros, J.; Gonçalves, D. Durability of Steel Fiber Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 80, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granju, J.L.; Balouch, S.U. Corrosion of Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete from the Cracks. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, N.C.; Ström, M.A.; Shipway, P.H.; Rudd, C.D. Corrosion Resistance of Zinc-Magnesium Coated Steel. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 3669–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentur, A.; Ben-Bassat, M.; Schneider, D. Durability of Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Cements with Different Alkali-Resistant Glass Fibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1985, 68, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Meyer, C.; Shimanovich, S. Improving the Interface Bond between f Iber Mesh and Cementitious Matrix. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollo, R.F. Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: An Overview after 30 Years of Development. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1997, 19, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, J.; Jun, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Monteiro, P.J.M. The Importance of the Network-Modifying Element Content in Fly Ash as a Simple Measure to Predict Its Strength Potential for Alkali-Activation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 57, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, S.; Fernandez-jime, A. Alkaline Activation of Fly Ashes: NMR Study of the Reaction Products. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 1145, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.; Cao, H.; Song, S. Tensile Behavior Contrast of Basalt and Glass Fibers after Chemical Treatment. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4244–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militký, J.; Kovačič, V.; Rubnerová, J. Influence of Thermal Treatment on Tensile Failure of Basalt Fibers. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2002, 69, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T. Advances in Inorganic Fibers. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2005, 178, 109–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, R.; Pazhani, K. Strength and durability properties of geopolymer concrete made with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag and Black Rice Husk Ash. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.F.V. Unified Nomenclature for Plant Fibres for Industrial Use. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2000, 7, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.; Muñoz-Dorado, J.; De La Rubia, T.; Martínez, J. Biodegradation and Biological Treatments of Cellulose, Hemicellulose and Lignin: An Overview. Int. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukontasukkul, P.; Pongsopha, P.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Songpiriyakij, S. Flexural Performance and Toughness of Hybrid Steel and Polypropylene Fibre Reinforced Geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Talebian, S.; Mehrali, M.; Kuenzel, C.; Cornelis Metselaar, H.S.; Jumaat, M.Z. Mechanisms of Interfacial Bond in Steel and Polypropylene Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 122, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, M.F.; Ma, C.K.; Apandi, N.M.; Chin, S.; Awang, A.Z.; Mansur, S.A.; Omar, W. A Review on Bond and Anchorage of Confined High-Strength Concrete. Structures 2017, 11, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Shi, Q.; Yu, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.; Sun, T. Progress of the Surface Modification of PP Fiber Used in Concrete. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2006, 45, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inti, S.; Sharma, M.; Tandon, V. Ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS) and rice husk ash (RHA) uses in the production of geopolymer concrete. In Geo-Chicago 2016: Geotechnics for Sustainable Energy, GSP 270; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2016; pp. 621–632. [Google Scholar]
- Trejbal, J.; Kopecký, L.; Tesárek, P.; Fládr, J.; Antoš, J.; Somr, M.; Nežerka, V. Impact of Surface Plasma Treatment on the Performance of PET Fiber Reinforcement in Cementitious Composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 89, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Buendía, A.M.; Romero-Sánchez, M.D.; Climent, V.; Guillem, C. Surface Treated Polypropylene (PP) Fibres for Reinforced Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 54, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, P.; Jang, J.; Wang, Z.; Hwang, B.; Lawrence, K. Interfacial Evaluation and Durability of Modified Jute Fibers/Polypropylene (PP) Composites Using Micromechanical Test and Acoustic Emission. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 1042–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Shukla, A.; Brown, R. Pullout Behavior of Polypropylene Fibers from Cementitious Matrix. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Shaad, K.; Rahman, M.; Bhowmik, P. Influence of rice husk ash on the properties of concrete. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2016, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjbar, N.; Zhang, M. Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymer Composites: A Review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 107, 103498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, K.H.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Yap, S.P.; Lee, S.C. Green concrete partially comprised of farming waste residues: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 117, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar Reddy, K. Investigation of Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete with GGBFS and Metakaolin: Novel Raw Material for Geopolymerisation. Silicon 2021, 13, 4565–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawileh, R.A.; Abdalla, J.A.; Fardmanesh, F.; Shahsana, P.; Khalili, A. Performance of Reinforced Concrete Beams Cast with Different Percentages of GGBS Replacement to Cement. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2017, 17, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Kumar, R.A. Strength Studies on Metakaolin Blended High Volume Fly Ash Concrete. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. IJEAT 2014, 3, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Gülşan, M.E.; Alzeebaree, R.; Rasheed, A.A.; Niş, A.; Kurtoğlu, A.E. Development of Fly Ash/Slag Based Self-Compacting Geopolymer Concrete Using Nano-Silica and Steel Fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Darkwa, J.; Zhou, G. Thermo-Mechanical and Moisture Absorption Properties of Fly Ash-Based Lightweight Geopolymer Concrete Reinforced by Polypropylene Fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, N.; Indira, P.V. Engineering properties of steel fibre reinforced geopolymer concrete. Adv. Concr. Constr. 2013, 1, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, H.Q.; Jaf, D.K.; Yaseen, S.A. Flexural Capacity and Behaviour of Geopolymer Concrete Beams Reinforced with Glass Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Bars. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2020, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Gupta, N.; Gupta, A. Development of green concrete using waste marble dust. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 2590–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomayri, T.; Low, I.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Mechanical Properties in Cotton Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymer Composites. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2013, 1, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohseni, E. Assessment of Na2SiO3 to NaOH Ratio Impact on the Performance of Polypropylene Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymer Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, A.; Manzi, S.; Bignozzi, M.C. Procedia Engineering Novel Fiber-Reinforced Composite Materials Based on Sustainable Geopolymer Matrix. Procedia Eng. 2011, 21, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.; Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Song, X.; Ye, J.; Duan, P.; Zhang, Z. Sulfate Resistance of Hybrid Fiber Reinforced Metakaolin Geopolymer Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.; Lokuge, W.; Karunasena, W. Fibre-Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete with Ambient Curing for in Situ Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 4297–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karthik, A.; Sudalaimani, K.; Kumar, C.V. Investigation on mechanical properties of fly ash-ground granulated blast furnace slag based self-curing bio-geopolymer concrete, Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. Short Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer Composites Manufactured by Extrusion. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2005, 17, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.; Allouche, E.N. Strain Sensing of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2011, 44, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, K.H.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Liu, M.Y.J.; Lim, J. Assessing some durability properties of sustainable lightweight oil palm shell concrete incorporating slag and manufactured sand. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saafi, M.; Andrew, K.; Tang, P.L.; McGhon, D.; Taylor, S.; Rahman, M.; Yang, S.; Zhou, X. Multifunctional Properties of Carbon Nanotube/Fly Ash Geopolymeric Nanocomposites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Maalej, M.; Paramasivam, P. Strain-hardening behaviour of hybrid fiber reinforced cement composites. J. Ferrocem. 2003, 33, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Majidi, M.H.; Lampropoulos, A.; Cundy, A.B. Steel Fibre Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete (SFRGC) with Improved Microstructure and Enhanced Fibre-Matrix Interfacial Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 286–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.; Xia, J.; Chai, H.; Lu, T.M. Properties of Fresh and Hardened Glass Fiber Reinforced Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Concrete. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 595, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferna, A. Structure of Calcium Silicate Hydrates Formed in Alkaline-Activated Slag: Influence of the Type of Alkaline Activator. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 94, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, L.; Park, Y.D.; Shah, S.P. A Method for Mix-Design of Fiber-Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polydorou, T.; Spanou, M.; Savva, P.; Sakkas, K.; Oikonomopoulou, K.; Petrou, M.F.; Nicolaides, D. Development of a High Strength Geopolymer Incorporating Quarry Waste Diabase Mud (DM) and Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag (GGBS). Materials 2022, 15, 5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korniejenko, K.; Łach, M.; Chou, S.Y.; Lin, W.T.; Cheng, A.; Hebdowska-Krupa, M.; Gadek, S.; Mikuła, J. Mechanical Properties of Short Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymers Made by Casted and 3D Printing Methods: A Comparative Study. Materials 2020, 13, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, D.P.; Thaumaturgo, C. Fracture Toughness of Geopolymeric Concretes Reinforced with Basalt Fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, G.; Rickard, W.D.A.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Riessen, A. Van The Effect of Organic and Inorganic Fibres on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Aluminate Activated Geopolymers. Compos. Part B 2015, 76, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.T.; Jones, S.W.; Mahmud, G.H. Experimental Test Methods to Determine the Uniaxial Tensile and Compressive Behaviour of Ultra High Performance Fibre Reinforced Concrete (UHPFRC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, P.; Rathinam, K.; Kanagarajan, V. Effect of Aspect Ratio and Volume Fraction of Steel Fibers in Strength Properties of Geopolymer Concrete. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 9, 3314–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Ghazali, N.B.; Yusoff, S.; Bashar, I.I. Influence of Steel Fibers on the Mechanical Properties and Impact Resistance of Lightweight Geopolymer Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Kim, J.S.; Ha, G.J.; Kim, Y.Y. Tensile and Fiber Dispersion Performance of ECC (Engineered Cementitious Composites) Produced with Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.D.; Scrivener, K.L.; Pratt, P.L. Factors Affecting the Strength of Alkali-Activated Slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 1994, 24, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, J. Impact Characterization of Basalt Fiber Reinforced Geopolymeric Concrete Using a 100-Mm-Diameter Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 514, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaplana, J.L.; Baeza, F.J.; Galao, O.; Alcocel, E.G.; Zornoza, E.; Garcés, P. Mechanical Properties of Alkali Activated Blast Furnace Slag Pastes Reinforced with Carbon Fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 116, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Eddie; Chau, C. Impact Properties of Geopolymer Based Extrudates Incorporated with Fly Ash and PVA Short Fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanithi, S. Experimental Studies on Punching Shear and Impact Resistance of Steel Fibre Reinforced Slag Based Geopolymer Concrete. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2017, 2017, 9210968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, F.; Amat, T.; Ferna, A. Mechanical and Durable Behaviour of Alkaline Cement Mortars Reinforced with Polypropylene Fibres. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiş, C.D.; Karahan, O. Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Fly Ash Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Choi, J.I.; Song, J.K.; Lee, B.Y. Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Fiber- Reinforced Alkali-Activated Composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, R.N.; Mangat, P.S. Influence of Fibre-Aggregate Interaction on Some Properties of Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete. Matériaux Constr. 1974, 7, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Baradan, B. The Effect of Fiber Properties on High Performance Alkali-Activated Slag/Silica Fume Mortars. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaut, F.; Mokéddem, S.; Chateau, X.; Roussel, N.; Ovarlez, G. Cement and Concrete Research Effect of Coarse Particle Volume Fraction on the Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Yu, Q.L.; Yu, R.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Evaluation of Hybrid Steel Fiber Reinforcement in High Performance Geopolymer Composites. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2017, 50, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaxman, A.; Narkis, M.; Siegmann, A.; Kenig, S. Short-fiber-reinforced Thermoplastics. Part III: Effect of Fiber Length on Rheological Properties and Fiber Orientation. Polym. Compos. 1989, 10, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, N.A.; Sheikh, M.N.; Hadi, M.N.S. Engineering Properties of Ambient Cured Alkali-Activated Fly Ash–Slag Concrete Reinforced with Different Types of Steel Fiber. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nematollahi, B.; Vijay, P.; Sanjayan, J.; Nazari, A.; Xia, M.; Nerella, V.N.; Mechtcherine, V. Effect of Polypropylene Fibre Addition on Properties of Geopolymers Made by 3D Printing for Digital Construction. Materials 2018, 11, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panda, B.; Tan, M.J. Author’s Accepted Manuscript. Ceram. Int. 2018, 4, 10258–10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzeer, M.; MacKenzie, K. Synthesis and Mechanical Properties of Novel Composites of Inorganic Polymers (Geopolymers) with Unidirectional Natural Flax Fibres (Phormium Tenax). Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 75–76, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzel, C.; Vandeperre, L.J.; Donatello, S.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Cheeseman, C. Ambient Temperature Drying Shrinkage and Cracking in Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 3270–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuenzel, C.; Li, L.; Vandeperre, L.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Cheeseman, C.R. Influence of Sand on the Mechanical Properties of Metakaolin Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnejad, Z.; Mastali, M.; Mastali, M.; Dalvand, A. Comparative Study on the Effects of Recycled Glass–Fiber on Drying Shrinkage Rate and Mechanical Properties of the Self-Compacting Mortar and Fly Ash–Slag Geopolymer Mortar. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwa, Z.N.; Yousif, B.F.; Manalo, A.C.; Karunasena, W. A Review on the Degradability of Polymeric Composites Based on Natural Fibres. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akkaya, Y.; Peled, A.; Shah, S.P. Parameters Related to Fiber Length and Processing in Cementitious Composites. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2000, 33, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Aluminosilicate and aluminosilicate-based polymer composites: Present status, applications and future trends. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2014, 89, 239–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucsi, G.; Szenczi, Á.; Nagy, S. Fiber Reinforced Geopolymer from Synergetic Utilization of Fly Ash and Waste Tire. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
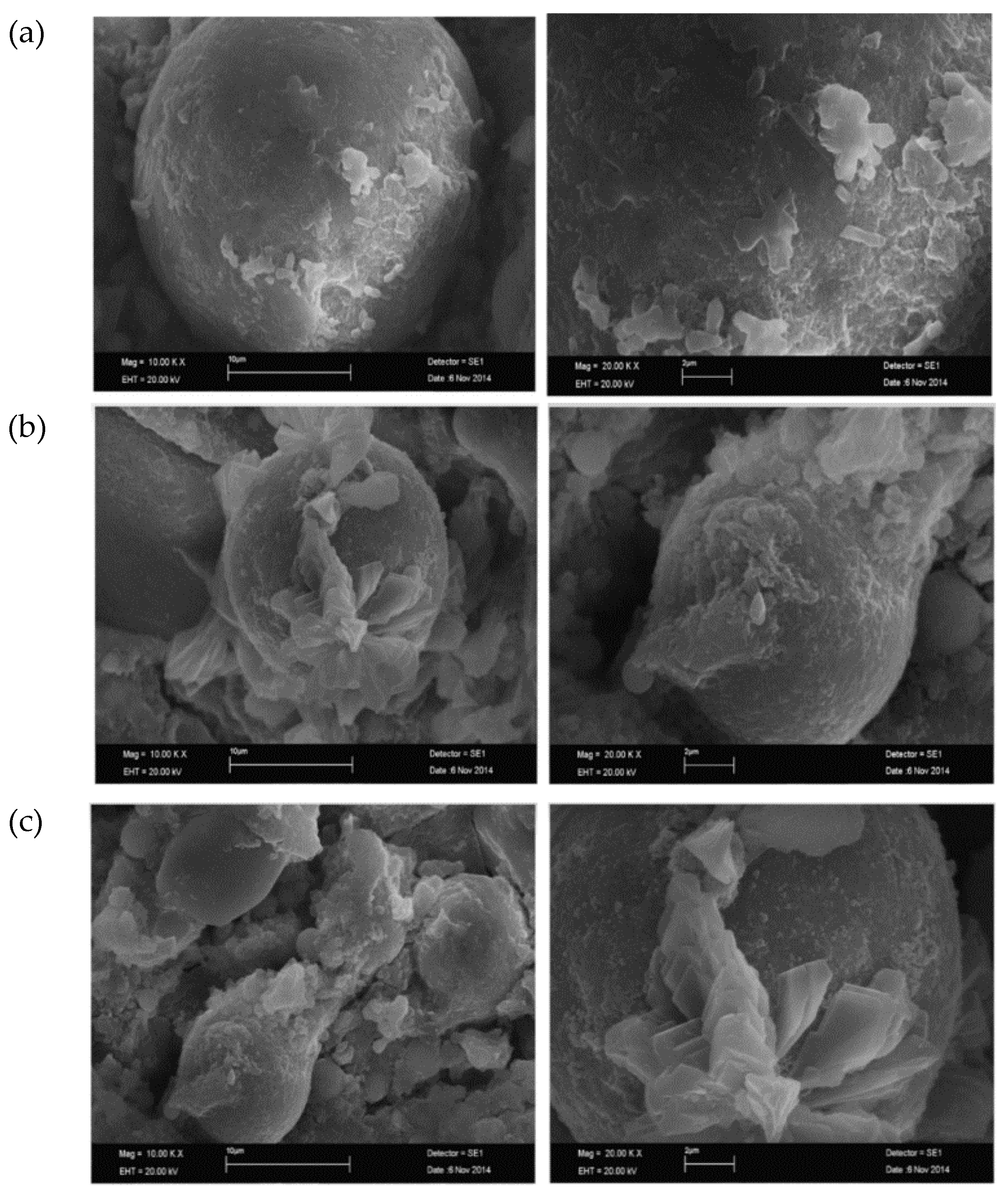
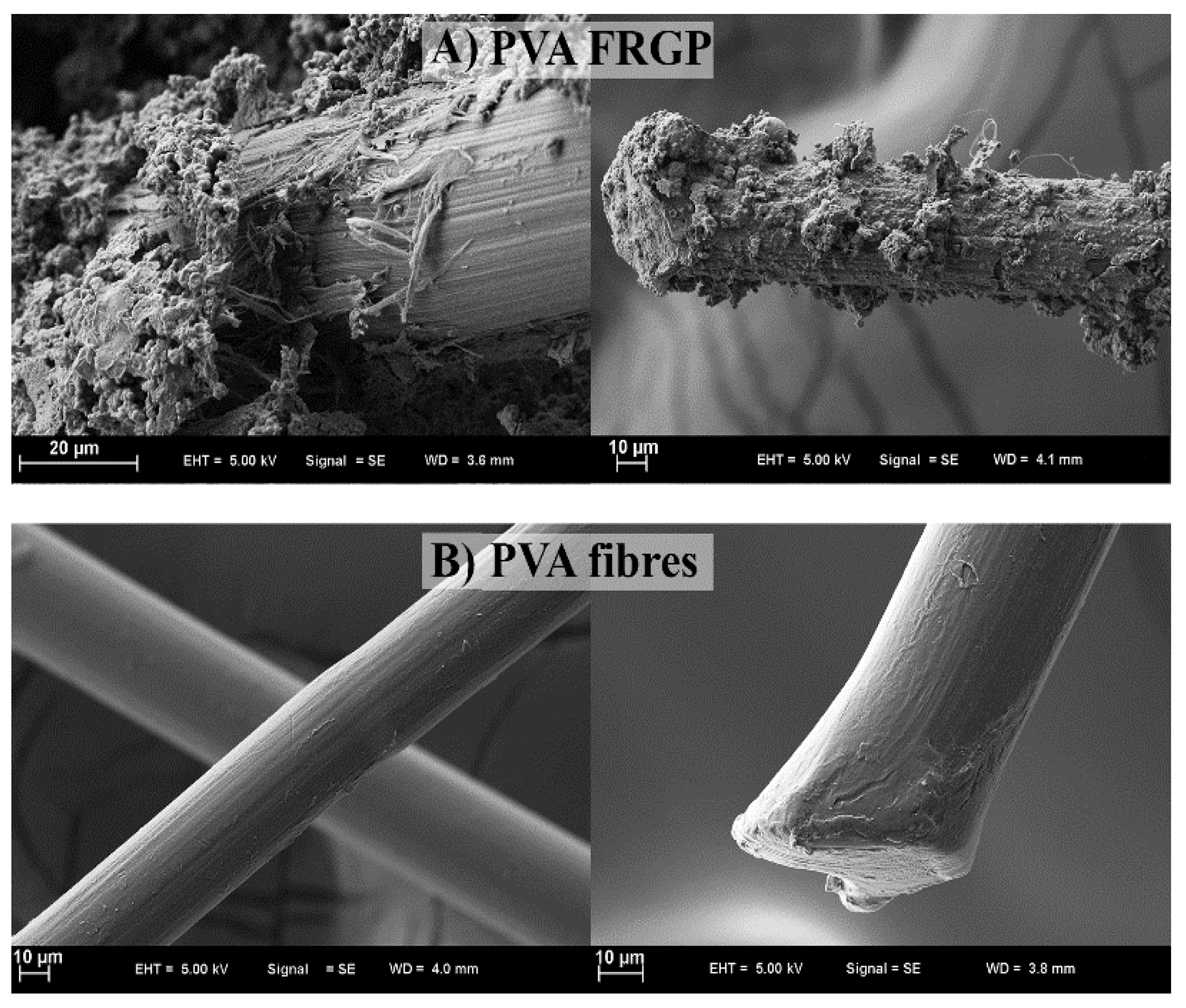







| Ref | Material Name | SO3 | S | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Na2O | TiO2 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [90] | Fly ash | 0.10 | - | 1.60 | 62.33 | 21.14 | 7.15 | 2.40 | 0.38 | - | 3.37 |
| [91] | Fly ash | - | - | 1.73 | 55.2 | 26.2 | 3.106 | 1.45 | 0.35 | - | 1.879 |
| [89] | Fly ash | - | - | 0.12 | 54.89 | 15.31 | 21.83 | 2.51 | - | - | - |
| [92] | Fly ash | - | - | 1.07 | 55.36 | 27.74 | 9.74 | - | - | 3.55 | - |
| [93] | Fly ash | 0.58 | - | 2.65 | 55.2 | 25.3 | 8.34 | 1.56 | 0.58 | - | 1.39 |
| [94] | Fly ash | 0.73 | - | 2.02 | 54.08 | 26.08 | 6.68 | 2.676 | 0.79 | - | - |
| [95] | Fly ash | 0.38 | - | 1.78 | 50 | 28.25 | 13.5 | 0.89 | 0.32 | - | 0.46 |
| [90] | GGBS | 0.49 | - | 34.12 | 36.40 | 11.39 | 1.69 | 10.30 | 0.35 | - | 3.63 |
| [94] | GGBS | 0.18 | - | 35.58 | 40.55 | 12.83 | 1.10 | 5.87 | 0.79 | - | - |
| [89] | GGBS | - | - | 2.53 | 42.21 | 21.12 | 7.32 | 2.98 | - | - | - |
| [90] | NS | - | - | - | 99.80 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [93] | OPC | 2.52 | - | 64.39 | 21.10 | 5.24 | 3.10 | 1.10 | 0.23 | - | 0.57 |
| [93] | SF | 0.05 | - | - | 93.0 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.51 | 0.2 | - | 0.22 |
| [24] | GBFS | 0.66 | - | 43.92 | 31.08 | 13.98 | 3.09 | 1.79 | - | - | - |
| [96] | Metakaolin | 0 | - | 0.22 | 52.1 | 43.8 | 2.6 | 0.21 | 0.11 | - | 0.32 |
| [97] | Metakaolin | - | - | 0.08 | 47.6 | 37.7 | 1.6 | - | - | 1.7 | - |
| [97] | Ladle slag | - | - | 54.5 | 16.4 | 11.1 | 8.7 | 4.0 | - | 0.3 | - |
| Ref. | Material Name | LoI | SG | Surface Area (m2/g) | Diameter | Length | Elongation (%) | Fineness | Colour | Aspect Ratio | Bulk Density (kg/m3) | Dry Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [87] | Metakaolin | - | 1.13 | - | 0.024 | 15 mm | - | - | Greyish white | - | 1744 | - |
| Coarse aggregate | - | 2.62 | Grading zone 3 | - | - | 14.9 | 2.50 (Modulus) | - | - | - | - | |
| [90] | FA | 1.58 | 2.29 | - | - | - | - | 379 (Blaine) | - | - | - | - |
| GGBFS | 1.64 | 2.79 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| NS | <1.00 | 2.20 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.91 | - | |
| [91] | PP fibre | - | - | - | 0.017 | - | 19 | - | - | - | - | 1430–1740 |
| Standard sand | - | - | - | 0.39 | - | - | - | - | - | 520–540 | - | |
| Coarse aggregate | - | - | - | 5–10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| [89] | FA | 0.7 | 2.46 | - | - | - | - | 7.62 | - | - | - | - |
| GGBS | - | 2.91 | - | - | - | - | 3.11 | - | - | - | - | |
| Hook end steel fibre | - | - | - | 0.75 | 35–60 | - | - | - | 45–80 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baskar, P.; Annadurai, S.; Sekar, K.; Prabakaran, M. A Review on Fresh, Hardened, and Microstructural Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete. Polymers 2023, 15, 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061484
Baskar P, Annadurai S, Sekar K, Prabakaran M. A Review on Fresh, Hardened, and Microstructural Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete. Polymers. 2023; 15(6):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061484
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaskar, Prabu, Shalini Annadurai, Kaviya Sekar, and Mayakrishnan Prabakaran. 2023. "A Review on Fresh, Hardened, and Microstructural Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete" Polymers 15, no. 6: 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061484
APA StyleBaskar, P., Annadurai, S., Sekar, K., & Prabakaran, M. (2023). A Review on Fresh, Hardened, and Microstructural Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Geopolymer Concrete. Polymers, 15(6), 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061484












